Gαq-Stimulated Gene Expression Is Insensitive to Bromo Extra Terminal Domain Inhibitors in HEK 293 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Functional Validation of DREADD Constructs
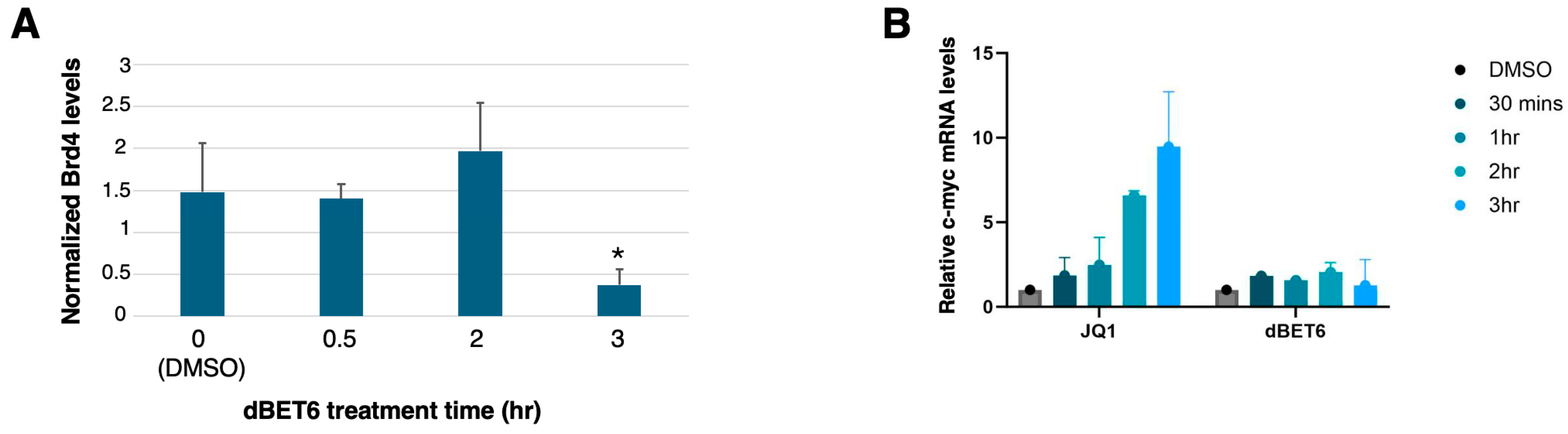
2.2. Confirmation of BET Inhibitor Activity
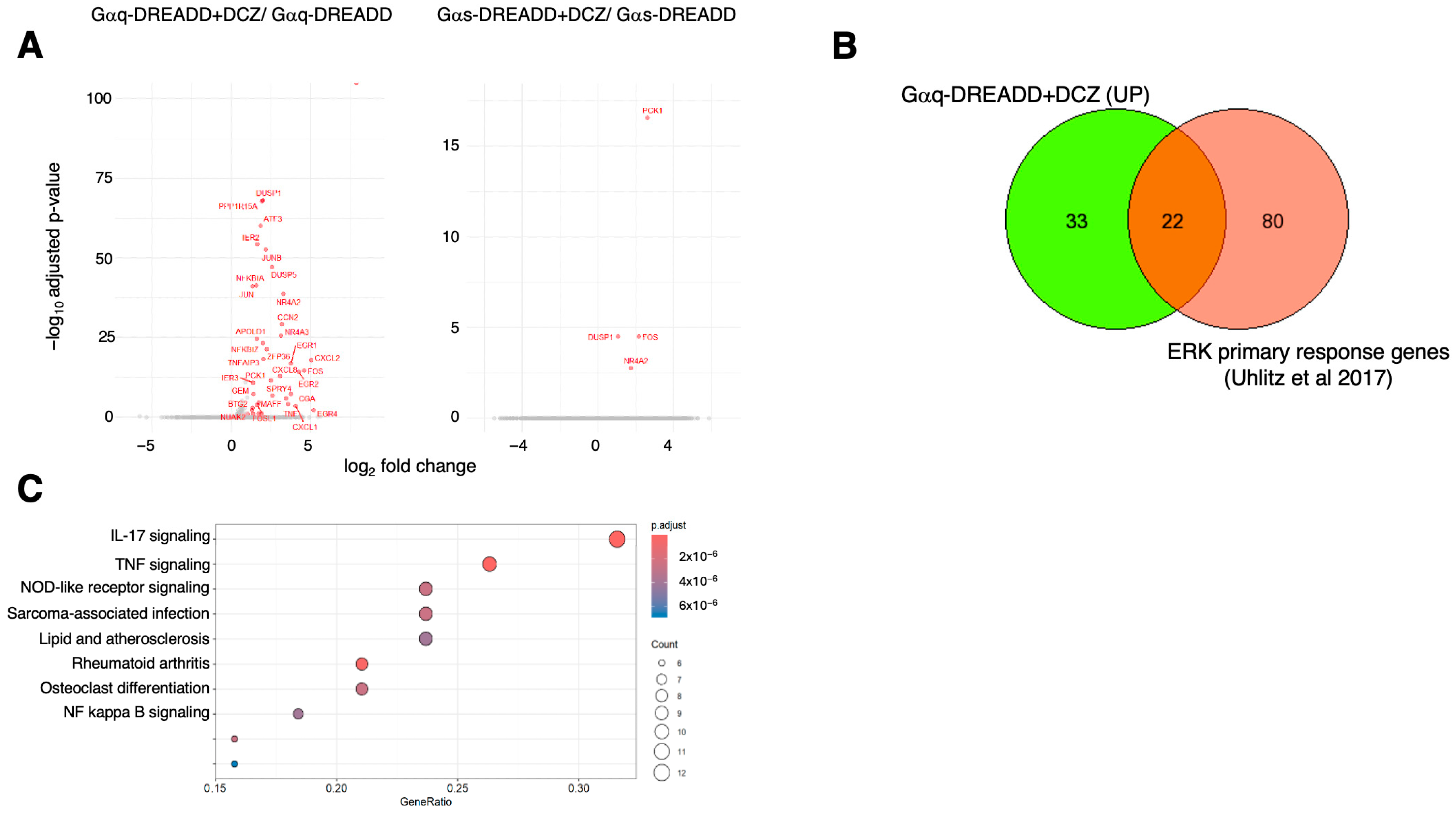
2.3. Analysis of G Protein Activation by RNA Sequencing
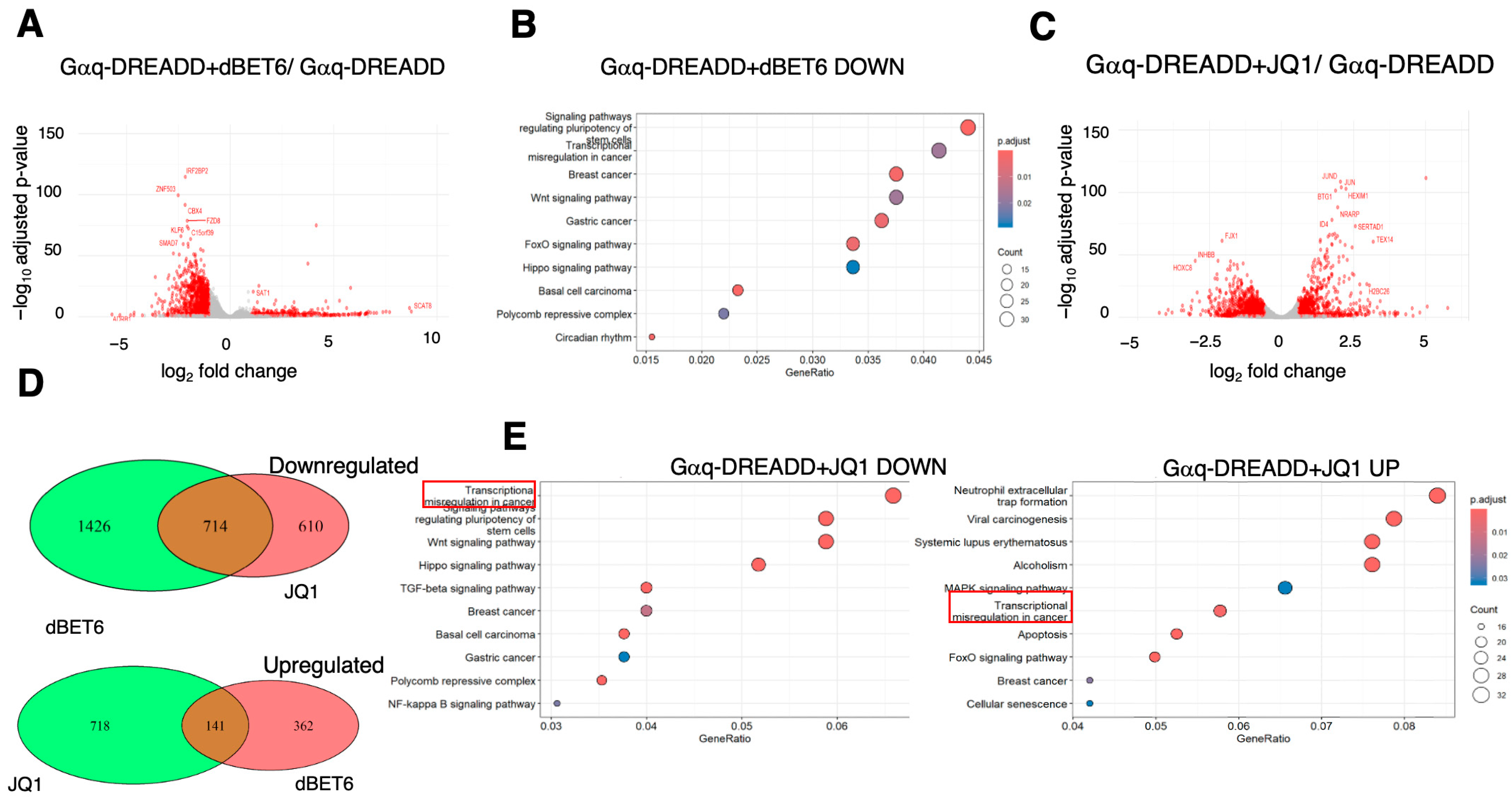
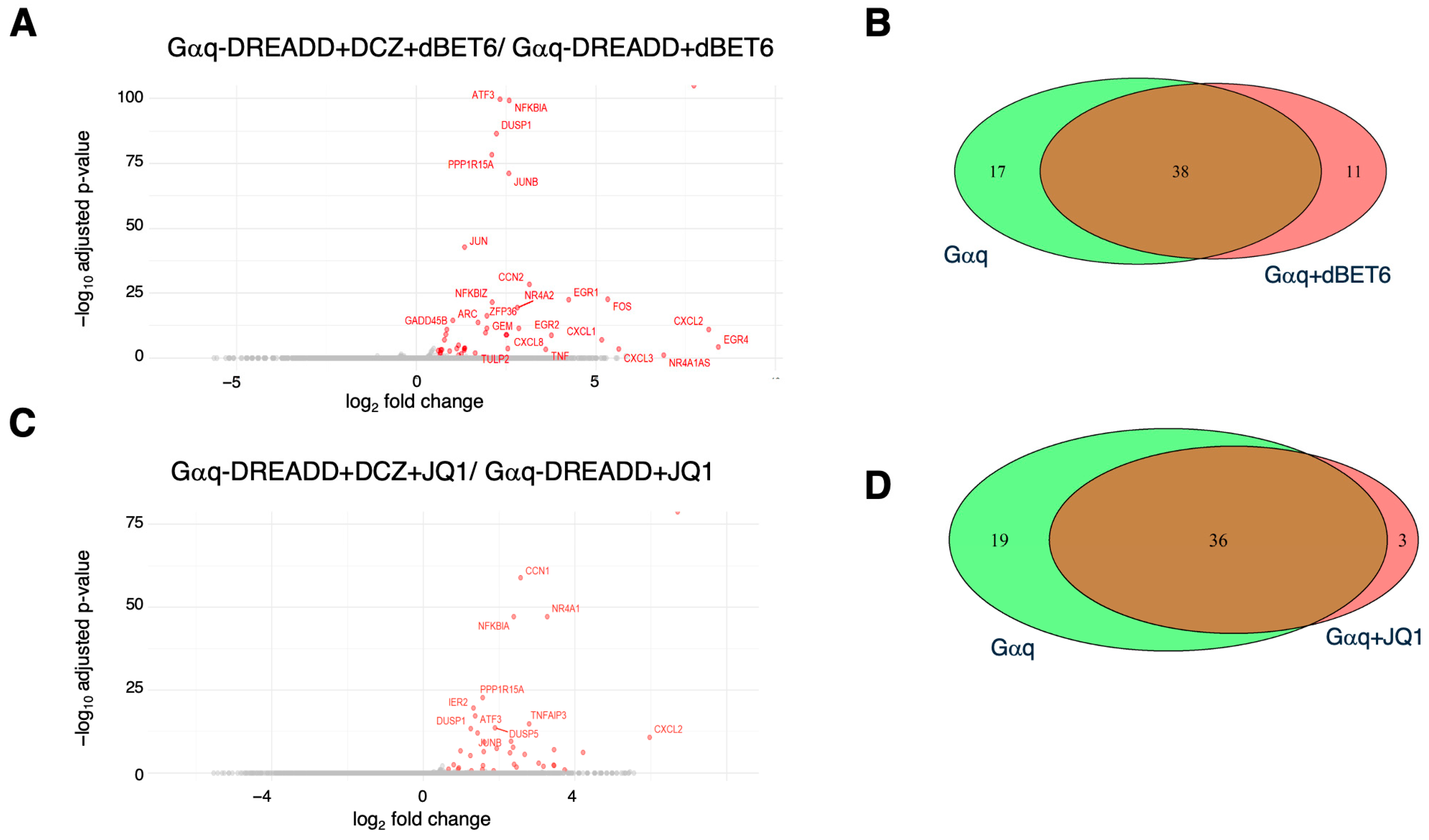
2.4. Effects of BET Inhibition on Gαq and Gαs-Mediated Gene Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Drugs
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Bioluminescence Resonance Transfer (BRET) Biosensor Assays
4.4. BRET Analysis
4.5. Protein Extraction and Immunoblotting
4.6. RNA Analysis by RT-qPCR
4.7. RNA-Sequencing
4.8. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fujisawa, T.; Filippakopoulos, P. Functions of bromodomain-containing proteins and their roles in homeostasis and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 246–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Vakoc, C.R. The mechanisms behind the therapeutic activity of BET bromodomain inhibition. Mol. Cell 2014, 54, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; McMahon, S.; Anand, P.; Shah, H.; Thomas, S.; Salunga, H.T.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Sahadevan, A.; Lemieux, M.E.; et al. BET bromodomain inhibition suppresses innate inflammatory and profibrotic transcriptional networks in heart failure. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah5084, Erratum in Sci. Transl. Med. 2025, 17, eadw3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Brown, J.D.; Lin, C.Y.; Qi, J.; Zhang, R.; Artero, P.C.; Alaiti, M.A.; Bullard, J.; Alazem, K.; Margulies, K.B.; et al. BET bromodomains mediate transcriptional pause release in heart failure. Cell 2013, 154, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiltoir, J.I.; Stratton, M.S.; Cavasin, M.A.; Demos-Davies, K.; Reid, B.G.; Qi, J.; Bradner, J.E.; McKinsey, T.A. BET acetyl-lysine binding proteins control pathological cardiac hypertrophy. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2013, 63, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzuk, M.M.; McKeown, M.R.; Filippakopoulos, P.; Li, Q.; Ma, L.; Agno, J.E.; Lemieux, M.E.; Picaud, S.; Yu, R.N.; Qi, J.; et al. Small-Molecule Inhibition of BRDT for Male Contraception. Cell 2012, 150, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wu, R.; Tang, D.; Kang, R. The BET family in immunity