Protease-Activated Receptor F2R Is a Potential Target for New Diagnostic/Prognostic and Treatment Applications for Patients with Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
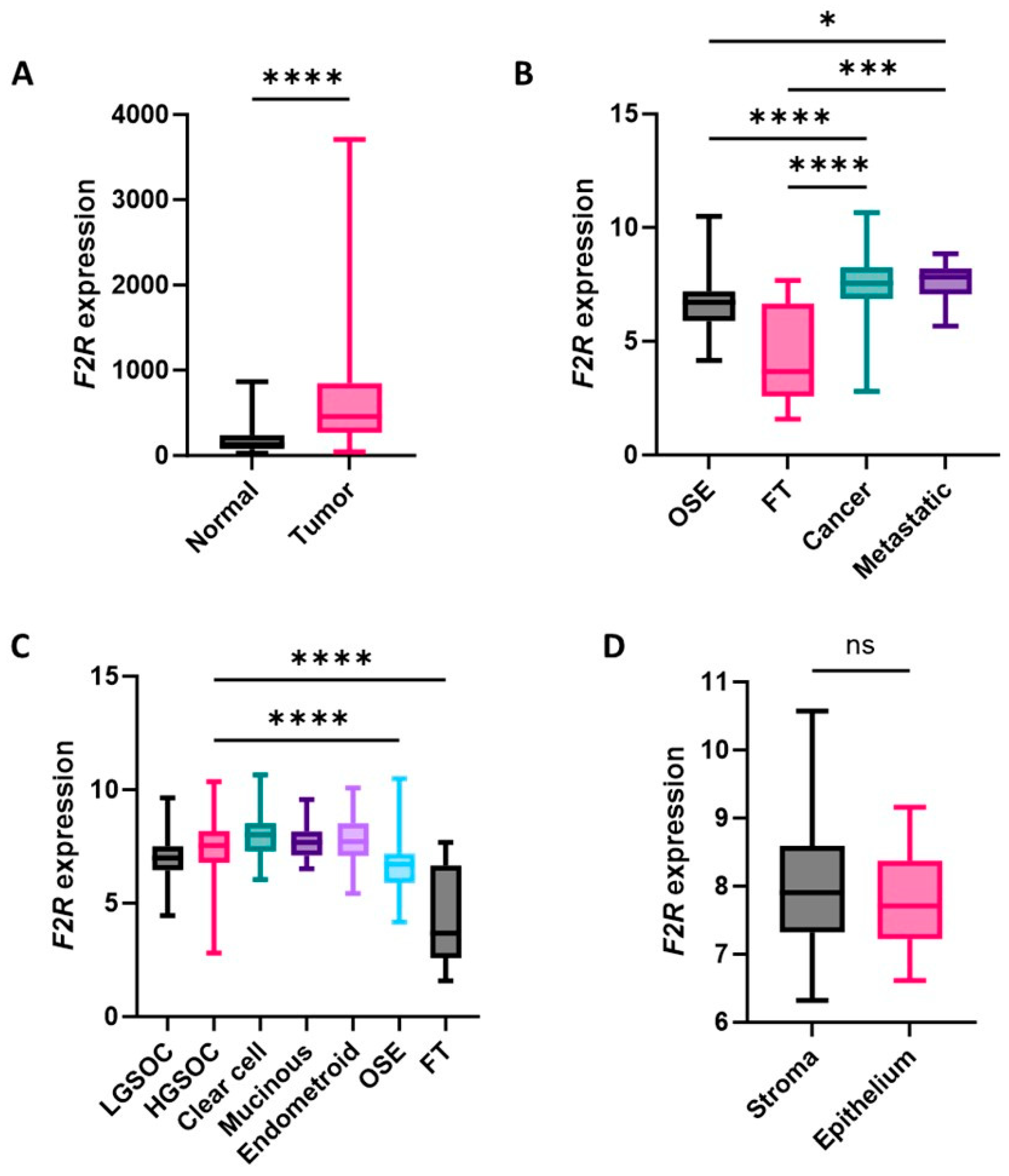
