Airborne PM10 Decreases Ku80 Expression and Ku70–Ku80 Heterodimer Levels of the Non-Homologous End Joining Repair Pathway in Lung Epithelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
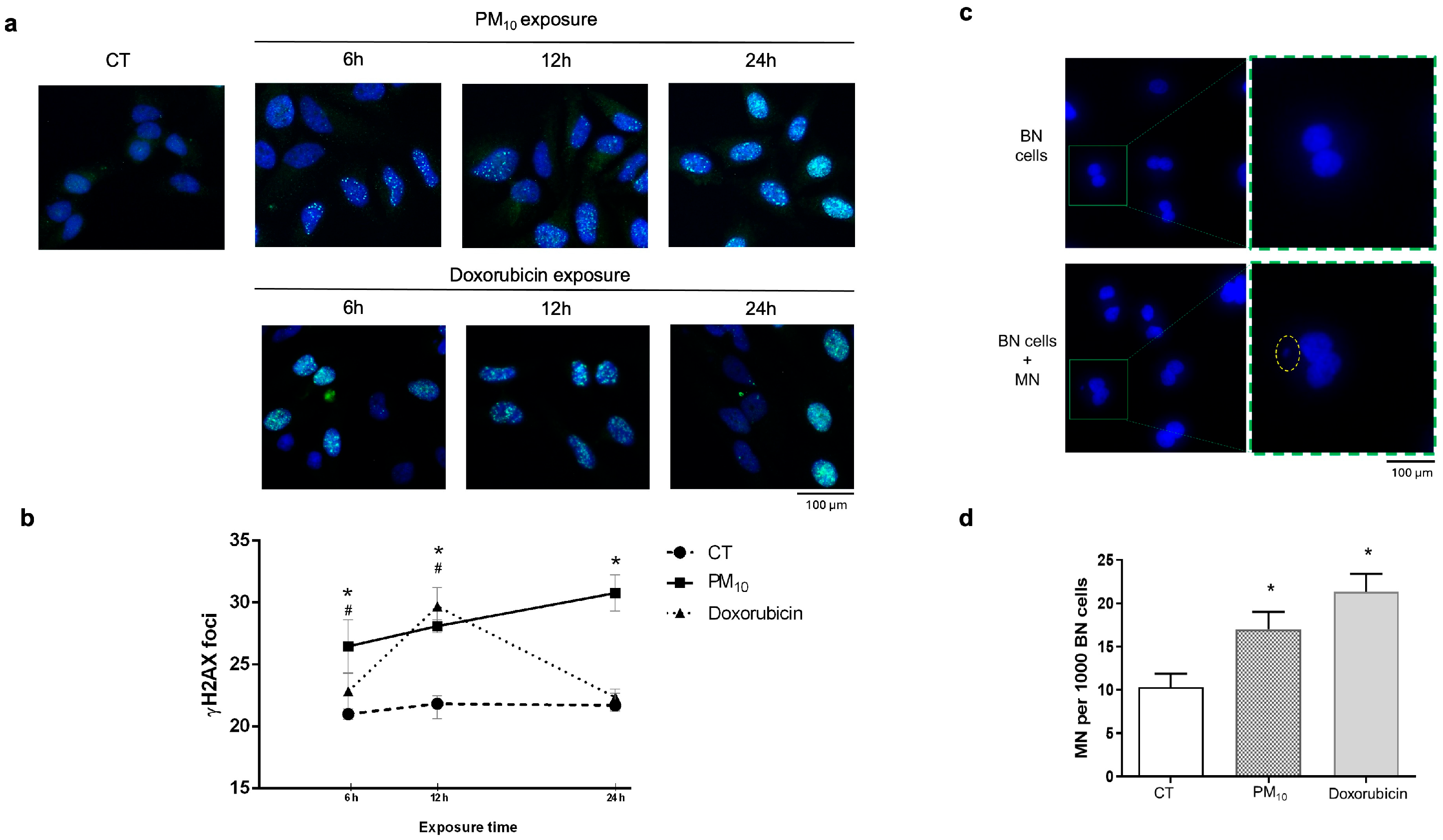
2.1. PM10 Induces DNA Damage Accumulation Through DSBs Without Causing Cell Cycle Arrest
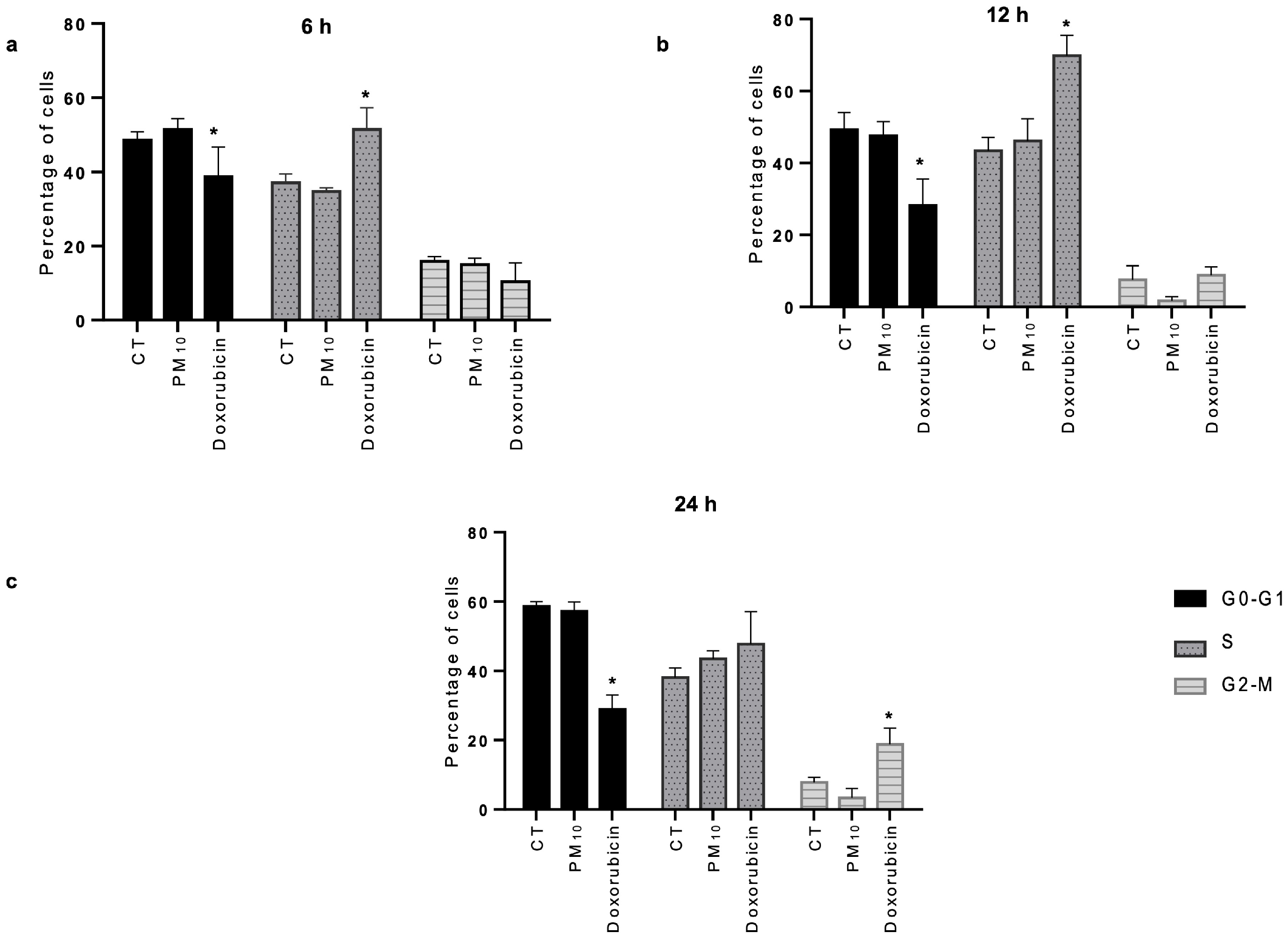
2.2. PM10 Does Not Cause Cell Cycle Arrest Despite DNA Damage
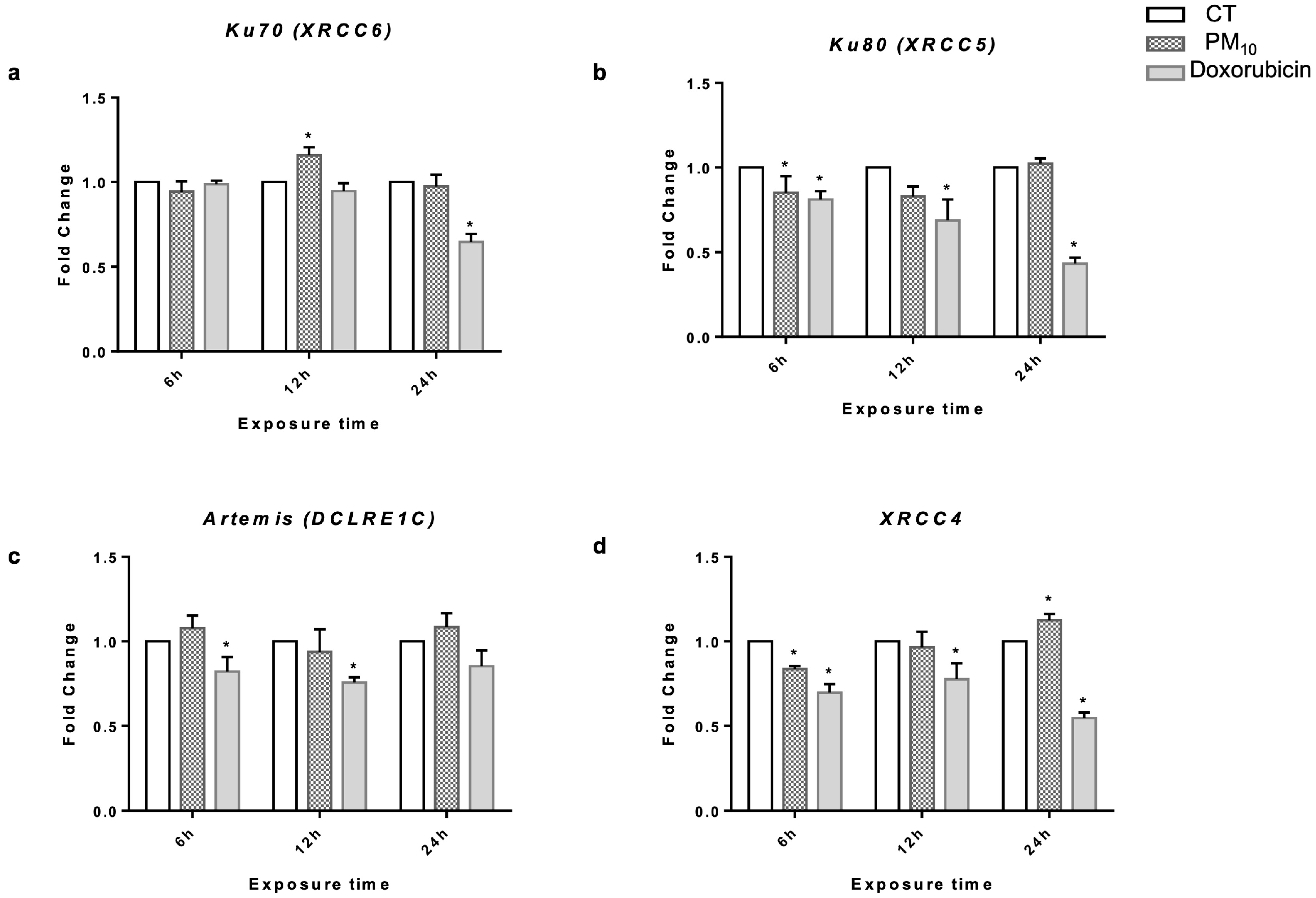
