Novel 3-Dehydroteasterone Derivatives with 23,24-Dinorcholanic Side Chain and Benzoate Groups at C-22: Synthesis and Activity Evaluation by Rice Lamina Inclination Test and Bean Second-Internode Bioassay
Abstract
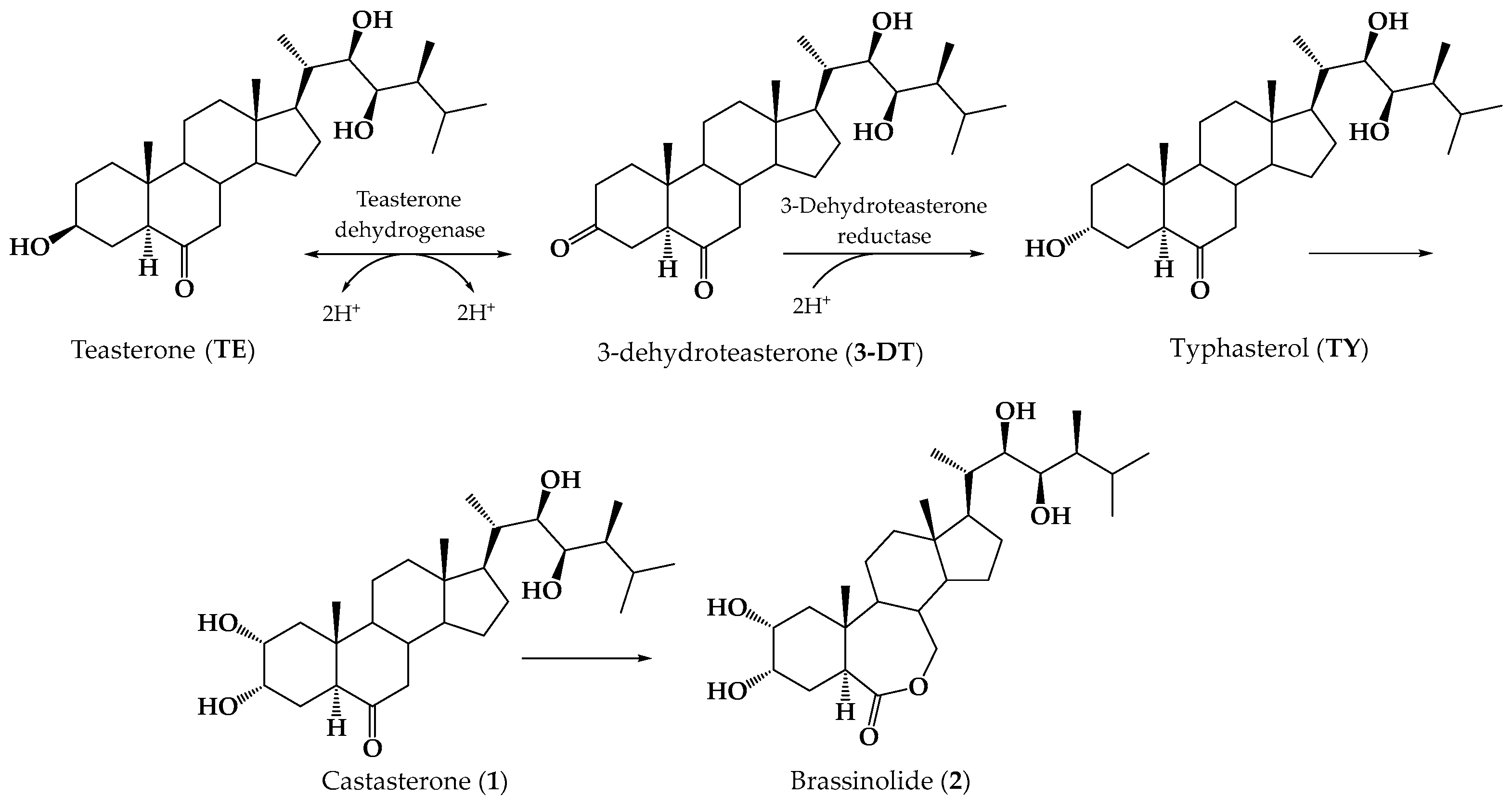
1. Introduction
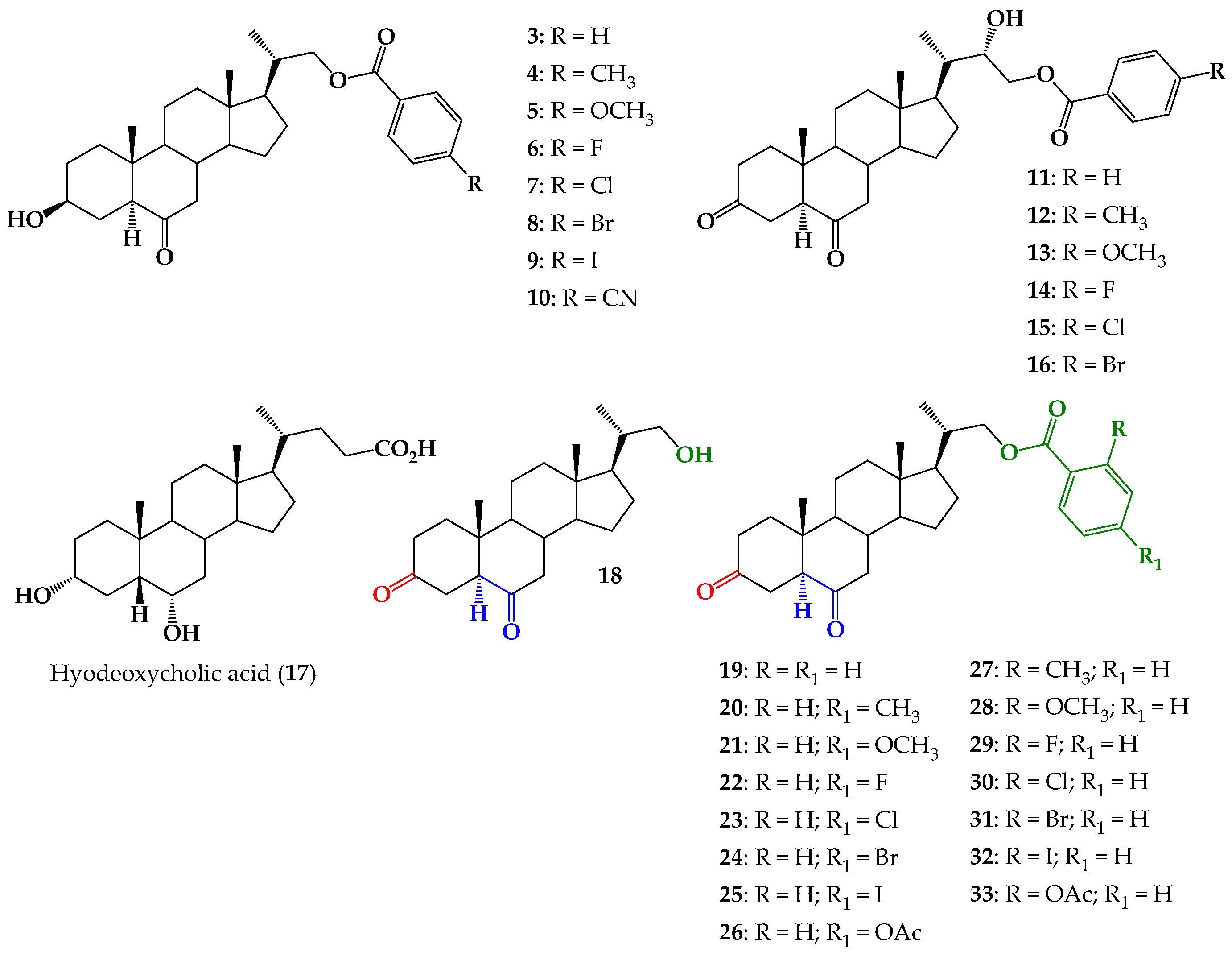
2. Results and Discussion
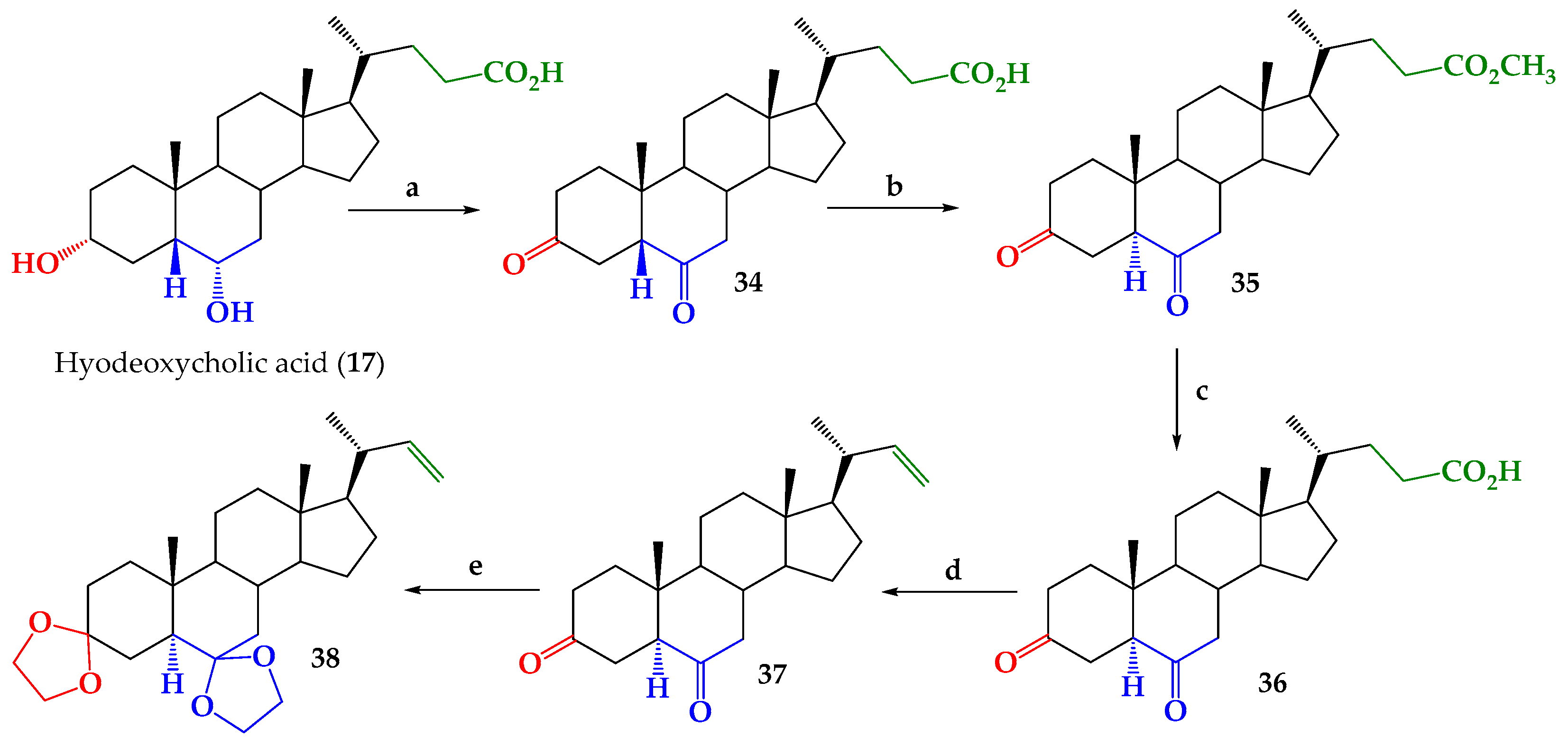
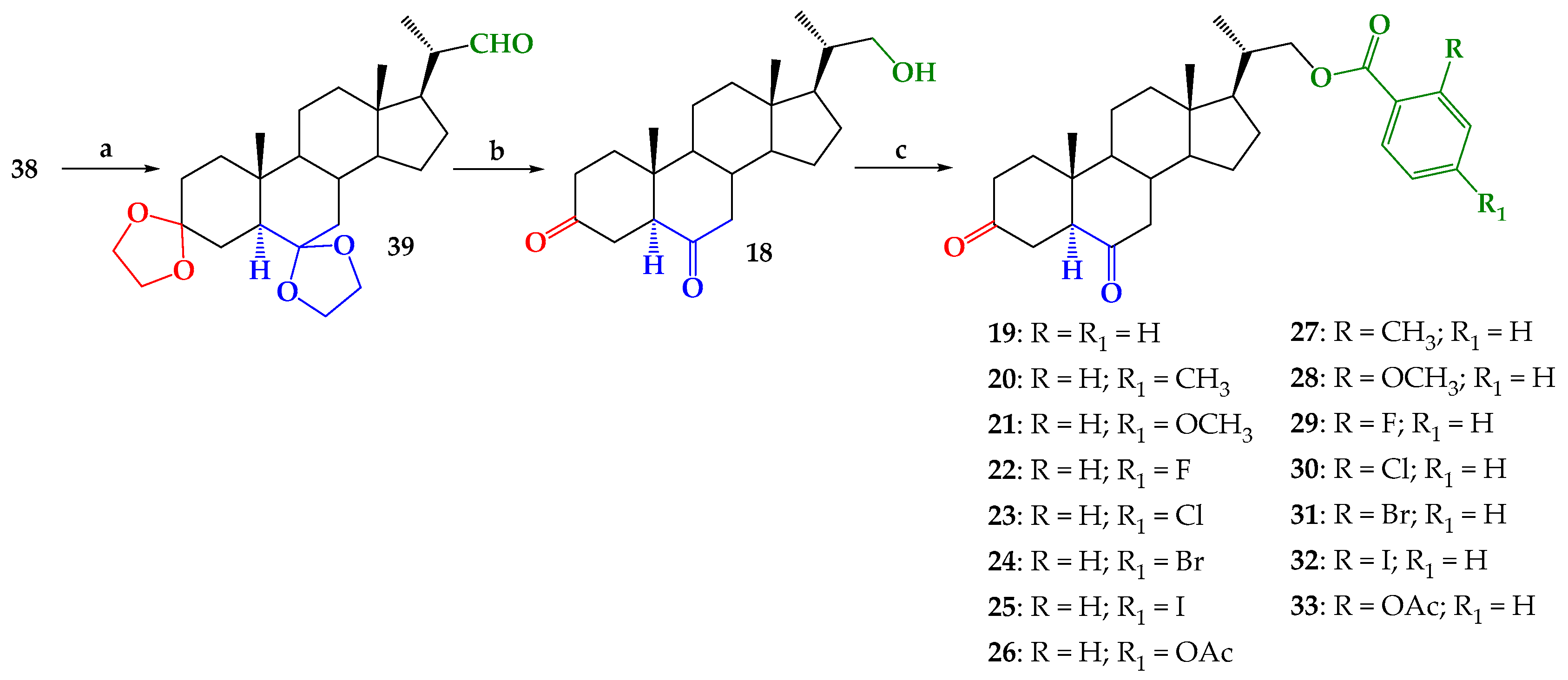
2.1. Chemical Synthesis
2.2. Biological Activity
2.2.1. Bioactivity in the Rice Lamina Inclination Test (RLIT)
2.2.2. Bioactivity in Bean Second-Internode Bioassay (BSI)
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Chemicals and Methods
3.2. Synthesis
3.2.1. 3,6-Dioxo-5β-cholan-24-oic acid (34)
3.2.2. Methyl 3,6-Dioxo-5α-cholan-24-oate (35)
3.2.3. 3,6-Dioxo-5α-cholan-24-oic Acid (36)
3.2.4. 24-Nor-5α-chol-22-ene-3,6-dione (37)
3.2.5. 3,6-Didioxolan-24-nor-5α-cholan-22-ene (38)
3.2.6. 3,6-Didioxolan-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-22-al (39)
3.2.7. 22-Hydroxy-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-3,6-dione (18)
3.2.8. 3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-substituted or 2-substituted)-benzoate-22-yl (19–33)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-benzoate-22-yl (19)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-methyl)-benzoate-22-yl (20)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-methoxy)-benzoate-22-yl (21)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-fluoro)-benzoate-22-yl (22)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-chloro)-benzoate-22-yl (23)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-bromo)-benzoate-22-yl (24)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-iodo)-benzoate-22-yl (25)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(4-acetoxy)-benzoate-22-yl (26)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-methyl)-benzoate-22-yl (27)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-methoxy)-benzoate-22-yl (28)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-fluoro)-benzoate-22-yl (29)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-chloro)-benzoate-22-yl (30)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-bromo)-benzoate-22-yl (31)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-iodo)-benzoate-22-yl (32)
3,6-Dioxo-23,24-dinor-5α-cholan-(2-acetoxy)-benzoate-22-yl (33)
3.3. Bioactivity Measurements
3.3.1. Rice Lamina Inclination Test (RLIT)
3.3.2. Bean Second-Internode Bioassay
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suzuki, H.; Fujioka, S.; Takatsuto, S.; Yokota, T.; Murofushi, N.; Sakurai, A. Biosynthesis of Brassinolide from Teasterone Via Typhasterol and Castasterone in Cultured-Cells of Catharanthus-Roseus. J. Plant Growth Regul. 1994, 13, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, S.; Inoue, T.; Takatsuto, S.; Yanagisawa, T.; Yokota, T.; Sakurai, A. Identification of a New Brassinosteroid, Cathasterone, in Cultured Cells of Catharanthus roseus as a Biosynthetic Precursor of Teasterone. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 1543–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, S.; Tomo, I.; Suguru, T.; Tadashi, Y.; Takao, Y.; Sakurai, A. Biological Activities of Biosynthetically-related Congeners of Brassinolide. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 1973–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajguz, A. Metabolism of brassinosteroids in plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 45, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, D.; Sun, X.; Ding, T.; Lei, B.; Zhang, C. Structure-activity relationship of brassinosteroids and their agricultural practical usages. Steroids 2017, 124, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuñez, M.; Wang, Y.; Russinova, E.; Estévez-Braun, A.; Amesty, A.; Olea, A.F.; Mellado, M.; Díaz, K.; Espinoza Catalán, L. Synthesis, Biological Activity, and Molecular-Docking Studies of New Brassinosteroid Analogs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorquera, S.; Soto, M.; Díaz, K.; Nuñez, M.; Cuellar, M.A.; Olea, A.F.; Espinoza-Catalán, L. Novel Brassinosteroid Analogues with 3,6 Dioxo Function, 24-Nor-22(S)-Hydroxy Side Chain and p-Substituted Benzoate Function at C-23—Synthesis and Evaluation of Plant Growth Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvasnica, M.; Oklestkova, J.; Bazgier, V.; Rárová, L.; Korinkova, P.; Mikulík, J.; Budesinsky, M.; Béres, T.; Berka, K.; Lu, Q.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological activities of new brassinosteroid analogues with a phenyl group in the side chain. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 8691–8701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korinkova, P.; Bazgier, V.; Oklestkova, J.; Rarova, L.; Strnad, M.; Kvasnica, M. Synthesis of novel aryl brassinosteroids through alkene cross-metathesis and preliminary biological study. Steroids 2017, 127, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.X.; Zheng, L.T.; Shi, J.J.; Gao, B.; Chen, Y.K.; Yang, H.C.; Chen, H.L.; Li, Y.C.; Zhen, X.C. Synthesis of 5 alpha-cholestan-6-one derivatives and their inhibitory activities of NO production in activated microglia: Discovery of a novel neuroinflammation inhibitor. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1222–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal, R.; Gonzalez, C.; Olea, A.F.; Fuentealba, M.; Espinoza, L. Synthesis of 2-Deoxybrassinosteroids Analogs with 24-nor, 22(S)-23-Dihydroxy-Type Side Chains from Hyodeoxycholic Acid. Molecules 2018, 23, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappo, R.; Allen, J.D.; Lemieux, R.; Johnson, W. Notes—Osmium Tetroxide-Catalyzed Periodate Oxidation of Olefinic Bonds. J. Org. Chem. 1956, 21, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonchick, A.P.; Schneider, B.; Zhabinskii, V.N.; Khripach, V.A. Synthesis of [26,27-2H6]brassinosteroids from 23,24-bisnorcholenic acid methyl ester. Steroids 2004, 69, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numazawa, M.; Sohtome, N.; Nagaoka, M. Stereochemistry of NaBH4 reduction of a 19-carbonyl group of 3-deoxy androgens. Synthesis of [19S-3H]- and [19R-3H]-labeled aromatase inhibitors having a 19-hydroxy group. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jones, S.R.; Selinsky, B.S.; Rao, M.N.; Zhang, X.; Kinney, W.A.; Tham, F.S. Efficient Route to 7α-(Benzoyloxy)-3-dioxolane Cholestan-24(R)-ol, a Key Intermediate in the Synthesis of Squalamine. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 3786–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wang, J.J.; Xue, H.W.; Zhang, G.H. Leaf direction: Lamina joint development and environmental responses. Plant Cell Environ. 2021, 44, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takatsuto, S.; Ikekawa, N.; Morishita, T.; Abe, H. Structure Activity Relationship of Brassinosteroids with Respect to the A/B-Ring Functional-Groups. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1987, 35, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Castillo, E.; Ramírez-Echemendía, D.P.; Hernández-Campoalegre, G.; Mesa-Tejeda, D.; Coll-Manchado, F.; Coll-García, Y. In silico identification of new potentially active brassinosteroid analogues. Steroids 2018, 138, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, V.; Diaz, K.; Soto, M.; Olea, A.F.; Cuellar, M.A.; Nuñez, M.; Espinoza-Catalán, L. New Brassinosteroid Analogs with 23,24-Dinorcholan Side Chain, and Benzoate Function at C-22: Synthesis, Assessment of Bioactivity on Plant Growth, and Molecular Docking Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, H.; Jang, S. Rice Lamina Joint Inclination Assay. Bio-Protoc. 2017, 7, e2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavikova, B.; Kohout, L.; Budesinsky, M.; Swaczynova, J.; Kasal, A. Brassinosteroids: Synthesis and Activity of Some Fluoro Analogues. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3979–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| RLIT Activities ± (Standard Error) 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | 1 × 10−8 M | 1 × 10−7 M | 1 × 10−6 M |
| Brassinolide (2) | 2.3 ± 1.4 d | 3.13 ± 1.7 e | 4.17 ± 1.5 f |
| 18 | - | 0.13 ± 3.8 a | 0.70 ± 4.2 a |
| 19 (p-H) | 1.65 ± 5.2 c | 1.22 ± 4.9 c | 0.48 ± 4.1 b |
| 20 (p-CH3) | 1.83 ± 8.2 c | 1.83 ± 4.2 d | 1.30 ± 4.9 d |
| 27 (o-CH3) | 0.52 ± 5.8 a | 1.13 ± 5.2 c | 1.48 ± 4.1 d |
| 21 (p-OCH3) | 0.83 ± 5.5 b | 1.22 ± 4.1 c | 2.70 ± 8.8 e |
| 28 (o-OCH3) | 1.87 ± 5.8 c | 0.91 ± 4.1 b | 0.26 ± 2.0 a |
