The Effect of Diabetes Mellitus on Central Corneal Thickness Values: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Search Strategy
- -
- “Central corneal thickness” OR “CCT”
- -
- “Diabetes mellitus” OR “type 1 diabetes” OR “type 2 diabetes”
- -
- “Corneal disease”
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
- -
- Population: Adults with diabetes mellitus (type 1 or type 2);
- -
- Intervention/Exposure: Diabetes mellitus with varying disease durations or glycemic control (HbA1c);
- -
- Comparison: Non-diabetic individuals or diabetic patients with better metabolic control;
- -
- Outcomes: Central corneal thickness (CCT) measurements.
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Collection Process
- -
- First author and publication year;
- -
- Country/region of study;
- -
- Population characteristics (age, sex, sample size, type of diabetes);
- -
- Duration of diabetes and HbA1c levels;
- -
- CCT values (mean, SD, measurement method);
- -
- Study design and clinical considerations.
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Statistical Methods
2.8. Subgroup Analysis
3. Results
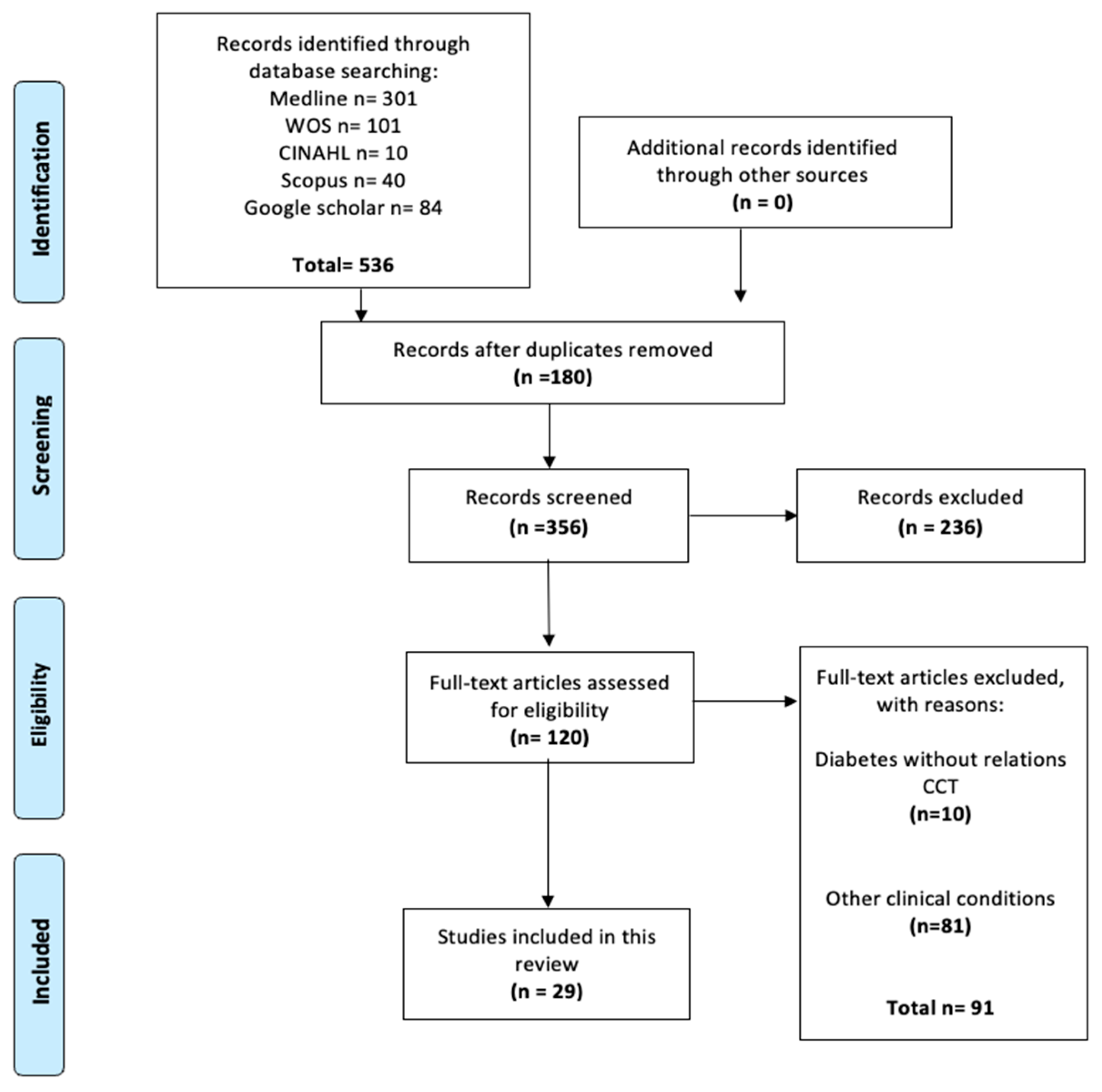
3.1. Included Studies
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Anatomy and Histology of the Eye and Cornea
3.4. Statistical Results
3.5. Robins Risk of Bias
3.6. Clinical Considerations
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010, 33 (Suppl. 1), S62–S69, Erratum in Diabetes Care. 2010, 33, e57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, J.E.; Sicree, R.A.; Zimmet, P.Z. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 87, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storr-Paulsen, A.; Singh, A.; Jeppesen, H.; Norregaard, J.C.; Thulesen, J. Corneal endothelial morphology and central thickness in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morikubo, S.; Takamura, Y.; Kubo, E.; Tsuzuki, S.; Akagi, Y. Corneal changes after small-incision cataract surgery in patients with diabetes mellitus. Arch Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 966–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugod, M.; Storr-Paulsen, A.; Norregaard, J.C.; Nicolini, J.; Larsen, A.B.; Thulesen, J. Corneal endothelial cell changes associated with cataract surgery in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cornea 2011, 30, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrado, M.J.; Popper, M.; Morgado, A.M.; Murta, J.N.; Van Best, J.A. Diabetes and corneal cell densities in humans by in vivo confocal microscopy. Cornea 2006, 25, 761–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Gao, J.H. Effects of Mydrin eye-drops on central corneal thickness values in adult patients with myopia. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2017, 100, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insler, M.S.; Baumann, J.D. Corneal thinning syndromes. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1986, 18, 74–75. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Auffarth, G.U.; Wang, L.; Völcker, H.E. Keratoconus evaluation using the Orbscan Topography System. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2000, 26, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Pflugfelder, S.C. Corneal thickness is reduced in dry eye. Cornea 1999, 18, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copt, R.P.; Thomas, R.; Mermoud, A. Corneal thickness in ocular hypertension, primary open-angle glaucoma, and normal tension glaucoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 1999, 117, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Chatterjee, A.; Mathai, M.; Kelly, S.P.; Kwartz, J.; Henson, D.; McLeod, D. Relationship between corneal thickness and measured intraocular pressure in a general ophthalmology clinic. Ophthalmology 1999, 106, 2154–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudouin, C. The pathology of dry eye. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2001, 45 (Suppl. 2), S211–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busted, N.; Olsen, T.; Schmitz, O. Clinical observations on the corneal thickness and the corneal endothelium in diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1981, 65, 687–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.; Busted, N.; Schmitz, O. Corneal thickness in diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1980, 315, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, L.I.; Bourne, W.M.; Pach, J.M.; Brubaker, R.F. Structure and function of the corneal endothelium in diabetes mellitus type I and type II. Arch Ophthalmol. 1996, 114, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, N.A.; Brand, R.J.; Polse, K.A.; Bourne, W.M. Corneal function during normal and high serum glucose levels in diabetes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roszkowska, A.M.; Tringali, C.G.; Colosi, P.; Squeri, C.A.; Ferreri, G. Corneal endothelium evaluation in type I and type II diabetes mellitus. Ophthalmologica 1999, 213, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.E.; Tervo, T.M.; Immonen, I.J.; Müller, L.J.; Grönhagen-Riska, C.; Vesaluoma, M.H. Corneal structure and sensitivity in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 2915–2921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Oum, B.S.; Choi, H.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Cho, B.M. Differences in corneal thickness and corneal endothelium related to duration in diabetes. Eye 2006, 20, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, D.H.; Wong, T.Y.; Wong, W.L.; Saw, S.M.; Tan, D.T.; Shen, S.Y.; Loon, S.C.; Foster, P.J.; Aung, T.; Singapore Malay Eye Study Group. Diabetes, hyperglycemia, and central corneal thickness: The Singapore Malay Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 964–968.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriowo, O.M. Profile of central corneal thickness in diabetics with and without dry eye in a Saudi population. Optometry 2009, 80, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Módis, L., Jr.; Szalai, E.; Kertész, K.; Kemény-Beke, A.; Kettesy, B.; Berta, A. Evaluation of the corneal endothelium in patients with diabetes mellitus type I and II. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdamar, Y.; Cankaya, B.; Ozalp, S.; Acaroglu, G.; Karakaya, J.; Ozkan, S.S. Is there a correlation between diabetes mellitus and central corneal thickness? J. Glaucoma 2010, 19, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo-Maroto, A.M.; Cerviño, A.; Perez-Cambrodí, R.J.; García-Lázaro, S.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A. Quantitative corneal anatomy: Evaluation of the effect of diabetes duration on the endothelial cell density and corneal thickness. Ophthalmic Physiol. Opt. 2015, 35, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, S.; Osuagwu, U.L.; AlHarthi, E.M. Manifestations of type 2 diabetes in corneal endothelial cell density, corneal thickness and intraocular pressure. J. Biomed Res. 2015, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Alonso, L.; Rahhal, M.; Bastir, M.; Perez-Bermejo, M.; Belda-Salmeron, L. Corneal thickness differences between type 2 diabetes and non-diabetes subjects during preoperative laser surgery examination. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2017, 31, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Altay, Y.; Balta, O.; Demirok, G.; Burcu, A.; Balta, O.B.; Ornek, F. Agreement between Corneal Thickness Measurements Using Pentacam Scheimpflug Camera, Noncontact Specular Microscopy, and Ultrasonographic Pachymetry in Diabetic Patients. Curr. Eye Res. 2017, 42, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Declaración PRISMA 2020: Una guía actualizada para la publicación de revisiones sistemáticas. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 46, e112. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.; Higgins, J.; Rothstein, H. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis V2; Biostat: Englewood, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumbar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, B.; Bhadra, S.; Mittal, P.; Shyam, K. Corneal endothelial morphology and central corneal thickness in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 69, 1718–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.I.; Nagpal, S. Corneal thickness and endothelial cell density in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Oman J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 12, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Kato, S.; Inoue, Y.; Amano, S.; Oshika, T. The corneal endothelium and thickness in type II diabetes mellitus. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 46, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, A.; Verma, A.; Alagorie, A.R. Association of severity of diabetic retinopathy with corneal endothelial and thickness changes in patients with diabetes mellitus. Eye 2022, 36, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, K.W.; Wan Mohd, M.A.; Nik-Ahmad-Zuky, N.L.; Shatriah, I. Central Corneal Thickness and Intraocular Pressure in Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Cureus 2023, 15, e35996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keoleian, G.M.; Pach, J.M.; Hodge, D.O.; Trocme, S.D.; Bourne, W.M. Structural and functional studies of the corneal endothelium in diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1992, 113, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, T.G. The effects of type 2 diabetes mellitus on the corneal endothelium and central corneal thickness. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, R.O.; Matsuda, M.; Yee, R.W.; Edelhauser, H.F.; Schultz, K.J. Corneal endothelial changes in type I and type II diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1984, 98, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, B.; Bozkurt, B.; Atmaca, A.; Irkec, M.; Orhan, M.; Aslan, U. Effect of glycemic control on refractive changes in diabetic patients with hyperglycemia. Cornea 2005, 24, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhir, R.R.; Raman, R.; Sharma, T. Changes in the corneal endothelial cell density and morphology in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A population-based study, Sankara Nethralaya Diabetic Retinopathy and Molecular Genetics Study (SN-DREAMS, Report 23). Cornea 2012, 31, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, M.; Moiroux, P.; d’Athis, P.; Bron, A.; Brun, J.M.; Creuzot-Garcher, C. Assessment of induced corneal hypoxia in diabetic patients. Cornea 2002, 21, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zulhisham, M.; Suhaimi, H.; Shatriah, I. Central Corneal Thickness and Intraocular Pressure in Children with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Korean