Ivermectin Binds to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) and Inhibits Allosteric Integrin Activation by TNF and Other Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Docking Simulation Predicts That IVM Binds to Site 2 of Integrin αvβ3
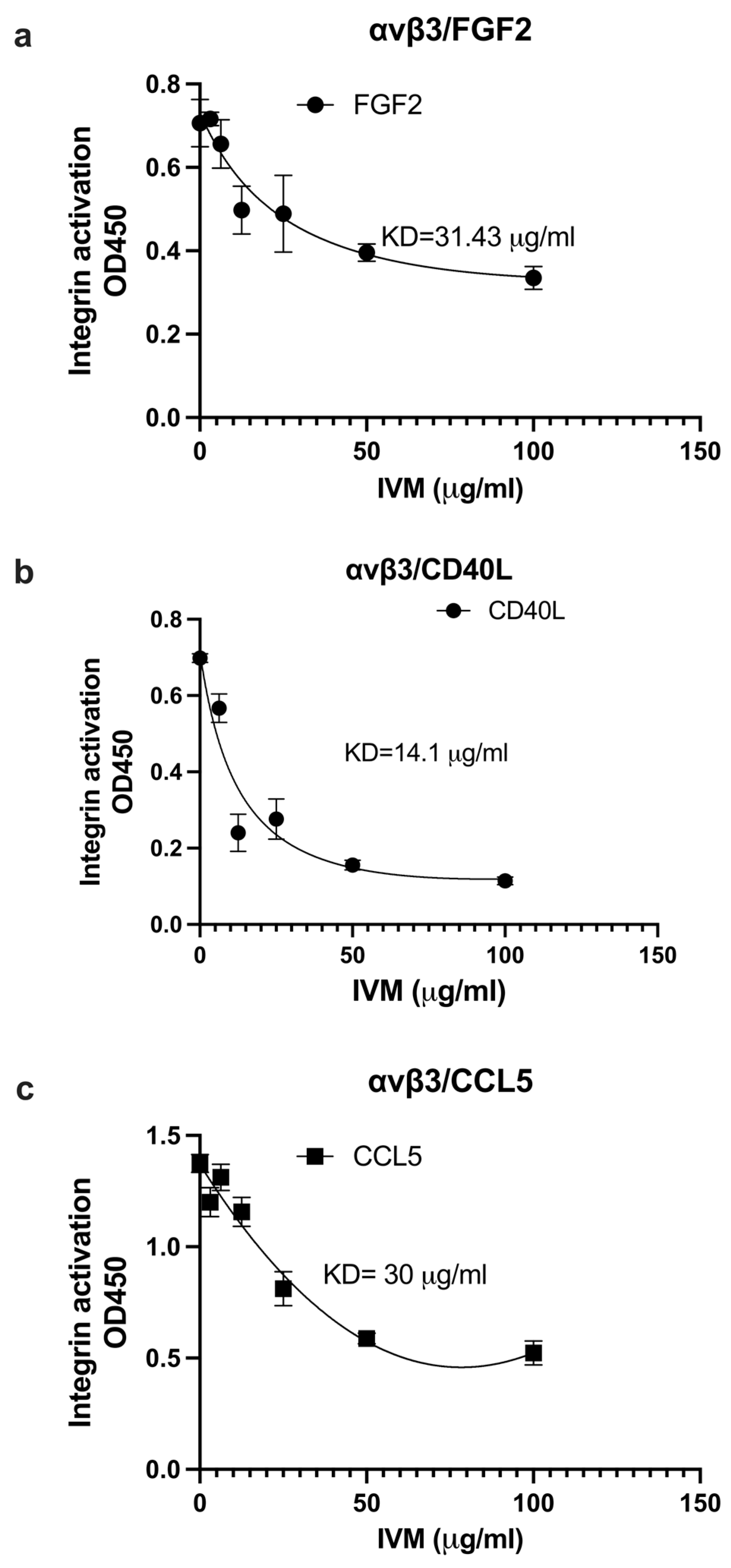
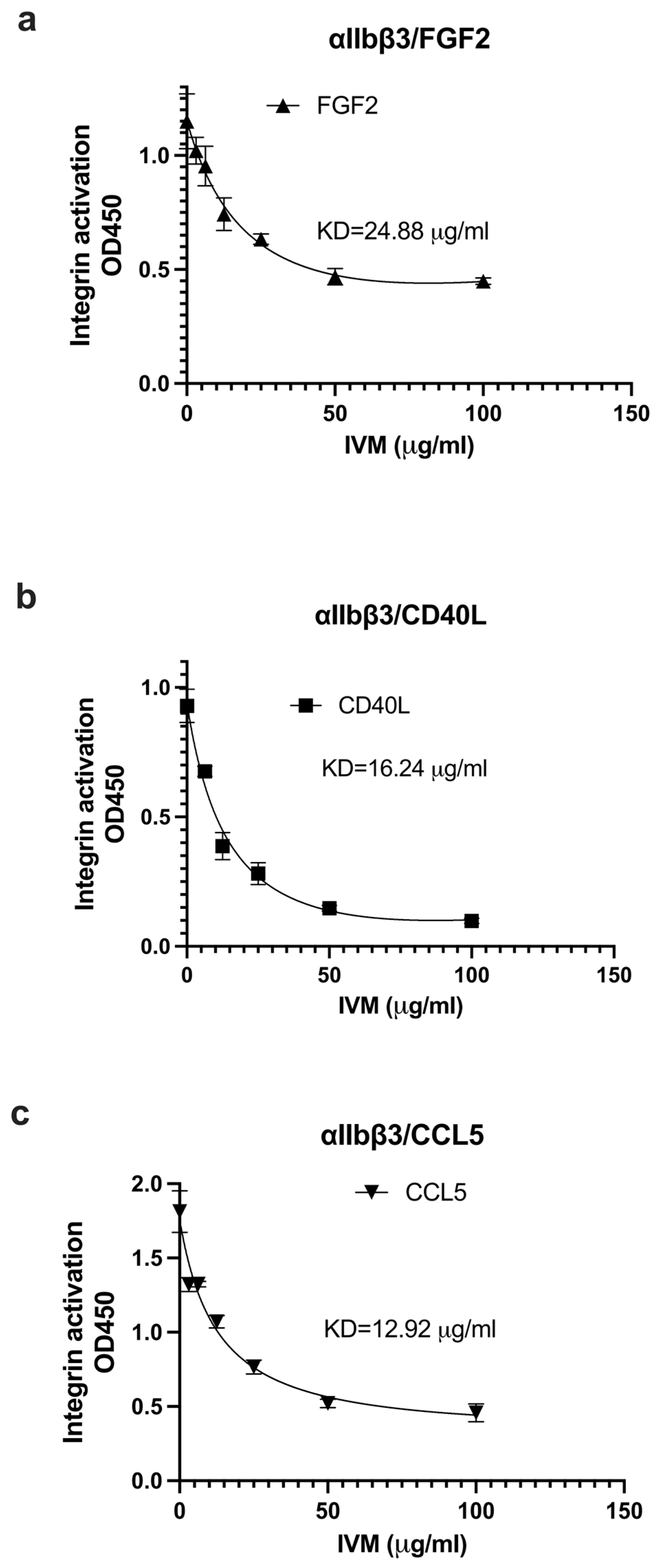
2.2. IVM Inhibits Allosteric Integrin Activation Induced by Multiple Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
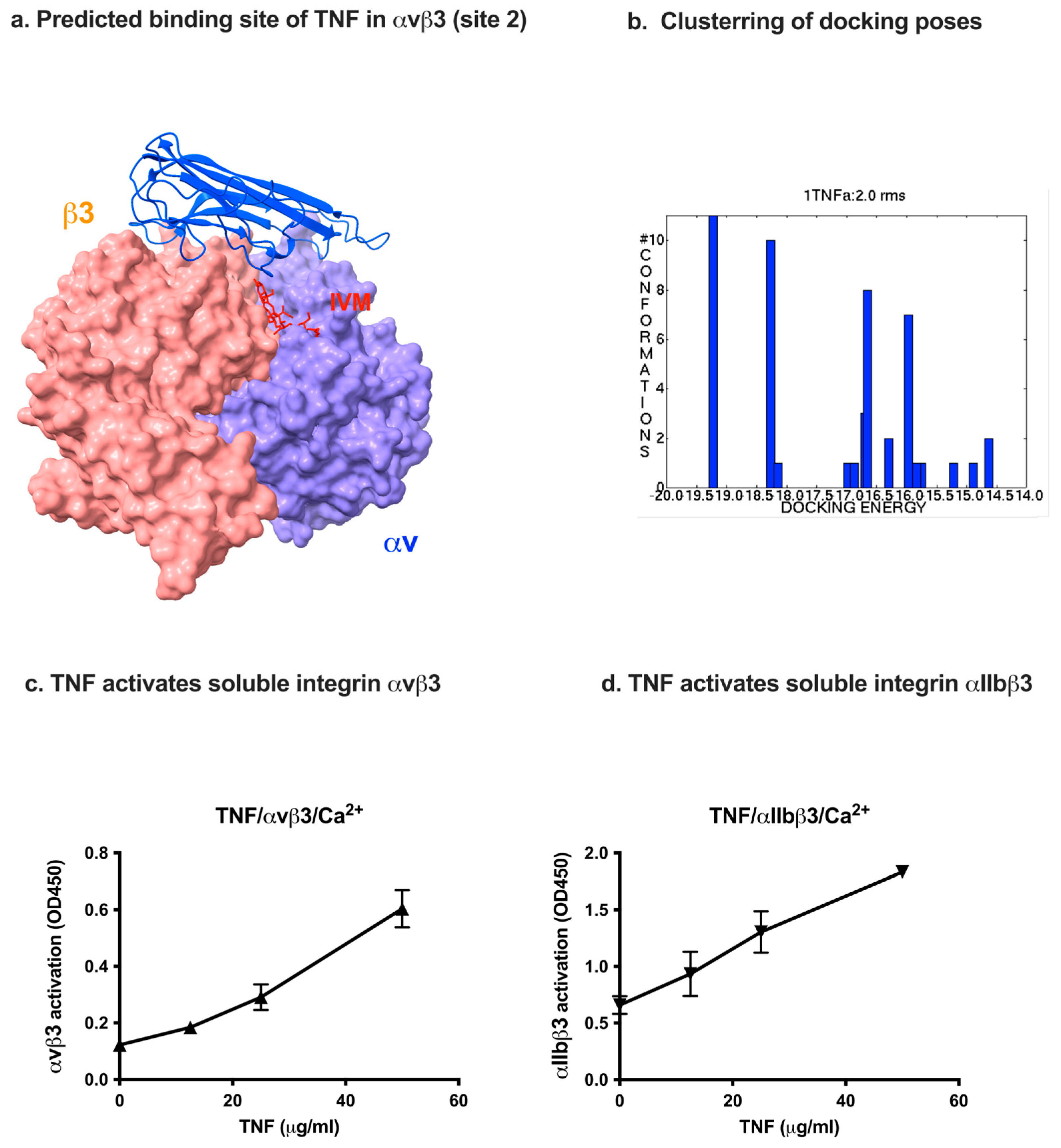
2.3. Docking Simulation Predicts That TNF Binds to Integrin
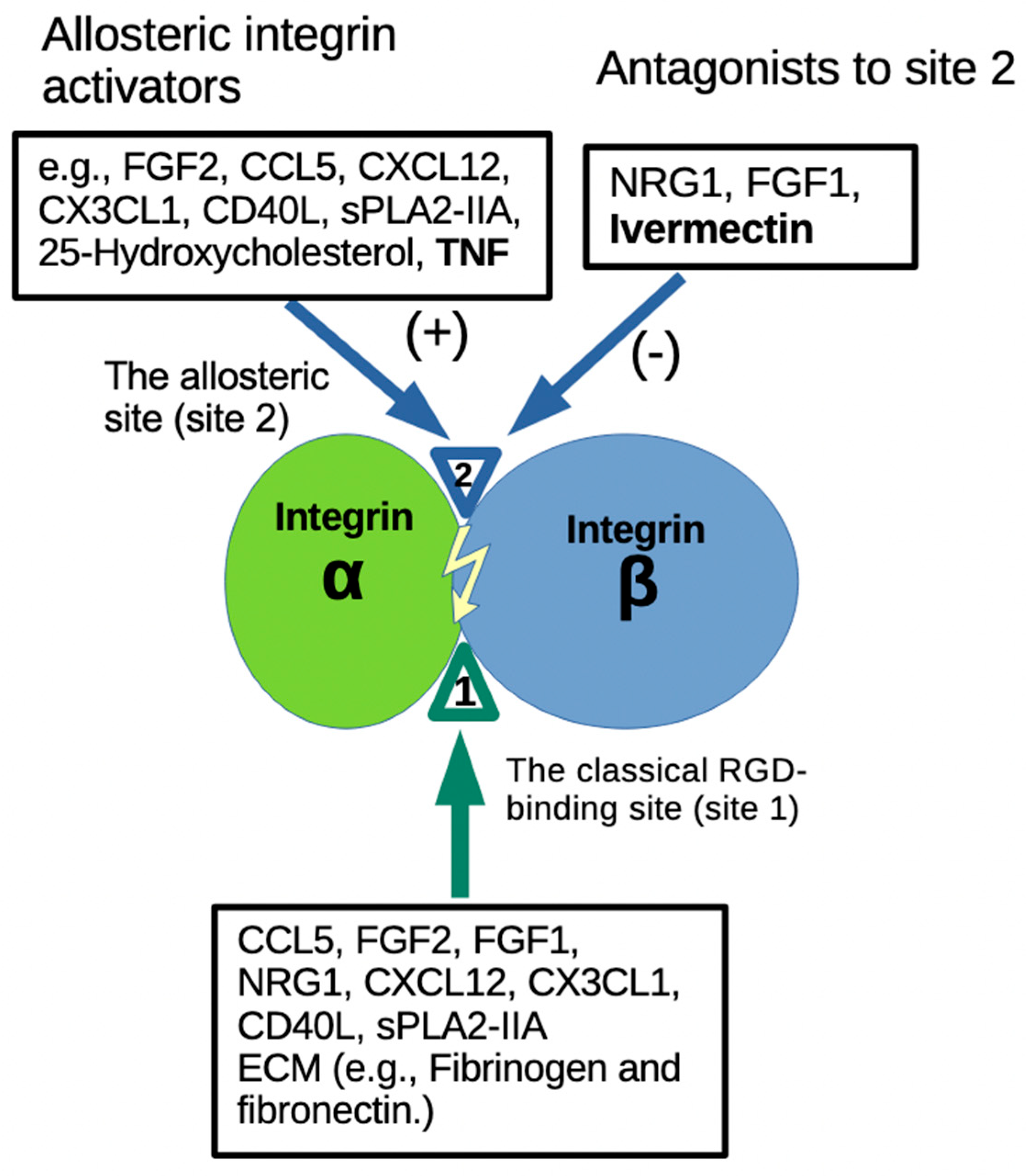
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Protein Expression
4.3. Docking Simulation
4.4. Binding of Soluble Integrins to TNF
4.5. Activation of Soluble αIIbβ3 and αvβ3
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Takada, Y.; Ye, X.; Simon, S. The integrins. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Wu, C.Y.; Yamaji, S.; Saegusa, J.; Shi, B.; Ma, Z.; Kuwabara, Y.; Lam, K.S.; Isseroff, R.R.; Takada, Y.K.; et al. Direct binding of integrin alphavbeta3 to FGF1 plays a role in FGF1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18066–18075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Hatori, N.; Kawaguchi, N.; Hamada, Y.; Shih, T.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Lam, K.S.; Matsuura, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Takada, Y.K.; et al. The integrin-binding defective FGF2 mutants potently suppress FGF2 signaling and angiogenesis. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20170173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saegusa, J.; Yamaji, S.; Ieguchi, K.; Wu, C.Y.; Lam, K.S.; Liu, F.T.