Large-Scale Screening and Identification of S-RNase Alleles in Chinese and European Apricot Accessions Reveal Their Diversity and Geographic Distribution Patterns
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of S-Alleles in Apricot
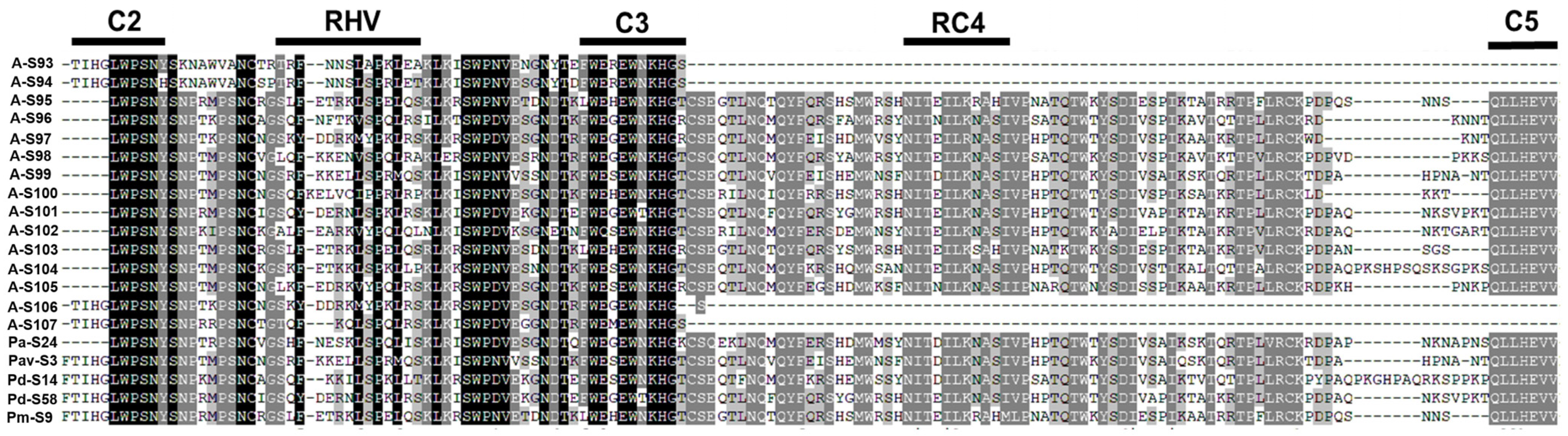
2.2. Identification of New S-Alleles in Apricot
2.3. Identification of Sc-Allele
2.4. Analysis of S-Genotypes of 168 Apricot Cultivars
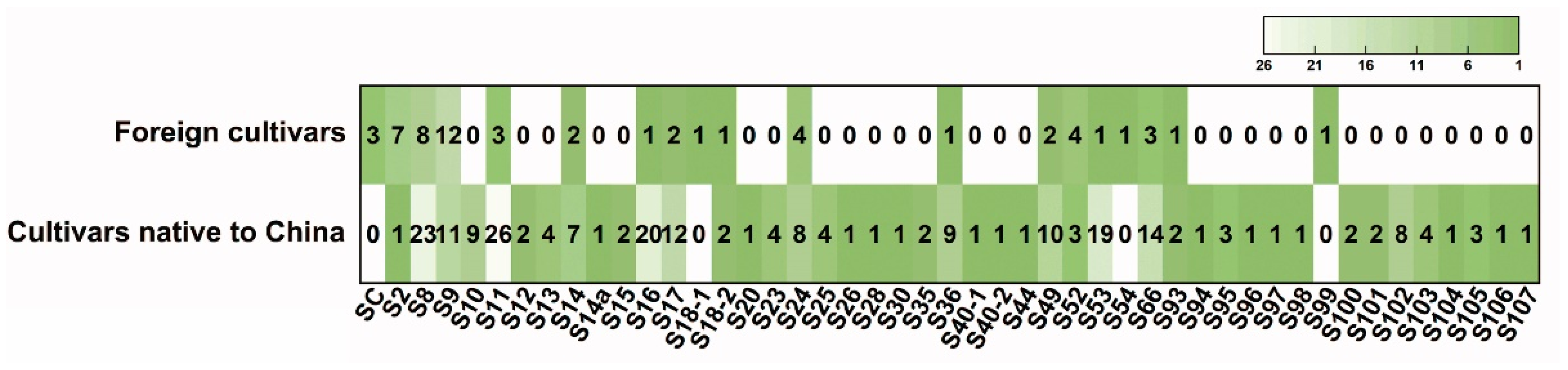
2.5. S-Allele Frequency Distribution Patterns Between Chinese and Foreign Apricot Accessions
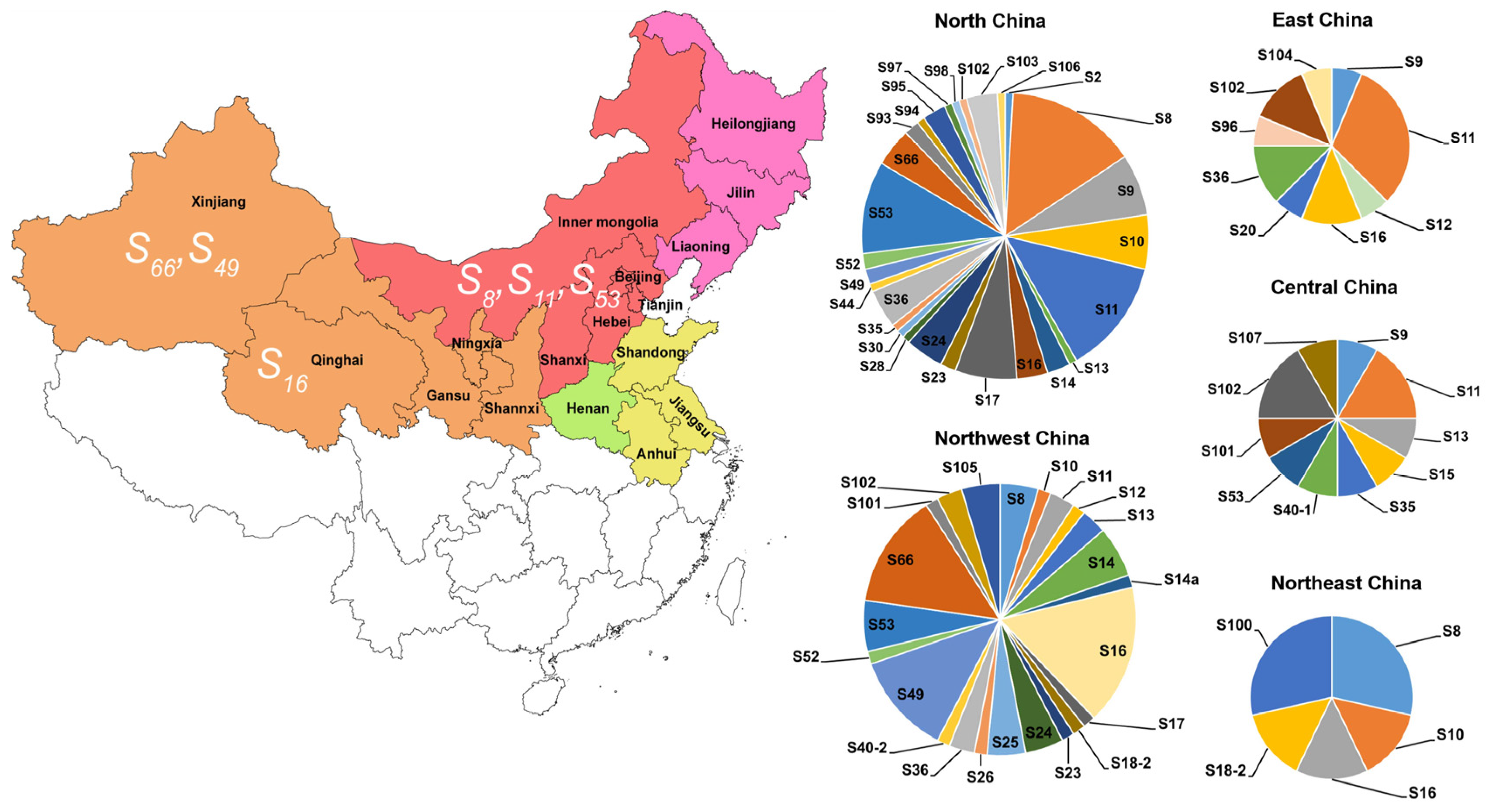
2.6. Geographic Distribution Patterns of S-Allele Frequencies in Chinese Apricot Cultivars
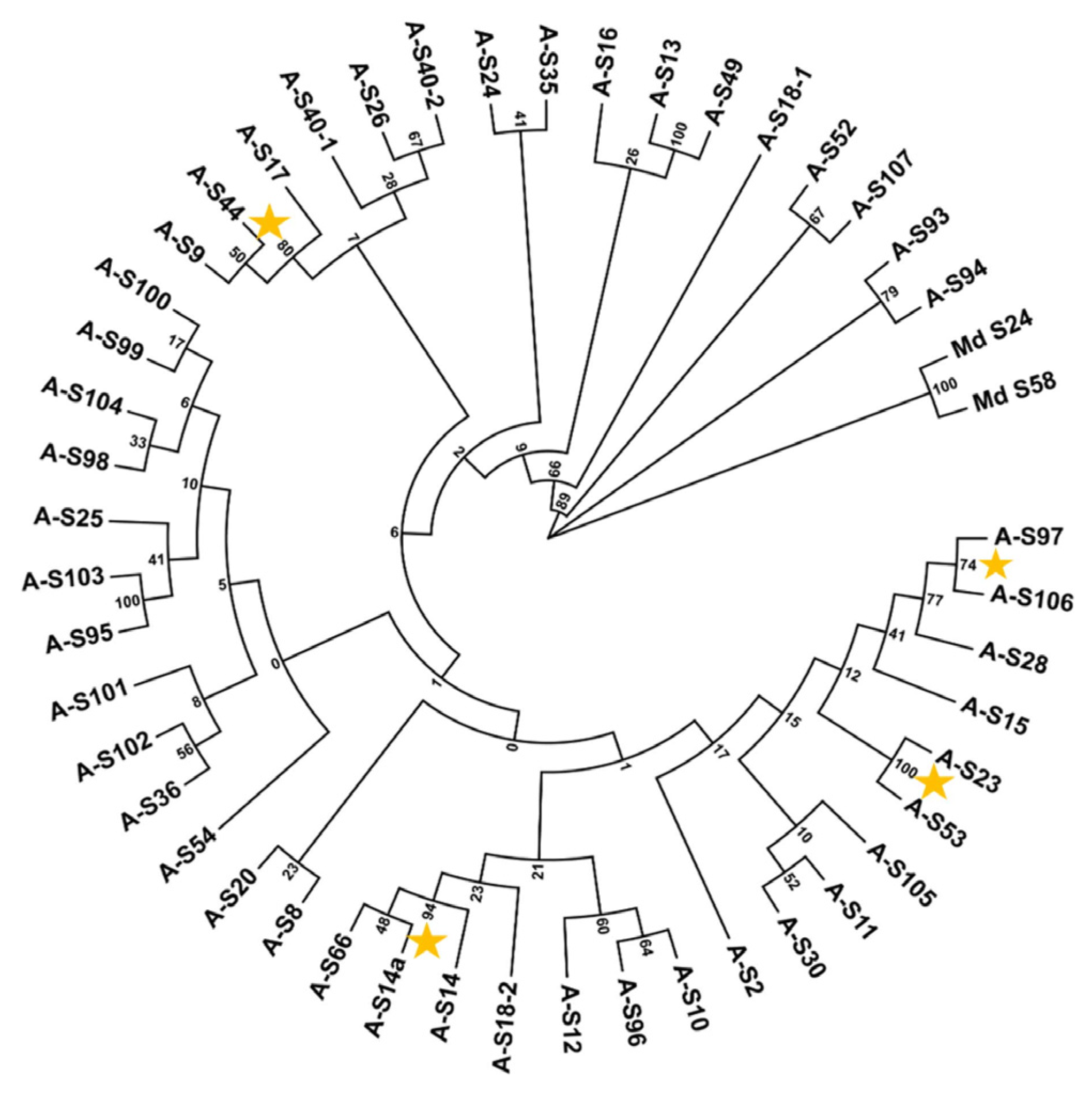
2.7. S-RNase Gene Sequence Alignment and Phylogeny
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. DNA Extraction
4.3. PCR Amplification
4.4. Cloning and Sequencing of S-Alleles
4.5. Analysis for Sequence Data and Identification of S-Alleles
4.6. Construction of Phylogenetic Tree Based on S-RNase Gene Sequences
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Pu, C.; Hao, Y.; Yao, Y.; Chang, J. Investigation on the affinity of different on pollinating combinations among apricot species. J. Fruit Sci. 1995, 15, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; He, T.; Feng, J.; Liang, Q.; Liu, W.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L. Inheritance and correlation of self-compatibility and other yield components in the apricot hybrid F1 populations. Euphytica 2006, 150, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audergon, J.M.; Guerriero, R.; Monteleone, P.; Viti, R. Contribution to the study of inheritance of the character self-incompatibility in apricot. Acta Hortic. 1999, 488, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, L.; Peréz-Tornero, O.; Ballester, J.; Olmos, E. Detection and inheritance of stylar ribonucleases associated with incompatibility alleles in apricot. Sex. Plant Reprod. 1998, 11, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, J.; Pedryc, A.; Ercisli, S.; Yilmaz, K.U.; Hegedűs, A. S-genotyping supports the genetic relationships between Turkish and Hungarian apricot germplasm. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2010, 135, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.; Vilanova, S.; Burgos, L.; Martinez-Calvo, J.; Vicente, M.; Llácer, G.; Badenes, M.L. Analysis of the S-locus structure in Prunus armeniaca L. Identification of S-haplotype S-RNase and F-box genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2004, 56, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gu, C.; Du, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, W.S.; Liu, N.; Lu, J.; Zhang, S.L. Self-compatibility of ‘Katy’ apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) is associated with pollen-part mutations. Sex. Plant Reprod. 