Role of RhoGEFs or RhoGAPs in Pyk2-Mediated RhoA Activation in Depolarization-Induced Contraction of Rat Caudal Arterial Smooth Muscle
Abstract
1. Introduction
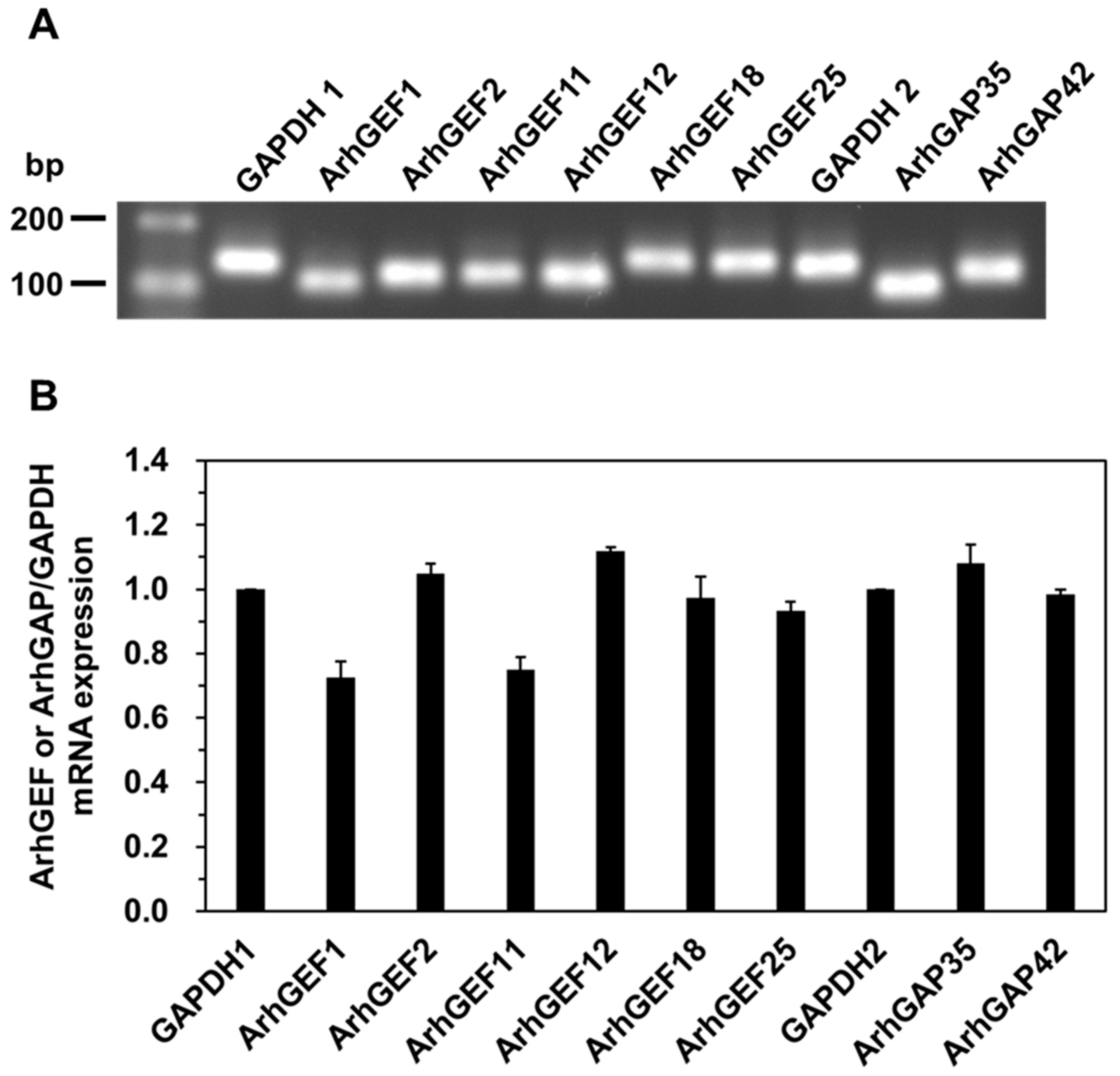
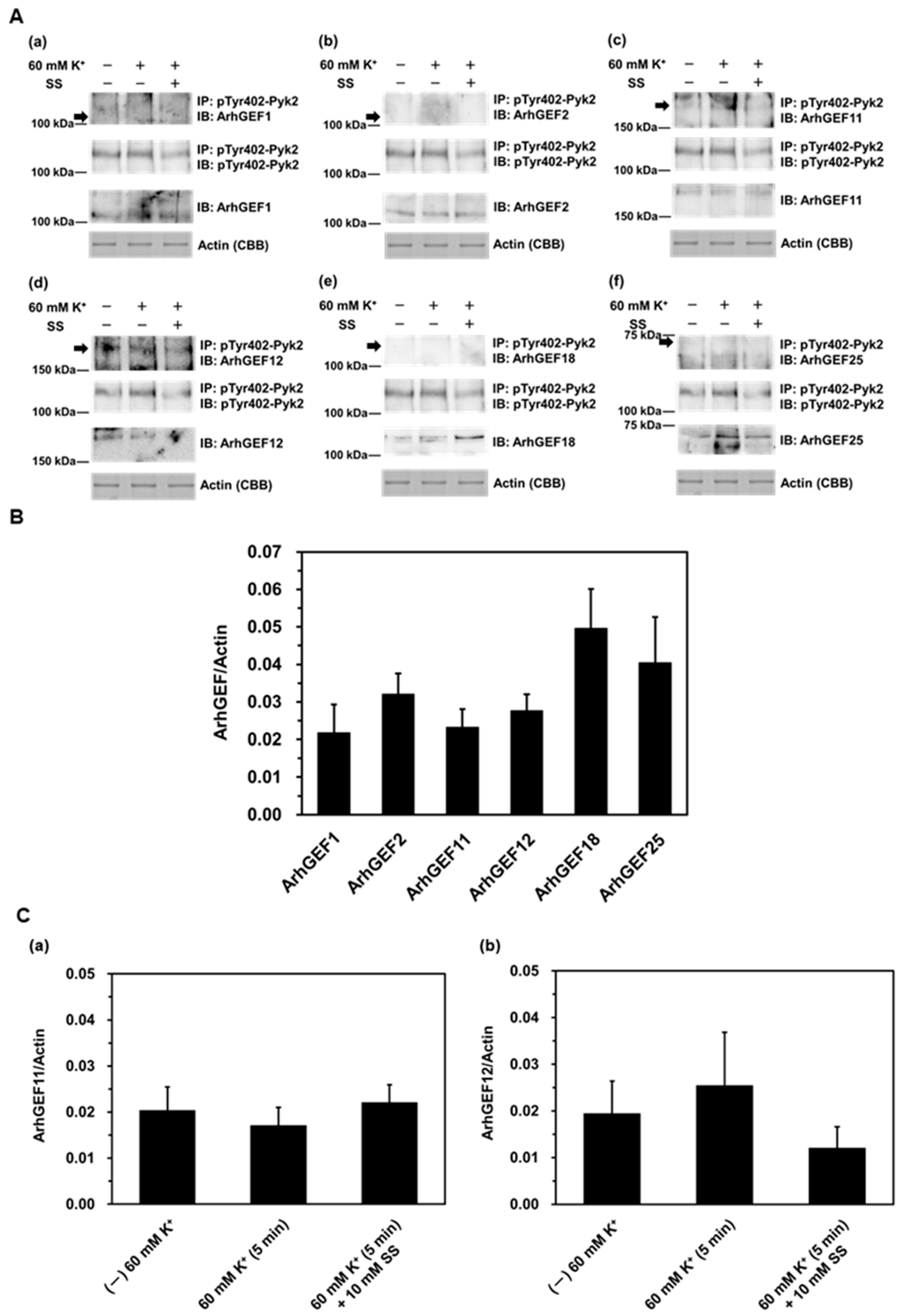
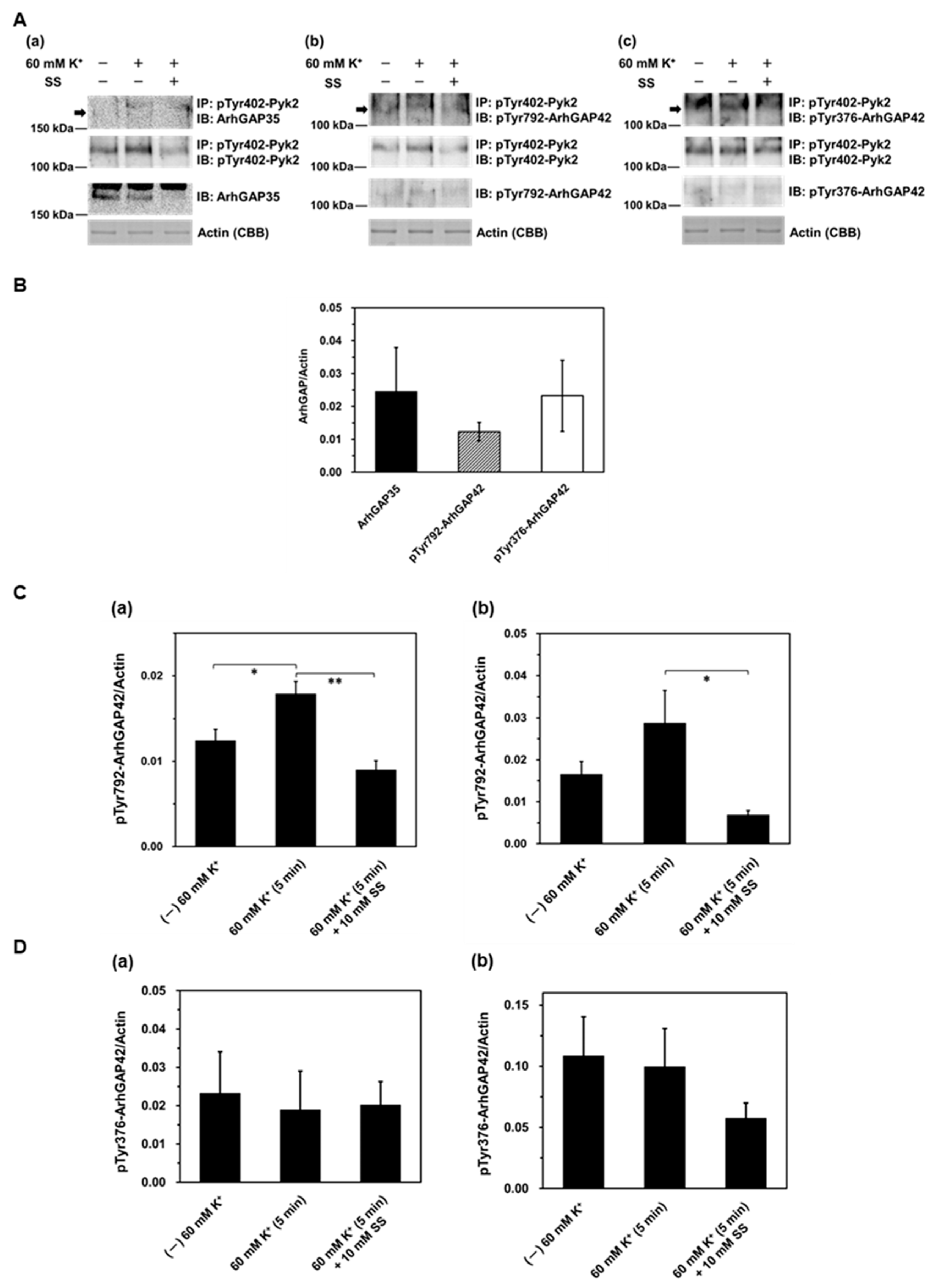
2. Results
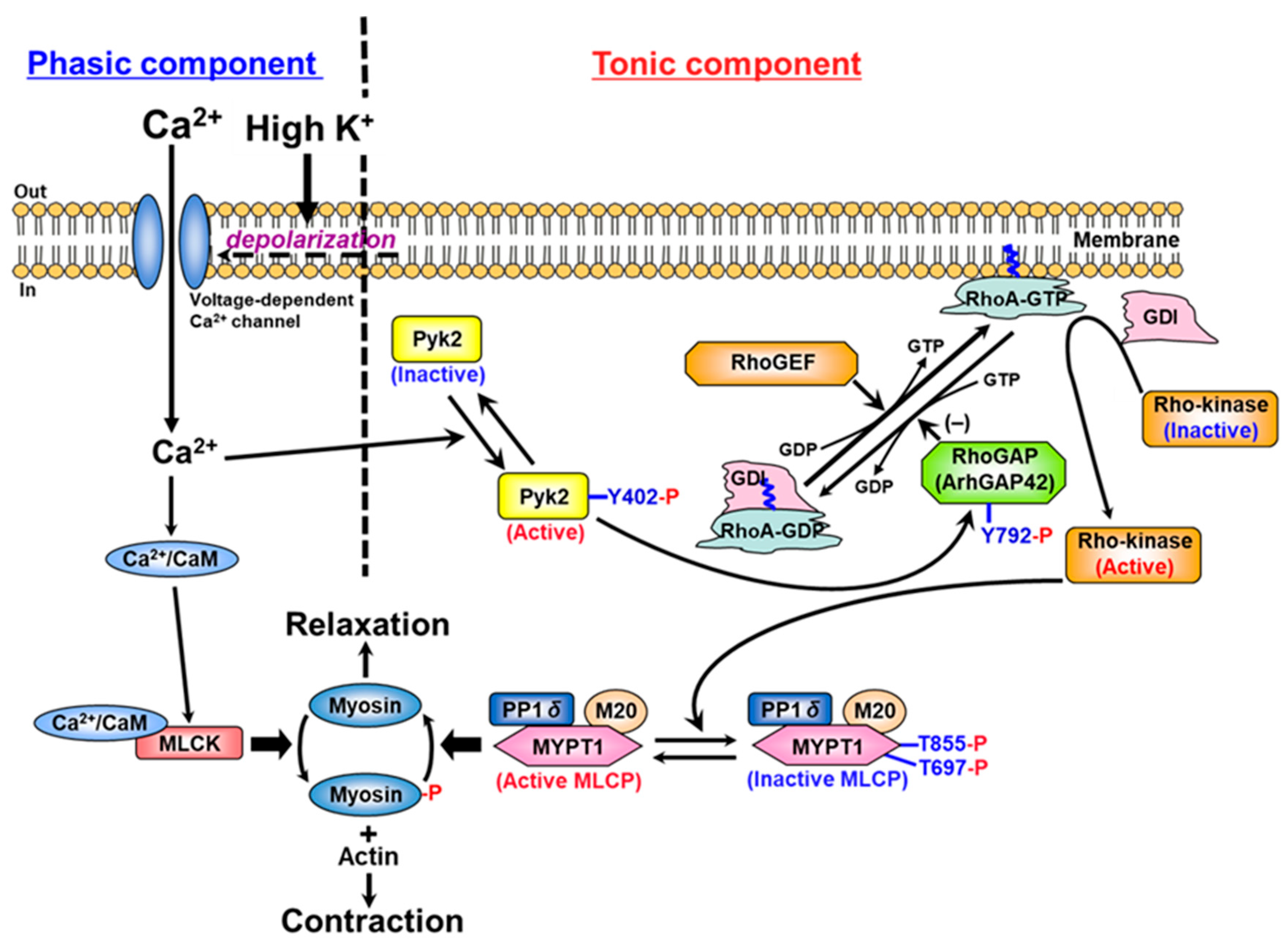
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Smooth Muscle Strips
4.3. qRT-PCR
4.4. Protein Extraction and Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [Ca2+]i | cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration |
| CaM | calmodulin |
| RhoGAP | Rho GTPase-activating protein |
| RhoGEF | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| H-T solution | Hepes-Tyrode solution |
| LC20 | 20 kDa light chain of myosin |
| MLCK | myosin light chain kinase |
| MLCP | myosin light chain phosphatase |
| MYPT1 | myosin-targeting subunit of MLCP |
| Pyk2 | proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 |
| ROCK | Rho-associated kinase |
References
- Hartshorne, D.J.; Ito, M.; Erdödi, F. Role of protein phosphatase type 1 in contractile functions: Myosin phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 37211–37214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamm, K.E.; Stull, J.T. Dedicated myosin light chain kinases with diverse cellular functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 4527–4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyo, A.P.; Somlyo, A.V. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: Modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol. Rev. 2003, 83, 1325–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swärd, K.; Mita, M.; Wilson, D.P.; Deng, J.T.; Susnjar, M.; Walsh, M.P. The role of RhoA and Rho-associated kinase in vascular smooth muscle contraction. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2003, 5, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loirand, G.; Pacaud, P. The role of Rho protein signaling in hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2010, 7, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, M.J.; Cherng, W.J. Coronary vasospastic angina: Current understanding and the role of inflammation. Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2013, 29, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Yasue, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Harada, E. Coronary artery spasm—Clinical features, pathogenesis and treatment. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2019, 95, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases: Biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2005, 21, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossman, K.L.; Der, C.J.; Sondek, J. GEF means go: Turning on RHO GTPases with guanine nucleotide-exchange factors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loirand, G.; Scalbert, E.; Bril, A.; Pacaud, P. Rho exchange factors in the cardiovascular system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2008, 8, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cario-Toumaniantz, C.; Ferland-McCollough, D.; Chadeuf, G.; Toumaniantz, G.; Rodriguez, M.; Galizzi, J.-P.; Lockhart, B.; Bril, A.; Scalbert, E.; Loirand, G.; et al. RhoA guanine exchange factor expression profile in arteries: Evidence for a Rho kinase-dependent negative feedback in angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C1394–C1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Lenhart, K.C.; Bird, K.E.; Suen, A.A.; Rojas, M.; Kakoki, M.; Li, F.; Smithies, O.; Mack, C.P.; Taylor, J.M. The smooth muscle-selective RhoGAP GRAF3 is a critical regulator of vascular tone and hypertension. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strassheim, D.; Gerasimovskaya, E.; Irwin, D.; Dempsey, E.C.; Stenmark, K.; Karoor, V. RhoGTPase in Vascular Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilluy, C.; Brégeon, J.; Toumaniantz, G.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M.; Retailleau, K.; Loufrani, L.; Henrion, D.; Scalbert, E.; Bril, A.; Torres, R.M.; et al. The Rho exchange factor Arhgef1 mediates the effects of angiotensin II on vascular tone and blood pressure. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.L.; Chadeuf, G.; Heurtebise-Chretien, S.; Prieur, X.; Quillard, T.; Goueffic, Y.; Vaillant, N.; Rio, M.; Castan, L.; Durand, M.; et al. Leukocyte RhoA exchange factor Arhgef1 mediates vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 4516–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Jin, L.; Dorrance, A.M.; Webb, R.C. Increased expression of mRNA for regulator of G protein signaling domain-containing Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors in aorta from stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yu, L.; Quinn, D.A.; Garg, H.G.; Hales, C.A. Heparin inhibits pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell proliferation through guanine nucleotide exchange factor-H1/RhoA/Rho kinase/p27. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2011, 44, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgers, R.H.; Todd, J., Jr.; Webb, R.C. Increased PDZ-RhoGEF/RhoA/Rho kinase signaling in small mesenteric arteries of angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats. J. Hypertens. 2007, 25, 1687–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Giachini, F.R.; Tostes, R.C.; Webb, R.C. PYK2/PDZ-RhoGEF links Ca2+ signaling to RhoA. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.; Juang, J.; Chang, S.; Wu, C.; Tsai, C.; Tseng, Y.; Chiang, F. Angiotensin II regulates the LARG/RhoA/MYPT1 axis in rat vascular smooth muscle in vitro. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2012, 33, 1502–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, M. Role of Rac1 GTPase in salt-sensitive hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2013, 22, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirth, A.; Benyo, Z.; Lukasova, M.; Leutgeb, B.; Wettschureck, N.; Gorbey, S.; Orsy, P.; Horvath, B.; Maser-Gluth, C.; Greiner, E.; et al. G12-G13–LARG–mediated signaling in vascular smooth muscle is required for salt-induced hypertension. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 64–68, Erratum in Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Hajicek, N.; Kozasa, T. Regulation and physiological functions of G12/13-mediated signaling pathways. Neurosignals 2009, 17, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Z.; Jin, L.; Palmer, T.; Webb, R.C. Angiotensin II up-regulates leukemia-associated Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (LARG), a RGS domain containing RhoGEF, in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 69, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Profirovic, J.; Pan, H.; Vaiskunaite, R.; Voyno-Yasenetskaya, T. G Protein betagamma subunits stimulate p114RhoGEF, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for RhoA and Rac1: Regulation of cell shape and reactive oxygen species production. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomquist, A.; Schwörer, G.; Schablowski, H.; Psoma, A.; Lehnen, M.; Jakobs, K.H.; Rümenapp, U. Identification and characterization of a novel Rho-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor. Biochem. J. 2000, 352 Pt 2, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momotani, K.; Somlyo, A.V. p63RhoGEF: A new switch for G(q)-mediated activation of smooth muscle. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2012, 22, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuertz, C.M.; Lorincz, A.; Vettel, C.; Thomas, M.A.; Wieland, T.; Lutz, S. p63RhoGEF—A key mediator of angiotensin II-dependent signaling and processes in vascular smooth muscle cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 4865–4876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bregeon, J.; Loirand, G.; Pacaud, P.; Rolli-Derkinderen, M. Angiotensin II induces RhoA activation through SHP2-dependent dephosphorylation of the RhoGAP p190A in vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C1062–C1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammoto, T.; Parikh, S.M.; Mammoto, A.; Gallagher, D.; Chan, B.; Mostoslavsky, G.; Ingber, D.E.; Sukhatme, V.P. Angiopoietin-1 requires p190 RhoGAP to protect against vascular leakage in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23910–23918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Mangum, K.; Kakoki, M.; Smithies, O.; Mack, C.P.; Taylor, J.M. GRAF3 