Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effect of Ellagic Acid and Punicalagin in Dermal Fibroblasts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
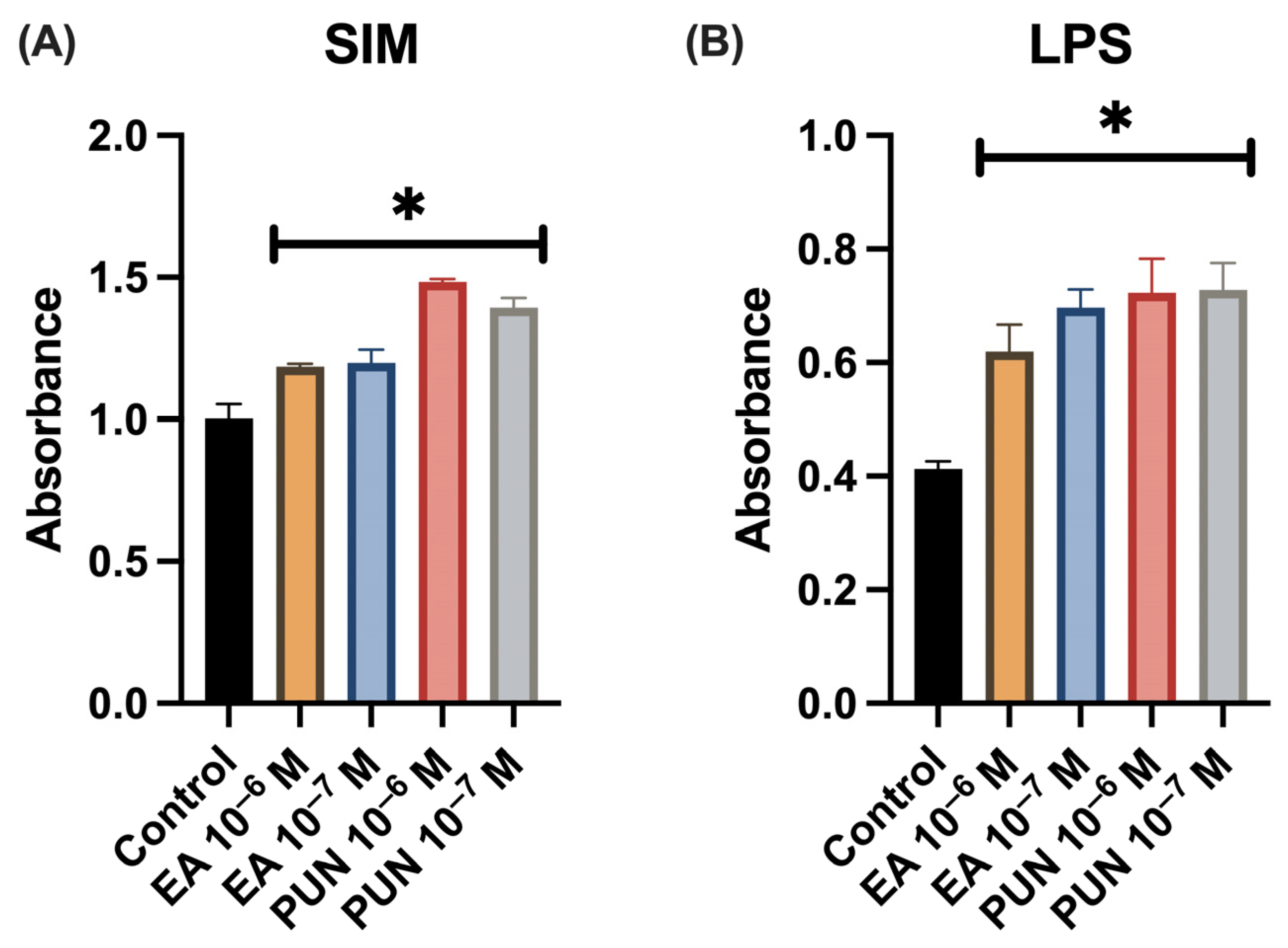
2.1. Cell Proliferation Assay in the Presence of SIM, and LPS Medium
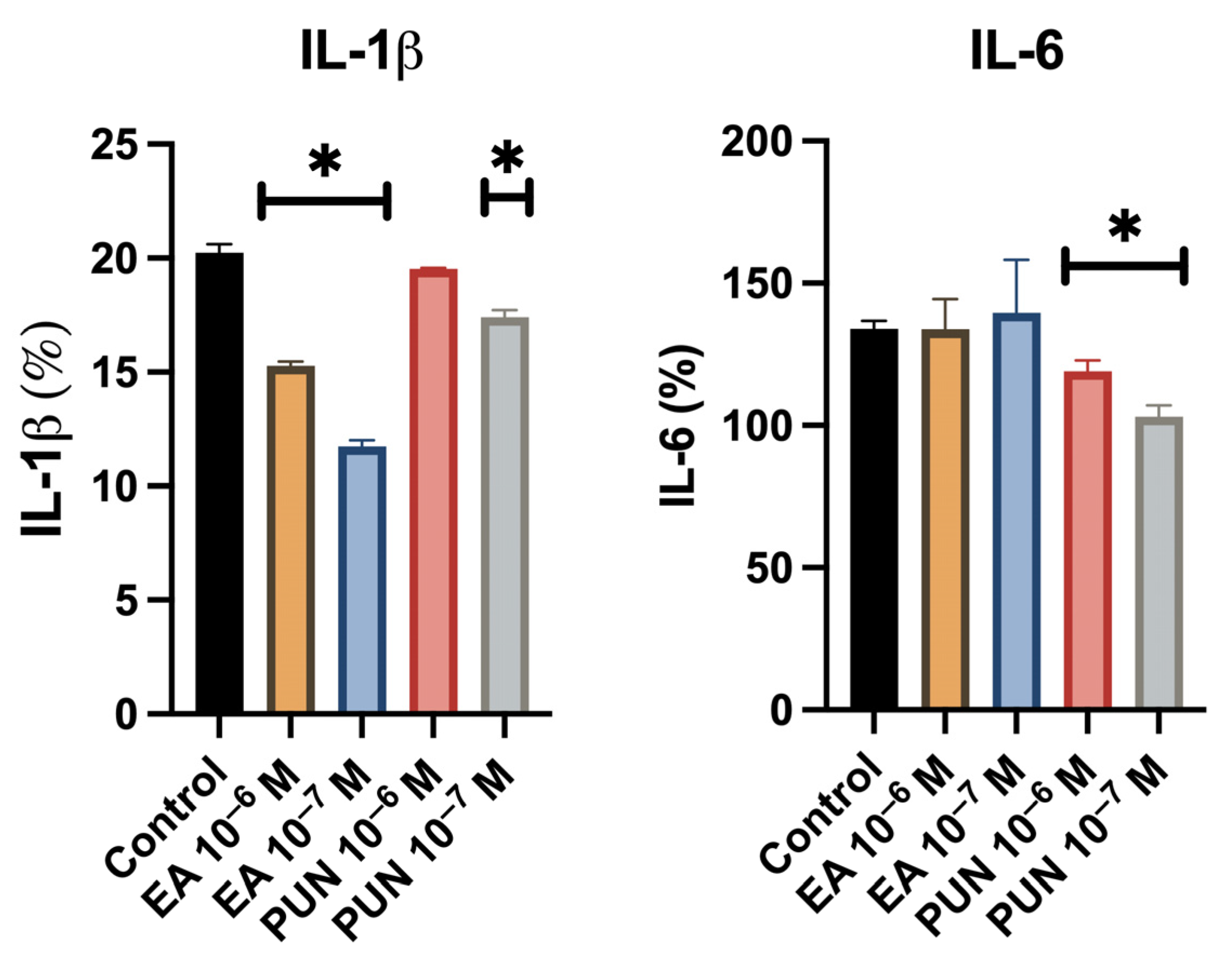
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activity Assay
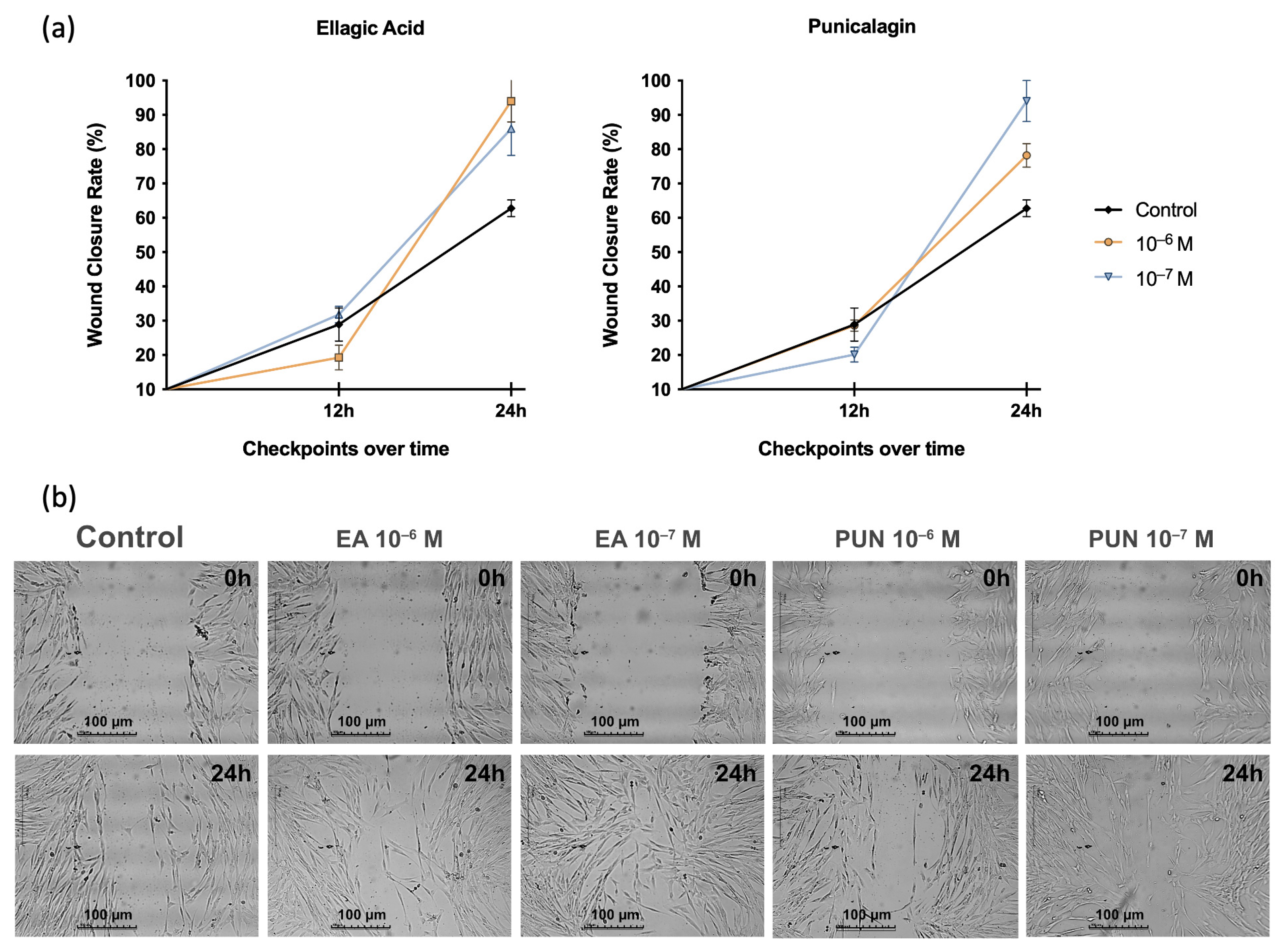
2.3. Cell Migration Assay in the Presence of SIM
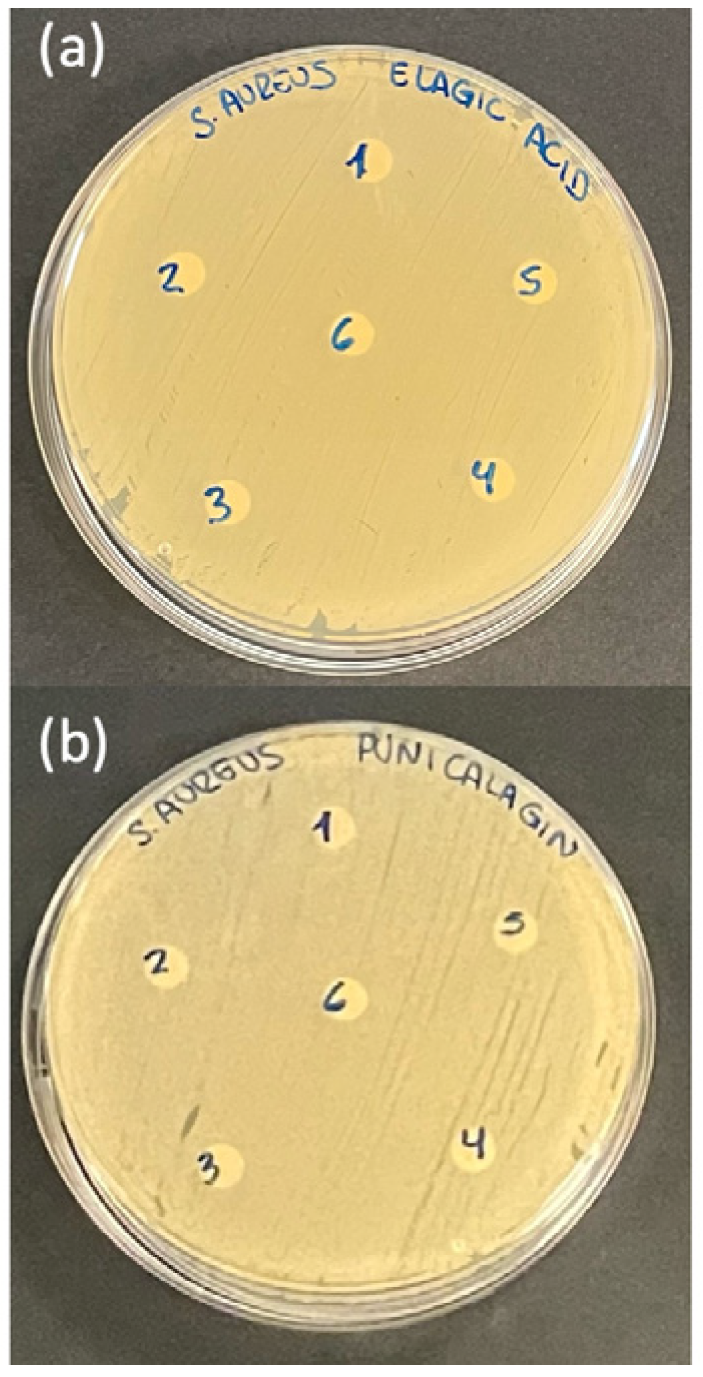
2.4. Antimicrobial Activity Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation and Dilution of Treatment Solutions
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Analysis of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Production
4.5. Cell Migration Assay
4.6. Antimicrobial Capacity Assay
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| α-SMA | α -Smooth Muscle Actin |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| SIM | Simulated Inflammatory Medium |
| IL-1β | Interleukuin-1β |
| IL-6 | Interleuquin-6 |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| EA | Ellagic Acid |
| PUN | Punicalagin |
| NF-κB | Factor Nuclear Kappa B |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases |
| JNK | Jun N-terminal kinases |
| IL-10 | Interleuquin-10 |
| MMPs | Matrix Metalloproteinases |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assa |
| MHA | Mueller–Hinton agar |
| TSB | Tryptic Soy Broth |
References
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, O.A.; Martin, P. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Skin Wound Healing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024, 25, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, R. Keloid and Hypertrophic Scars Are the Result of Chronic Inflammation in the Reticular Dermis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Liang, H.; Clarke, E.; Jackson, C.; Xue, M. Inflammation in Chronic Wounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnsholt, T. The Role of Bacterial Biofilms in Chronic Infections. APMIS Suppl. 2013, 121, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, P.G.; Duerden, B.I.; Armstrong, D.G. Wound Microbiology and Associated Approaches to Wound Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2001, 14, 244–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.; Shai, S.; Shahane, A.; Kaushik, K.S. Recent Advances in Non-Conventional Antimicrobial Approaches for Chronic Wound Biofilms: Have We Found the ‘Chink in the Armor’? Biomedicines 2019, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinnell, F. Fibroblasts, Myofibroblasts, and Wound Contraction. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 124, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, M.T.; Han, Y.-P.; Yan, C.; Shaw, M.C.; Garner, W.L. TNF-Alpha Suppresses Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin Expression in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: An Implication for Abnormal Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2645–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, J.J.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B.; Chaponnier, C.; Brown, R.A. Myofibroblasts and Mechano-Regulation of Connective Tissue Remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, B. The Myofibroblast: Paradigm for a Mechanically Active Cell. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, T.J.; DiPietro, L.A. Inflammation and Wound Healing: The Role of the Macrophage. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2011, 13, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celiksoy, V.; Moses, R.L.; Sloan, A.J.; Moseley, R.; Heard, C.M. Evaluation of the In Vitro Oral Wound Healing Effects of Pomegranate (Punica Granatum) Rind Extract and Punicalagin, in Combination with Zn (II). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgun, C.; Aşir, F. Effect of Ellagic Acid on Damage Caused by Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion in Rats. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 8209–8215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venusova, E.; Kolesarova, A.; Horky, P.; Slama, P. Physiological and Immune Functions of Punicalagin. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shitany, N.A.; El-Bastawissy, E.A.; El-desoky, K. Ellagic Acid Protects against Carrageenan-Induced Acute Inflammation through Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B, Inducible Cyclooxygenase and Proinflammatory Cytokines and Enhancement of Interleukin-10 via an Antioxidant Mechanism. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 19, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollebeeck, S.; Winand, J.; Hérent, M.-F.; During, A.; Leclercq, J.; Larondelle, Y.; Schneider, Y.