2011, 24, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cachi, A.M.; Wünsch, A. Characterization of self-compatibility in sweet cherry varieties by crossing experiments and molecular genetic analysis. Tree Genet. Genom. 2014, 10, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Yamane, H.; Sassa, H.; Mori, H.; Gradziel, T.M.; Dandekar, A.M.; Sugiura, A. Identification of stylar RNases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility in almond (Prunus dulcis). Plant Cell Physiol. 1997, 38, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, J.; Hegedűs, A.; Hermán, R.; Stefanovits-Bányai, É.; Pedryc, A. New self-incompatibility alleles in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) revealed by stylar ribonuclease assay and S-PCR analysis. Euphytica 2005, 145, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraket, G.; Abdallah, D.; Mustapha, S.B.; Tamarzizt, H.B.; Salhi-Hannachi, A. Combination of simple sequence repeat, S-Locus polymorphism and phenotypic data for identification of Tunisian plum species (Prunus spp.). Biochem. Genet. 2019, 57, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, J.; Makovics-Zsohár, N.; Szőke, F.; Ercisli, S.; Hegedűs, A. Simple sequence repeat and S-locus genotyping to assist the genetic characterization and breeding of polyploid Prunus species, P. spinosa and P. domestica subsp. insititia. Biochem. Genet. 2021, 59, 1065–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.P.; Gao, Z.H.; Ni, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, B.H. Self-compatibility in ‘Zaohong’ Japanese apricot is associated with the loss of function of pollen S genes. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2013, 40, 6485–6493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonneveld, T.; Tobutt, K.R.; Robbins, T.P. Allele-specific PCR detection of sweet cherry self-incompatibility (S) alleles S1 to S16 using consensus and allele-specific primers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 1059–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivistik, A.; Jakobson, L.; Kahu, K.; Laanemets, K. Wild and rare self-incompatibility allele S17 found in 24 sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) cultivars. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 40, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, M.; Ushijima, K.; Sassa, H.; Hirano, H.; Tao, R.; Gradziel, T.M.; Dandekar, A.M. Identification of self-incompatibility genotypes of almond by allele-specific PCR analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Wang, K.; Feng, J.; Sun, S.; Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Tian, W.; Wang, G.; Li, Z.; et al. Identification of S-RNase genotype and analysis of its origin and evolutionary patterns in Malus plants. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 1205–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Yang, W.; Su, S.; Fu, L.; Yi, H.; Chen, C.; Deng, X.; Chai, L. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of S-RNase involved in the self-incompatibility of citrus. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2017, 292, 315–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ge, C.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Gao, Z.; Sassa, H.; Qiao, Y. Molecular characteristics of S-RNase alleles as the determinant of self-incompatibility in the style of Fragaria viridis. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Xu, O.; Liu, C.; Liu, B.; Deng, C.; Chen, C.; Wei, Z.; Ahmad, M.H.; Peng, K.; Wen, H.; et al. Downregulated expression of S2-RNase attenuates self-incompatibility in “Guiyou No. 1” pummelo. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodad, O.; Hegedűs, A.; Company, R.S.; Halász, J. Self-(in)compatibility genotypes of Moroccan apricots indicate differences and similarities in the crop history of European and North African apricot germplasm. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, S.; Rodrigo, J.; Hormaza, J.I.; Lora, J. Identification of self-incompatibility alleles by specific PCR analysis and S-RNase sequencing in apricot. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, A.; Krichen, L.; Batnini, M.A.; Trifi-Farah, N.; Roch, G.; Audergon, J.M.; Bourguiba, H. Self-(in)compatibility analysis of apricot germplasm in Tunisia: S-RNase allele identification, S-genotype determination and crop history evolution. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 276, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Gai, S.; Zhang, J.; Gu, M.; Shu, H. Identification of self-incompatibility genotypes of apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) by S-allele-specific PCR analysis. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 1205–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Ci, Z.J.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, C. Identification of self-incompatibility (S-) genotypes of Chinese apricot cultivars. Euphytica 2008, 160, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Gu, C.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, S.J.; Wu, H.Q.; Hen, W. Identification of S-haplotype-specific S-RNase and SFB alleles in native Chinese apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, D.; Feng, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X. Identification of self-incompatibility S-RNase genotypes for apricot cultivars in South of Xinjiang area. J. Fruit Sci. 2012, 29, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wuyu, T.; Li, H.; Du, H.; Yang, S. Eight new S-gene identification of Chinese plum and Chinese apricot. J. Cent. S. Univer. Forest. Technol. 2011, 31, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, S.; Romerot, S.; Llácer, G.; Badenes, M.L.; Burgos, L. Identifcation of self-(in)compatibility alleles in apricot by PCR and sequence analysis. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 2005, 130, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sanz, J.V.; Zuriaga, E.; López, I.; Badenes, M.L.; Romero, C. Self-(in)compatibility in apricot germplasm is controlled by two major loci, S and M. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, N.; Egea, J.; Pérez-Tornero, O.; Burgos, L. Genotyping apricot cultivars for self-(in)compatibility by means of RNases associated with S alleles. Plant Breed. 2002, 121, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.; Brown, A.G. Genetic response to selection in cultivated plants: Gene frequencies in Prunus avium. Heredity 1956, 10, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.; Pedryc, A.; Munoz, V.; Llácer, G.; Badenes, M.L. Genetic diversity of different apricot geographical groups determined by SSR markers. Genome 2003, 46, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Ning, N.; Yang, L. Construction and evaluation of a primary core collection of apricot germplasm in China. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 128, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, F.; Yu, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H. Jingren 2: A new kernel-using apricot cultivar of Prunus armeniaca × Prunus amygdalus. HortScience 2024, 59, 1845–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, B.G.; Robbins, T.P.; Tobutt, K.R. Primers amplifying a range of Prunus S-alleles. Plant Breed. 2004, 123, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Yamane, H.; Sugiura, A.; Murayama, H.; Sassa, H.; Mori, H. Molecular typing of S-alleles through identification, characterization and cDNA cloning for S-RNases in sweet cherry. J. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1999, 124, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, J.; Pedryc, A.; Hegedűs, A. Origin and dissemination of the pollen-part mutated SC-haplotype which confers self-compatibility in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). New Phytol. 2007, 176, 792–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| S-Allele | PCR Fragment Size (bp)/Intron Sizes (bp) | Genebank Accession No. | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM-PC2consFD, | Pru-C2, | Pru-C2, | ASI II, | PaCons II-F, | ||
| EM-PC3consRD | Amy-C5 | PCE-R | Amy-C5 | PaCons II-R | ||
| S2 | 895/706 | 1096/706 | AY587562.1 | |||
| S8 | 827/410 | 573/409 | 928/411 | AY884212.1 | ||
| S9 | 885/467 | AY853594.1 | ||||
| S10 | 266/180 | AY846872.1 | ||||
| S11 | 464/275 | 672/275 | DQ868316.1 | |||
| S12 | 359/171 | DQ870628.1 | ||||
| S13 | 401/212 | DQ870629.1 | ||||
| S14 | 493/305 | DQ870630.1 | ||||
| S14a | 495/309 | GU574199.1 | ||||
| S15 | 469/283 | DQ870631.1 | ||||
| S16 | 481/292 | 700/292 | DQ870631.1 | |||
| S17 | 657/461 | DQ270001.1 | ||||
| S18-1 * | 307/108 | DQ270000.1 | ||||
| S18-2 * | 1337/1148 | 1546/1148 | DQ870634.1 | |||
| S20 | 1936/1749 | EF160078.1 | ||||
| S23 | 693/505 | EU037262.1 | ||||
| S24 | 357/168 | 588/168 | EU037263.1 | |||
| S25 | 772/583 | 994/584 | EU037264.1 | |||
| S26 | 416/289 | EU037265.1 | ||||
| S28 | 1352/946 | EU836684.1 | ||||
