Fabrication of Protein–Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Composites Incorporated with Magnetite Nanoparticles as Acellular Matrices
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. NMR Spectrum
2.2. Zeta Potential
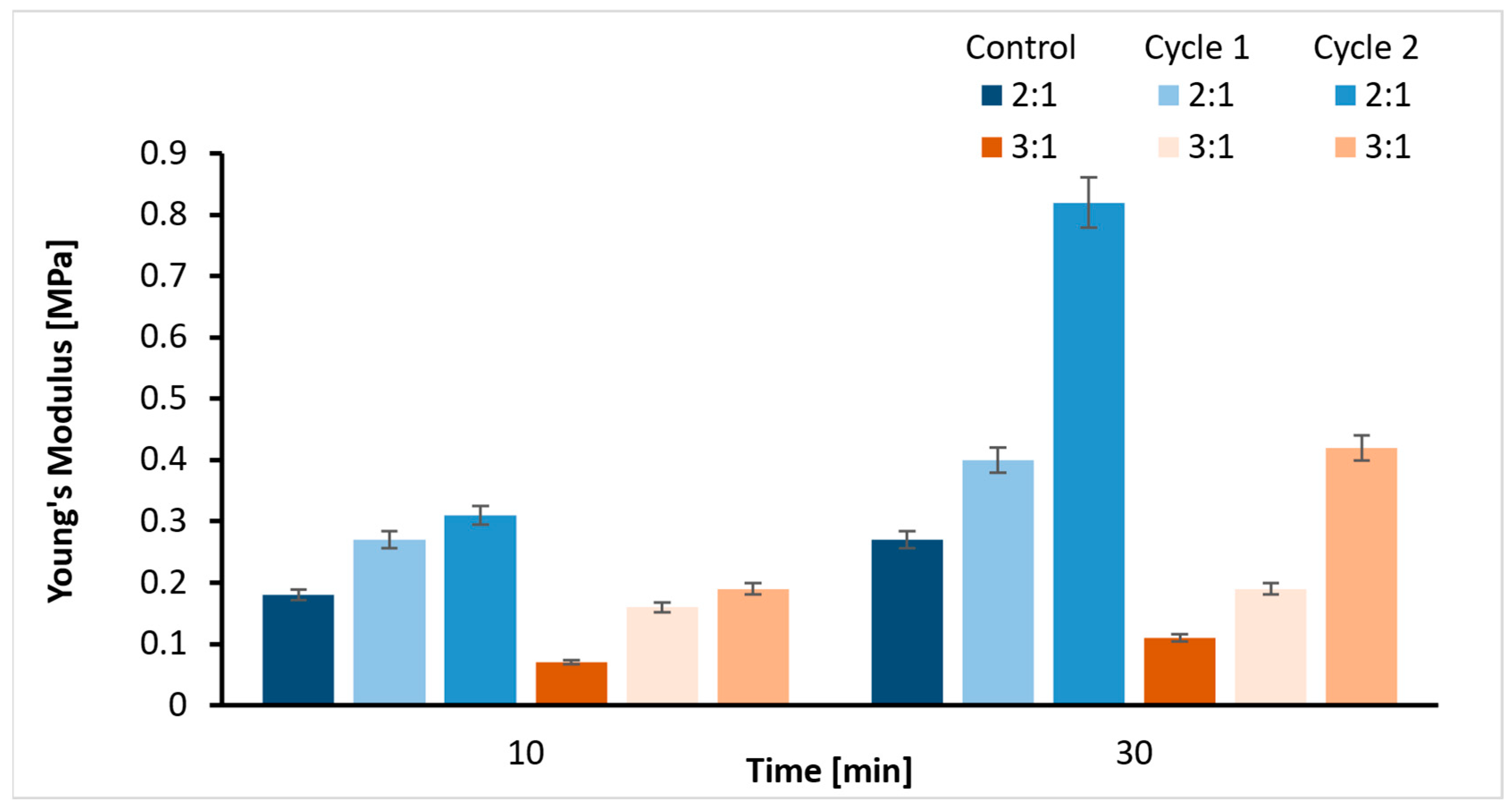
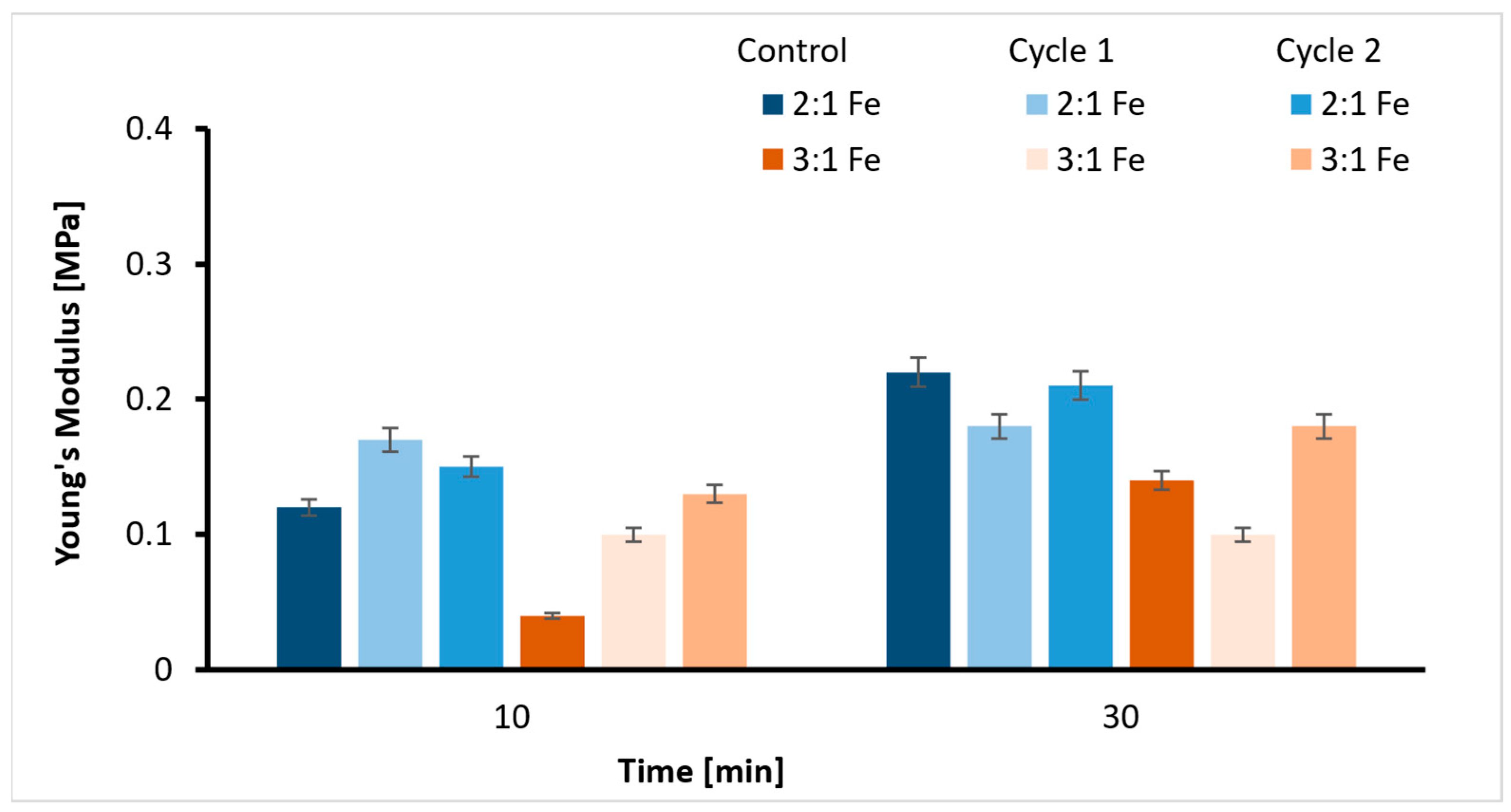
2.3. Tensile Strength
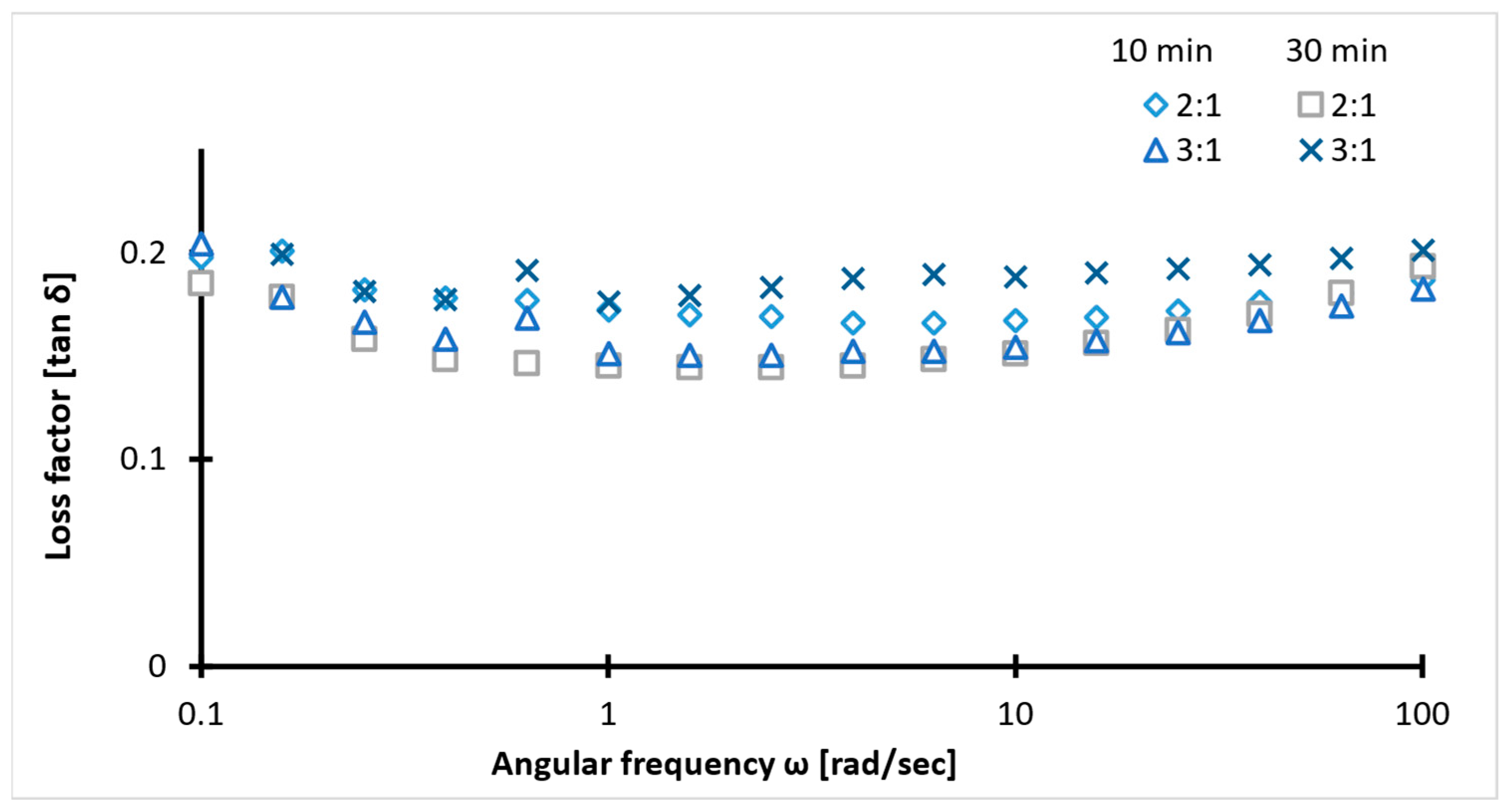
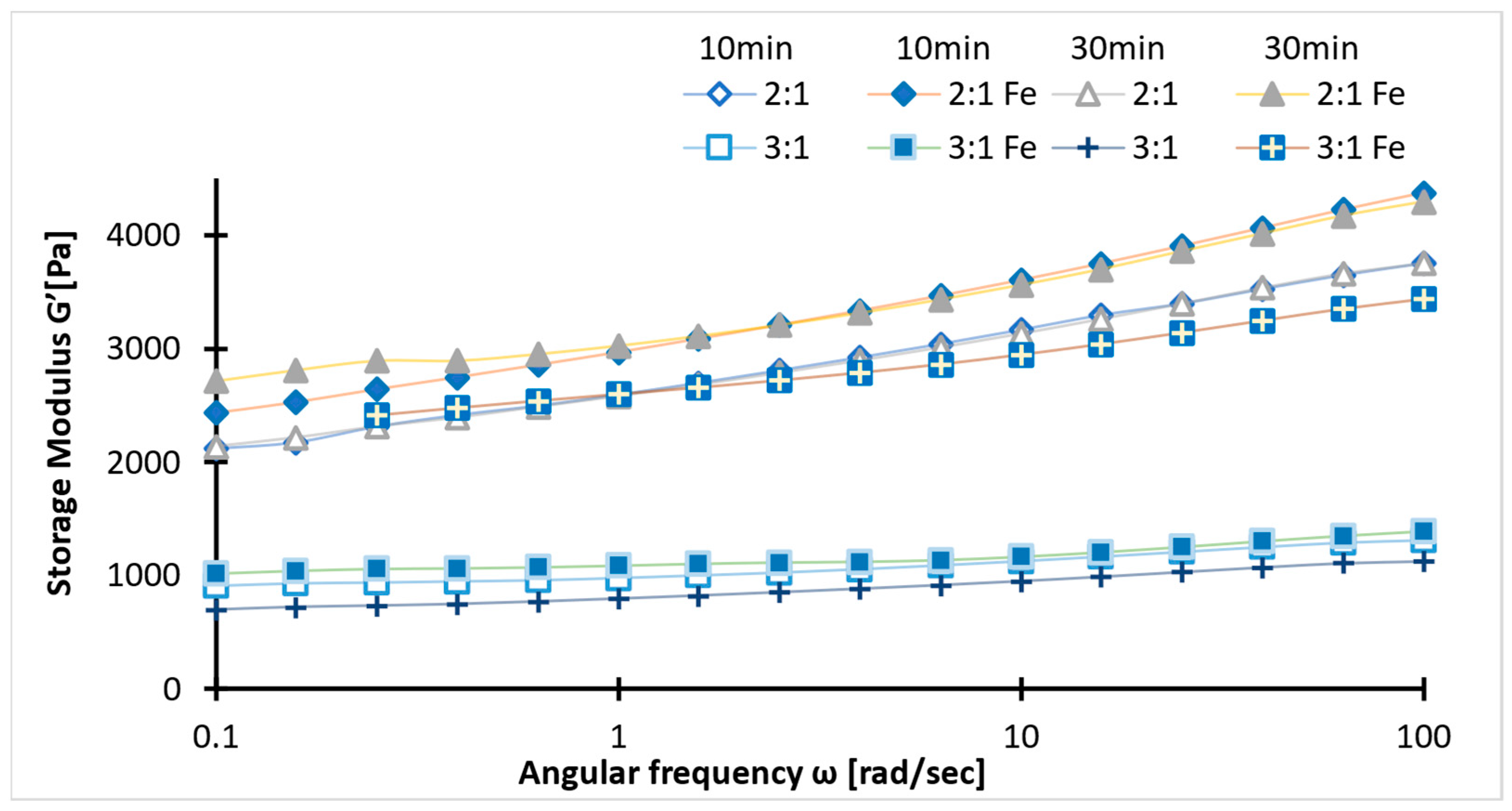
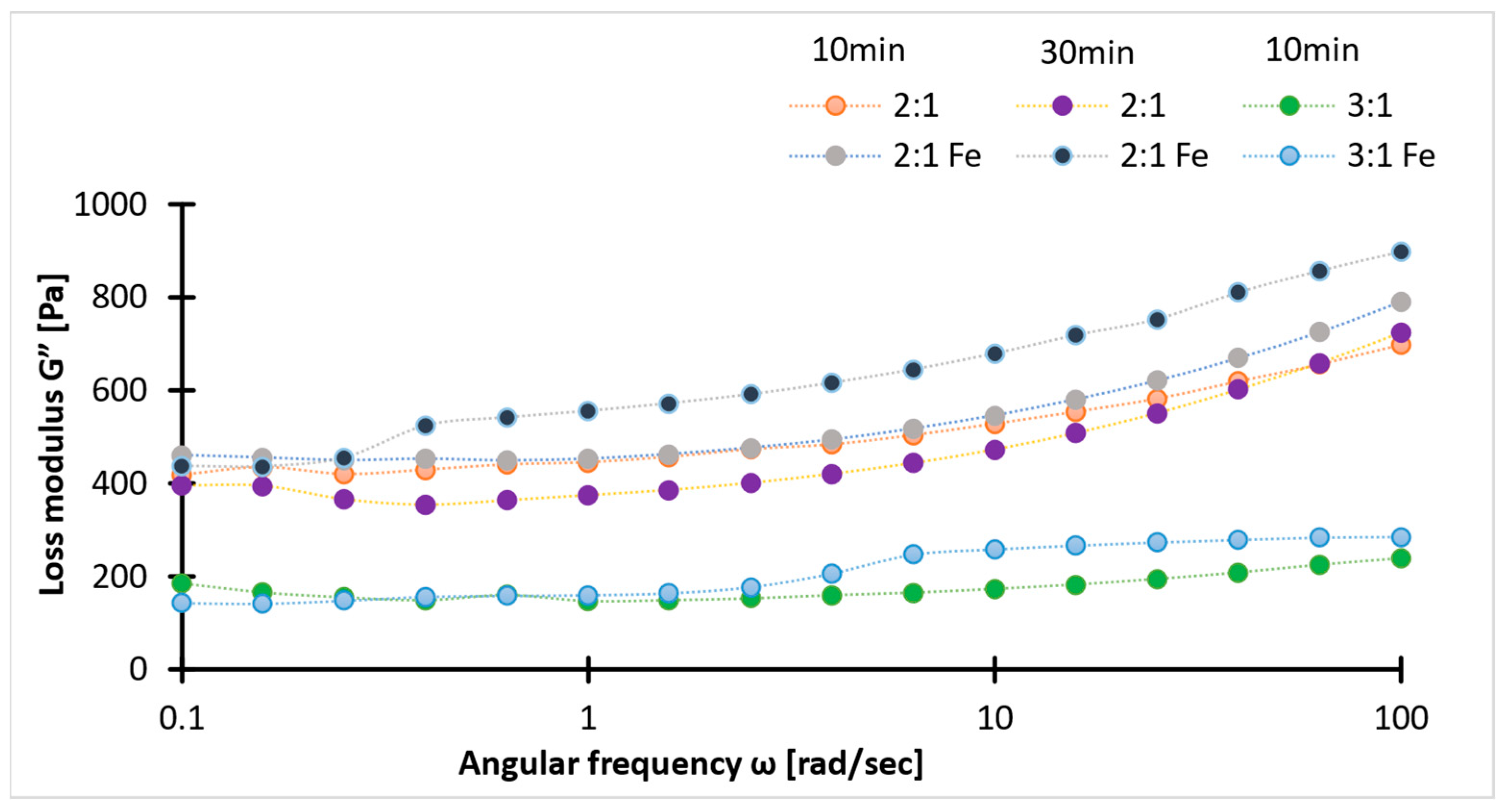
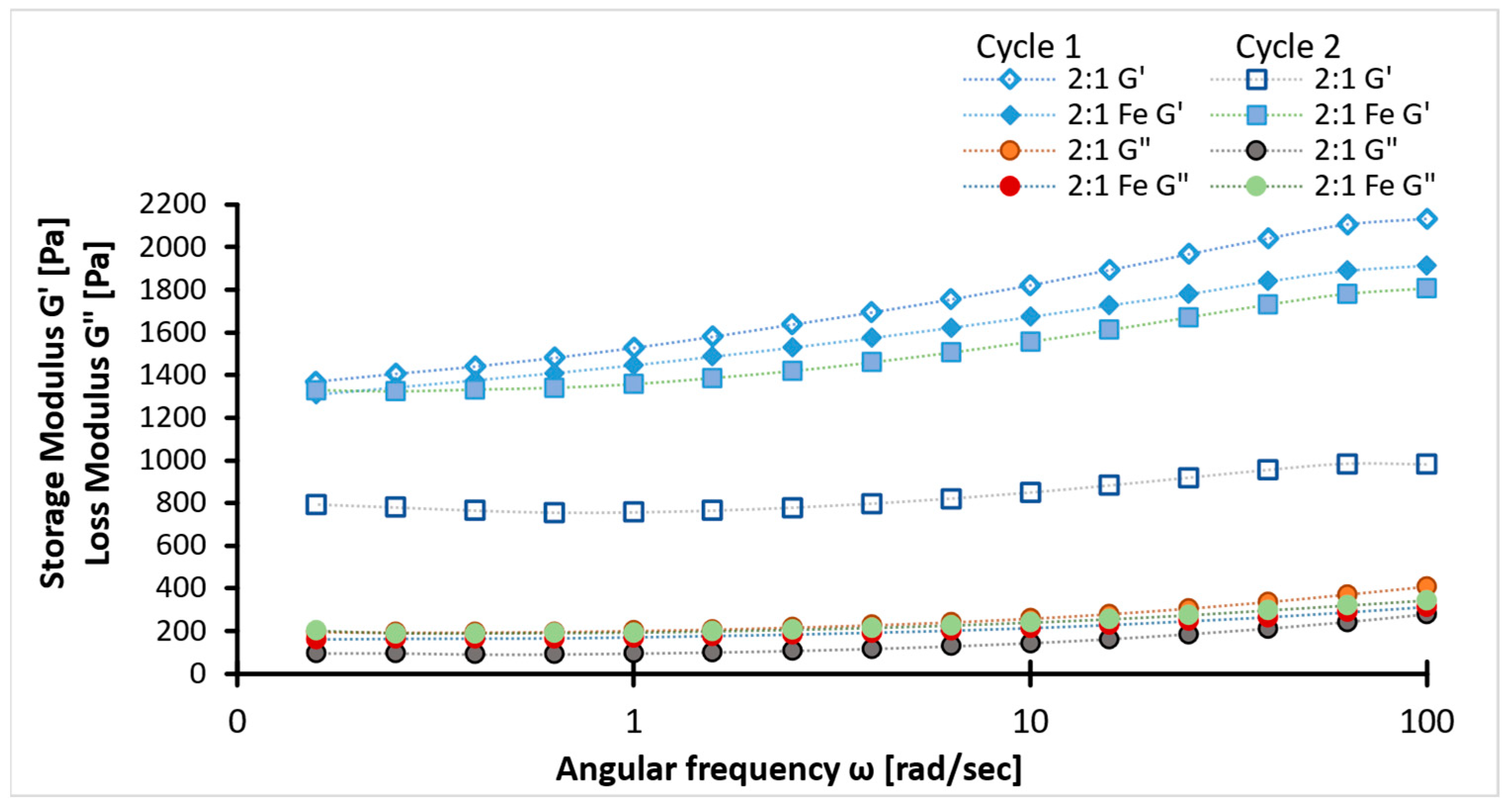
2.4. Rheology
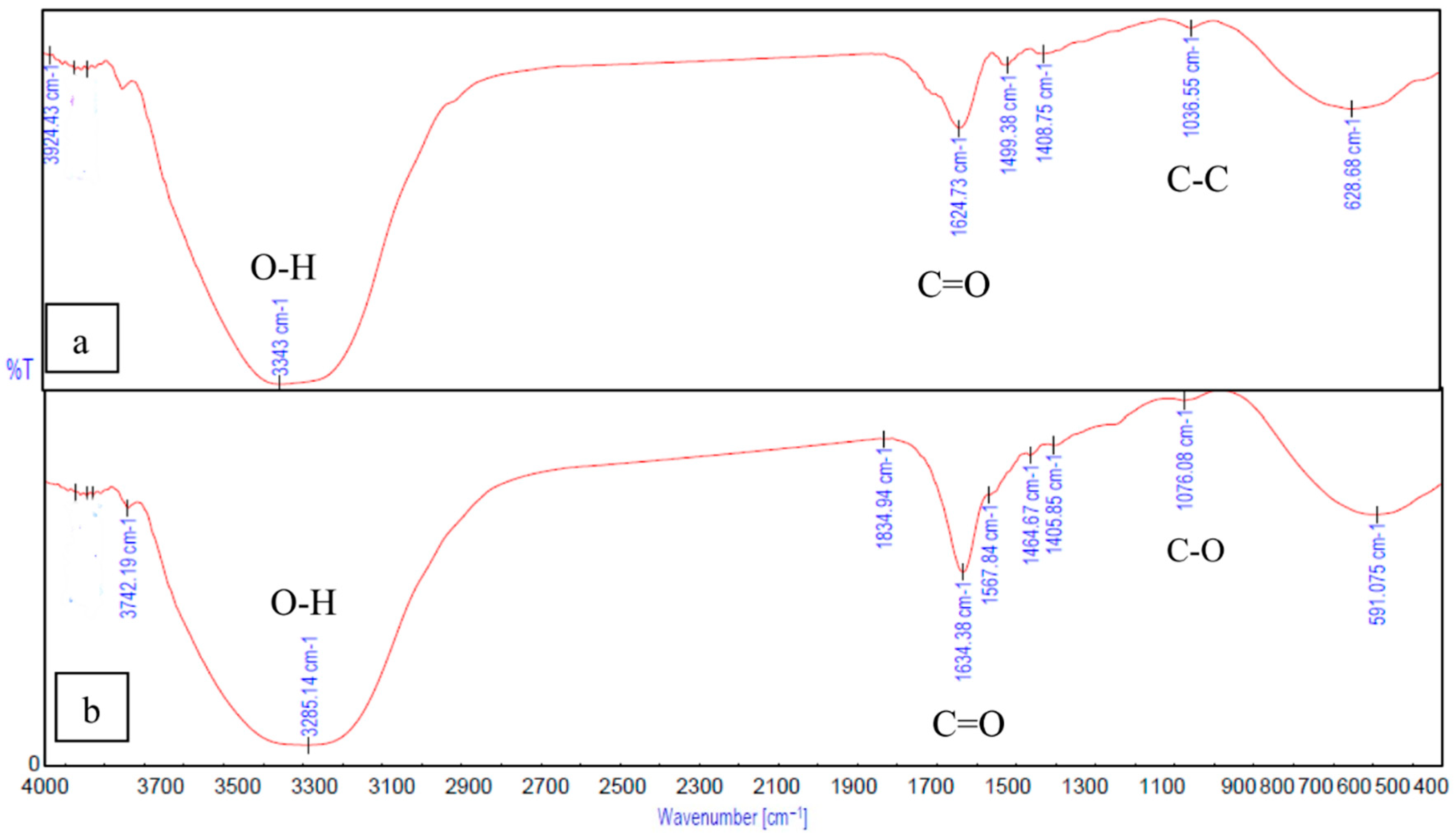
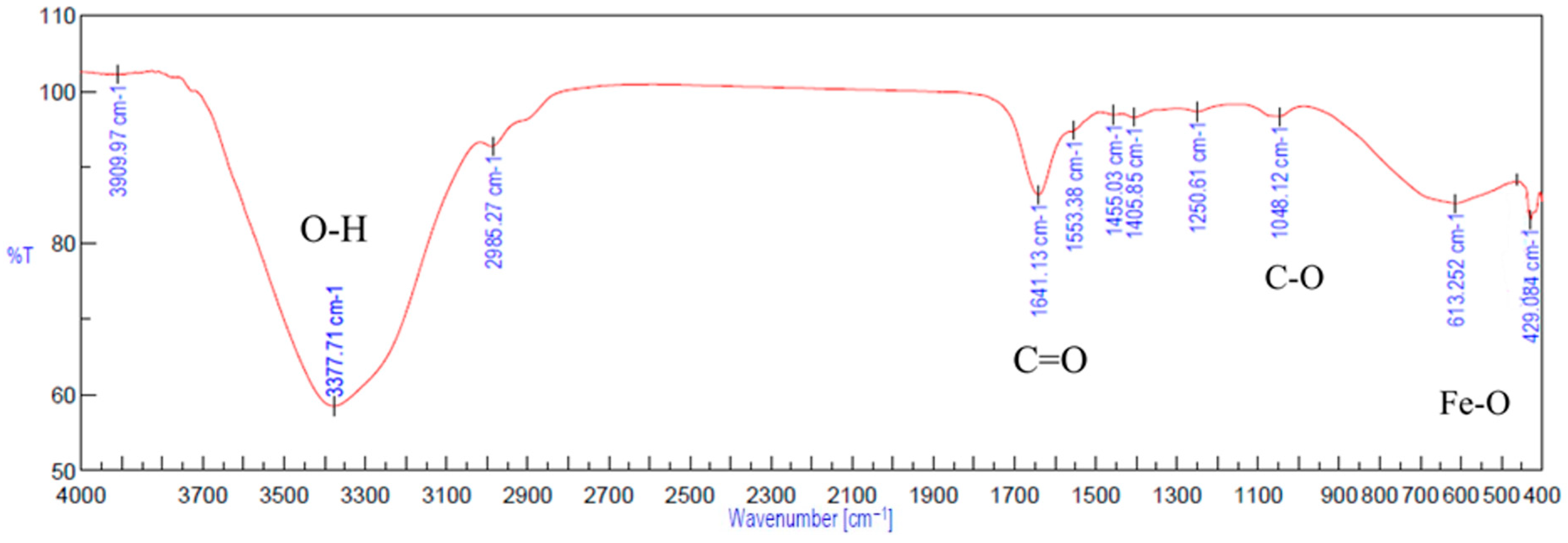
2.5. FTIR Spectra
3. Discussion
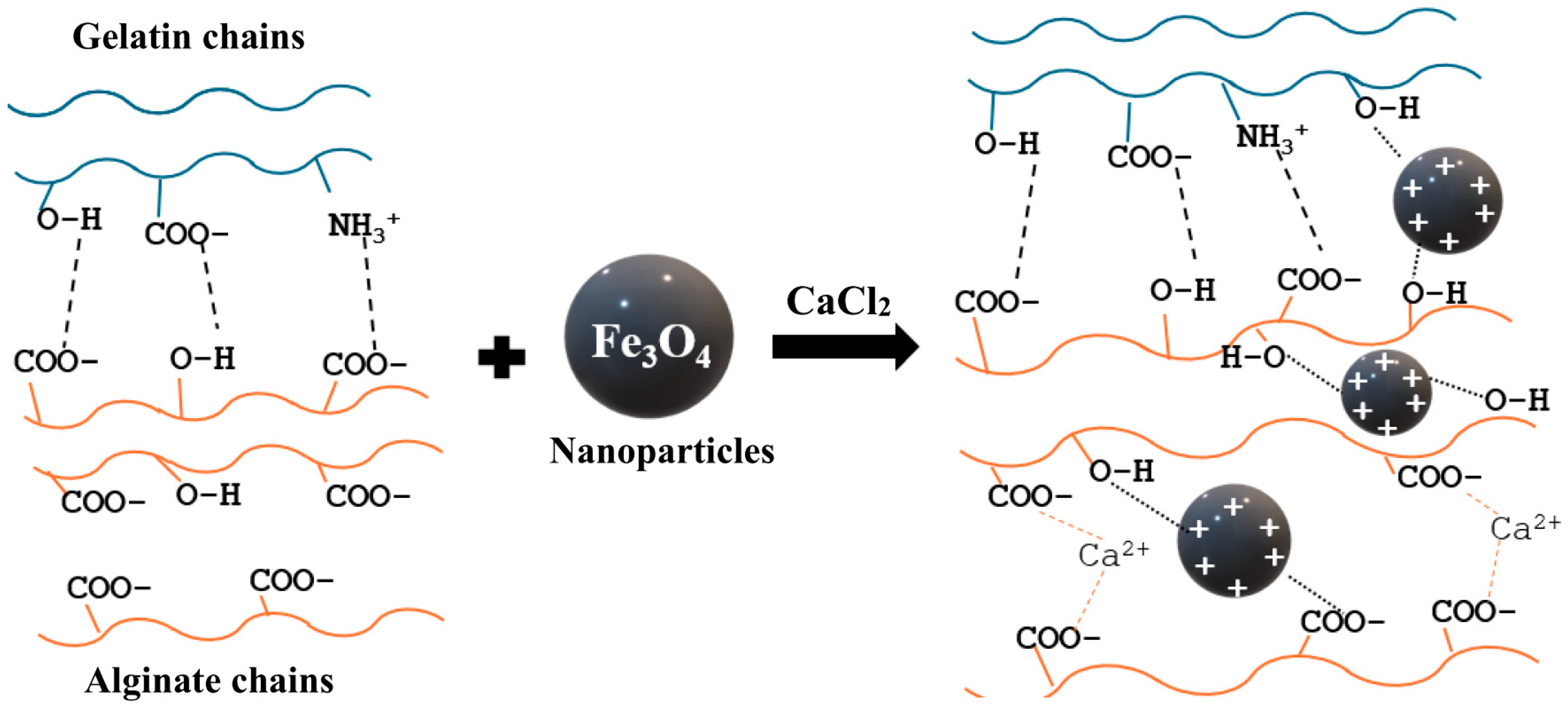
3.1. Gel-SA Interactions
3.2. Interactions of Gel-SA with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Hydrogel (Gel-SA)
4.3. Addition of Magnetite Nanoparticle (Gel-SA-Fe3O4)
4.4. Variables in Hydrogel Formulation
4.5. Characterization
4.5.1. NMR Spectroscopy
4.5.2. Zeta Potentiometer
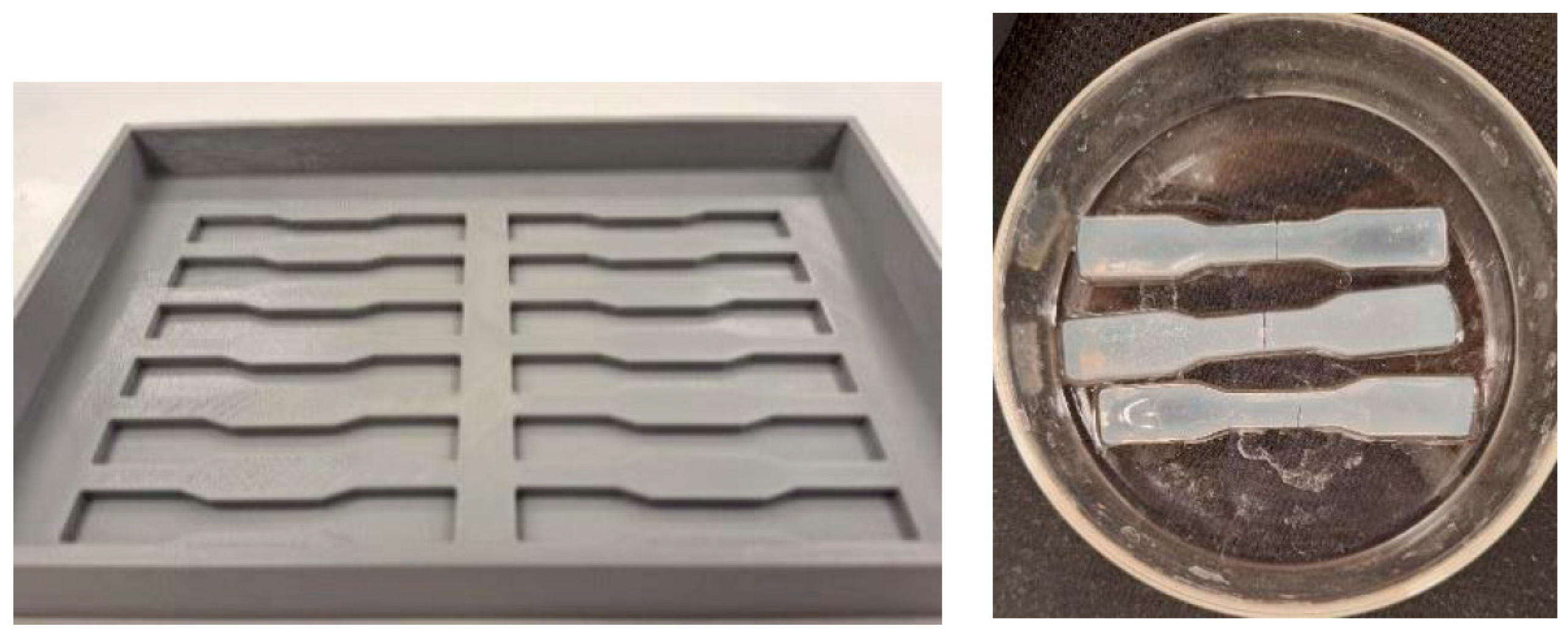
4.5.3. Tensile Test
4.5.4. Rheometry
4.5.5. FTIR Spectroscopy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tran, H.D.N.; Park, K.D.; Ching, Y.C.; Huynh, C.; Nguyen, D.H. A Comprehensive Review on Polymeric Hydrogel and Its Composite: Matrices of Choice for Bone and Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 89, 58–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Kanemaru, K.; Serpe, M.J. Light-Degradable Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Antibacterial Wound Dressing Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2024, 12, 4686–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrali, M.; Thakur, A.; Pennisi, C.P.; Talebian, S.; Arpanaei, A.; Nikkhah, M.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A. Nanoreinforced Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Biomaterials That Are Compatible with Load-Bearing and Electroactive Tissues. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1603612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoniyot, P.; Tan, M.J.; Karim, A.A.; Young, D.J.; Loh, X.J. Nanoparticle–Hydrogel Composites: Concept, Design, and Applications of These Promising, Multi-Functional Materials. Adv. Sci. 2015, 2, 1400010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.; Clegg, J.R.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S. Hydrogels in the Clinic. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2020, 5, e10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.T.; Rioux, L.-E.; Turgeon, S.L. Formation and Functional Properties of Protein–Polysaccharide Electrostatic Hydrogels in Comparison to Protein or Polysaccharide Hydrogels. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 239, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, H.; Zhu, C.; Fan, D. Optimization of Human-like Collagen Composite Polysaccharide Hydrogel Dressing Preparation Using Response Surface for Burn Repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 239, 116249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.J.; Perlman, G.; Morris, M.; Komarova, S.V. Extracellular Matrix Composition of Connective Tissues: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafezi, M.; Nouri Khorasani, S.; Zare, M.; Esmaeely Neisiany, R.; Davoodi, P. Advanced Hydrogels for Cartilage Tissue Engineering: Recent Progress and Future Directions. Polymers 2021, 13, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Gebeyehu, A.; Miranda, M.; Bahadur, D.; Patel, N.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Rishi, A.K.; Singh, M. Characterization and Printability of Sodium Alginate -Gelatin Hydrogel for Bioprinting NSCLC Co-Culture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Tuszynska, M.; Kaźmierski, Ł.; Bartniak, M.; Bajek, A. Gelatin–Sodium