-J. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Husk Ellagitannins in Caco-2 Cells, an in Vitro Model of Human Intestine. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; He, Y.; Du, L.; Zuo, F.; Wang, W. Lung-Protective Effect of Punicalagin on LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Biosci. Rep. 2022, 42, BSR20212196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, L.R.; Romer, J.; Bugge, T.H.; Nielsen, B.S.; Frandsen, T.L.; Degen, J.L.; Stephens, R.W.; Danø, K. Functional Overlap between Two Classes of Matrix-Degrading Proteases in Wound Healing. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4645–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, N.B.; Ward, K.R.; Witten, T.M.; Bonchev, D.G.; Diegelmann, R.F. Impaired Wound Healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggeri, M.; Bianchi, E.; Rossi, S.; Vigani, B.; Bonferoni, M.C.; Caramella, C.; Sandri, G.; Ferrari, F. Nanotechnology-Based Medical Devices for the Treatment of Chronic Skin Lesions: From Research to the Clinic. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illescas-Montes, R.; Rueda-Fernández, M.; González-Acedo, A.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; García-Recio, E.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; García-Martínez, O. Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro: A Preliminary Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential. Nutrients 2023, 16, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olchowik-Grabarek, E.; Sekowski, S.; Mierzwinska, I.; Zukowska, I.; Abdulladjanova, N.; Shlyonsky, V.; Zamaraeva, M. Cell Type-Specific Anti- and Pro-Oxidative Effects of Punica granatum L. Ellagitannins. Membranes 2024, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-González, G.M.; Esparza-González, S.C.; Nery-Flores, S.D.; Morlett-Chávez, J.A.; Ascacio-Valdés, J.A.; Flores-Gallegos, A.C.; Saenz-Galindo, A.; Rodríguez-Herrera, R. Anticancer Activity of Polyphenolic Punica Granatum Peel Extracts Obtained by Hybrid Ultrasound-Microwave Assisted Extraction: Evaluation on HeLa and HepG2 Cells. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2024, 33, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.-P.; Uen, Y.-H.; Kang, N.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Tian, Y.-F.; Fang, C.-L.; Lin, K.