A Novel Approach to Prognostic Factors and Risk Stratification in Pediatric AML: Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Prognostic Factors
2.1. Patient-Related Factors
2.2. Disease-Related Factors
2.3. Genetics of Pediatric AML
2.4. Measurable Residual Disease
3. Risk Stratification in Pediatric AML
4. Risk-Adapted Treatment Approach
4.1. Upfront Therapy
4.2. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant
4.3. Molecular Targeted Therapy
4.4. Immunotherapy
5. Future Directions
6. Case Report
6.1. Medical History and Complaints at Presentation
6.2. Results at Admission
6.3. Patient Management During Hospitalization
6.4. Case Approach and Results
6.5. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute Myeloid Leukemia |
| ALL | Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| HRG | High-Risk Group |
| MUD | Matched Unrelated Donor |
| SCT | Stem Cell Transplantation |
| OS | Overall Survival |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| HSCT | Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation |
| WBC | White Blood Cell |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CR | Complete Remission |
| FAB | French–American–British |
| PFS | Progression-Free Survival |
| BM | Bone Marrow |
| EFS | Event-Free Survival |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| RFS | Relapse-Free Survival |
| DIC | Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation |
| TLS | Tumor Lysis Syndrome |
| CBF | Core-Binding Factor |
| WES | Whole-Exome Sequencing |
| MRD | Measurable Residual Disease |
| DFS | Disease-Free Survival |
| MPFC | Multiparameter Flow Cytometry |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ddPCR | Digital Droplet Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ELN | European Leukemia Net |
| GO | Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin |
| SMMHC | Smooth Muscle Myosin Heavy Chain |
| NPM1 | Nucleophosmin 1 |
| FLT3-ITD | FLT3-Internal Tandem Duplications |
| FLT3-TKD | FLT3-Tyrosine Kinase Domain |
| allo-HSCT | allogenic HSCT |
| TRM | Treatment-Related Mortality |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| COG | Children’s Oncology Group |
| HAR | High Allelic Ratio |
| CR1 | First Complete Remission |
| GVL | Graft Versus Leukemia |
| GVHD | Graft-Versus-Host Disease |
| TBI | Total Body Irradiation |
| BuCy | busulfan–cyclophosphamide |
| BuCyMel | busulfan–cyclophosphamide–melphalan |
| CloFluBu | clofarabine–fludarabine–busulfan |
| TDM | Therapeutic Drug Monitoring |
| LFS | Leukemia-Free Survival |
| MAC | Myeloablative Conditioning |
| RIC | Reduced-Intensity Conditioning |
| DLI | Donor Lymphocyte Infusion |
| BCL-2 | B-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma-2 |
| JM | Juxtamembrane |
| MCL-1 | Myeloid Cell Leukemia 1 |
| BH3 | BCL-2 homology 3 |
| MOMP | Mitochondrial Outer Membrane Permeabilization |
| HMA | Hypomethylating Agent |
| HDAC | Histone Deacetylase |
| HDACi | Histone Deacetylases inhibitor |
| AZA | Azacitidine |
| DEC | Decytabine |
| HATs | Histone Acetyltransferases |
| MHC | Major Histocompatibility Complex |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| CAR-T | Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cell |
| ADCs | Antibody–Drug Conjugates |
| BiTE | Bispecific T-cell Engager |
| DART | Dual-Affinity Retargeting |
| MNs | Modal Numbers |
| ctDNA | Circulating Tumor DNA |
| cfDNA | Circulating Free Cell DNA |
| miRNA-29a | microRNA-29a |
| miRNA-100 | microRNA-100 |
| CRGs | Cuproptosis-Related Genes |
| FC-MRD | Flow-Cytometry-Measurable Residual Disease |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| ISCN | International System of Human Cytogenomic Nomenclature |
| AIEOP-BMF | Associazione Italiana Ematologia Oncologia Pediatrica-Berlin, Frankfurt, Münster |
| PBSCT | Peripheral Blood Stem Cell Transplantation |
| CK | Complex Karyotype |
References
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html (accessed on 19 July 2025).
- Rubnitz, J.E.; Kaspers, G.J.L. How I Treat Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Port, M.; Böttcher, M.; Thol, F.; Ganser, A.; Schlenk, R.; Wasem, J.; Neumann, A.; Pouryamout, L. Prognostic Significance of FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication, Nucleophosmin 1, and CEBPA Gene Mutations for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients with Normal Karyotype and Younger than 60 Years: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Hematol. 2014, 93, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlen, M.; Klusmann, J.-H.; Hoell, J.I. Molecular Approaches to Treating Pediatric Leukemias. Front. Pediatr. 2019, 7, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasche, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Borschel, L.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Dworzak, M.; Klingebiel, T.; Lehrnbecher, T.; Creutzig, U.; Klusmann, J.-H.; Reinhardt, D. Successes and Challenges in the Treatment of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Retrospective Analysis of the AML-BFM Trials from 1987 to 2012. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Mullighan, C.G. Pediatric Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Haematologica 2020, 105, 2524–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.A. Leukemia in Children. Pediatr. Rev. 2019, 40, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of AML in Adults: 2022 Recommendations from an International Expert Panel on Behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Childhood Cancer Registry Explorer (NCCR*Explorer). Available online: https://nccrexplorer.ccdi.cancer.gov/ (accessed on 19 July 2025).
- De Rooij, J.D.E.; Zwaan, C.M.; Van den Heuvel-Eibrink, M. Pediatric AML: From Biology to Clinical Management. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 127–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarlock, K.; Meshinchi, S. Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Biology and Therapeutic Implications of Genomic Variants. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 62, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomizawa, D.; Tsujimoto, S.-I. Risk-Stratified Therapy for Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2023, 15, 4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arber, D.A.; Orazi, A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Borowitz, M.J.; Calvo, K.R.; Kvasnicka, H.-M.; Wang, S.A.; Bagg, A.; Barbui, T.; Branford, S.; et al. International Consensus Classification of Myeloid Neoplasms and Acute Leukemias: Integrating Morphologic, Clinical, and Genomic Data. Blood 2022, 140, 1200–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, O.; Abdalla, K.; AlAzmi, A.A.; Elimam, N.; Abrar, M.B.; Jastaniah, W. FLAG/FLAG-IDA Regimen for Children with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Leukemia in the Era of Targeted Novel Therapies. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2019, 25, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspers, G. How I Treat Paediatric Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 166, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; Grob, T.; Hanekamp, D.; Kavelaars, F.G.; Al Hinai, A.; Zeilemaker, A.; Erpelinck-Verschueren, C.A.J.; Gradowska, P.L.; Meijer, R.; Cloos, J.; et al. Molecular Minimal Residual Disease in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertuccio, S.N.; Anselmi, L.; Masetti, R.; Lonetti, A.; Cerasi, S.; Polidori, S.; Serravalle, S.; Pession, A. Exploiting Clonal Evolution to Improve the Diagnosis and Treatment Efficacy Prediction in Pediatric AML. Cancers 2021, 13, 1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommert, L.; Tarlock, K. The Evolution of Targeted Therapy in Pediatric AML: Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin, FLT3/IDH/BCL2 Inhibitors, and Other Therapies. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2022, 2022, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciciarello, M.; Corradi, G.; Forte, D.; Cavo, M.; Curti, A. Emerging Bone Marrow Microenvironment-Driven Mechanisms of Drug Resistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Tangle or Chance? Cancers 2021, 13, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noviello, M.; Manfredi, F.; Ruggiero, E.; Perini, T.; Oliveira, G.; Cortesi, F.; De Simone, P.; Toffalori, C.; Gambacorta, V.; Greco, R.; et al. Bone Marrow Central Memory and Memory Stem T-Cell Exhaustion in AML Patients Relapsing after HSCT. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, H.; Estey, E.; Grimwade, D.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Büchner, T.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of AML in Adults: 2017 ELN Recommendations from an International Expert Panel. Blood 2017, 129, 424–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, B.; Zhang, J. Epidemiological Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Acute Leukemia in Children and Adolescents and Adults: A Large Population-Based Study. Hematology 2024, 29, 2327916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.J.; Xie, L.; Caywood, E.H. Prognostic Factors of Childhood and Adolescent Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Survival: Evidence from Four Decades of US Population Data. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Løhmann, D.J.A.; Abrahamsson, J.; Ha, S.-Y.; Jónsson, Ó.G.; Koskenvuo, M.; Lausen, B.; Palle, J.; Zeller, B.; Hasle, H. Effect of Age and Body Weight on Toxicity and Survival in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results from NOPHO-AML 2004. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Rong, L.; Wu, P.; Kang, M.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Q.; Fang, Y. Impact of Age on the Survival of Pediatric Leukemia: An Analysis of 15083 Children in the SEER Database. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83767–83774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blais, S.; Boutroux, H.; Pasquet, M.; Leblanc, T.; Fenneteau, O.; Gandemer, V.; Bertrand, Y.; Ducassou, S.; Michel, G.; Nelken, B.; et al. Is Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia in Children Under 2 Years of Age a Specific Entity? A Report from the FRENCH ELAM02 Study Group. Hemasphere 2019, 3, e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, Y.; Shiba, N.; Yamato, G.; Ohki, K.; Tabuchi, K.; Sotomatsu, M.; Tomizawa, D.; Kinoshita, A.; Arakawa, H.; Saito, A.M.; et al. Patients Aged Less than 3 Years with Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Characterize a Molecularly and Clinically Distinct Subgroup. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 188, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawińska-Wąsikowska, K.; Czogała, M.; Bukowska-Strakova, K.; Surman, M.; Rygielska, M.; Książek, T.; Sadowska, B.; Pac, A.; Skalska-Sadowska, J.; Samborska, M.; et al. Treatment Outcomes of Adolescents Compared to Younger Pediatric Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Do They Need a Special Approach? Cancers 2024, 16, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dwyer, K.; Freyer, D.R.; Horan, J.T. Treatment Strategies for Adolescent and Young Adult Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-P.; Zhang, A.-L.; Ruan, M.; Chang, L.-X.; Liu, F.; Chen, X.; Qi, B.-Q.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; et al. Prognostic Stratification of Molecularly and Clinically Distinct Subgroup in Children with Acute Monocytic Leukemia. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 3647–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conneely, S.E.; McAtee, C.L.; Gupta, R.; Lubega, J.; Scheurer, M.E.; Rau, R.E. Association of Race and Ethnicity with Clinical Phenotype, Genetics, and Survival in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 4992–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, B.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Mrózek, K.; Zhao, Q.; Fisher, J.L.; Nicolet, D.; Walker, C.J.; Mims, A.S.; Oakes, C.; Giacopelli, B.; et al. Poor Survival and Differential Impact of Genetic Features of Black Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, K.T.; Nicolet, D.; Kelly, B.J.; Mrózek, K.; LaHaye, S.; Miller, K.E.; Wijeratne, S.; Wheeler, G.; Kohlschmidt, J.; Blachly, J.S.; et al. High Early Death Rates, Treatment Resistance, and Short Survival of Black Adolescents and Young Adults with AML. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 5570–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Newton, J.G.; Getz, K.D.; Huang, Y.-S.; Seif, A.E.; Fisher, B.T.; Aplenc, R.; Winestone, L.E. Comparable On-Therapy Mortality and Supportive Care Requirements in Black and White Patients Following Initial Induction for Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2019, 66, e27583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winestone, L.E.; Getz, K.D.; Rao, P.; Li, Y.; Hall, M.; Huang, Y.-S.V.; Seif, A.E.; Fisher, B.T.; Aplenc, R. Disparities in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Clinical Trial Enrollment. Leuk. Lymphoma 2019, 60, 2190–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamba, J.K.; Marrero, R.; Wu, H.; Cao, X.; Parcha, P.K.; Karol, S.E.; Inaba, H.; Kuo, D.J.; Degar, B.A.; Heym, K.; et al. Pharmacogenomics, Race, and Treatment Outcome in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2411726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Cheung, Y.T.; Tang, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, M.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Association Between Body Mass Index at Diagnosis and Outcomes in Chinese Children with Newly Diagnosed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 2850–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, A.; Chen, Y.; Hageman, L.; Hoppmann, A.L.; Angiolillo, A.; Dickens, D.S.; Lew, G.; Neglia, J.P.; Ravindranath, Y.; Ritchey, A.K.; et al. Body Mass Index during Maintenance Therapy and Relapse Risk in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: A Children’s Oncology Group Report. Cancer 2023, 129, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, H.; Surprise, H.C.; Pounds, S.; Cao, X.; Howard, S.C.; Ringwald-Smith, K.; Buaboonnam, J.; Dahl, G.; Bowman, W.P.; Taub, J.W.; et al. Effect of Body Mass Index on the Outcome of Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer 2012, 118, 5989–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, M.; Stall, M.; Wang, L.; Panetta, J.C.; Triplett, B.M.; Pui, C.-H.; Ribeiro, R.C.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Pounds, S.B.; Inaba, H. Changes in Body Mass Index, Weight, and Height in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia and the Associations with Outcome. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 2824–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, X.; He, H.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, W.; Yu, J.; Fan, J.; Huang, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Longitudinal Changes in Body Mass Index, Height, and Weight in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Dai, G.; Zhao, J. Impact of Body Mass Index at Diagnosis on Outcomes of Pediatric Acute Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0302879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, A. Profile of down Syndrome–Associated Malignancies: Epidemiology, Clinical Features and Therapeutic Aspects. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. J. 2021, 6, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triarico, S.; Trombatore, G.; Capozza, M.A.; Romano, A.; Mastrangelo, S.; Attinà, G.; Maurizi, P.; Ruggiero, A. Hematological Disorders in Children with Down Syndrome. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2022, 15, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmidou, A.; Tragiannidis, A.; Gavriilaki, E. Myeloid Leukemia of Down Syndrome. Cancers 2023, 15, 3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risitano, A.M.; Marotta, S.; Calzone, R.; Grimaldi, F.; Zatterale, A.; RIAF Contributors. Twenty Years of the Italian Fanconi Anemia Registry: Where We Stand and What Remains to Be Learned. Haematologica 2016, 101, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rama, H.; Gupta, D.; Chatterjee, T.; Gupta, S. Fanconi Anemia with MDS RAEB-2 Rapidly Progressing to AML in a 5-Year-Old Boy. Indian J. Hematol. Blood Transfus. 2014, 30, 379–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Poppe, B.; Van Limbergen, H.; Van Roy, N.; Vandecruys, E.; De Paepe, A.; Benoit, Y.; Speleman, F. Chromosomal Aberrations in Bloom Syndrome Patients with Myeloid Malignancies. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2001, 128, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dror, Y.; Freedman, M.H. Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome. Br. J. Haematol. 2002, 118, 701–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jongmans, M.C.J.; van der Burgt, I.; Hoogerbrugge, P.M.; Noordam, K.; Yntema, H.G.; Nillesen, W.M.; Kuiper, R.P.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; van Kessel, A.G.; van Krieken, J.H.J.M.; et al. Cancer Risk in Patients with Noonan Syndrome Carrying a PTPN11 Mutation. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 19, 870–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.S.; Kozyra, E.J.; Wlodarski, M.W. Germline Predisposition in Myeloid Neoplasms: Unique Genetic and Clinical Features of GATA2 Deficiency and SAMD9/SAMD9L Syndromes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.L.; Cavenagh, J.D.; Lister, T.A.; Fitzgibbon, J. Mutation of CEBPA in Familial Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 2403–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.; Seipel, K.; Pemov, A.; Dewan, R.; Brown, C.; Ravichandran, S.; Luke, B.T.; Malasky, M.; Suman, S.; Yeager, M.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals a C-Terminal Germline Variant in CEBPA-Associated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: 45-Year Follow up of a Large Family. Haematologica 2016, 101, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, H.; Chen, P.-H.; Pine, A.B.; Siddon, A.J.; Bale, A.E.; Gowda, L.; Killie, A.; Richards, J.; Varin-Tremblay, C.; Kloss, R.; et al. A Case of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Unusual Germline CEBPA Mutation: Lessons Learned about Mutation Detection, Location, and Penetrance. Leuk. Lymphoma 2021, 62, 1251–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawana, K.; Rio-Machin, A.; Preudhomme, C.; Fitzgibbon, J. Familial CEBPA-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Semin. Hematol. 2017, 54, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrigan, A.M.; Trottier, A.M. Hereditary Acute Myeloid Leukemia Associated with C-Terminal CEBPA Germline Variants. Fam. Cancer 2023, 22, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Hahn, C.N.; Scott, H.S. Secondary Leukemia in Patients with Germline Transcription Factor Mutations (RUNX1, GATA2, CEBPA). Blood 2020, 136, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.N.; Chong, C.-E.; Carmichael, C.L.; Wilkins, E.J.; Brautigan, P.J.; Li, X.-C.; Babic, M.; Lin, M.; Carmagnac, A.; Lee, Y.K.; et al. Heritable GATA2 Mutations Associated with Familial Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, C.C.; Venugopal, P.; Arts, P.; Shahrin, N.H.; Feurstein, S.; Rawlings, L.; Lawrence, D.M.; Andrews, J.; King-Smith, S.L.; Harvey, N.L.; et al. GATA2 Deficiency Syndrome: A Decade of Discovery. Hum. Mutat. 2021, 42, 1399–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Seraihi, A.F.; Rio-Machin, A.; Tawana, K.; Bödör, C.; Wang, J.; Nagano, A.; Heward, J.A.; Iqbal, S.; Best, S.; Lea, N.; et al. GATA2 Monoallelic Expression Underlies Reduced Penetrance in Inherited GATA2-Mutated MDS/AML. Leukemia 2018, 32, 2502–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Churpek, J.E.; Keel, S.B.; Walsh, T.; Lee, M.K.; Loeb, K.R.; Gulsuner, S.; Pritchard, C.C.; Sanchez-Bonilla, M.; Delrow, J.J.; et al. Germline ETV6 Mutations in Familial Thrombocytopenia and Hematologic Malignancy. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feurstein, S.; Godley, L.A. Germline ETV6 Mutations and Predisposition to Hematological Malignancies. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 106, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejar, R.; Stevenson, K.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Galili, N.; Nilsson, B.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Kantarjian, H.; Raza, A.; Levine, R.L.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Clinical Effect of Point Mutations in Myelodysplastic Syndromes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2496–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, L.; Holmfeldt, L.; Wu, G.; Heatley, S.L.; Payne-Turner, D.; Easton, J.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Rusch, M.; et al. The Genetic Basis of Early T-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia. Nature 2012, 481, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vlierberghe, P.; Ambesi-Impiombato, A.; Perez-Garcia, A.; Haydu, J.E.; Rigo, I.; Hadler, M.; Tosello, V.; Della Gatta, G.; Paietta, E.; Racevskis, J.; et al. ETV6 Mutations in Early Immature Human T Cell Leukemias. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noetzli, L.; Lo, R.W.; Lee-Sherick, A.B.; Callaghan, M.; Noris, P.; Savoia, A.; Rajpurkar, M.; Jones, K.; Gowan, K.; Balduini, C.; et al. Germline Mutations in ETV6 Are Associated with Thrombocytopenia, Red Cell Macrocytosis and Predisposition to Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Metzger, M.L.; Wu, G.; Nishii, R.; Qian, M.; Devidas, M.; Yang, W.; Cheng, C.; Cao, X.; Quinn, E.; et al. Germline Genetic Variation in ETV6 and Risk of Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia: A Systematic Genetic Study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongmans, M.C.J.; Kuiper, R.P.; Carmichael, C.L.; Wilkins, E.J.; Dors, N.; Carmagnac, A.; Schouten-van Meeteren, A.Y.N.; Li, X.; Stankovic, M.; Kamping, E.; et al. Novel RUNX1 Mutations in Familial Platelet Disorder with Enhanced Risk for Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Clues for Improved Identification of the FPD/AML Syndrome. Leukemia 2010, 24, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preudhomme, C.; Renneville, A.; Bourdon, V.; Philippe, N.; Roche-Lestienne, C.; Boissel, N.; Dhedin, N.; André, J.-M.; Cornillet-Lefebvre, P.; Baruchel, A.; et al. High Frequency of RUNX1 Biallelic Alteration in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Secondary to Familial Platelet Disorder. Blood 2009, 113, 5583–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.L.; Arts, P.; Carmichael, C.L.; Babic, M.; Dobbins, J.; Chong, C.-E.; Schreiber, A.W.; Feng, J.; Phillips, K.; Wang, P.P.S.; et al. RUNX1-Mutated Families Show Phenotype Heterogeneity and a Somatic Mutation Profile Unique to Germline Predisposed AML. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Feurstein, S.; Mohan, S.; Porter, C.C.; Jackson, S.A.; Keel, S.; Chicka, M.; Brown, A.L.; Kesserwan, C.; Agarwal, A.; et al. ClinGen Myeloid Malignancy Variant Curation Expert Panel Recommendations for Germline RUNX1 Variants. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2962–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homan, C.C.; King-Smith, S.L.; Lawrence, D.M.; Arts, P.; Feng, J.; Andrews, J.; Armstrong, M.; Ha, T.; Dobbins, J.; Drazer, M.W.; et al. The RUNX1 Database (RUNX1db): Establishment of an Expert Curated RUNX1 Registry and Genomics Database as a Public Resource for Familial Platelet Disorder with Myeloid Malignancy. Haematologica 2021, 106, 3004–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, A.; Decker, M.; Schlegelberger, B.; Ripperger, T. Beyond Pathogenic RUNX1 Germline Variants: The Spectrum of Somatic Alterations in RUNX1-Familial Platelet Disorder with Predisposition to Hematologic Malignancies. Cancers 2022, 14, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei, H.; DiNardo, C.D. Hereditary Myeloid Malignancies. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2019, 32, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noris, P.; Perrotta, S.; Seri, M.; Pecci, A.; Gnan, C.; Loffredo, G.; Pujol-Moix, N.; Zecca, M.; Scognamiglio, F.; De Rocco, D.; et al. Mutations in ANKRD26 Are Responsible for a Frequent Form of Inherited Thrombocytopenia: Analysis of 78 Patients from 21 Families. Blood 2011, 117, 6673–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippucci, T.; Savoia, A.; Perrotta, S.; Pujol-Moix, N.; Noris, P.; Castegnaro, G.; Pecci, A.; Gnan, C.; Punzo, F.; Marconi, C.; et al. Mutations in the 5′ UTR of ANKRD26, the Ankirin Repeat Domain 26 Gene, Cause an Autosomal-Dominant Form of Inherited Thrombocytopenia, THC2. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutroux, H.; Petit, A.; Auvrignon, A.; Lapillonne, H.; Ballerini, P.; Favier, R.; Leverger, G. Childhood Diagnosis of Genetic Thrombocytopenia with Mutation in the Ankyrine Repeat Domain 26 Gene. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 1399–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougeard, G.; Renaux-Petel, M.; Flaman, J.-M.; Charbonnier, C.; Fermey, P.; Belotti, M.; Gauthier-Villars, M.; Stoppa-Lyonnet, D.; Consolino, E.; Brugières, L.; et al. Revisiting Li-Fraumeni Syndrome from TP53 Mutation Carriers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.J.; Dodd-Eaton, E.B.; Peng, G.; Bojadzieva, J.; Chen, J.; Amos, C.I.; Frone, M.N.; Khincha, P.P.; Mai, P.L.; Savage, S.A.; et al. Penetrance of Different Cancer Types in Families with Li-Fraumeni Syndrome: A Validation Study Using Multicenter Cohorts. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frebourg, T.; Bajalica Lagercrantz, S.; Oliveira, C.; Magenheim, R.; Evans, D.G.; European Reference Network GENTURIS. Guidelines for the Li-Fraumeni and Heritable TP53-Related Cancer Syndromes. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.; Kirschner-Schwabe, R.; Groeneveld-Krentz, S.; Escherich, G.; Möricke, A.; von Stackelberg, A.; Stanulla, M.; Bailey, S.; Richter, L.; Steinemann, D.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Characteristics of Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia and Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, M.; Bannon, S.A.; Routbort, M.; Naqvi, K.; Kadia, T.M.; Takahashi, K.; Alvarado, Y.; Ravandi-Kashani, F.; Patel, K.P.; Champlin, R.; et al. Hematologic Malignancies and Li-Fraumeni Syndrome. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2019, 5, a003210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, M.; Tanase-Nakao, K.; Shima, H.; Shirai, R.; Yoshida, K.; Osumi, T.; Deguchi, T.; Mori, M.; Arakawa, Y.; Takagi, M.; et al. Prevalence of Germline GATA2 and SAMD9/9L Variants in Paediatric Haematological Disorders with Monosomy 7. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumi, S.; Amano, N.; Ishii, T.; Katsumata, N.; Muroya, K.; Adachi, M.; Toyoshima, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Fukuzawa, R.; Miyako, K.; et al. SAMD9 Mutations Cause a Novel Multisystem Disorder, MIRAGE Syndrome, and Are Associated with Loss of Chromosome 7. Nat Genet 2016, 48, 792–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidsson, J.; Puschmann, A.; Tedgård, U.; Bryder, D.; Nilsson, L.; Cammenga, J. SAMD9 and SAMD9L in Inherited Predisposition to Ataxia, Pancytopenia, and Myeloid Malignancies. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1106–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.C.; Bryant, V.; Lamprecht, T.; Ma, J.; Walsh, M.; Schwartz, J.; Del Pilar Alzamora, M.; Mullighan, C.G.; Loh, M.L.; Ribeiro, R.; et al. Germline SAMD9 and SAMD9L mutations are associated with extensive genetic evolution and diverse hematologic outcomes. JCI Insight. 2018, 3, e121086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chabot-Richards, D.S.; George, T.I. Leukocytosis. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2014, 36, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittivisuit, S.; Jongthitinon, N.; Sripornsawan, P.; Songthawee, N.; Chavananon, S.; Limratchapong, C.; McNeil, E.B.; Chotsampancharoen, T. Hyperleukocytosis in Childhood Acute Leukemia: Early Complications and Survival Outcomes. Cancers 2023, 15, 3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Liu, L.; Zong, S.; Chang, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zou, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Hyperleukocytosis with WBC Count Greater than 50 × 109/L. Int. J. Hematol. 2023, 118, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaventure, A.; Harewood, R.; Stiller, C.A.; Gatta, G.; Clavel, J.; Stefan, D.C.; Carreira, H.; Spika, D.; Marcos-Gragera, R.; Peris-Bonet, R.; et al. Worldwide Comparison of Survival from Childhood Leukaemia for 1995-2009, by Subtype, Age, and Sex (CONCORD-2): A Population-Based Study of Individual Data for 89 828 Children from 198 Registries in 53 Countries. Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e202–e217, Erratum in Lancet Haematol. 2017, 4, e201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bewersdorf, J.P.; Zeidan, A.M. Hyperleukocytosis and Leukostasis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Can a Better Understanding of the Underlying Molecular Pathophysiology Lead to Novel Treatments? Cells 2020, 9, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.-H.; Wang, J.-W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F.-Y. Hyperleukocytosis Predicts Inferior Clinical Outcome in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Hematology 2020, 25, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshinchi, S.; Arceci, R.J. Prognostic Factors and Risk-Based Therapy in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncologist 2007, 12, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankiewicz, J.; Demidowicz, E.; Bartoszewicz, N.; Kołtan, A.; Kołtan, S.; Czyżewski, K.; Richert-Przygońska, M.; Dębski, R.; Pogorzała, M.; Tejza, B.; et al. Relapsed Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Prognostic Factors and Outcomes: Experience from a Single Oncology Center. Acta Haematol. Pol. 2023, 54, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, R.; Vendemini, F.; Zama, D.; Biagi, C.; Gasperini, P.; Pession, A. All-Trans Retinoic Acid in the Treatment of Pediatric Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2012, 12, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, C.J.; Hills, R.K.; Moorman, A.V.; Grimwade, D.J.; Hann, I.; Webb, D.K.H.; Wheatley, K.; de Graaf, S.S.N.; van den Berg, E.; Burnett, A.K.; et al. Cytogenetics of Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: United Kingdom Medical Research Council Treatment Trials AML 10 and 12. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2674–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conneely, S.E.; Rau, R.E. The Genomics of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 189–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, R.; Bertuccio, S.N.; Astolfi, A.; Chiarini, F.; Lonetti, A.; Indio, V.; De Luca, M.; Bandini, J.; Serravalle, S.; Franzoni, M.; et al. Hh/Gli Antagonist in Acute Myeloid Leukemia with CBFA2T3-GLIS2 Fusion Gene. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolouri, H.; Farrar, J.E.; Triche, T.; Ries, R.E.; Lim, E.L.; Alonzo, T.A.; Ma, Y.; Moore, R.; Mungall, A.J.; Marra, M.A.; et al. The Molecular Landscape of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Reveals Recurrent Structural Alterations and Age-Specific Mutational Interactions. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 103–112, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 526; Erratum in Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creutzig, U.; Zimmermann, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Rasche, M.; von Neuhoff, C.; Alpermann, T.; Dworzak, M.; Perglerová, K.; Zemanova, Z.; Tchinda, J.; et al. Changes in Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics in Acute Myeloid Leukemia from Childhood to Adult Age Groups. Cancer 2016, 122, 3821–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, R.; Bertuccio, S.N.; Guidi, V.; Cerasi, S.; Lonetti, A.; Pession, A. Uncommon Cytogenetic Abnormalities Identifying High-Risk Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children. Future Oncol. 2020, 16, 2747–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Garrett-Bakelman, F.E.; Chung, S.S.; Sanders, M.A.; Hricik, T.; Rapaport, F.; Patel, J.; Dillon, R.; Vijay, P.; Brown, A.L.; et al. Distinct Evolution and Dynamics of Epigenetic and Genetic Heterogeneity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
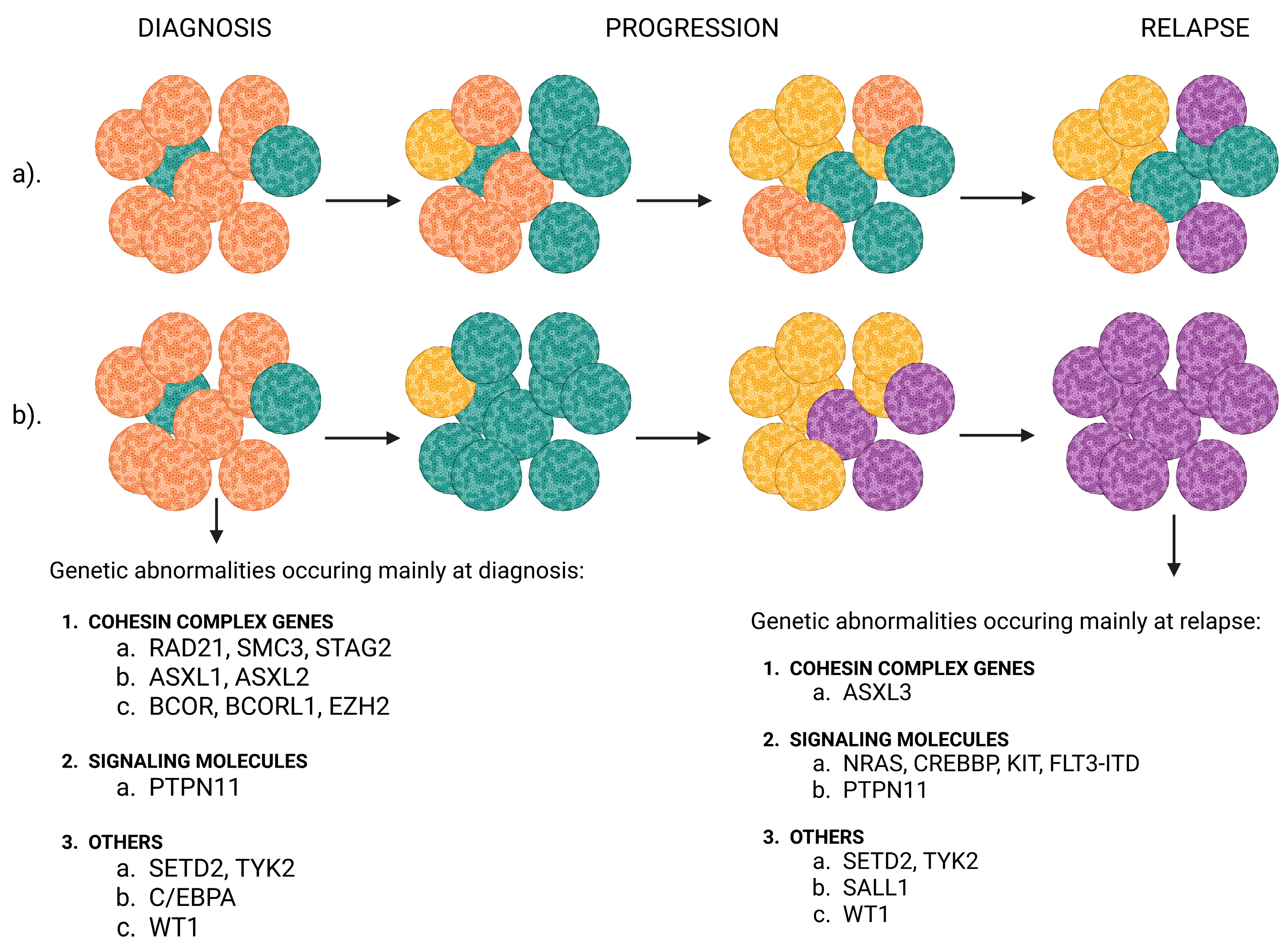