| S30 | 726/285 | EF185301.1 | ||||
| S35 | 312/124 | GU574196.1 | ||||
| S36 | 718/299 | GU574198.1 | ||||
| S40-1 * | 539/353 | 749/353 | GU354239.1 | |||
| S40-2 * | 542/164 | HQ342870.1 | ||||
| S44 | 635/464 | HQ342874.1 | ||||
| S49 | 653/212 | HQ342879.1 | ||||
| S52 | 1296/1111 | 1512/1110 | KF951503.2 | |||
| S53 | 965/508 | KF975455.2 | ||||
| S54 | 1296/891 | KT223013.1 | ||||
| S66 | 704/308 | JQ317152.1 | ||||
| S-Alleles | Cultivar No. | Cultivar Name | Primer Pairs and PCR Fragment Size (bp)/Intron Sizes (bp) | GeneBank Accession No. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EM-PC2consFD, EM-PC3consRD | Pru-C2, Amy-C5 | ||||
| S93 | 22 | Jingjia No. 2 | 273/90 | PV206781 | |
| S94 | 46 | Dafeng | 502/319 | PV206782 | |
| S95 | 28 | Jingren No.4 | 683/275 | PV206783 | |
| S96 | 74 | Hongjinzhen | 575/173 | PV206784 | |
| S97 | 58 | Xingtaihongjiexing | 746/458 | PV206785 | |
| S98 | 25 | Jingren No.1 | 871/460 | PV206791 | |
| S99 | 158 | Harmat | 884/460 | PV206786 | |
| S100 | 82 | Dongning No.2 | 924/522 | PV206792 | |
| S101 | 96 | Lintonghongxing | 1348/928 | PV206787 | |
| S102 | 23 | Jingluofeng | 1416/996 | PV206793 | |
| S103 | 52 | Longwangmao | 1452/1044 | PV206788 | |
| S104 | 75 | Jinkaite | 1466/1035 | PV206789 | |
| S105 | 100 | Niujiaobangzi | 1625/1214 | PV206794 | |
| S106 | 31 | Longquanwuxiangbai | 533/346 | PV206790 | |
| S107 | 69 | Yuhankui | 1227/1046 | PV206780 | |
| No. | Cultivar | Province, Country of Origin | S-Genotype | Areas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Baixing 10-38 | Beijing, China | S9S10 | North China |
| 2 | Beianhe | Beijing, China | S9S17 | |
| 3 | Beishandabian | Beijing, China | S10S53 | |
| 4 | Beizhaihongxing | Beijing, China | S93S103 | |
| 5 | Chuanling | Beijing, China | S8S53 | |
| 6 | Dabada | Beijing, China | S36 | |
| 7 | Fangshanhongxing | Beijing, China | S11 | |
| 8 | Fangshanxiangbai | Beijing, China | S17S53 | |
| 9 | Guajiayutianhexiangbai | Beijing, China | S8S17 | |
| 10 | H20-5 | Beijing, China | S9S95 | |
| 11 | H21-25 | Beijing, China | S23S53 | |
| 12 | H23-37 | Beijing, China | S14S66 | |
| 13 | H23-43 | Beijing, China | S14S66 | |
| 14 | H23-44 | Beijing, China | S14S66 | |
| 15 | H-48 | Beijing, China | S8S52 | |
| 16 | Honghuomeizi | Beijing, China | S8S53 | |
| 17 | Huangjianzui | Beijing, China | S2S66 | |
| 18 | Jingcuihong | Beijing, China | S10S11 | |
| 19 | Jingfeihong | Beijing, China | S8S11 | |
| 20 | P35-146 | Beijing, China | S8S30 | |
| 21 | Jingjia No.1 | Beijing, China | S24S49 | |
| 22 | Jingjia No.2 | Beijing, China | S24S93 | |
| 23 | Jingluofeng | Beijing, China | S11S102 | |
| 24 | Jingluohong | Beijing, China | S8S95 | |
| 25 | Jingren No.1 | Beijing, China | S98 | |
| 26 | Jingren No.2 | Beijing, China | S8 | |
| 27 | Jingren No.3 | Beijing, China | S103 | |
| 28 | Jingren No.4 | Beijing, China | S95 | |
| 29 | Jingren No.5 | Beijing, China | S24 | |
