In Silico Assessment of Potential Geroprotectors: From Separate Endpoints to Complex Pharmacotherapeutic Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Activities
2.1.1. Prevention of Free Radical Oxidation
- Free radical scavenger;
- Antioxidant;
- Adenosine deaminase inhibitor;
- Lipid peroxidase inhibitor;
- Phosphatidic acid synthesis inhibitor;
- Chelator (Iron).
2.1.2. Maintenance of Mitochondrial Function
- Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor;
- Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) agonist.
2.1.3. Proteostasis Support
- RAGE receptor antagonist;
- Antiamyloidogenic;
- Autophagy inducer.
2.1.4. Senolytics/Senostatics
- Senolytic activity.
2.1.5. Suppression of Genomic Instability
- Antimutagenic;
- Telomerase stimulant;
- DNA-directed RNA polymerase inhibitor.
2.1.6. Epigenetic Regulators
- Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors (classes I–IV, isoforms 1–11, SIRT1–7);
- Sir2p inhibitor;
- Histone acetyltransferase (HAT) inhibitors (KAT2A/B, KAT5–7, p300, PCAF, RTT109);
- Nuclear receptor coactivator 1/3 inhibitors.
2.1.7. Aging-Related Signaling Pathway Inhibitors
- mTOR complex 1 inhibitor;
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors (alpha, beta, delta, gamma);
- Myc inhibitor;
- Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist;
- AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) subunit inhibitors.
2.1.8. Anti-Inflammatory Agents
- NF-κB pathway inhibitors (NF-κB1, NF-κB2, RelA, RelB);
- NRF2 stimulant;
- COX-2, iNOS inhibitors;
- IGF-1–6 antagonists;
- HIF-1α inhibitor.
2.1.9. Antifibrotic Agents
- TGF-β antagonists (isoforms 1–3);
- TGF-β receptor type I kinase inhibitor;
- SMAD3 inhibitor.
2.1.10. Neurotrophic Factors
- Neurotrophic factor enhancer;
- TRKB agonist.
2.1.11. Barrier Function Preservation
- Metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor.
2.1.12. Immunomodulators
- Estradiol 17β-dehydrogenase inhibitors (isoforms 1–3);
- 5-Alpha-reductase inhibitors (isoforms 1–2);
- Melatonin receptor agonists (subtypes 1–5);
- JAK/STAT pathway inhibitors (JAK1–3, STAT1–6).
2.1.13. Miscellaneous
- 5 Hydroxytryptamine 3 antagonist;
- 5 Hydroxytryptamine 7 agonist;
- Age-related macular degeneration treatment;
- Alpha 2 adrenoreceptor antagonist;
- Insulin growth factor antagonist;
- Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor.
2.2. Implementation
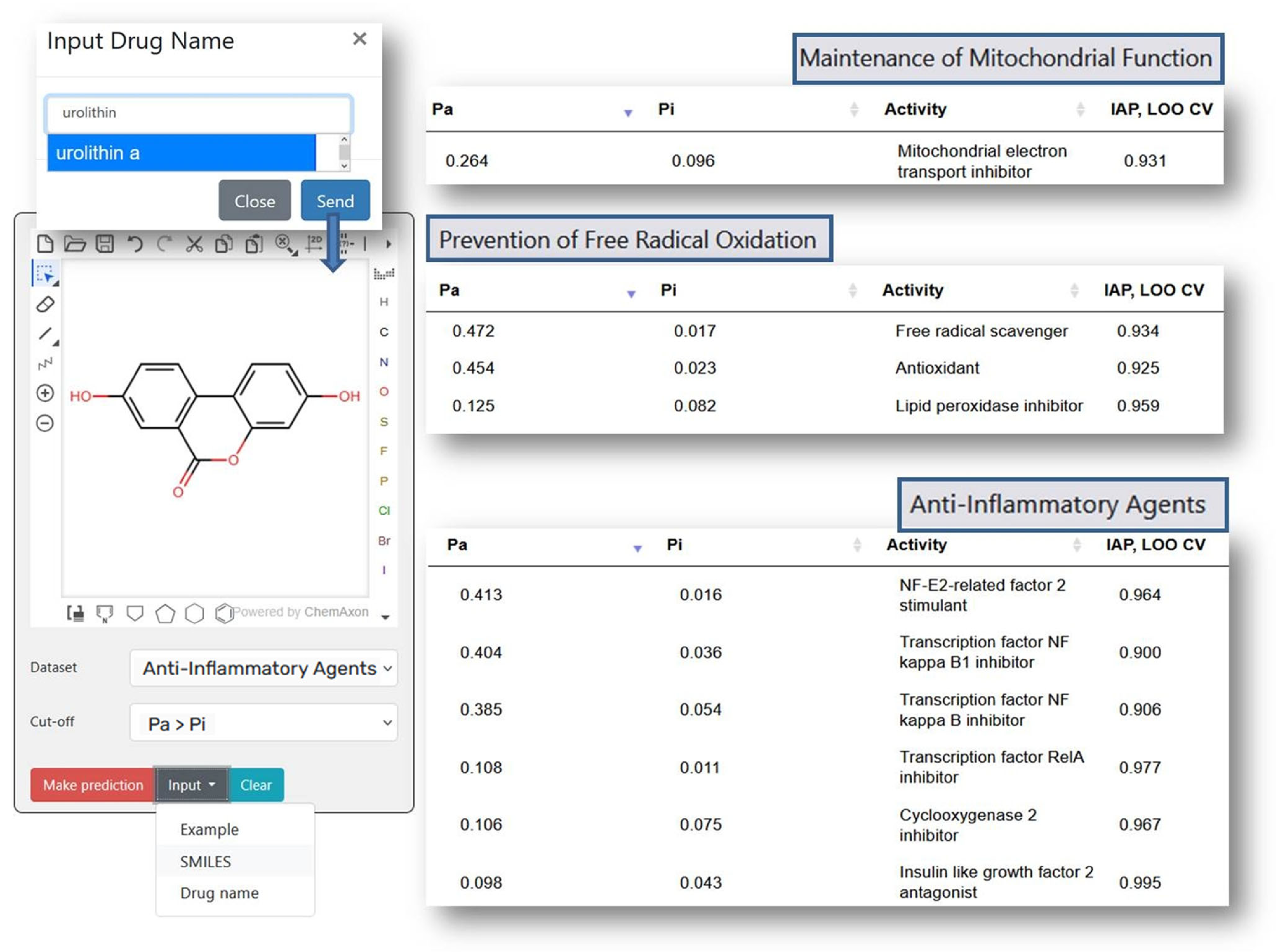
2.3. Web Application
3. Discussion
3.1. Relationship Between Mechanisms of Action and Predicted Activities
3.2. Polypharmacology and Prioritizing Predictions
3.3. Confidence, Validation, and Overprediction
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. The Training Set
- The number of substances in the training set: 1,483,030;
- The number of unique MNA descriptors: 141,153;
- The number of activities selected for the prediction: 117.
4.2. SAR Knowledgebase for Geroprotective Activities
4.3. Web Application
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IAP | Invariant Accuracy of Prediction |
| LOO CV | Leave-One-Out Cross-Validation |
| MoA | Mechanism of Action |
| PASS | Prediction of Activity Spectra for Substances |
| SAR | Structure-Activity Relationships |
References
- Harris, J.R.; Korolchuk, V.I. (Eds.) Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part I Biomedical Science; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 90, ISBN 978-981-13-2834-3. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, J.R.; Korolchuk, V.I. (Eds.) Biochemistry and Cell Biology of Ageing: Part II Clinical Science; Subcellular Biochemistry; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 91, ISBN 978-981-13-3680-5. [Google Scholar]
