Recombinant Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Expressing Mouse Interleukin-12 and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (rVSV-dM51-mIL12-mGMCSF) for Immunotherapy of Lung Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Production and Characterization of rVSVs
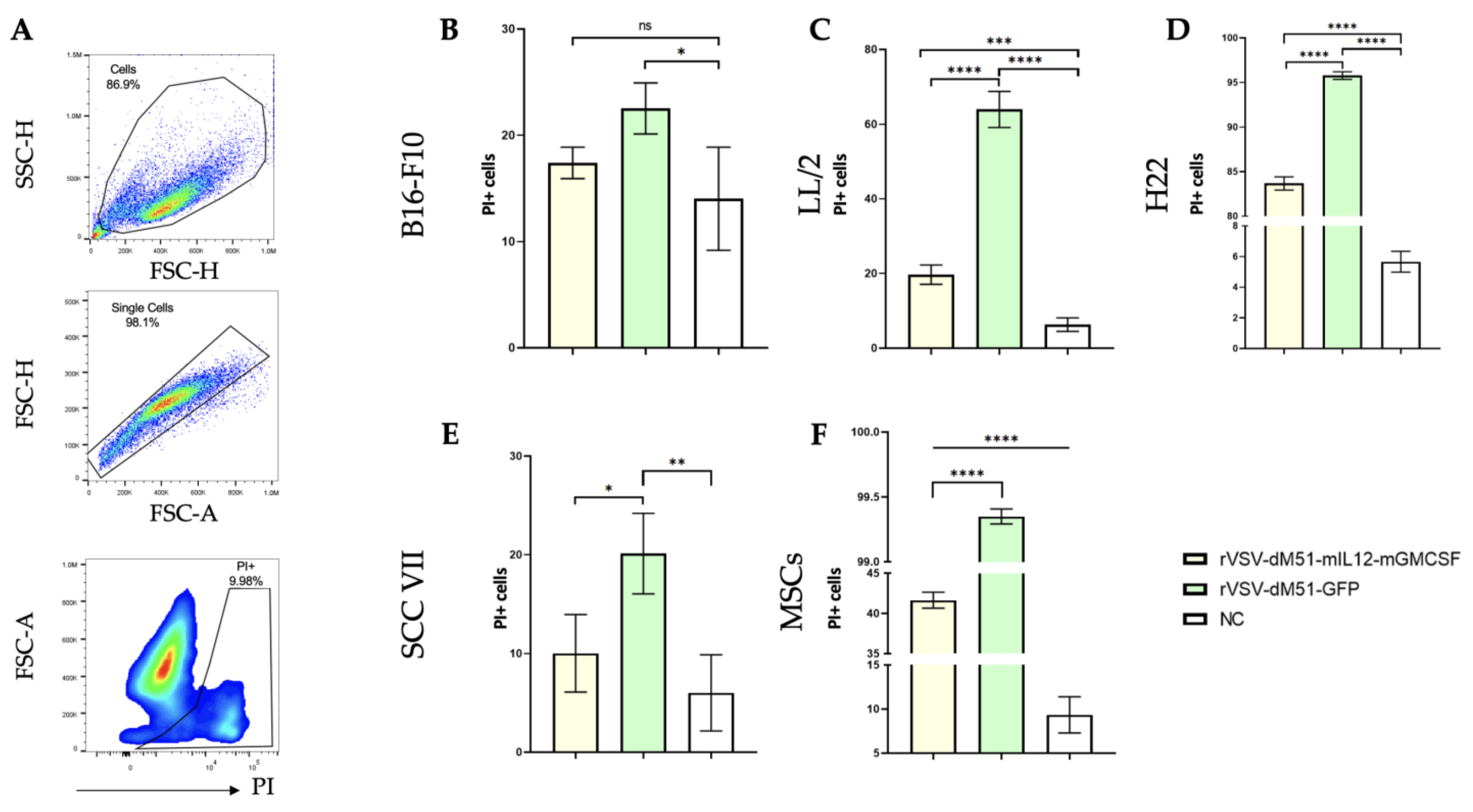
2.2. Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells LL/2 Are More Susceptible to the VSV Oncolytic Effect than the B16-F10 Melanoma Cells
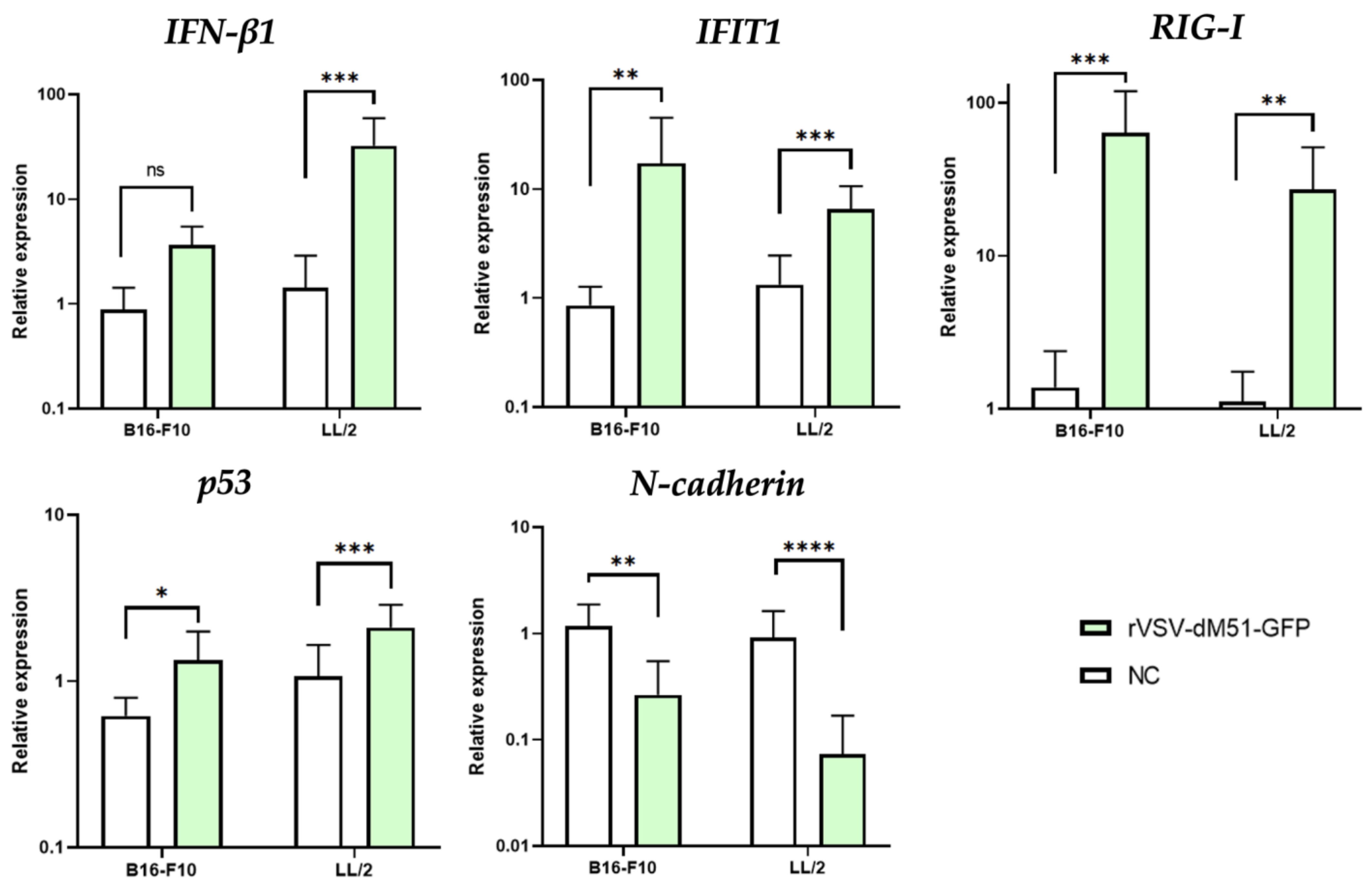
2.3. Induction of Antiviral and Pro-Apoptotic Genes in Response to rVSV Infection in B16-F10 and LL/2 Cells
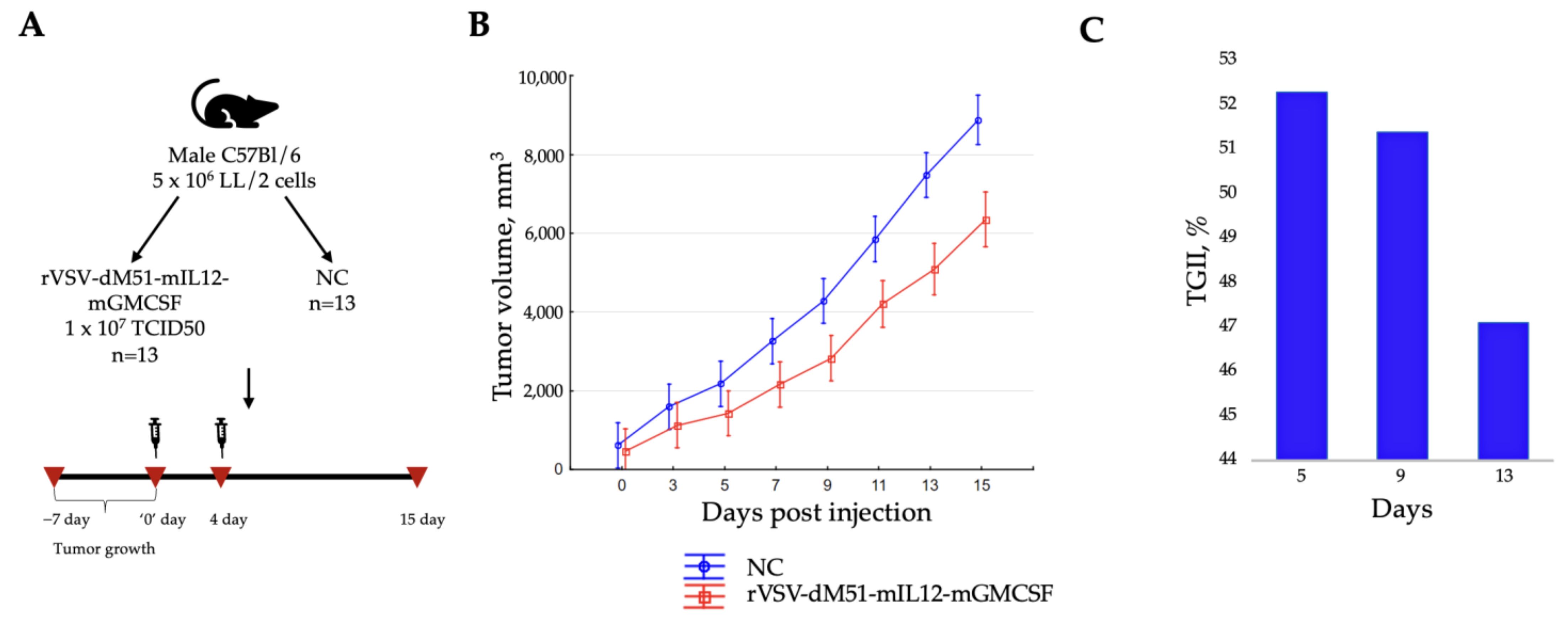
2.4. Intratumoral Injection of rVSV-dM51-mIL12-mGMCSF Suppresses the LL/2-Induced Tumor Growth
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Isolation of Murine Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) from Bone Marrow
4.3. Construction of Plasmids
4.4. Rescue and Purification of Recombinant VSV
4.5. Median Tissue Culture Infectious Dose Assay
4.6. Infection of Cell Lines
4.7. ELISA Assay
4.8. Flow Cytometry
4.9. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription (RT) Reaction, and qPCR Assay for the Analysis of Gene Expression in VSV-Infected Cells
4.10. In Vivo Studies
4.11. Phenotyping of the Spleen Immune Cells
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OVs | Oncolytic viruses |
| VSV | Vesicular stomatitis virus |
| dM51 | The methionine deletion in position 51 of M protein |
| GFP | Green fluorescence protein |
| mIL12 | Mouse interleukin-12 |
| mGMCSF | Mouse granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| TGII | Tumor growth inhibition index |
| IFNs | Interferons |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| GSDME | Gasdermin E |
| rVSV | Recombinant VSV |
| wt | Wild-type |
| LL/2 | Lewis lung carcinoma |
| SCC VII | Squamous-cell carcinoma |
| H22 | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| CAG | Cytomegalovirus immediate-early enhancer/chicken β-actin promoter |
| CPE | Cytopathic effect |
| NC | Negative control |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| Treg | Regulatory T lymphocytes |
| RFP | Red fluorescence protein |
| FlaB | Bacterial flagellin (subunit B) of Vibrio vulnificus |
| LDLR | Low-density lipoprotein receptor |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| RTK | Receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 |
| Th1 | T-helper 1 lymphocytes |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Minimal Medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| T7RNAP | T7 RNA polymerase |
| PEI | Polyethylenimine |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| RT | Real time |
References
