Preliminary Evidence for Sex-Specific Trends in Probiotic Modulation of Gut Saccharibacteria in Familial Mediterranean Fever Patients: Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 and Escherichia coli M-17
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitative Distribution of Gut Candidatus saccharibacteria spp. in Male FMF Patients
2.2. Effects of Probiotics Narine and Colibacteron on the Gut Candidatus saccharibacteria spp. Distribution in FMF Patients
2.3. Gut Schaalia odontolytica Distribution in FMF-Affected and Healthy Women
2.4. Gut Schaalia odontolytica Distribution in FMF-Affected and Healthy Men
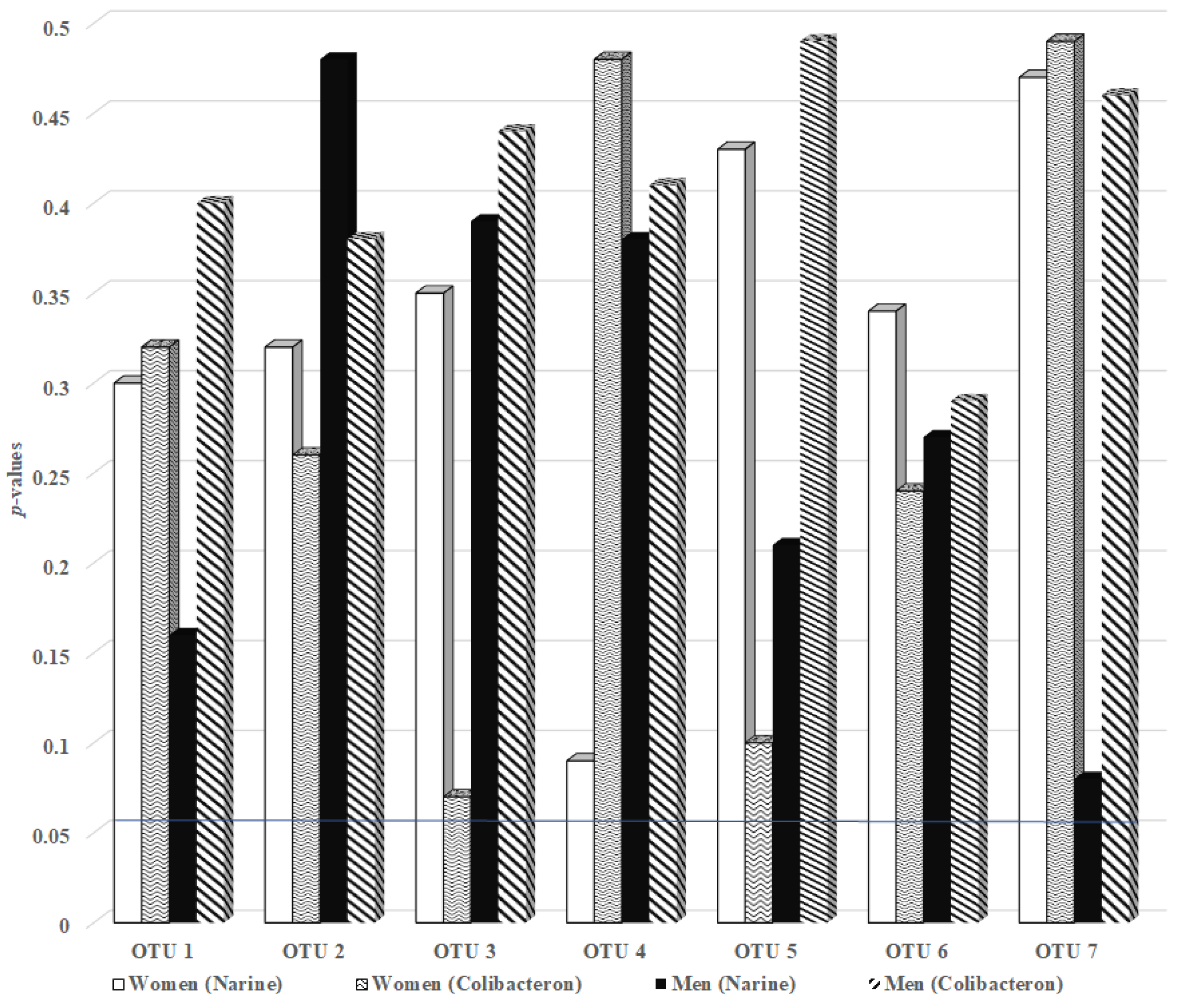
2.5. The Effect of Probiotic Narine and Colibacteron on the Gut Schaalia odontolytica OTUs in FMF-Affected Men and Women
- OTU 2 increased from 1975.00 ± 1135.00 to 4611.00 ± 2725.00 (p = 0.063),
- OTU 3 from 2098.00 ± 788.00 to 2835.00 ± 1477.00 (p = 0.081),
- OTU 4 from 2285.00 ± 695.00 to 5480.00 ± 2944.00 (p = 0.074).