J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 37, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemer, N.G.; Dubbelman, M.; Kostense, P.J.; Ringens, P.J.; Polak, B.C. The influence of chronic diabetes mellitus on the thickness and the shape of the anterior and posterior surface of the cornea. Cornea 2007, 26, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, S.P.; Collin, H.B. Functional morphology of the cornea of the Little Penguin Eudyptula minor (Aves). J. Anat. 2021, 239, 732–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, V.; Aronen, P.; Pramodkumar, T.A.; Looker, H.; Chetrit, A.; Bloigu, A.H.; Juutilainen, A.; Bianchi, C.; La Sala, L.; Anjana, R.M.; et al. Accuracy of 1-Hour Plasma Glucose During the Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes in Adults: A Meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1062–1069, Erratum in Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1457. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc21-er06c. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Ge, X.; Sun, R.; Zhai, X. Early detection of type 2 diabetes risk: Limitations of current diagnostic criteria. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1260623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; He, M.; Chen, Z. Changes in corneal biomechanics in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Diabetol. 2020, 57, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Maroto, A.M.; Pérez-Cambrodí, R.J.; Esteve-Taboada, J.J.; García-Lázaro, S.; Cerviño, A.N. Corneal backscatter in insulin-dependent and non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients: A pilot study. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2017, 80, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Bermejo, M.; Cervino, A.; Calvo-Maroto, A.M.; Moscardo, M.; Murillo-Llorente, M.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A. Corneal Thickness Response after Anesthetic Eye Drops: Our Own Results and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4743721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensio, I.; Rahhal, S.M.; Alonso, L.; Palanca-Sanfrancisco, J.M.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A. Corneal thickness values before and after oxybuprocaine 0.4% eye drops. Cornea 2003, 22, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, P.; Cerviño, A.; Quiles-Guiñau, L.; Albarran-Diego, C.; Garcia-Lazaro, S.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A. Corneal thickness differences between sexes after oxybuprocaine eye drops. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2015, 92, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Palanca-Sanfrancisco, J.M.; García-Lázaro, S.; Madrid-Costa, D.; Cerviño, A. The effect of anesthetic eye drop instillation on the distribution of corneal thickness. Cornea 2013, 32, e102–e105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Herrera, M.; Lleó-Pérez, A.; Alonso, L.; Rahhal, M.S.; Martínez-Soriano, F. Quantitative anatomical differences in central corneal thickness values determined with scanning-slit corneal topography and noncontact specular microscopy. Cornea 2009, 25, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; Lleo-Perez, A.; Casanova, J.; Alonso, L.; Rahhal, S.M. Inter-observer variability of central corneal thickness measurements using non-contact specular microscopy after laser in situ keratomileusis. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2004, 87, 15–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchís-Gimeno, J.A.; Lleó-Pérez, A.; Alonso, L.; Rahhal, M.S. Paquimetría Orbscan: Diferencias entre observadores al realizar mediciones del espesor corneal [Orbscan pachymetry: Differences between observers when carrying out measurements of the corneal thickness]. Arch Soc. Esp. Oftalmol. 2005, 80, 283–287. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Type of DM | Geographical Region | Medication | Sample Size | Study Quality | Gender | Age (years) | Diabetes Duration (Years) | HbA1c Levels (%) | Pachymetry | CCT Values (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olsen et al. (1980) [15] | 1 | Finlandia | NA | 81 | 4 | NA | NA | 15 | NA | NA | 561 ± 27 |
| Busted et al. (1981) [14] | 1 | Dinamarca | NA | 81 | 4 | NA | 30 | 15 | 7.5 | Haag-Streit pachymeter | 544 ± 28 |
| Schultz et al. (1984) [40] | 2 | EE.UU. | NA | 25 | 3 | NA | 40 to 49 | 21 | NA | Digital pachymeter | 540 ± 20 |
| 50 to 59 | 530 ± 70 | ||||||||||
| 60 to 69 | 540 ± 60 | ||||||||||
| 70 to 79 | 540 ± 80 | ||||||||||
| 1 | 17 | 20 to 29 | >10 | 540 ± 80 | |||||||
| 30 to 39 | 540 ± 10 | ||||||||||
| 40 to 59 | 540 ± 80 | ||||||||||
| Keoleian et al. (1992) [38] | 1 | EE.UU. | NA | 28 | 3 | NA | 33 ± 12.0 | 22 ± 11 | 10 ± 1.4 | Specular microscopy | 560 ± 20 |
| Larsson et al. (1996) [16] | 1 | Suecia | Insulin | 49 | 3 | NA | 36 ± 12.0 | 20 ± 11 | 10.4 ± 2.1 | Specular microscopy | 580 ± 50 |
| 2 | Insulin, OAA, diet | 60 | 60 ± 10.0 | 13 ± 8.0 | 9.9 ± 2.1 | 570 ± 50 | |||||
| McNamara et al. (1998) [17] | 1 | EE.UU. | Insulin | 42 | 4 | 23 M, 19 F | 39.6 ± 8.8 | 22.1 ± 10.1 | 10.2 ± 1.52 | Haag-Streit pachymeter | 524 |
| Roszkowska et al. (1999) [18] | 1 | Italia | Insulin | 70 | 2 | 75 M, 62 F | 29.76 ± 3.43 | 15.3 ± 1.2 | <9.5 | Specular microscopy | 580 ± 20 |
| 2 | OHT | 23 | 49.6 ± 6.16 | 17.2 ± 2.2 | 570 ± 20 | ||||||
| Rosenberg et al. (2000) [19] | 1 | Finlandia | Insulin | 32 | 4 | NA | 45.2 ± 10.0 | 25.9 ± 8.1 | NA | In vivo confocal microscopy | 576.9 ± 48 |
| Inoue et al. (2002) [35] | 2 | Japón | NA | 196 | 2 | NA | 65.5 ± 7.5 | 9.1 ± 8.2 | 6.9 ± 1.3 | Ultrasound pachymeter | 538 ± 36 |
| Ziadi et al. (2002) [43] | 1 | France | NA | 6 | 3 | 4 M, 2 F | 36 ± 9.0 | 14 ± 9.0 | 8.2 ± 1.7 | Ultrasound pachymeter | 560 ± 38 |
| 2 | 9 | 2 M, 7 F | 55 ± 8.0 | 9.0 ± 6.0 | 547 ± 34 | ||||||
| Sonmez et al. (2005) [41] | NA | Turquía | Insulin and OHA | 18 | 3 | 6 M, 12 F | 56.17 ± 5.98 | 8.67 | 10.58 | Corneal pachymetry and ultrasonic biometry | 542.89 ± 37.18 |
| Lee et al. (2006) [20] | 1 | Corea | NA | 300 | 3 | 153 M, 147 F | 57.5 ± 8.5 | 10.87 ± 5.9 | NA | Ultrasonic pachymetry | 588.2 ± 2.7 |
| Wiemer et al. (2007) [45] | 1 | Países Bajos- Europa | Insulin, OAM | 102 | 3 | 58 M, 44 F | 39.96 ± 10.8 | 21.06 ± 11.7 | 8.1 ± 1.6 | Scheimpflug camera | 586 ± 30 |
| 2 | 101 | 54 M, 47 F | 56.46 ± 7.0 | 8.8 6 ± 7.5 | 7.5 ± 1.4 | 578 ± 30 | |||||
| Su et al. (2008) [21] | NA | Singapur | NA | 748 | 4 | NA | 62.59 ± 9.36 | NA | 8.4 ± 2.0 | Ultrasonic pachymetry | 547.2 |
| Oriowo et al. (2009) [22] | 1 | Arabia Saudita | Insulin | 86 | 1 | NA | 53.96 ± 11.9 | 13.5 | NA | Ultrasonic pachymetry | 610 |
| Ozdamar et al. (2010) [24] | 1 | Turquía | NA | 245 | 3 | 112 M, 133 F | 58.4 ± 8.6 | 10.0 ± 7.7 | NA | Ultrasonic pachymetry | 564 ± 30 |
| Módis et al. (2010) [23] | 1 | Hungría | NA | 21 | 2 | 12 M, 9 F | 40.97 ± 15.46 | 10.88 ± 8.06 | 8.55 ± 1.83 | Specular microscopy | 570 ± 40 |
| 2 | 30 | 10 M, 20 F | 64.36 ± 10.47 | 13.61 ± 6.50 | 8.79 ± 2.01 | 560 ± 30 | |||||
| Sudhir et al. (2012) [42] | 2 | India | NA | 1312 | 3 | 695 M, 617 F | 54.8 ± 9.5 | NA | NA | Ultrasonic pachymetry | 524.75 ± 34.52 |
