Dual Effects of In Situ Coal Combustion on CaO Pellets for CO2 Capture: High-Temperature Sintering and Ash Stabilization
Abstract
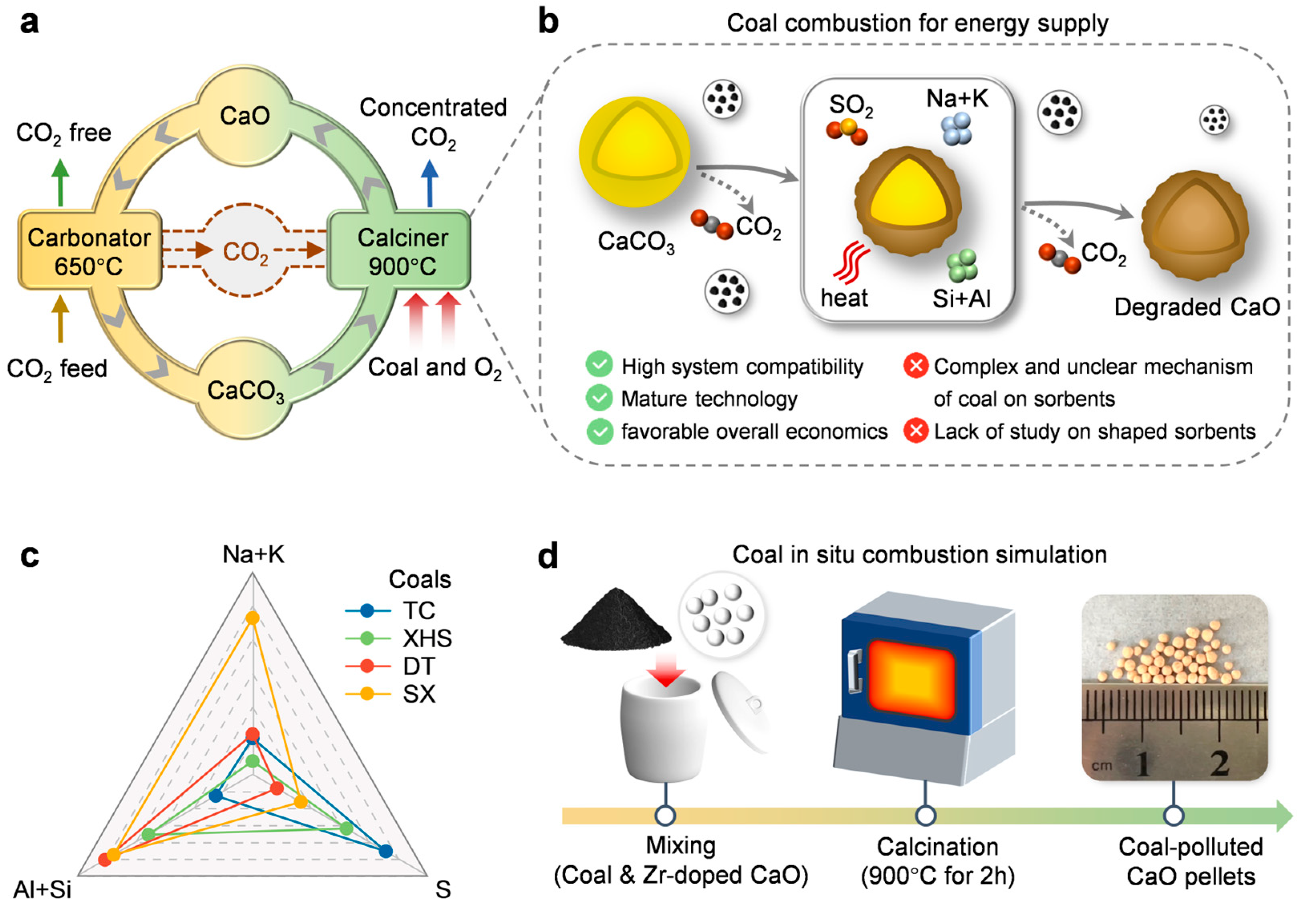
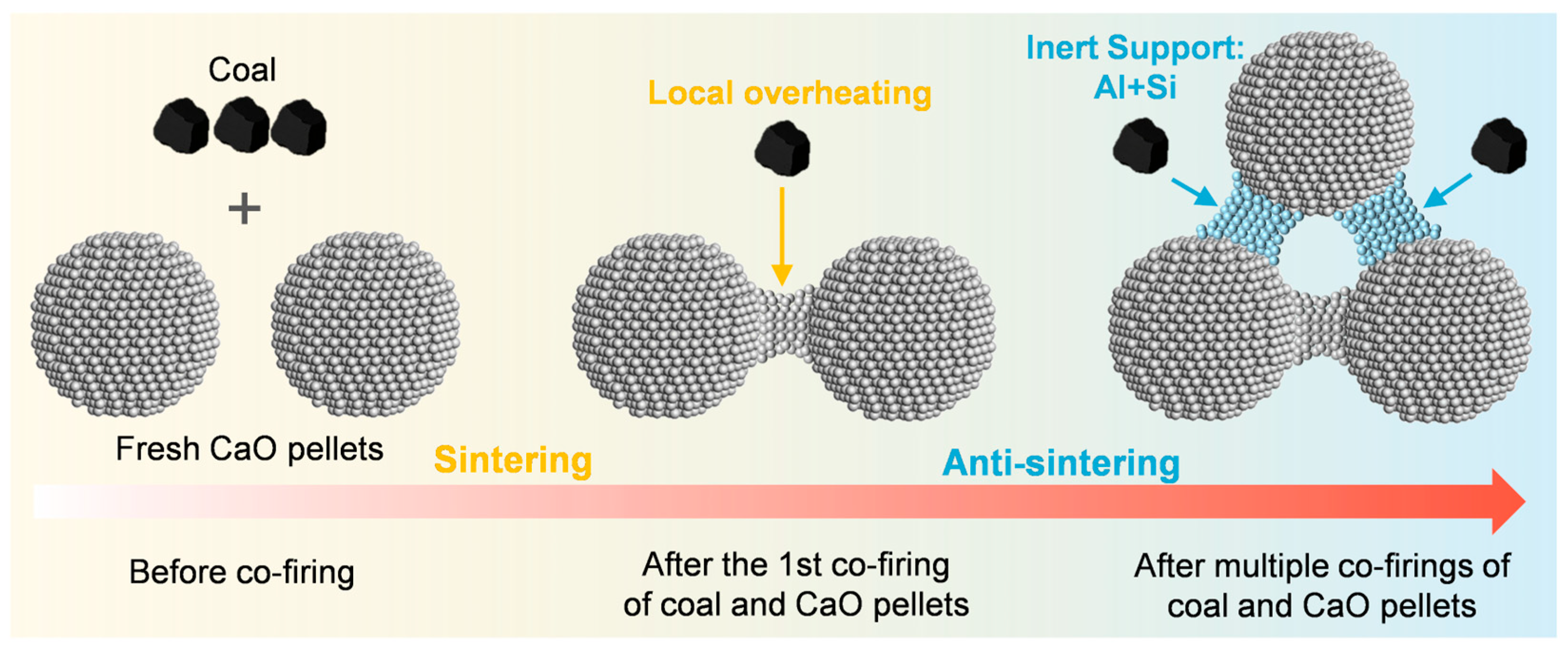
1. Introduction
2. Results
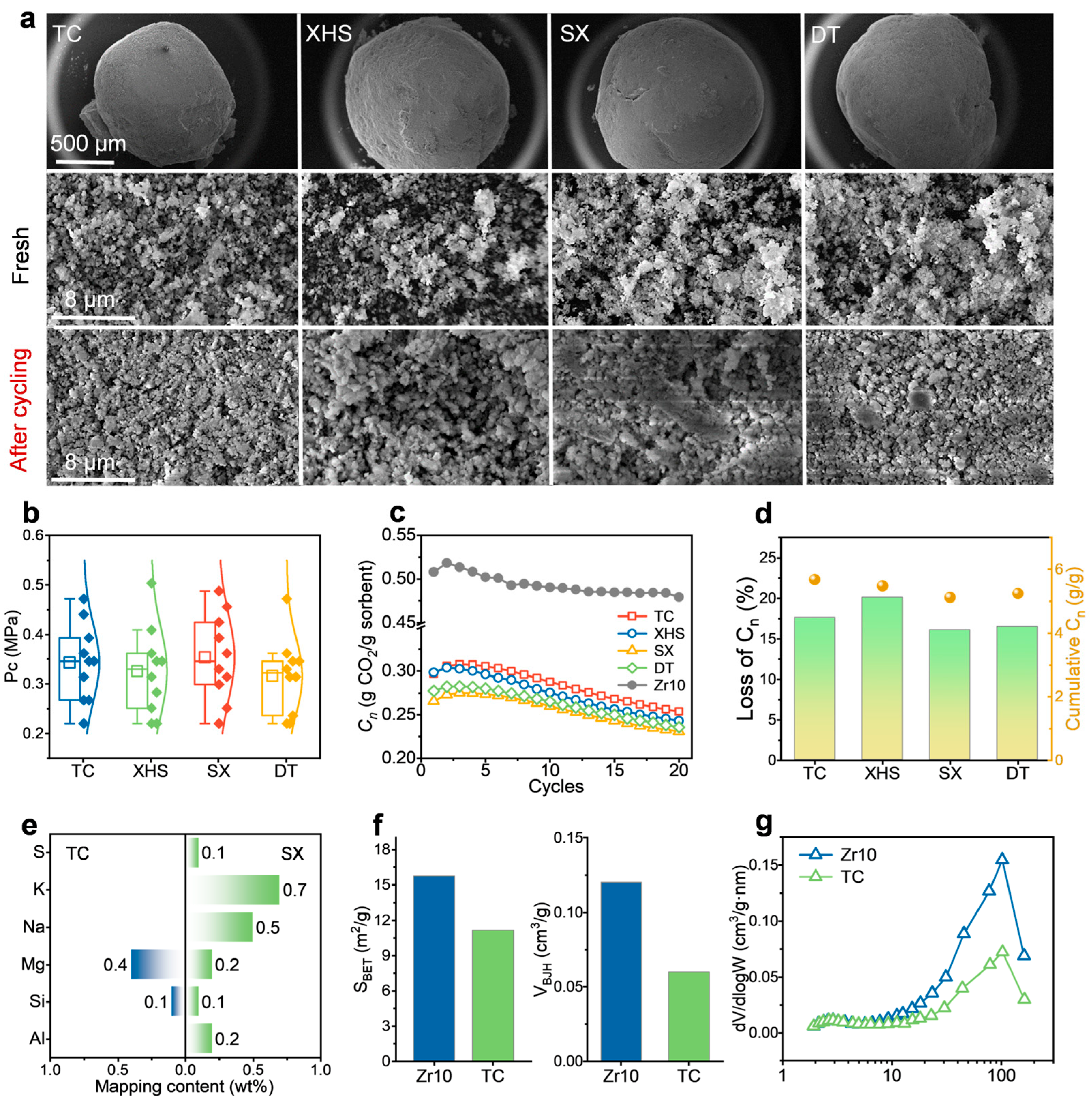
2.1. Performance After First Co-Firing
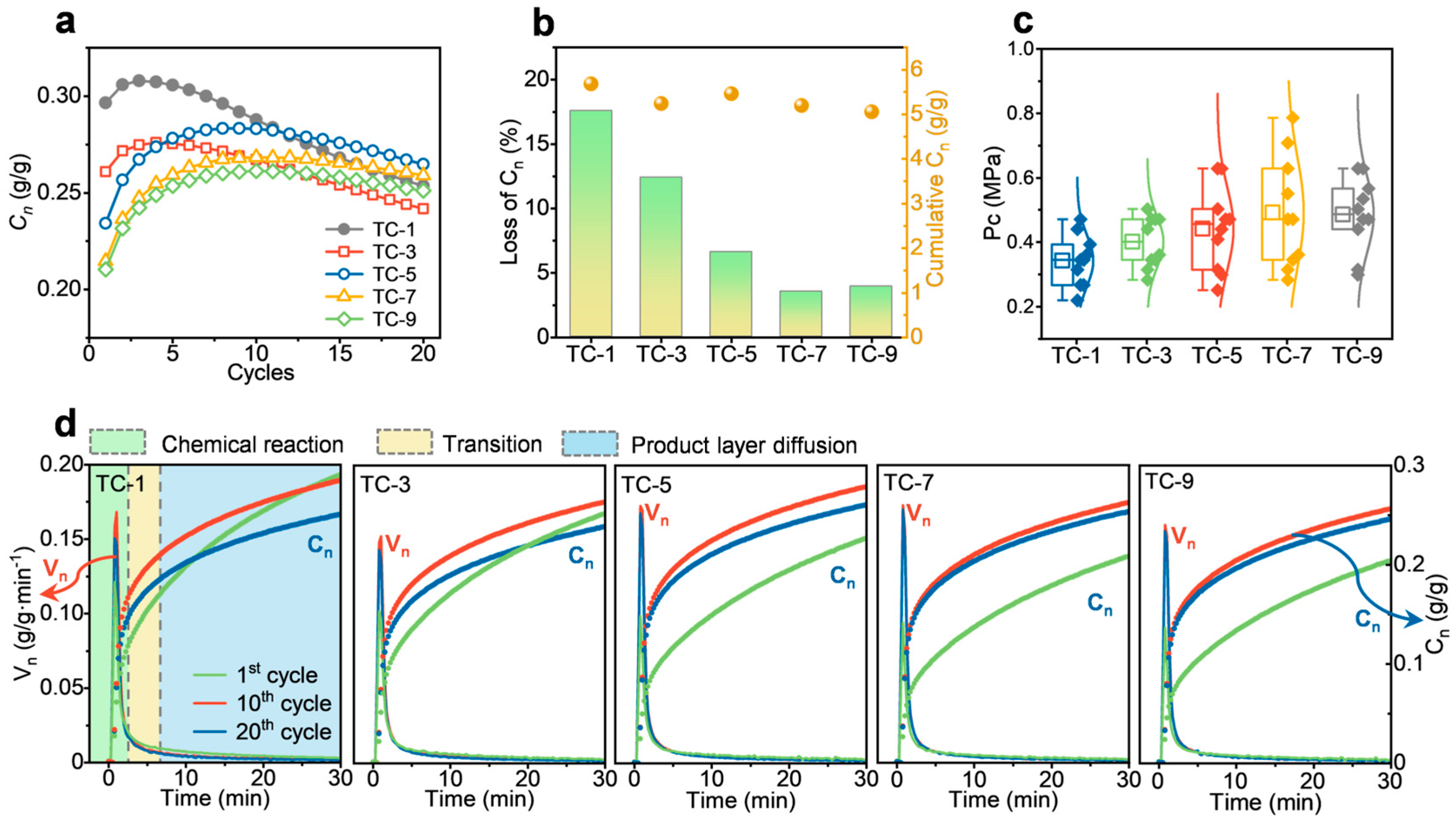
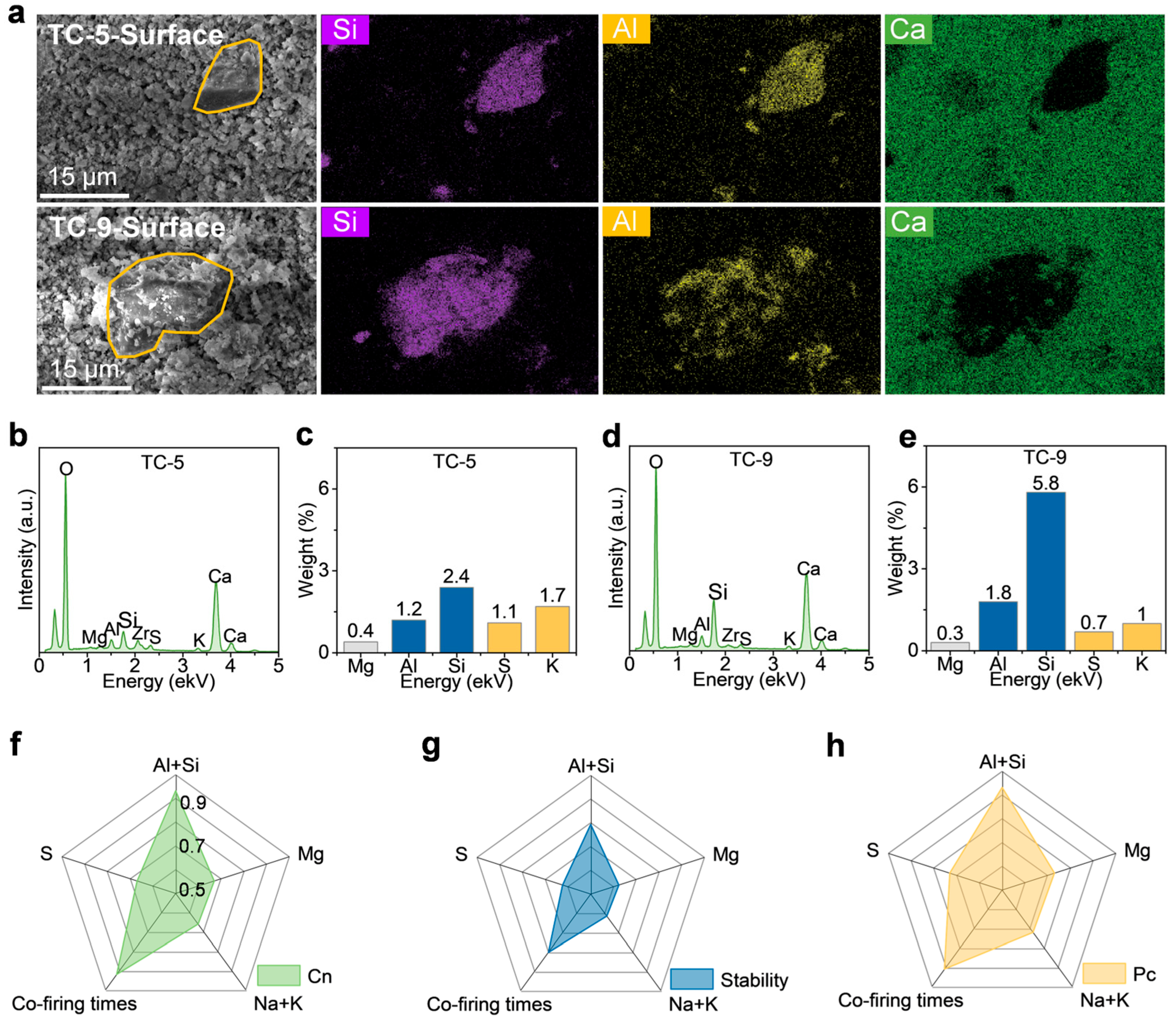
2.2. Performance After Multiple Co-Firings
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Coal Selection
4.2. In Situ Coal Combustion Simulation
4.3. CO2 Capture Capacity Testing
4.4. Mechanical Property Testing
4.5. Gray Relational Analysis
4.6. Characterization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haszeldine, R.S. Carbon capture and storage: How green can black be? Science 2009, 325, 1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramochi, T.; Ramírez, A.; Turkenburg, W.; Faaij, A. Comparative assessment of CO2 capture technologies for carbon-intensive industrial processes. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2012, 38, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, M.; Adjiman, C.S.; Bardow, A.; Anthony, E.J.; Boston, A.; Brown, S.; Fennell, P.S.; Fuss, S.; Galindo, A.; Hackett, L.A. Carbon capture and storage (CCS): The way forward. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhu, B.; Davis, S.J.; Ciais, P.; Guan, D.; Gong, P.; Liu, Z. Global carbon emissions and decarbonization in 2024. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blamey, J.; Anthony, E.; Wang, J.; Fennell, P. The calcium looping cycle for large-scale CO2 capture. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2010, 36, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witoon, T.; Mungcharoen, T.; Limtrakul, J. Biotemplated synthesis of highly stable calcium-based sorbents for CO2 capture via a precipitation method. Appl. Energy 2014, 118, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Sun, Z. Review on the development of sorbents for calcium looping. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Duan, L.; Anthony, E.J. A calcium looping process for simultaneous CO2 capture and peak shaving in a coal-fired power plant. Appl. Energy 2019, 235, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perejón, A.; Romeo, L.M.; Lara, Y.; Lisbona, P.; Martínez, A.; Valverde, J.M. The Calcium-Looping technology for CO2 capture: On the important roles of energy integration and sorbent behavior. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armutlulu, A.; Naeem, M.A.; Liu, H.J.; Kim, S.M.; Kierzkowska, A.; Fedorov, A.; Müller, C.R. Multishelled CaO Microspheres Stabilized by Atomic Layer Deposition of Al2O3 for Enhanced CO2 Capture Performance. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1702896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Fang, F.; Tang, X.; Cai, N.S. Effect of temperature on the carbonation reaction of CaO with CO2. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, C.; Valverde, J.; Chacartegui, R.; Benítez-Guerrero, M.; Perejón, A.; Romeo, L. The Oxy-CaL process: A novel CO2 capture system by integrating partial oxy-combustion with the Calcium-Looping process. Appl. Energy 2017, 196, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ramkumar, S.; Fan, L.