- Araghi, M.; Mannani, R.; Heidarnejad maleki, A.; Hamidi, A.; Rostami, S.; Safa, S.H.; Faramarzi, F.; Khorasani, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Recent Advances in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeted Therapy; an Update Review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toropko, M.; Chuvpilo, S.; Karabelsky, A. MiRNA-Mediated Mechanisms in the Generation of Effective and Safe Oncolytic Viruses. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malogolovkin, A.; Gasanov, N.; Egorov, A.; Weener, M.; Ivanov, R.; Karabelsky, A. Combinatorial Approaches for Cancer Treatment Using Oncolytic Viruses: Projecting the Perspectives through Clinical Trials Outcomes. Viruses 2021, 13, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinovieva, M.; Ryapolova, A.; Karabelsky, A.; Minskaia, E. Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus: Optimisation Strategies for Anti-Cancer Therapies. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2024, 29, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorona, K.A.; Moroz, V.D.; Gasanov, N.B.; Karabelsky, A.V. Recombinant VSVS: A Promising Tool for Virotherapy. Acta Naturae 2024, 16, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felt, S.A.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Ecent Advances in Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Oncolytic Virotherapy: A 5-Year Update. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2895–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, J.H.; Naczki, C.; Koumenis, C.; Lyles, D.S. Replication and Cytopathic Effect of Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus in Hypoxic Tumor Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 8960–8970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wen, F.; Zhang, P.; Tang, R.; Li, Q. Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Is a Potent Agent for the Treatment of Malignant Ascites. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, S.; Kong, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Junqueira, C.; Meza-Sosa, K.F.; Mok, T.M.Y.; Ansara, J.; et al. Gasdermin E Suppresses Tumour Growth by Activating Anti-Tumour Immunity. Nature 2020, 579, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Liu, F.; Gao, F.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Q.; Sun, S.; Li, Z.; et al. Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Sensitizes Immunologically Cold Tumors to Checkpoint Blockade by Inducing Pyroptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryapolova, A.; Minskaia, E.; Gasanov, N.; Moroz, V.; Krapivin, B.; Egorov, A.D.; Laktyushkin, V.; Zhuravleva, S.; Nagornych, M.; Subcheva, E.; et al. Development of Recombinant Oncolytic RVSV-DM51-MIL12-MGMCSF for Cancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquis, K.A.; Becker, R.L.; Weiss, A.N.; Morris, M.C.; Ferran, M.C. The VSV Matrix Protein Inhibits NF-ΚB and the Interferon Response Independently in Mouse L929 Cells. Virology 2020, 548, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, E.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Vesicular Stomatitis Virus as a Flexible Platform for Oncolytic Virotherapy against Cancer. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2529–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goad, D.W.; Nesmelova, A.Y.; Yohe, L.R.; Grdzelishvili, V.Z. Intertumoral Heterogeneity Impacts Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Efficacy in Mouse Pancreatic Cancer Cells. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e01005-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakiba, Y.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Naumenko, V.A.; Kochetkov, D.V.; Zajtseva, K.V.; Valikhov, M.P.; Yusubalieva, G.M.; Gumennaya, Y.D.; Emelyanov, E.A.; Semkina, A.S.; et al. Oncolytic Efficacy of a Recombinant Vaccinia Virus Strain Expressing Bacterial Flagellin in Solid Tumor Models. Viruses 2023, 15, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.; Milo, T.; Isaacson, A.; Halperin, C.; Miyara, S.; Stein, Y.; Lior, C.; Pevsner-Fischer, M.; Tzahor, E.; Mayo, A.; et al. The Tumor Microenvironment Shows a Hierarchy of Cell-Cell Interactions Dominated by Fibroblasts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The Evolving Tumor Microenvironment: From Cancer Initiation to Metastatic Outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The Tumor Microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R921–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Lin, L.; Cao, G.; Chen, Q.; Shou, P.; Huang, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y. Interferon-α-Secreting Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exert Potent Antitumor Effect in Vivo. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5047–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, P.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, J.; Xu, C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, M.; Velletri, T.; Cao, W.; Huang, Y.; et al. Type i Interferons Exert Anti-Tumor Effect via Reversing Immunosuppression Mediated by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 5953–5962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melzer, M.K.; Lopez-Martinez, A.; Altomonte, J. Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus as a Viro-Immunotherapy: Defeating Cancer with a “Hammer” and “Anvil”. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelshtein, D.; Werman, A.; Novick, D.; Barak, S.; Rubinstein, M. LDL Receptor and Its Family Members Serve as the Cellular Receptors for Vesicular Stomatitis Virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7306–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Gagnon, C.; Hou, X.; Hardy, P. Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor Mediates Anti-VEGF Effect of Lymphocyte T-Derived Microparticles in Lewis Lung Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gal, D.; Macdonald, P.C.; Porter, J.C.; Smith, J.W.; Simpson, E.R. Effect of Cell Density and Confluency on Cholesterol Metabolism in Cancer Cells in Monolayer Culture1. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 473–477. [Google Scholar]