| 22 (p-F) | 1.78 ± 5.2 c | 0.87 ± 2.0 b | 0.83 ± 4.5 c |
| 29 (o-F) | 0.56 ± 4.5 a | 0.83 ± 2.6 b | 2.52 ± 3.2 e |
| 23 (p-Cl) | 1.04 ± 3.3 b | 0.74 ± 2.7 b | 1.22 ± 4.1 d |
| 30 (o-Cl) | - | 0.56 ± 4.1 a | 1.43 ± 4.5 d |
| 24 (p-Br) | - | 0.13 ± 1.1 a | 0.13 ± 1.0 a |
| 31 (o-Br) | 1.78 ± 5.2 c | 1.34 ± 2.6 d | 0.70 ± 7.5 b |
| 25 (p-I) | 1.78 ± 8.2 c | 1.74 ± 2.0 d | 0.78 ± 2.6 c |
| 32 (o-I) | 2.0 ± 2.3 c | 1.4 ± 4.9 d | 0.96 ± 3.8 c |
| 26 (p-OAc) | 1.74 ± 3.8 c | 1.83 ± 2.7 d | 0.83 ± 5.0 c |
| 33 (o-OAc) | 2.74 ± 6.6 d | 1.87 ± 4.5 e | 1.04 ± 2.6 c |
| 3-DT | Activity | TE | Activity (Ref. [6]) | 3-DT(C22-OH) | Activity (Ref. [7]) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 * | - | (*) | 0.95 | (*) | 0.32 |
| 19 (p-H) | 0.72 | 3 (p-H) | 0.95 | 11 (p-H) | 0.24 |
| 20 (p-CH3) | 0.80 | 4 (p-CH3) | 1.05 | 12 (p-CH3) | 0.24 |
| 21 (p-OCH3) | 0.36 | 5 (p-OCH3) | 1.50 | 13 (p-OCH3) | - |
| 22 (p-F) | 0.77 | 6 (p-F) | 0.73 | 14 (p-F) | 0.47 |
| 23 (p-Cl) | 0.45 | 7 (p-Cl) | 0.55 | 15 (p-Cl) | 0.40 |
| 24 (p-Br) | - | 8 (p-Br) | 0.68 | 16 (p-Br) | 0.93 |
| 25 (p-I) | 0.77 | 9 (p-I) | 1.73 | ||
| 26 (p-OAc) | 0.76 | ||||
| 33 (o-OAc) | 1.19 |
| Compounds | Elongation of the Second Internode, mm ± SD |
|---|---|
| Brassinolide (2) | 7.67 ± 2.35 b |
| 18 | 2.67 ± 1.0 d,e |
| 19 (p-H) | 3.17 ± 0.89 d,e |
| 20 (p-CH3) | 1.67 ± 1.0 e,f |
| 27 (o-CH3) | 6.83 ± 3.0 b |
| 21 (p-OCH3) | 13.67 ± 2.90 a |
| 28 (o-OCH3) | 6.00 ± 2.0 b,c |
| 22 (p-F) | 6.17 ± 1.79 b,c |
| 29 (o-F) | 7.00 ± 2.48 b |
| 23 (p-Cl) | 3.17 ± 0.89 e,f |
| 30 (o-Cl) | 7.17 ± 2.8 b |
| 24 (p-Br) | 0.00 ± 0 |
| 31 (o-Br) | 2.17 ± 0.89 d,e,f |
| 25 (p-I) | 2.50 ± 1.51 d,e |
| 32 (o-I) | 5.83 ± 2.8 b,c |
| 26 (p-OAc) | 1.83 ± 1.0 e,f |
