Exosomal miRNAs: Key Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biogenesis and miRNA Sorting of Exosomes
3. Cancer and Cancer Stem Cells
4. Exosomal miRNA-Mediated Tumor Microenvironment Remodeling and Malignant Progression
4.1. Exosomal miRNA-Mediated Immune Regulation and Immune Evasion
4.1.1. Exosomal miRNA Regulation of CAFs
4.1.2. Exosomal miRNA Regulation of Macrophages
4.1.3. Exosomal miRNA Regulation of DC and NK Cells
4.1.4. Exosomal miRNA Regulation of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells
4.1.5. Exosomal miRNA Regulation of T Cells
4.2. Promotion of Tumor Angiogenesis
4.3. Promotion of EMT and Metastasis
4.4. Roles of Exosomal miRNAs in Drug Resistance and Metabolic Reprogramming
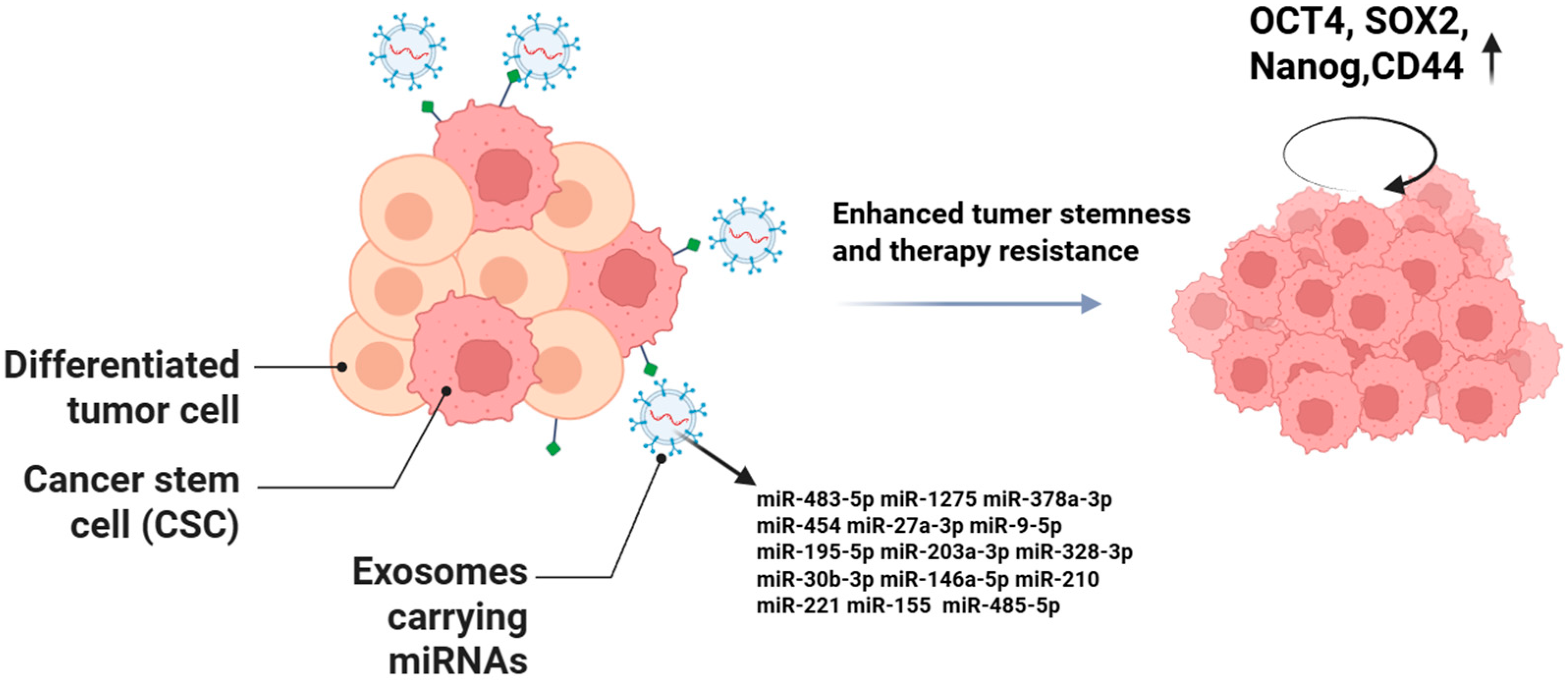
5. Roles of Exosomal miRNAs in Cancer Stem Cells
5.1. Maintenance of CSC Stemness Characteristics and Self-Renewal
5.2. Mediation of CSC Therapy Resistance
6. Translational Applications of Exosomal miRNAs in Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy
6.1. Potential Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers
6.2. Potential Therapeutic Targets
6.2.1. Targeted Delivery of Exosomal miRNAs to Tumor Cells
6.2.2. Targeted Delivery of Exosomal miRNAs to Cancer Stem Cells
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.R.; Sethi, I.; Sadida, H.Q.; Rah, B.; Mir, R.; Algehainy, N.; Albalawi, I.A.; Masoodi, T.; Subbaraj, G.K.; Jamal, F.; et al. Cancer cell plasticity: From cellular, molecular, and genetic mechanisms to tumor heterogeneity and drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024, 43, 197–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.J.J.; Liu, D.; To, S.K.Y.; Wong, A.S.T. Exosomes in cancer nanomedicine: Biotechnological advancements and innovations. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, T.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Chen, H.; Luo, S.; Chen, D.; Cai, C.; Li, W. The role of Exosomal miRNAs in cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.; Shu, Y. Role of exosomal non-coding RNAs from tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor microenvironment. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 3133–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, H.; Pu, W.; Chen, L.; Guo, D.; Jiang, H.; He, B.; Qin, S.; Wang, K.; Li, N.; et al. Cancer metabolism and tumor microenvironment: Fostering each other? Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 236–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, F.; Pan, W.; Liu, G.; Zhang, H.; Yan, D.; Zheng, S.; Ma, Z.; Ren, X. Tumor-associated exosomes in cancer progression and therapeutic targets. MedComm 2024, 5, e709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, Z.X. Roles of miRNAs in regulating ovarian cancer stemness. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallasamy, P.; Nimmakayala, R.K.; Parte, S.; Are, A.C.; Batra, S.K.; Ponnusamy, M.P. Tumor microenvironment enriches the stemness features: The architectural event of therapy resistance and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López de Andrés, J.; Griñán-Lisón, C.; Jiménez, G.; Marchal, J.A. Cancer stem cell secretome in the tumor microenvironment: A key point for an effective personalized cancer treatment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Li, D.; Jie, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, W.; Qiu, C. Exosome-based nanoparticles and cancer immunotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 179, 117296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, A.; Varshney, A.; Bajaj, R.; Pokharkar, V. Exosomes as New Generation Vehicles for Drug Delivery: Biomedical Applications and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.C.; Dean, S.; Davies, B.A.; Azmi, I.F.; Pashkova, N.; Payne, J.A.; Staffenhagen, J.; West, M.; Piper, R.C.; Odorizzi, G.; et al. Bro1 stimulates Vps4 to promote intralumenal vesicle formation during multivesicular body biogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 220, e202102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, J.H. ESCRTs are everywhere. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2398–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, B.A.; Lee, J.R.; Oestreich, A.J.; Katzmann, D.J. Membrane protein targeting to the MVB/lysosome. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 1575–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, S.V.; Feng, D. The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Hagiwara, K.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Ochiya, T. Neutral sphingomyelinase 2 (nSMase2)-dependent exosomal transfer of angiogenic microRNAs regulate cancer cell metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10849–10859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, L.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Roizman, B.; Zhou, G.G. hnRNPA2B1 Associated with Recruitment of RNA into Exosomes Plays a Key Role in Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Release from Infected Cells. J. Virol. 2020, 94, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Zeng, Z.; Song, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Ke, X.; Hu, X. YBX-1 mediated sorting of miR-133 into hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced EPC-derived exosomes to increase fibroblast angiogenesis and MEndoT. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife 2016, 5, e19276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, A.J.; Hoshino, D.; Hong, N.H.; Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Coffey, R.J.; Patton, J.G.; Weaver, A.M. KRAS-MEK Signaling Controls Ago2 Sorting into Exosomes. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, A.; Villar-Prados, A.; Oliphint, P.A.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; De Hoff, P.; Morey, R.; Liu, J.; Roszik, J.; Clise-Dwyer, K.; et al. Mechanisms of nuclear content loading to exosomes. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaax8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayob, A.Z.; Ramasamy, T.S. Cancer stem cells as key drivers of tumour progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapidot, T.; Sirard, C.; Vormoor, J.; Murdoch, B.; Hoang, T.; Caceres-Cortes, J.; Minden, M.; Paterson, B.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Dick, J.E. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature 1994, 367, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Wang, J.; Li, X. Cancer stem cells and their niche in cancer progression and therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, K.E.; Wu, F.; Keysar, S.B.; Morton, J.J.; Miller, B.; Chimed, T.S.; Le, P.N.; Nieto, C.; Chowdhury, F.N.; Tyagi, A.; et al. Cancer Cell CD44 Mediates Macrophage/Monocyte-Driven Regulation of Head and Neck Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 4185–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eini, L.; Naseri, M.; Karimi-Busheri, F.; Bozorgmehr, M.; Ghods, R.; Madjd, Z. Preventive cancer stem cell-based vaccination modulates tumor development in syngeneic colon adenocarcinoma murine model. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 4101–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Huang, Z.W.; Li, L.X.; Fu, J.J.; Xiao, B. Identification of CD200+ colorectal cancer stem cells and their gene expression profile. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2252–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Heidt, D.G.; Dalerba, P.; Burant, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Adsay, V.; Wicha, M.; Clarke, M.F.; Simeone, D.M. Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, B.; Park, J.; Park, S.; Yoo, G.; Yum, S.; Kang, W.; Lee, J.M.; Youn, H.; Youn, B. Cancer stem cells: Landscape, challenges and emerging therapeutic innovations. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Mare, J.A.; Sterrenberg, J.N.; Sukhthankar, M.G.; Chiwakata, M.T.; Beukes, D.R.; Blatch, G.L.; Edkins, A.L. Assessment of potential anti-cancer stem cell activity of marine algal compounds using an in vitro mammosphere assay. Cancer Cell Int. 2013, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, J.J.; Ma, S. Hallmarks of cancer stemness. Cell Stem Cell 2024, 31, 617–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wei, X.; Luo, M. Regulation and signaling pathways in cancer stem cells: Implications for targeted therapy for cancer. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Yuan, C.; Zeng, C.; Sun, C.; Xia, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J.; Ding, Z.Y. Cancer stem cells and niches: Challenges in immunotherapy resistance. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Si, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, S.; Qu, X.; Yu, X. Exosomal miR-146a-5p and miR-155-5p promote CXCL12/CXCR7-induced metastasis of colorectal cancer by crosstalk with cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Ning, T.; Deng, T.; et al. Exosomal miR-27a Derived from Gastric Cancer Cells Regulates the Transformation of Fibroblasts into Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 869–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Liu, J.; He, L.; Wang, F.; Xiong, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, X. The long noncoding RNA noncoding RNA activated by DNA damage (NORAD)-microRNA-496-Interleukin-33 axis affects carcinoma-associated fibroblasts-mediated gastric cancer development. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 11738–11755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scognamiglio, I.; Cocca, L.; Puoti, I.; Palma, F.; Ingenito, F.; Quintavalle, C.; Affinito, A.; Roscigno, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Chianese, R.V.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs synergistically trigger stromal fibroblasts in breast cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 28, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Lv, M.; Yu, Q.; Bao, J.; Lou, K.; Li, X. MicroRNA-370-3p shuttled by breast cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles induces fibroblast activation through the CYLD/Nf-κB axis to promote breast cancer progression. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, J.; Dickman, C.; Towle, R.; Jabalee, J.; Javer, A.; Garnis, C. Extracellular vesicle secretion of miR-142-3p from lung adenocarcinoma cells induces tumor promoting changes in the stroma through cell-cell communication. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yan, T.; Huang, C.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, E.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, K.; Shao, Z.; et al. Melanoma cell-secreted exosomal miR-155-5p induce proangiogenic switch of cancer-associated fibroblasts via SOCS1/JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Spassova, I.; Gravemeyer, J.; Ritter, C.; Horny, K.; Lange, A.; Gambichler, T.; Ødum, N.; Schrama, D.; Schadendorf, D.; et al. Merkel cell carcinoma-derived exosome-shuttle miR-375 induces fibroblast polarization by inhibition of RBPJ and p53. Oncogene 2021, 40, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, T.; Lv, H.; Lv, G.; Li, T.; Wang, C.; Han, Q.; Yu, L.; Su, B.; Guo, L.; Huang, S.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-1247-3p induces cancer-associated fibroblast activation to foster lung metastasis of liver cancer. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Wu, Q.; Wu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Jiang, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Epithelial ovarian cancer-secreted exosomal miR-222-3p induces polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43076–43087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kγ to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Pan, J.; Zheng, S.; Cai, D.; Luo, A.; Xia, Z.; Huang, J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-21-5p Induces Macrophage M2 Polarization by Targeting RhoB. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerloff, D.; Lützkendorf, J.; Moritz, R.K.C.; Wersig, T.; Mäder, K.; Müller, L.P.; Sunderkötter, C. Melanoma-Derived Exosomal miR-125b-5p Educates Tumor Associated Macrophages (TAMs) by Targeting Lysosomal Acid Lipase A (LIPA). Cancers 2020, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Zhou, L.; Shen, T.; Cao, L. IFN-γ induces the upregulation of RFXAP via inhibition of miR-212-3p in pancreatic cancer cells: A novel mechanism for IFN-γ response. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3760–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, G.; Zhou, L.; Qian, Y.; Fu, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xiang, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic cancer-derived exosomes transfer miRNAs to dendritic cells and inhibit RFXAP expression via miR-212-3p. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29877–29888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghikhani, A.; Hassan, Z.M.; Ebrahimi, M.; Moazzeni, S.M. microRNA modified tumor-derived exosomes as novel tools for maturation of dendritic cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9417–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Ding, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic cancer derived exosomes regulate the expression of TLR4 in dendritic cells via miR-203. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 292, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.J.; Xie, X.L.; Qi, W.; Yang, Y.C.; Bai, Y.; Han, J.; Ding, Q.; Jiang, H.Q. Cell-free miR-17-5p as a diagnostic biomarker for gastric cancer inhibits dendritic cell maturation. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 2661–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Yu, S.C.; Ping, Y.F.; Yang, J.; Xu, S.L.; Ye, X.Z.; Xu, C.; et al. Metastatic consequences of immune escape from NK cell cytotoxicity by human breast cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5746–5757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Lin, W.; Zheng, Q. Exosomal transfer of HCC-derived miR-17-5p downregulates NK cell function by targeting RUNX1-NKG2D axis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 136, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Chen, I.H.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, P.J.; Tseng, H.P.; Huang, K.T.; Hu, T.H.; Li, L.C.; Goto, S.; Cheng, Y.F.; et al. Circulating exosomal miR-92b: Its role for cancer immunoediting and clinical value for prediction of posttransplant hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. Am. J. Transplant. 2019, 19, 3250–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.H.; Zhang, Z.J.; Shang, L.R.; Luo, Y.W.; Lin, Y.F.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, S.M. Hepatoma cell-secreted exosomal microRNA-103 increases vascular permeability and promotes metastasis by targeting junction proteins. Hepatology 2018, 68, 1459–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; You, B.; Shi, S.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yue, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Metastasis-associated miR-23a from nasopharyngeal carcinoma-derived exosomes mediates angiogenesis by repressing a novel target gene TSGA10. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2873–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadokoro, H.; Umezu, T.; Ohyashiki, K.; Hirano, T.; Ohyashiki, J.H. Exosomes derived from hypoxic leukemia cells enhance tube formation in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 34343–34351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Seubert, B.; Stahl, E.; Dietz, H.; Reuning, U.; Moreno-Leon, L.; Ilie, M.; Hofman, P.; Nagase, H.; Mari, B.; et al. Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 induces a pro-tumourigenic increase of miR-210 in lung adenocarcinoma cells and their exosomes. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3640–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Luo, F.; Wang, B.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, X.; Shi, L.; Lu, X.; Xu, W.; Lu, L.; et al. STAT3-regulated exosomal miR-21 promotes angiogenesis and is involved in neoplastic processes of transformed human bronchial epithelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Hung, J.Y.; Chang, W.A.; Lin, Y.S.; Pan, Y.C.; Tsai, P.H.; Wu, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Hypoxic lung cancer-secreted exosomal miR-23a increased angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting prolyl hydroxylase and tight junction protein ZO-1. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4929–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi-Dehghi, S.; Babashah, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M. microRNA-141-3p-containing small extracellular vesicles derived from epithelial ovarian cancer cells promote endothelial cell angiogenesis through activating the JAK/STAT3 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 14, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, K.; Babashah, S.; Sadeghizadeh, M.; Mowla, S.J.; Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Ataei, F.; Dana, N.; Javan, M. MicroRNA-100 shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes suppresses in vitro angiogenesis through modulating the mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF signaling axis in breast cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. 2017, 40, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, F.; Tan, J.J.; Deng, Y.Q.; Peng, X.H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, B.; Xu, X.; Li, X.P. Exosomal miR-9 inhibits angiogenesis by targeting MDK and regulating PDK/AKT pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xing, T.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J. Exosome-mediated miR-200b promotes colorectal cancer proliferation upon TGF-β1 exposure. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, T.; Lin, W.L.; Yan, I.K.; Braconi, C.; Patel, T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: A mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Zhu, A.; Gong, L. Exosomes of glioma cells deliver miR-148a to promote proliferation and metastasis of glioblastoma via targeting CADM1. Bull. Cancer 2018, 105, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Ren, Z.J.; Tang, J.H.; Yu, Q. Exosomal MicroRNA MiR-1246 Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Drug Resistance by Targeting CCNG2 in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Li, M.; Cui, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K.; Li, L. Shikonin Inhibits the Proliferation of Human Breast Cancer Cells by Reducing Tumor-Derived Exosomes. Molecules 2016, 21, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Li, C.; et al. Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells Deliver miR-21 to Normoxic Cells to Elicit a Prometastatic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1770–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, G.; Zhao, D.; Wang, J.; Bai, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wang, H.; Fang, R.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z.; et al. CD103-positive CSC exosome promotes EMT of clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Role of remote MiR-19b-3p. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Sai, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lin, F.; Sun, W.; Zhu, W.; Fang, D.; Luo, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L. Exosome-transmitted miRNA-335-5p promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by facilitating EMT via targeting RASA1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ali, D.J.; Tian, T.; Xu, H.; Si, K.; Sun, B.; Chen, B.; Xiao, Z. Engineered exosomes for targeted co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and chemotherapeutics to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Lai, X.; Yu, S.; Chen, S.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yao, L.; Zhang, J. Exosomal miR-221/222 enhances tamoxifen resistance in recipient ER-positive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 147, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraktar, R.; Van Roosbroeck, K. miR-155 in cancer drug resistance and as target for miRNA-based therapeutics. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayyed, A.A.; Gondaliya, P.; Mali, M.; Pawar, A.; Bhat, P.; Khairnar, A.; Arya, N.; Kalia, K. MiR-155 Inhibitor-Laden Exosomes Reverse Resistance to Cisplatin in a 3D Tumor Spheroid and Xenograft Model of Oral Cancer. Mol. Pharm. 2021, 18, 3010–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Demirkhanyan, L.; Gondi, C.S. The Multifaceted Role of miR-21 in Pancreatic Cancers. Cells 2024, 13, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisan, E.D.; Rencuzogullari, O.; Cieza-Borrella, C.; Miralles Arenas, F.; Dwek, M.; Lange, S.; Uysal-Onganer, P. MiR-21 Is Required for the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Su, F.; Yao, H.; Song, E. Up-regulation of miR-21 mediates resistance to trastuzumab therapy for breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 19127–19137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Tong, R.; Wu, J.; Li, C.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Cheng, Q.; Chen, J.; et al. High-metastatic cancer cells derived exosomal miR92a-3p promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of low-metastatic cancer cells by regulating PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6529–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, L.F.; Zhang, H.W.; Hu, S.; Lu, M.H.; Liang, S.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, E.D.; et al. A novel miR-155/miR-143 cascade controls glycolysis by regulating hexokinase 2 in breast cancer cells. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Wang, D.; Xu, H.; Mei, F.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, B. miR-21 promotes non-small cell lung cancer cells growth by regulating fatty acid metabolism. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wu, K.; Sharma, S.; Xing, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Tyagi, A.; Deshpande, R.; Singh, R.; Wabitsch, M.; Mo, Y.Y.; et al. Exosomal miR-1304-3p promotes breast cancer progression in African Americans by activating cancer-associated adipocytes. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Hu, S.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Cheng, S.; et al. Cancer-cell-secreted miR-204-5p induces leptin signalling pathway in white adipose tissue to promote cancer-associated cachexia. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Y.; Yeh, K.Y.; Liu, B.F.; Chang, T.M.; Chang, C.H.; Liao, Y.F.; Liu, Y.W.; Her, G.M. MicroRNA-21 Plays Multiple Oncometabolic Roles in Colitis-Associated Carcinoma and Colorectal Cancer via the PI3K/AKT, STAT3, and PDCD4/TNF-α Signaling Pathways in Zebrafish. Cancers 2021, 13, 5565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, J.; Pan, P.; Shang, H.; Liu, C.; Wang, C. Down-Regulating the Expression of miRNA-21 Inhibits the Glucose Metabolism of A549/DDP Cells and Promotes Cell Death Through the PI3K/AKT/mTOR/HIF-1α Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 653596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godlewski, J.; Nowicki, M.O.; Bronisz, A.; Nuovo, G.; Palatini, J.; De Lay, M.; Van Brocklyn, J.; Ostrowski, M.C.; Chiocca, E.A.; Lawler, S.E. MicroRNA-451 regulates LKB1/AMPK signaling and allows adaptation to metabolic stress in glioma cells. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 620–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Ma, L.; Zhu, J. miR-483-5p promotes growth, invasion and self-renewal of gastric cancer stem cells by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3421–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, N.; Zou, C.