- Vosberg, S.; Greif, P.A. Clonal Evolution of Acute Myeloid Leukemia from Diagnosis to Relapse. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2019, 58, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrar, J.E.; Schuback, H.L.; Ries, R.E.; Wai, D.; Hampton, O.A.; Trevino, L.R.; Alonzo, T.A.; Guidry Auvil, J.M.; Davidsen, T.M.; Gesuwan, P.; et al. Genomic Profiling of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Reveals a Changing Mutational Landscape from Disease Diagnosis to Relapse. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, N.; Yoshida, K.; Shiraishi, Y.; Okuno, Y.; Yamato, G.; Hara, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Chiba, K.; Tanaka, H.; Terui, K.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Reveals the Spectrum of Gene Mutations and the Clonal Evolution Patterns in Paediatric Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masetti, R.; Castelli, I.; Astolfi, A.; Bertuccio, S.N.; Indio, V.; Togni, M.; Belotti, T.; Serravalle, S.; Tarantino, G.; Zecca, M.; et al. Genomic Complexity and Dynamics of Clonal Evolution in Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia Studied with Whole-Exome Sequencing. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 56746–56757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, H.; Shuai, X.; Nguyen-Lefebvre, A.T.; Giri, B.; Ren, M.; Rauchman, M.; Robbins, L.; Hou, W.; Korkaya, H.; Ma, Y. SALL1 Expression in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7442–7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuurhuis, G.J.; Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.; Béné, M.-C.; Buccisano, F.; Cloos, J.; Grimwade, D.; Haferlach, T.; Hills, R.K.; Hourigan, C.S.; et al. Minimal/Measurable Residual Disease in AML: A Consensus Document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2018, 131, 1275–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segerink, W.H.; de Haas, V.; Kaspers, G.J.L. Measurable Residual Disease in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2021, 21, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, K.; de Haas, V.; Kaspers, G.J.L. Clinical Challenges in de Novo Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Expert Rev. Anticancer. Ther. 2018, 18, 277–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Zhou, S.; Fu, C.; Berry, D.A.; Walter, R.B.; Freeman, S.D.; Hourigan, C.S.; Huang, X.; Nogueras Gonzalez, G.; Hwang, H.; et al. Association of Measurable Residual Disease with Survival Outcomes in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1890–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paietta, E. Consensus on MRD in AML? Blood 2018, 131, 1265–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, B.C.; Kebriaei, P.; de Lima, M.; Jimenez Jimenez, A.M. Measurable Residual Disease Testing and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for AML: Adapting Pre-MEASURE to Clinical Practice. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2025, 60, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tettero, J.M.; Freeman, S.; Buecklein, V.; Venditti, A.; Maurillo, L.; Kern, W.; Walter, R.B.; Wood, B.L.; Roumier, C.; Philippé, J.; et al. Technical Aspects of Flow Cytometry-Based Measurable Residual Disease Quantification in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Experience of the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Hemasphere 2022, 6, e676, Erratum in Hemasphere 2022, 6, e703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.D.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Buccisano, F.; Hourigan, C.S.; Ngai, L.L.; Tettero, J.M.; Bachas, C.; Baer, C.; Béné, M.-C.; et al. 2021 Update on MRD in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Consensus Document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2021, 138, 2753–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, N.; van der Pol, M.A.; van Stijn, A.; Weijers, G.W.D.; Westra, A.H.; Evertse, B.W.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Schuurhuis, G.J. MRD Parameters Using Immunophenotypic Detection Methods Are Highly Reliable in Predicting Survival in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1380–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooimans, R.A.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Boeckx, N.; Slomp, J.; Preijers, F.; Te Marvelde, J.G.; Van, N.M.; Heijs, A.; Huys, E.; van der Holt, B.; et al. Immunophenotypic Measurable Residual Disease (MRD) in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Is Multicentric MRD Assessment Feasible? Leuk. Res. 2019, 76, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, B.L. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Minimal Residual Disease Detection: The Difference from Normal Approach. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2020, 93, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hourigan, C.S.; Gale, R.P.; Gormley, N.J.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Walter, R.B. Measurable Residual Disease Testing in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, L.L.; Kelder, A.; Janssen, J.J.W.M.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Cloos, J. MRD Tailored Therapy in AML: What We Have Learned So Far. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 603636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.M. Genetic Susceptibility to Breast Cancer in Lymphoma Survivors. Blood 2019, 133, 1004–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, S.; Leblanc, T.; Fenaux, P.; Witz, F.; Blaise, D.; Pigneux, A.; Thomas, X.; Rigal-Huguet, F.; Lioure, B.; Auvrignon, A.; et al. A White Blood Cell Index as the Main Prognostic Factor in t(8;21) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): A Survey of 161 Cases from the French AML Intergroup. Blood 2002, 99, 3517–3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilde, L.; Cooper, J.; Wang, Z.-X.; Liu, J. Clinical, Cytogenetic, and Molecular Findings in Two Cases of Variant t(8;21) Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, S.; Aljurf, M.; Mohty, M.; Almohareb, F.; Ahmed, S.O.A. An Update on the Molecular Pathogenesis and Potential Therapeutic Targeting of AML with t(8;21)(Q22;Q22.1);RUNX1-RUNX1T1. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailova, E.V.; Kashpor, S.A.; Zerkalenkova, E.A.; Semchenkova, A.A.; Dubrovina, M.E.; Plyasunova, S.A.; Olshanskaya, Y.V.; Kalinina, I.I.; Maschan, M.A.; Maschan, A.A.; et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with inv(16)(p13.1q22)/t(16;16)(p13.1;q22)/CBFb-MYH11. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. Immunopathol. 2021, 20, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordonnier, G.; Mandoli, A.; Cagnard, N.; Hypolite, G.; Lhermitte, L.; Verhoeyen, E.; Asnafi, V.; Dillon, N.; Macintyre, E.; Martens, J.H.A.; et al. CBFβ-SMMHC Affects Genome-Wide Polycomb Repressive Complex 1 Activity in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 299–307.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, S.; Liapis, I.; Papadhimitriou, S.I.; Spanoudakis, E.; Kotsianidis, I.; Liapis, K. Approach to Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Increased Eosinophils and Basophils. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustun, C.; Marcucci, G. Emerging Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches in Core Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Kaspers, G.; Harrison, C.J.; Beverloo, H.B.; Reedijk, A.; Bongers, M.; Cloos, J.; Pession, A.; Reinhardt, D.; Zimmerman, M.; et al. Clinical Impact of Additional Cytogenetic Aberrations, cKIT and RAS Mutations, and Treatment Elements in Pediatric t(8;21)-AML: Results from an International Retrospective Study by the International Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 4247–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solh, M.; Yohe, S.; Weisdorf, D.; Ustun, C. Core-Binding Factor Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Heterogeneity, Monitoring, and Therapy. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, J.; Zhou, D.; Qiu, K. CEBPA Are Independent Good Prognostic Factors in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlock, K.; Lamble, A.J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Gerbing, R.B.; Ries, R.E.; Loken, M.R.; Brodersen, L.E.; Pardo, L.; Leonti, A.; Smith, J.L.; et al. CEBPA-bZip Mutations Are Associated with Favorable Prognosis in de Novo AML: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Blood 2021, 138, 1137–1147, Erratum in Blood 2022, 139, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgarten, C.W.; Aplenc, R. Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Updates on Biology, Risk Stratification, and Therapy. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2020, 32, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
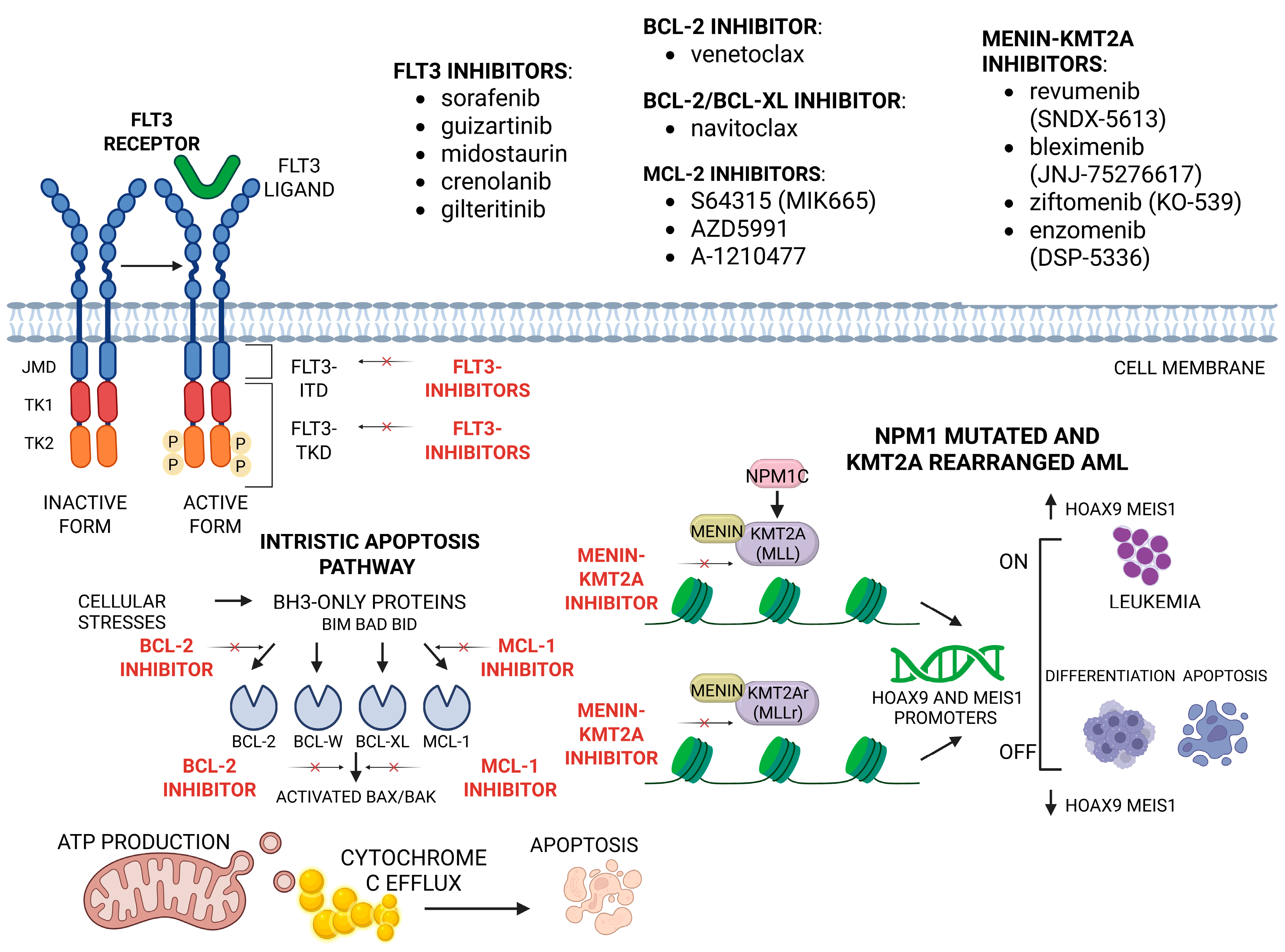
