Substrate Specificity and Peptide Motif Preferences of β-Lytic and L5 Proteases from Lysobacter spp. Revealed by LC–MS/MS Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
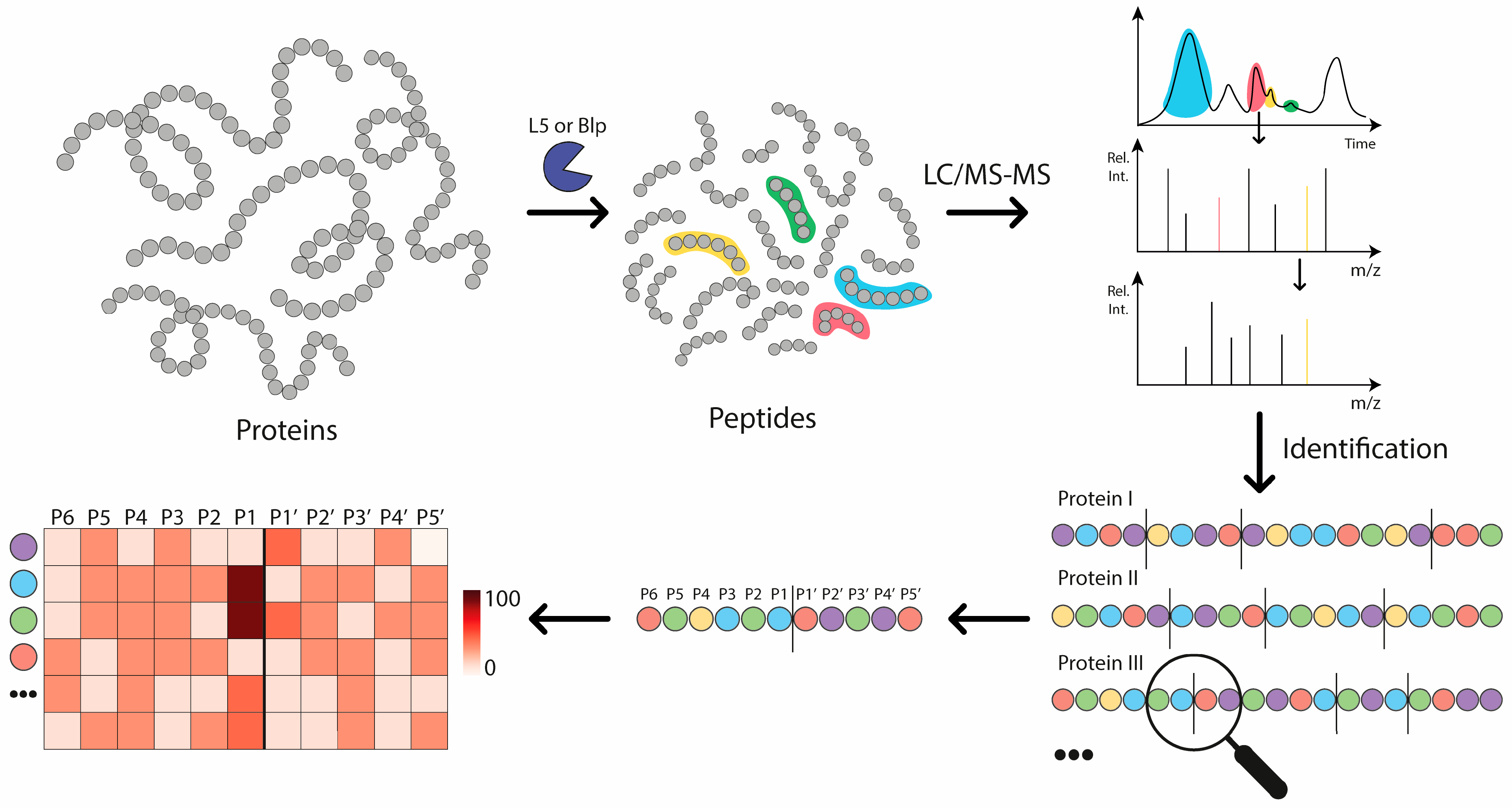
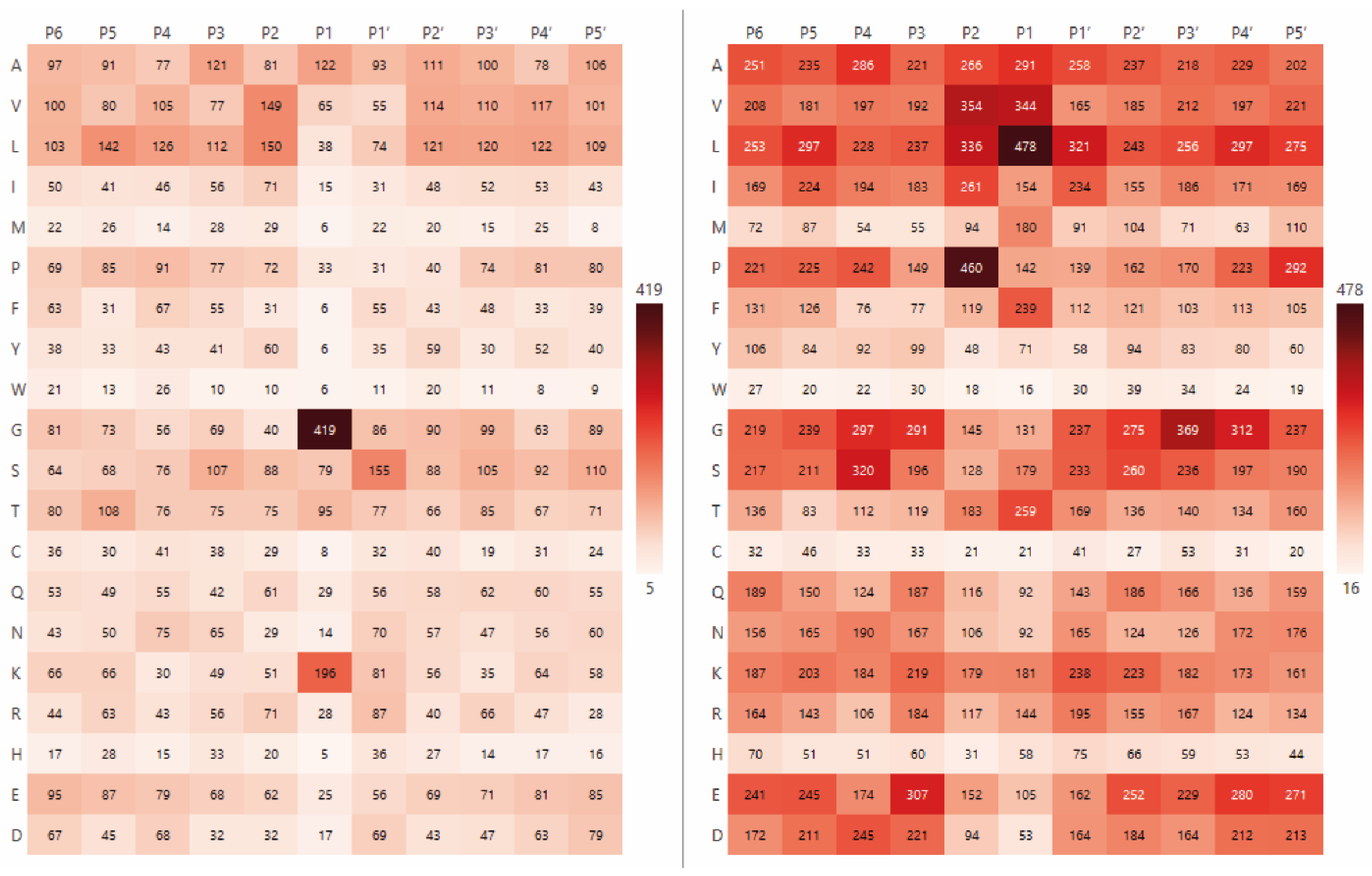
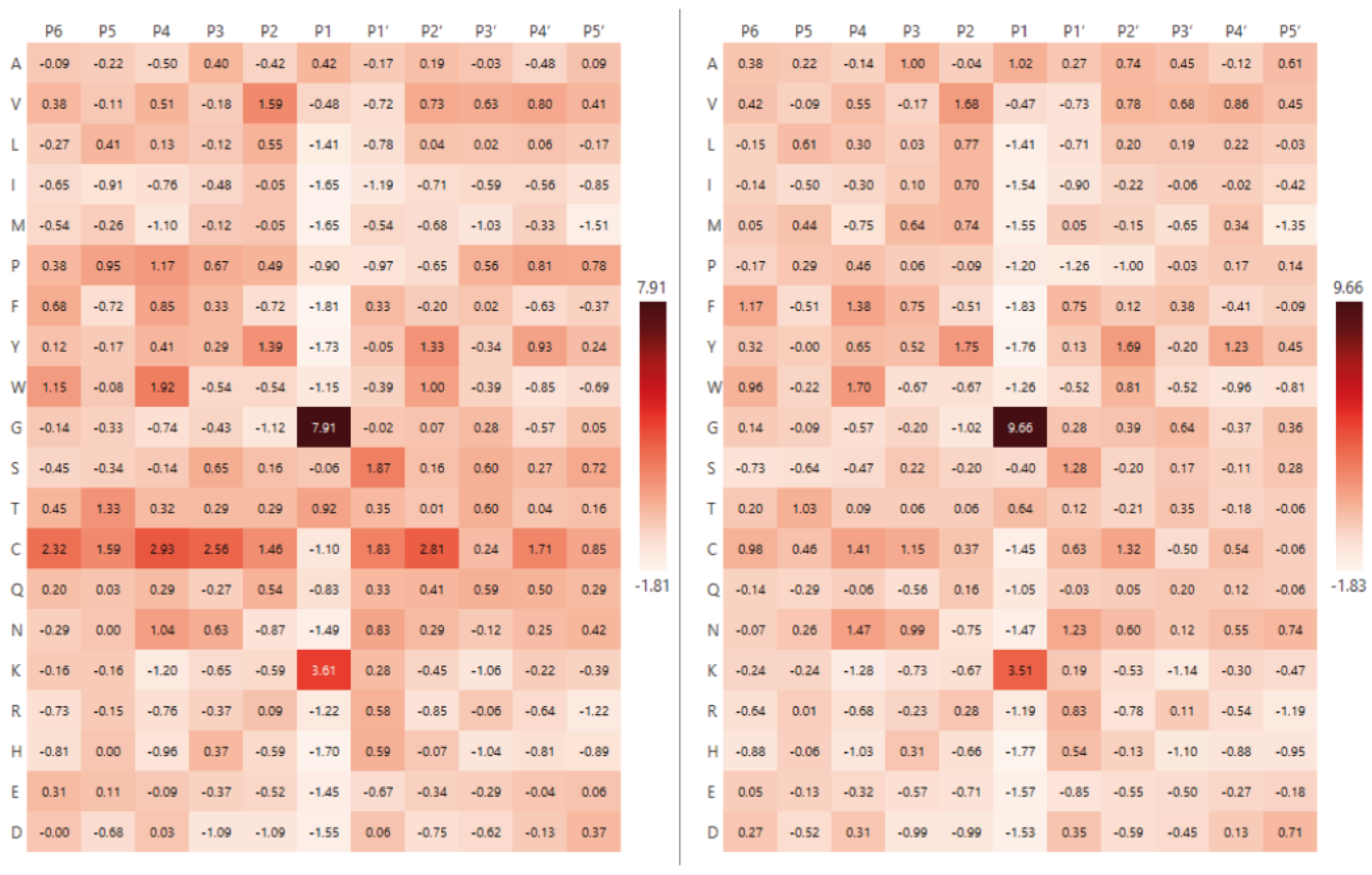
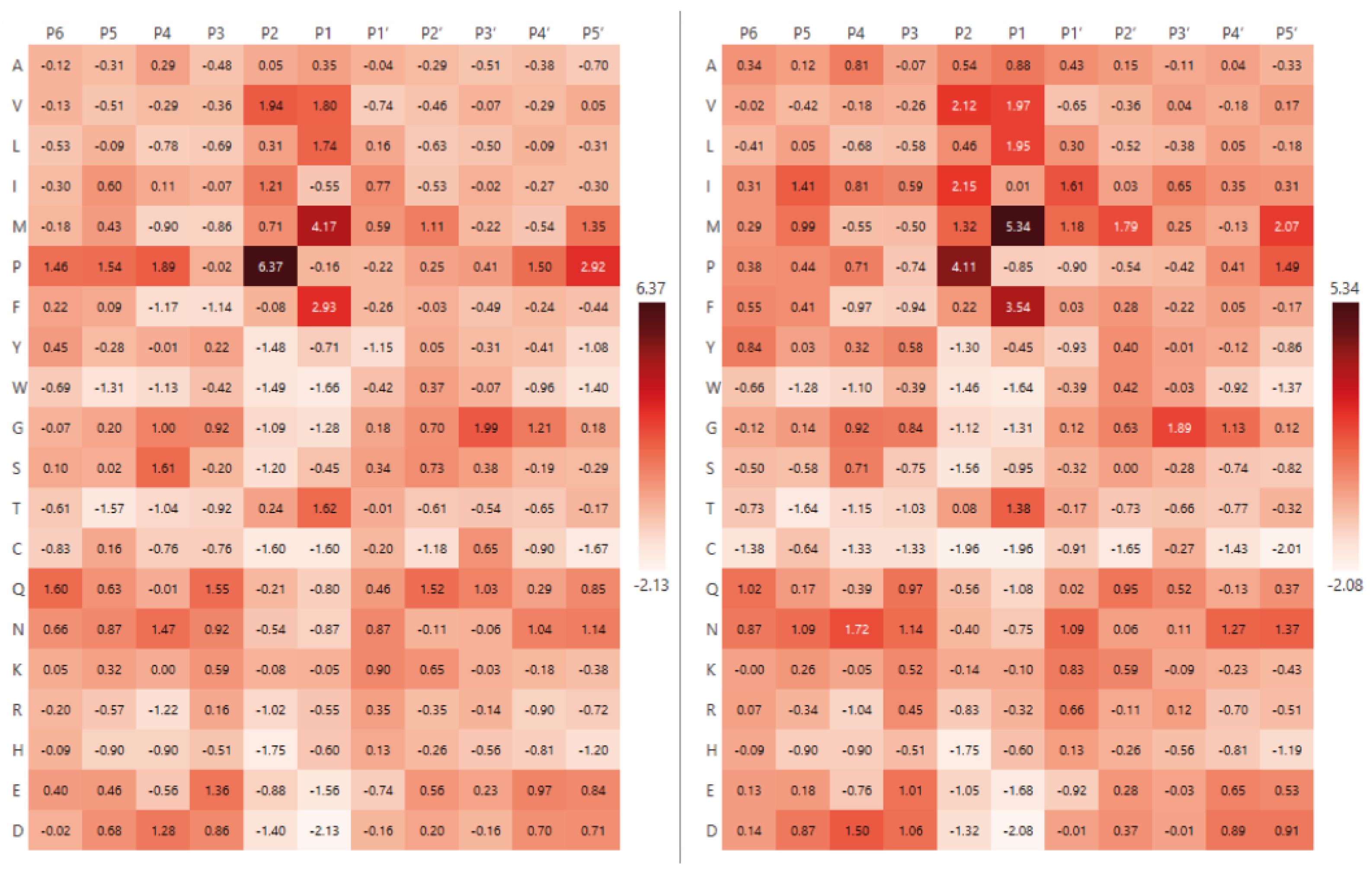
2.1. The Analysis of Protease Specificity and the Subsequent Visualisation of the Results
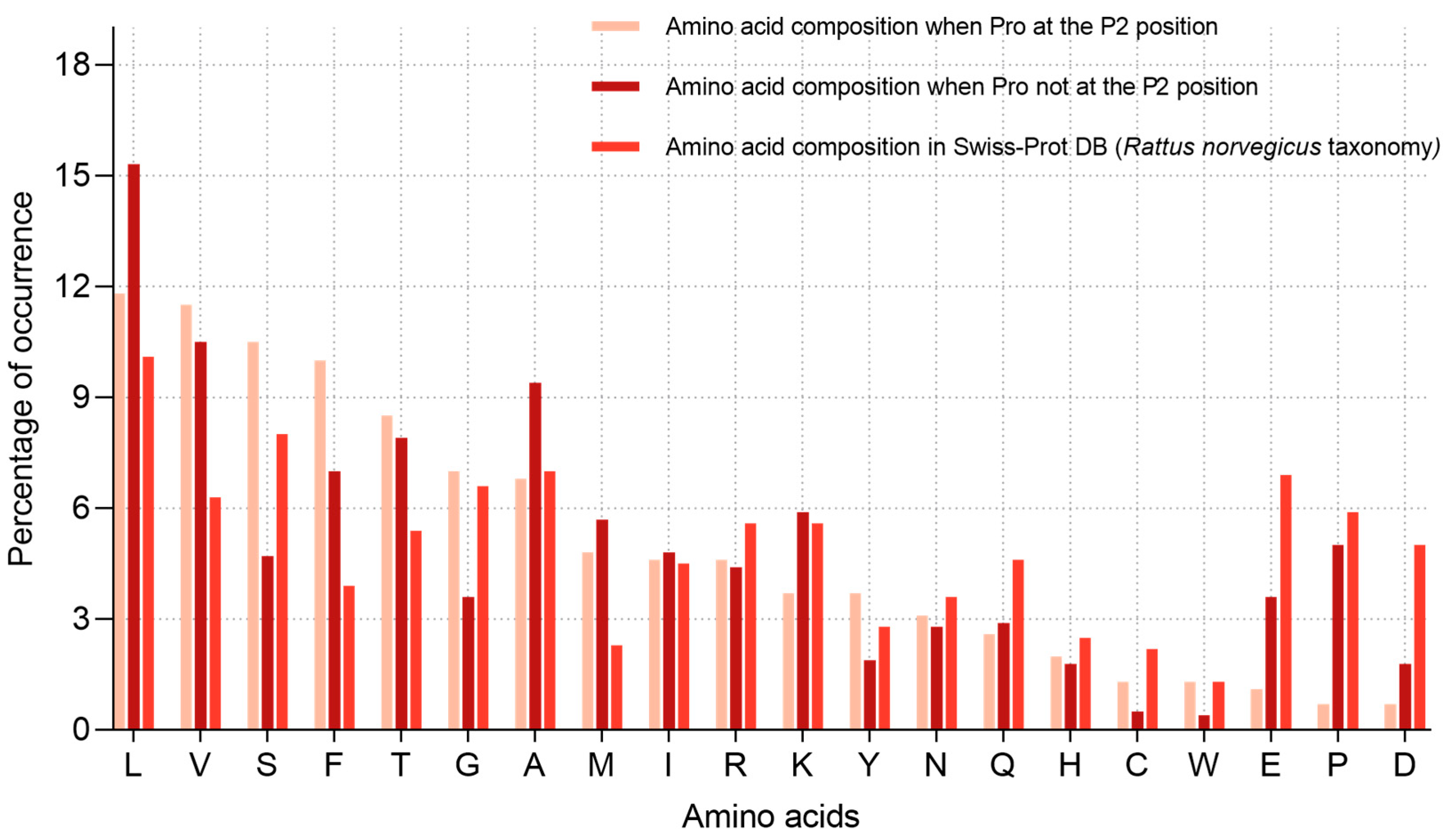
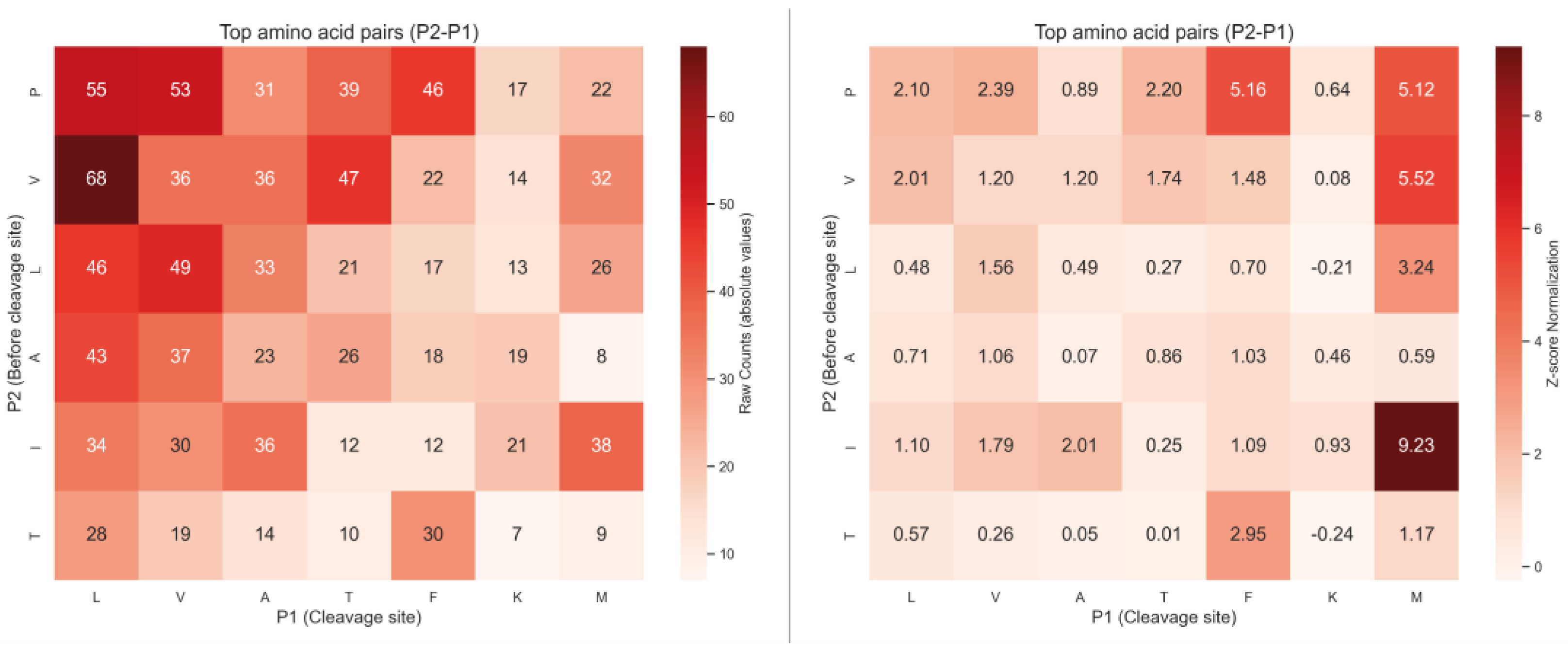
2.2. Analysis of Hydrolysis Motifs for the L5 Protease
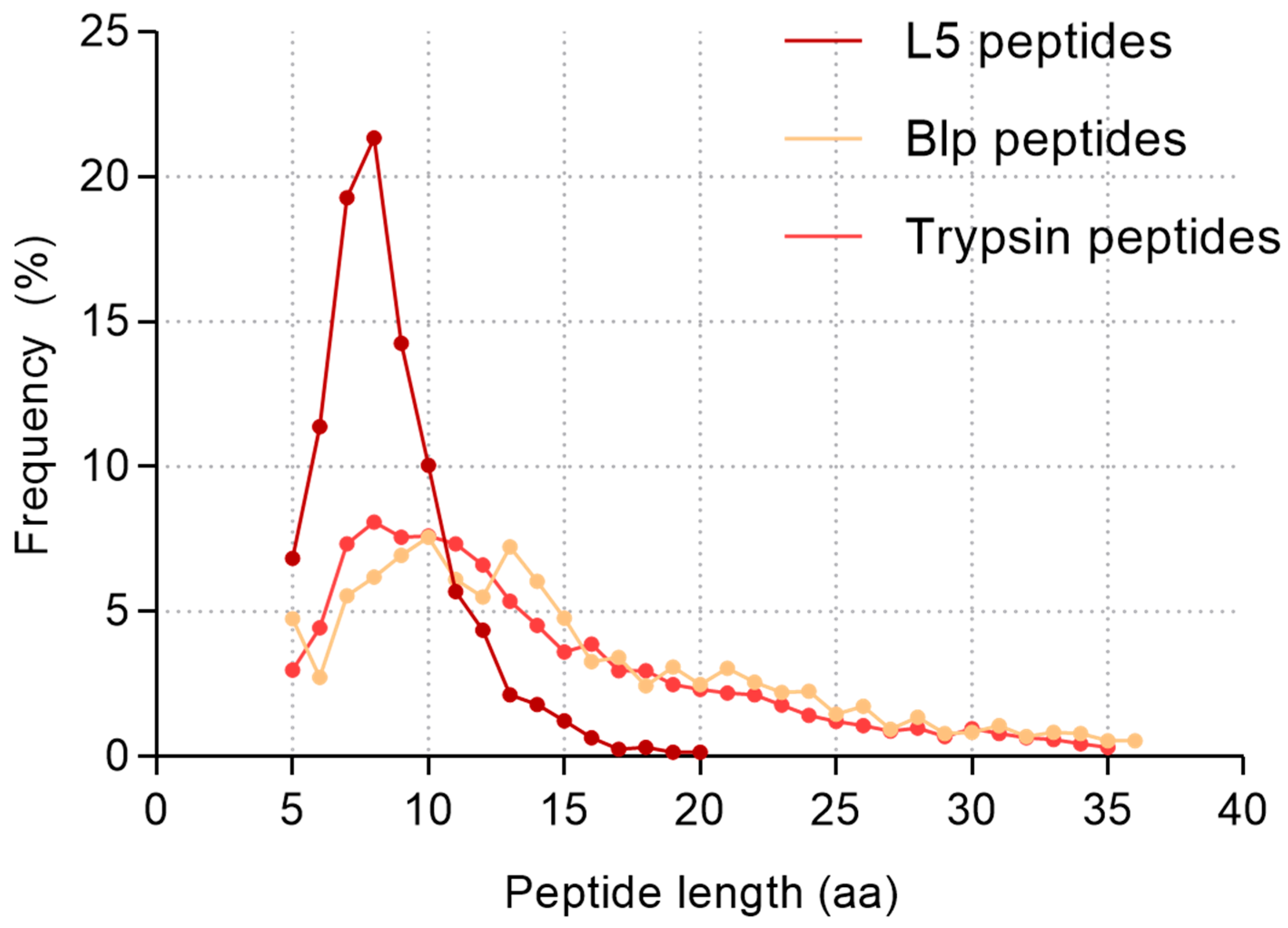
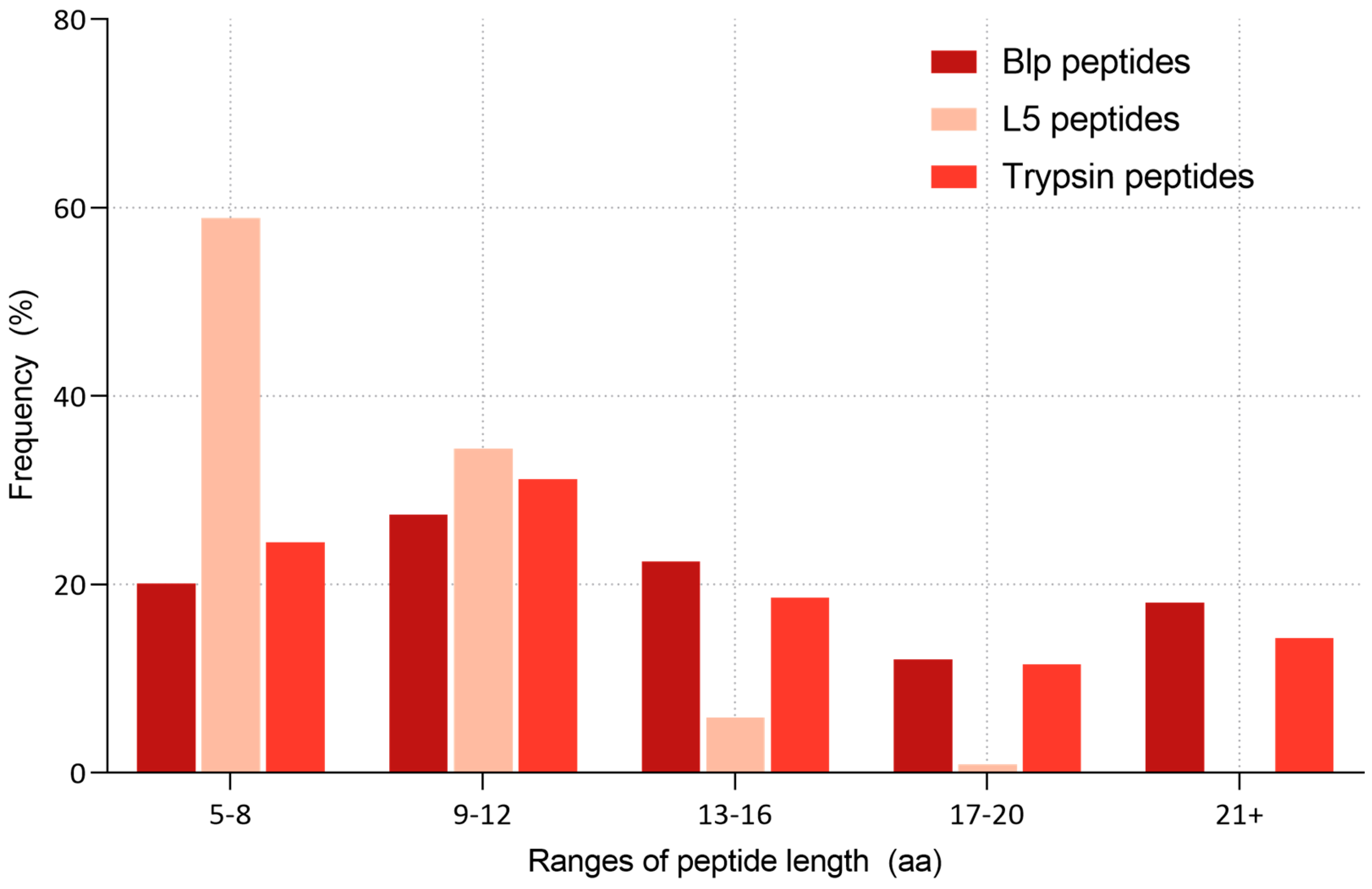
2.3. Comparative Analysis of the Specificity of Blp and L5 Enzymes on the Length of Identified Peptides
3. Discussion
3.1. Enzyme Specificity Analysis
3.2. Peptide Length Distribution
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples and Chemicals
4.2. Preparation of Intact Liver Tissue Lysate
4.3. Human Blood Serum Sample Collection
4.4. Adherence to Ethical Standards
4.5. Size-Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) Fractionationating
4.6. Hydrolysis of Proteins
4.7. LC–MS/MS Analysis
4.8. Bioinformatic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Alp | α-lytic protease |
| Blp | β-lytic protease |
| WaLP | wild type α-lytic proteas |
| MaLP | mutant type α-lytic protease |
| SEC | size-exclusion chromatography |
| LC–MS/MS | liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry |
| MALDI-TOF MS | matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| UHPLC | ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography |
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| FA | formic acid |
Appendix A
| Protein | Peptide with Missed Cleavages | Missed Cleavages | Expected Unidentified Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPSM_RAT | HPSSVAGEVV | 1 | HPSSVAG, EVV |
| CPSM_RAT | HPSSVAGEVVFNT | 1 | HPSSVAG, EVVFNT |
| CPSM_RAT | EVIKAERPDGLILG | 2 | EVIK, AERPDG, LILG, EVIKAERPDG, AERPDGLILG |
| SVEP1_MOUSE | SDPKIQLIFNIT | 1 | SDPK, IQLIFNIT |
| CPSM_RAT | ADTIGYPVMIRS | 1 | ADTIG, YPVMIRS |
| CPSM_RAT | NMENVDAMGVHTG | 1 | NMENVDAMG, VHTG |
| CPSM_RAT | QSVDFVDPNKQNLIAEVSTK | 1 | QSVDFVDPNK, QNLIAEVSTK |
| ALDH2_MESAU | STEVGHLIQVA | 1 | STEVG, HLIQVA |
| ALDH2_MESAU | SHEDVDKVAFTG | 1 | SHEDVDK, VAFTG |
| ALDH2_MESAU | NPFDSRTEQGPQVDETQFK | 1 | NPFDSRTEQG, PQVDETQFK |
| BHMT1_RAT | RQVADEGDALVAG | 1 | RQVADEG, DALVAG |
| JHD2C_MOUSE | NSQAVGERRL | 1 | NSQAVG, ERRL |
| MVP_RAT | AARIEGEGSVLQA | 2 | AARIEG, EG, SVLQA… |
References
- López-Otín, C.; Bond, J.S. Proteases: Multifunctional Enzymes in Life and Disease. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30433–30437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heutinck, K.M.; ten Berge, I.J.M.; Hack, C.E.; Hamann, J.; Rowshani, A.T. Serine Proteases of the Human Immune System in Health and Disease. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1943–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkina, E.I.; Bogdanov, I.