serves as a blood volume-sensitive rheostat to control smooth muscle contractility and blood pressure. Small GTPases 2018, 11, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, M.; Yanagihara, H.; Hishinuma, S.; Saito, M.; Walsh, M.P. Membrane depolarization-induced contraction of rat caudal arterial smooth muscle involves Rho-associated kinase. Biochem. J. 2002, 364, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mita, M.; Tanaka, H.; Yanagihara, H.; Nakagawa, J.; Hishinuma, S.; Sutherland, C.; Walsh, M.P.; Shoji, M. Membrane depolarization-induced RhoA/rho-associated kinase activation and sustained contraction of rat caudal arterial smooth muscle involves genistein-sensitive tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Smooth Muscle Res. 2013, 49, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, R.D.; Mita, M.; Nakagawa, J.; Shoji, M.; Sutherland, C.; Walsh, M.P. A role for the tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in depolarization-induced contraction of vascular smooth muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 8677–8692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, R.D.; Mita, M.; Walsh, M.P. A role for the Ca2+-dependent tyrosine kinase Pyk2 in tonic depolarization-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2015, 36, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aida, K.; Mita, M.; Ishii-Nozawa, R. Difference in contractile mechanisms between the early and sustained components of ionomycin-induced contraction in rat caudal arterial smooth muscle. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 47, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, A.L.; Ferguson, A.G.; Lucchesi, P.A.; Samarel, A.M. Pyk2 expression and phosphorylation in neonatal and adult cardiomyocytes. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2001, 33, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Jácamo, R.O.; Vong, S.K.; Rozengurt, E. Differential regulation of Pyk2 phosphorylation at Tyr-402 and Tyr-580 in intestinal epithelial cells: Roles of calcium, Src, Rho kinase, and the cytoskeleton. Cell Signal. 