| Storr-Paulsen et al. (2014) [3] | 2 | Dinamarca | OAM, PDM | 235 | 4 | 100 M, 135 F | 72.1 ± 11.0 | NA | 7.3 ± 0.2 | Non-contact specular microscopy | 546 ± 7 |
| Calvo-Maroto et al. (2015) [25] | 2 | España | NA | 157 | 3 | 75 M, 82 F | 45.5 ± 2.5 | 0.38 ± 0.12 | 7.66 ± 0.78 | Ultrasonic pachymeter | 546 ± 13 |
| 52.2 ± 1.8 | 10.2 ± 0.8 | 7.78 ± 0.66 | 569 ± 11 | ||||||||
| Briggs et al. (2015) [26] | 2 | Arabia Saudita | Insulin and OAM | 215 | 1 | 118 M, 97 F | 56.5 ± 11.9 | 14.9 ± 8.3 | NA | HR Pentacam tomography | 539.7 ± 33.6 |
| <10 | |||||||||||
| >10 | |||||||||||
| Sanchis-Gimeno et al. (2017) [27] | 2 | España | NA | 83 | 3 | 40 M, 43 F | 33.6 ±3.2 | 5.9 ± 1.2 | 6.7 ± 0.3 | Non-contact scanning-slit corneal topography | 567.4 ± 10.9 |
| Altay et al. (2017) [28] | 2 | Turquía | NA | 264 | 3 | NA | NA | 0–4 | NA | Scheimpflug camera | 532.67 ± 39.35 |
| 4–9 | 524.54 ± 29.07 | ||||||||||
| >10 | 537.20 ± 29.36 | ||||||||||
| 0–4 | Non-contact specular microscopy | 553.13 ± 38.62 | |||||||||
| 4–9 | 544.59 ± 33.87 | ||||||||||
| >10 | 558.00 ± 35.76 | ||||||||||
| 0–4 | Ultrasonic pachymeter | 550.65 ± 38.68 | |||||||||
| 4–9 | 537.72 ± 36.36 | ||||||||||
| >10 | 553.58 ± 40.08 | ||||||||||
| Fernandes et al. (2019) [34] | 1 | India | NA | 100 | 52 M, 48 F | 12.22 ± 2.82 | 3.91 ± 1.65 | 5.8 ± 15.8 | NA | 525.16 ± 33.14 | |
| Chowdhury et al. (2021) [33] | 2 | India | NA | 262 | 138 M, 124 F | 53.26 ± 6.24 | 7.29 ± 6.00 | 6.97 ± 0.99 | Non-contact specular microscopy | 514.54 ± 38.17 | |
| Kim and Kim (2021) [39] | 2 | Corea | NA | 1411 | 597 M, 814 F | 65.6 ± 11.1 | 10.8 ± 8.7 | 7.54 ± 1.78 | Non-contact specular microscope and a Pentacam Scheimpfug camera. | 551.80 ± 34.10 | |
| Jha et al. (2022) [36] | 2 | India | NA | 1188 | NA | 62.17 ± 9.49 | 8.1 ± 5.5 | 7.5 ± 1.7 | Specular microscope with an auto-tracking system. | 522.1 ± 36.6 | |
| Kan et al. (2023) [37] | 2 | Malasia | NA | 184 | 184 F | 28 ± 4.2 | 0–9 months | 6% | Topcon SP-2000P non-contact specular microscope, and ultrasonography | 552.28 ± 22.5 | |
| Zulhisham et al. (2023) [44] | 1 | Malasia | NA | 76 | 37 M, 39 F | 14.02 ± 2.66 | 5.13 ± 2.12 | 10.68 ± 2.49 | Optical coherence tomography | 542.18 ± 20.40 |
| Author | Diabetes Duration (Years) | CCT |
|---|---|---|
| Olsen et al. (1980) [15] | 15 | 561 |
| Busted et al. (1981) [14] | 15 | 544 |
| Schultz et al. (1984) [40] | 21 | 537.5 |
| Keoleian et al. (1992) [38] | 22 | 560 |
| Larsson et al. (1996) [16] | 16.5 | 575 |
| McNamara et al. (1998) [17] | 22.1 | 524 |
| Roszkowska et al. (1999) [18] | 16.25 | 575 |
| Rosenberg et al. (2000) [19] | 25.9 | 576.9 |
| Inoue et al. (2002) [35] | 9.1 | 538 |
| Ziadi et al. (2002) [43] | 11.5 | 553.5 |
| Sonmez et al. (2005) [41] | 8.67 | 542.89 |
| Lee et al. (2006) [20] | 10.87 | 588.2 |
| Wiemer et al. (2007) [45] | 14.96 | 582 |
| Su et al. (2008) [21] | NA | 547.2 |
| Oriowo et al. (2009) [22] | 13.5 | 610 |
| Ozdamar et al. (2010) [24] | 10.0 | 564 |
| Módis et al. (2010) [23] | 12.245 | 565 |
| Sudhir et al. (2012) [42] | NA | 524.75 |
| Storr-Paulsen et al. (2014) [3] | NA | 546 |
| Calvo-Maroto et al. (2015) [25] | 5.29 | 557.5 |
| Briggs et al. (2015) [26] | 14.9 | 539.36 |
| Sanchis-Gimeno et al. (2017) [27] | 5.9 | 567.4 |
| Altay et al. (2017) [28] | 0–10 | 543.49 |
| Fernandes et al. (2019) [34] | 3.91 | 525.16 |
| Chowdhury et al. (2021) [33] | 7.29 | 514.54 |
| Kim and Kim (2021) [39] | 10.8 | 551.80 |
| Jha et al. (2022) [36] | 8.1 | 522.1 |
| Kan et al. (2023) [37] | 1.0 | 552.28 |
| Zulhisham et al. (2023) [44] | 5.13 | 542.18 |
| Range Diabetes Duration (Years) | Mean/SD of CCT | Difference Mean 95% |
|---|---|---|
