Protective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen Against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Male Wistar Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
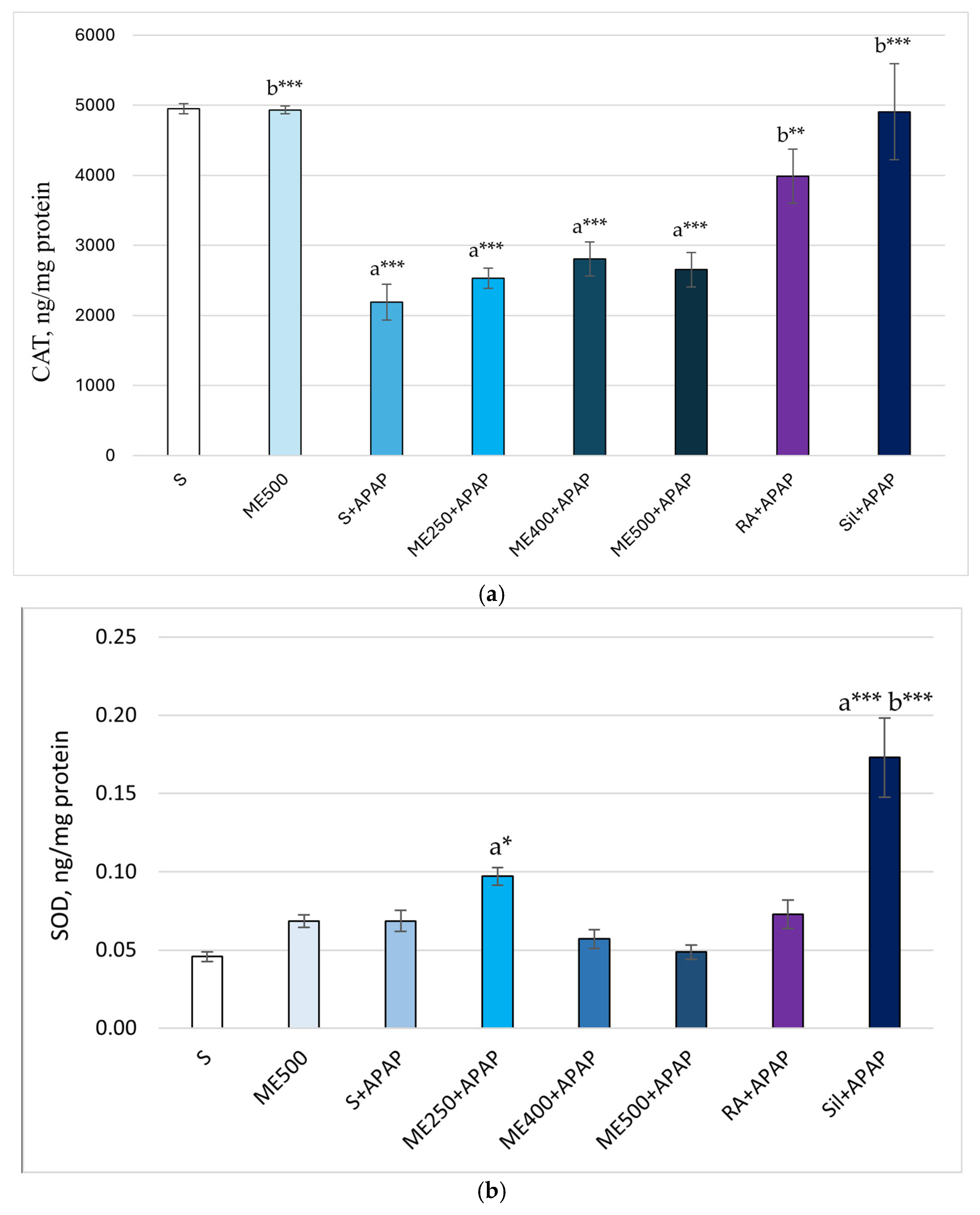
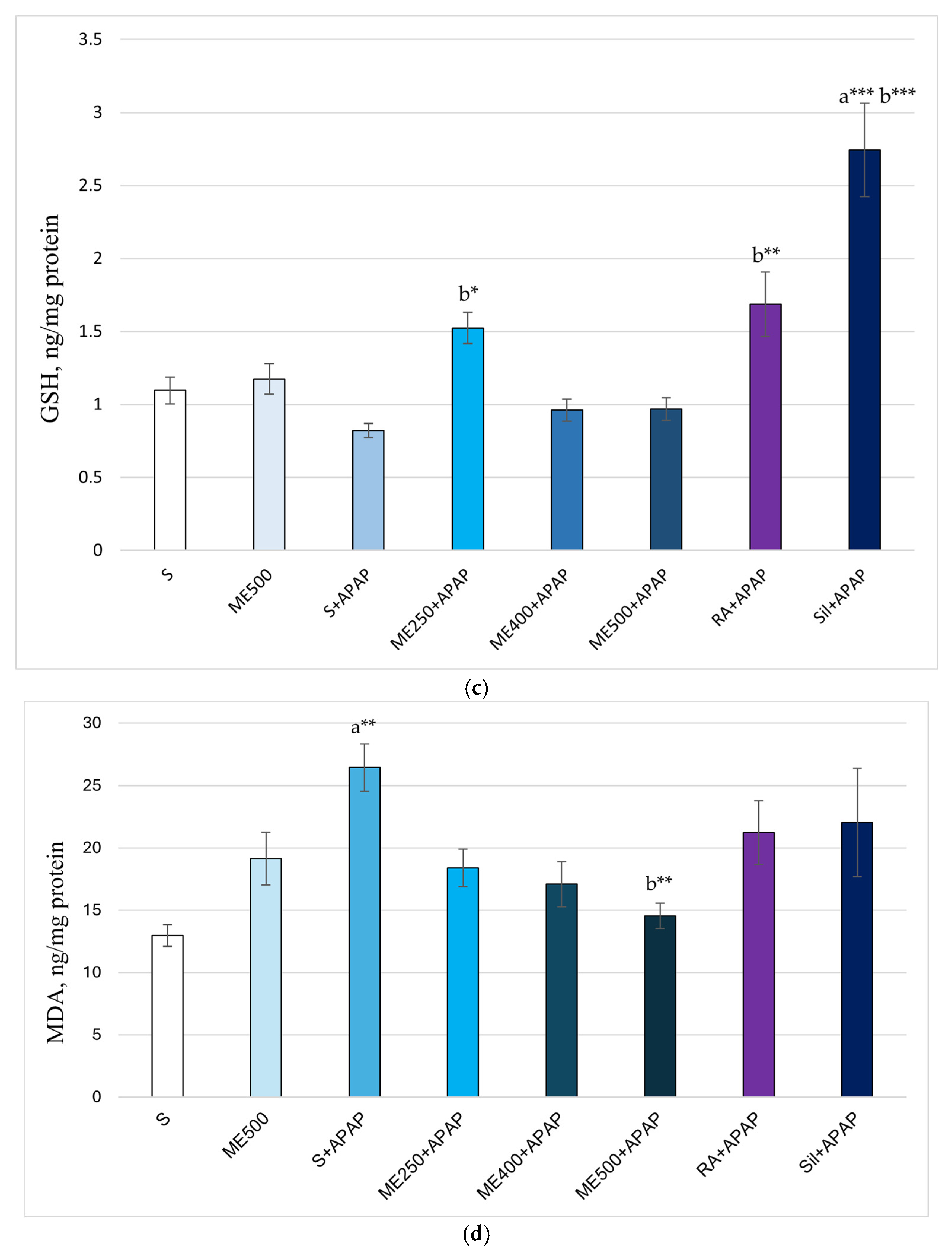
2. Results
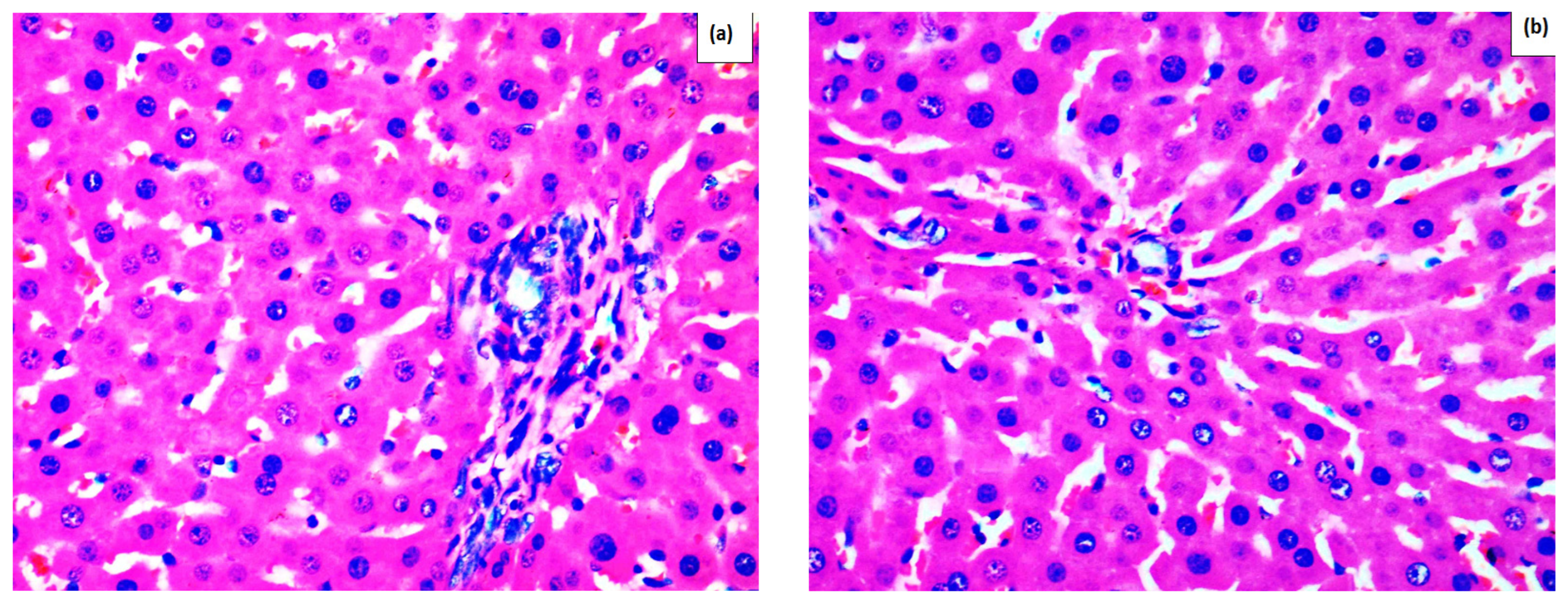
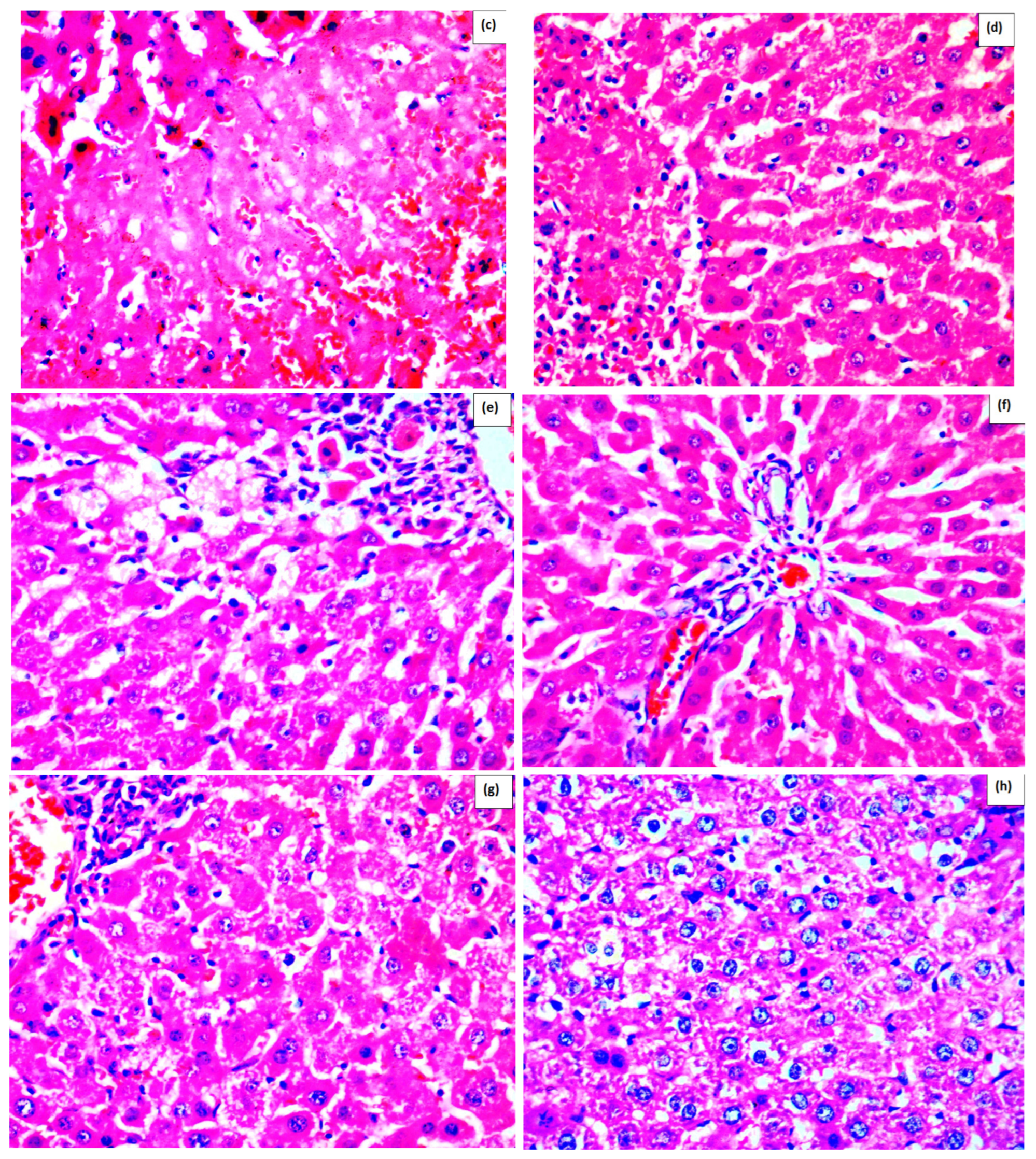
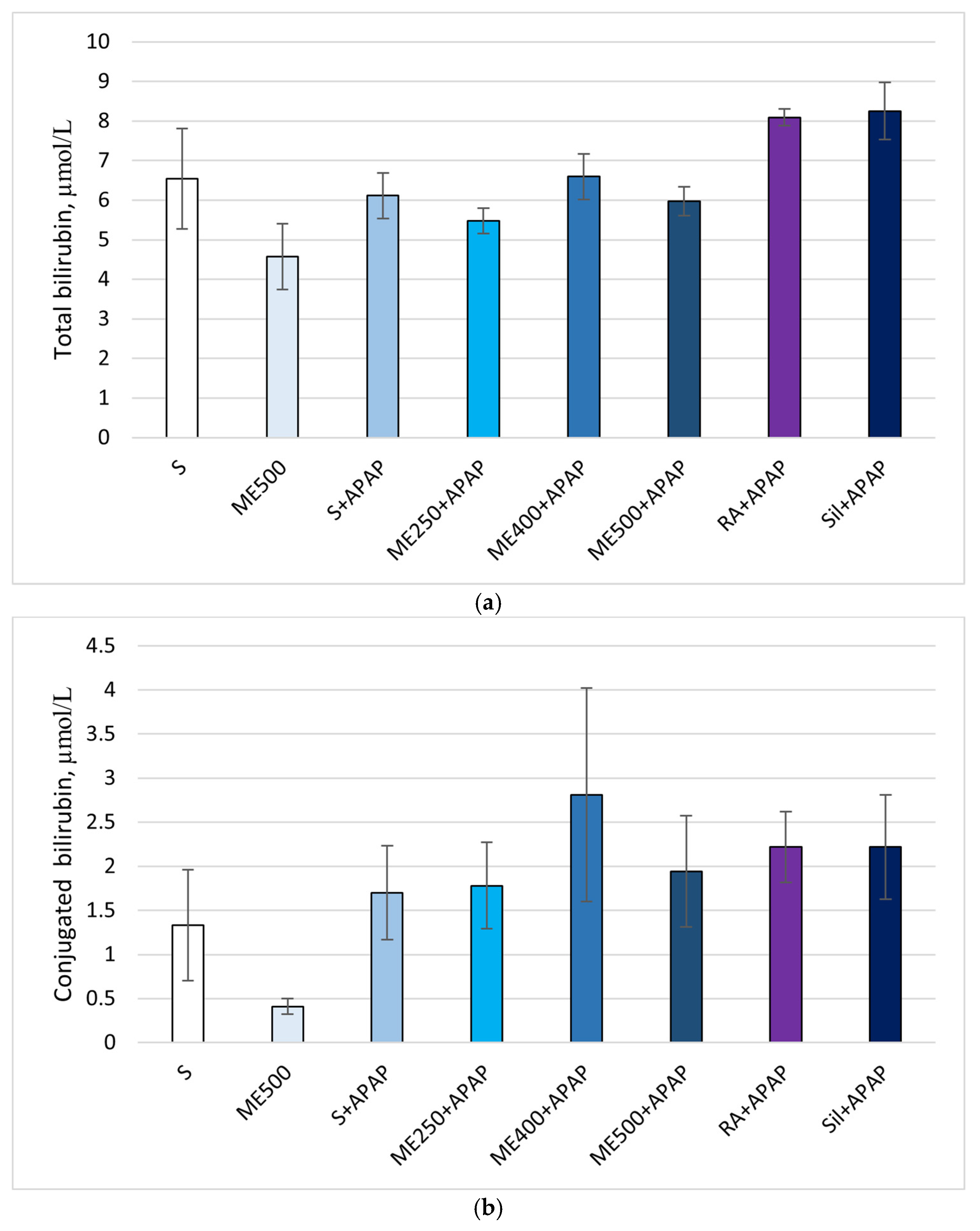
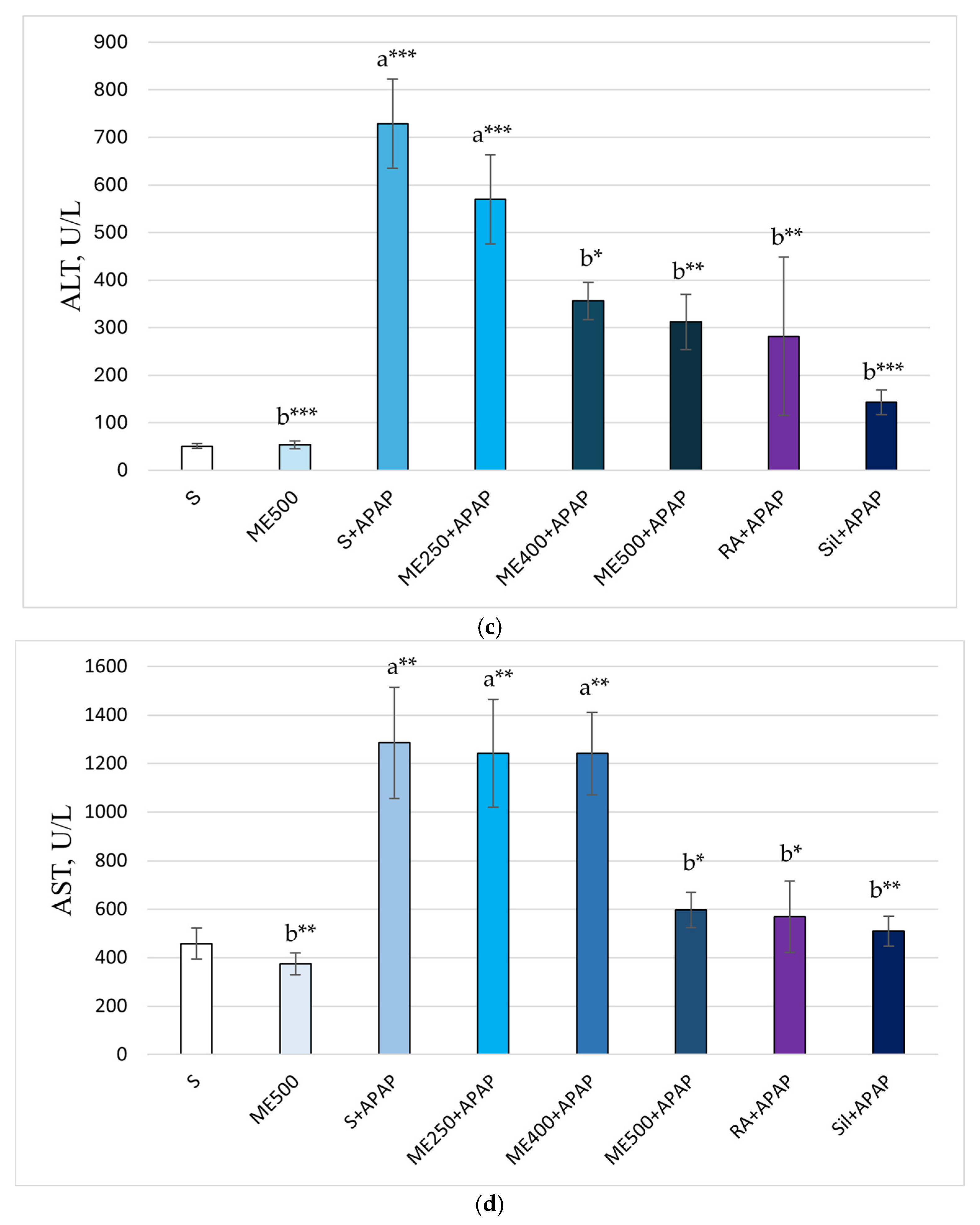
Effect of Methanolic Extract of M. frivaldszkyana in APAP-Induced Liver Toxicity
3. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Plant Material and Preparation of the Methanolic Extract
4.3. Animals and Treatment
4.3.1. Histopathological Observation
- Tissues were immersed in formalin for 24 h, thoroughly rinsed, and then soaked in distilled water for 30 min to eliminate any residual fixative.
- Dehydration was achieved through progressive immersion in 95% and then 100% ethanol (Histanol® 100%), each step lasting 4–5 h.
- After dehydration, the tissues were treated with acetone for 20 min, followed by xylol for 30 min. They were then embedded in molten paraffin and formed into blocks. Thin slices, 5 μm in thickness, were obtained from these blocks and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for microscopic examination.
4.3.2. Preparation of Liver Homogenates and Evaluation of Tissue-Specific Toxicity Markers
4.3.3. Biochemical Markers in Serum
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 8-OH-dG | 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine |
| ABTS | 2,2-azinobis (3)-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| APAP | Acetaminophen (paracetamol) |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CCL4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| CUPRAC | Cupric ion reducing antioxidant capacity |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| DPPH | 2,2′-diphenylpicrylhydrazyl |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FRAP | Ferric reducing antioxidant power |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MIC | Minimum inhibitory concentration |
| NAC | N-acetylcysteine |
| NAPQI | N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine |
| ORAC | Oxygen radical absorbance capacity |
| RA | Rosmarinic acid |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| t-BHP | Tert-butyl hydroperoxide |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| UPLC-MS/MS | Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry |
References