2006, 18, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Loftus, J.C. Targeting Pyk2 for therapeutic intervention. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 14, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, T.; Matsuda, E.; Sasaki, H.; Sasaki, T. Protein-tyrosine kinase CAKβ/PYK2 is activated by binding Ca2+/calmodulin to FERM F2 α2 helix and thus forming its dimer. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burridge, K.; Chrzanowska-Wodnicka, M. Focal adhesions, contractility, and signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996, 12, 463–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roof, R.W.; Haskell, M.D.; Dukes, B.D.; Sherman, N.; Kinter, M.; Parsons, S.J. Phosphotyrosine (p-Tyr)-dependent and -independent mechanisms of p190 RhoGAP-p120 RasGAP interaction: Tyr 1105 of p190, a substrate for c-Src, is the sole p-Tyr mediator of complex formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 7052–7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, J.; Kaziro, Y.; Satoh, T. Activation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor Dbl following ACK1-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 268, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Ying, Z.; Hilgers, R.H.; Yin, J.; Zhao, X.; Imig, J.D.; Webb, R.C. Increased RhoA/Rho-kinase signaling mediates spontaneous tone in aorta from angiotensin II-induced hypertensive rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2006, 318, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Brecher, P. Salicylate inhibits phosphorylation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinases, proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 and c-Src. Hypertension 2001, 37, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ying, Z.; Giachini, F.R.; Tostes, R.C.; Webb, R.C. Salicylates dilate blood vessels through inhibiting PYK2-mediated RhoA/Rho-kinase activation. Cardiovasc. Res. 2009, 83, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mistry, A.; Chang, J.S.; Cunningham, D.; Griffor, M.; Bonnette, P.C.; Wang, H.; Chrunyk, B.A.; Aspnes, G.E.; Walker, D.P.; et al. Structural characterization of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (PYK2) reveals a unique (DFG-out) conformation and enables inhibitor design. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13193–13201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Dhruv, H.; Kwiatkowska-Piwowarczyk, A.; Ruggieri, R.; Kloss, J.; Symons, M.; Pirrotte, P.; Eschbacher, J.M.; Tran, N.L.; Loftus, J.C. PDZ-RhoGEF is a signaling effector for TROY-induced glioblastoma cell invasion and survival. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 1045–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Marchioni, F.; Evelyn, C.R.; Sipes, N.; Zhou, X.; Seibel, W.; Wortman, M.; Zheng, Y. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting G-protein-coupled Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3155–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, K.; Ishii-Nozawa, R.; Mita, M. Effects of Rho inhibitors on membrane depolarization-induced contraction of male rat caudal arterial smooth muscle. Physiol. Rep. 2025, 13, e70293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Janoštiak, R.; Tolde, O.; Ryzhova, L.M.; Koudelková, L.; Dibus, M.; Brábek, J.; Hanks, S.K.; Rosel, D. ARHGAP42 is activated by Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation to promote cell motility. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 2382–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, R.M.; Wilkes, J.J.; Chao, M.V.; Resh, M.D. Tyrosine phosphorylation of p190 RhoGAP by Fyn regulates oligodendrocyte differentiation. J. Neurobiol. 2001, 49, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Salazar, S.V.; Cox, T.O.; Strittmatter, S.M. Pyk2 Signaling through Graf1 and RhoA GTPase is required for amyloid-β oligomer-triggered synapse loss. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 1910–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | RT-PCR Amplicon |
|---|---|---|---|