2.3. PM10 Induces Changes in Gene Expression of Ku70 and XRCC4
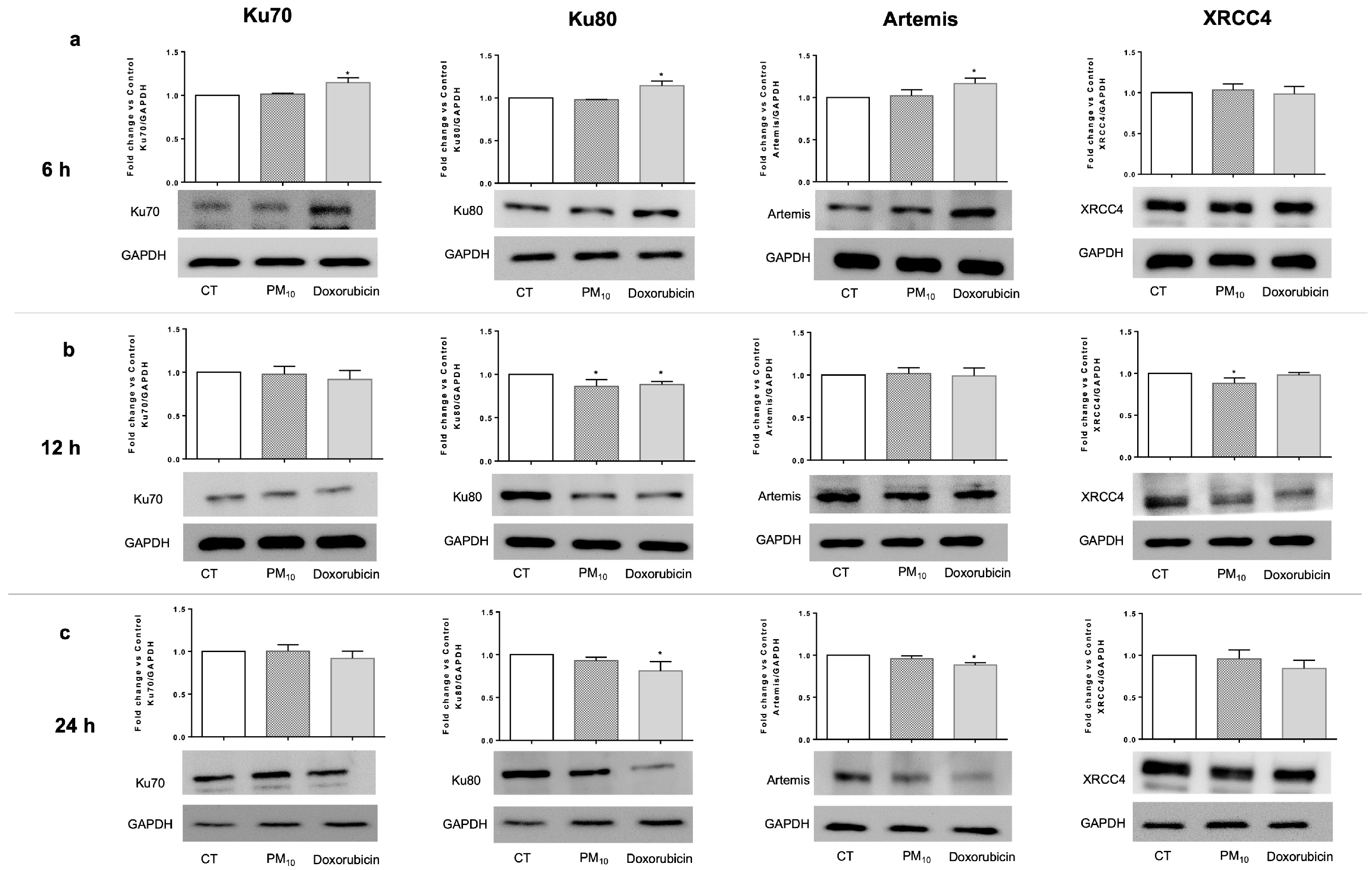
2.4. PM10 Decreases the Protein Levels of Ku80 and XRCC4
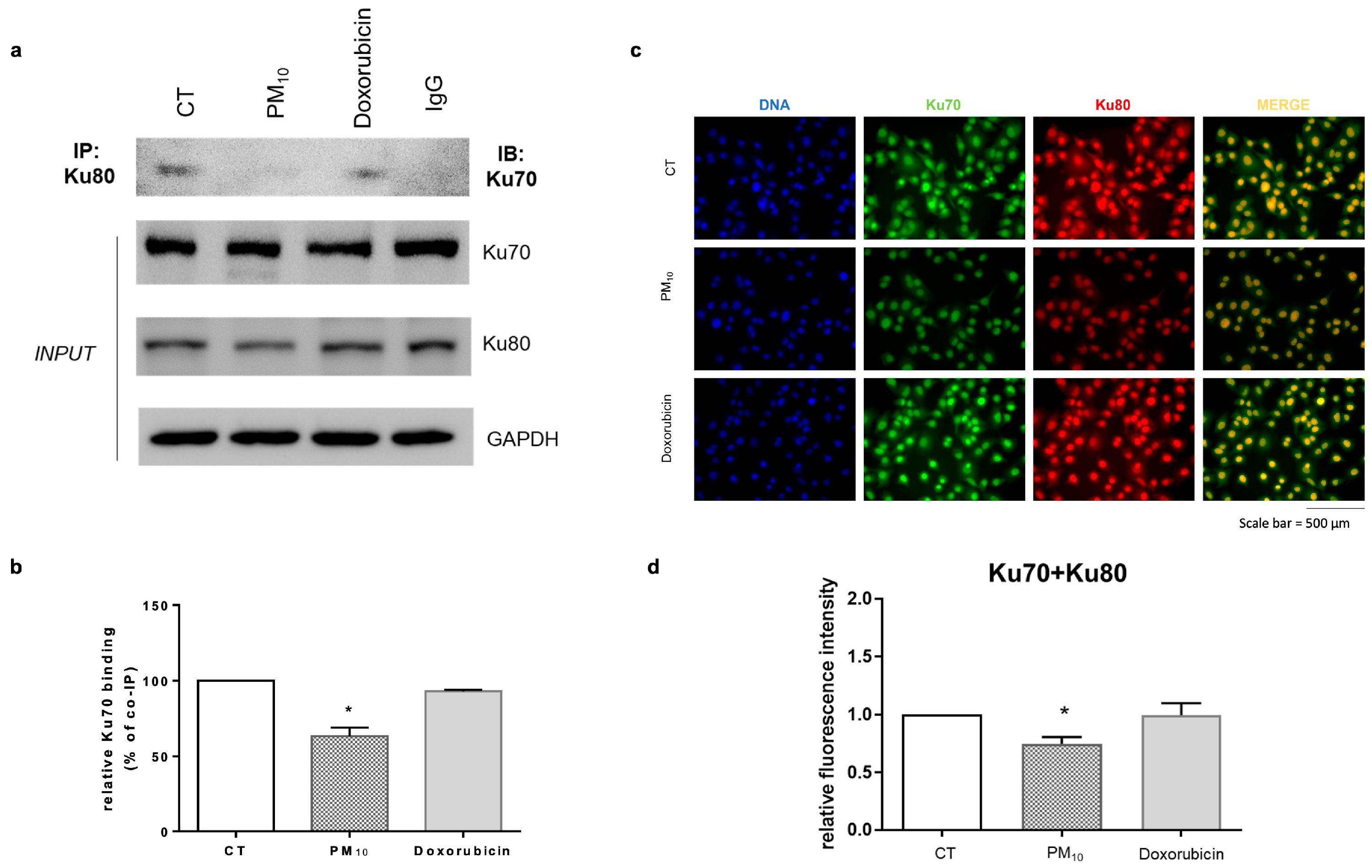
2.5. PM10 Decreases the Abundance of the DSB Recognition Complex
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. PM10 Collection and Composition Characterization
4.2. Cell Culture and PM10 Exposure
4.3. Double-Strand Break Determination and Protein Localization via Immunodetection
4.4. Micronucleus Assay
4.5. Cell Cycle Analysis via Flow Cytometry
4.6. RNA Analysis Expression via qRT-PCR
4.7. Protein Level Determination via Western Blot
4.8. Protein Complex Formation Analysis via Co-Immunoprecipitation Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PM | Particulate matter |
| NHEJ | Non-homologous end joining |
| DSBs | Double-strand breaks |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| ƔH2AX | Phosphorylation at Ser-139 residue of the histone variant H2AX |
References
- Song, H.; Zhuo, H.; Fu, S.; Ren, L. Air pollution characteristics, health risks, and source analysis in Shanxi Province, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loomis, D.; Huang, W.; Chen, G. The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) evaluation of the carcinogenicity of outdoor air pollution: Focus on China. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IARC. Outdoor Air Pollution; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2015; Volume 109, pp. 1–448.