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Lei, Y.; Tang, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; et al. HIF-1ɑ-regulated miR-1275 maintains stem cell-like phenotypes and promotes the progression of LUAD by simultaneously activating Wnt/β-catenin and Notch signaling. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2553–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhao, S.; Shi, Z.; Cao, L.; Liu, J.; Pan, T.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J. Chemotherapy-elicited exosomal miR-378a-3p and miR-378d promote breast cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the activation of EZH2/STAT3 signaling. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; He, M.; Fu, L.; Jin, Y. Exosomal release of microRNA-454 by breast cancer cells sustains biological properties of cancer stem cells via the PRRT2/Wnt axis in ovarian cancer. Life Sci. 2020, 257, 118024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xin, X.; Li, X.; Geng, J.; Sun, Y. Exosomes secreted by M2 macrophages promote cancer stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-27a-3p/TXNIP pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 107585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Dong, C.; Ruan, X.; Yan, W.; Cao, M.; Pizzo, D.; Wu, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, L.; Ren, X.; et al. Chemotherapy-Induced Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs Promote Breast Cancer Stemness by Targeting ONECUT2. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3608–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Banerjee, A.; Cui, T.; Han, C.; Cai, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, D.; Cui, R.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Inhibition of miR-328-3p Impairs Cancer Stem Cell Function and Prevents Metastasis in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 2314–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Ge, X.; Shi, Z.; Yu, C.; Lu, C.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, A.; Wang, X.; Yan, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from hypoxic glioma stem-like cells confer temozolomide resistance on glioblastoma by delivering miR-30b-3p. Theranostics 2021, 11, 1763–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Shen, L.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Hao, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Ge, S.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast-Derived miR-146a-5p Generates a Niche That Promotes Bladder Cancer Stemness and Chemoresistance. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1611–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, N.; Cui, J.; Wu, H.; Xiong, J.; Peng, T. Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukohyama, J.; Isobe, T.; Hu, Q.; Hayashi, T.; Watanabe, T.; Maeda, M.; Yanagi, H.; Qian, X.; Yamashita, K.; Minami, H.; et al. miR-221 Targets QKI to Enhance the Tumorigenic Capacity of Human Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 5151–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.C.; Lima, N.D.S.; Sarian, L.O.; Matheu, A.; Ribeiro, M.L.; Derchain, S.F.M. Exosome-mediated breast cancer chemoresistance via miR-155 transfer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, T.H.; Huang, W.C.; Tung, S.L.; Lin, S.C.; Chen, P.M.; Cho, C.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Yen, T.C.; Lo, G.H.; Chuang, S.E.; et al. MicroRNA-485-5p targets keratin 17 to regulate oral cancer stemness and chemoresistance via the integrin/FAK/Src/ERK/β-catenin pathway. J. Biomed. Sci. 2022, 29, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, L.; Jordāo, M.J.C.; Joyce, J.A. Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 933–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.; Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Xia, X. TME-Related Biomimetic Strategies Against Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 109–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, L.; Pollard, J.W. A timeline of tumour-associated macrophage biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 238–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, F.; Jin, S.; Ho, P.C.; Liu, P.S.; Xie, X. Functional polarization of tumor-associated macrophages dictated by metabolic reprogramming. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, J.; Gu, H.; Tang, M.; Zhao, J.; Cattral, M.S. Tumor Dendritic Cells (DCs) Derived from Precursors of Conventional DCs Are Dispensable for Intratumor CTL Responses. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; To, K.K.W.; Zeng, Q.; Fu, L. Effect of Extracellular Vesicles Derived From Tumor Cells on Immune Evasion. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2417357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, S.; Liang, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mei, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, J.; Su, X.; Cao, S.; Zhong, X.; et al. Multiple tumor-associated microRNAs modulate the survival and longevity of dendritic cells by targeting YWHAZ and Bcl2 signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 2437–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, N.D.; Cursons, J.; Rautela, J. The cancer-natural killer cell immunity cycle. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, S.A.; Ozbay Kurt, F.G.; Arkhypov, I.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 21, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Shen, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Wang, S. Tumor-derived exosomes, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and tumor microenvironment. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Ye, Y.; Yu, W.; Guo, X.; Yu, J. Cancer exosome-derived miR-9 and miR-181a promote the development of early-stage MDSCs via interfering with SOCS3 and PIAS3 respectively in breast cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4681–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, S.; Ozbay Kurt, F.G.; Fritz, L.; Gutzeit, N.; De La Torre, C.; Altevogt, P.; Utikal, J.; Umansky, V. Generation of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Mediated by MicroRNA-125a-5p in Melanoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Cao, B.; Liang, X.; Lu, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Lang, J.; Zhu, G. Microenvironmental oxygen pressure orchestrates an anti- and pro-tumoral γδ T cell equilibrium via tumor-derived exosomes. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2830–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Qiu, W.; Liu, Q.; Qian, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, X.; Chen, Z.; Xue, H.; Li, G. Immunosuppressive effects of hypoxia-induced glioma exosomes through myeloid-derived suppressor cells via the miR-10a/Rora and miR-21/Pten Pathways. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4239–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Feng, Q.; Feng, H.; Tong, Y.; Rong, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Exosomal miRNA-107 induces myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 4023–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Tang, Y.; Ren, Q.; Xiao, B.; Wan, Y.; Jiang, S. miR-21a in exosomes from Lewis lung carcinoma cells accelerates tumor growth through targeting PDCD4 to enhance expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncogene 2020, 39, 6354–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, L.; Cai, Q.; Tang, S.; Ouyang, Q.; Zheng, J. Extracellular vesicle-mediated communication between CD8(+) cytotoxic T cells and tumor cells. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1376962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, C.; Wangmo, D.; Subramanian, S. Tumor-Secreted Extracellular Vesicles Regulate T-Cell Costimulation and Can Be Manipulated To Induce Tumor-Specific T-Cell Responses. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 560–574.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Ren, J.; Jing, Y.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, Q.; Huang, J.; Tao, Y.; Lei, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.; et al. Tumour-derived small extracellular vesicles suppress CD8+ T cell immune function by inhibiting SLC6A8-mediated creatine import in NPM1-mutated acute myeloid leukaemia. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Xie, L.; Qiu, S.; Jiang, T.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xia, Y.; Lv, J.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Helicobacter Pylori-Infected Gastric Cancer Cells Induce Lymphangiogenesis and Lymphatic Remodeling via Transfer of miR-1246. Small 2024, 20, e2308688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, G.; Li, F.; Bu, P.; Hao, Y.; Huang, L.; Bai, X. Cancer cell-derived exosomal miR-20a-5p inhibits CD8(+) T-cell function and confers anti-programmed cell death 1 therapy resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2024, 115, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Cui, J.; Ge, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, Y.; Han, B.; Liu, B. Tumor stem cell-derived exosomal microRNA-17-5p inhibits anti-tumor immunity in colorectal cancer via targeting SPOP and overexpressing PD-L1. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoye, I.S.; Coomes, S.M.; Pelly, V.S.; Czieso, S.; Papayannopoulos, V.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Wilson, M.S. MicroRNA-Containing T-Regulatory-Cell-Derived Exosomes Suppress Pathogenic T Helper 1 Cells. Immunity 2014, 41, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffaker, T.B.; Hu, R.; Runtsch, M.C.; Bake, E.; Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Round, J.L.; Baltimore, D.; O’Connell, R.M. Epistasis between microRNAs 155 and 146a during T cell-mediated antitumor immunity. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugano, R.; Ramachandran, M.; Dimberg, A. Tumor angiogenesis: Causes, consequences, challenges and opportunities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 1745–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Shi, K.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, W. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brabletz, T.; Kalluri, R.; Nieto, M.A.; Weinberg, R.A. EMT in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, J.; Qian, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; You, Y.; et al. A glucose-enriched lung pre-metastatic niche triggered by matrix stiffness-tuned exosomal miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clara, J.A.; Monge, C.; Yang, Y.; Takebe, N. Targeting signalling pathways and the immune microenvironment of cancer stem cells—A clinical update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashouri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Aref, A.R.; Ahadi, A.M.; Molaei, F.; Alahari, S.K. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis, and mechanisms in cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Zhang, J.; Yarden, Y.; Fu, L. The key roles of cancer stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Teng, Y. Harnessing cancer stem cell-derived exosomes to improve cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, K.A.; Selvakumar, S.C.; Ross, K.; Jayaraman, S.; Tusubira, D.; Sekar, D. Liquid biopsy: Exosomal microRNAs as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Yu, L.; Lin, X.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, S.; Chen, D.; Pan, X.; Huang, Y. Combination of Serum miRNAs with Serum Exosomal miRNAs in Early Diagnosis for Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Mao, J.H.; Wang, B.Y.; Wang, L.X.; Wen, H.Y.; Xu, L.J.; Fu, J.X.; Yang, H. Exosomal miR-1910-3p promotes proliferation, metastasis, and autophagy of breast cancer cells by targeting MTMR3 and activating the NF-κB signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Dong, Y.; Wang, K.J.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, W.; Shen, H.F. Plasma exosomal miR-125a-5p and miR-141-5p as non-invasive biomarkers for prostate cancer. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Guo, X.; Li, X.; Liao, C.; Wang, X.; He, K. Plasma-Derived Exosomal microRNA-130a Serves as a Noninvasive Biomarker for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 5547911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, P.; Leng, K.; Xu, Y.; Mei, L.; Han, P.; Zhang, B.; Yao, K.; Li, C.; et al. Colorectal cancer-derived exosomal miR-106b-3p promotes metastasis by down-regulating DLC-1 expression. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, X.M.; Cha, E.J.; Yun, S.J.; Kim, W.J. Role of Exosomal miRNA in Bladder Cancer: A Promising Liquid Biopsy Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, R.; Baghaei, K.; Amani, D.; Piccin, A.; Hashemi, S.M.; Asadzadeh Aghdaei, H.; Zali, M.R. Exosome-mediated delivery of functionally active miRNA-375-3p mimic regulate epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) of colon cancer cells. Life Sci. 2021, 269, 119035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, B.; Ye, J.; Cao, S.; Shi, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sang, J.; Yao, Y.; Guan, W.; et al. Exosomal miRNA-139 in cancer-associated fibroblasts inhibits gastric cancer progression by repressing MMP11 expression. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Mo, C.; Guo, S.; Zhuang, J.; Huang, B.; Mao, X. Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived microRNA-205-containing exosomes impede the progression of prostate cancer through suppression of RHPN2. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhao, W. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying miR-486-5p inhibit glycolysis and cell stemness in colorectal cancer by targeting NEK2. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, R.; Xiong, J.; Yao, Y.L.; Wu, J.H.; Li, G.X. Macrophage-secreted Exosomes Delivering miRNA-21 Inhibitor can Regulate BGC-823 Cell Proliferation. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 4203–4209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Fang, M.; Qian, D. Targeting exosomes enveloped EBV-miR-BART1-5p-antagomiRs for NPC therapy through both anti-vasculogenic mimicry and anti-angiogenesis. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 12608–12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, K.; Yan, I.K.; Lewis-Tuffin, L.; Patel, T. Targeting Liver Cancer Stem Cells Using Engineered Biological Nanoparticles for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Cancer. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 298–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossa, A.; Fonsato, V.; Grange, C.; Tritta, S.; Tapparo, M.; Calvetti, R.; Cedrino, M.; Fallo, S.; Gontero, P.; Camussi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicles from human liver stem cells inhibit renal cancer stem cell-derived tumor growth in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1694–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Yang, H.; Duan, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Mao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ye, J. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal miR-145-5p reduced non-small cell lung cancer cell progression by targeting SOX9. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.M.; Hossain, A.; Gumin, J.; Momin, E.N.; Shimizu, Y.; Ledbetter, D.; Shahar, T.; Yamashita, S.; Parker Kerrigan, B.; Fueyo, J.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as natural biofactories for exosomes carrying miR-124a in the treatment of gliomas. Neuro-Oncology 2018, 20, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, Z.; Oskuee, R.K.; Forouzandeh-Moghadam, M.; Jaafari, M.R. Delivery of LNA-antimiR-142-3p by Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes to Breast Cancer Stem Cells Reduces Tumorigenicity. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2020, 16, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Functional Module | Exosomal miRNA | Source | Function | Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAF Regulation | miR-146a-5p, miR-155-5p | Colorectal cancer | CAF activation | JAK2-STAT3/NF-κB pathway; increased IL-6, TGF-β, CXCL12 secretion | [37] |
| miR-27a | Gastric cancer | Induces CAF phenotype | Fibroblast reprogramming | [38] | |
| miR-496 | Gastric cancer | Enhances pro-tumorigenic CAF traits | Upregulates IL-33, promotes proliferation, EMT, migration, invasion | [39] | |
| miR-185-5p, miR-652-5p, miR-1246 | Breast cancer | Induces CAF-like phenotype | — | [40] | |
| miR-370-3p | Breast cancer | CAF activation | CYLD/NF-κB signaling pathway | [41] | |
| miR-142-3p | Lung cancer | Promotes CAF formation | Non-canonical TGF-β signaling | [42] | |
| miR-155 | Melanoma | Induces angiogenic CAFs | Suppresses SOCS1, activates JAK2/STAT3 | [43] | |
| miR-375 | Merkel cell carcinoma | Fibroblast polarization | Inhibits RBPJ and p53 | [44] | |
| miR-1247-3p | Hepatocellular carcinoma | CAF activation | Targets B4GALT3; β1-integrin/NF-κB pathway | [45] | |
| TAM Regulation | miR-222-3p | Epithelial ovarian cancer | M2 polarization | Suppresses SOCS3; activates STAT3 | [46] |
| miR-301a-3p | Pancreatic cancer (hypoxia) | M2 polarization | PTEN inhibition; PI3Kγ activation | [47] | |
| miR-21-5p | Hepatocellular carcinoma | M2 polarization | RhoB/MAPK pathway; enhances TGF-β and IL-10 secretion | [48] | |
| miR-125b-5p | Melanoma | Promotes pro-tumor TAM phenotype | Enhances macrophage survival | [49] | |
| DC & NK Cell Regulation | miR-212-3p | Pancreatic cancer | Impairs DC function | Targets RFXAP; reduces HLA class II expression | [50,51] |
| miR-let-7i | Multiple cancers | Suppresses DC-mediated immune response | Regulates IL-6, IL-17, TGF-β, SOCS1, TLR4 | [52] | |
| miR-203 | Multiple cancers | Inhibits DC maturation | Downregulates TLR4 | [53] | |
| miR-17-5p | Multiple cancers | DC immunoregulation | Suppresses TNF-α and IL-12; promotes IL-10 secretion | [54] | |