2.1. F2R Gene Expression Levels Were Elevated in Ovarian Cancers
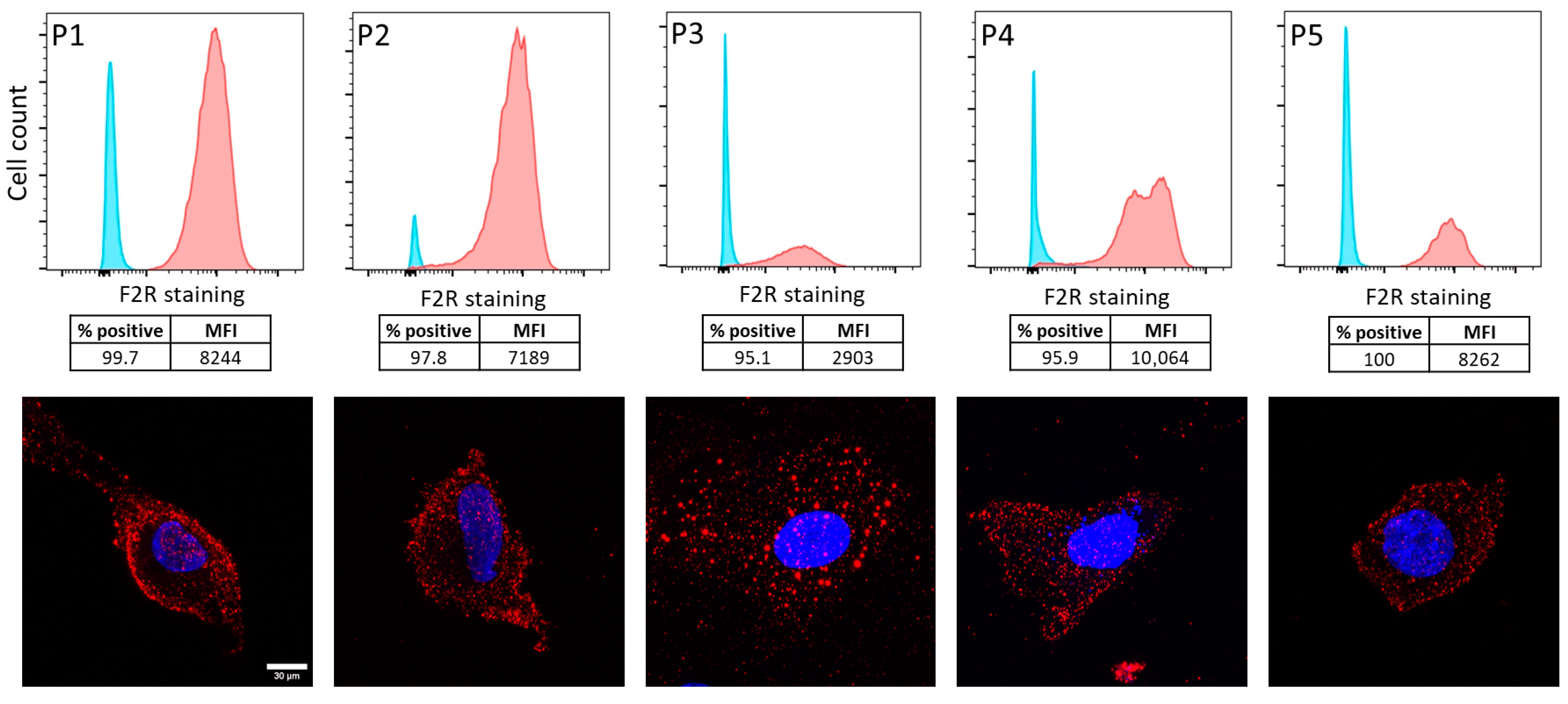
2.2. F2R Protein Was Expressed in Ascites-Derived Ovarian Cancer Cells
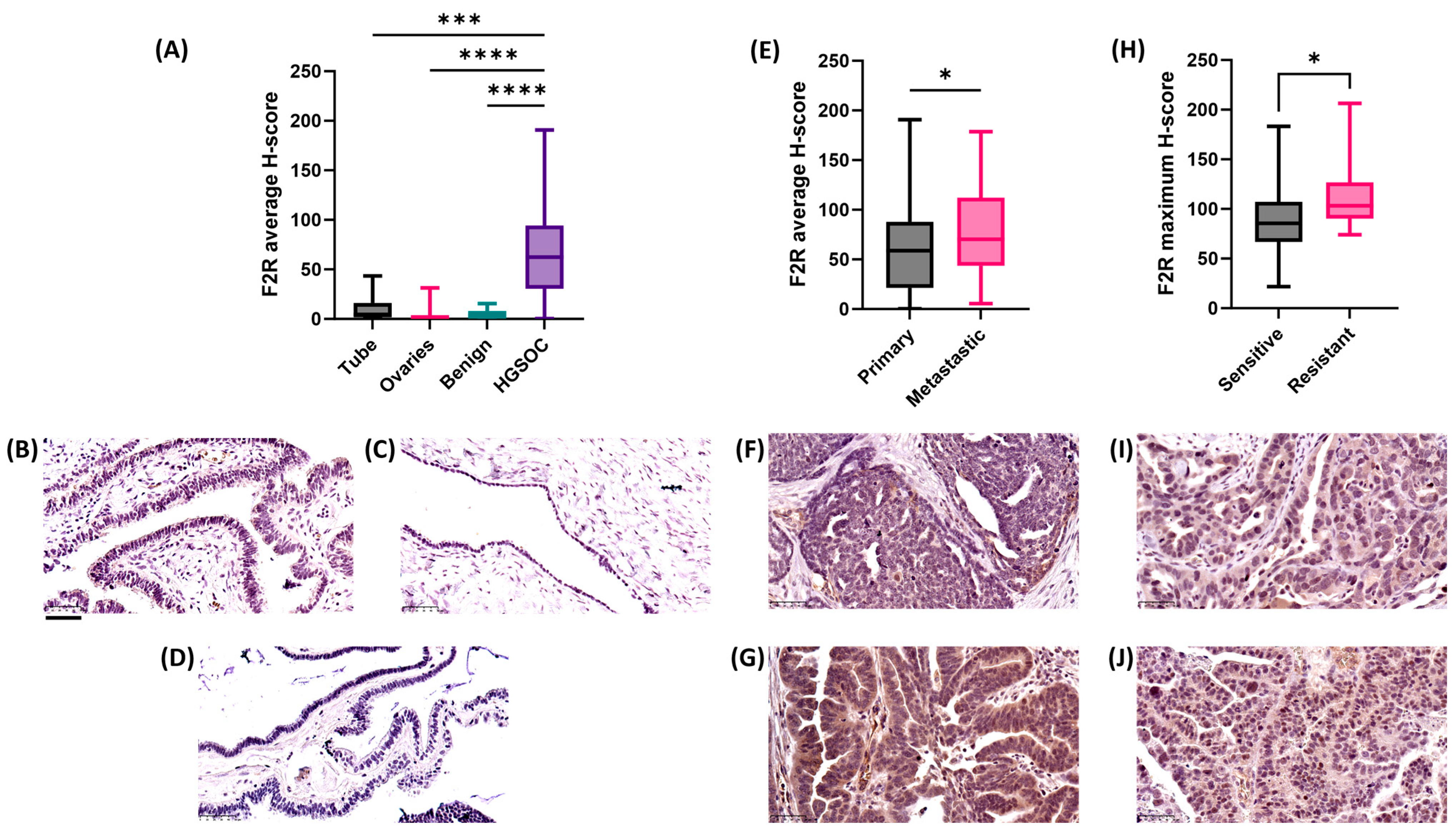