3. Discussion
3.1. Potential Association Between Candidatus saccharibacteria spp. and Schaalia odontolytica in Healthy Individuals and FMF Patients: Trends Observed Under Placebo Conditions
3.2. Differential Response of Candidatus saccharibacteria and Schaalia odontolytica to Narine Administration in FMF Patients Relative to Placebo
3.3. Differential Response of Candidatus saccharibacteria and Schaalia odontolytica to Colibacteron Administration in FMF Patients Relative to Placebo
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
4.3. Intervention and Controls
4.4. DNA Extraction and PhyloChip Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CPR | Candidate Phyla Radiation |
| FMF | Familial Mediterranean fever |
| OTU | Operational Taxonomic Unit |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acid |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| IL | Interleukin |
| QS | Quorum Sensing |
References
- Danczak, R.E.; Johnston, M.D.; Kenah, C.; Slattery, M.; Wrighton, K.C.; Wilkins, M.J. Members of the Candidate Phyla Radiation are functionally differentiated by carbon-and nitrogen-cycling capabilities. Microbiome 2017, 5, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, S.; Gao, P.; Wang, B.; Jiang, J. Widespread but poorly understood bacteria: Candidate Phyla Radiation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheims, H.; Rainey, F.A.; Stackebrandt, E. A Molecular approach to search for diversity among bacteria in the environment. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1996, 17, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bor, B.; Bedree, J.K.; Shi, W.; McLean, J.S.; He, X. Saccharibacteria (TM7) in the human oral microbiome. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.M.; Overholt, W.A.; Figueroa-Gonzalez, P.A.; Taubert, M.; Bornemann, T.L.V.; Probst, A.J.; Hölzer, M.; Marz, M.; Küsel, K. The economical lifestyle of CPR bacteria in groundwater allows little preference for environmental drivers. Environ. Microbiome 2021, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Méheust, R.; Burstein, D.; Castelle, C.J.; Banfield, J.F. The Distinction of CPR bacteria from other bacteria based on protein family content. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipashvili, O.; Utter, D.R.; Bedree, J.K.; Ma, Y.; Schulte, F.; Mascarin, G.; Alayyoubi, Y.; Chouhan, D.; Hardt, M.; Bidlack, F.; et al. Episymbiotic Saccharibacteria suppresses gingival inflammation and bone loss in mice through host bacterial modulation. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 1649–1662.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, D.; Zivanovic, Y.; López-Archilla, A.I. Reductive evolution and unique predatory mode in the CPR bacterium Vampirococcus lugosii. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harutyunyan, N.; Stepanyan, L.; Malkhasyan, L.; Pepoyan, A. Dietary trials and gut candidate phyla radiation bacteria: The effect of placebo on the prevalence of Saccharibacteria in healthy Armenian women and women with familial Mediterranean fever. AgriSci. Technol. 2024, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A. Gut Akkermansia muciniphila, Prevotellaceae, and Enterobacteriaceae spp. as Possible Markers in Women-Related Nutritional and Clinical Trials: Familial Mediterranean Fever Disease. Womens Health Rep. 2024, 5, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutt, C.; Siegel, D.M. Autoinflammatory diseases/periodic fevers. Pediatr. Rev. 2023, 44, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, E.K.; Park, S.D.; Shim, J.J.; Lee, J.L.; Yoo, H.H. Effects of plant-based extract mixture on alcohol metabolism and hangover improvement in humans: A randomized, double-blind, paralleled, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnangi, S.; Sundjaja, J.H.; Singh, K.; Dua, A.; Angus, L.D. Placebo effect. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics consensus statement on the scope and appropriate use of the term probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaturyan, V.; Poghosyan, A.; Toczyłowski, M.; Pepoyan, A. Evaluation of malondialdehyde levels, oxidative stress and host–bacteria interactions: Escherichia coli and Salmonella Derby. Cells 2022, 11, 2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balayan, M.; Manvelyan, A.; Marutyan, S.; Isajanyan, M.; Tsaturyan, V.; Pepoyan, A.; Marotta, F.; Torok, T. Impact of Lactobacillus acidophilus INMIA 9602 Er-2 and Escherichia coli M-17 on some clinical blood characteristics of familial Mediterranean fever disease patients from the Armenian cohort. Int. J. Probiotics Prebiotics 2015, 10, 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.M.; Teng, J.; Wang, Y. Chronic colchicine poisoning with neuromyopathy, gastric ulcers and myelosuppression in a gout patient: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 11050–11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A.Z.; Manvelyan, A.M.; Balayan, M.H.; Harutyunyan, N.A.; Tsaturyan, V.V.; Batikyan, H.; Bren, A.B.; Chistyakov, V.; Weeks, R.; Chikindas, M.L. Tetracycline resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from water, human stool, and fish gills from the lake Sevan basin. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2023, 76, ovad021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchingolo, F.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Malcangi, G.; De Leonardis, N.; Sardano, R.; Pezzolla, C.; de Ruvo, E.; Di Venere, D.; Palermo, A.; Inchingolo, A.D.; et al. The benefits of probiotics on oral health: Systematic review of the literature. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A.Z.; Pepoyan, E.S.; Galstyan, L.; Harutyunyan, N.A.; Tsaturyan, V.V.; Torok, T.; Ermakov, A.M.; Popov, I.V.; Weeks, R.; Chikindas, M.L. The effect of immunobiotic/psychobiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus strain INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 Narine on gut Prevotella in familial Mediterranean fever: Gender-associated effects. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2021, 13, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A.Z.; Manvelyan, A.M.; Balayan, M.H.; McCabe, G.; Tsaturyan, V.V.; Melnikov, V.G.; Chikindas, M.L.; Weeks, R.; Karlyshev, A.V. The Effectiveness of potential probiotics Lactobacillus rhamnosus Vahe and Lactobacillus delbrueckii IAHAHI in irradiated rats depends on the nutritional stage of the host. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1439–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A.; Balayan, M.; Manvelyan, A.; Pepoyan, S.; Malkhasyan, L.; Bezhanyan, T.; Paronikyan, R.; Malakyan, M.; Bajinyan, S.; Tsaturyan, V.; et al. Radioprotective Effects of Lactobacilli with Antagonistic Activities Against Human Pathogens. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 665a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kriegshäuser, G.; Enko, D.; Hayrapetyan, H.; Atoyan, S.; Oberkanins, C.; Sarkisian, T. Clinical and genetic heterogeneity in a large cohort of Armenian patients with late-onset familial Mediterranean fever. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1583–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.-X.; Chen, X.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufan, A.; Lachmann, H.J. Familial Mediterranean Fever, from Pathogenesis to Treatment: A Contemporary Review. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1591–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.H.; Shousha, G.A.; El-Sayed, Z.A. The spectrum of urological disease in familial Mediterranean fever: Amyloidosis and beyond. Egypt. J. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 20, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotskiy, P.O.; Sotskaya, O.L.; Hayrapetyan, H.S.; Sarkisian, T.F.; Yeghiazaryan, A.R.; Atoyan, S.A.; Ben-Chetrit, E. Infertility causes and pregnancy outcome in patients with familial Mediterranean fever and controls. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batu, E.D.; Bayindir, Y.; Sener, S.; Balik, Z.; Aliyev, E.; Kasap Cuceoglu, M.; Basaran, O.; Bilginer, Y.; Ozen, S. A treatment algorithm for familial Mediterranean fever patients with menstruation-associated attacks. Rheumatology 2025, 64, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepoyan, A.; Balayan, M.; Manvelyan, A.; Galstyan, L.; Pepoyan, S.; Petrosyan, S.; Tsaturyan, V.; Kamiya, S.; Torok, T.; Chikindas, M. Probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus Strain INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 Administration Reduces the Numbers of Candida albicans and Abundance of Enterobacteria in the Gut Microbiota of Familial Mediterranean Fever Patients. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliskan, E.B.; Bingel, U.; Kunkel, A. translating knowledge on placebo and nocebo effects into clinical practice. Pain. Rep. 2024, 9, e1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullish, B.H.; Michael, D.R.; Dabcheva, M.; Webberley, T.S.; Coates, N.; John, D.A.; Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; Plummer, S.F.; Marchesi, J.R. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study assessing the impact of probiotic supplementation on the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in females. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2024, 36, e14751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, L.; Gong, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; He, J. Autoinducer-2 quorum sensing is an active universal signaling system in sociomicrobiology. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2025, 65, e70024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Utter, D.R.; Kerns, K.A.; Lamont, E.I.; Hendrickson, E.L.; Liu, J.; Wu, T.; He, X.; McLean, J.; Bor, B. Strain-level variation and diverse host bacterial responses in episymbiotic Saccharibacteria. mSystems 2022, 7, e01488-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.; Maatouk, M.; Rajaonison, A.; Zgheib, R.; Haddad, G.; Bou Khalil, J.; Raoult, D.; Bittar, F. Adapted protocol for Saccharibacteria cocultivation: Two new members join the club of Candidate Phyla radiation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01069-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manvelyan, A.; Balayan, M.; Miralimova, S.; Chistyakov, V.; Pepoyan, A. biofilm formation and auto-aggregation abilities of novel targeted aqua-probiotics. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2023, 13, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzabekyan, S.; Harutyunyan, N.; Manvelyan, A.; Malkhasyan, L.; Balayan, M.; Miralimova, S.; Chikindas, M.L.; Chistyakov, V.; Pepoyan, A. Fish probiotics: Cell surface properties of fish intestinal Lactobacilli and Escherichia coli. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A.; Trchounian, A. Biophysics, molecular and cellular biology of probiotic activity of bacteria. In Bacterial Membranes; Trchunyan, A.H., Ed.; Research Signpost: Kerala, India, 2009; pp. 275–287. [Google Scholar]