and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexanian, M.; Padmanabhan, A.; Nishino, T.; Travers, J.G.; Ye, L.; Pelonero, A.; Lee, C.Y.; Sadagopan, N.; Huang, Y.; Auclair, K.; et al. Chromatin remodelling drives immune cell–fibroblast communication in heart failure. Nature 2024, 635, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Sowa, M.E.; Ottinger, M.; Smith, J.A.; Shi, Y.; Harper, J.W.; Howley, P.M. The Brd4 Extraterminal Domain Confers Transcription Activation Independent of pTEFb by Recruiting Multiple Proteins, Including NSD3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 2641–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.-P.; Picaud, S.; Fujisawa, T.; Hou, H.; Savitsky, P.; Uusküla-Reimand, L.; Gupta, G.D.; Abdouni, H.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Tucholska, M.; et al. Interactome Rewiring Following Pharmacological Targeting of BET Bromodomains. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 621–638.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisgrove, D.A.; Mahmoudi, T.; Henklein, P.; Verdin, E. Conserved P-TEFb-interacting domain of BRD4 inhibits HIV transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13690–13695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwat, A.S.; Roe, J.-S.; Mok, B.Y.L.; Hohmann, A.F.; Shi, J.; Vakoc, C.R. BET Bromodomain Inhibition Releases the Mediator Complex from Select cis-Regulatory Elements. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.K.; Mochizuki, K.; Zhou, M.; Jeong, H.S.; Brady, J.N.; Ozato, K. The bromodomain protein Brd4 is a positive regulatory component of P-TEFb and stimulates RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription. Mol. Cell 2005, 19, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, M.A.; Prinjha, R.K.; Dittmann, A.; Giotopoulos, G.; Bantscheff, M.; Chan, W.I.; Robson, S.C.; Chung, C.W.; Hopf, C.; Savitski, M.M.; et al. Inhibition of BET recruitment to chromatin as an effective treatment for MLL-fusion leukaemia. Nature 2011, 478, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picaud, S.; Wells, C.; Felletar, I.; Brotherton, D.; Martin, S.; Savitsky, P.; Diez-Dacal, B.; Philpott, M.; Bountra, C.; Lingard, H.; et al. RVX-208, an inhibitor of BET transcriptional regulators with selectivity for the second bromodomain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19754–19759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilan, O.; Rioja, I.; Knezevic, K.; Bell, M.J.; Yeung, M.M.; Harker, N.R.; Lam, E.Y.N.; Chung, C.; Bamborough, P.; Petretich, M.; et al. Selective targeting of BD1 and BD2 of the BET proteins in cancer and immunoinflammation. Science 2020, 368, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borck, P.C.; Guo, L.