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Strokach, N.N.; Melnikova, D.N.; Toropygin, I.Y.; Matveevskaya, N.S.; Ovchinnikova, T.V. Structural and Immunologic Properties of the Major Soybean Allergen Gly m 4 Causing Anaphylaxis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Fu, R.; Wei, F. Microbial Proteases and Their Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1236368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavano, O.L.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Secundo, F.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Biotechnological Applications of Proteases in Food Technology. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solanki, P.; Putatunda, C.; Kumar, A.; Bhatia, R.; Walia, A. Microbial Proteases: Ubiquitous Enzymes with Innumerable Uses. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Nadeem, F.; Mehmood, T.; Bilal, M.; Anwar, Z.; Amjad, F. Protease—A Versatile and Ecofriendly Biocatalyst with Multi-Industrial Applications: An Updated Review. Catal. Lett. 2021, 151, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salque, M.; Bogucki, P.I.; Pyzel, J.; Sobkowiak-Tabaka, I.; Grygiel, R.; Szmyt, M.; Evershed, R.P. Earliest Evidence for Cheese Making in the Sixth Millennium Bc in Northern Europe. Nature 2013, 493, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craik, C.S.; Page, M.J.; Madison, E.L. Proteases as Therapeutics. Biochem. J. 2011, 435, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthee, S.; Hamamoto, H.; Paudel, A.; Sekimizu, K. Lysobacter Species: A Potential Source of Novel Antibiotics. Arch. Microbiol. 