-S. Energy penalty of CO2 capture for the carbonation-calcination Reaction (CCR) Process: Parametric effects and comparisons with alternative processes. Fuel 2013, 104, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Pu, G.; Qin, C.; Gong, R.; Tan, L.; Ran, J. Impacts and action mechanism of coal ash on CaO-based sorbents for CO2 capture under an oxy-fuel calcination environment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 15143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.W.; Macchi, A.; Lu, D.Y.; Anthony, E.J. Changes in Limestone Sorbent Morphology during CaO-CaCO3 Looping at Pilot Scale. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2009, 32, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, A.; Huang, Y.; Haaf, M.; Rezvani, S.; MclIveen-Wright, D.; Hewitt, N. Integration of the calcium carbonate looping process into an existing pulverized coal-fired power plant for CO2 capture: Techno-economic and environmental evaluation. Appl. Energy 2018, 222, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qian, N. The effects of water vapor and coal ash on the carbonation behavior of CaO-sorbent supported by γ-Al2O3 for CO2 capture. Fuel Process. Technol. 2018, 177, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanisalim, A.H.; Sedghkerdar, M.H.; Karami, D.; Mahinpey, N. Pelletizing and coating of synthetic zirconia stabilized calcium-based sorbents for application in calcium looping CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liang, C.; Tong, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Lu, P. Evaluation of high-temperature CO2 capture performance of cellulose-templated CaO-based pellets. Fuel 2019, 239, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Xu, M. Enhanced performance of extruded-spheronized carbide slag pellets for high temperature CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werther, J.; Saenger, M.; Hartge, E.U.; Ogada, T.; Siagi, Z. Combustion of agricultural residues. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2000, 26, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, M.; Xu, K.; Liu, W.; Luo, G.; Yao, H. Limestone decomposition in an O2/CO2/steam atmosphere integrated with coal combustion. Energy Fuels 2016, 30, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, J.J.; Qin, C.L.; Ding, N.; Zheng, C.G.; Feng, B. Effect of Sulfation during Oxy-Fuel Calcination Stage in Calcium Looping on CO2 Capture Performance of CaO-Based Sorbents. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Khalili, N. Fly-ash-modified calcium-based sorbents tailored to CO2 capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, F.; Zhao, C.; Khalili, N. The effect of fly ash on reactivity of calcium based sorbents for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Qin, C.; Manovic, V.; Ran, J.; Feng, B. Study on the interaction between CaO-based sorbents and coal ash in calcium looping process. Fuel Process. Technol. 2017, 156, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, M.; Arias, B.; Fernández, J.R.; Bughin, O.; Abanades, C. Measuring attrition properties of calcium looping materials in a 30 kW pilot plant. Powder Technol. 