- Kelishadi, R.; Hashemipour, M.; Sarrafzadegan, N.; Mohammadifard, N.; Alikhasy, H.; Beizaei, M.; Sajjadi, F.; Poursafa, P.; Amin, Z.; Ghatreh-Samani, S.; et al. Effects of a Lifestyle Modification Trial among Phenotypically Obese Metabolically Normal and Phenotypically Obese Metabolically Abnormal Adolescents in Comparison with Phenotypically Normal Metabolically Obese Adolescents. Matern. Child Nutr. 2010, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Breton, C.; Barber, G.N.; Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.-W. Retargeting Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Using Measles Virus Envelope Glycoproteins. Hum. Gene Ther. 2011, 23, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, S.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Q. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Is a Co-Factor for Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Entry. Virology 2018, 521, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zeng, F.; Forrester, S.J.; Eguchi, S.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Harris, R.C. Expression and Function of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in Physiology and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1025–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, X.; Hao, M.; Hassan, S.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, H.; Yang, D.; Liu, L.; et al. IGFBP2 Regulates PD-L1 Expression by Activating the EGFR-STAT3 Signaling Pathway in Malignant Melanoma. Cancer Lett. 2020, 477, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, B.; Jacobs, K.; Ferdinande, L.; Taildeman, J.; Lambert, J.; Peeters, M.; Bracke, M.; Pauwels, P.; Brochez, L. EGFR in Melanoma: Clinical Significance and Potential Therapeutic Target. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2011, 38, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Niemetz-Rahn, A.; Nonnenmacher, A.; Tucholski, J.; Keilholz, U.; Fusi, A. Expression and Activity of EGFR in Human Cutaneous Melanoma Cell Lines and Influence of Vemurafenib on the EGFR Pathway. Target. Oncol. 2015, 10, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selman, M.; Rousso, C.; Bergeron, A.; Son, H.H.; Krishnan, R.; El-Sayes, N.A.; Varette, O.; Chen, A.; Le Boeuf, F.; Tzelepis, F.; et al. Multi-Modal Potentiation of Oncolytic Virotherapy by Vanadium Compounds. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeron, A.; Kostenkova, K.; Selman, M.; Murakami, H.A.; Owens, E.; Haribabu, N.; Arulanandam, R.; Diallo, J.-S.; Crans, D.C. Enhancement of Oncolytic Virotherapy by Vanadium(V) Dipicolinates. BioMetals 2019, 32, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, L.-S.; Lund, E.; Dahlberg, J.E. Inhibition of Ran Guanosine Triphosphatase-Dependent Nuclear Transport by the Matrix Protein of Vesicular Stomatitis Virus. Science 1997, 276, 1845–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Kobbe, C.; Van Deursen, J.M.A.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Sitterlin, D.; Bachi, A.; Wu, X.; Wilm, M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Izaurralde, E. Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Matrix Protein Inhibits Host Cell Gene Expression by Targeting the Nucleoporin Nup98. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terstegen, L.; Gatsios, P.; Ludwig, S.; Pleschka, S.; Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Heinrich, P.C.; Graeve, L. The Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Matrix Protein Inhibits Glycoprotein 130-Dependent STAT Activation. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5209–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.D.; Yen, M.C.; Lin, C.M.; Tu, C.F.; Wang, C.C.; Lin, P.S.; Yang, H.J.; Lin, C.C. The Effects of DNA Formulation and Administration Route on Cancer Therapeutic Efficacy with Xenogenic EGFR DNA Vaccine in a Lung Cancer Animal Model. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2009, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Alemany, R.; Krasnykh, V.; Marini, F.C.; Xu, J.; Alonso, M.M.; Conrad, C.A.; Aldape, K.D.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; et al. Oncolytic Adenovirus Retargeted to Delta-EGFR Induces Selective Antiglioma Activity. Cancer Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, H.; Marzulli, M.; Nakano, K.; Goins, W.F.; Chan, J.; Hong, C.S.; Mazzacurati, L.; Yoo, J.Y.; Haseley, A.; Nakashima, H.; et al. Effective Treatment of an Orthotopic Xenograft Model of Human Glioblastoma Using an EGFR-Retargeted Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xu, J.; Guo, L.; Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y. Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus-Induced Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Activation Impairs the Antiviral Activity of Type I Interferon. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, H.D.; Eisfeld, A.J.; Stratton, K.G.; Heller, N.C.; Bramer, L.M.; Wen, J.; McDermott, J.E.; Gralinski, L.E.; Sims, A.C.; Le, M.Q. The Role of EGFR in Influenza Pathogenicity: Multiple Network-Based Approaches to Identify a Key Regulator of Non-Lethal Infections. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueki, I.F.; Min-Oo, G.; Kalinowski, A.; Ballon-Landa, E.; Lanier, L.L.; Nadel, J.A.; Koff, J.L. Respiratory Virus–Induced EGFR Activation Suppresses IRF1-Dependent Interferon λ and Antiviral Defense in Airway Epithelium. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 1929–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasek, W.; Zagożdżon, R.; Jakobisiak, M. Interleukin 12: Still a Promising Candidate for Tumor Immunotherapy? Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2014, 63, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Kang, X.; Chen, K.S.; Jehng, T.; Jones, L.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.F.; Chen, S.Y. An Engineered Oncolytic Virus Expressing PD-L1 Inhibitors Activates Tumor Neoantigen-Specific T Cell Responses. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Wan, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, R.; et al. CD40L-Armed Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus Suppresses Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Facilitating the Tumor Microenvironment Favorable to Cytotoxic T Cell Response in the Syngeneic Mouse Model. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakao, S.; Arai, Y.; Tasaki, M.; Yamashita, M.; Murakami, R.; Kawase, T.; Amino, N.; Nakatake, M.; Kurosaki, H.; Mori, M.; et al. Intratumoral expression of IL-7 and IL-12 Using an Oncolytic Virus Increases Systemic Sensitivity to Immune Checkpoint Blockade. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaax7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougan, M.; Dranoff, G.; Dougan, S.K. GM-CSF, IL-3, and IL-5 Family of Cytokines: Regulators of Inflammation. Immunity 2019, 50, 796–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileva, N.; Ageenko, A.; Dmitrieva, M.; Nushtaeva, A.; Mishinov, S.; Kochneva, G.; Richter, V.; Kuligina, E. Double Recombinant Vaccinia Virus: A Candidate Drug against Human Glioblastoma. Life 2021, 11, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Yang, J.; Hu, J.; Sun, X. On the Calculation of TCID50 for Quantitation of Virus Infectivity. Virol. Sin. 2021, 36, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryapolova, A.; Zinovieva, M.; Vorona, K.; Krapivin, B.; Moroz, V.; Gasanov, N.; Imatdinov, I.; Imatdinov, A.; Ivanov, R.; Karabelsky, A.; et al. Recombinant Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Expressing Mouse Interleukin-12 and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (rVSV-dM51-mIL12-mGMCSF) for Immunotherapy of Lung Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178567
Ryapolova A, Zinovieva M, Vorona K, Krapivin B, Moroz V, Gasanov N, Imatdinov I, Imatdinov A, Ivanov R, Karabelsky A, et al. Recombinant Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Expressing Mouse Interleukin-12 and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (rVSV-dM51-mIL12-mGMCSF) for Immunotherapy of Lung Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178567
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyapolova, Anastasia, Margarita Zinovieva, Kristina Vorona, Bogdan Krapivin, Vasiliy Moroz, Nizami Gasanov, Ilnaz Imatdinov, Almaz Imatdinov, Roman Ivanov, Alexander Karabelsky, and et al. 2025. "Recombinant Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Expressing Mouse Interleukin-12 and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (rVSV-dM51-mIL12-mGMCSF) for Immunotherapy of Lung Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178567
APA StyleRyapolova, A., Zinovieva, M., Vorona, K., Krapivin, B., Moroz, V., Gasanov, N., Imatdinov, I., Imatdinov, A., Ivanov, R., Karabelsky, A., & Minskaia, E. (2025). Recombinant Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus Expressing Mouse Interleukin-12 and Granulocyte-Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor (rVSV-dM51-mIL12-mGMCSF) for Immunotherapy of Lung Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178567