- Dkhil, M.A.; Abdel Moneim, A.E.; Hafez, T.A.; Mubaraki, M.A.; Mohamed, W.F.; Thagfan, F.A.; Al-Quraishy, S. Myristica fragrans Kernels prevent paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity by inducing anti-apoptotic genes and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, M.E. Epidemiology of acetaminophen toxicity. In Acetaminophen Toxicity; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Stavrakeva, K.; Popova, M.; Esad, M.; Apostolova, E.; Kokova, V.; Bacelova, M.; Alakidi, A.; Bivolarska, A. Drug-induced liver toxicity. Acta Medica Bulg. 2024, 51, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Shehata, H.H.; El-Saeed, G.S.M.; Abou Gabal, H.H.; El-Daly, S.M. Paracetamol overdose induces acute liver injury accompanied by oxidative stress and inflammation. Egypt. J. Chem. 2023, 66, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashafaq, M.; Hussain, S.; Alshahrani, S.; Madkhali, O.; Siddiqui, R.; Khuwaja, G.; Alam, M.I.; Islam, F. Role of cinnamon oil against acetaminophen overdose induced neurological aberrations through brain stress and cytokine upregulation in rat brain. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 45, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, Y.M.; Azmy, R.M.; Samaka, R.M.; Salem, M.F. Pleurotus ostreatus opposes mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in acetaminophen-induced hepato-renal injury. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanein, P.; Sharifi, M. Effects of rosmarinic acid on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Okamura, T.; Inoue, T.; Tasaki, M.; Umemura, T.; Nishikawa, A. Dietary catechol causes increased oxidative DNA damage in the livers of mice treated with acetaminophen. Toxicology 2009, 263, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenkel, O.; Mossanen, J.C.; Tacke, F. Immune mechanisms in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2014, 3, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolbright, B.L.; Jaeschke, H. Role of the inflammasome in acetaminophen-induced liver injury and acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.T.; Arjumand, W.; Nafees, S.; Seth, A.; Ali, N.; Rashid, S.; Sultana, S. Hesperidin alleviates acetaminophen induced toxicity in Wistar rats by abrogation of oxidative stress, apoptosis and inflammation. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 208, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adetuyi, B.O.; Adebisi, O.A.; Adetuyi, O.A.; Ogunlana, O.O.; Toloyai, P.E.; Egbuna, C.; Uche, C.Z.; Khan, J.; Adumanya, O.C.U.; Patrick-Iwuanyanwu, K.C. Ficus exasperata attenuates acetaminophen-induced hepatic damage via NF-κB signaling mechanism in experimental rat model. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6032511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaolapo, O.J.; Adekola, M.A.; Azeez, T.O.; Salami, K.; Onaolapo, A.Y. l-Methionine and silymarin: A comparison of prophylactic protective capabilities in acetaminophen-induced injuries of the liver, kidney and cerebral cortex. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 85, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Dzhakova, Z.; Staynova, R.; Ivanov, K. Salvia verticillata (L.)—Biological activity, chemical profile, and future perspectives. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotio, A.L.; Nguepi, M.S.D.; Tonfack, L.B.; Temdie, R.J.G.; Nguelefack, T.B. Acetaminophen induces liver injury and depletes glutathione in mice brain: Prevention by Moringa oleifera extract. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 129, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mladenova, T.; Stoyanov, P.; Denev, P.; Dimitrova, S.; Katsarova, M.; Teneva, D.; Todorov, K.; Bivolarska, A. Phytochemical composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of the Balkan endemic Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen. (Lamiaceae). Plants 2021, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrakeva, K.; Metodieva, K.; Benina, M.; Bivolarska, A.; Dimov, I.; Choneva, M.; Kokova, V.; Alseekh, S.; Ivanova, V.; Vatov, E.; et al. Metabolic composition of methanolic extract of the Balkan endemic species Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen and its anti-inflammatory effect on male Wistar rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolova, E.; Stavrakeva, K.; Kokova, V.; Dimov, I.; Choneva, M.; Delev, D.; Kostadinov, I.; Bivolarski, I.; Koleva, M.; Mladenova, T.; et al. Subchronic toxicity and effect of the methanolic extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen on cognition in male Wistar rats. Plants 2025, 14, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolova, M.; Aneva, I.; Zhelev, P.; Dimitrova, M. Flavonoid compounds and antioxidant activity of Bulgarian species of Micromeria. Annu. L’université Sofia “Kliment Ohridski” Fac. Biol. 2017, 102, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova, S.; Pashova, S.; Dyankov, S.; Georgieva, Y.; Ivanov, K.; Benbassat, N.; Koleva, N.; Bozhkova, M.; Karcheva-Bahchevanska, D. Chemical composition and future perspectives of essential oil obtained from a wild population of Stachys germanica L. distributed in the Balkan Mountains in Bulgaria. Int. J. Anal Chem. 2023, 2023, 4275213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Di, X. Linarin inhibits the acetylcholinesterase activity in-vitro and ex-vivo. Ira. J. Phar. Res. 2015, 14, 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Naveed, M.; Hejazi, V.; Abbas, M.; Kamboh, A.A.; Khan, G.J.; Shumzaid, M.; Ahmad, F.; Babazadeh, D.; Xia, F.F.; Modarresi-Ghazani, F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid (CGA): A pharmacological review and call for further research. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Park, H.R.; Lee, K.A. A comparative study of rutin and rutin glycoside: Antioxidant activity, anti-inflammatory effect, effect on platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lan, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, T. Linarin protects against CCl4-induced acute liver injury via activating autophagy and inhibiting the inflammatory response: Involving the TLR4/MAPK/Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2023, 17, 3589–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonyarikpunchai, W.; Sukrong, S.; Towiwat, P. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of rosmarinic acid isolated from Thunbergia laurifolia Lindl. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Zheng, Z.; Shi, L.; Jin, Y.; Ji, L. Natural polyphenol chlorogenic acid protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by activating ERK/Nrf2 antioxidative pathway. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 162, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Nabila, J.; Adelusi Temitope, I.; Wang, S. Current etiological comprehension and therapeutic targets of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; Murray, F.J.; Monnot, A.D.; Jacobson-Kram, D.; Cohen, S.M.; Hardisty, J.F.; Atillasoy, E.; Hermanowski-Vosatka, A.; Kuffner, E.; Wikoff, D.; et al. Assessment of the biochemical pathways for acetaminophen toxicity: Implications for its carcinogenic hazard potential. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 120, 104859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Huo, Y.; Yin, S.; Hu, H. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver injury and its implications for therapeutic interventions. Redox Biol. 2018, 17, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennon-McGill, S.; McGill, M.R. Extrahepatic toxicity of acetaminophen: Critical evaluation of the evidence and proposed mechanisms. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2017, 3, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licata, A.; Minissale, M.G.; Stankevičiūtė, S.; Sanabria-Cabrera, J.; Lucena, M.I.; Andrade, R.J.; Almasio, P.L. N-Acetylcysteine for Preventing Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 828565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Hong, C.O.; Lee, G.P.; Kim, C.T.; Lee, K.W. The hepatoprotection of caffeic acid and rosmarinic acid, major compounds of Perilla frutescens, against t-BHP-induced oxidative liver damage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 55, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratchanova, M.; Denev, P.; Ciz, M.; Lojek, A.; Mihailov, A. Evaluation of antioxidant activity of medicinal plants containing polyphenol compounds. Comparison of two extraction systems. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2010, 57, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Cheng, N.; Gao, H.; Xue, X.; Cao, W.; Sun, L. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective activity of vitex honey against paracetamol induced liver damage in mice. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 2339–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valavanidis, A.; Vlachogianni, T.; Fiotakis, C. 8-hydroxy-2′ -deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): A critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2009, 27, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussan, F.; Mansor, A.S.; Hassan, S.N.; Tengku Nor Effendy Kamaruddin, T.N.; Budin, S.B.; Othman, F. Anti-Inflammatory Property of Plantago major Leaf Extract Reduces the Inflammatory Reaction in Experimental Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 347861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellappan, T.; Ramar, M.; Manikrishnan, R.; Melepuram, S.G.; Balaji, P.; Sekar, V.K.; Chidambaram, K. Protective effect of Ceiba pentandra (L) Gaertn on CCl4-induced oxidative stress and liver damage in rats. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2022, 5, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottaghipisheh, J.; Taghrir, H.; Boveiri Dehsheikh, A.; Zomorodian, K.; Irajie, C.; Mahmoodi Sourestani, M.; Iraji, A. Linarin, a glycosylated flavonoid, with potential therapeutic attributes: A comprehensive review. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gvozdeva, Y.; Staynova, R. pH-dependent drug delivery systems for ulcerative colitis treatment. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Guang, C.; Zhao, N.; Feng, X.; Qiu, F. LC–MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of Linarin and its metabolites in rat plasma and liver tissue samples: Application to pharmacokinetic and liver tissue distribution study after oral administration of Linarin. Molecules 2019, 24, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, S.; Gvozdeva, Y.; Staynova, R.; Grekova-Kafalova, D.; Nalbantova, V.; Benbassat, N.; Koleva, N.; Ivanov, K. Essential oils—A review of the natural evolution of applications and some future perspectives. Pharmacia 2025, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Ouyang, H.; Guo, Q.; Wei, M.; Lu, B.; Kai, G.; Ji, L. Chlorogenic acid alleviated liver fibrosis in methionine and choline deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice and its mechanism. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 106, 109020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Guo, Q.; Wei, M.; Huang, Z.; Shi, L.; Sheng, Y.; Ji, L. Chlorogenic acid alleviates acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice via regulating Nrf2-mediated HSP60-initiated liver inflammation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 883, 173286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Gu, X.; Li, H.; Zheng, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Lu, B.