| 30 | Jingxianghong | Beijing, China | S10S11 | |
| 31 | Jingzaohong | Beijing, China | S9S36 | |
| 31 | Longquanwuxiangbai | Beijing, China | S53S106 | |
| 33 | Luotuohuang | Beijing, China | S8S11 | |
| 34 | Mituoluo | Beijing, China | S11 | |
| 35 | P51-54 | Beijing, China | S11S17 | |
| 36 | Pingguohong | Beijing, China | S8S66 | |
| 37 | Shanbaixing | Beijing, China | S17S53 | |
| 38 | Shanhuangxing | Beijing, China | S8S11 | |
| 39 | Xiaoyubada | Beijing, China | S23S53 | |
| 40 | Yingchun | Beijing, China | S24S36 | |
| 41 | Zaoxiangbai | Beijing, China | S10S53 | |
| 42 | Zhuyaozi | Beijing, China | S10S35 | |
| 43 | Guanlaoyelian | Tianjin province, China | S8S16 | |
| 44 | Wanxiangbai | Tianjin province, China | S17S53 | |
| 45 | Cangzaotian No.1 | Hebei province, China | S11S49 | |
| 46 | Chuanzhihong | Hebei province, China | S8S24 | |
| 46 | Dafeng | Hebei province, China | S8S94 | |
| 48 | Erhongxing | Hebei province, China | S11S17 | |
| 49 | Ganyu | Hebei province, China | S8S16 | |
| 50 | Jiguang | Hebei province, China | S8S9 | |
| 51 | Jinyu | Hebei province, China | S13S52 | |
| 52 | Longwangmao | Hebei province, China | S11S103 | |
| 53 | Muguaxing | Hebei province, China | S11S16 | |
| 54 | Qingmisha | Hebei province, China | S9S44 | |
| 55 | Shizixing | Hebei province, China | S10S53 | |
| 56 | Tianedan | Hebei province, China | S9S16 | |
| 57 | Xingtaidahongxing | Hebei province, China | S17S36 | |
| 58 | Xingtaihongjiexing | Hebei province, China | S8S97 | |
| 59 | You No.1 | Hebei province, China | S11S103 | |
| 60 | You No.2 | Hebei province, China | S11 | |
| 61 | Zaohongxing | Hebei province, China | S36 | |
| 62 | Zaohuang | Hebei province, China | S9S53 | |
| 63 | Guanyelian | Shanxi province, China | S28 | |
| 64 | Hongbada | Henan province, China | S101 | Central China |
| 65 | Lixing | Henan province, China | S40-1 | |
| 66 | Mixiangxing | Henan province, China | S11S15 | |
| 67 | Yangshaohuang No.1 | Henan province, China | S13S102 | |
| 68 | Yangshaohuang No.2 | Henan province, China | S36S102 | |
| 69 | Yuhankui | Henan province, China | S11S107 | |
| 70 | Yuzaoguan | Henan province, China | S9S53 | |
| 71 | Badou | Anhui, China | S36S102 | East China |
| 72 | Caizihuang | Shandong province, China | S11S16 | |
| 73 | Honghebao | Shandong province, China | S9S16 | |
| 74 | Hongjinzhen | Shandong province, China | S96 | |
| 75 | Jinkaite | Shandong province, China | S11S104 | |
| 76 | Kuijin | Shandong province, China | S11S102 | |
| 77 | Laoshanhong | Shandong province, China | S11 | |
| 78 | Pingdingzhen | Shandong province, China | S12S36 | |
| 79 | Qingdaodahong | Shandong province, China | S11 | |
| 80 | Zaoyu | Shandong province, China | S20 | |
| 81 | Dongning No.1 | Heilongjiang province, China | S16S100 | Northeast China |
| 82 | Dongning No.2 | Heilongjiang province, China | S100 | |
| 83 | Baixing | Liaoning province, China | S10 | |
| 84 | Daxingmei | Liaoning province, China | S8 | |