- Proshkina, E.; Shaposhnikov, M.; Moskalev, A. Genome-Protecting Compounds as Potential Geroprotectors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, C.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Li, T.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhen, H.; Ding, J.; et al. Distinct Biological Ages of Organs and Systems Identified from a Multi-Omics Study. Cell Rep. 2022, 38, 110459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenchov, R.; Sasso, J.M.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.A. Aging Hallmarks and Progression and Age-Related Diseases: A Landscape View of Research Advancement. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Huang, X.; Dou, L.; Yan, M.; Shen, T.; Tang, W.; Li, J. Aging and Aging-Related Diseases: From Molecular Mechanisms to Interventions and Treatments. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Magalhães, J.P. Distinguishing between Driver and Passenger Mechanisms of Aging. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothermund, K.; Englert, C.; Gerstorf, D. Explaining Variation in Individual Aging, Its Sources, and Consequences: A Comprehensive Conceptual Model of Human Aging. Gerontology 2023, 69, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, H.S.-H.; Rutledge, J.; Nachun, D.; Pálovics, R.; Abiose, O.; Moran-Losada, P.; Channappa, D.; Urey, D.Y.; Kim, K.; Sung, Y.J.; et al. Organ Aging Signatures in the Plasma Proteome Track Health and Disease. Nature 2023, 624, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalev, A.; Guvatova, Z.; Lopes, I.D.A.; Beckett, C.W.; Kennedy, B.K.; De Magalhaes, J.P.; Makarov, A.A. Targeting Aging Mechanisms: Pharmacological Perspectives. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 266–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjaneyulu, J.; Godbole, A. Small Organism Models for Mode of Action Research on Anti-Ageing and Nootropic Herbs, Foods, and Formulations. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 28, 744–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.B.; Kaeberlein, M. Translational Geroscience: From Invertebrate Models to Companion Animal and Human Interventions. Transl. Med. Aging 2018, 2, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, C.E.; Gill, M.S.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; Austad, S.N.; Barzilai, N.; Kirkland, J.L. Barriers to the Preclinical Development of Therapeutics That Target Aging Mechanisms: Table 1. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2016, 71, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, R.; Zi, Z.; Liu, B. A New Clinical Age of Aging Research. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 36, 440–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskalev, A.A. Potential Geroprotectors—From Bench to Clinic. Biochem. Mosc. 2023, 88, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
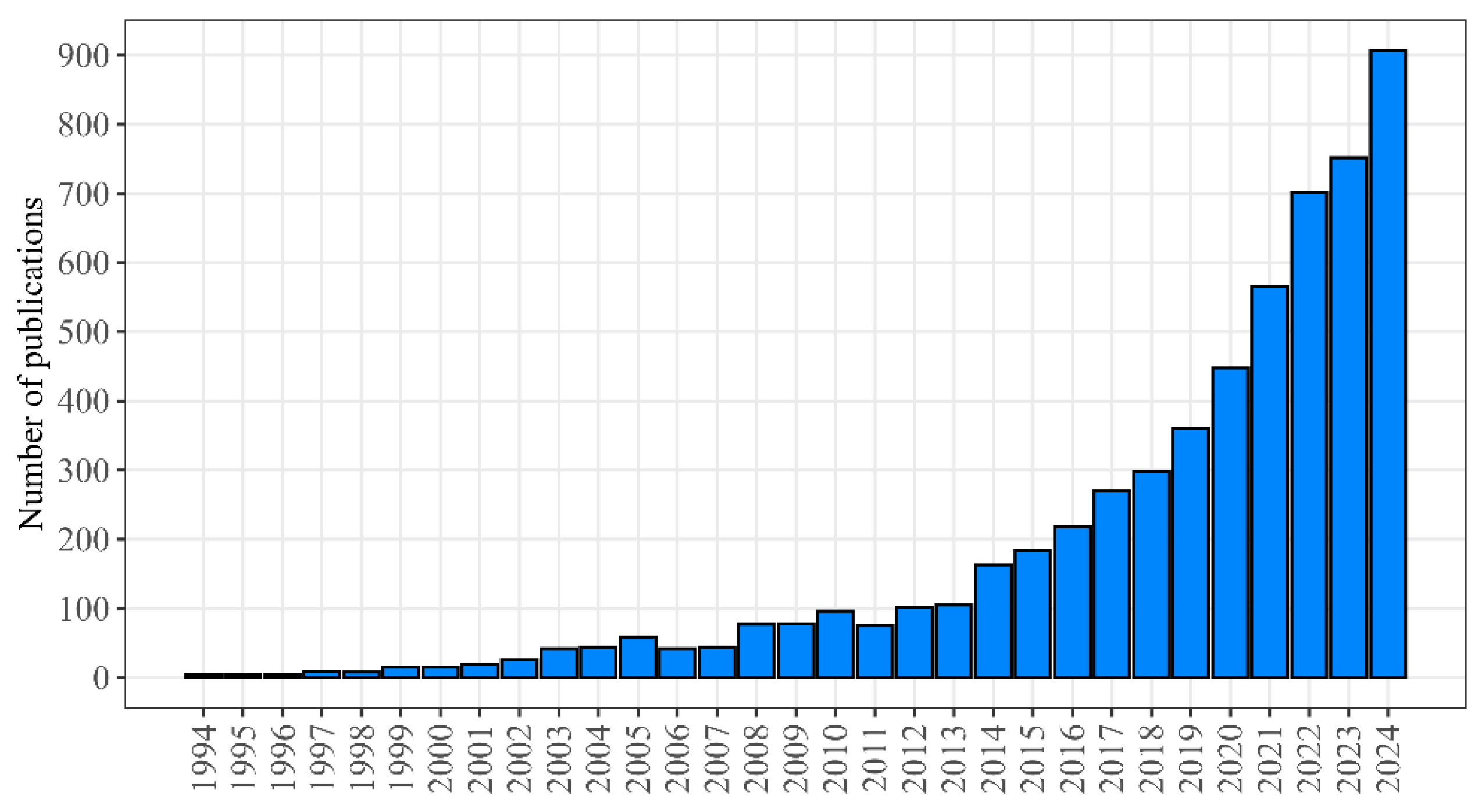
- PubMed. 2025. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=geroprotector+OR+antiaging+medicine (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, W. Review on Ginseng and Its Potential Active Substance G-Rg2 against Age-Related Diseases: Traditional Efficacy and Mechanism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 337, 118781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Luo, X.; Jia, K.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Qiao, G.; Zhang, C.; Yi, J. Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification to Explore the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Asparagus against Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Ovarian Res. 2023, 16, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, F.; Omori, S.; Donghia, N.M.; Zheng, E.J.; Collins, J.J. Discovering Small-Molecule Senolytics with Deep Neural Networks. Nat. Aging 2023, 3, 734–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smer-Barreto, V.; Quintanilla, A.; Elliott, R.J.R.; Dawson, J.C.; Sun, J.; Campa, V.M.; Lorente-Macías, Á.; Unciti-Broceta, A.; Carragher, N.O.; Acosta, J.C.; et al. Discovery of Senolytics Using Machine Learning. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliper, A.; Jellen, L.; Cortese, F.; Artemov, A.; Karpinsky-Semper, D.; Moskalev, A.; Swick, A.G.; Zhavoronkov, A. Towards Natural Mimetics of Metformin and Rapamycin. Aging 2017, 9, 2245–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhavoronkov, A.; Mamoshina, P.; Vanhaelen, Q.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; Moskalev, A.; Aliper, A. Artificial Intelligence for Aging and Longevity Research: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 49, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Mittal, A.; Duari, S.; Chauhan, S.; Dixit, N.K.; Mohanty, S.K.; Sharma, A.; Solanki, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Gautam, V.; et al. Discovering Geroprotectors through the Explainable Artificial Intelligence-Based Platform AgeXtend. Nat. Aging 2024, 5, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mervin, L.H.; Afzal, A.M.; Drakakis, G.; Lewis, R.; Engkvist, O.; Bender, A. Target Prediction Utilising Negative Bioactivity Data Covering Large Chemical Space. J. Cheminform. 2015, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocharova, O.A.; Ionov, N.S.; Kazeev, I.V.; Shevchenko, V.E.; Bocharov, E.V.; Karpova, R.V.; Sheychenko, O.P.; Aksyonov, A.A.; Chulkova, S.V.; Kucheryanu, V.G.; et al. Computer-aided Evaluation of Polyvalent Medications’ Pharmacological Potential. Multiphytoadaptogen as a Case Study. Mol. Inform. 2023, 42, 2200176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corominas-Faja, B.; Santangelo, E.; Cuyàs, E.; Micol, V.; Joven, J.; Ariza, X.; Segura-Carretero, A.; García, J.; Menendez, J.A. Computer-Aided Discovery of Biological Activity Spectra for Anti-Aging and Anti-Cancer Olive Oil Oleuropeins. Aging 2014, 6, 731–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillbro, J.M.; Lundahl, M.; Westman, M.; Baral, R.; Al-Bader, T.; Mavon, A. Structural Activity Relationship Analysis (SAR) and in Vitro Testing Reveal the Anti-ageing Potential Activity of Acetyl Aspartic Acid. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Madani, B.; Burzangi, A.S.; Alsieni, M.; Bazuhair, M.A.; Jamal, M.; Daghistani, H.; Barasheed, M.O.; Alkreathy, H.; Khan, M.A.; et al. Urolithin A’s Antioxidative, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antiapoptotic Activities Mitigate Doxorubicin-Induced Liver Injury in Wistar Rats. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- URO A Clinical Study. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32694802 (accessed on 6 August 2025).
- Milanović, Ž. Comprehensive Kinetic Investigation of Antiradical Activity of Urolithins and Their Potential Inhibitory Effect on Xanthine Dehydrogenase. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 408, 125330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.N.; Grillari, J. Current Senolytics: Mode of Action, Efficacy and Limitations, and Their Future. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 217, 111888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, S.E.; Khosla, S.; Baur, J.A.; De Cabo, R.; Musi, N. Drugs Targeting Mechanisms of Aging to Delay Age-Related Disease and Promote Healthspan: Proceedings of a National Institute on Aging Workshop. J. Gerontol. Ser. A 2023, 78, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushchenko, A.K.; Matchekhina, L.V.; Tkacheva, O.N.; Balashova, A.V.; Melnitskaia, A.A.; Churov, A.V.; Strazhesko, I.D. Senolytic Drugs: Implications for Clinical Practice. Probl. Gerosci. 2023, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsli, S.; Bellantuono, I. The Use of Geroprotectors to Prevent Multimorbidity: Opportunities and Challenges. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 193, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusri, K.; Kumar, S.; Fong, S.; Gruber, J.; Sorrentino, V. Towards Healthy Longevity: Comprehensive Insights from Molecular Targets and Biomarkers to Biological Clocks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramwell, L.R.; Frankum, R.; Harries, L.W. Repurposing Drugs for Senotherapeutic Effect: Potential Senomorphic Effects of Female Synthetic Hormones. Cells 2024, 13, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.M.; Park, J.H. Pleiotropic Benefits of DPP-4 Inhibitors Beyond Glycemic Control. Clin. Med. Insights Endocrinol. Diabetes 2021, 14, 11795514211051698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajebishak, Y.; Alivand, M.; Faghfouri, A.H.; Moludi, J.; Payahoo, L. The Effects of Vitamins and Dietary Pattern on Epigenetic Modification of Non-Communicable Diseases: A Review. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2023, 93, 362–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagosklonny, M.V. Anti-Aging: Senolytics or Gerostatics (Unconventional View). Oncotarget 2021, 12, 1821–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhou, X.; Xu, K.; Liu, S.; Zhu, X.; Yang, J. The Safety and Antiaging Effects of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide in Human Clinical Trials: An Update. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 1416–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-D.; Luo, M.; Huang, S.-Y.; Saimaiti, A.; Shang, A.; Gan, R.-Y.; Li, H.-B. Effects and Mechanisms of Resveratrol on Aging and Age-Related Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9932218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, A.; Wolf, B.; Huang, C.-K.; Glage, S.; Hofer, S.J.; Bankstahl, M.; Bär, C.; Thum, T.; Kahl, K.G.; Sigrist, S.J.; et al. Novel Aspects of Age-Protection by Spermidine Supplementation Are Associated with Preserved Telomere Length. GeroScience 2021, 43, 673–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín-Márquez, R.; Alarcón-Aguilar, A.; López-Diazguerrero, N.E.; Chondrogianni, N.; Königsberg, M. Sulforaphane—Role in Aging and Neurodegeneration. GeroScience 2019, 41, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan, C.; Tyler, E.J.; Ecker, S.; Webster, A.P.; Stead, E.R.; Martinez-Miguel, V.E.; Milligan, D.; Garbe, J.C.; Stampfer, M.R.; Beck, S.; et al. An Expedited Screening Platform for the Discovery of Anti-Ageing Compounds in Vitro and in Vivo. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuerec, A.H.; Lim, X.K.; Khoo, A.L.; Sandalova, E.; Guan, L.; Feng, L.; Maier, A.B. Targeting Aging with Urolithin A in Humans: A Systematic Review. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 100, 102406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavenier, J.; Nehlin, J.O.; Houlind, M.B.; Rasmussen, L.J.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L.; Andersen, O.; Rasmussen, L.J.H. Fisetin as a Senotherapeutic Agent: Evidence and Perspectives for Age-Related Diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 222, 111995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, D.A.; Druzhilovskiy, D.S.; Lagunin, A.A.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Rudik, A.V.; Dmitriev, A.V.; Pogodin, P.V.; Poroikov, V.V. Computer-Aided Prediction of Biological Activity Spectra for Chemical Compounds: Opportunities and Limitation. Biomed. Chem. Res. Methods 2018, 1, e00004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V. Probabilistic Approaches in Activity Prediction. In Chemoinformatics Approaches to Virtual Screening; Varnek, A., Tropsha, A., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2008; pp. 182–216. ISBN 978-0-85404-144-2. [Google Scholar]