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. EGR1 is crucial for the chlorogenic acid-provided promotion on liver regeneration and repair after APAP-induced liver injury. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2023, 39, 2685–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Wei, M.; Ji, L. Chlorogenic acids: A pharmacological systematic review on their hepatoprotective effects. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2023, 118, 154961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Yu, Y.H.; Wang, S.T.; Ren, J.; Camer, D.; Hua, Y.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, J.; Xue, D.L.; Zhang, X.F.; et al. Chlorogenic acid protects D-galactose-induced liver and kidney injury via antioxidation and anti-inflammation effects in mice. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriscensia, E.; Arham, A.A.; Wibowo, E.C.; Gracius, L.; Nathanael, J.; Hartrianti, P. Eupatorin from Orthosiphon aristatus: A review of the botanical origin, pharmacological effects and isolation methods. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 2023, 19, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janbaz, K.H.; Saeed, S.A.; Gilani, A.H. Protective effect of rutin on paracetamol- and CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity in rodents. Fitoterapia 2002, 73, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muvhulawa, N.; Dludla, P.V.; Ziqubu, K.; Mthembu, S.X.H.; Mthiyane, F.; Nkambule, B.B.; Mazibuko-Mbeje, S.E. Rutin ameliorates inflammation and improves metabolic function: A comprehensive analysis of scientific literature. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 178, 106163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; Kalantar, M.; Sadeghi, E.; Karamallah, M.H.; Kalantar, H. Protective effects of apigenin on altered lipid peroxidation, inflammation, and antioxidant factors in methotrexate-induced hepatotoxicity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2021, 394, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, O.M.; Fahim, H.I.; Ahmed, H.Y.; Al-Muzafar, H.M.; Ahmed, R.R.; Amin, K.A.; El-Nahass, E.S.; Abdelazeem, W.H. The preventive effects and the mechanisms of action of navel orange peel hydroethanolic extract, naringin, and naringenin in N-Acetyl-p-aminophenol-induced liver injury in Wistar rats. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 2745352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zou, L.; Sun, H.; Peng, J.; Gao, C.; Bao, L.; Ji, R.; Jin, Y.; Sun, S. A review of the anti-inflammatory effects of rosmarinic acid on inflammatory diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elufioye, T.O.; Habtemariam, S. Hepatoprotective effects of rosmarinic acid: Insight into its mechanisms of action. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palani, S.; Raja, S.; Karthi, S.; Archana, S.; Kumar, B.S. In vivo analysis of nephro- and hepatoprotective effects and antioxidant activity of Madhuca longifolia against acetaminophen-induced toxicity and oxidative stress. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Hanafy, A.; Aldawsari, H.M.; Badr, J.M.; Ibrahim, A.K.; Abdel-Hady, S.E.-S. Evaluation of hepatoprotective activity of Adansonia digitata extract on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4579149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.M.A.; Rahman, M.A.; Hossen, M.A.; Reza, A.S.M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Rashid, M.M.; Rafi, M.K.J.; Siddiqui, M.T.A.; Al-Noman, A.; Uddin, M.N. Epiphytic Acampe ochracea orchid relieves paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity by inhibiting oxidative stress and upregulating antioxidant genes in in vivo and virtual screening. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Dai, S.; Yin, Z.; Lu, H.; Jia, R.; Xu, J.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, X. Toxicological assessment of combined lead and cadmium: Acute and sub-chronic toxicity study in rats. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.; Dadhaniya, P.; Hingorani, L.; Soni, M.G. Safety assessment of pomegranate fruit extract: Acute and subchronic toxicity studies. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2728–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuet Ping, K.; Darah, I.; Chen, Y.; Sreeramanan, S.; Sasidharan, S. Acute and subchronic toxicity study of Euphorbia hirta L. methanol extract in rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 182064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berends, M.; van Oijen, M.; Snoek, J.; van de Kerkhof, P.; Drenth, J.; Han van Krieken, J.; de Jong, E. Reliability of the Roenigk classification of liver damage after methotrexate treatment for psoriasis: A clinicopathologic study of 160 liver biopsy specimens. Arch Dermatol. 2007, 143, 1515–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.V.; Kamenov, V.I.; Boyadjiev, N.P.; Georgieva, K.N.; Bivolarska, A.V.; Draganova-Filipova, M.N.; Angelova-Hristova, P.A.; Delchev, S.; Daskalova, E.; Gerginska, F.; et al. Impact of a high-fat diet on the development of chronic inflammation in heart of Wistar rats. Folia Medica 2019, 61, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asiwe, J.N.; Daubry, T.M.E.; Okon, I.A.; Akpotu, A.E.; Adagbada, L.C.; Eruotor, H.; Agbugba, L.C.; Buduburisi, B.R. Ginkgo biloba supplement reverses lead (II) acetate–induced haematological imbalances, hepatic and renal dysfunctions in male Wistar rat. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 5134–5144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Marker | ME500+APAP | RA+APAP | Sil+APAP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total bilirubin | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Conjugated bilirubin | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| ALT | - | - | - |