| 1–5.9 | 548.90/14.39 | p = 0.412 |
| 6.0–10.9 | 545.63/21.73 | |
| 11–15.9 | 564.98/22.55 | |
| 16–20.9 | 575/0 | |
| 21–25.9 (4) | 549.6/20.34 |
| Author | HbA1c Levels (%) | CCT |
|---|---|---|
| Olsen et al. (1980) [15] | NA | 561 |
| Busted et al. (1981) [14] | 7.5 | 544 |
| Schultz et al. (1984) [40] | NA | 537.5 |
| Keoleian et al. (1992) [38] | 10 | 560 |
| Larsson et al. (1996) [16] | 10.15 | 575 |
| McNamara et al. (1998) [17] | 10.2 | 524 |
| Roszkowska et al. (1999) [18] | <9.5 | 575 |
| Rosenberg et al. (2000) [19] | NA | 576.9 |
| Inoue et al. (2002) [35] | 6.9 | 538 |
| Ziadi et al. (2002) [43] | 8.2 | 553.5 |
| Sonmez et al. (2005) [41] | 10.58 | 542.89 |
| Lee et al. (2006) [20] | NA | 588.2 |
| Wiemer et al. (2007) [45] | 7.86 | 582 |
| Su et al. (2008) [21] | 8.4 | 547.2 |
| Oriowo et al. (2009) [22] | NA | 610 |
| Ozdamar et al. (2010) [24] | NA | 564 |
| Módis et al. (2010) [23] | 8.67 | 565 |
| Sudhir et al. (2012) [42] | NA | 524.75 |
| Storr-Paulsen et al. (2014) [3] | 7.3 | 546 |
| Calvo-Maroto et al. (2015) [25] | 7.72 | 557.5 |
| Briggs et al. (2015) [26] | NA | 539.37 |
| Sanchis-Gimeno et al. (2017) [27] | 6.7 | 567.4 |
| Altay et al. (2017) [28] | NA | 543.49 |
| Fernandes et al. (2019) [34] | 5.8 | 525.16 |
| Chowdhury et al. (2021) [33] | 6.97 | 514.54 |
| Kim and Kim (2021) [39] | 7.54 | 551.80 |
| Jha et al. (2022) [36] | 7.5 | 522.1 |
| Kan et al. (2023) [37] | 6 | 552.28 |
| Zulhisham et al. (2023) [44] | 10.68 | 542.18 |
| Subjects | Average Age | Months of Diabetes Mellitus (2) | HbA1c | Level of CCT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 29 |
| Mean | 271 | 42.7 | 131 | 5.66 | 553 |
| Std. error mean | 71.5 | 3.83 | 15.4 | 0.754 | 4.07 |
| 95% CI mean lower bound | 124 | 34.8 | 99.6 | 4.11 | 544 |
| 95% CI mean upper bound | 417 | 50.5 | 163 | 7.20 | 561 |
| Median | 109 | 48.2 | 130 | 7.30 | 552 |
| Standard deviation | 385 | 20.6 | 82.8 | 4.06 | 21.9 |
| Variance | 148,377 | 425 | 6863 | 16.5 | 480 |
| Range | 1396 | 72.1 | 311 | 10.7 | 95.5 |
| Minimum | 15 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 515 |
| Maximum | 1411 | 72.1 | 311 | 10.7 | 610 |
| Skewness | 2.24 | −0.911 | 0.222 | −0.545 | 0.491 |
| Std. error skewness | 0.434 | 0.434 | 0.434 | 0.434 | 0.434 |
| Kurtosis | 4.00 | −0.072 | −0.388 | −1.37 | 0.303 |
| Std. error kurtosis | 0.845 | 0.845 | 0.845 | 0.845 | 0.845 |
| Shapiro-Wilk W | 0.620 | 0.897 | 0.969 | 0.806 | 0.975 |
| Shapiro-Wilk p | <0.001 | 0.008 | 0.532 | <0.001 | 0.708 |
| Author | Confounding | Selection | Measurement of Intervention | Missing Data | Measurement of Outcomes | Reported Result | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olsen et al., 1980 [15] | Low | High (only pregnant women and a small sample) | Low | Not mentioned | High | Not determined | High |
| Busted et al., 1981 [14] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Schultz et al., 1984 [40] | Low | High (only patients with DM, selection based on age, same duration of diabetes, and those who are insulin dependent) | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Keoleian et al., 1992 [38] | Low | High (small sample) | Low | Not mentioned | Low | Low | High |
| Larsson et al., 1996 [16] | High | High (patients with DM I and II, and only 30 patients without diabetes) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| McNamara et al., 1998 [17] | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Low |