- Filimonov, D.A.; Lagunin, A.A.; Gloriozova, T.A.; Rudik, A.V.; Druzhilovskii, D.S.; Pogodin, P.V.; Poroikov, V.V. Prediction of the Biological Activity Spectra of Organic Compounds Using the Pass Online Web Resource. Chem. Heterocycl. Compd. 2014, 50, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V.; Borodina, Y.; Gloriozova, T. Chemical Similarity Assessment through Multilevel Neighborhoods of Atoms: Definition and Comparison with the Other Descriptors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 1999, 39, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N * | IAP ** | Geroprotective Activity |
|---|---|---|
| Category | Prevention of Free Radical Oxidation | |
| 2641 | 0.934 | Free radical scavenger |
| 4991 | 0.925 | Antioxidant |
| 315 | 0.988 | Adenosine deaminase inhibitor |
| 1153 | 0.959 | Lipid peroxidase inhibitor |
| 799 | 0.967 | Chelator |
| 45 | 0.986 | Chelator, Iron |
| Category | Maintenance of Mitochondrial Function | |
| 4 | 0.931 | Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor |
| 3444 | 0.986 | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist |
| Category | Proteostasis Support | |
| 56 | 0.919 | RAGE receptor antagonist |
| 3286 | 0.931 | Antiamyloidogenic |
| 500 | 0.836 | Autophagy inducer |
| Category | Senolytics/senostatics | |
| 44 | 0.897 | Senolytic |
| Category | Suppression of Genomic Instability | |
| 40 | 0.974 | Antimutagenic |
| 11 | 0.999 | Telomerase stimulant |
| 3232 | 0.967 | DNA-directed RNA polymerase inhibitor |
| Category | Epigenetic Regulators | |
| 4997 | 0.993 | Histone deacetylase 1 inhibitor |
| 2138 | 0.992 | Histone deacetylase 2 inhibitor |
| 1744 | 0.996 | Histone deacetylase 3 inhibitor |
| 1110 | 0.994 | Histone deacetylase 4 inhibitor |
| 1879 | 0.993 | Histone deacetylase 5 inhibitor |
| 3455 | 0.994 | Histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor |
| 533 | 0.992 | Histone deacetylase 7 inhibitor |
| 1637 | 0.992 | Histone deacetylase 8 inhibitor |
| 501 | 0.990 | Histone deacetylase 9 inhibitor |
| 581 | 0.995 | Histone deacetylase 10 inhibitor |
| 656 | 0.994 | Histone deacetylase 11 inhibitor |
| 8 | 1.000 | Histone deacetylase 1A inhibitor |
| 42 | 1.000 | Histone deacetylase 1B inhibitor |
| 337 | 0.956 | Histone deacetylase SIRT1 inhibitor |
| 311 | 0.981 | Histone deacetylase SIRT1 stimulant |
| 586 | 0.986 | Histone deacetylase SIRT2 inhibitor |
| 5 | 0.999 | Histone deacetylase SIRT2 stimulant |
| 161 | 0.982 | Histone deacetylase SIRT3 inhibitor |
| 68 | 0.995 | Histone deacetylase SIRT5 inhibitor |
| 14 | 0.885 | Histone deacetylase SIRT6 inhibitor |
| 6219 | 0.992 | Histone deacetylase class I inhibitor |
| 5008 | 0.993 | Histone deacetylase class II inhibitor |
| 2566 | 0.993 | Histone deacetylase class IIa inhibitor |
| 3485 | 0.994 | Histone deacetylase class IIb inhibitor |
| 803 | 0.968 | Histone deacetylase class III inhibitor |
| 656 | 0.994 | Histone deacetylase class IV inhibitor |
| 10,985 | 0.984 | Histone deacetylase inhibitor |
| 35 | 0.955 | Histone acetyltransferase KAT2A inhibitor |
| 97 | 0.990 | Histone acetyltransferase KAT2B inhibitor |
| 21 | 0.965 | Histone acetyltransferase KAT5 inhibitor |
| 243 | 0.999 | Histone acetyltransferase KAT6A inhibitor |
| 11 | 0.980 | Histone acetyltransferase KAT7 inhibitor |
| 41 | 0.973 | Histone acetyltransferase PCAF inhibitor |
| 84 | 0.989 | Histone acetyltransferase RTT109 inhibitor |
| 1100 | 0.935 | Histone acetyltransferase inhibitor |
| 399 | 0.974 | Histone acetyltransferase p300 inhibitor |
| 115 | 0.891 | Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 inhibitor |
| 171 | 0.840 | Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor |
| Category | Aging-related Signaling Pathway Inhibitors | |
| 310 | 0.964 | mTOR complex 1 inhibitor |
| 11,736 | 0.989 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha inhibitor |
| 2922 | 0.988 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase beta inhibitor |