-Y. Punicalagin Restricts Growth, Promotes Apoptosis, and Reduces Invasion in Human Gastric Cancer Cells. Dose-Response Publ. Int. Hormesis Soc. 2024, 22, 15593258241264954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, G.; Francisco, V.; Lopes, M.C.; Cruz, M.T.; Batista, M.T. Intracellular Signaling Pathways Modulated by Phenolic Compounds: Application for New Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Discovery. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 2876–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olędzka, A.J.; Czerwińska, M.E. Role of Plant-Derived Compounds in the Molecular Pathways Related to Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, T. The Nuclear Factor NF-kappaB Pathway in Inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Simard, M.J.; Huot, J. Endothelial microRNAs Regulating the NF-κB Pathway and Cell Adhesion Molecules during Inflammation. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4070–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, Z.; Koh, Y.-S. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases in Inflammation. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 2012, 42, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Protein Kinase Cascades Activated by Stress and Inflammatory Cytokines. BioEssays 1996, 18, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, C.S.; Kirkwood, K.L. P38 MAPK Signaling in Oral-Related Diseases. J. Dent. Res. 2007, 86, 812–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, W.; Han, B.; Lu, J. Ellagic Acid Protects against LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury through Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B, Proinflammatory Cytokines and Enhancement of Interleukin-10. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 1347–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenSaad, L.A.; Kim, K.H.; Quah, C.C.; Kim, W.R.; Shahimi, M. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Ellagic Acid, Gallic Acid and Punicalagin A&B Isolated from Punica Granatum. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Deng, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Sun, L.; Sun, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhou, H. Ellagic Acid Protects Lipopolysaccharide/D-Galactosamine-Induced Acute Hepatic Injury in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 22, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Huang, H.