| Roszkowska et al., 1999 [18] | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Rosenberg et al., 2000 [19] | Low | High (low number in the control group) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Inoue et al., 2002 [35] | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ziadi et al., 2002 [43] | High | High (with controlled information) | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Sonmez et al., 2005 [41] | Low | High (only patients with DM) | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Lee et al., 2006 [20] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Wiemer et al., 2007 [45] | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Su et al., 2008 [21] | High | High (only people with DM) | High | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Oriowo et al., 2009 [22] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Ozdamar et al., 2010 [24] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Módis et al., 2010 [23] | Low | High (only people with DM) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Sudhir et al., 2012 [42] | High | High (Only people with DM) | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Storr-Paulsen et al., 2014 [3] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Calvo-Maroto et al., 2015 [25] | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | Low |
| Briggs et al., 2015 [26] | Low | Low | Low | ||||
| Sanchis-Gimeno et al., 2017 [27] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Altay et al., 2017 [28] | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Fernandes et al., 2019 [34] | Low | Low | Low | The participants are not mentioned, only the data. | Low | Low | Low |
| Chowdhury et al., 2021 [33] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| Kim and Kim 2021 [39] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | The procedure is not explained very well with respect to the conclusion. | High |
| Jha et al., 2022 [36] | High | Low | Low | Not mentioned the sample size, only the results | Low | Low | Low |
| Kan et al., 2023 [37] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| Zulhisham et al., 2023 [44] | Low | High (small sample) | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uzunoglu, A.; Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J.J.; Morales-Calderón, K.; Aguilar-Aguirre, I.; Bruna-Mejias, A.; Nova-Baeza, P.; Orellana-Donoso, M.; Oyanedel-Amaro, G.; Suazo-Santibañez, A.; Sanchis-Gimeno, J.A.; et al. The Effect of Diabetes Mellitus on Central Corneal Thickness Values: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178695
Uzunoglu A, Valenzuela-Fuenzalida JJ, Morales-Calderón K, Aguilar-Aguirre I, Bruna-Mejias A, Nova-Baeza P, Orellana-Donoso M, Oyanedel-Amaro G, Suazo-Santibañez A, Sanchis-Gimeno JA, et al. The Effect of Diabetes Mellitus on Central Corneal Thickness Values: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178695
Chicago/Turabian StyleUzunoglu, Arda, Juan José Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, Karin Morales-Calderón, Isidora Aguilar-Aguirre, Alejandro Bruna-Mejias, Pablo Nova-Baeza, Mathias Orellana-Donoso, Gustavo Oyanedel-Amaro, Alejandra Suazo-Santibañez, Juan A. Sanchis-Gimeno, and et al. 2025. "The Effect of Diabetes Mellitus on Central Corneal Thickness Values: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178695
APA StyleUzunoglu, A., Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J. J., Morales-Calderón, K., Aguilar-Aguirre, I., Bruna-Mejias, A., Nova-Baeza, P., Orellana-Donoso, M., Oyanedel-Amaro, G., Suazo-Santibañez, A., Sanchis-Gimeno, J. A., León Rojas, J. E., & Granite, G. (2025). The Effect of Diabetes Mellitus on Central Corneal Thickness Values: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178695