| miR-20a | Breast cancer | Inhibits NK cells | Downregulates NKG2D ligands MICA/MICB | [55] | |
| miR-17-5p | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Impairs NK cell cytotoxicity | Suppresses RUNX1; reduces NKG2D expression | [56] | |
| miR-92b | Liver cancer | Diminishes NK cell activity | Inhibits CD69 expression | [57] | |
| Angiogenesis | miR-103 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Promotes angiogenesis | Targets VE-cadherin, p120-catenin, ZO-1 | [58] |
| miR-23a | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Enhances endothelial proliferation, migration, tube formation | Suppresses TSGA10 | [59] | |
| miR-210 | Leukemia (hypoxia) | Stimulates angiogenesis | Targets Ephrin-A3; activates VEGF/VEGFR2 | [60,61] | |
| miR-21 | Multiple cancers | Promotes angiogenesis | Activates STAT3; upregulates VEGF | [62] | |
| miR-23a | Hypoxic lung cancer | Increases vascular permeability | Suppresses PHD and ZO-1 | [63] | |
| miR-141-3p | Ovarian cancer (SKOV-3) | Promotes angiogenesis | Activates JAK-STAT3 pathway | [64] | |
| miR-100 | Mesenchymal stem cells | Facilitates angiogenesis | Regulates mTOR/HIF-1α/VEGF axis | [65] | |
| miR-9 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | Modulates angiogenesis | PDK/Akt pathway | [66] | |
| EMT & Metastasis | miR-200b | Colorectal cancer | Promotes tumor growth | Binds p27 3′UTR; suppresses expression | [67] |
| miR-584 | Hepatocellular carcinoma | Promotes progression and metastasis | Targets TAK1; inhibits MAPK-JNK tumor-suppressive pathway | [68] | |
| miR-148a | Glioblastoma | Enhances proliferation, invasion, metastasis | Suppresses CADM1; activates STAT3 | [69] | |
| miR-1246 | Breast cancer | Promotes proliferation and chemoresistance | Downregulates CCNG2; disrupts cell cycle | [70] | |
| miR-128 | Breast cancer | Inhibits apoptosis; enhances metastasis | Modulates Bax and Bcl-2 family proteins | [71] | |
| miR-21 | Multiple cancers | Induces EMT; increases migration and invasion | Upregulates Snail; alters vimentin/E-cadherin ratio | [72] | |
| miR-19b-3p | Renal CSC | EMT induction and metastasis | Suppresses PTEN | [73] | |
| miR-193a-3p, miR-210-3p, miR-5100 | MSC (hypoxia) | Triggers EMT; increases invasiveness | Activates STAT3 signaling | [74] | |
| miR-335-5p | Colorectal cancer | Accelerates EMT, invasion, metastasis | Targets RASA1 | [75] | |
| Drug Resistance & Metabolic Reprogramming | miR-21 | Colorectal cancer | 5-FU resistance | Suppresses PTEN, hMSH2 | [76] |
| miR-221/222 | Breast cancer | Tamoxifen resistance | Downregulates p27 and ERα | [77] | |
| miR-155 | Multiple cancers | Anti-apoptosis; promotes chemoresistance | Inhibits PTEN and Fas ligand | [78,79] | |
| miR-21, miR-27a | Pancreatic, breast cancer | EMT induction; enhances chemoresistance | Downregulates E-cadherin; upregulates mesenchymal markers | [80,81,82] | |
| miR-92a-3p | Hepatocellular carcinoma | EMT and metastasis | Activates PTEN/Akt pathway | [83] | |
| miR-155 | Multiple cancers | Enhances glycolysis | Suppresses miR-143; upregulates HK2 | [84] | |
| miR-21 | NSCLC | Promotes lipogenesis | Upregulates FASN, ACC1 | [85] | |
| miR-1304-3p | Breast cancer | Activates cancer-associated adipocytes | Reprograms adipose tissue; promotes tumor progression | [86] | |
| miR-204-5p | Tumor | White adipose tissue metabolic reprogramming | Modulates leptin signaling; enhances lipolysis | [87] | |
| miR-21 | Multiple cancers | Glycolysis promotion | Activates PI3K/AKT pathway | [88,89] | |
| miR-451 | Multiple cancers | Energy metabolism regulation | AMPK signaling | [90] | |
| CSC Stemness & Therapy Resistance | miR-483-5p | Gastric CSC | Maintains stemness; self-renewal | Activates Wnt/β-catenin pathway | [91] |
| miR-1275 | Lung adenocarcinoma | Enhances stemness; promotes metastasis | Activates Wnt/β-catenin and Notch pathways | [92] | |
| miR-378a-3p | Breast cancer (post-chemotherapy) | Enhances stemness; chemoresistance | Activates Wnt/Notch pathways | [93] | |
| miR-454 | Breast cancer | Maintains CSC stemness | Activates PRRT2/Wnt axis | [94] | |
| miR-27a-3p | M2 macrophage | Promotes CSC proliferation and tumorigenicity | Activates TXNIP signaling | [95] | |
| miR-9-5p, miR-195-5p, miR-203a-3p | Breast cancer | Induces CSC phenotype; upregulates stemness genes | Targets ONECUT2 | [96] | |
| miR-328-3p | Ovarian CSC | Maintains stemness | Suppresses DNA damage-binding protein 2; low ROS enhances ERK signaling | [97] | |
| miR-30b-3p | Glioma CSC (hypoxia) | Anti-apoptosis; chemoresistance | Targets RHOB; reduces apoptosis | [98] | |
| miR-146a-5p | Bladder CSC | Maintains stemness; enhances chemoresistance | Regulates cell cycle and apoptosis pathways | [99] | |
| miR-210 | Pancreatic CSC (gemcitabine-resistant) | Confers drug resistance | Upregulates MDR1, YB-1, BCRP; activates mTOR | [100] | |
| miR-221 | Colorectal CSC | Promotes stemness and chemoresistance | Targets QKI mRNA 3′UTR | [101] | |
| miR-155 | Breast CSC | Induces EMT and chemoresistance in sensitive cells | Downregulates C/EBP-β; inhibits TGF-β, C/EBP-β, FOXO3a | [102] | |
| miR-485-5p | Oral CSC | Maintains stemness and chemoresistance | Suppresses KRT17; regulates integrin-mediated FAK/Src/ERK signaling and β-catenin nuclear translocation | [103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, S.; Jin, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Exosomal miRNAs: Key Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199323
Wang S, Jin S, Zhang J, Wang X. Exosomal miRNAs: Key Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199323
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Shuangmin, Sikan Jin, Jidong Zhang, and Xianyao Wang. 2025. "Exosomal miRNAs: Key Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199323
APA StyleWang, S., Jin, S., Zhang, J., & Wang, X. (2025). Exosomal miRNAs: Key Regulators of the Tumor Microenvironment and Cancer Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199323