| 85 | Guofeng | Liaoning province, China | S8S18-2 | |
| 86 | Caoxing | Gansu province, China | S8S17 | Northwest China |
| 87 | Dajiexing | Gansu province, China | S16 | |
| 88 | Dapiantou | Gansu province, China | S36S102 | |
| 89 | Zhupishui | Gansu province, China | S8 | |
| 90 | Taoxing | Ningxia province, China | S16 | |
| 91 | Meixing | Qinghai province, China | S25 | |
| 92 | Caopixing | Shaanxi province, China | S16 | |
| 93 | Haidongxing | Shaanxi province, China | S16 | |
| 94 | Jidanxing | Shaanxi province, China | S25S26 | |
| 95 | Lanzhuhong | Shaanxi province, China | S16S23 | |
| 96 | Lingtonghongxing | Shaanxi province, China | S101 | |
| 97 | Lintonghongxing No.2 | Shaanxi province, China | S16 | |
| 98 | Liquanerzhuanzi | Shaanxi province, China | S16 | |
| 99 | Machuanling | Shaanxi province, China | S11S16 | |
| 100 | Niujiaobangzi | Shaanxi province, China | S105 | |
| 101 | Niujiaohuang | Shaanxi province, China | S105 | |
| 102 | Qinwang | Shaanxi province, China | S40-2 | |
| 103 | Touwojie | Shaanxi province, China | S16 | |
| 104 | Xinong 25 | Shaanxi province, China | S10S36 | |
| 105 | Yinxiangbai | Shaanxi province, China | S36S53 | |
| 106 | Zaotianhe | Shaanxi province, China | S16S105 | |
| 107 | Zhanggongyuan | Shaanxi province, China | S24S25 | |
| 108 | Ake | Xinjiang, China | S12S66 | |
| 109 | Chibangzi | Xinjiang, China | S13S49 | |
| 110 | Cuijianali | Xinjiang, China | S49S66 | |
| 111 | Dabaiyou | Xinjiang, China | S18-2S49 | |
| 112 | Daguohuanna | Xinjiang, China | S14S49 | |
| 113 | Dayoujia | Xinjiang, China | S49S66 | |
| 114 | Heiyexing | Xinjiang, China | S16S66 | |
| 115 | Kezimayisang | Xinjiang, China | S14aS66 | |
| 116 | Kuikepiman | Xinjiang, China | S11S53 | |
| 117 | Kumaiti | Xinjiang, China | S49S66 | |
| 118 | Liguangxing | Xinjiang, China | S24S49 | |
| 119 | Muyage | Xinjiang, China | S14S66 | |
| 120 | Pinaizi | Xinjiang, China | S13S49 | |
| 121 | Qiaoerpang | Xinjiang, China | S14S66 | |
| 122 | Saimaiti | Xinjiang, China | S24S53 | |
| 123 | Shushangganxing | Xinjiang, China | S14S66 | |
| 124 | Xinjiangshaxing | Xinjiang, China | S8S102 | |
| 125 | Xinshisheng | Xinjiang, China | S52S53 | |
| 126 | Bingtangwei | China | S17S25 | Unclear |
| 127 | Haihongzhen | China | S9S17 | |
| 128 | Haiquanhong | China | S8S11 | |
| 129 | Hongxing | China | S11 | |
| 130 | Kuhehonglian | China | S16S102 | |
| 131 | Longjingbaixing | China | S15S16 | |
| 131 | Xiaopuxiangbai | China | S17S53 | |
| 133 | Yinxing | China | S23S53 | |
| 134 | Meiwuming | American | S2S8 | Foreign areas |
| 135 | 99-2 | Czech Republic | S8S9 | |
| 136 | 99-12 | Czech Republic | S24 | |
| 137 | 99-15 | Czech Republic | S8S9 | |
| 138 | 99-27 | Czech Republic | S52 | |
| 139 | 99-31 | Czech Republic | S8S66 | |
| 140 | 99-37 | Czech Republic | S17S18-2 | |
| 141 | 99-38 | Czech Republic | S11 | |
| 142 | 99-43 | Czech Republic | S9S17 | |
| 143 | 99-44 | Czech Republic | S24S9 | |