| 4994 | 0.989 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase delta inhibitor |
| 6895 | 0.986 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase gamma inhibitor |
| 18,093 | 0.984 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor |
| 507 | 0.986 | Myc inhibitor |
| 6176 | 0.994 | Angiotensin AT1 receptor antagonist |
| 1625 | 0.998 | Angiotensin AT1A receptor antagonist |
| 1413 | 0.999 | Angiotensin AT1B receptor antagonist |
| 394 | 0.934 | AMP-activated protein kinase inhibitor |
| 311 | 0.930 | AMP-activated protein kinase, alpha-1 subunit inhibitor |
| 43 | 0.955 | AMP-activated protein kinase, alpha-2 subunit inhibitor |
| 18 | 0.892 | AMP-activated protein kinase, beta-1 subunit inhibitor |
| 15 | 0.945 | AMP-activated protein kinase, gamma-1 subunit inhibitor |
| Category | Anti-Inflammatory Agents | |
| 1787 | 0.906 | Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor |
| 483 | 0.900 | Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor |
| 74 | 0.995 | Transcription factor NF kappa B2 inhibitor |
| 99 | 0.977 | Transcription factor RelA inhibitor |
| 10 | 0.964 | NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant |
| 4885 | 0.992 | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 inhibitor |
| 1699 | 0.980 | Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor |
| 7079 | 0.967 | Cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor |
| 2327 | 0.960 | Ribosomal protein S6 kinase inhibitor |
| 3898 | 0.979 | Insulin growth factor antagonist |
| 3854 | 0.979 | Insulin like growth factor 1 antagonist |
| 3 | 0.995 | Insulin like growth factor 2 antagonist |
| 44 | 1.000 | Insulin like growth factor 3 antagonist |
| 2125 | 0.913 | Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha inhibitor |
| Category | Antifibrotic Agents | |
| 4088 | 0.929 | Fibrosis treatment |
| 2115 | 0.988 | Transforming growth factor beta 1 antagonist |
| 182 | 0.991 | Transforming growth factor beta 2 antagonist |
| 75 | 0.965 | Transforming growth factor beta 3 antagonist |
| 2367 | 0.980 | Transforming growth factor beta antagonist |
| 210 | 0.996 | TGF beta receptor type I kinase inhibitor |
| 29 | 0.857 | SMAD3 inhibitor |
| Category | Neurotrophic Factors | |
| 524 | 0.963 | Neurotrophic factor |
| 77 | 0.934 | Neurotrophic factor enhancer |
| 59 | 0.974 | TRKB agonist |
| Category | Barrier Function Preservation | |
| 2975 | 0.980 | Metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor |
| Category | Immunomodulators | |
| 704 | 0.997 | Estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase 1 inhibitor |
| 579 | 0.994 | Estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase 2 inhibitor |
| 302 | 0.996 | Estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase 3 inhibitor |
| 1232 | 0.994 | Estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase inhibitor |
| 687 | 0.996 | 5-Alpha-reductase 1 inhibitor |
| 642 | 0.994 | 5-Alpha-reductase 2 inhibitor |
| 1738 | 0.994 | 5-Alpha-reductase inhibitor |
| 372 | 0.995 | Melatonin receptor 1 agonist |
| 188 | 0.997 | Melatonin receptor 2 agonist |
| 615 | 0.995 | Melatonin receptor agonist |
| 6346 | 0.992 | Janus tyrosine kinase 1 inhibitor |
| 10,871 | 0.980 | Janus tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor |
| 8003 | 0.983 | Janus tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitor |
| 15,102 | 0.978 | Janus tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| 1174 | 0.918 | Transcription factor STAT inhibitor |
| 26 | 0.831 | Transcription factor STAT1 inhibitor |
| 881 | 0.925 | Transcription factor STAT3 inhibitor |
| 47 | 0.874 | Transcription factor STAT5 inhibitor |
| 247 | 0.957 | Transcription factor STAT6 inhibitor |
| Category | Miscellaneous | |
| 2435 | 0.988 | 5 Hydroxytryptamine 3 antagonist |
| 91 | 0.986 | 5 Hydroxytryptamine 7 agonist |