- Harutyunyan, N.; Kushugulova, A.; Hovhannisyan, N.; Pepoyan, A. One Health probiotics as biocontrol agents: One Health tomato probiotics. Plants 2022, 11, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Hashemi, S.M.B. Lactic acid production—Producing microorganisms and substrates sources—State of art. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanada, A.; Kurogi, T.; Giang, N.M.; Yamada, T.; Kamimoto, Y.; Kiso, Y.; Hiraishi, A. Bacteria of the candidate phylum TM7 are prevalent in acidophilic nitrifying sequencing-batch reactors. Microbes Environ. 2014, 29, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedree, J.K.; Bor, B.; Cen, L.; Edlund, A.; Lux, R.; McLean, J.S.; Shi, W.; He, X. Quorum sensing modulates the epibiotic-parasitic relationship between Actinomyces odontolyticus and its Saccharibacteria epibiont, a Nanosynbacter lyticus strain, TM7x. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casula, E.; Pisano, M.B.; Serreli, G.; Zodio, S.; Melis, M.P.; Corona, G.; Costabile, A.; Cosentino, S.; Deiana, M. Probiotic lacto-bacilli attenuate oxysterols-induced alteration of intestinal epithelial cell monolayer permeability: Focus on tight junction modulation. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 172, 113558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.L.; Ren, L.F.; Li, Z.J.; Zhang, L. How do intestinal probiotics restore the intestinal barrier? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 929346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, E.C.; Odle, J.; Blikslager, A.T.; Ziegler, A.L. Probiotics, Prebiotics and Epithelial Tight Junctions: A Promising Approach to Modulate Intestinal Barrier Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepoyan, A.Z.; Arutunian, N.; Grigorian, A.; Tsaturian, V.V.; Manvelian, A.M.; Dilnian, E.; Balaian, M.A.; Torok, T. The certain clinical characteristics of blood in patients with familial Mediterranean fever of Armenian population. Klin. Lab. Diagn. 2015, 60, 46–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pepoyan, A.Z.; Balayan, M.A.; Harutyunyan, N.A.; Grigoryan, A.G.; Tsaturyan, V.V.; Manvelyan, A.M.; Dilanyan, E.; Pitseno, I.; Torok, T. Antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli of the intestinal microbiota in patients with familial Mediterranean fever. Klin. Med. (Mosk.) 2015, 93, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pepoyan, E.; Marotta, F.; Manvelyan, A.; Galstyan, A.; Stepanyan, L.; Grigoryan, H.; Grigoryan, L.; Mikayelyan, M.; Balayan, M.; Harutyunyan, N.; et al. Placebo-resistant gut bacteria: Akkermansia muciniphila spp. and familial Mediterranean fever Disease. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1336752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepoyan, E.S.; Tsaturyan, V.V.; Pepoyan, A.Z. Characteristics of placebo–gut microbiota interactions in female patients with familial Mediterranean fever disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2024, 194, S8–S9. [Google Scholar]
- Tsaturyan, V.; Manvelyan, A.; Balayan, M.; Harutyunyan, N.; Pepoyan, E.; Torok, T.; Chikindas, M.; Pepoyan, A. Host genetics and gut microbiota composition: Baseline gut microbiota composition as a possible prognostic factor for the severity of COVID-19 in patients with familial Mediterranean fever disease. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1107485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galstyan, L.; Tsaturyan, V.; Pepoyan, A. Efficiency of pre- and probiotic therapy for the management of periodic disease and hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy of newborns: NLRP3 inflammasome. Parma 2018, 57, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.S.; Unno, T.; Kim, B.Y.; Park, M.S. Sex differences in gut microbiota. World J. Men’s Health 2020, 38, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Wang, Q.; Bai, F.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.; Yu, Y. Age-related alterations in gut homeostasis are microbiota dependent. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2025, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Guan, G.; Jia, H.; Li, H.; Zhuoga, S.; Zheng, S. The association between gut microbiota and accelerated aging and frailty: A Mendelian randomization study. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2025, 37, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, M.; Barone, L.; Longo, S.; Prandi, F.R.; Lecis, D.; Mollace, R.; Margonato, D.; Muscoli, S.; Sergi, D.; Federici, M.; et al. Gut microbiota composition and cardiovascular disease: A potential new therapeutic target? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D.; Petitfils, C.; De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; El-Omar, E.M. What defines a healthy gut microbiome? Gut 2024, 73, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinninella, E.; Tohumcu, E.; Raoul, P.; Fiorani, M.; Cintoni, M.; Mele, M.C.; Cammarota, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ianiro, G. The role of diet in shaping human gut microbiota. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 62–63, 101828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, A.; Velázquez, L.; Díaz, R.; Huaiquipán, R.; Pérez, I.; Muñoz, A.; Valdés, M.; Sepúlveda, N.; Paz, E.; Quiñones, J. Impact of Novel foods on the human gut microbiome: Current status. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, H. The impact of dietary patterns on gut microbiota for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Nutr. J. 2025, 24, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Koletic, C.; Mrad, A.; Martin, A.; Devkota, S. Diet’s impact on gut microbial assemblage in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e184319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Procházková, N.; Laursen, M.F.; La Barbera, G.; Tsekitsidi, E.; Jørgensen, M.S.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Raes, J.; Licht, T.R.; Dragsted, L.O.; Roager, H.M. Gut physiology and environment explain variations in human gut microbiome composition and metabolism. Nat. Microbiol. 2024, 9, 3210–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, P.; Caldarelli, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Gambassi, G.; Cianci, R. The Impact of Climate Change on Immunity and Gut Microbiota in the Development of Disease. Diseases 2024, 12, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, F.; Valentino, V.; Sequino, G.; Borriello, G.; Riccardi, M.G.; Pierri, B.; Cerino, P.; Pizzolante, A.; Pasolli, E.; Esposito, M.; et al. Exposure to environmental pollutants selects for xenobiotic-degrading functions in the human gut microbiome. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernfors, T.; Lavrinienko, A.; Vareniuk, I.; Landberg, R.; Fristedt, R.; Tkachenko, O.; Taskinen, S.; Tukalenko, E.; Mappes, T.; Watts, P.C. Association between gut health and gut microbiota in a polluted environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, C.A.; Piceno, Y.M.; Tom, L.M.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Gray, M.A.; Zawada, D.G.; Andersen, G.L. Comparing bacterial community composition between healthy and white plague-like disease states in Orbicella annularis using PhyloChip™ G3 microarrays. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| OTU | Healthy Men Before | Healthy Men After | p (Healthy) | FMF Men Before | FMF Men After | p (FMF) | p (Healthy vs. FMF) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OTU 1 | 4870.98 ± 1117.07 | 5363.95 ± 727.29 | 0.39 | 6099.00 ± 1429.00 | 5816.00.00 ± 2018 | 0.36 | >0.05 |
| OTU 2 | 373.53 ± 40.42 | 462.18 ± 173.55 | 0.28 | 943.00 ± 699.00 | 1173.00 ± 769.00 | 0.25 | >0.05 |
| OTU 3 | 573.04 ± 635.78 | 369.85 ± 212.22 | 0.61 | 688.00 ± 1373.00 | 653.00 ± 741.00 | 0.47 | >0.05 |
| OTU 4 | 4094.13 ± 1261.68 | 4717.18 ± 392.56 | 0.44 | 3852.00 ± 1989.00 | 5120.00 ± 2089.00 | 0.09 | >0.05 |