-W.; Plutzky, J. BET Epigenetic Reader Proteins in Cardiovascular Transcriptional Programs. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1190–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, K.; Lu, J.; Qian, Y.; Altieri, M.; Gordon, D.; Rossi, A.M.K.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Dong, H.; Siu, K.; et al. PROTAC-induced BET protein degradation as a therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7124–7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, G.E.; Mayer, A.; Buckley, D.L.; Erb, M.A.; Roderick, J.E.; Vittori, S.; Reyes, J.M.; di Iulio, J.; Souza, A.; Ott, C.J.; et al. BET Bromodomain Proteins Function as Master Transcription Elongation Factors Independent of CDK9 Recruitment. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 5–18.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmore, J.E.; Issa, G.C.; Lemieux, M.E.; Rahl, P.B.; Shi, J.; Jacobs, H.M.; Kastritis, E.; Gilpatrick, T.; Paranal, R.M.; Qi, J.; et al. BET Bromodomain Inhibition as a Therapeutic Strategy to Target c-Myc. Cell 2011, 146, 904–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovén, J.; Hoke, H.A.; Lin, C.Y.; Lau, A.; Orlando, D.A.; Vakoc, C.R.; Bradner, J.E.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Selective Inhibition of Tumor Oncogenes by Disruption of Super-Enhancers. Cell 2013, 153, 320–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, W.A.; Orlando, D.A.; Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lin, C.Y.; Kagey, M.H.; Rahl, P.B.; Lee, T.I.; Young, R.A. Master Transcription Factors and Mediator Establish Super-Enhancers at Key Cell Identity Genes. Cell 2013, 153, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hnisz, D.; Abraham, B.J.; Lee, T.I.; Lau, A.; Saint-André, V.; Sigova, A.A.; Hoke, H.A.; Young, R.A. Super-Enhancers in the Control of Cell Identity and Disease. Cell 2013, 155, 934–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, F.H.; Johnsen, S.A. Super enhancers—New analyses and perspectives on the low hanging fruit. Transcription 2018, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Bedi, U.; Budida, A.; Hamdan, F.H.; Mishra, V.K.; Najafova, Z.; Xie, W.; Alawi, M.; Indenbirken, D.; Knapp, S.; et al. BRD4 promotes p63 and GRHL3 expression downstream of FOXO in mammary epithelial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3130–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafova, Z.; Tirado-Magallanes, R.; Subramaniam, M.; Hossan, T.; Schmidt, G.; Nagarajan, S.; Baumgart, S.J.; Mishra, V.K.; Bedi, U.; Hesse, E.; et al. BRD4 localization to lineage-specific enhancers is associated with a distinct transcription factor repertoire. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Lee, A.Y.; Lai, H.T.; Zhang, H.; Chiang, C.M. Phospho switch triggers Brd4 chromatin binding and activator recruitment for gene-specific targeting. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 843–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Yang, X.-D.; Zhou, M.-M.; Ozato, K.; Chen, L.-F. Brd4 Coactivates Transcriptional Activation of NF-κB via Specific Binding to Acetylated RelA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 1375–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, L.; Wu, Y.; Deng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Li, J.; Kang, T.; Tao, M.; et al. Disrupting the interaction of BRD4 with diacetylated Twist suppresses tumorigenesis in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Cao, X.J.; Kulej, K.; Liu, W.; Ma, T.; MacDonald, M.; Chiang, C.M.; Garcia, B.A.; You, J. Uncovering BRD4 hyperphosphorylation associated with cellular transformation in NUT midline carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5352–E5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yang, J.F.; Ho, F.; Robertson, E.S.; You, J. Bromodomain-Containing Protein BRD4 Is Hyperphosphorylated in Mitosis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, E.; Herre, M.; Zucker-Scharff, I.; Darnell, R.B.; Allis, C.D. BET protein Brd4 activates transcription in neurons and BET inhibitor Jq1 blocks memory in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2015, 18, 1464–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, Y.-A.; Xiao, Q.; Lee, W.C.; Cheng, B.; Niu, Z.; Oguz, G.; Feng, M.; Lee, P.L.; Li, B.; et al. Stromal induction of BRD4 phosphorylation Results in Chromatin Remodeling and BET inhibitor Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Gan, W.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, W.; Huang, L.; Liu, S.; Zhong, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Prostate cancer-associated SPOP mutations confer resistance to BET inhibitors through stabilization of BRD4. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, D.; Ding, D.; Ma, T.; Ye, Z.; Jimenez, R.; Wang, L.; Wu, H.; Huang, H. DUB3 Promotes BET Inhibitor Resistance and Cancer Progression by Deubiquitinating BRD4. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 592–605.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, S.; Gao, K.; Ye, Z.; Wang, S.; Pan, C.-W.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, Y.; et al. Intrinsic BET inhibitor resistance in SPOP-mutated prostate cancer is mediated by BET protein stabilization and AKT–mTORC1 activation. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.D.; Sun, Y.; MacKinnon, S.; Cuccia, L.; Pagé, V.; Hébert, T.E.; Tanny, J.C. Differential Activation of P-TEFb Complexes in the Development of Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy following Activation of Distinct G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2020, 40, e00048-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, R.D.; Sun, Y.; Bourque, K.; Audet, N.; Inoue, A.; Tanny, J.C.; Hébert, T.E. Receptor- and cellular compartment-specific activation of the cAMP/PKA pathway by α1-adrenergic and ETA endothelin receptors. Cell. Signal. 2018, 44, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armbruster, B.N.; Li, X.; Pausch, M.H.; Herlitze, S.; Roth, B.L. Evolving the lock to fit the key to create a family of G protein-coupled receptors potently activated by an inert ligand. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guettier, J.-M.; Gautam, D.; Scarselli, M.; de Azua, I.R.; Li, J.H.; Rosemond, E.; Ma, X.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Armbruster, B.N.; Lu, H.; et al. A chemical-genetic approach to study G protein regulation of β cell function in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19197–19202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, D.J.; Roth, B.L. DREADDs (Designer Receptors Exclusively Activated by Designer Drugs): Chemogenetic Tools with Therapeutic Utility. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, Y.; Miyakawa, N.; Takuwa, H.; Hori, Y.; Oyama, K.; Ji, B.; Takahashi, M.; Huang, X.-P.; Slocum, S.T.; DiBerto, J.F.; et al. Deschloroclozapine, a potent and selective chemogenetic actuator enables rapid neuronal and behavioral modulations in mice and monkeys. Nat. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 1157–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, E.; Rappaport, A.R.; Herrmann, H.; Sison, E.A.; Magoon, D.; Qi, J.; Blatt, K.; Wunderlich, M.; et al. RNAi screen identifies Brd4 as a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukaemia. Nature 2011, 478, 524–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartholomeeusen, K.; Xiang, Y.; Fujinaga, K.; Peterlin, B.M. Bromodomain