Effect of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on the Small-Intestinal Environment, Including the Gut Flora, Immune System, and Mucosal Barrier Integrity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Social Interaction Test in CSDS Mice
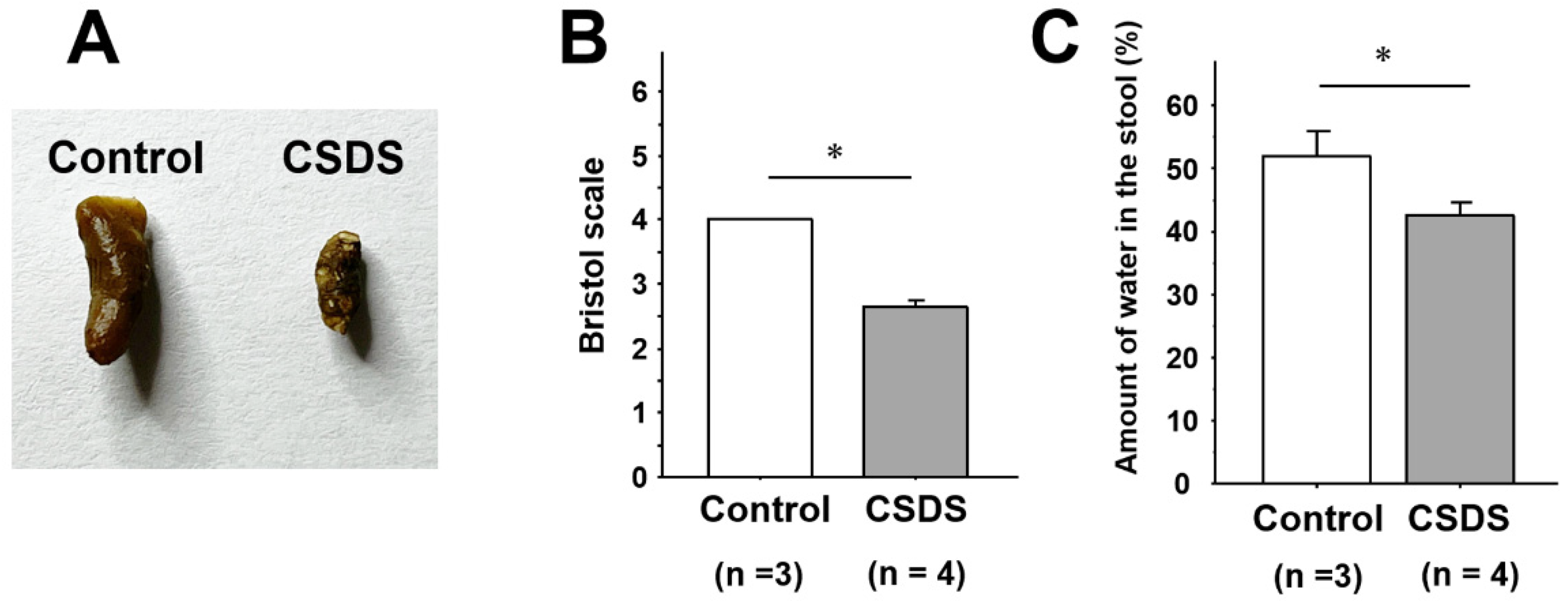
2.2. Stool Properties in Mice Subjected to CSDS
2.3. Effect of CSDS on the Small-Intestinal Gut Flora
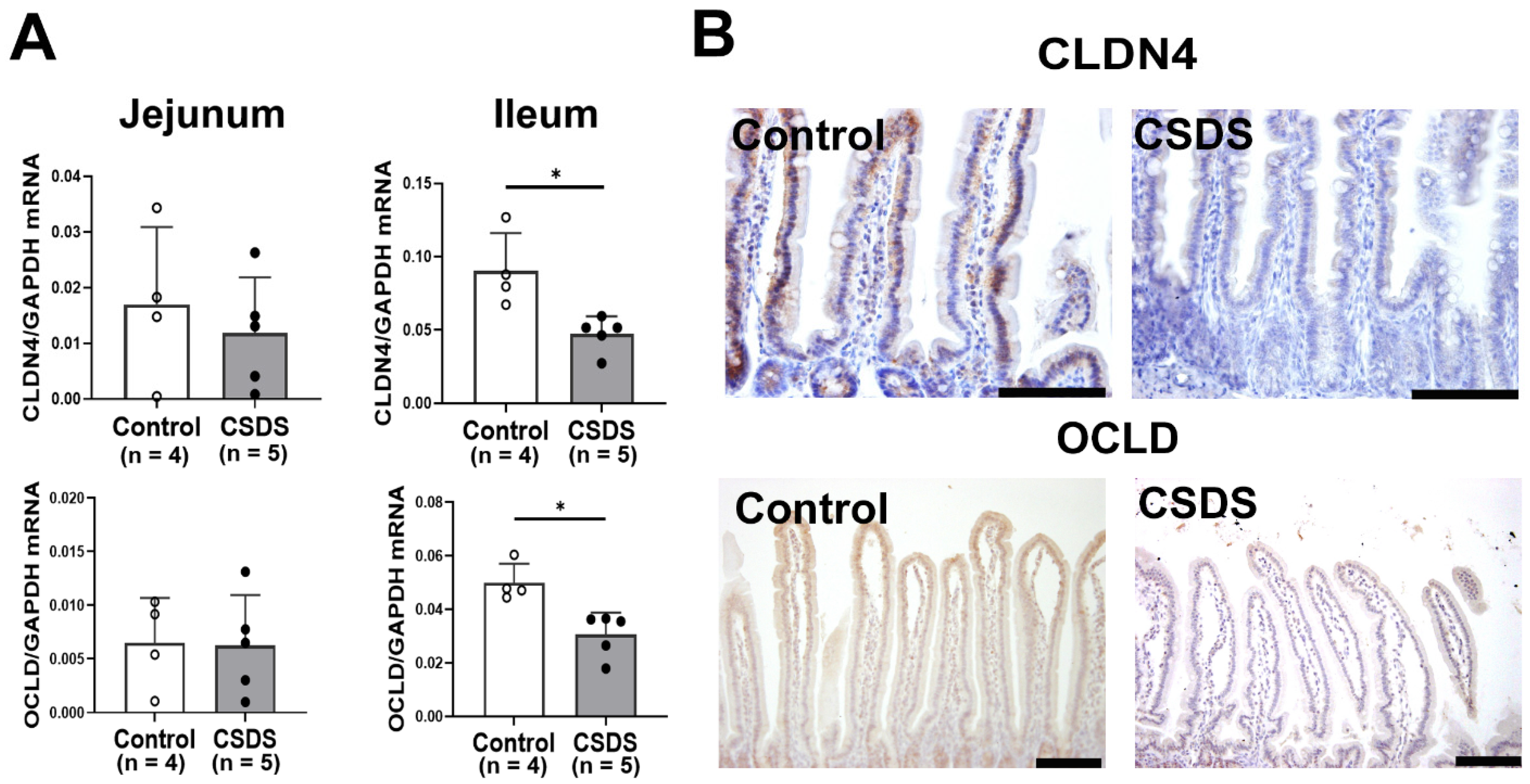
2.4. Effect of CSDS on Tight Junction Proteins Expression, Morphology and Permeability in the Small-Intestinal Mucosa
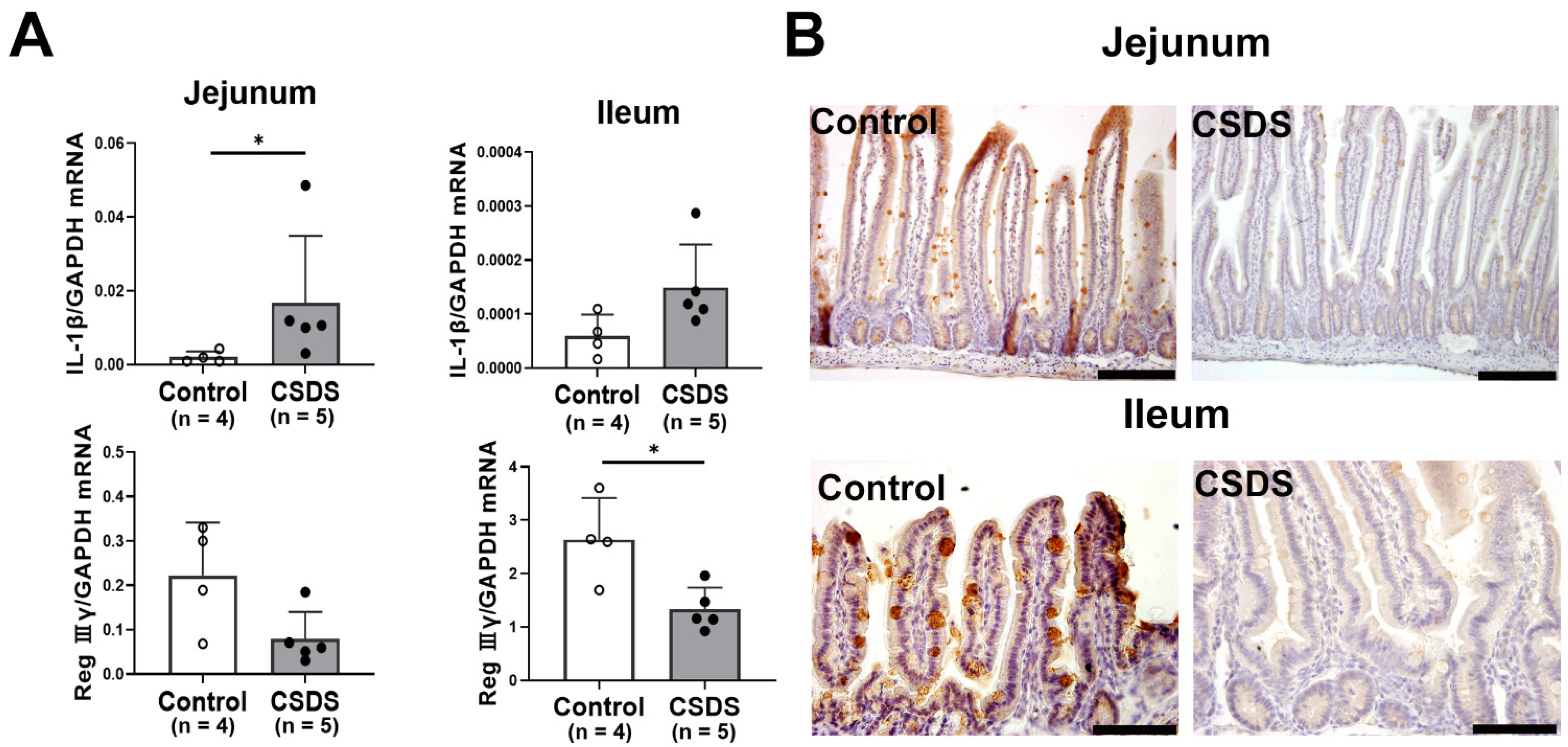
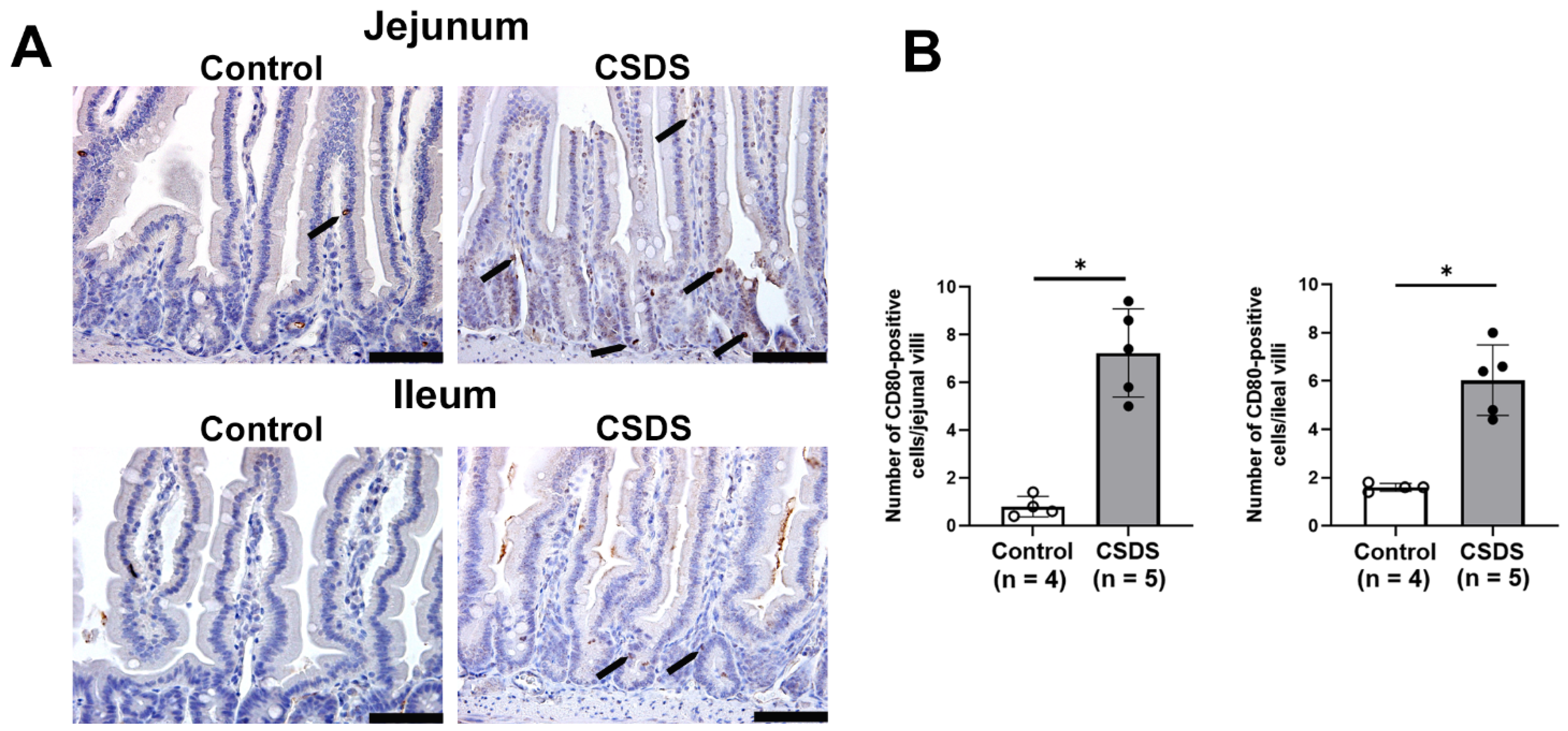
2.5. Expression of Antimicrobial Peptides, Cytokines, LPS, and CD80 in the Small Intestine of CSDS Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model of Chronic Social Defeat Stress
4.2. Social Interaction Test
4.3. Sampling of Stools and Intestinal Tissues
4.4. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome
4.5. Real-Time RT-PCR
4.6. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Measurement of Transepithelial Electrical Resistance
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD80 | Cluster of differentiation |
| CSDS | Chronic social defeat stress |
| ENS | Enteric nervous system |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| ICR | Institute of cancer research |
| IL | Interleukin |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| Reg | Regenerating gene |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SE | Standard error |
| TJPs | Tight junction proteins |
References
- Ge, L.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Hu, G.; Xu, C.; Song, W. Psychological stress in inflammatory bowel disease: Psychoneuroimmunological insights into bidirectional gut–brain communications. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1016578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, R.; Kiecolt-Glaser, J.K. Stress-induced immune dysfunction: Implications for health. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leigh, S.J.; Uhlig, F.; Wilmes, L.; Sanchez-Diaz, P.; Gheorghe, C.E.; Goodson, M.S.; Kelly-Loughnane, N.; Hyland, N.P.; Cryan, J.F.; Clarke, G. The impact of acute and chronic stress on gastrointestinal physiology and function: A microbiota–gut–brain axis perspective. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 4491–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradesi, S.; Schwetz, I.; Ennes, H.S.; Lamy, C.M.R.; Ohning, G.; Fanselow, M.; Pothoulakis, C.; McRoberts, J.A.; Mayer, E.A. Repeated exposure to water avoidance stress in rats: A new model for sustained visceral hyperalgesia. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 289, G42–G53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larauche, M.; Gourcerol, G.; Million, M.; Adelson, D.W.; Taché, Y. Repeated psychological stress-induced alterations of visceral sensitivity and colonic motor functions in mice: Influence of surgery and postoperative single housing on visceromotor responses. Stress 2010, 13, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mönnikes, H.; Tebbe, J.J.; Hildebrandt, M.; Arck, P.; Osmanoglou, E.; Rose, M.; Klapp, B.; Wiedenmann, B.; Heymann-Mönnikes, I. Role of Stress in Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Evidence for Stress-Induced Alterations in Gastrointestinal Motility and Sensitivity. Dig. Dis. 2001, 19, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drossman, D.A.; Hasler, W.L. Rome IV—Functional GI disorders: Disorders of gut–brain interaction. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Chan, A.O.O.; Hui, W.M.; Lam, S.K. Coping strategies, illness perception, anxiety and depression of patients with idiopathic constipation: A population-based study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballou, S.; Katon, J.; Singh, P.; Rangan, V.; Lee, H.N.; McMahon, C.; Iturrino, J.; Lembo, A.; Nee, J. Chronic diarrhea and constipation are more common in depressed individuals. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 2696–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Smith, M.R.B.; Hall, L.J.; Cleare, A.J.; Stone, J.M.; Young, A.H. Perturbations in gut microbiota composition in psychiatric disorders: A review and meta-analysis. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1343–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlsson, L.; Gustafsson, A.; Lavant, E.; Suneson, K.; Brundin, L.; Westrin, Å.; Ljunggren, L.; Lindqvist, D. Leaky gut biomarkers in depression and suicidal behavior. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2019, 139, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H.; Xu, X.; Miwa, H. Role of Gut Microbiota-Gut Hormone Axis in the Pathophysiology of Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2018, 24, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The microbiota–gut–brain axis: From motility to mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Liwinski, T.; Elinav, E. Interaction between microbiota and immunity in health and disease. Cell Res. 2020, 30, 492–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, H.; Arbab, S.