Alginate Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Squaric Acid and Dialdehyde Starch as a Potential Bio-Ink. Polymers 2024, 16, 2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipal, J.; Mohd Pu’ad, N.A.S.; Lee, T.C.; Nayan, N.H.M.; Sahari, N.; Basri, H.; Idris, M.I.; Abdullah, H.Z. A Review of Gelatin: Properties, Sources, Process, Applications, and Commercialisation. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 42, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, E.; Huang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wei, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z. Application of Gelatin-Based Composites in Bone Tissue Engineering. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulat, M.; Akalin, G.O. Preparation and Characterization of Gelatin Hydrogel Support for Immobilization of Candida Rugosa Lipase. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2013, 41, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Joshi, N.; Jayakrishnan, A.; Banerjee, R. Self-Crosslinked Oxidized Alginate/Gelatin Hydrogel as Injectable, Adhesive Biomimetic Scaffolds for Cartilage Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 3650–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Ao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Ao, Q.; Rodríguez-Argüelles, C.; Simón-Vázquez, R. Marine Drugs Preparation of Alginate-Based Biomaterials and Their Applications in Biomedicine. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijian, R.S.; Yusefi, M.; Shameli, K. Plant Extract Loaded Sodium Alginate Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications: A Review. J. Res. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2022, 6, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, Y.; Akimoto, J.; Kobatake, E.; Ito, Y. Gelation and Release Behavior of Visible Light-Curable Alginate. Polym. J. 2020, 52, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Ions-Induced Gelation of Alginate: Mechanisms and Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Sun, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, Y. Gelation Behavior and Mechanism of Alginate with Calcium: Dependence on Monovalent Counterions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 294, 119788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xiao, P.; Hou, S.; Huang, Y. Graphene Based Self-Healing Materials. Carbon 2019, 146, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paramasivam, G.; Palem, V.V.; Meenakshy, S.; Suresh, L.K.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Antherjanam, S.; Sundramoorthy, A.K. Advances on Carbon Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Medical Diagnosis and Drug Delivery. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2024, 241, 114032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardo, A.; Gómez-Florit, M.; Barbosa, S.; Taboada, P.; Domingues, R.M.A.; Gomes, M.E. Magnetic Nanocomposite Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Design Concepts and Remote Actuation Strategies to Control Cell Fate. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 175–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghizadeh, S.; Tayebi, L.; Akbarzadeh, M.; Lohrasbi, P.; Savardashtaki, A. Magnetic Hydrogel Applications in Articular Cartilage Tissue Engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2024, 112, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante-Torres, M.; Romero-Fierro, D.; Estrella-Nuñez, J.; Arcentales-Vera, B.; Chichande-Proaño, E.; Bucio, E. Polymeric Composite of Magnetite Iron Oxide Nanoparticles and Their Application in Biomedicine: A Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massana Roquero, D.; Othman, A.; Melman, A.; Katz, E. Iron(iii)-Cross-Linked Alginate Hydrogels: A Critical Review. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 1849–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czichy, C.; Spangenberg, J.; Günther, S.; Gelinsky, M.; Odenbach, S. Determination of the Young’s Modulus for Alginate-Based Hydrogel with Magnetite-Particles Depending on Storage Conditions and Particle Concentration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2020, 501, 166395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, H.; Yang, C.H.; Zheng, W.J.; Yang, J.H.; Wang, M.X.; Yang, S.; Zrínyi, M.; Osada, Y.; Suo, Z.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Exceptionally Tough and Notch-Insensitive Magnetic Hydrogels. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8253–8261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, A.M.G.C.; Hussain, A.; Marcos, A.S.; Roque, A.C.A. A Biotechnological Perspective on the Application of Iron Oxide Magnetic Colloids Modified with Polysaccharides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 142–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, A.N.; Rose, A.L.; Feitz, A.J.; Waite, T.D. Kinetics of Fe(III) Precipitation in Aqueous Solutions at PH 6.0–9.5 and 25°C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasdalen, H. High-Field, 1H-n.m.r. Spectroscopy of Alginate: Sequential Structure and Linkage Conformations. Carbohydr. Res. 1983, 118, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasdalen, H.; Larsen, B.; Smidsrød, O. A p.m.r. Study of the Composition and Sequence of Uronate Residues in Alginates. Carbohydr. Res. 1979, 68, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, T.A.; Llanes, F.; Volesky, B.; Diaz-Pulido, G.; McCook, L.; Mucci, A. 1H-NMR Study of Na Alginates Extracted from Sargassum spp. in Relation to Metal Biosorption. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2003, 110, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadros, T.R.; Erices, A.A.; Aguilera, J.M. Porous Matrix of Calcium Alginate/Gelatin with Enhanced Properties as Scaffold for Cell Culture. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 46, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smidsrød, O.; Glover, R.M.; Whittington, S.G. The Relative Extension of Alginates Having Different Chemical Composition. Carbohydr. Res. 1973, 27, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draget, K.I.; Gåserød, O.; Aune, I.; Andersen, P.O.; Storbakken, B.; Stokke, B.T.; Smidsrød, O. Effects of Molecular Weight and Elastic Segment Flexibility on Syneresis in Ca-Alginate Gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Bligh, M.W.; Kinsela, A.S.; Waite, T.D. Effect of Iron on Membrane Fouling by Alginate in the Absence and Presence of Calcium. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 497, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Y.; Lin, L.; Gan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Feng, C. Preparation of Chitosan/Sodium Alginate Conductive Hydrogels with High Salt Contents and Their Application in Flexible Supercapacitors. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 278, 118927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela-Feijoo, A.; Ponton, A. Study of the Tunable Mechanical and Swelling Properties of Magnetic Sensitive Calcium Alginate Nanocomposite Hydrogels. Rheol. Acta 2023, 62, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.W.; Chan, L.W.; Kho, S.B.; Heng, P.W.S. Design of Controlled-Release Solid Dosage Forms of Alginate and Chitosan Using Microwave. J. Control. Release 2002, 84, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saarai, A.; Kasparkova, V.; Sedlacek, T.; Saha, P. On the Development and Characterisation of Crosslinked Sodium Alginate/Gelatine Hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 18, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkasa, D.P.; Erizal, E.; Purwanti, T.; Tontowi, A.E. Characterization of Semi-Interpenetrated Network Alginate/Gelatin Wound Dressing Crosslinked at Sol Phase. Indones. J. Chem. 2018, 18, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafin, A.; Culebras, M.; Collins, M.N. Synthesis and Evaluation of Alginate, Gelatin, and Hyaluronic Acid Hybrid Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 233, 123438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaihre, B.; Khil, M.; Lee, D.; Kim, H. Gelatin-Coated Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Carrier System: Drug Loading and in Vitro Drug Release Study. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 365, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.; Siegrist, M.; Wang, X.; Hunziker, E. Development of Mechanically Stable Alginate/Chondrocyte Constructs: Effects of Guluronic Acid Content and Matrix Synthesis. J. Orthop. Res. 2001, 19, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enobakhare, B.; Bader, D.L.; Lee, D.A. Concentration and M/G Ratio Influence the Physiochemical and Mechanical Properties of Alginate Constructs for Tissue Engineering. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2006, 4, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Arnedo, A.; Sarmiento, P.; Cruz, J.C.; Munoz-Camargo, C.; Salcedo, F.; Groot, H.; Narvaez, D.M. 3D Alginate Hydrogels with Controlled Mechanical Properties for Mammalian Cell Encapsulation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IX International Seminar of Biomedical Engineering (SIB), Bogota, Colombia, 16–18 May 2018; IEEE: Bogota, Colombia, 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM Committee. Standard Test Methods for Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Rubbers and Thermoplastic Elastomers-Tension [D412-98]; American National Standards Institute: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]