2016, 198, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afoshin, A.S.; Kudryakova, I.V.; Borovikova, A.O.; Suzina, N.E.; Toropygin, I.Y.; Shishkova, N.A.; Vasilyeva, N.V. Lytic Potential of Lysobacter Capsici VKM B-2533T: Bacteriolytic Enzymes and Outer Membrane Vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giansanti, P.; Tsiatsiani, L.; Low, T.Y.; Heck, A.J.R. Six Alternative Proteases for Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics beyond Trypsin. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, J.G.; Kim, S.; Maltby, D.A.; Ghassemian, M.; Bandeira, N.; Komives, E.A. Expanding Proteome Coverage with Orthogonal-Specificity α-Lytic Proteases. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.L.; Backes, B.J.; Leonetti, F.; Mahrus, S.; Ellman, J.A.; Craik, C.S. Rapid and General Profiling of Protease Specificity by Using Combinatorial Fluorogenic Substrate Libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 7754–7759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, A.J.; Eroy-Reveles, A.A.; Knudsen, G.M.; Ingram, J.; Zhou, M.; Statnekov, J.B.; Greninger, A.L.; Hostetter, D.R.; Qu, G.; Maltby, D.A.; et al. Global Identification of Peptidase Specificity by Multiplex Substrate Profiling. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1095–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uliana, F.; Vizovišek, M.; Acquasaliente, L.; Ciuffa, R.; Fossati, A.; Frommelt, F.; Goetze, S.; Wollscheid, B.; Gstaiger, M.; De Filippis, V.; et al. Mapping Specificity, Cleavage Entropy, Allosteric Changes and Substrates of Blood Proteases in a High-Throughput Screen. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Main, K.; Wang, H.; Julien, O.; Dufour, A. Biochemical Tools for Tracking Proteolysis. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 5264–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, D.R.; Roy, C.; Tsai, C.S.; Jurásek, L. Lytic Enzymes of Sorangium Sp. A Comparison of the Proteolytic Properties of the Alpha- and Beta-Lytic Proteases. Can. J. Biochem. 1965, 43, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Chohnan, S.; Ohashi, H.; Hirata, T.; Masaki, T.; Sakiyama, F. Purification, Bacteriolytic Activity, and Specificity of β-Lytic Protease from Lysobacter Sp. IB-9374. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2003, 95, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afoshin, A.S.; Konstantinov, M.A.; Toropygin, I.Y.; Kudryakova, I.V.; Vasilyeva, N.V. β-Lytic Protease of Lysobacter Capsici VKM B-2533T. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauperl, M.; Fuchs, J.E.; Waldner, B.J.; Huber, R.G.; Kramer, C.; Liedl, K.R. Characterizing Protease Specificity: How Many Substrates Do We Need? PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, Y.; Köditz, J.; Ulbrich-Hofmann, R.; Arnold, U. Proline versus Charge Concept for Protein Stabilization against Proteolytic Attack. Protein Eng. 2003, 16, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, N.V.; Shishkova, N.A.; Marinin, L.I.; Ledova, L.A.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Muranova, T.A.; Stepnaya, O.A.; Kulaev, I.S. Lytic Peptidase L5 of Lysobacter Sp. XL1 with Broad Antimicrobial Spectrum. J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryakova, I.V.; Gabdulkhakov, A.G.; Tishchenko, S.V.; Lysanskaya, V.Y.; Suzina, N.E.