| OTU 5 | 396.35 ± 97.72 | 422.86 ± 212.87 | 0.71 | 460.00 ± 361.00 | 457.00 ± 145.00 | 0.49 | >0.05 |
| OTU 6 | 4026.52 ± 1735.20 | 3478.66 ± 735.08 | 0.58 | 3912.00 ± 1999.00 | 4046.00 ± 1448.00 | 0.43 | >0.05 |
| OTU 7 | 2768.55 ± 1718.45 | 3202.88 ± 1481.22 | 0.64 | 3081.00 ± 948.00 | 3017.00 ± 1362.00 | 0.45 | >0.05 |
| OTUs | Hybridization Scores | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Women | FMF Women | |||||
| Before the Placebo Administration | After the Placebo Administration | p Before/After Placebo Administration | After the Placebo Administration | Before the Placebo Administration | p Before/After Placebo Administration | |
| OTU 1 | 5089.00 ± 2419.00 | 4854.00 ± 1620.00 | 0.400 | 3804.00 ± 619.00 | 3655.00 ± 870.00 | 0.38 |
| OTU 2 | 3484.00 ± 3325.00 | 2019.00 ± 1128.00 | 0.054 | 4051.00 ± 2751.00 | 5063.00 ± 2811.00 | 0.29 |
| OTU 3 | 2185.00 ± 1305.00 | 1457.00 ± 637.00 | 0.048 | 2216.00 ± 1034.00 | 2523.00 ± 976.00 | 0.32 |
| OTU 4 | 3494.00 ± 3711.00 | 1836.00 ± 1136.00 | 0.057 | 3802.00 ± 2865.00 | 4959.00 ± 2990.00 | 0.27 |
| OTU | Hybridization Scores (Mean ± SD). | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Healthy Men | FMF Men | |||||
| Before the Placebo Administration | After the Placebo Administration | p Before/After Placebo Administration | After the Placebo Administration | Before the Placebo Administration | p Before/After Placebo Administration | |
| OTU 1 | 4033.00 ± 2110.00 | 5551.40 ± 1880.57 | 0.16 | 3234.00 ± 1075.00 | 3580.00 ± 1461.00 | 0.28 |
| OTU 2 | 2749.00 ± 1118.00 | 2609.87 ± 953.00 | 0.43 | 3311.00 ± 1759.00 | 3917.00 ± 2158.00 | 0.25 |
| OTU 3 | 2034.00 ± 887.00 | 2015.68 ± 779.50 | 0.49 | 2202.00 ± 623.00 | 2540.00 ± 691.00 | 0.13 |
| OTU 4 | 2502.00 ± 1123.00 | 2275.89 ± 687.91 | 0.37 | 3154.00 ± 1589.00 | 3725.00 ± 2327.00 | 0.26 |
| OTU | FMF Women | FMF Men | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narine | Colibacteron | Narine | Colibacteron | |
| OTU 1 | 0.352 | 0.290 | 0.490 | 0.190 |
| OTU 2 | 0.063 | 0.170 | 0.470 | 0.310 |
| OTU 3 | 0.081 | 0.080 | 0.490 | 0.340 |
| OTU 4 | 0.074 | 0.130 | 0.390 | 0.390 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Harutyunyan, N.; Stepanyan, L.; Balayan, M.; Manvelyan, A.; Pepoyan, E.; Tsaturyan, V.; Torok, T.; Pepoyan, A. Preliminary Evidence for Sex-Specific Trends in Probiotic Modulation of Gut Saccharibacteria in Familial Mediterranean Fever Patients: Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 and Escherichia coli M-17. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188959
Harutyunyan N, Stepanyan L, Balayan M, Manvelyan A, Pepoyan E, Tsaturyan V, Torok T, Pepoyan A. Preliminary Evidence for Sex-Specific Trends in Probiotic Modulation of Gut Saccharibacteria in Familial Mediterranean Fever Patients: Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 and Escherichia coli M-17. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188959
Chicago/Turabian StyleHarutyunyan, Natalya, Lena Stepanyan, Marine Balayan, Anahit Manvelyan, Elya Pepoyan, Vardan Tsaturyan, Tamas Torok, and Astghik Pepoyan. 2025. "Preliminary Evidence for Sex-Specific Trends in Probiotic Modulation of Gut Saccharibacteria in Familial Mediterranean Fever Patients: Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 and Escherichia coli M-17" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188959
APA StyleHarutyunyan, N., Stepanyan, L., Balayan, M., Manvelyan, A., Pepoyan, E., Tsaturyan, V., Torok, T., & Pepoyan, A. (2025). Preliminary Evidence for Sex-Specific Trends in Probiotic Modulation of Gut Saccharibacteria in Familial Mediterranean Fever Patients: Effects of Lactobacillus acidophilus INMIA 9602 Er 317/402 and Escherichia coli M-17. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8959. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188959