| 116 | 0.916 | Age-related macular degeneration treatment |
| 2772 | 0.975 | Alpha 2 adrenoreceptor antagonist |
| 2226 | 0.998 | Sodium/glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor |
| Name and Structure | MoA * | Predicted Activities |
|---|---|---|
Atorvastatin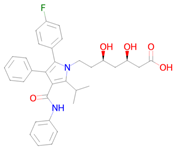 | Targeting senescent cells, inhibition of CDKN2A expression [36] | Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor Senolytic |
Acetylsalicylic acid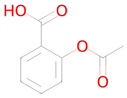 | Targeting senescent cells, inhibition of CDKN2A expression [36] | Transcription factor STAT1 inhibitor Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor SMAD3 inhibitor Autophagy inducer Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor Free radical scavenger Transcription factor STAT inhibitor NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Antioxidant Antimutagenic Histone deacetylase SIRT6 inhibitor Neurotrophic factor enhancer Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor Chelator |
Vildagliptin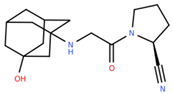 | Reduction in stress-induced cellular senescence rate [37] | Senolytic |
Dasatinib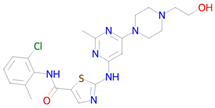 | Targeting senescent cells, inhibition of PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase) [14] | Senolytic |
Quercetin | Targeting senescent cells, inhibition of PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase) [14] | Senolytic |
Curcumin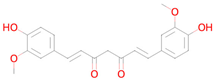 | Inhibitor of DNMT1, DNMT3B, HATs, HDAC2, and HDAC8 [38] | Free radical scavenger Antioxidant Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor Antimutagenic Antiamyloidogenic Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor Autophagy inducer SMAD3 inhibitor Transcription factor STAT inhibitor Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor Histone acetyltransferase inhibitor Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor Lipid peroxidase inhibitor Chelator NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor Insulin like growth factor 2 antagonist Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 inhibitor |
Metformin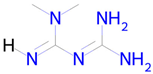 | Autophagy, mitochondrial biogenesis [14] | Histone deacetylase SIRT6 inhibitor Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant |
Navitoclax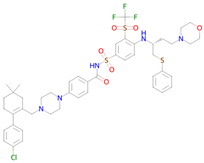 | Targeting senescent cells, inhibition of Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl [39] | Senolytic Transcription factor STAT5 inhibitor |
Nicotinamide riboside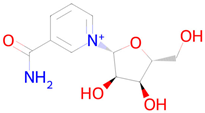 | Replenishment of NAD+ deficiency [40] | Autophagy inducer Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor Transcription factor NF kappa inhibitor Histone deacetylase SIRT1 stimulant Transcription factor STAT inhibitor Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor |
Rapamycin (Sirolimus)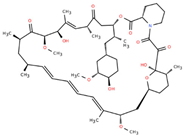 | Targeting senescent cells, mTOR inhibitor [14] | Senolytic mTOR complex 1 inhibitor Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor Neurotrophic factor Fibrosis treatment Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor |
Resveratrol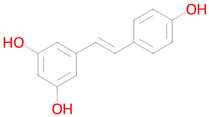 | Reduction in oxidative stress, anti-inflammatory effect, improvement of mitochondrial function, regulation of apoptosis [41] | Autophagy inducer Antimutagenic Free radical scavenger Antioxidant SMAD3 inhibitor Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor Antiamyloidogenic Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor Histone deacetylase SIRT2 stimulant Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Chelator Lipid peroxidase inhibitor Histone deacetylase SIRT1 stimulant Transcription factor STAT inhibitor Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 inhibitor Neurotrophic factor enhancer Insulin like growth factor 2 antagonist Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor Histone acetyltransferase inhibitor Transcription factor RelA inhibitor Senolytic |
