Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics for Seafood Allergen Detection and Quantification: Current Trends and Technological Frontiers
Abstract
1. Introduction
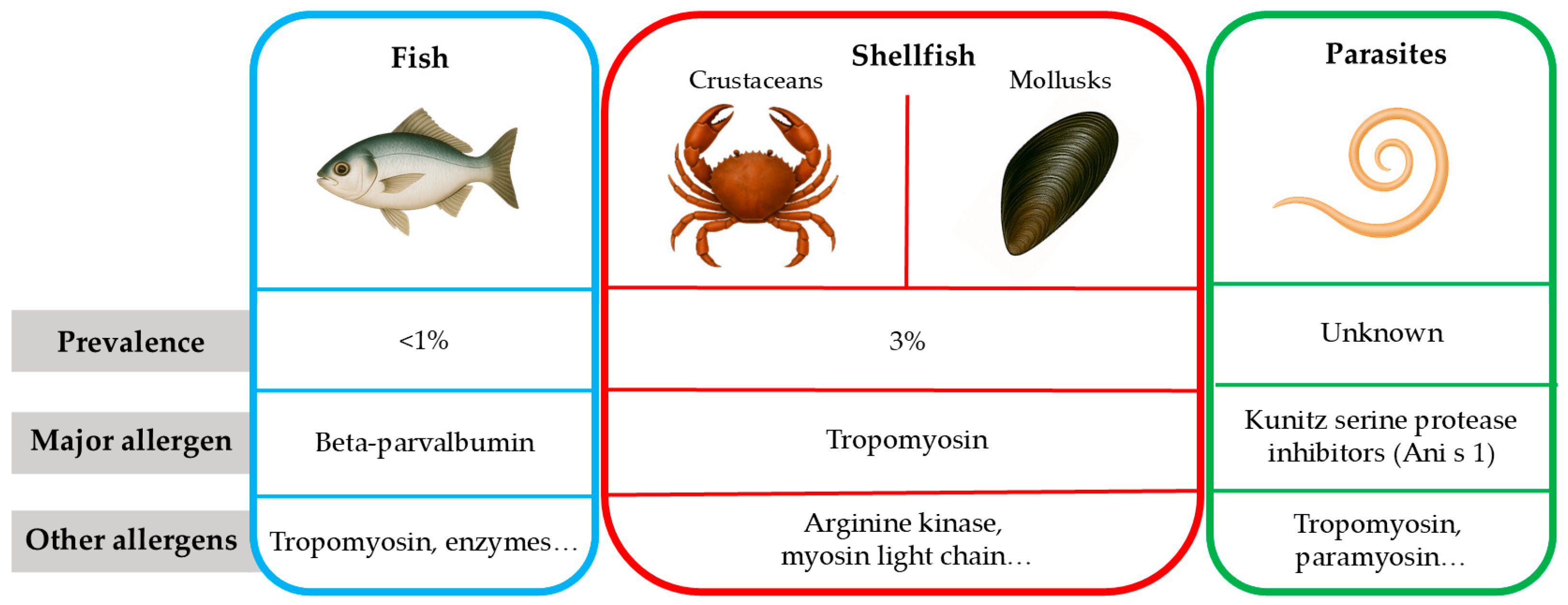
2. Allergens in Seafood
2.1. Fish Allergens
2.2. Shellfish Allergens
2.3. Seafood Parasites Allergens
2.4. Emerging New Allergens by Globalization and Climate Change
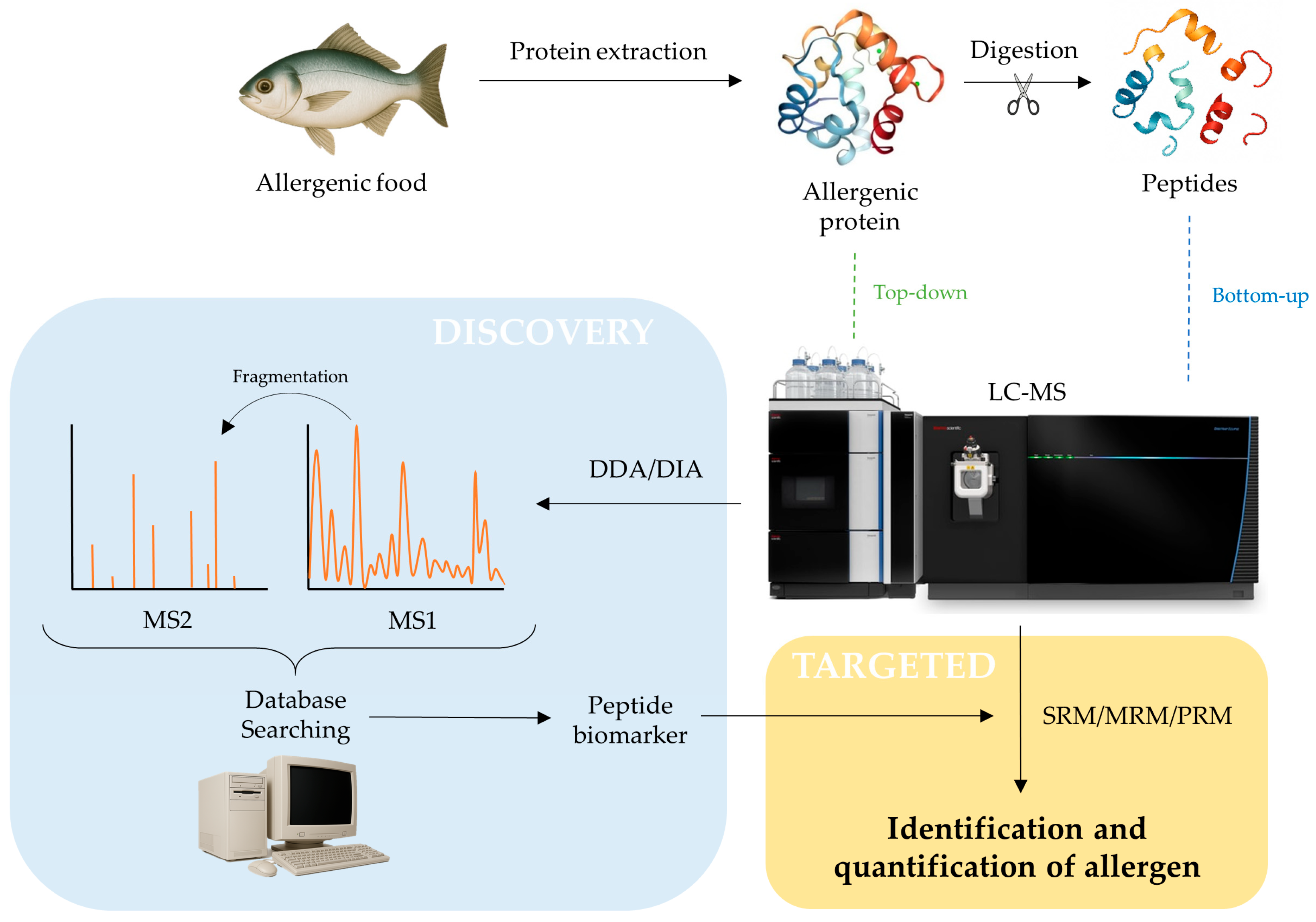
3. Mass Spectrometry-Based Methodologies for Allergen Detection and Quantification
3.1. Sample Preparation
3.2. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
3.2.1. Bottom-Up Approach
| MS Technique | Sensitivity | Complexity | Cost | Best Use Cases | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DIA | Moderate; biased toward abundant peptides | Moderate; limited MS2 scans performed | Medium | Discovery proteomics; identifying high-abundance allergens | [13] |
| DDA | High; improved reproducibility across samples | High; advanced data analysis required | Medium–High | Biomarker discovery in complex matrices; quantitative proteomics | [13] |
| SRM | High; very specific for targeted peptides | Moderate | Medium | Targeted allergen detection; validation of biomarkers | [50] |
| MRM | High; very specific for targeted peptides | Moderate | Medium | Routine quantification of known allergens in food products | [50] |
| PRM | Very high; full MS/MS spectrum increases specificity | Medium | High; requires high-resolution MS | Targeted quantification with high specificity; verification of allergenic peptides | [51] |
| LFQ | Moderate; dependent on instrument stability | Low–Moderate | Low | Large-scale comparative studies; relative quantification without labels | [52] |
| SILAC | High; accurate relative quantification | High; requires metabolic labeling | High | Model systems, cell culture studies; precise quantitative proteomics | [53] |
| TMT | Very high; high multiplexing | High; requires chemical labeling | Very high; expensive reagents | Large-scale comparative proteomics; simultaneous analysis of multiple food matrices | [54] |
| AQUA | Very high; absolute concentration determination | Medium; must be combined with SRM, MRM, or PRM | Medium–High; requires synthetic peptides | Accurate quantification of specific allergens; establishing thresholds (e.g., VITAL levels) | [55] |
| MS3 | Very high; reduces interference in complex samples | Very high | Very high; advanced instrumentation required | Quantification of low-abundance allergens in highly complex food matrices | [56] |
3.2.2. Top-Down Approach
3.3. Quantification via LC-MS
3.4. System Biology and Machine Learning
4. Applications in Seafood Allergen Detection and Quantification
4.1. Fish
4.2. Shellfish
4.3. Anisakids
5. Current Challenges and Future Directions
5.1. Limitations of MS and Emerging Technologies
5.2. Need for Harmonization
5.3. Research Gaps
5.4. Biosensors for On Site Allergen Detection
5.5. Hypoallergenic Proteins
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 2-DE | Two-dimensional Gel Electrophoresis |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AK | Arginine kinase |
| AQUA | Absolute quantification |
| DDA | Data-dependent acquisition |
| DIA | Data-independent acquisition |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) |
| ESI | Electrospray Ionization |
| HIFU | High-intensity focused ultrasound |
| HSP | Heat-shock protein |
| IMS | Immunomagnetic separation |
| IT | Ion Trap |
| iTRAQ | Isobaric Tags for Relative and Absolute Quantification |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography coupled to Mass Spectrometry |
| LFQ | Label-free quantitation |
| LIT | Linear Ion Trap |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantitation |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization–Time of Flight |
| MRM | Multiple Reaction Monitoring |
| PAL | Precautionary Allergen Labeling |
| PASEF | Parallel Accumulation–Serial Fragmentation |
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| PRM | Parallel Reaction Monitoring |
| PTM | Post-translational modification |
| QqQ | Triple–quadrupole |
| SCP | Sarcoplasmic calcium-binding protein |
| SIL | Stable Isotope–Labeled peptide |
| SRM | Single Reaction Monitoring |
| timsTOF | Trapped-Ion Mobility Spectrometry–TOF |
| TM | Tropomyosin |
| TMT | Tandem Mass Tag |
| UVPD | Ultraviolet photodissociation |
| VITAL | Voluntary Incidental Trace Allergen Labelling |
| β-PVALB | Beta-parvalbumin |
References
- Dramburg, S.; Hilger, C.; Santos, A.F.; De Las Vecillas, L.; Aalberse, R.C.; Acevedo, N.; Aglas, L.; Altmann, F.; Arruda, K.L.; Asero, R.; et al. EAACI Molecular Allergology User’s Guide 2.0. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 34, e13854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, R.L.; Krawiec, M.; Koplin, J.J.; Santos, A.F. Update on Food Allergy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 32, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food Allergy: A Review and Update on Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, Prevention, and Management. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iweala, O.I.; Choudhary, S.K.; Commins, S.P. Food Allergy. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2018, 20, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.L.K.; Mullins, R.J. Food Allergy: Is Prevalence Increasing? Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.; Eng, L.; Chang, C. Food Allergy Labeling Laws: International Guidelines for Residents and Travelers. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 65, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugyi, Z.; Muskovics, G.; Tömösközi, S. Rethinking Precautionary Allergen Labelling—Threshold Doses, Risk Assessment Approaches and Analytical Implications. Acta Aliment. 2023, 52, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DunnGalvin, A.; Roberts, G.; Regent, L.; Austin, M.; Kenna, F.; Schnadt, S.; Sanchez, A.; Hernandez, P.; Hjorth, B.; Fernandez, M.; et al. Understanding How Consumers with Food Allergies Make Decisions Based on Precautionary Labelling. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Johnston, E.B.; Nugraha, R.; Le, T.T.K.; Kalic, T.; McLean, T.R.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Seafood Allergy: A Comprehensive Review of Fish and Shellfish Allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 28–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, C.M.; Gupta, R.S.; Aktas, O.N.; Diaz, V.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Clinical Management of Seafood Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pr. 2020, 8, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonlokke, J.H.; Bang, B.; Aasmoe, L.; Rahman, A.M.A.; Syron, L.N.; Andersson, E.; Dahlman-Höglund, A.; Lopata, A.L.; Jeebhay, M. Exposures and Health Effects of Bioaerosols in Seafood Processing Workers—A Position Statement. J. Agromedicine 2019, 24, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moonesinghe, H.; Mackenzie, H.; Venter, C.; Kilburn, S.; Turner, P.; Weir, K.; Dean, T. Prevalence of Fish and Shellfish Allergy: A Systematic Review. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2016, 117, 264–272.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aebersold, R.; Mann, M. Mass-Spectrometric Exploration of Proteome Structure and Function. Nature 2016, 537, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzano, V.; Tilocca, B.; Fiocchi, A.G.; Vernocchi, P.; Levi Mortera, S.; Urbani, A.; Roncada, P.; Putignani, L. Perusal of Food Allergens Analysis by Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Pazos, M.; Gasset, M. Proteomics-Based Methodologies for the Detection and Quantification of Seafood Allergens. Foods 2020, 9, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, R.; Oberleitner, D.; Brockmeyer, J. Determination of Food Allergens by LC-MS: Impacts of Sample Preparation, Food Matrix, and Thermal Processing on Peptide Detectability and Quantification. J. Proteom. 2019, 196, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Horka, P.; Zdenkova, K.; Cermakova, E. Parvalbumin: A Major Fish Allergen and a Forensically Relevant Marker. Genes 2023, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, J.M.; Kuehn, A.; Sugihara, E.; Kondo, Y. Exploring Fish Parvalbumins through Allergen Names and Gene Identities. Genes 2024, 15, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, J.N.; Sharp, M.F.; Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.; Campbell, D.E.; Lopata, A.L. Allergenicity of Bony and Cartilaginous Fish—Molecular and Immunological Properties. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Kobayashi, Y.; Shiomi, K.; Hamada-Sato, N. Reduction in IgE Reactivity of Pacific Mackerel Parvalbumin by Heat Treatment. Food Chem. 2016, 206, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Tavarez, R.; Carrera, M.; Pedrosa, M.; Quirce, S.; Rodríguez-Pérez, R.; Gasset, M. Reconstruction of Fish Allergenicity from the Content and Structural Traits of the Component β-Parvalbumin Isoforms. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-L.; Perng, K.; Hou, Y.-C.; Shen, C.-J.; Chen, I.-N.; Chen, Y.-T. Effect of Species, Muscle Location, Food Processing and Refrigerated Storage on the Fish Allergens, Tropomyosin and Parvalbumin. Food Chem. 2023, 402, 134479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Kamath, S.; Taki, A.; Le, T.; Karnaneedi, S.; Nugraha, R.; Cao, T.; Nie, S.; Williamson, N.; Mehr, S.; et al. Tropomyosin Is A Novel Major Fish Allergen Of Unrecognized Importance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, AB226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, H.; Sun, D. An Overview of Tropomyosin as an Important Seafood Allergen: Structure, Cross-Reactivity, Epitopes, Allergenicity, and Processing Modifications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emoto, A.; Ishizaki, S.; Shiomi, K. Tropomyosins in Gastropods and Bivalves: Identification as Major Allergens and Amino Acid Sequence Features. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannetti, A.; Pession, A.; Bettini, I.; Ricci, G.; Giannì, G.; Caffarelli, C. IgE Mediated Shellfish Allergy in Children—A Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, C.; Bartolomé, B.; Rodríguez, V.; Armisén, M.; Linneberg, A.; González-Quintela, A. Sensitization Pattern of Crustacean-Allergic Individuals Can Indicate Allergy to Molluscs. Allergy 2015, 70, 1493–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanović, J.; Baltić, M.Ž.; Bošković, M.; Kilibarda, N.; Dokmanović, M.; Marković, R.; Janjić, J.; Baltić, B. Anisakis Allergy in Human. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Zuberbier, T.; Werfel, T. (Eds.) Allergic Diseases—From Basic Mechanisms to Comprehensive Management and Prevention; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 268, ISBN 978-3-030-84047-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hazebrouck, S.; Awad, Y.; Bernard, H. Nouvelles Sources Protéiques et Nouveaux Allergènes: Sensibilisation de novo et Réactivité Croisée. Rev. Française D’allergologie 2025, 65, 104203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, Y.; Bernard, H.; Adel-Patient, K.; Hazebrouck, S. New Dietary Trends and Alternative Proteins: The Emergence of Novel Food Allergens. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2025, 28, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvin, K.; Dasgupta, D.; Krinner, G.; Mukherji, A.; Thorne, P.W.; Trisos, C.; Romero, J.; Aldunce, P.; Barrett, K.; Blanco, G.; et al. IPCC, 2023: Climate Change 2023: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Lee, H., Romero, J., Eds.; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Poloczanska, E.S.; Burrows, M.T.; Brown, C.J.; García Molinos, J.; Halpern, B.S.; Hoegh-Guldberg, O.; Kappel, C.V.; Moore, P.J.; Richardson, A.J.; Schoeman, D.S.; et al. Responses of Marine Organisms to Climate Change across Oceans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2016, 3, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottacini, D.; Pollux, B.J.A.; Nijland, R.; Jansen, P.A.; Naguib, M.; Kotrschal, A. Lionfish (Pterois miles) in the Mediterranean Sea: A Review of the Available Knowledge with an Update on the Invasion Front. NeoBiota 2024, 92, 233–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asea, A.A.A.; Kaur, P. (Eds.) Regulation of Heat Shock Protein Responses; Heat Shock Proteins; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 13, ISBN 978-3-319-74714-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liebler, D.C. Introduction to Proteomics: Tools for the New Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2002; ISBN 978-0-89603-991-9. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarz, B.; Jiang, X.; Hsieh, Y.-H.P.; Rao, Q. Matrix Effect on Food Allergen Detection—A Case Study of Fish Parvalbumin. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, R.; Ruethers, T.; Johnston, E.B.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L. Effects of Extraction Buffer on the Solubility and Immunoreactivity of the Pacific Oyster Allergens. Foods 2021, 10, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, L.; Timira, V.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, L.; Lin, H.; Li, Z. Improved Protein Extraction from Thermally Processed Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) for Reliable Immunodetection via a Synergistic Effect of Buffer Additives. LWT 2022, 154, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, M.; Vasiljevic, T.; Donkor, O.N. A Review on Methodologies for Extraction, Identification and Quantification of Allergenic Proteins in Prawns. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Ma, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, W.; Li, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Determination of Tropomyosin in Shrimp and Crab by Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Based on Immunoaffinity Purification. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 848294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anđelković, U.; Martinović, T.; Josić, D. Foodomic Investigations of Food Allergies. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 4, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Khangurha, J.; Roberts, J.; Buddhadasa, S.; Clarke, D.; Hedges, C.E.; Campbell, D.E.; Kamath, S.D.; Lopata, A.L.; et al. Commercial Fish ELISA Kits Have a Limited Capacity to Detect Different Fish Species and Their Products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4353–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Abril, A.G.; Pazos, M.; Calo-Mata, P.; Villa, T.G.; Barros-Velázquez, J. Proteins and Peptides: Proteomics Approaches for Food Authentication and Allergen Profiling. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2024, 57, 101172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeberl, M.; Clarke, D.; Lopata, A.L. Next Generation of Food Allergen Quantification Using Mass Spectrometric Systems. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 3499–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fonslow, B.R.; Shan, B.; Baek, M.-C.; Yates, J.R.I., 3rd. Protein Analysis by Shotgun/Bottom-up Proteomics. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 2343–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.M.; Smith, L.M. Overview and Considerations in Bottom-up Proteomics. Analyst 2023, 148, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radauer, C.; Breiteneder, H. Allergen Databases—A Critical Evaluation. Allergy 2019, 74, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borràs, E.; Sabidó, E. What Is Targeted Proteomics? A Concise Revision of Targeted Acquisition and Targeted Data Analysis in Mass Spectrometry. Proteomics 2017, 17, 1700180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aebersold, R.; Bensimon, A.; Collins, B.C.; Ludwig, C.; Sabido, E. Applications and Developments in Targeted Proteomics: From SRM to DIA/SWATH. Proteomics 2016, 16, 2065–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.C.; Russell, J.D.; Bailey, D.J.; Westphall, M.S.; Coon, J.J. Parallel Reaction Monitoring for High Resolution and High Mass Accuracy Quantitative, Targeted Proteomics. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2012, 11, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Cong, X.; Zhai, L.; Hu, H.; Xu, J.-Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, M.; Tan, M.; Ye, B.-C. Comparative Evaluation of Label-Free Quantification Strategies. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kani, K. Quantitative Proteomics Using SILAC. In Proteomics: Methods and Protocols; Comai, L., Katz, J.E., Mallick, P., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 1550, pp. 171–184. ISBN 978-s1-4939-6747-6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Elias, J.E. Relative Protein Quantification Using Tandem Mass Tag Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1550, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenbach, A.N.; Rush, J.; Gerber, S.A. Absolute Quantification of Protein and Post-Translational Modification Abundance with Stable Isotope–Labeled Synthetic Peptides. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Improved Peptide Identification in Proteomics by Two Consecutive Stages of Mass Spectrometric Fragmentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13417–13422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, J.R.; Kelleher, N.L. Top Down Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehn, A.; Swoboda, I.; Arumugam, K.; Hilger, C.; Hentges, F. Fish Allergens at a Glance: Variable Allergenicity of Parvalbumins, the Major Fish Allergens. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Gordo, M.; Lin, J.; Bardina, L.; Pastor-Vargas, C.; Cases, B.; Vivanco, F.; Cuesta-Herranz, J.; Sampson, H.A. Epitope Mapping of Atlantic Salmon Major Allergen by Peptide Microarray Immunoassay. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 157, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodbelt, J.S.; Morrison, L.J.; Santos, I. Ultraviolet Photodissociation Mass Spectrometry for Analysis of Biological Molecules. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3328–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Weisbrod, C.; Lopez-Ferrer, D.; Huguet, R.; Gallardo, J.M.; Schwartz, J.; Huhmer, A. Top-Down, High-throughput of Thermo-Stable Allergens Using Complementary MS/MS Fragmentation Strategies; PN64488-EN 0615S; ThermoFisher Scientific: San Jose, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Remington, B.C.; Westerhout, J.; Meima, M.Y.; Blom, W.M.; Kruizinga, A.G.; Wheeler, M.W.; Taylor, S.L.; Houben, G.F.; Baumert, J.L. Updated Population Minimal Eliciting Dose Distributions for Use in Risk Assessment of 14 Priority Food Allergens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 139, 111259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhout, J.; Baumert, J.L.; Blom, W.M.; Allen, K.J.; Ballmer-Weber, B.; Crevel, R.W.R.; Dubois, A.E.J.; Fernández-Rivas, M.; Greenhawt, M.J.; Hourihane, J.O.; et al. Deriving Individual Threshold Doses from Clinical Food Challenge Data for Population Risk Assessment of Food Allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1290–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VITAL® Voluntary Incidental Trace Allergen Labelling. Available online: https://vital.allergenbureau.net/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Taylor, S.B.; Christensen, G.; Grinter, K.; Sherlock, R.; Warren, L. The Allergen Bureau VITAL Program. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzhauser, T.; Johnson, P.; Hindley, J.P.; O’Connor, G.; Chan, C.-H.; Costa, J.; Fæste, C.K.; Hirst, B.J.; Lambertini, F.; Miani, M.; et al. Are Current Analytical Methods Suitable to Verify VITAL® 2.0/3.0 Allergen Reference Doses for EU Allergens in Foods? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilm, M. Quantitative Proteomics in Biological Research. Proteomics 2009, 9, 4590–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.-L.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chow, N.-H.; Chen, S.-H. Stable-Isotope Dimethyl Labeling for Quantitative Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 6843–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhart, J.M.; Vaudel, M.; Zahedi, R.P.; Martens, L.; Sickmann, A. iTRAQ Protein Quantification: A Quality-Controlled Workflow. Proteomics 2011, 11, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavage, M.; Van Vlierberghe, K.; Van Poucke, C.; De Loose, M.; Gevaert, K.; Dieu, M.; Renard, P.; Arnould, T.; Filee, P.; Gillard, N. Comparative Study of Concatemer Efficiency as an Isotope-Labelled Internal Standard for Allergen Quantification. Food Chem. 2020, 332, 127413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandi, S.; Savaryn, J.P.; Ji, Q.C.; Jenkins, G.J. Use of In-Sample Calibration Curve Approach for Quantification of Peptides with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Mesa, M.; Ropartz, D.; García-Campaña, A.M.; Rogniaux, H.; Dervilly-Pinel, G.; Le Bizec, B. Ion Mobility Spectrometry in Food Analysis: Principles, Current Applications and Future Trends. Molecules 2019, 24, 2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M. Proteómica y biología de sistemas para el estudio de la alergia alimentaria. Arbor 2020, 196, a546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokesch-Himmelreich, J.; Wittek, O.; Race, A.M.; Rakete, S.; Schlicht, C.; Busch, U.; Römpp, A. MALDI