2018, 336, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Sedghkerdar, M.H.; Saayman, J.; Mahinpey, N.; Ellis, N.; Zhao, D.; Kaliaguine, S. A Facile fabrication of mesoporous core–shell CaO-Based pellets with enhanced reactive stability and resistance to attrition in cyclic CO2 capture. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 16577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M. Structurally improved, core-in-shell, CaO-based sorbent pellets for CO2 capture. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, L.; Long, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, M. Comparative investigation on CO2 uptake performance of limestone-derived sorbents with different supports synthesized by impregnated layer solution combustion method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 332, 125737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, M. Stabilized CO2 capture performance of extruded-spheronized CaO-based pellets by microalgae templating. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, P.; Sun, J.; Li, K.; Jiang, L.; Sun, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Z. Insight into the deactivation mechanism of CaO-based CO2 sorbent under in-situ coal combustion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 346, 127529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhu, J.; Tong, X.; Zhao, C. Strengthening performance of Al-stabilized, CaO-based CO2 sorbent pellets by the combination of impregnated layer solution combustion and graphite-moulding. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 315, 123757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z. General rate equation theory for gas-solid reaction kinetics and its application to CaO carbonation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 227, 115902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, H.; Cai, N. Rate equation theory for the carbonation reaction of CaO with CO2. Energy Fuels 2012, 26, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cai, N. Understanding the enhancement effect of high-temperature steam on the carbonation reaction of CaO with CO2. Fuel 2014, 127, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, C.; Gómez-Barea, A.; Leckner, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Piao, G. The effect of H2O on the oxy-fuel combustion of a bituminous coal char particle in a fluidized bed: Experiment and modeling. Combust. Flame 2020, 218, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Proximate Analysis | Ultimate Analysis | Low Calorific Value Q (kJ/kg) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mad | Vad | Aad | FCad | Cad | Had | Oad | Nad | Sad | ||
| Tianchi coal | 13.62 | 33.92 | 12.22 | 40.24 | 55.44 | 4.37 | 38.57 | 0.55 | 1.07 | 21,098 |
| Xiheishan coal | 13.15 | 26.90 | 25.53 | 34.42 | 44.22 | 3.88 | 50.96 | 0.54 | 0.40 | 17,121 |
| Datong coal | 2.10 | 38.10 | 27.20 | 32.60 | 75.00 | 4.60 | 17.90 | 1.30 | 1.20 | 23,862 |
| Shanxi coal | 3.14 | 16.57 | 11.95 | 68.34 | 53.87 | 3.77 | 36.84 | 0.87 | 4.65 | 19,327 |