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Li, K. Crosstalk between gut microbiota and host immune system and its response to traumatic injury. Front. Immunol. 2004, 15, 1413485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Pereira, J.S.; Rea, K.; Nolan, Y.M.; O’Leary, O.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Depression’s unholy trinity: Dysregulated stress, immunity, and the microbiome. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2020, 71, 49–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammen, C. Stress and depression. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005, 1, 293–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Kim, Y.K. Animal models for the study of depressive disorder. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radley, J.J.; Herman, J.P. Preclinical models of chronic stress: Adaptation or pathology? Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 94, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Nakamura, K.; Shimizu, Y.; Yokoi, Y.; Ohira, S.; Hagiwara, M.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Aizawa, T.; Ayabe, T. Decrease of α-defensin impairs intestinal metabolite homeostasis via dysbiosis in mouse chronic social defeat stress model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K.; Ahmad, R.; Moshfegh, C.M.; Sankarasubramanian, J.; Joshi, V.; Elkhatib, S.K.; Chhonker, Y.S.; Murry, D.J.; Talmon, G.A.; Guda, C.; et al. Repeated social defeat stress induces an inflammatory gut milieu by altering the mucosal barrier integrity and gut microbiota homeostasis. Biol. Psychiatry Glob. Open Sci. 2023, 3, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwani, A.; Mian, M.F.; Foster, J.A.; Surette, M.G.; Bienenstock, J.; Forsythe, P. Structural & functional consequences of chronic psychosocial stress on the microbiome & host. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 63, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, P. Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: From pathogenesis to treatment. EBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, S.J.; Heaton, K.W. Stool Form Scale as a Useful Guide to Intestinal Transit Time. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 32, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Perkins, M.H.; Novaes, L.S.; Qian, F.; Zhang, T.; Neckel, P.H.; Scherer, S.; Ley, R.E.; Han, W.; de Araujo, I.E. Stress-sensitive neural circuits change the gut microbiome via duodenal glands. Cell 2024, 187, 5393–5412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanuytsel, T.; van Wanrooy, S.; Vanheel, H.; Vanormelingen, C.; Verschueren, S.; Houben, E.; Rasoel, S.S.; Tóth, J.; Holvoet, L.; Farré, R.; et al. Psychological stress and corticotropin-releasing hormone increase intestinal permeability in humans by a mast cell-dependent mechanism. Gut 2014, 63, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Teng, T.; Jiang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Fan, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Xie, P. Comparative analysis of gut microbiota and fecal metabolome features among multiple depressive animal models. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 314, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spellman, T.; Liston, C. Toward circuit mechanisms of pathophysiology in depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatake, Y.; Furuie, H.; Yamada, M.; Kuniishi, H.; Ukezono, M.; Yoshizawa, K.; Yamada, M. The effects of emotional stress are not identical to those of physical stress in mouse model of social defeat stress. Neurosci. Res. 2020, 158, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Solinska, A.; De Miguel, Z.; Azkona, G.; Vegas, O. Behavioral coping with chronic defeat stress in mice: A systematic review of current protocols. Neurobiol. Stress 2024, 33, 100689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X. Association between constipation and major depression in adult Americans: Evidence from NHANES 2005–2010. Front. Psychiatry. 2003, 14, 1152435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachsmuth, H.R.; Weninger, S.N.; Duca, F.A.; Wachsmuth, H.R.; Weninger, S.N.; Duca, F.A. Role of the gut–brain axis in energy and glucose metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Ren, C.; Mei, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Gut microbiota and irritable bowel syndrome: Status and prospect. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1429133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, W.D.; Wang, Y.D. The Relationship Between Gut Microbiota and Inflammatory Diseases: The Role of Macrophages. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, R.A.; Foster, J.A. Gut brain axis: Diet microbiota interactions and implications for modulation of anxiety and depression. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, S.; Forsythe, P.; Bienenstock, J. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder: Does the Gut Microbiome Hold the Key? Can. J. Psychiatry. 2016, 61, 204–213. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gallagher, L.A.; Andrade, P.A.; Liu, A.; Humphreys, I.R.; Turkarslan, S.; Cutler, K.J.; Arrieta-Ortiz, M.L.; Li, Y.; Radey, M.C.; et al. Genetic manipulation of Patescibacteria provides mechanistic insights into microbial dark matter and the epibiotic lifestyle. Cell 2023, 186, 4803–4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.T.; Hug, L.A.; Thomas, B.C.; Sharon, I.; Castelle, C.J.; Singh, A.; Wilkins, M.J.; Wrighton, K.C.; Williams, K.H.; Banfield, J.F. Unusual biology across a group comprising more than 15% of domain Bacteria. Nature 2015, 523, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, M.C.; Bulzu, P.A.; Andrei, A.S.; Okazaki, Y.; Nakano, S.; Haber, M.; Kavagutti, V.S.; Layoun, P.; Ghai, R.; Salcher, M.M. Ecogenomics sheds light on diverse lifestyle strategies in freshwater CPR. Microbiome 2022, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; McLean, J.S.; Edlund, A.; Yooseph, S.; Hall, A.P.; Liu, S.Y.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Esquenazi, E.; Hunter, R.C.; Cheng, G.; et al. Cultivation of a human-associated TM7 phylotype reveals a reduced genome and epibiotic parasitic lifestyle. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 112, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Song, F.; Gu, H.; Wei, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, H. Comparative Evaluation of the Salivary and Buccal Mucosal Microbiota by 16S rRNA Sequencing for Forensic Investigations. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 777882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, B.; Snow, M.; Herrman, E.; Ray, N.; Mansukhani, K.; Patel, K.A.; Said, A.N.N.; Maier, T.; Machida, C.A. Interconnections between the Oral and Gut Microbiomes: Reversal of Microbial Dysbiosis and the Balance between Systemic Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, S.; Kamada, N. Periodontal connection with intestinal inflammation: Microbiological and immunological mechanisms. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 89, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Qian, X.; Zhu, J.; Hu, X.; Jiang, P.; Cui, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Alterations in fecal microbiota composition and cytokine expression profiles in adolescents with depression: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Fan, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yang, D.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; Zhao, B.; Zhan, X.; Qi, Z.; Ren, Y.; et al. Gut microbiota dysbiosis promotes cognitive impairment via bile acid metabolism in major depressive disorder. Transl. Psychiatry. 2024, 14, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjabzadeh, D.; Bosch, J.A.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Ikram, M.A.; van Meurs, J.B.J.; Luik, A.I.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Lok, A.; van Duijn, C.M.; et al. Gut microbiome-wide association study of depressive symptoms. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebisutani, N.; Fukui, H.; Nishimura, H.; Nakanishi, T.; Morimoto, K.; Itou, S.; Nakamura, A.; Masutani, M.; Hori, M.; Tomita, T.; et al. Decreased Colonic Guanylin/Uroguanylin Expression and Dried Stool Property in Mice With Social Defeat Stress. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 599582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.H.; Hasnain, S.Z. Mucus and Mucins: The Underappreciated Host Defence System. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 856962. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, M.F.; Romero-Calvo, I.; Mascaraque, C.; Martínez-Augustin, O. Intestinal Inflammation and Mucosal Barrier Function. Inflamm. Bowel. Dis. 2014, 20, 2394–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, T.; Miwa, H. Gastrointestinal mucosal barrier function and diseases. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, R.; Hu, X.; Zhang, F.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. The Role of Intestinal Mucosal Barrier in Autoimmune Disease: A Potential Target. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 871713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wouw, M.; Boehme, M.; Lyte, J.M.; Wiley, N.; Strain, C.; O’Sullivan, O.; Clarke, G.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Short-chain fatty acids: Microbial metabolites that alleviate stress-induced brain-gut axis alterations. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 4923–4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.M.; Blank, N.; Alvarez, Y.; Thum, K.; Lundgren, P.; Litichevskiy, L.; Sleeman, M.; Bahnsen, K.; Kim, J.; Kardo, S.; et al. The enteric nervous system relays psychological stress to intestinal inflammation. Cell 2023, 186, 2823–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitaoka, S.; Tomohiro, A.; Ukeshima, S.; Liu, K.; Wake, H.; Kimura, S.H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Nishibori, M.; Furuyashiki, T. Repeated Social Defeat Stress Induces HMGB1 Nuclear Export in Prefrontal Neurons, Leading to Social Avoidance in Mice. Cells 2023, 12, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Furuyashiki, T.; Kitaoka, S.; Senzai, Y.; Imoto, Y.; Segi-Nishida, E.; Deguchi, Y.; Breyer, R.M.; Breyer, M.D.; Narumiya, S. Prostaglandin E2-Mediated Attenuation of Mesocortical Dopaminergic Pathway Is Critical for Susceptibility to Repeated Social Defeat Stress in Mice. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4319–4329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alemi, F.; Poole, D.P.; Chiu, J.; Schoonjans, K.; Cattaruzza, F.; Grider, J.R.; Bunnett, N.W.; Corvera, C.U. The receptor TGR5 mediates the prokinetic actions of intestinal bile acids and is required for normal defecation in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.S.; Schmauss, C.; Cuenca, A.; Ratcliffe, E.; Gershon, M.D. Physiological modulation of intestinal motility by enteric dopaminergic neurons and the D2 receptor: Analysis of dopamine receptor expression, location, development, and function in wild-type and knock-out mice. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 2798–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, T.; Fukui, H.; Wang, X.; Nishiumi, S.; Yokota, H.; Makizaki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Ohno, H.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; et al. Effect of a high-fat diet on the small-intestinal environment and mucosal integrity in the gut-liver axis. Cells. 2021, 10, 3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fukui, H.; Ran, Y.; Xu, X.; Ebisutani, N.; Nakanishi, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Maeda, A.; Makizaki, Y.; Tomita, T.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum G9-1 has a preventive effect on the acceleration of colonic permeability and M1 macrophage population in maternally separated rats. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Fukui, H.; Eda, H.; Xu, X.; Kitayama, Y.; Hara, K.; Kodani, M.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; Watari, J.; et al. Involvement of gut microbiota in association between GLP-1/GLP-1 receptor expression and gastrointestinal motility. Am. J. Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2017, 312, G367–G373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. HGF aggravated periodontitis-associated gut barrier and microbial dysfunction: Implications for oral-gut axis regulation. Biology 2025, 14, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitayama, Y.; Fukui, H.; Hara, K.; Eda, H.; Kodani, M.; Yang, M.; Sun, C.; Yamagishi, H.; Tomita, T.; Oshima, T.; et al. Role of regenerating gene I in claudin expression and barrier function in the small intestine. Transl. Res. 2016, 173, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corridoni, D.; Pastorelli, L.; Mattioli, B.; Locovei, S.; Ishikawa, D.; Arseneau, K.O.; Chieppa, M.; Cominelli, F.; Pizarro, T.T. Probiotic Bacteria Regulate Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Experimental Ileitis by a TNF-Dependent Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yagi, S.; Fukui, H.; Shiraishi, T.; Kaku, K.; Wakita, M.; Takagi, Y.; Ikenouchi, M.; Sato, T.; Kawai, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; et al. Effect of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on the Small-Intestinal Environment, Including the Gut Flora, Immune System, and Mucosal Barrier Integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199359
Yagi S, Fukui H, Shiraishi T, Kaku K, Wakita M, Takagi Y, Ikenouchi M, Sato T, Kawai M, Yokoyama Y, et al. Effect of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on the Small-Intestinal Environment, Including the Gut Flora, Immune System, and Mucosal Barrier Integrity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199359
Chicago/Turabian StyleYagi, Soichi, Hirokazu Fukui, Tetsuya Shiraishi, Koji Kaku, Midori Wakita, Yasuhiro Takagi, Maiko Ikenouchi, Toshiyuki Sato, Mikio Kawai, Yoko Yokoyama, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on the Small-Intestinal Environment, Including the Gut Flora, Immune System, and Mucosal Barrier Integrity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199359
APA StyleYagi, S., Fukui, H., Shiraishi, T., Kaku, K., Wakita, M., Takagi, Y., Ikenouchi, M., Sato, T., Kawai, M., Yokoyama, Y., Takagawa, T., Tomita, T., Kitaoka, S., & Shinzaki, S. (2025). Effect of Chronic Social Defeat Stress on the Small-Intestinal Environment, Including the Gut Flora, Immune System, and Mucosal Barrier Integrity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199359