Mass Spectrometry Imaging: From Constituents in Fresh Food to Ingredients, Contaminants and Additives in Processed Food. Food Chem. 2022, 385, 132529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING Database in 2023: Protein-Protein Association Networks and Functional Enrichment Analyses for Any Sequenced Genome of Interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.G.; Muhoberac, M.; Randolph, C.E.; Beveridge, C.H.; Wijewardhane, P.R.; Kenttämaa, H.I.; Chopra, G. Recent Developments in Machine Learning for Mass Spectrometry. ACS Meas. Sci. Au 2024, 4, 233–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessulat, S.; Schmidt, T.; Zolg, D.P.; Samaras, P.; Schnatbaum, K.; Zerweck, J.; Knaute, T.; Rechenberger, J.; Delanghe, B.; Huhmer, A.; et al. Prosit: Proteome-Wide Prediction of Peptide Tandem Mass Spectra by Deep Learning. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frejno, M.; Berger, M.T.; Tüshaus, J.; Hogrebe, A.; Seefried, F.; Graber, M.; Samaras, P.; Ben Fredj, S.; Sukumar, V.; Eljagh, L.; et al. Unifying the Analysis of Bottom-up Proteomics Data with CHIMERYS. Nat. Methods 2025, 22, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Gallardo, J.M. Rapid Direct Detection of the Major Fish Allergen, Parvalbumin, by Selected MS/MS Ion Monitoring Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, W.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Ge, M.; Ahmed, I.; Pavase, T.R. Development of a Method for the Quantification of Fish Major Allergen Parvalbumin in Food Matrix via Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry with Multiple Reaction Monitoring. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piovesana, S.; Capriotti, A.L.; Caruso, G.; Cavaliere, C.; La Barbera, G.; Zenezini Chiozzi, R.; Laganà, A. Labeling and Label Free Shotgun Proteomics Approaches to Characterize Muscle Tissue from Farmed and Wild Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata). J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1428, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westfalewicz, B.; Dietrich, M.A.; Irnazarow, I.; Ciereszko, A. Identification of 5–15 kDa Substances in Carp Seminal Plasma Using Mass Spectrometry. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2015, 31, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruethers, T.; Taki, A.C.; Nugraha, R.; Cao, T.T.; Koeberl, M.; Kamath, S.D.; Williamson, N.A.; O’Callaghan, S.; Nie, S.; Mehr, S.S.; et al. Variability of Allergens in Commercial Fish Extracts for Skin Prick Testing. Allergy 2019, 74, 1352–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sui, Z.; Feng, N.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ahmed, I.; Ruethers, T.; Liang, H.; Li, Z.; Lopata, A.L.; et al. Characterization, Epitope Confirmation, and Cross-Reactivity Analysis of Parvalbumin from Lateolabrax maculatus by Multiomics Technologies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20077–20090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Cañas, B.; Vázquez, J.; Gallardo, J.M. Extensive de novo Sequencing of New Parvalbumin Isoforms Using a Novel Combination of Bottom-Up Proteomics, Accurate Molecular Mass Measurement by FTICR−MS, and Selected MS/MS Ion Monitoring. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4393–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, D.; Materazzi, S.; Risoluti, R.; Thangavel, H.; Di Donna, L.; Mazzotti, F.; Casadonte, F.; Siciliano, C.; Sindona, G.; Napoli, A. A Major Allergen in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Complete Sequences of Parvalbumin by MALDI Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11, 2373–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, J.; Long, S.; Soko, W.C.; Qin, Q.; Qiao, L.; Bi, H. MALDI-TOF MS and Magnetic Beads for Rapid Seafood Allergen Tests. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12909–12918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Bi, H. Impact of Boiling on the Allergens in Fish Bone Samples Identified by Microfluidic Chips and MALDI-TOF MS. Food Chem. 2025, 465, 141868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, F.; Soko, W.C.; Xie, J.; Bi, H. On-Chip Discovery of Allergens from the Exudate of Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Muscle Food by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 13546–13553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, M.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Saraiva, J.A.; Aubourg, S.P. Effects of High-Pressure Treatment on the Muscle Proteome of Hake by Bottom-Up Proteomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 4559–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yao, K.; Yang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Xing, Y.; Niu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Dai, C.; et al. A SILAC-Based Accurate Quantification of Shrimp Allergen Tropomyosin in Complex Food Matrices Using UPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2024, 439, 138170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, C.-W.; Hsu, J.-L.; Chen, S.-H.; Liaw, E.-T.; Liu, S.-S.; Huang, E.S.; Chen, Y.-K.; Jean Huang, C.-C.; Yu, H.-S. Development and Validation of Mass Spectrometry-Based Method for Detecting Shrimp Allergen Tropomyosin. LWT 2021, 152, 112367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, H.