| Na2O | K2O | MgO | Al2O3 | SiO2 | P2O5 | Cl | CaO | Fe2O3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianchi coal | 6.90 | 0.75 | 2.75 | 13.82 | 38.86 | 1.18 | 1.16 | 16.83 | 17.74 |
| Xiheishan coal | 3.74 | 1.65 | 3.91 | 18.54 | 57.35 | 1.15 | 0.74 | 4.90 | 8.03 |
| Datong coal | 0.95 | 0.45 | 1.04 | 35.45 | 55.37 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 2.70 | 3.60 |
| Shanxi coal | 1.73 | 1.03 | 1.51 | 36.09 | 51.65 | 0.47 | 0.00 | 3.89 | 3.62 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, Y.; Wang, C.; Xu, R.; Liu, L.; Zeng, P.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, M. Dual Effects of In Situ Coal Combustion on CaO Pellets for CO2 Capture: High-Temperature Sintering and Ash Stabilization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178535
Long Y, Wang C, Xu R, Liu L, Zeng P, Zhou Z, Xu M. Dual Effects of In Situ Coal Combustion on CaO Pellets for CO2 Capture: High-Temperature Sintering and Ash Stabilization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178535
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Yun, Changqing Wang, Ruichang Xu, Lei Liu, Pengxin Zeng, Zijian Zhou, and Minghou Xu. 2025. "Dual Effects of In Situ Coal Combustion on CaO Pellets for CO2 Capture: High-Temperature Sintering and Ash Stabilization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178535
APA StyleLong, Y., Wang, C., Xu, R., Liu, L., Zeng, P., Zhou, Z., & Xu, M. (2025). Dual Effects of In Situ Coal Combustion on CaO Pellets for CO2 Capture: High-Temperature Sintering and Ash Stabilization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178535