- Tseng, C.H.; Tsuang, B.J.; Chiang, C.J.; Ku, K.C.; Tseng, J.S.; Yang, T.Y.; Hsu, K.H.; Chen, K.C.; Yu, S.L.; Lee, W.C.; et al. The Relationship Between Air Pollution and Lung Cancer in Nonsmokers in Taiwan. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.U.; Yoon, H.K. Narrative review: Association between lung cancer development and ambient particulate matter in never-smokers. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Chu, C.; Sang, S. Global burden of lung cancer attributable to ambient fine particulate matter pollution in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019. Environ. Res. 2022, 204 Pt A, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consonni, D.; Carugno, M.; De Matteis, S.; Nordio, F.; Randi, G.; Bazzano, M.; Caporaso, N.E.; Tucker, M.A.; Bertazzi, P.A.; Pesatori, A.C.; et al. Outdoor particulate matter (PM10) exposure and lung cancer risk in the EAGLE study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadei, M.; Aboosaedi, Z.; Naddafi, K. Carcinogenic risks and chemical composition of particulate matter recovered by two methods: Wet and dry extraction. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirino, Y.I.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R.; Rosas, I.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. Sampling and composition of airborne particulate matter (PM10) from two locations of Mexico City. Data Brief. 2015, 4, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Qian, L.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Fu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, B.; Qian, J. Biological and chemical compositions of atmospheric particulate matter during hazardous haze days in Beijing. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 34540–34549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibáñez-Andrade, M.; Quezada-Maldonado, E.M.; Quintana-Belmares, R.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Rosas-Perez, I.; Amador-Munoz, O.; Miranda, J.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. Sampling, composition, and biological effects of Mexico City airborne particulate matter from multiple periods. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, M.; Gu, Y.; Liu, J.; Tang, X. Spatial and Temporal Variability of the PM2.5/PM10 Ratio in Wuhan, Central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, H.; Yu, E.; Ting, L. PM2.5/PM10 Ratios in Eight Economic Regions and Their Relationship with Meteorology in China. Adv. Meteorol. 2019, 15, 5295726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, E.; Eidels, S.; Ruiz, H.; López-Veneroni, D.; Sosa, G.; Gonzalez, E.; Gasca, J.; Mora, V.; Reyes, E.; Sánchez-Reyna, G.; et al. Particulate Air Pollution in Mexico City: A Detailed View. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 10, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward-Caviness, C.K.; Weaver, A.M.; Buranosky, M.; Pfaff, E.R.; Neas, L.M.; Devlin, R.B.; Schwartz, J.; Di, Q.; Cascio, W.E.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Associations Between Long-Term Fine Particulate Matter Exposure and Mortality in Heart Failure Patients. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e012517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuempel, E.D.; Sweeney, L.M.; Morris, J.B.; Jarabek, A.M. Advances in Inhalation Dosimetry Models and Methods for Occupational Risk Assessment and Exposure Limit Derivation. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2015, 12 (Suppl. S1), S18–S40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepers, C.; Andre, V.; Dergham, M.; Billet, S.; Verdin, A.; Garcon, G.; Dewaele, D.; Cazier, F.; Sichel, F.; Shirali, P. Xenobiotic metabolism induction and bulky DNA adducts generated by particulate matter pollution in BEAS-2B cell line: Geographical and seasonal influence. J. Appl. Toxicol. JAT 2014, 34, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon-Garciduenas, L.; Herrera-Soto, A.; Jury, N.; Maher, B.A.; Gonzalez-Maciel, A.; Reynoso-Robles, R.; Ruiz-Rudolph, P.; van Zundert, B.; Varela-Nallar, L. Reduced repressive epigenetic marks, increased DNA damage and Alzheimer’s disease hallmarks in the brain of humans and mice exposed to particulate urban air pollution. Environ. Res. 2020, 183, 109226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, A.; Tamrakar, S.; Aglawe, A.; Lad, H.; Srivastava, R.K.; Mishra, D.K.; Tiwari, R.; Chaudhury, K.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Mishra, P.K. Ultrafine particulate matter impairs mitochondrial redox homeostasis and activates phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase mediated DNA damage responses in lymphocytes. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Maldonado, E.M.; Chirino, Y.I.; Gonsebatt, M.E.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. Nucleotide Excision Repair Pathway Activity Is Inhibited by Airborne Particulate Matter (PM10) through XPA Deregulation in Lung Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.; Chen, L.C.; Gordon, T.; Rom, W.; Tang, M.S. Particulate matter inhibits DNA repair and enhances mutagenesis. Mutat. Res. 2008, 657, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, B.Y.; Li, W.K.; Li, J.S.; Hong, Q.H.; Khodahemmati, S.; Gao, J.F.; Zhou, Z.X. Effects of DNA Damage and Oxidative Stress in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed to PM2.5 from Beijing, China, in Winter. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, N.; Walker, G.C. Mechanisms of DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 235–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakarougkas, A.; Jeggo, P.A. DNA DSB repair pathway choice: An orchestrated handover mechanism. Br. J. Radiol. 2014, 87, 20130685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, T.L.; Mostoslavsky, R. DNA repair as a shared hallmark in cancer and ageing. Mol. Oncol. 2022, 16, 3352–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roubicek, D.A.; Gutierrez-Castillo, M.E.; Sordo, M.; Cebrian-Garcia, M.E.; Ostrosky-Wegman, P. Micronuclei induced by airborne particulate matter from Mexico City. Mutat. Res. 2007, 631, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfitzer, L.; Moser, C.; Gegenfurtner, F.; Arner, A.; Foerster, F.; Atzberger, C.; Zisis, T.; Kubisch-Dohmen, R.; Busse, J.; Smith, R.; et al. Targeting actin inhibits repair of doxorubicin-induced DNA damage: A novel therapeutic approach for combination therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesen, C.; Uhl, M.; Pannicke, U.; Schwarz, K.; Miltner, E.; Debatin, K.M. DNA-ligase IV and DNA-protein kinase play a critical role in deficient caspases activation in apoptosis-resistant cancer cells by using doxorubicin. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3283–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ceccaldi, R.; Rondinelli, B.; D’Andrea, A.D. Repair Pathway Choices and Consequences at the Double-Strand Break. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tung, E.W.; Philbrook, N.A.; Belanger, C.L.; Ansari, S.; Winn, L.M. Benzo[a]pyrene increases DNA double strand break repair in vitro and in vivo: A possible mechanism for benzo[a]pyrene-induced toxicity. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2014, 760, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshioka, K.I.; Kusumoto-Matsuo, R.; Matsuno, Y.; Ishiai, M. Genomic Instability and Cancer Risk Associated with Erroneous DNA Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Haber, J.E. Sources of DNA double-strand breaks and models of recombinational DNA repair. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Chirino, Y.I.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Gutierrez-Ruiz, C.; Vazquez-Lopez, I.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. DNA damage response of A549 cells treated with particulate matter (PM10) of urban air pollutants. Cancer Lett. 2009, 278, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossner, P., Jr.; Rossnerova, A.; Beskid, O.; Tabashidze, N.; Libalova, H.; Uhlirova, K.; Topinka, J.; Sram, R.J. Nonhomologous DNA end joining and chromosome aberrations in human embryonic lung fibroblasts treated with environmental pollutants. Mutat. Res. 2014, 763–764, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Gao, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, M.; Ma, P.; Shang, P.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. GSDMD-miR-223-NLRP3 axis involved in B(a)P-induced inflammatory injury of alveolar epithelial cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 232, 113286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, K.A.; Oster, C.G.; Mayer, M.M.; Avery, M.L.; Audus, K.L. Characterization of the A549 cell line as a type II pulmonary epithelial cell model for drug metabolism. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 243, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ge, X.; Nie, D.; Wang, M.; Zhou, H.; Chen, M. In vitro toxicity evaluation of heavy metals in urban air particulate matter on human lung epithelial cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chondrou, V.; Trochoutsou, K.; Panayides, A.; Efthimiou, M.; Stephanou, G.; Demopoulos, N.A. Combined study on clastogenic, aneugenic and apoptotic properties of doxorubicin in human cells in vitro. J. Biol. Res. 2018, 25, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fant, C.; Granzotto, A.; Mestas, J.L.; Ngo, J.; Lafond, M.; Lafon, C.; Foray, N.; Padilla, F. DNA Double-Strand Breaks in Murine Mammary Tumor Cells Induced by Combined Treatment with Doxorubicin and Controlled Stable Cavitation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2021, 47, 2941–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedelnikova, O.A.; Rogakou, E.P.; Panyutin, I.G.; Bonner, W.M. Quantitative detection of 125IdU-induced DNA double-strand breaks with gamma-H2AX antibody. Radiat. Res. 2002, 158, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Collins, L.B.; Chen, T.H.; Herr, N.; Takeda, S.; Sun, W.; Swenberg, J.A.; Nakamura, J. Oxidative stress at low levels can induce clustered DNA lesions leading to NHEJ mediated mutations. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25377–25390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bee, L.; Fabris, S.; Cherubini, R.; Mognato, M.; Celotti, L. The efficiency of homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining systems in repairing double-strand breaks during cell cycle progression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibanez-Andrade, M.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Chirino, Y.I.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Herrera, L.A.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. Airborne particulate matter induces mitotic slippage and chromosomal missegregation through disruption of the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). Chemosphere 2019, 235, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio, I.C.; Barros, S.B.; Roubicek, D.A. Water-soluble and organic extracts of airborne particulate matter induce micronuclei in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2016, 812, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrì, M.; Gea, M.; Marangon, D.; Pitasi, F.A.; Fontana, M.; Bonetta, S.; Schilirò, T.; Bonetta, S. In vitro evaluation of genotoxicity and methylation changes induced by particulate matter from the Padana Plain. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, C. Physicochemical properties, in vitro cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of PM1.0 and PM2.5 from Shanghai, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 19508–19516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupina, K.; Goginashvili, A.; Cleveland, D.W. Causes and consequences of micronuclei. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2021, 70, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhang, F.; Rui, W.; Long, F.; Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Chen, D.; Ding, W. PM2.5-induced oxidative stress triggers autophagy in human lung epithelial A549 cells. Toxicol. Vitr. 2013, 27, 1762–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.H.; Wang, X.; Pan, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Chowdhury, D.; Kimmelman, A.C. Inhibition of non-homologous end joining repair impairs pancreatic cancer growth and enhances radiation response. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A.; Kayani, M.A.; Parry, J.M.; Parry, E.; Anderson, D. Aneugenic and clastogenic effects of doxorubicin in human lymphocytes. Mutagenesis 2003, 18, 487–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, F.; Sherwani, A.F.; Afzal, M. Chromosomal aberration and micronucleus studies of two topoisomerase (II) targeting anthracyclines. J. Environ. Biol. 2009, 30, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Lim, J.S.; Tang, R.M.; Zhang, L.; Chen, E.S. Fitness profiling links topoisomerase II regulation of centromeric integrity to doxorubicin resistance in fission yeast. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pérez, Y.; Chirino, Y.I.; Osornio-Vargas, Á.; Herrera, L.A.; Morales-Bárcenas, R.; López-Saavedra, A.; González-Ramírez, I.; Miranda, J.; García-Cuellar, C.M. Cytoplasmic p21(CIP1/WAF1), ERK1/2 activation, and cytoskeletal remodeling are associated with the senescence-like phenotype after airborne particulate matter (PM10) exposure in lung cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 225, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Bozzella, M.; Seluanov, A.; Gorbunova, V. DNA repair by nonhomologous end joining and homologous recombination during cell cycle in human cells. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2902–2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, A.J.; Rabinovitch, P.S. The cell cycle phases of DNA damage and repair initiated by topoisomerase II-targeting chemotherapeutic drugs. Mutat. Res. 2005, 572, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothkamm, K.; Kruger, I.; Thompson, L.H.; Lobrich, M. Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003, 23, 5706–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, J.M.; Yamada, N.A.; Salazar, E.P.; Tebbs, R.S.; Thompson, L.H. Influence of double-strand-break repair pathways on radiosensitivity throughout the cell cycle in CHO cells. DNA Repair 2005, 4, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenbaum, D.; Colangelo, C.; Williams, K.; Gerstein, M. Comparing protein abundance and mRNA expression levels on a genomic scale. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brion, C.; Lutz, S.M.; Albert, F.W. Simultaneous quantification of mRNA and protein in single cells reveals post-transcriptional effects of genetic variation. Elife 2020, 9, e60645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Juhn, K.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.H.; Min, B.H.; Lee, K.M.; Cho, M.H.; Park, G.H.; Lee, K.H. SIRT1 promotes DNA repair activity and deacetylation of Ku70. Exp. Mol. Med. 2007, 39, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaldi, C.; Pizzul, P.; Casari, E.; Mangiagalli, M.; Tisi, R.; Longhese, M.P. The Ku complex promotes DNA end-bridging and this function is antagonized by Tel1/ATM kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 1783–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spagnolo, L.; Rivera-Calzada, A.; Pearl, L.H.; Llorca, O. Three-dimensional structure of the human DNA-PKcs/Ku70/Ku80 complex assembled on DNA and its implications for DNA DSB repair. Mol. Cell 2006, 22, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonn, I.; Hennesen, J.; Dartsch, D.C. Ku70 and Rad51 vary in their importance for the repair of doxorubicin-versus etoposide-induced DNA damage. Apoptosis An. Int. J. Program. Cell Death 2011, 16, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossnerova, A.; Elzeinova, F.; Chvojkova, I.; Honkova, K.; Sima, M.; Milcova, A.; Pastorkova, A.; Schmuczerova, J.; Rossner, P., Jr.; Topinka, J.; et al. Effects of various environments on epigenetic settings and chromosomal damage. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wei, J.; Cheng, Y.; Subedi, K.; Verma, V. Synergistic and Antagonistic Interactions among the Particulate Matter Components in Generating Reactive Oxygen Species Based on the Dithiothreitol Assay. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 2261–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Puthussery, J.V.; Yu, H.; Verma, V. Synergistic and antagonistic interactions among organic and metallic components of the ambient particulate matter (PM) for the cytotoxicity measured by Chinese hamster ovary cells. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 736, 139511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartwig, A.; Asmuss, M.; Ehleben, I.; Herzer, U.; Kostelac, D.; Pelzer, A.; Schwerdtle, T.; Burkle, A. Interference by toxic metal ions with DNA repair processes and cell cycle control: Molecular mechanisms. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110 (Suppl. S5), 797–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meaza, I.; Williams, A.R.; Lu, H.; Kouokam, J.C.; Toyoda, J.H.; Croom-Perez, T.J.; Wise, S.S.; Aboueissa, A.E.; Wise, J.P., Sr. Prolonged particulate hexavalent chromium exposure induces RAD51 foci inhibition and cytoplasmic accumulation in immortalized and primary human lung bronchial epithelial cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2023, 479, 116711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Gu, X.; Zhang, X.; Kong, J.; Ding, N.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Huang, D. Cadmium delays non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair via inhibition of DNA-PKcs phosphorylation and downregulation of XRCC4 and Ligase IV. Mutat. Res. 2015, 779, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.; Lim, J.W.; Kim, H. alpha-Lipoic Acid Inhibits Apoptosis by Suppressing the Loss of Ku Proteins in Helicobacter pylori-Infected Human Gastric Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.M.; Kang, T.H. Transcriptional and Posttranslational Regulation of Nucleotide Excision Repair: The Guardian of the Genome against Ultraviolet Radiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bane, K.; Desouza, J.; Rojewale, A.; Katkam, R.R.; Fernandes, G.; Sawant, R.; Dudhedia, U.; Warty, N.; Chauhan, A.; Chaudhari, U.; et al. Dysregulation of X-ray repair cross-complementing 4 expression in the eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis. Reproduction 2022, 163, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, W.; Wang, J.; Cao, G.; Cai, Z. PM2.5-induced DNA oxidative stress in A549 cells and regulating mechanisms by GST DNA methylation and Keap1/Nrf2 pathway. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 2024, 34, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirino, Y.I.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Gutierrez-Ruiz, M.C.; Segura-Garcia, Y.; Rosas, I.