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Li, Z. Quantification of Allergic Crustacean Tropomyosin Using Shared Signature Peptides in Processed Foods with a Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomic Strategy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 11672–11681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Yang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shao, B.; Zhang, Y. Labeled Peptide-Free UHPLC–MS/MS Method Used for Simultaneous Determination of Shrimp and Soybean in Sauce Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 7149–7157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, R.; Monneuse, J.-M.; Gemrot, E.; Metton, I.; Humpf, H.-U.; Brockmeyer, J. New High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled Mass Spectrometry Method for the Detection of Lobster and Shrimp Allergens in Food Samples via Multiple Reaction Monitoring and Multiple Reaction Monitoring Cubed. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6219–6227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisomsap, C.; Nonthawong, K.; Chokchaichamnankit, D.; Svasti, J.; Phiriyangkul, P. Shotgun Proteomics Characterization of Potential Allergens in Dried and Powdered Krill and Fresh and Powdered Whiteleg Shrimp. Food Biosci. 2023, 54, 102803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugraha, R.; Kamath, S.D.; Johnston, E.; Zenger, K.R.; Rolland, J.M.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Lopata, A.L. Rapid and Comprehensive Discovery of Unreported Shellfish Allergens Using Large-Scale Transcriptomic and Proteomic Resources. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1501–1504.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, J.M.; Varese, N.P.; Abramovitch, J.B.; Anania, J.; Nugraha, R.; Kamath, S.; Hazard, A.; Lopata, A.L.; O’Hehir, R.E. Effect of Heat Processing on IgE Reactivity and Cross-Reactivity of Tropomyosin and Other Allergens of Asia-Pacific Mollusc Species: Identification of Novel Sydney Rock Oyster Tropomyosin Sac g 1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1800148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, T.-J.; Huan, F.; Li, M.-S.; Xia, F.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.-H.; Chen, G.-X.; Cao, M.-J.; Liu, G.-M. Effects of Thermal Processing on the Allergenicity, Structure, and Critical Epitope Amino Acids of Crab Tropomyosin. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrera, M.; Gallardo, J.M.; Pascual, S.; González, Á.F.; Medina, I. Protein Biomarker Discovery and Fast Monitoring for the Identification and Detection of Anisakids by Parallel Reaction Monitoring (PRM) Mass Spectrometry. J. Proteom. 2016, 142, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fæste, C.K.; Moen, A.; Schniedewind, B.; Haug Anonsen, J.; Klawitter, J.; Christians, U. Development of Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry Methods for the Quantitation of Anisakis Simplex Proteins in Fish. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1432, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fæste, C.K.; Jonscher, K.R.; Dooper, M.M.W.B.; Egge-Jacobsen, W.; Moen, A.; Daschner, A.; Egaas, E.; Christians, U. Characterisation of Potential Novel Allergens in the Fish Parasite Anisakis Simplex. EuPA Open Proteom. 2014, 4, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Griesmeier, U.; Susani, M.; Radauer, C.; Briza, P.; Erler, A.; Bublin, M.; Alessandri, S.; Himly, M.; Vàzquez-Cortés, S.; et al. Comparison of Natural and Recombinant Forms of the Major Fish Allergen Parvalbumin from Cod and Carp. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52 (Suppl. S2), S196–S207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-C.; Ochiai, Y. Fish Fast Skeletal Muscle Tropomyosins Show Species-Specific Thermal Stability. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 141, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasanayaka, B.P.; Li, Z.; Pramod, S.N.; Chen, Y.; Khan, M.U.; Lin, H. A Review on Food Processing and Preparation Methods for Altering Fish Allergenicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 1951–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, X.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, B. Effect of Thermal Processing on Food Allergenicity: Mechanisms, Application, Influence Factor, and Future Perspective. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 20225–20240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taki, A.C.; Ruethers, T.; Nugraha, R.; Karnaneedi, S.; Williamson, N.A.; Nie, S.; Leeming, M.G.; Mehr, S.S.; Campbell, D.E.; Lopata, A.L. Thermostable Allergens in Canned Fish: Evaluating Risks for Fish Allergy. Allergy 2023, 78, 3221–3234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrama, D.; Raposo De Magalhães, C.; Cerqueira, M.; Carrilho, R.; Revets, D.; Kuehn, A.; Engrola, S.; Rodrigues, P.M. Fish Processing and Digestion Affect Parvalbumins Detectability in Gilthead Seabream and European Seabass. Animals 2022, 12, 3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, H. Research Progress on Shrimp Allergens and Allergenicity Reduction Methods. Foods 2025, 14, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.U.; Ahmed, I.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Costa, J.; Mafra, I.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Y.