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Afoshin, A.S.; Vasilyeva, N.V. Structural and Functional Properties of Antimicrobial Protein L5 of Lysobacter Sp. XL1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 10043–10053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhoof, G.; Goossens, F.; De Meester, I.; Hendriks, D.; Scharpé, S. Proline Motifs in Peptides and Their Biological Processing. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnikov, S.; Mailliot, J.; Rigger, L.; Neuner, S.; Shin, B.; Yusupova, G.; Dever, T.E.; Micura, R.; Yusupov, M. Molecular Insights into Protein Synthesis with Proline Residues. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 1776–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahai, M.A.; Kehoe, T.A.K.; Koo, J.C.P.; Setiadi, D.H.; Chass, G.A.; Viskolcz, B.; Penke, B.; Pai, E.F.; Csizmadia, I.G. First Principle Computational Study on the Full Conformational Space of l-Proline Diamides. J. Phys. Chem. A 2005, 109, 2660–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hioki, T.; Yamashita, D.; Tohata, M.; Endo, K.; Kawahara, A.; Okuda, M. Heterologous Production of Active Form of Beta-Lytic Protease by Bacillus Subtilis and Improvement of Staphylolytic Activity by Protein Engineering. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvo, I.; Ferraro, F.; Merlino, A.; Zuberbühler, K.; O’Donoghue, A.J.; Pastro, L.; Pi-Denis, N.; Basika, T.; Roche, L.; McKerrow, J.H.; et al. Substrate Specificity of Cysteine Proteases Beyond the S2 Pocket: Mutagenesis and Molecular Dynamics Investigation of Fasciola hepatica Cathepsins L. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, N.V.; Tsfasman, I.M.; Suzina, N.E.; Stepnaya, O.A.; Kulaev, I.S. Secretion of Bacteriolytic Endopeptidase L5 of Lysobacter Sp. XL1 into the Medium by Means of Outer Membrane Vesicles. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 3827–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudryakova, I.; Afoshin, A.; Leontyevskaya, E.; Leontyevskaya Vasilyeva, N. The First Homologous Expression System for the β-Lytic Protease of Lysobacter Capsici VKM B-2533T, a Promising Antimicrobial Agent. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappsilber, J.; Mann, M.; Ishihama, Y. Protocol for Micro-Purification, Enrichment, Pre-Fractionation and Storage of Peptides for Proteomics Using StageTips. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Qian, X. Transferred Subgroup False Discovery Rate for Rare Post-Translational Modifications Detected by Mass Spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 1359–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaert, N.; Helsens, K.; Martens, L.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Gevaert, K. Improved Visualization of Protein Consensus Sequences by IceLogo. Nat. Methods 2009, 6, 786–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
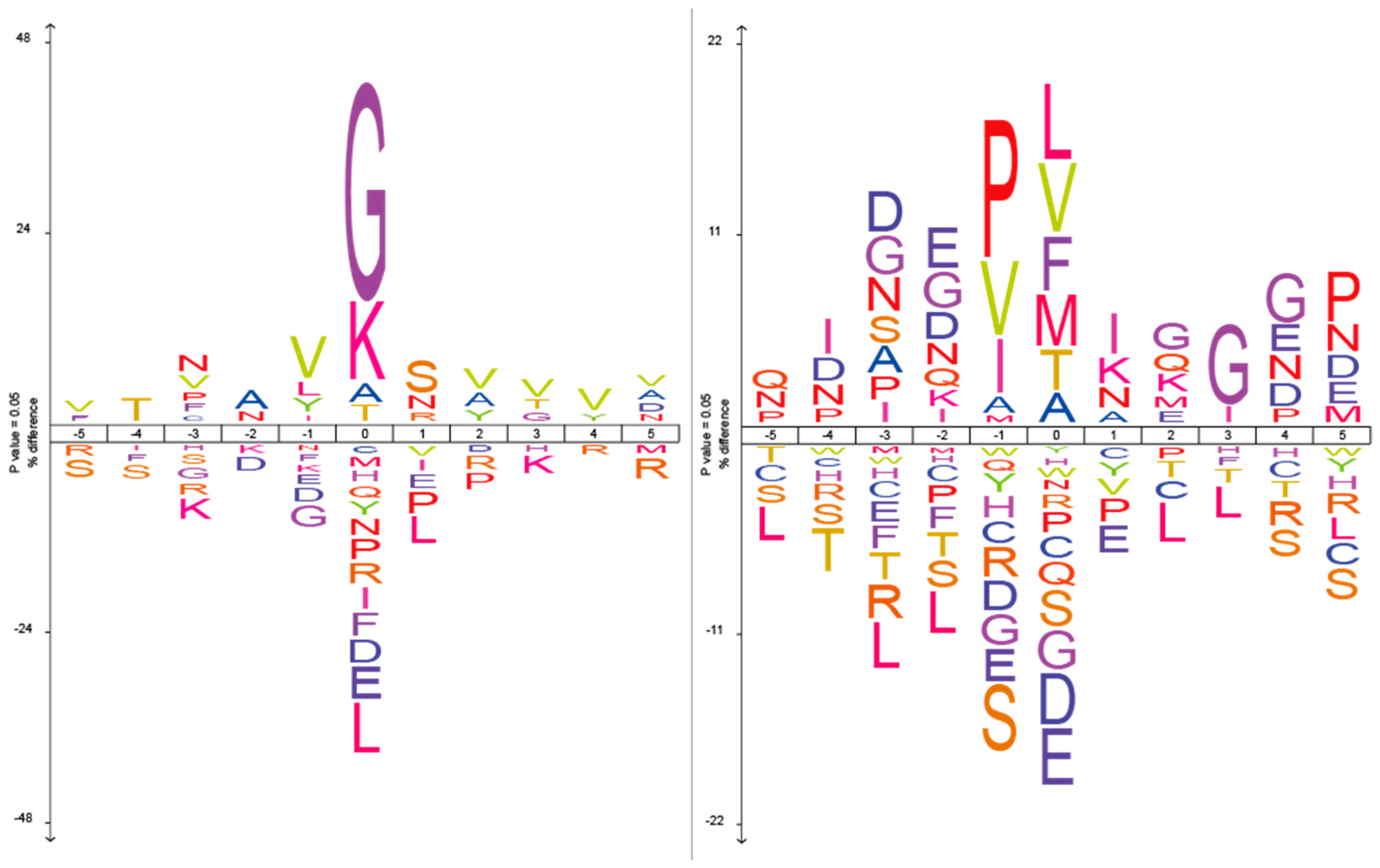
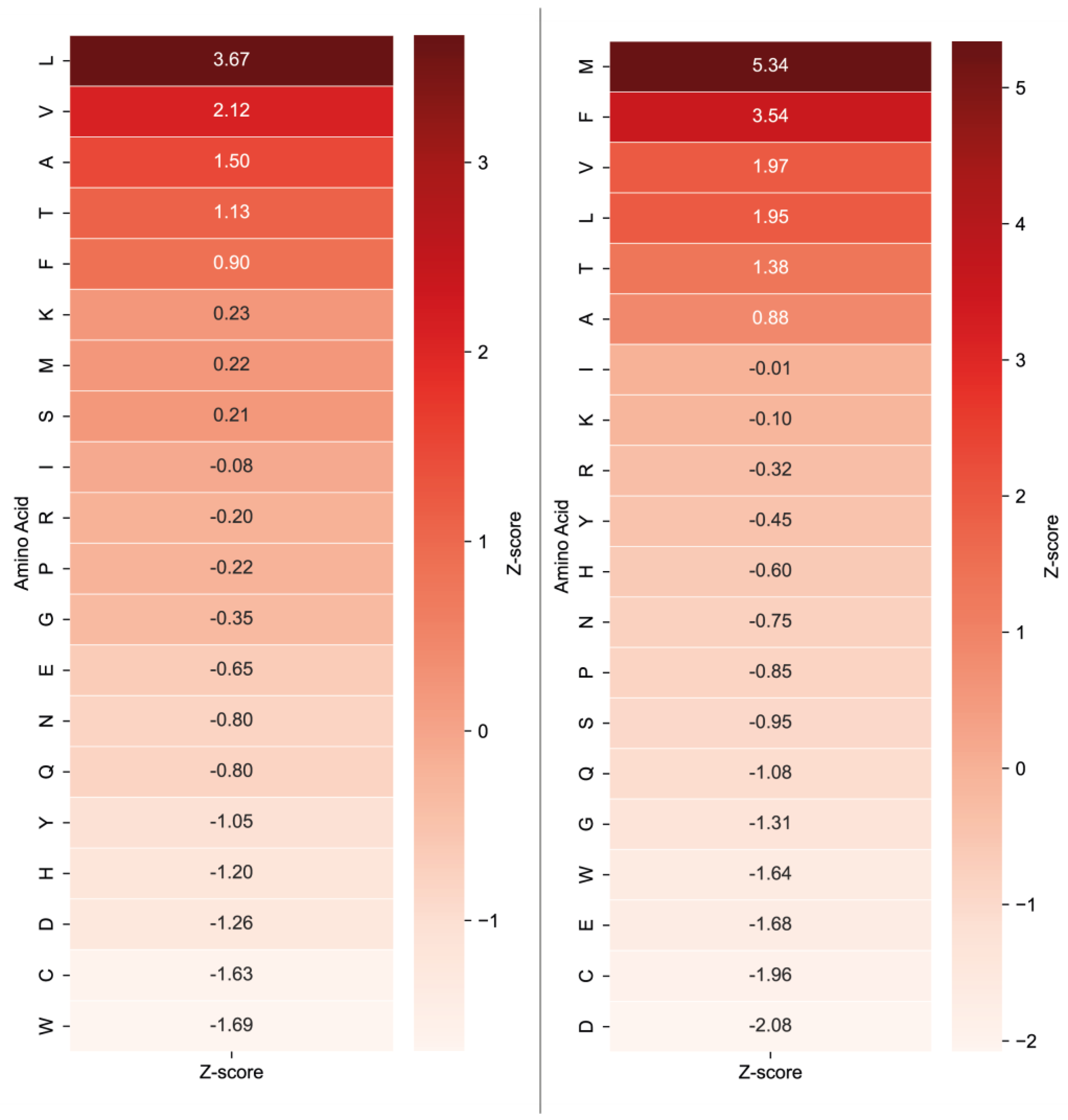
| Amino Acid | Blp (%) | Blp Norm (%) | L5 (%) | L5 Norm (%) | Group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| G | 34.5 | 32.5 | – | – | Non-polar |