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. The direct binding of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) to integrin alphavbeta3 is involved in IGF-1 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 24106–24114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedano Prieto, D.M.; Cheng, Y.; Chang, C.C.; Yu, J.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Direct integrin binding to insulin-like growth factor-2 through the C-domain is required for insulin-like growth factor receptor type 1 (IGF1R) signaling. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieguchi, K.; Fujita, M.; Ma, Z.; Davari, P.; Taniguchi, Y.; Sekiguchi, K.; Wang, B.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Direct binding of the EGF-like domain of neuregulin-1 to integrins ({alpha}v{beta}3 and {alpha}6{beta}4) is involved in neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 31388–31398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Tran, V.; Nishikawa, K.; Kaneda, T.; Hamada, Y.; Kawaguchi, N.; Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Matsuura, N.; Zhao, M.; et al. A dominant-negative FGF1 mutant (the R50E mutant) suppresses tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57927, Erratum in PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.K.; Shimoda, M.; Maverakis, E.; Felding, B.H.; Cheng, R.H.; Takada, Y. Soluble CD40L activates soluble and cell-surface integrins alphavbeta3, alpha5beta1 and alpha4beta1 by binding to the allosteric ligand-binding site (site 2). J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Shimoda, M.; Takada, Y. CD40L Activates Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 by Binding to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) in a KGD-Independent Manner and HIGM1 Mutations Are Clustered in the Integrin-Binding Sites of CD40L. Cells 2023, 12, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Izumiya, Y.; Takada, Y. The binding of monomeric C-reactive protein (mCRP) to Integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 is related to its pro-inflammatory action. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Zhu, K.; Fujita, C.K.; Zhao, M.; Lam, K.S.; Kurth, M.J.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Proinflammatory secreted phospholipase A2 type IIA (sPLA-IIA) induces integrin activation through direct binding to a newly identified binding site (site 2) in integrins alphavbeta3, alpha4beta1, and alpha5beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Davari, P.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 (CXCL12) activates integrins by direct binding to an allosteric ligand-binding site (site 2) of integrins without CXCR4. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Fujita, M.; Takada, Y. Pro-Inflammatory Chemokines CCL5, CXCL12, and CX3CL1 Bind to and Activate Platelet Integrin alphaIIbbeta3 in an Allosteric Manner. Cells 2022, 11, 3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Simon, S.I.; Takada, Y. The C-type lectin domain of CD62P (P-selectin) functions as an integrin ligand. Life Sci. Alliance 2023, 6, e202201747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, M.H. Integrin activation. BMB Rep. 2014, 47, 655–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shattil, S.J.; Kim, C.; Ginsberg, M.H. The final steps of integrin activation: The end game. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 288–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pokharel, S.M.; Shil, N.K.; Gc, J.B.; Colburn, Z.T.; Tsai, S.Y.; Segovia, J.A.; Chang, T.-H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Natesan, S.; Jones, J.C.R.; et al. Integrin activation by the lipid molecule 25-hydroxycholesterol induces a proinflammatory response. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.-R.; Yang, S.-H. The Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-alpha) in Autoimmune Disease and Current TNF-alpha Inhibitors in Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, Y. Tumor necrosis factor and cancer, buddies or foes? Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.M.; Lee, J.; Pilch, P.F. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced insulin resistance in 3T3-L1 adipocytes is accompanied by a loss of insulin receptor substrate-1 and GLUT4 expression without a loss of insulin receptor-mediated signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Ding, L.; Lan, J.; Niu, J.; He, Y.; Song, L. Fibroblast Growth Factor-1 Improves Insulin Resistance via Repression of JNK-Mediated Inflammation. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, J.M.; Jonker, J.W.; Ahmadian, M.; Goetz, R.; Lackey, D.; Osborn, O.; Huang, Z.; Liu, W.; Yoshihara, E.; van Dijk, T.H.; et al. Endocrinization of FGF1 produces a neomorphic and potent insulin sensitizer. Nature 2014, 513, 436–439, Erratum in Nature 2015, 520, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Qin, J. LINC00659 exacerbates endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities by activating DNMT3A-mediated FGF1 promoter methylation. Thromb. J. 2023, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupte, M.; Lal, H.; Ahmad, F.; Sawyer, D.B.; Hill, M.F. Chronic Neuregulin-1beta Treatment Mitigates the Progression of Postmyocardial Infarction Heart Failure in the Setting of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus by Suppressing Myocardial Apoptosis, Fibrosis, and Key Oxidant-Producing Enzymes. J. Card. Fail. 2017, 23, 887–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Kuang, H.; He, Y.; Idiga, S.O.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Cai, X.; Zhang, K.; Potthoff, M.J.; et al. NRG1-Fc improves metabolic health via dual hepatic and central action. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Wu, X.; Wei, D.; Hwang, S.; Takada, Y. FGF1 Suppresses Allosteric Activation of beta3 Integrins by FGF2: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Thrombotic Action of FGF1. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) Binds to the Allosteric Binding Site (Site 2) and Suppresses Allosteric Integrin Activation by Inflammatory Cytokines: A Potential Mechanism of Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Fibrosis Action of NRG1. Cells 2025, 14, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryannejad, A.; Tabary, M.; Noroozi, N.; Mashinchi, B.; Iranshahi, S.; Tavangar, S.M.; Jafari, R.M.; Rashidian, A.; Dehpour, A.R. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Ivermectin in the Treatment of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats: Involvement of GABA(B) Receptors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 3672–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabary, M.; Aryannejad, A.; Noroozi, N.; Tavangar, S.M.; Mohammad Jafari, R.; Araghi, F.; Dadkhahfar, S.; Dehpour, A.R. Ivermectin Increases Random-Pattern Skin Flap Survival in Rats: The Novel Role of GABAergic System. J. Surg. Res. 2021, 259, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Ci, X.; Chen, N.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Chu, X.; Li, J.; Deng, X. Anti-inflammatory effects of ivermectin in mouse model of allergic asthma. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Feng, X.; Rong, H.; Pan, Z.; Inaba, Y.; Qiu, L.; Zheng, W.; Lin, S.; Wang, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, M.; Chahinian, H.; La Scola, B.; Fantini, J. Characterization and Fluctuations of an Ivermectin Binding Site at the Lipid Raft Interface of the N-Terminal Domain (NTD) of the Spike Protein of SARS-CoV-2 Variants. Viruses 2024, 16, 1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twum-Danso, N.A. Serious adverse events following treatment with ivermectin for onchocerciasis control: A review of reported cases. Filaria J. 2003, 2 (Suppl. S1), S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, Y.K.; Yu, J.; Shimoda, M.; Takada, Y. Integrin Binding to the Trimeric Interface of CD40L Plays a Critical Role in CD40/CD40L Signaling. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; He, C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 44, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Kim, C.; Ginsberg, M.H. Reconstruction of integrin activation. Blood 2012, 119, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Fakhry, Y.; Alturaihi, H.; Yacoub, D.; Liu, L.; Guo, W.; Leveille, C.; Jung, D.; Khzam, L.B.; Merhi, Y.; Wilkins, J.A.; et al. Functional interaction of CD154 protein with alpha5beta1 integrin is totally independent from its binding to alphaIIbbeta3 integrin and CD40 molecules. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18055–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Zhang, X.P.; Medved, L.; Takada, Y. Specific binding of integrin alpha v beta 3 to the fibrinogen gamma and alpha E chain C-terminal domains. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 5872–5877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. The chemokine fractalkine can activate integrins without CX3CR1 through direct binding to a ligand-binding site distinct from the classical RGD-binding site. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, M.; Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Integrins alphavbeta3 and alpha4beta1 act as coreceptors for fractalkine, and the integrin-binding defective mutant of fractalkine is an antagonist of CX3CR1. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 5809–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
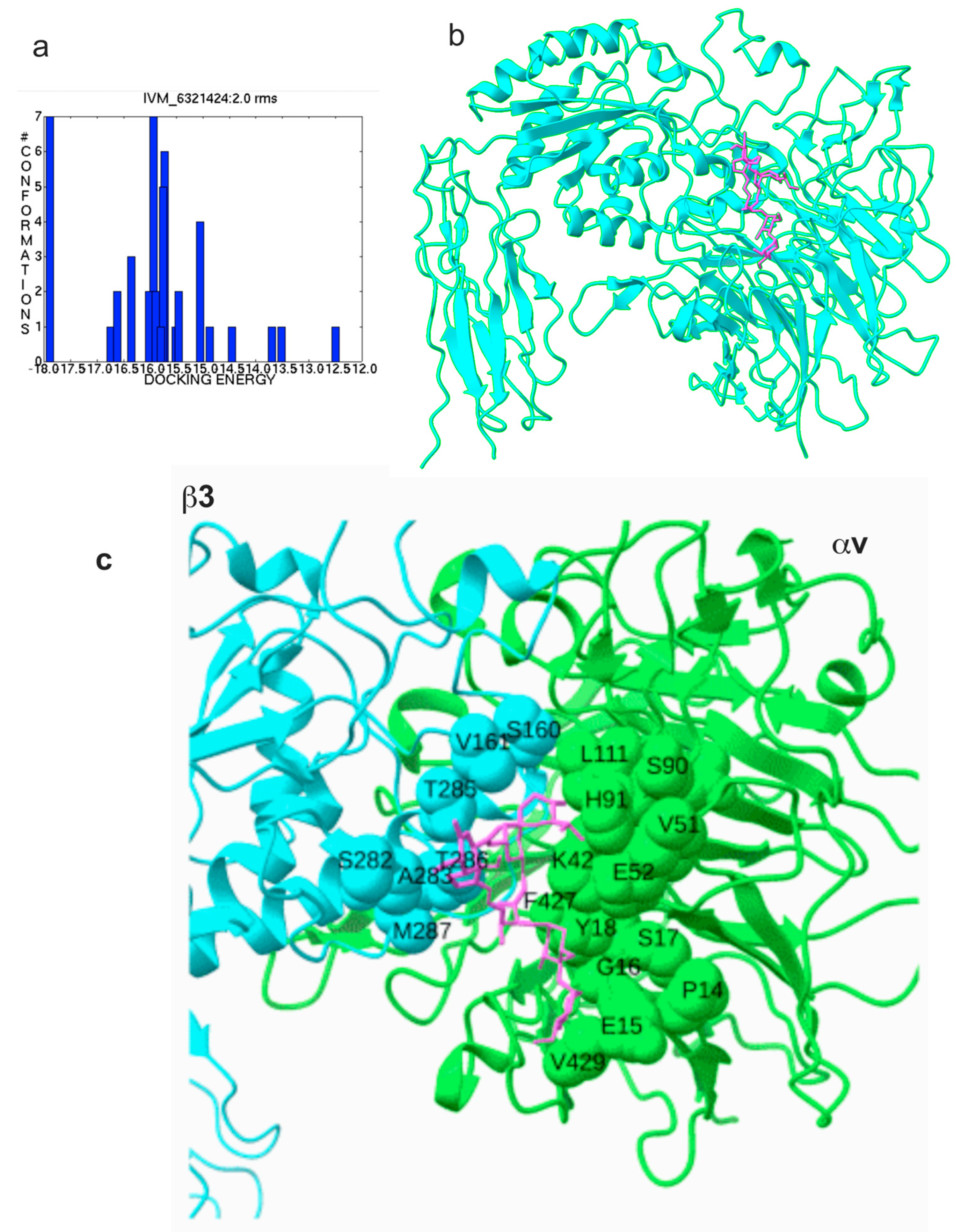

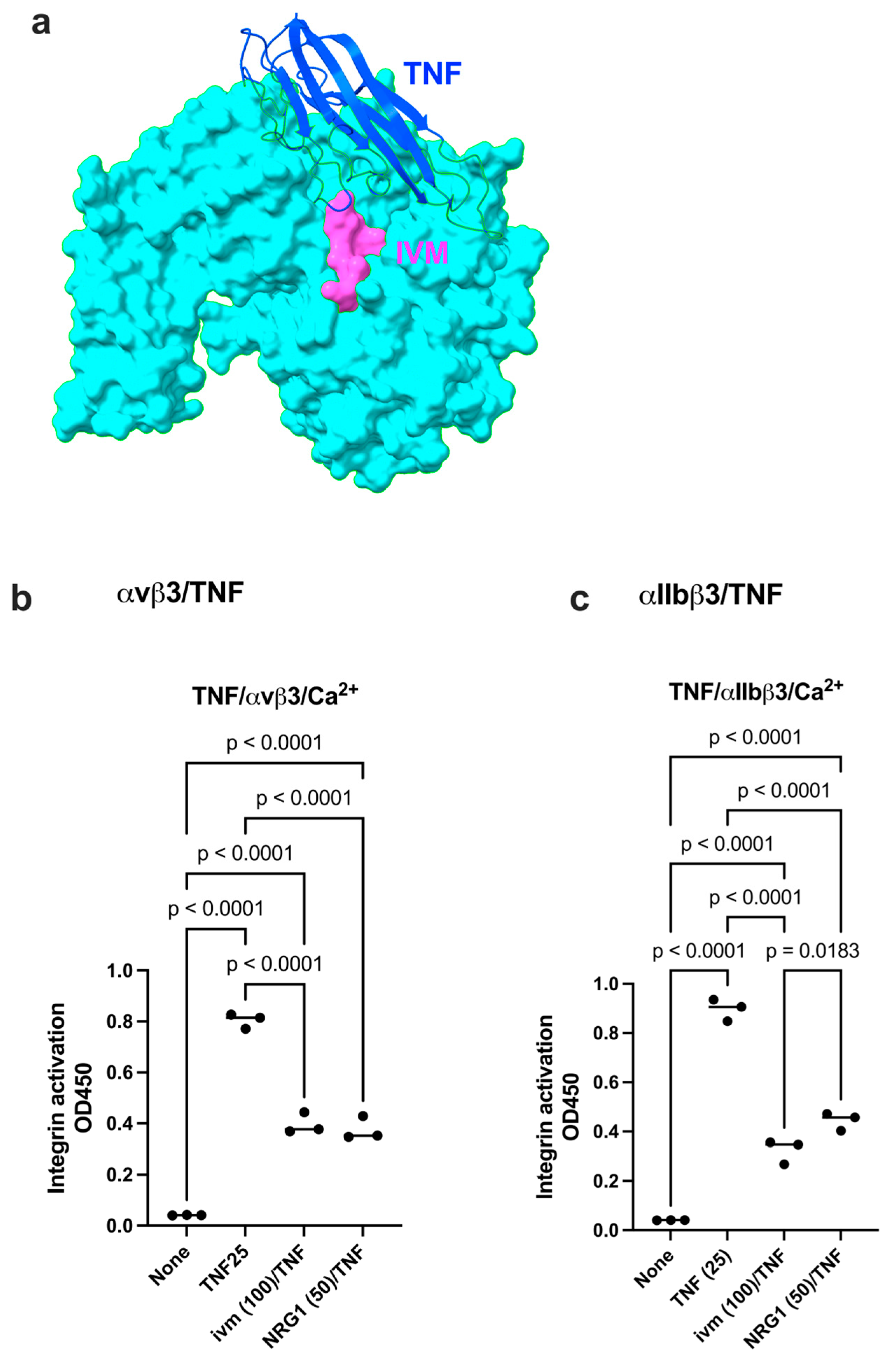
| αv (1JV2.pdb) | β3 (1JV2.pdb) |
| Pro14, Glu15, Gly16, Ser17, Tyr18, Lys42, Val51, Glu52, Ser90, His91, Gln92, Trp93, Leu111, Phe427, Gly428, Val429, Asp430 | Val161, Ser162, Ser282, Ala283, Thr285, Thr286, Met287 |
| TNF (1TNF.pdb) | αv (1JV2) | β3 (1JV2) |