-N. Potential Efficacy of Processing Technologies for Mitigating Crustacean Allergenicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2807–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birse, N.; Burns, D.T.; Walker, M.J.; Quaglia, M.; Elliott, C.T. Food Allergen Analysis: A Review of Current Gaps and the Potential to Fill Them by Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 3984–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guergues, J.; Wohlfahrt, J.; Stevens, S.M. Enhancement of Proteome Coverage by Ion Mobility Fractionation Coupled to PASEF on a TIMS-QTOF Instrument. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 2036–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krieger, J.R.; Wybenga-Groot, L.E.; Tong, J.; Bache, N.; Tsao, M.S.; Moran, M.F. Evosep One Enables Robust Deep Proteome Coverage Using Tandem Mass Tags While Significantly Reducing Instrument Time. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 2346–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.; Guercetti, J.; Geballa-Koukoula, A.; Tsagkaris, A.S.; Nelis, J.L.D.; Marco, M.-P.; Salvador, J.-P.; Gerssen, A.; Hajslova, J.; Elliott, C.; et al. ASSURED Point-of-Need Food Safety Screening: A Critical Assessment of Portable Food Analyzers. Foods 2021, 10, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planque, M.; Arnould, T.; Renard, P.; Delahaut, P.; Dieu, M.; Gillard, N. Highlight on Bottlenecks in Food Allergen Analysis: Detection and Quantification by Mass Spectrometry. J. AOAC Int. 2017, 100, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Pedreschi, R.; Nørgaard, J.; Maquet, A. Current Challenges in Detecting Food Allergens by Shotgun and Targeted Proteomic Approaches: A Case Study on Traces of Peanut Allergens in Baked Cookies. Nutrients 2012, 4, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paez, V.; Barrett, W.B.; Deng, X.; Diaz-Amigo, C.; Fiedler, K.; Fuerer, C.; Hostetler, G.L.; Johnson, P.; Joseph, G.; Konings, E.J.M.; et al. AOAC SMPR® 2016.002. J. AOAC Int. 2016, 99, 1122–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planque, M.; Arnould, T.; Dieu, M.; Delahaut, P.; Renard, P.; Gillard, N. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Detecting Ten Allergens in Complex and Incurred Foodstuffs. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1530, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Clifford, R.; Oppermann, U. Simultaneous Detection of 13 Allergens in Thermally Processed Food Using Targeted LC–MS/MS Approach. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Rahman, A.M.; Lopata, A.L.; O’Hehir, R.E.; Robinson, J.J.; Banoub, J.H.; Helleur, R.J. Characterization and de novo Sequencing of Snow Crab Tropomyosin Enzymatic Peptides by Both Electrospary Ionization and Matrix-assisted Laser Desorption Ionization QqToF Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mykles, D.L.; Cotton, J.L.S.; Taniguchi, H. Cloning of Tropomyosins from Lobster (Homarus americanus) Striated Muscles: Fast and Slow Isoforms May Be Generated from the Same Transcript. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1998, 19, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Reddy, Y.V.M.; Park, T.J.; Park, J.P. Recent Advances in Analytical Strategies and Microsystems for Food Allergen Detection. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, J.P.; Freitas, M.; Geraldo, D.; Bento, F.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Nouws, H.P.A. Electrochemical Magnetic Immunoassay for the Determination of the Fish Allergen β-Parvalbumin. Biosensors 2024, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xiang, X.; Wang, L. A Biomimetic Skin Microtissue Biosensor for the Detection of Fish Parvalbumin. Bioelectrochemistry 2025, 161, 108805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, R.; Rahamn, A.A.; AlZabn, R.; Kamath, S.; Lopata, A.L.; Abu-Salah, K.M.; Zourob, M. Aptameric Biosensor for the Sensitive Detection of Major Shrimp Allergen, Tropomyosin. Food Chem. 2020, 314, 126133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzadeh Tabrizi, M.; Shamsipur, M.; Saber, R.; Sarkar, S.; Ebrahimi, V. A High Sensitive Visible Light-Driven Photoelectrochemical Aptasensor for Shrimp Allergen Tropomyosin Detection Using Graphitic Carbon Nitride-TiO2 Nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 98, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, H. An Aptamer-Initiated Catalytic Hairpin Assembly Fluorescent Biosensor for Simultaneous Detection of Major Seafood Allergens in Food System. Microchem. J. 2025, 208, 112315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, Q.S.; Burks, A.W. Peptide and Recombinant Allergen Vaccines for Food Allergy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 55, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swoboda, I.; Balic, N.; Klug, C.; Focke, M.; Weber, M.; Spitzauer, S.; Neubauer, A.; Quirce, S.; Douladiris, N.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; et al. A General Strategy for the Generation of Hypoallergenic Molecules for the Immunotherapy of Fish Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 979–981.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freidl, R.; Gstoettner, A.; Baranyi, U.; Swoboda, I.; Stolz, F.; Focke-Tejkl, M.; Wekerle, T.; Van Ree, R.; Valenta, R.; Linhart, B. Blocking Antibodies Induced by Immunization with a Hypoallergenic Parvalbumin Mutant Reduce Allergic Symptoms in a Mouse Model of Fish Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 1897–1905.