| 144 | 99-45 | Czech Republic | S11 | |
| 145 | Aurora | Czech Republic | S8S9 | |
| 146 | Betinka | Czech Republic | S8S52 | |
| 147 | Hargand | Czech Republic | S2 | |
| 148 | Jennycot | Czech Republic | S2S9 | |
| 149 | Jitka | Czech Republic | S24S49 | |
| 150 | LE5137 | Czech Republic | S24 | |
| 151 | Rumjanaja | Czech Republic | S8S53 | |
| 152 | Bergeron | France | S2SC | |
| 153 | Canino | France | S2S9 | |
| 154 | Early orange | France | S9S11 | |
| 155 | Cegledi bibor kajszi | Hungary | S14S66 | |
| 156 | Cegledi orias | Hungary | S14S66 | |
| 157 | Cegledi piroska | Hungary | S36 | |
| 158 | Harmat | Hungary | S99 | |
| 159 | B088 | Italy | S54 | |
| 160 | B089 | Italy | S2S9 | |
| 161 | B095 | Italy | S49S93 | |
| 162 | Bora | Italy | S9SC | |
| 163 | Corlate | Italy | S18-1 | |
| 164 | Ninfa | Italy | S2SC | |
| 165 | Wondercot | Italy | S9S52 | |
| 166 | Yidalixing | Italy | S52 | |
| 167 | Pinghexing | Japan | S8S9 | |
| 168 | Xinzhoudashi | Japan | S16 |
| Number | Primer Name | Sequence (5′ to 3′) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | EM-PC2consFD | TCACM * ATYCATGGCCTATGG | Sutherland et al., 2004 [36] |
| EM-PC3consRD | AW * CTR * CCRTGY * TTGTTCCATTC | ||
| 2 | Pru-C2 | CTATGGCCAAGTAATTATTCAAACC | Tao et al., 1999 [37] |
| Pru-C5 | TACCACTTCATGTAACAACTGAG | ||
| 3 | Pru-C2 | CTATGGCCAAGTAATTATTCAAACC | Tao et al., 1999; Wu et al., 2009 [26,37] |
| PCE-R | TGTTTGTTCCATTCGCCTTCCC | ||
| 4 | AS1II | TATTTTCAATTTGTGCAATGG | Tamura et al., 2000 [16] |
| AmyC5R | CAAAATACCACTTCATGTAACAAC | ||
| 5 | PaCons II-F | GGCCAAGTAATTATTCAAACC | Sonneveld et al., 2003 [14] |
| PaCons II-R | CATAACAAARTACCACTTCATGTAAC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, W.; Jiang, F.; Yang, L.; Ling, J.; Sun, H. Large-Scale Screening and Identification of S-RNase Alleles in Chinese and European Apricot Accessions Reveal Their Diversity and Geographic Distribution Patterns. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178667
Zhang J, Zhang M, Yu W, Jiang F, Yang L, Ling J, Sun H. Large-Scale Screening and Identification of S-RNase Alleles in Chinese and European Apricot Accessions Reveal Their Diversity and Geographic Distribution Patterns. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178667
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Junhuan, Meiling Zhang, Wenjian Yu, Fengchao Jiang, Li Yang, Juanjuan Ling, and Haoyuan Sun. 2025. "Large-Scale Screening and Identification of S-RNase Alleles in Chinese and European Apricot Accessions Reveal Their Diversity and Geographic Distribution Patterns" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178667
APA StyleZhang, J., Zhang, M., Yu, W., Jiang, F., Yang, L., Ling, J., & Sun, H. (2025). Large-Scale Screening and Identification of S-RNase Alleles in Chinese and European Apricot Accessions Reveal Their Diversity and Geographic Distribution Patterns. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178667