-J.; Sheu, S.-Y.; Liu, Y.-C.; Lee, I.-J.; Chiang, S.-C.; Lin, A.M.-Y. Oral Ellagic Acid Attenuated LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in Rat Brain: MEK1 Interaction and M2 Microglial Polarization. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 248, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, J.; Ren, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, X.; Yang, L. Punicalagin Prevents Inflammation in LPS- Induced RAW264.7 Macrophages by Inhibiting FoxO3a/Autophagy Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olajide, O.A.; Kumar, A.; Velagapudi, R.; Okorji, U.P.; Fiebich, B.L. Punicalagin Inhibits Neuroinflammation in LPS-Activated Rat Primary Microglia. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58, 1843–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.E.; Hwang, C.J.; Lee, H.P.; Kim, C.S.; Son, D.J.; Ham, Y.W.; Hellström, M.; Han, S.-B.; Kim, H.S.; Park, E.K.; et al. Inhibitory Effect of Punicalagin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress and Memory Impairment via Inhibition of Nuclear Factor-kappaB. Neuropharmacology 2017, 117, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohel, M.S.; Windhaber, R.A.J.; Tarlton, J.F.; Whyman, M.R.; Poskitt, K.R. The Relationship between Cytokine Concentrations and Wound Healing in Chronic Venous Ulceration. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 48, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burian, E.A.; Enevold, C.; Karlsmark, T.; Ågren, M.S. Cytokine Stability in Chronic Wound Fluid and Its Association to Fibroblast Proliferation. Wound Repair Regen. 2024, 32, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgeer; Hasan, U.H.; Uttra, A.M.; Qasim, S.; Ikram, J.; Saleem, M.; Niazi, Z.R. Phytochemicals Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinases Regulating Tissue Degradation in Inflammation and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Phytomedicine 2020, 66, 153134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Acedo, A.; Illescas-Montes, R.; de Luna-Bertos, E.; Ruiz, C.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; García-Martínez, O.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L. Extra Virgin Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds Modulate the Gene Expression of Biomarkers Involved in Fibroblast Proliferation and Differentiation. Genes 2024, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Han, D. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Diquat-Induced Jejunum Oxidative Stress in C57BL/6 Mice through Activating Nrf2 Mediated Signaling Pathway. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, R.; Wang, N.; Deng, Y.; Tan, B.; Yin, Y.; Qi, M.; Wang, J. Ellagic Acid Alleviates Oxidative Stress by Mediating Nrf2 Signaling Pathways and Protects against Paraquat-Induced Intestinal Injury in Piglets. Antioxid. Basel Switz. 2022, 11, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Guo, H.; DaSilva, N.; Li, D.; Zhang, K.; Wan, Y.; Gao, X.-H.; Chen, H.-D.; Seeram, N.; Ma, H. Pomegranate (Punica Granatum) Phenolics Ameliorate Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress and Cytotoxicity in Human Keratinocytes. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 54, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, W.; Zou, Y.; Xia, X. Antimicrobial Activity and Mechanisms of Punicalagin against Vibrio Parahaemolyticus. Foods 2024, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, C.; Wu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, G.; Peng, X.; Xia, X. Antimicrobial Activity of Punicalagin Against Staphylococcus Aureus and Its Effect on Biofilm Formation. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2017, 14, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macêdo, N.S.; Barbosa, C.R.D.S.; Bezerra, A.H.; Silveira, Z.d.S.; da Silva, L.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Dashti, S.; Kim, B.; da Cunha, F.A.B.; da Silva, M.V. Evaluation of Ellagic Acid and Gallic Acid as Efflux Pump Inhibitors in Strains of Staphylococcus Aureus. Biol. Open 2022, 11, bio059434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Martínez, M.S.; Truchado, P.; Castro-Ibáñez, I.; Allende, A. Antimicrobial Activity of Hydroxytyrosol: A Current Controversy. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekse, C.; Bohlin, J.; Skjerve, E.; Vegarud, G.E. Growth Comparison of Several Escherichia Coli Strains Exposed to Various Concentrations of Lactoferrin Using Linear Spline Regression. Microb. Inform. Exp. 2012, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosch, A.; Lobmann, R.; Pott, A.; Preissler, J. Interleukin-6 Concentrations in Wound Fluids Rather than Serological Markers Are Useful in Assessing Bacterial Triggers of Ulcer Inflammation. Int. Wound J. 2008, 5, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassig, A.A.D.; Lindgren, B.R.; Itabiyi, R.; Joseph, A.M.; Gupta, K. Excessive Inflammation Portends Complications: Wound Cytokines and Head and Neck Surgery Outcomes. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, E238–E246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, R.E.; Fang, M.M.; Ennis, W.J.; Koh, T.J. Blocking Interleukin-1β Induces a Healing-Associated Wound Macrophage Phenotype and Improves Healing in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2013, 62, 2579–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Tercero, L.; Delgado, L.M.; Bosch-Rué, E.; Perez, R.A. Evaluation of the Immunomodulatory Effects of Cobalt, Copper and Magnesium Ions in a pro Inflammatory Environment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappiello, F.; Casciaro, B.; Mangoni, M.L. A Novel In Vitro Wound Healing Assay to Evaluate Cell Migration. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2018, 133, 56825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; González-Acedo, A.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Ruiz, C.; De Luna-Bertos, E.; Illescas-Montes, R.; García-Martínez, O. Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effect of Ellagic Acid and Punicalagin in Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178681
Ramos-Torrecillas J, González-Acedo A, Melguizo-Rodríguez L, Ruiz C, De Luna-Bertos E, Illescas-Montes R, García-Martínez O. Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effect of Ellagic Acid and Punicalagin in Dermal Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178681
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos-Torrecillas, Javier, Anabel González-Acedo, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Concepción Ruiz, Elvira De Luna-Bertos, Rebeca Illescas-Montes, and Olga García-Martínez. 2025. "Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effect of Ellagic Acid and Punicalagin in Dermal Fibroblasts" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178681
APA StyleRamos-Torrecillas, J., González-Acedo, A., Melguizo-Rodríguez, L., Ruiz, C., De Luna-Bertos, E., Illescas-Montes, R., & García-Martínez, O. (2025). Anti-Inflammatory and Antimicrobial Effect of Ellagic Acid and Punicalagin in Dermal Fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178681