| ArhGEF1 | ArhGEF1 forward | ATCAAGCTGTCCGTGACATG | 109 bp |
| ArhGEF1 reverse | TTGAACTCGCTCAGCATTGG | ||
| ArhGEF2 | ArhGEF2 forward | AGCATTACAGCCAAGGAAGC | 122 bp |
| ArhGEF2 reverse | AGCAGTGCAGCTTTCTGTTG | ||
| ArhGEF11 | ArhGEF11 forward | TTGTTCAGCGCTGTGTCATC | 124 bp |
| ArhGEF11 reverse | TTCACACCAGCTTTCATGGC | ||
| ArhGEF12 | ArhGEF12 forward | AACAGAAAGTCGAACGCAGCAC | 119 bp |
| ArhGEF12 reverse | ACAGCGCTGAACAAGACCATAG | ||
| ArhGEF18 | ArhGEF18 forward | ATCCGGCAAACTCAAGAACG | 146 bp |
| ArhGEF18 reverse | GCAAAAGCACATCGGTCAAC | ||
| ArhGEF25 | ArhGEF25 forward | TTAAACCGGTGCAGCGAATC | 142 bp |
| ArhGEF25 reverse | ATATCATTGCAGCGCTTGGG | ||
| ArhGAP35 | ArhGAP35 forward | TGCATGCTCTGAAGGAAGTG | 103 bp |
| ArhGAP35 reverse | ACCTTGTTGTTGTGGCTGAC | ||
| ArhGAP42 | ArhGAP42 forward | AGCTGCCTCCAAAAATGTGC | 121 bp |
| ArhGAP42 reverse | TTGAGCGACCCAGCATTTTC | ||
| GAPDH1 | GAPDH1 forward | AGTTCAACGGCACAGTCAAG | 119 bp |
| GAPDH1 reverse | ATACTCAGCACCAGCATCACC | ||
| GAPDH2 | GAPDH2 forward | TGATGCTGGTGCTGAGTATGTC | 135 bp |
| GAPDH2 reverse | ATCACAAACATGGGGGCATC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aida, K.; Mita, M.; Ishii-Nozawa, R. Role of RhoGEFs or RhoGAPs in Pyk2-Mediated RhoA Activation in Depolarization-Induced Contraction of Rat Caudal Arterial Smooth Muscle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178676
Aida K, Mita M, Ishii-Nozawa R. Role of RhoGEFs or RhoGAPs in Pyk2-Mediated RhoA Activation in Depolarization-Induced Contraction of Rat Caudal Arterial Smooth Muscle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178676
Chicago/Turabian StyleAida, Kazuki, Mitsuo Mita, and Reiko Ishii-Nozawa. 2025. "Role of RhoGEFs or RhoGAPs in Pyk2-Mediated RhoA Activation in Depolarization-Induced Contraction of Rat Caudal Arterial Smooth Muscle" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178676
APA StyleAida, K., Mita, M., & Ishii-Nozawa, R. (2025). Role of RhoGEFs or RhoGAPs in Pyk2-Mediated RhoA Activation in Depolarization-Induced Contraction of Rat Caudal Arterial Smooth Muscle. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178676