| Asn19, Glu23, Gln25, Gln27, Trp28, leu29, Arg31, Glu42, Arg44, Asp45, Asn46, Gln47, Val49, Cys69, Pro70, Ser71, Thr72, His73, Leu75, Leu76, Thr77, Thr79, Ser81, Ile83, Val85, Gln88, Thr89, Lys90, Val91, Asn92, Ile97, Gln102, Arg103, Thr105, Glu107, Gly129, Arg131, Glu135, Asn137 | Gly76, Asn77, Asp79, Ala81, Lys82, Asp83, Asp84, Pro85 | Glu171, Glu174, Asn175, Thr182, Thr183, Cys184, Leu185, Pro186, Lys191, His192, Val193, Leu194, Thr195, Arg202, Glu205, Glu206, Val207, Lys208, Lys209, Gln210, Ser211, Gly276, Ser277, Asp278 Asn279, His280, Ser282, Thr285, Thr286 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takada, Y.K.; Takada, Y. Ivermectin Binds to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) and Inhibits Allosteric Integrin Activation by TNF and Other Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178655
Takada YK, Takada Y. Ivermectin Binds to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) and Inhibits Allosteric Integrin Activation by TNF and Other Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178655
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakada, Yoko K., and Yoshikazu Takada. 2025. "Ivermectin Binds to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) and Inhibits Allosteric Integrin Activation by TNF and Other Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178655
APA StyleTakada, Y. K., & Takada, Y. (2025). Ivermectin Binds to the Allosteric Site (Site 2) and Inhibits Allosteric Integrin Activation by TNF and Other Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8655. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178655