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, X.; Fang, L.; Qin, X.; Gu, R.; Lu, J.; Li, G. Hypoallergenic Mutants of the Major Oyster Allergen Cra g 1 Alleviate Oyster Tropomyosin Allergenic Potency. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 164, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, F.; Gao, S.; Ni, L.-N.; Wu, M.-X.; Gu, Y.; Yun, X.; Liu, M.; Lai, D.; Xiao, A.-F.; Liu, G.-M. Development of Hypoallergenic Derivatives of Cra a 1 with B Cell Epitope Deletion and T Cell Epitope Retention. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 19494–19504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Method | Biomarker | Performance | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fish | ||||
| PRM targeting 19 selected peptides in a LIT | β-PVALB | Detection time < 2 h | Rapid detection of β-PVALBs | [80] |
| MRM/AQUA quantification in a QTRAP | β-PVALB | LOD = 0.02–0.04 µg/g LOQ = 0.07–0.12 µg/g | Absolute quantification of β-PVALB | [81] |
| Shotgun proteomics approach comparing LFQ and dimethyl labeling in an Orbitrap | - | - | Compare the muscle proteome of farmed and wild gilthead sea bream | [82] |
| Top-down approach using UVPD in an Orbitrap | β-PVALB | - | Detection of intact β-PVALB | [61] |
| SDS-PAGE separation and MALDI-TOF MS | - | - | Detect substances of 5–15 kDa in carp seminal plasma | [83] |
| DDA in an Orbitrap followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting | - | - | Analyze commercial fish extracts for the presence and concentration of fish proteins | [84] |
| Multi-omics approach combining HPLC-HRMS, genomics, and immunoinformatics | β-PVALB | - | Characterization, epitope confirmation, and cross-reactivity analysis of β-PVALB | [85] |
| Mass determination by FTICR-MS of intact proteins and SMIM of peptide mass gaps | β-PVALB | - | Complete de novo sequencing of 25 new β-PVALB isoforms | [86] |
| Top-down proteomics in a MALDI-TOF | β-PVALB | - | Sequencing of four PVALB isoforms from farmed rainbow trout | [87] |
| IMS followed by MS analysis | - | - | Identification of novel fish allergens | [88,89,90] |
| 2-DE and MALDI-TOF | - | - | Identification of heat-stable proteins in cod | [22] |
| 2-DE and bottom-up analysis in an Orbitrap | - | - | Detection of protein abundance variations after high-pressure treatment | [91] |
| Shellfish | ||||
| SILAC-based method using UPLC-MS | TM | LOD = 0.5–5 µg/g LOQ = 1–10 µg/g | Absolute quantification of TM in complex food matrices | [92] |
| AQUA-based method in an IT | TM | LOD = 0.072 ng/μL LOQ = 0.219 ng/μl | Comparison of TM levels in seven shrimp species | [93] |
| MRM using shared peptide markers | TM | LOD = 0.15 µg/g LOQ = 0.5 µg/g | Absolute quantification of TM | [94] |
| Immunoaffinity purification and MRM in a QqQ | TM | LOQ = 0.1 µg/g | Determination of TM in shrimp and crab | [41] |
| Standard addition method (label-free) in a QqQ | TM | LOQ = 0.25–5 µg/g | Cost-effective detection of shrimp in sauce | [95] |
| MRM3 in a QTRAP | Eight shellfish allergens | LOD = 25 µg/g | Sensitive detection of lobster and shrimp allergens in food samples | [96] |
| Shotgun proteomics combined with bioinformatic tools | - | - | Characterize potential allergens in powdered krill and whiteleg shrimp | [97] |
| Immunoblotting combined with shotgun proteomics | - | - | Identify novel allergens in Pacific oyster | [98] |
| SDS-PAGE, immunoblotting, and MS identification in an IT | - | - | Evaluate heat treatment on shellfish allergens | [99] |
| Primary structure determination in a QqQ using bioinformatic tools | - | - | Identification of critical amino acids in crab TM epitopes | [100] |
| Anisakids | ||||
| PRM method targeting four peptides in an LTQ | Ani s 9 | Detection time < 2 h | Rapid detection of Anisakids | [101] |
| LFQ in a QqQ | Ani s 13 Ani s 8 | LOD = 2 µg/mL | Semi-quantitative detection of Anisakids | [102] |
| AQUA in a QqQ | Ani s 13 Ani s 8 | LOD = 0.1 µg/mL | Absolute quantitative detection of Anisakids | [102] |
| SDS-PAGE of patient serum and protein identification by nLC/QqQ | - | - | Identification of novel allergens in Anisakids | [103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amado, M.G.; Pazos, M.; Carrera, M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics for Seafood Allergen Detection and Quantification: Current Trends and Technological Frontiers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188962
Amado MG, Pazos M, Carrera M. Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics for Seafood Allergen Detection and Quantification: Current Trends and Technological Frontiers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188962
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmado, Manuel G., Manuel Pazos, and Mónica Carrera. 2025. "Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics for Seafood Allergen Detection and Quantification: Current Trends and Technological Frontiers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188962
APA StyleAmado, M. G., Pazos, M., & Carrera, M. (2025). Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics for Seafood Allergen Detection and Quantification: Current Trends and Technological Frontiers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8962. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188962