- Ranieri, R.; Pianigiani, G.; Sciabolacci, S.; Perriello, V.M.; Marra, A.; Cardinali, V.; Pierangeli, S.; Milano, F.; Gionfriddo, I.; Brunetti, L.; et al. Current Status and Future Perspectives in Targeted Therapy of NPM1-Mutated AML. Leukemia 2022, 36, 2351–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falini, B.; Sorcini, D.; Perriello, V.M.; Sportoletti, P. Functions of the Native NPM1 Protein and Its Leukemic Mutant. Leukemia 2025, 39, 276–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoi, H.; Kawashima, N.; Ishikawa, Y. FLT3 Mutations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Therapeutic Paradigm beyond Inhibitor Development. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantilena, S.; Gasparoli, L.; Pal, D.; Heidenreich, O.; Klusmann, J.-H.; Martens, J.H.A.; Faille, A.; Warren, A.J.; Karsa, M.; Pandher, R.; et al. Direct Targeted Therapy for MLL-Fusion-Driven High-Risk Acute Leukaemias. Clin. Transl. Med. 2022, 12, e933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurer, A.; Glushakow-Smith, S.G.; Gritsman, K. Targeting Chromatin Modifying Complexes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2025, 14, szae089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, C.; Larghero, P.; Almeida Lopes, B.; Burmeister, T.; Gröger, D.; Sutton, R.; Venn, N.C.; Cazzaniga, G.; Corral Abascal, L.; Tsaur, G.; et al. The KMT2A Recombinome of Acute Leukemias in 2023. Leukemia 2023, 37, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Muntean, A.G. The YEATS Domain Epigenetic Reader Proteins ENL and AF9 and Their Therapeutic Value in Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2023, 124, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Crump, N.T.; Arentsen-Peters, S.T.C.J.M.; Smith, A.L.; Hagelaar, R.; Adriaanse, F.R.S.; Bos, R.S.; de Jong, A.; Nierkens, S.; Koopmans, B.; et al. Modelling Acquired Resistance to DOT1L Inhibition Exhibits the Adaptive Potential of KMT2A-Rearranged Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Ge, S. Targeting the Histone H3 Lysine 79 Methyltransferase DOT1L in MLL-Rearranged Leukemias. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quessada, J.; Cuccuini, W.; Saultier, P.; Loosveld, M.; Harrison, C.J.; Lafage-Pochitaloff, M. Cytogenetics of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Review of the Current Knowledge. Genes 2021, 12, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waack, K.; Schneider, M.; Walter, C.; Creutzig, U.; Klusmann, J.-H.; Rasche, M.; Boztug, H.; Jansen, K.; Escherich, G.; Frühwald, M.; et al. Improved Outcome in Pediatric AML—The AML-BFM 2012 Study. Blood 2020, 136, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noort, S.; Zimmermann, M.; Reinhardt, D.; Cuccuini, W.; Pigazzi, M.; Smith, J.; Ries, R.E.; Alonzo, T.A.; Hirsch, B.; Tomizawa, D.; et al. Prognostic Impact of t(16;21)(P11;Q22) and t(16;21)(Q24;Q22) in Pediatric AML: A Retrospective Study by the I-BFM Study Group. Blood 2018, 132, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgobind, B.V.; Raimondi, S.C.; Harbott, J.; Zimmermann, M.; Alonzo, T.A.; Auvrignon, A.; Beverloo, H.B.; Chang, M.; Creutzig, U.; Dworzak, M.N.; et al. Novel Prognostic Subgroups in Childhood 11q23/MLL-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Results of an International Retrospective Study. Blood 2009, 114, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, A.D.J.; Zwaan, C.M.; Kolb, E.A.; Karres, D.; Guillot, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Marshall, L.; Tasian, S.K.; Smith, M.; Cooper, T.; et al. Paediatric Strategy Forum for Medicinal Product Development for Acute Myeloid Leukaemia in Children and Adolescents: ACCELERATE in Collaboration with the European Medicines Agency with Participation of the Food and Drug Administration. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 136, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H. Treatments for Children and Adolescents with AML. Blood Res. 2020, 55, S5–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obszański, P.; Kozłowska, A.; Wańcowiat, J.; Twardowska, J.; Lejman, M.; Zawitkowska, J. Molecular-Targeted Therapy of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Molecules 2022, 27, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, P. Pediatric AML: State of the Art and Future Directions. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2025, 42, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, K.J.; Absalon, M.J.; Demissei, B.G.; Smith, A.M.; Gerbing, R.B.; Alonzo, T.A.; Narayan, H.K.; Hirsch, B.A.; Pollard, J.A.; Razzouk, B.I.; et al. Cardiotoxicity of CPX-351 in Children and Adolescents with Relapsed AML: A Children’s Oncology Group Report. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1347547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, T.M.; Absalon, M.J.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Leger, K.J.; Hirsch, B.A.; Pollard, J.; Razzouk, B.I.; Aplenc, R.; Kolb, E.A. Phase I/II Study of CPX-351 Followed by Fludarabine, Cytarabine, and Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor for Children with Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2170–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.A.; Guest, E.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Loken, M.R.; Brodersen, L.E.; Kolb, E.A.; Aplenc, R.; Meshinchi, S.; Raimondi, S.C.; et al. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Improves Event-Free Survival and Reduces Relapse in Pediatric KMT2A-Rearranged AML: Results from the Phase III Children’s Oncology Group Trial AAML0531. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3149–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blain, S.; Payette, N.; Bittencourt, H.; Johnston, D.L. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin Monotherapy Is a Well-Tolerated Palliative Chemotherapy Option in Pediatric Multiply Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Multicenter Case Series and Review of the Literature. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 45, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokke, J.L.; Bhojwani, D. Antibody-Drug Conjugates for the Treatment of Acute Pediatric Leukemia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, G.; Chopra, Y.; Mourad, S.; Chiang, K.-Y.; Hitzler, J. Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children: A Practical Perspective. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e28979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, J.A.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.; Brown, P.; Fox, E.; Choi, J.; Fisher, B.; Hirsch, B.; Kahwash, S.; Getz, K.; et al. Sorafenib in Combination with Standard Chemotherapy for Children with High Allelic Ratio FLT3/ITD+ Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group Protocol AAML1031. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2023–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conneely, S.E.; Stevens, A.M. Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children: Emerging Paradigms in Genetics and New Approaches to Therapy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aplenc, R.; Meshinchi, S.; Sung, L.; Alonzo, T.; Choi, J.; Fisher, B.; Gerbing, R.; Hirsch, B.; Horton, T.; Kahwash, S.; et al. Bortezomib with Standard Chemotherapy for Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia Does Not Improve Treatment Outcomes: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Haematologica 2020, 105, 1879–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramiz, S.; Elhaj, O.; Siddiqui, K.; Khan, S.; AlSaedi, H.; AlAnazi, A.; Al-Ahmari, A.; Al-Jefri, A.; Sahvan, O.; Ayas, M.; et al. Clofarabine in Pediatric Acute Relapsed or Refractory Leukemia: Where Do We Stand on the Bridge to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation? J. Hematol. 2023, 12, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Glasser, C.L. New and Emerging Targeted Therapies for Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Children 2020, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marszołek, A.; Leśniak, M.; Sekunda, A.; Siwek, A.; Skiba, Z.; Lejman, M.; Zawitkowska, J. Haploidentical HSCT in the Treatment of Pediatric Hematological Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarnegar-Lumley, S.; Caldwell, K.J.; Rubnitz, J.E. Relapsed Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children and Adolescents: Current Treatment Options and Future Strategies. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1951–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, S.; Lee, M.-E.; Lin, P.-C. A Review of Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Diagnosis and Novel Treatment. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasche, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Steidel, E.; Alonzo, T.; Aplenc, R.; Bourquin, J.-P.; Boztug, H.; Cooper, T.; Gamis, A.S.; Gerbing, R.B.; et al. Survival Following Relapse in Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report from AML-BFM and COG. Cancers 2021, 13, 2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlock, K.; Sulis, M.L.; Chewning, J.H.; Pollard, J.A.; Cooper, T.; Gamis, A.; Shenoy, S.; Kutny, M.; Horan, J.; Meshinchi, S.; et al. Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Pediatric Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2022, 28, 530–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, M.G.; Lang, P.J.; Albert, M.H.; Bader, P.; Creutzig, U.; Eyrich, M.; Greil, J.; Gruhn, B.; Holter, W.; Klingebiel, T.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation for Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia-Results of the AML SCT-BFM 2007 Trial. Leukemia 2020, 34, 613–624, Erratum in Leukemia 2020, 34, 1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluijs, A.B.; de Koning, C.C.H.; Lankester, A.C.; Nierkens, S.; Kollen, W.J.; Bresters, D.; Lindemans, C.A.; Boelens, J.J.; Bierings, M. Clofarabine-Fludarabine-Busulfan in HCT for Pediatric Leukemia: An Effective, Low Toxicity, TBI-Free Conditioning Regimen. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versluys, A.B.; Boelens, J.J.; Pronk, C.; Lankester, A.; Bordon, V.; Buechner, J.; Ifversen, M.; Jackmann, N.; Sundin, M.; Vettenranta, K.; et al. Hematopoietic Cell Transplant in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia after Similar Upfront Therapy; a Comparison of Conditioning Regimens. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 1426–1432, Erratum in Bone Marrow Transplant. 2021, 56, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, B.L.; Pasquini, M.C.; Fei, M.; Fraser, R.; Wu, J.; Devine, S.M.; Porter, D.L.; Maziarz, R.T.; Warlick, E.; Fernandez, H.F.; et al. Myeloablative versus Reduced-Intensity Conditioning for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation in Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndromes-Long-Term Follow-Up of the BMT CTN 0901 Clinical Trial. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 483.e1–483.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, T.; Thépot, S.; Peterlin, P.; Ceballos, P.; Bourgeois, A.L.; Garnier, A.; Orvain, C.; Giltat, A.; François, S.; Bris, Y.L.; et al. Prophylactic or Preemptive Low-Dose Azacitidine and Donor Lymphocyte Infusion to Prevent Disease Relapse Following Allogeneic Transplantation in Patients with High-Risk Acute Myelogenous Leukemia or Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 839.e1–839.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimentova, M.; Shelikhova, L.; Ilushina, M.; Kozlovskaya, S.; Blagov, S.; Popov, A.; Kashpor, S.; Fadeeva, M.; Olshanskaya, J.; Glushkova, S.; et al. Targeted Therapy with Venetoclax and Daratumumab as Part of HSCT Preparative Regimen in Children with Chemorefractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2023, 29, 127.e1–127.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.; Schlenk, R.F.; Russell, N.H.; Levis, M.J. Targeting FLT3 Mutations in AML: Review of Current Knowledge and Evidence. Leukemia 2019, 33, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negotei, C.; Colita, A.; Mitu, I.; Lupu, A.R.; Lapadat, M.-E.; Popovici, C.E.; Crainicu, M.; Stanca, O.; Berbec, N.M. A Review of FLT3 Kinase Inhibitors in AML. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, I.; Bodo, J.; Hill, B.T.; Hsi, E.D.; Almasan, A. Targeting BCL-2 in B-Cell Malignancies and Overcoming Therapeutic Resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Wei, A.H.; Huang, D.C.S. BCL2 and MCL1 Inhibitors for Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2021, 138, 1120–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, R.K.; Wang, E.S. Top Advances of the Year: Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer 2025, 131, e35834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.M.; Tarlock, K.; Cooper, T. Targeted Therapy in Pediatric AML: An Evolving Landscape. Paediatr. Drugs 2021, 23, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.C.; Thuring, J.W.; Querolle, O.; Dai, X.; Verhulst, T.; Pande, V.; Marien, A.; Goffin, D.; Wenge, D.V.; Yue, H.; et al. Preclinical Efficacy of the Potent, Selective Menin-KMT2A Inhibitor JNJ-75276617 (Bleximenib) in KMT2A- and NPM1-Altered Leukemias. Blood 2024, 144, 1206–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hao, S. A-1210477, a Selective MCL-1 Inhibitor, Overcomes ABT-737 Resistance in AML. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 5481–5489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
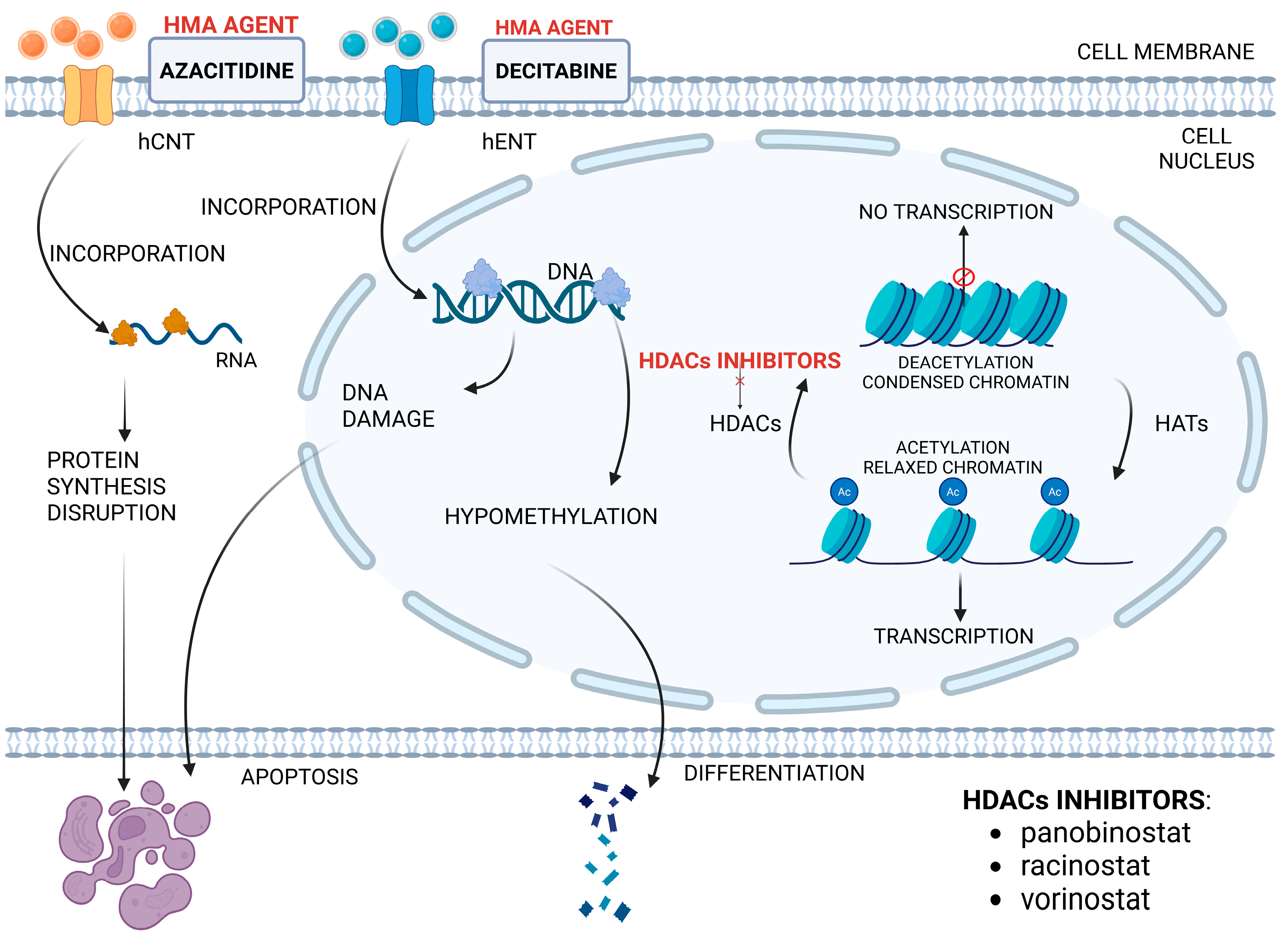
- Neuendorff, N.R.; Gagelmann, N.; Singhal, S.; Meckstroth, S.; Thibaud, V.; Zhao, Y.; Mir, N.; Shih, Y.-Y.; Amaro, D.M.C.; Roy, M.; et al. Hypomethylating Agent-Based Therapies in Older Adults with Acute Myeloid Leukemia—A Joint Review by the Young International Society of Geriatric Oncology and European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation Trainee Committee. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2023, 14, 101406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San José-Enériz, E.; Gimenez-Camino, N.; Agirre, X.; Prosper, F. HDAC Inhibitors in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2019, 11, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
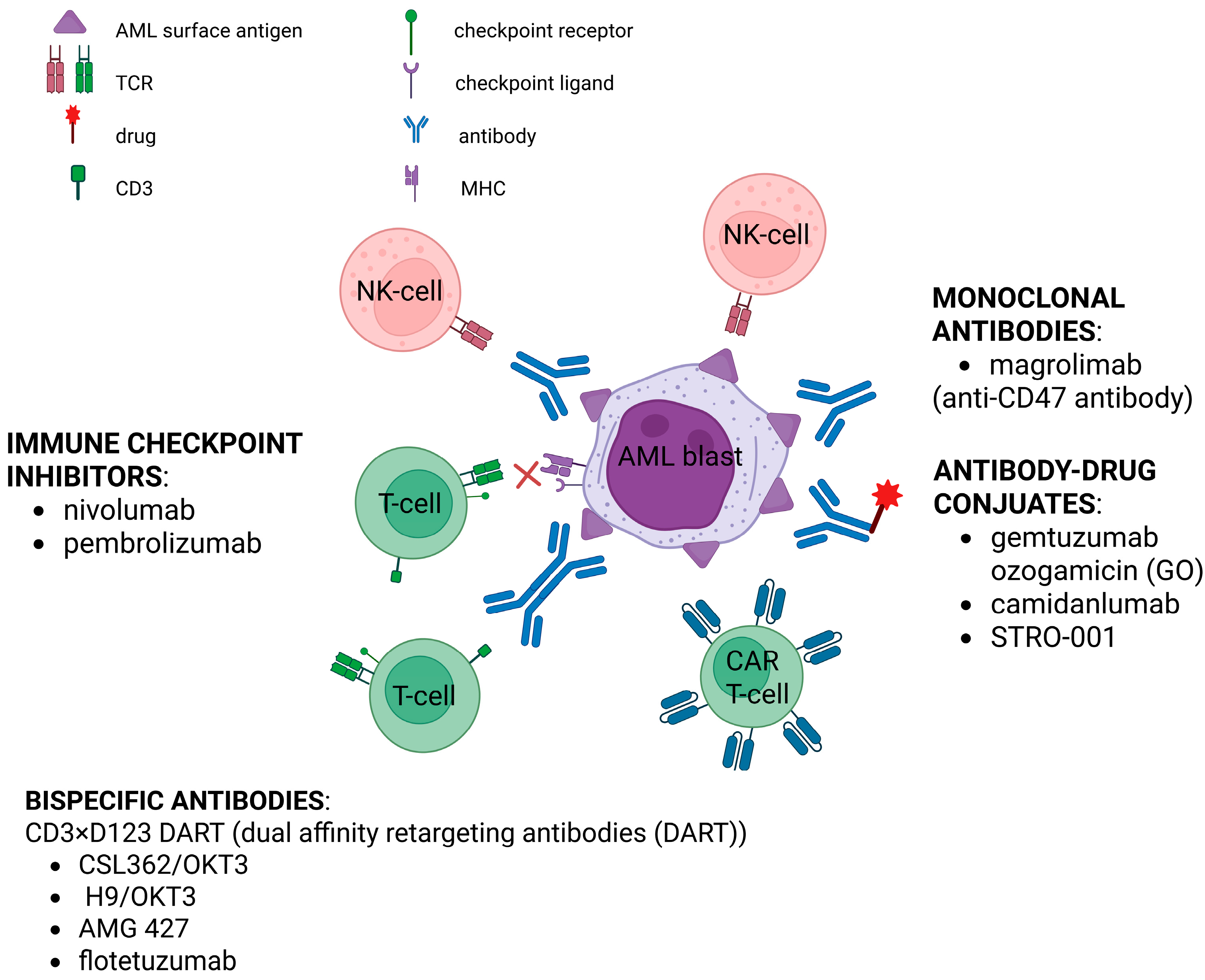
- Yang, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y. The Progress and Current Status of Immunotherapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1965–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perzolli, A.; Koedijk, J.B.; Zwaan, C.M.; Heidenreich, O. Targeting the Innate Immune System in Pediatric and Adult AML. Leukemia 2024, 38, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Malvar, J.; Lamble, A.; Chaudhury, S.; Agarwal, A.; Li, H.-T.; Liang, G.; Leong, R.; Brown, P.A.; et al. Nivolumab Plus 5-Azacitidine in Pediatric Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Phase I/II Trial Results from the Therapeutic Advances in Childhood Leukemia and Lymphoma (TACL) Consortium. Cancers 2024, 16, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.L.; Agarwal, A.M.; Verma, A.R. Checkpoint Inhibition in Pediatric Hematologic Malignancies. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 34, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epperly, R.; Gottschalk, S.; Velasquez, M.P. Harnessing T Cells to Target Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: CARs, BiTEs, and Beyond. Children 2020, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menssen, A.J.; Hudson, C.A.; Alonzo, T.; Gerbing, R.; Pardo, L.; Leonti, A.; Cook, J.A.; Hsu, F.-C.; Lott, L.L.; Dai, F.; et al. CD74 Is Expressed in a Subset of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients and Is a Promising Target for Therapy: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Haematologica 2024, 109, 3182–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizsán, S.; Péterffy, B.; Egyed, B.; Nagy, T.; Sebestyén, E.; Hegyi, L.L.; Jakab, Z.; Erdélyi, D.J.; Müller, J.; Péter, G.; et al. Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Genomic Profiling of Children with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Mol. Diagn. 2023, 25, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.S.B.; Juul-Dam, K.L.; Sandahl, J.D.; Abrahamsson, J.; Czogala, M.; Delabesse, E.; Haltrich, I.; Jahnukainen, K.; Kolb, E.A.; Kovács, G.; et al. Hypodiploidy Has Unfavorable Impact on Survival in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: An I-BFM Study Group Collaboration. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.; Liu, L.; Qi, B.; Chen, X.; Chang, L.; Zhang, A.; Liu, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Targeted Next-Generation Sequencing of Circulating Tumor DNA, Bone Marrow, and Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Pediatric AML. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 666470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, F.; Tantawy, M.; Sayed, A.; Ahmed, S. Clinical Significance of MicroRNA-29a and MicroRNA-100 Gene Expression in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 44, e391–e395, Erratum in J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 44, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Xie, M.; Sun, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, U. Development of a Prognostic Model Incorporating a Cuproptosis-Related Signature and CNN3 as a Predictor in Childhood Acute Myelocytic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1494777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellson, I.; Martorell-Marugán, J.; Carmona-Sáez, P.; Ramos-Mejia, V. MiRNA Expression as Outcome Predictor in Pediatric AML: Systematic Evaluation of a New Model. NPJ Genom. Med. 2024, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshref Razavi, H.; Minor, A. A Case of AML with Complex Karyotype and Chromosomal Rearrangement of KMT2A. Clin. Case Rep. 2024, 12, e9139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pais, A.; Pande, S.; Pradhan, G.; Patil, S. A Complex Karyotype with t(11;12)(Q23;P13) Translocation with Coexistent Clones of Deletion 5q and Cryptic Deletion 7q in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Indian J. Cancer 2020, 57, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capela de Matos, R.R.; Ney Garcia, D.R.; Othman, M.A.K.; Moura Ferreira, G.; Melo, J.B.; Carreira, I.M.; Meyer, C.; Marschalek, R.; Costa, E.S.; Land, M.G.P.; et al. A New Complex Karyotype Involving a KMT2A-r Variant Three-Way Translocation in a Rare Clinical Presentation of a Pediatric Patient with Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2019, 157, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimwade, D.; Walker, H.; Harrison, G.; Oliver, F.; Chatters, S.; Harrison, C.J.; Wheatley, K.; Burnett, A.K.; Goldstone, A.H.; Medical Research Council Adult Leukemia Working Party. The Predictive Value of Hierarchical Cytogenetic Classification in Older Adults with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Analysis of 1065 Patients Entered into the United Kingdom Medical Research Council AML11 Trial. Blood 2001, 98, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slovak, M.L.; Kopecky, K.J.; Cassileth, P.A.; Harrington, D.H.; Theil, K.S.; Mohamed, A.; Paietta, E.; Willman, C.L.; Head, D.R.; Rowe, J.M.; et al. Karyotypic Analysis Predicts Outcome of Preremission and Postremission Therapy in Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Southwest Oncology Group/Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Study. Blood 2000, 96, 4075–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhling, S.; Schlenk, R.F.; Kayser, S.; Morhardt, M.; Benner, A.; Döhner, K.; Döhner, H.; German-Austrian AML Study Group. Cytogenetics and Age Are Major Determinants of Outcome in Intensively Treated Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients Older than 60 Years: Results from AMLSG Trial AML HD98-B. Blood 2006, 108, 3280–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Dou, H.; Yang, Z.; Bi, J.; Huang, Y.; Lu, L.; Yu, J.; Bao, L. Cytogenetic and Mutational Analysis and Outcome Assessment of a Cohort of 284 Children with de Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia Reveal Complex Karyotype as an Adverse Risk Factor for Inferior Survival. Mol. Cytogenet. 2021, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.H.; Choi, Y.B.; Yi, E.-S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.W.; Sung, K.W.; Koo, H.H.; Yoo, K.H. Monosomal Karyotype Is Not a Predictor of Dismal Outcome in Childhood de Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2016, 50, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene | Region | Syndrome | Mean Age at Onset (Range and Average Age in Years) | Associated Malignancy/ies | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPA | 19q13.1 | Familial AML with mutated CEBPA | Early childhood to early adulthood (2 to 50, 25) | AML | [52,53,54,55,56,57] |
| GATA2 | 3q21.3 | Familial MDS/AML with mutated GATA2/GATA2 deficiency syndrome | Early teens to early twenties (<1 to 78, 20) | MDS/AML, CMML | [52,58,59,60,61] |
| ETV6 | 12p13.2 | Thrombocytopenia 5 | Childhood to early adulthood (2 to 82, 22) | MDS/AML, CMML, B-cell ALL, plasma cell neoplasm | [52,62,63,64,65,66,67,68] |
| RUNX1 | 21q22.12 | Familial platelet disorder with propensity to myeloid malignancies | Early childhood to late adulthood (6 to 76, 33) | MDS/AML, T-cell ALL | [52,58,69,70,71,72,73,74] |
| ANKRD26 | 10p12.1 | Thrombocytopenia 2 | Childhood to early adulthood (1 to 84, 38) | MDS/AML, CML, MPN, ALL, CLL, MM | [75,76,77,78] |
| TP53 | 17p13.1 | Li–Fraumeni syndrome | Childhood to late adulthood (20–70, 20) | MDS/AML, ALL, t-MN, lymphoma, MM, osteosarcoma, breast cancer, brain tumors, soft tissue sarcoma, adrenocortical carcinoma, and other solid tumors | [79,80,81,82,83] |
| SAMD9/9L | 7q21.2 | MIRAGE syndrome (SAMD9); ataxia-pancytopenia syndrome (ATXPC) (SAMD9L) | Early childhood (0 to 2, 2) | MDS/AML, CMML | [52,84,85,86,87] |
| Method | Sensitivity | Markers | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiparameter Flow Cytometry (MPFC) | 10−3 to 10−5 |
| [115,116,117,118,119] |
| Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) | 10−3 to 10−5 | NPM1, RUNX1-RUNX1T1, CBFB-MYH11, PML-RARA, KMT2A-MLLT3, DEK-NUP214, BCR-ABL, WT1 | [120,121] |
| Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) | 10−2 | CALR, CEBPA, DDX41, ETV6, EZH2, FLT3, IDH1, IDH2, JAK2, KIT, KRAS, MPL, NPM1, NRAS, PTPN11, RAD21, RUNX1, SF3B1, SRSF2, STAG2, TP53, U2AF1, WT1 | [116,121] |
| Risk | Molecular Abnormalities | Cytogenetic Abnormalities | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Favorable | t(8;21)(q22;q22.1) | RUNX1::RUNX1T1 | [21] |
| t(16;21)(q24;q22) | RUNX1::CBFA2T3 | [144] | |
| inv(16)(p13.1q22) t(16;16)(p13.1;q22) | CBFB::MYH11 | [125] | |
| t(9;11)(p22;q23) | KMT2A::AF9 (MLLT3) | [144] | |
| t(11;19)(q23;p13.1) | KMT2A::ELL | [144] | |
| CEBPA gene single or double mutations | [132] | ||
| NPM1 | [135] | ||
| del(7q) | [144] | ||
| Intermediate | t(11;19)(q23;p13.3) | KMT2A::MLLT1 | [140] |
| t(10;11)(p12;q14) | PICALM::MLLT10 | [144] | |
| t(8;16)(p11;p13) | KAT6A::CREBBP | [144] | |
| t(3;5)(q25;q35) | NPM1::MLF1 | [144] | |
| t(1;22)(p13;q13) | RBM15::MKL1 | [144] | |
| FLT3-ITD | [134] | ||
| Adverse | t(9;22)(q34;q11) | BCR::ABL1 | [21] |
| t(6;9)(p22;q34) | DEK::NUP214 | [21] | |
| t(7;12)(q36;p13) | ETV6::MNX1 | [144] | |
| inv(3)(q21.3q26.2) t(3;3)(q21.3;q26.2) | GATA2, MECOM (EVI1) | [144] | |
| t(9;11)(p21;q23) | KMT2A::MLLT3 | [145] | |
| t(5;11)(q35;p15) | NUP98::NSD1 | [144] | |
| t(11;12)(p15;p13) | NUP98::KMD5A | [144] | |
| t(16;21)(p11;q23) | FUS::ERG | [146] | |
| t(6;11)(q27;q23) t(4;11)(q21;q23) t(10;11)(p12;q23) | KMT2A::AF6 (MLLT4) | [147] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leśniak, M.; Sekunda, A.; Kamizela, E.; Deleszkiewicz, P.; Ozygała, A.; Zawitkowska, J.; Lejman, M. A Novel Approach to Prognostic Factors and Risk Stratification in Pediatric AML: Case Report and Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199269
Leśniak M, Sekunda A, Kamizela E, Deleszkiewicz P, Ozygała A, Zawitkowska J, Lejman M. A Novel Approach to Prognostic Factors and Risk Stratification in Pediatric AML: Case Report and Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(19):9269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199269
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeśniak, Maria, Anna Sekunda, Emilia Kamizela, Paulina Deleszkiewicz, Aleksandra Ozygała, Joanna Zawitkowska, and Monika Lejman. 2025. "A Novel Approach to Prognostic Factors and Risk Stratification in Pediatric AML: Case Report and Literature Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 19: 9269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199269
APA StyleLeśniak, M., Sekunda, A., Kamizela, E., Deleszkiewicz, P., Ozygała, A., Zawitkowska, J., & Lejman, M. (2025). A Novel Approach to Prognostic Factors and Risk Stratification in Pediatric AML: Case Report and Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(19), 9269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26199269