Spermidine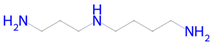 | Autophagy inducer [42] | Autophagy inducer Antimutagenic Histone deacetylase SIRT6 inhibitor Chelator Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Antiamyloidogenic Transcription factor STAT1 inhibitor Histone deacetylase SIRT1 inhibitor Inducible nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor SMAD3 inhibitor Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 inhibitor Transcription factor STAT inhibitor Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor |
Sulforophane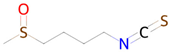 | Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, proteasome activation [43] | NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Transcription factor STAT1 inhibitor Inducible nitric-oxide synthase inhibitor Antioxidant Antiamyloidogenic |
Torin 2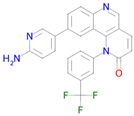 | Inhibitor of TORC1 and TORC2 [44] | Transcription factor STAT1 inhibitor Fibrosis treatment AMP-activated protein kinase inhibitor mTOR complex 1 inhibitor |
Urolithin A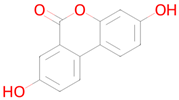 | Mitophagy [45] | Antimutagenic SMAD3 inhibitor RAGE receptor antagonist Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor Free radical scavenger Antioxidant Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Antiamyloidogenic Autophagy inducer Neurotrophic factor enhancer Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor Nuclear receptor coactivator 1 inhibitor Transcription factor STAT inhibitor Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor 17 beta-dehydrogenase 3 inhibitor Senolytic |
Fisetin | Targeting senescent cells, inhibition of PI3K (Phosphoinositide 3-kinase) [46] | Antimutagenic Free radical scavenger Antioxidant SMAD3 inhibitor Autophagy inducer TRKB agonist Nuclear receptor coactivator 3 inhibitor Transcription factor NF kappa B inhibitor Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibitor NF-E2-related factor 2 stimulant Transcription factor NF kappa B1 inhibitor Lipid peroxidase inhibitor Mitochondrial electron transport inhibitor Histone deacetylase SIRT2 stimulant Antiamyloidogenic Transcription factor STAT inhibitor Chelator Histone deacetylase SIRT1 stimulant RAGE receptor antagonist Estradiol 17 beta-dehydrogenase inhibitor Neurotrophic factor enhancer |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stolbov, L.; Rudik, A.; Lagunin, A.; Druzhilovskiy, D.; Filimonov, D.; Poroikov, V. In Silico Assessment of Potential Geroprotectors: From Separate Endpoints to Complex Pharmacotherapeutic Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188858
Stolbov L, Rudik A, Lagunin A, Druzhilovskiy D, Filimonov D, Poroikov V. In Silico Assessment of Potential Geroprotectors: From Separate Endpoints to Complex Pharmacotherapeutic Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(18):8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188858
Chicago/Turabian StyleStolbov, Leonid, Anastasia Rudik, Alexey Lagunin, Dmitry Druzhilovskiy, Dmitry Filimonov, and Vladimir Poroikov. 2025. "In Silico Assessment of Potential Geroprotectors: From Separate Endpoints to Complex Pharmacotherapeutic Effects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 18: 8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188858
APA StyleStolbov, L., Rudik, A., Lagunin, A., Druzhilovskiy, D., Filimonov, D., & Poroikov, V. (2025). In Silico Assessment of Potential Geroprotectors: From Separate Endpoints to Complex Pharmacotherapeutic Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(18), 8858. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26188858