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. PM10 impairs the antioxidant defense system and exacerbates oxidative stress driven cell death. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 193, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhanva, M.S.; Hariharasudhan, G.; Jun, S.; Seo, G.; Kamalakannan, R.; Kim, H.H.; Lee, J.H. MicroRNA-145 Impairs Classical Non-Homologous End-Joining in Response to Ionizing Radiation-Induced DNA Double-Strand Breaks via Targeting DNA-PKcs. Cells 2022, 11, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, E.; Ouyang, C.; Wei, G.; Wang, Y.; He, D.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; et al. LRIK interacts with the Ku70-Ku80 heterodimer enhancing the efficiency of NHEJ repair. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 3337–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quezada-Maldonado, E.M.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Chirino, Y.I.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. miRNAs deregulation in lung cells exposed to airborne particulate matter (PM10) is associated with pathways deregulated in lung tumors. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santibanez-Andrade, M.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; Chirino, Y.I.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.M. Long non-coding RNA NORAD upregulation induced by airborne particulate matter (PM10) exposure leads to aneuploidy in A549 lung cells. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osornio-Vargas, A.R.; Serrano, J.; Rojas-Bracho, L.; Miranda, J.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.; Reyna, M.A.; Flores, G.; Zuk, M.; Quintero, M.; Vazquez, I.; et al. In vitro biological effects of airborne PM2.5 and PM10 from a semi-desert city on the Mexico-US border. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarian, M.; Nicknam, M.H.; Mesdaghinia, A.; Yunesian, M.; Hassanvand, M.S.; Soleimanifar, N.; Rezaei, S.; Atafar, Z.; Ghanbarian, M.; Faraji, M.; et al. Investigation and Comparison of In Vitro Genotoxic Potency of PM10 Collected in Rural and Urban Sites at Tehran in Different Metrological Conditions and Different Seasons. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 301–310, Erratum in Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 189, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgie, M.; Ledoux, F.; Verdin, A.; Cazier, F.; Greige, H.; Shirali, P.; Courcot, D.; Dagher, Z. Genotoxic and epigenotoxic effects of fine particulate matter from rural and urban sites in Lebanon on human bronchial epithelial cells. Environ. Res. 2015, 136, 352–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badyda, A.; Gayer, A.; Czechowski, P.O.; Majewski, G.; Dabrowiecki, P. Pulmonary Function and Incidence of Selected Respiratory Diseases Depending on the Exposure to Ambient PM10. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ui, A.; Chiba, N.; Yasui, A. Relationship among DNA double-strand break (DSB), DSB repair, and transcription prevents genome instability and cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Maldonado, E.M.; Cerrato-Izaguirre, D.; Morales-Barcenas, R.; Bautista-Ocampo, Y.; Santibanez-Andrade, M.; Quintana-Belmares, R.; Chirino, Y.I.; Basurto-Lozada, P.; Robles-Espinoza, C.D.; Sanchez-Perez, Y.; et al. Mutational landscape induced by chronic exposure to environmental PM10 and PM2.5 in A549 lung epithelial cell. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Moreno, E.; Torres, V.; Miranda, J.; Martinez, L.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.; Nawrot, T.S.; Vanaudenaerde, B.; Hoet, P.; Ramirez-Lopez, P.; Rosas, I.; et al. Induction of IL-6 and inhibition of IL-8 secretion in the human airway cell line Calu-3 by urban particulate matter collected with a modified method of PM sampling. Environ. Res. 2009, 109, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfaro-Moreno, E.; Martinez, L.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.; Bonner, J.C.; Murray, J.C.; Rosas, I.; Rosales, S.P.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R. Biologic effects induced in vitro by PM10 from three different zones of Mexico City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hao, M.; Phalen, R.F.; Hinds, W.C.; Nel, A.E. Particulate air pollutants and asthma. A paradigm for the role of oxidative stress in PM-induced adverse health effects. Clin. Immunol. 2003, 109, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferecatu, I.; Borot, M.C.; Bossard, C.; Leroux, M.; Boggetto, N.; Marano, F.; Baeza-Squiban, A.; Andreau, K. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon components contribute to the mitochondria-antiapoptotic effect of fine particulate matter on human bronchial epithelial cells via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2010, 7, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quezada-Maldonado, E.M.; Lozolla-Ortiz, J.I.; Santibáñez-Andrade, M.; Morales-Bárcenas, R.; García-Cuellar, C.M.; Sánchez-Pérez, Y. Airborne PM10 Decreases Ku80 Expression and Ku70–Ku80 Heterodimer Levels of the Non-Homologous End Joining Repair Pathway in Lung Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188936
Quezada-Maldonado EM, Lozolla-Ortiz JI, Santibáñez-Andrade M, Morales-Bárcenas R, García-Cuellar CM, Sánchez-Pérez Y. Airborne PM10 Decreases Ku80 Expression and Ku70–Ku80 Heterodimer Levels of the Non-Homologous End Joining Repair Pathway in Lung Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188936
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuezada-Maldonado, Ericka Marel, Javier Ivan Lozolla-Ortiz, Miguel Santibáñez-Andrade, Rocío Morales-Bárcenas, Claudia M. García-Cuellar, and Yesennia Sánchez-Pérez. 2025. "Airborne PM10 Decreases Ku80 Expression and Ku70–Ku80 Heterodimer Levels of the Non-Homologous End Joining Repair Pathway in Lung Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188936
APA StyleQuezada-Maldonado, E. M., Lozolla-Ortiz, J. I., Santibáñez-Andrade, M., Morales-Bárcenas, R., García-Cuellar, C. M., & Sánchez-Pérez, Y. (2025). Airborne PM10 Decreases Ku80 Expression and Ku70–Ku80 Heterodimer Levels of the Non-Homologous End Joining Repair Pathway in Lung Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8936. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188936