| 33 (o-OAc) | 4.33 ± 2.48 c,d |
| Negative Control | 1.00 ± 0.0 f |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdés, E.; Díaz, K.; Núñez, M.; Olea, A.F.; Moral, J.F.Q.d.; Carvajal, R.; Cuellar, M.A.; Espinoza-Catalán, L. Novel 3-Dehydroteasterone Derivatives with 23,24-Dinorcholanic Side Chain and Benzoate Groups at C-22: Synthesis and Activity Evaluation by Rice Lamina Inclination Test and Bean Second-Internode Bioassay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178710
Valdés E, Díaz K, Núñez M, Olea AF, Moral JFQd, Carvajal R, Cuellar MA, Espinoza-Catalán L. Novel 3-Dehydroteasterone Derivatives with 23,24-Dinorcholanic Side Chain and Benzoate Groups at C-22: Synthesis and Activity Evaluation by Rice Lamina Inclination Test and Bean Second-Internode Bioassay. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178710
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdés, Ernesto, Katy Díaz, María Núñez, Andrés F. Olea, José F. Quilez del Moral, Rodrigo Carvajal, Mauricio A. Cuellar, and Luis Espinoza-Catalán. 2025. "Novel 3-Dehydroteasterone Derivatives with 23,24-Dinorcholanic Side Chain and Benzoate Groups at C-22: Synthesis and Activity Evaluation by Rice Lamina Inclination Test and Bean Second-Internode Bioassay" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178710
APA StyleValdés, E., Díaz, K., Núñez, M., Olea, A. F., Moral, J. F. Q. d., Carvajal, R., Cuellar, M. A., & Espinoza-Catalán, L. (2025). Novel 3-Dehydroteasterone Derivatives with 23,24-Dinorcholanic Side Chain and Benzoate Groups at C-22: Synthesis and Activity Evaluation by Rice Lamina Inclination Test and Bean Second-Internode Bioassay. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178710