| K | 16.1 | 15.5 | – | – | Polar charged |
| L | – | – | 14.8 | 8 | Non-polar |
| V | – | – | 10.6 | 8 | Non-polar |
| A | – | – | 9 | 6.3 | Non-polar |
| F | – | – | 7.4 | 10.5 | Non-polar |
| T | – | – | 8 | 7.1 | Polar uncharged |
| M | – | – | 5.5 | 13.4 | Non-polar |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konstantinov, M.; Kaluzhskiy, L.; Yablokov, E.; Zhdanov, D.; Ivanov, A.; Toropygin, I. Substrate Specificity and Peptide Motif Preferences of β-Lytic and L5 Proteases from Lysobacter spp. Revealed by LC–MS/MS Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178603
Konstantinov M, Kaluzhskiy L, Yablokov E, Zhdanov D, Ivanov A, Toropygin I. Substrate Specificity and Peptide Motif Preferences of β-Lytic and L5 Proteases from Lysobacter spp. Revealed by LC–MS/MS Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178603
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonstantinov, Mihail, Leonid Kaluzhskiy, Evgeniy Yablokov, Dmitry Zhdanov, Alexis Ivanov, and Ilya Toropygin. 2025. "Substrate Specificity and Peptide Motif Preferences of β-Lytic and L5 Proteases from Lysobacter spp. Revealed by LC–MS/MS Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178603
APA StyleKonstantinov, M., Kaluzhskiy, L., Yablokov, E., Zhdanov, D., Ivanov, A., & Toropygin, I. (2025). Substrate Specificity and Peptide Motif Preferences of β-Lytic and L5 Proteases from Lysobacter spp. Revealed by LC–MS/MS Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8603. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178603