| AST | - | - | - |
| CAT | 0 | + | + |
| SOD | 0 | 0 | + |
| GSH | 0 | + | + |
| MDA | - | 0 | 0 |
| 8-OH-dG | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| IL-6 | 0 | n/a | 0 |
| TNF-α | - | n/a | 0 |
| Grade 1 | Accumulation of Fats | Nuclear Pleomorphism | Fibrosis | Necrosis/Inflammation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mild or none | Mild or none | None | With or without mild portal inflammation |
| 2 | Moderate or severe | Moderate or severe | None | Moderate or severe portal inflammation |
| 3a | With or without | With or without | Mild (fibrosis extending into acini) | With or without |
| 3b | With or without | With or without | Moderate or severe | With or without |
| 4 | With or without | With or without | Cirrhosis | With or without |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Apostolova, E.; Stavrakeva, K.; Kokova, V.; Dimov, I.; Choneva, M.; Delev, D.; Kostadinov, I.; Bivolarski, I.; Koleva, M.; Mladenov, R.; et al. Protective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen Against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Male Wistar Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189112
Apostolova E, Stavrakeva K, Kokova V, Dimov I, Choneva M, Delev D, Kostadinov I, Bivolarski I, Koleva M, Mladenov R, et al. Protective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen Against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Male Wistar Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):9112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189112
Chicago/Turabian StyleApostolova, Elisaveta, Kristina Stavrakeva, Vesela Kokova, Ivica Dimov, Mariya Choneva, Delyan Delev, Ilia Kostadinov, Ilia Bivolarski, Maria Koleva, Rumen Mladenov, and et al. 2025. "Protective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen Against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Male Wistar Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 9112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189112
APA StyleApostolova, E., Stavrakeva, K., Kokova, V., Dimov, I., Choneva, M., Delev, D., Kostadinov, I., Bivolarski, I., Koleva, M., Mladenov, R., Stoyanov, P., & Bivolarska, A. (2025). Protective Effects of Methanolic Extract of Micromeria frivaldszkyana (Degen) Velen Against Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Toxicity in Male Wistar Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 9112. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26189112