| Hydrogel Composition | Mean pH Values (SD = ±0.12) |
| Pure gelatin solution (10% w/v) | 5.33 |
| Pure SA solution (5% w/v) | 7.24 |
| 2:1 Gel:SA | 5.55 |
| Addition of Fe3O4 Nanoparticle | Mean pH Values (SD = ±0.12) |
| Gel + Fe3O4 0.1% (w/v) | 5.26 |
| SA + Fe3O4 0.1% (w/v) | 7.42 |
| 2:1 Gel:SA + Fe3O4 0.1% (w/v) | 5.42 |
| Heating
40 ± 1 °C | Hydrogel | Weight Ratio | Crosslinking Time | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No heat/Cycle 1/Cycle 2 | Gel: SA | Gel: SA: Fe3O4 | 2:1 | 3:1 | 10 min | 30 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gigimon, A.V.; Machrafi, H.; Perfetti, C.; Hendrick, P.; Iorio, C.S. Fabrication of Protein–Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Composites Incorporated with Magnetite Nanoparticles as Acellular Matrices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199338
Gigimon AV, Machrafi H, Perfetti C, Hendrick P, Iorio CS. Fabrication of Protein–Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Composites Incorporated with Magnetite Nanoparticles as Acellular Matrices. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199338
Chicago/Turabian StyleGigimon, Anet Vadakken, Hatim Machrafi, Claire Perfetti, Patrick Hendrick, and Carlo S. Iorio. 2025. "Fabrication of Protein–Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Composites Incorporated with Magnetite Nanoparticles as Acellular Matrices" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199338
APA StyleGigimon, A. V., Machrafi, H., Perfetti, C., Hendrick, P., & Iorio, C. S. (2025). Fabrication of Protein–Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogel Composites Incorporated with Magnetite Nanoparticles as Acellular Matrices. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199338