and Extra-terminal (BET) Bromodomain Inhibition Activate Transcription via Transient Release of Positive Transcription Elongation Factor b (P-TEFb) from 7SK Small Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36609–36616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones-Tabah, J.; Martin, R.D.; Chen, J.J.; Tanny, J.C.; Clarke, P.B.S.; Hébert, T.E. A role for BET proteins in regulating basal, dopamine-induced and cAMP/PKA-dependent transcription in rat striatal neurons. Cell. Signal. 2022, 91, 110226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlitz, F.; Sieber, A.; Wyler, E.; Fritsche-Guenther, R.; Meisig, J.; Landthaler, M.; Klinger, B.; Blüthgen, N. An immediate–late gene expression module decodes ERK signal duration. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2017, 13, 928, Erratum in Mol Syst Biol. 2017, 13, 944. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20177986.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundmann, M.; Merten, N.; Malfacini, D.; Inoue, A.; Preis, P.; Simon, K.; Rüttiger, N.; Ziegler, N.; Benkel, T.; Schmitt, N.K.; et al. Lack of beta-arrestin signaling in the absence of active G proteins. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, M.; Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T.A.; Bourne, H.R. cAMP and beta gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins stimulate the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in COS-7 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 7851–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutkind, J.S. The Pathways Connecting G Protein-coupled Receptors to the Nucleus through Divergent Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Cascades*. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 1839–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cao, S.; He, L.; Gao, J.; Arab, J.P.; Cui, H.; Xuan, W.; Gao, Y.; Sehrawat, T.S.; Hamdan, F.H.; et al. Super enhancer regulation of cytokine-induced chemokine production in alcoholic hepatitis. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Browning, D.D.; Hay, N.; Mackman, N.; Ye, R.D. Activation of NF-κB by Bradykinin through a Gαq- and Gβγ-dependent Pathway That Involves Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase and Akt *. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24907–24914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.; Mehta, S.; Clark, M.; Walters, G.; Zhong, Y.; Lee, H.N.; Sunahara, R.K.; Zhang, J. Non-canonical β-adrenergic activation of ERK at endosomes. Nature 2022, 611, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.; Gold, S.; Iwanaszko, M.; Howard, B.C.; Wang, L.; Shilatifard, A. Distinct layers of BRD4-PTEFb reveal bromodomain-independent function in transcriptional regulation. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 2896–2910.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Zheng, R.; Tian, Y.; Jimenez, R.; Hou, X.; Weroha, S.J.; Wang, L.; Shi, L.; Huang, H. Retinoblastoma protein as an intrinsic BRD4 inhibitor modulates small molecule BET inhibitor sensitivity in cancer. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathert, P.; Roth, M.; Neumann, T.; Muerdter, F.; Roe, J.S.; Muhar, M.; Deswal, S.; Cerny-Reiterer, S.; Peter, B.; Jude, J.; et al. Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition. Nature 2015, 525, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukasheva, V.; Devost, D.; Le Gouill, C.; Namkung, Y.; Martin, R.D.; Longpre, J.M.; Amraei, M.; Shinjo, Y.; Hogue, M.; Lagace, M.; et al. Signal profiling of the b1AR reveals coupling to novel signalling pathways and distinct phenotypic responses mediated by b1AR and b2AR. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billard, E.; Torbey, A.; Inserra, A.; Grant, E.; Bertazzo, A.; De Gregorio, D.; Comai, S.; Chatenet, D.; Gobbi, G.; Hébert, T.E. Pharmacological characterization of cannabidiol as a negative allosteric modulator of the 5-HT2A receptor. Cell. Signal. 2025, 127, 111588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jain, A.; Pagé, V.; Devost, D.; Pétrin, D.; Hébert, T.E.; Tanny, J.C. Gαq-Stimulated Gene Expression Is Insensitive to Bromo Extra Terminal Domain Inhibitors in HEK 293 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188904
Jain A, Pagé V, Devost D, Pétrin D, Hébert TE, Tanny JC. Gαq-Stimulated Gene Expression Is Insensitive to Bromo Extra Terminal Domain Inhibitors in HEK 293 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188904
Chicago/Turabian StyleJain, Ashika, Viviane Pagé, Dominic Devost, Darlaine Pétrin, Terence E. Hébert, and Jason C. Tanny. 2025. "Gαq-Stimulated Gene Expression Is Insensitive to Bromo Extra Terminal Domain Inhibitors in HEK 293 Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188904
APA StyleJain, A., Pagé, V., Devost, D., Pétrin, D., Hébert, T. E., & Tanny, J. C. (2025). Gαq-Stimulated Gene Expression Is Insensitive to Bromo Extra Terminal Domain Inhibitors in HEK 293 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188904