2.3. F2R Protein Expression Was Elevated in Ovarian Cancer Compared to Normal Tissues
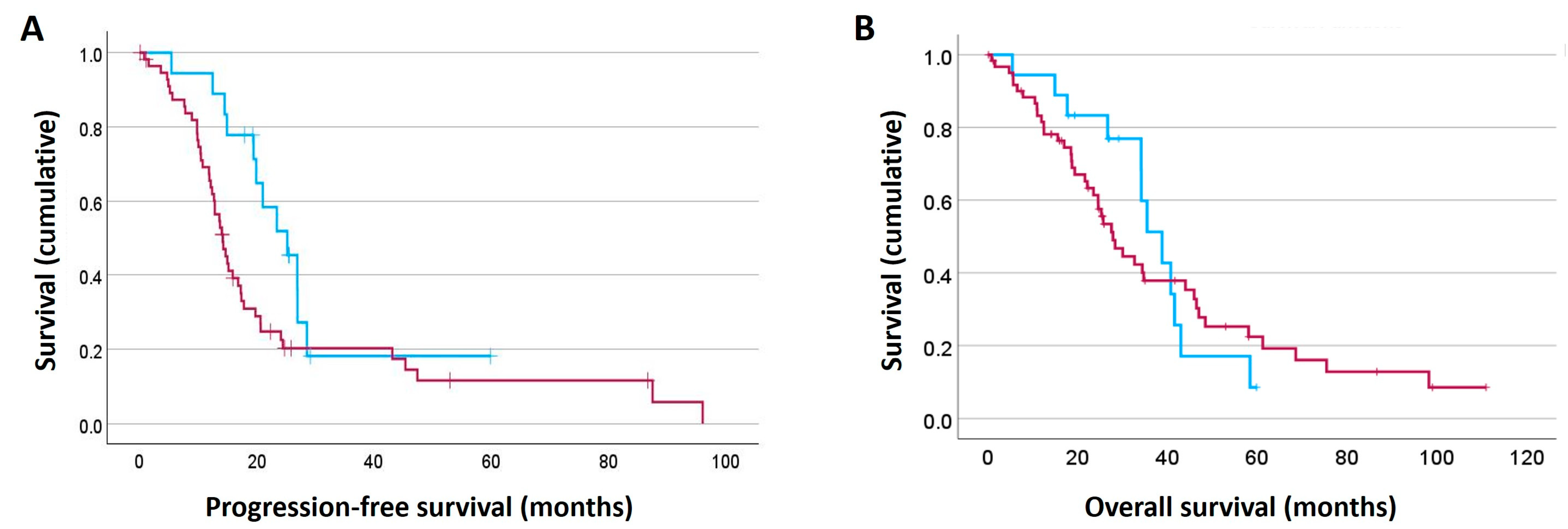
2.4. High F2R Protein Expression in HGSOC Patients Was Linked to Poor Patient Outcome
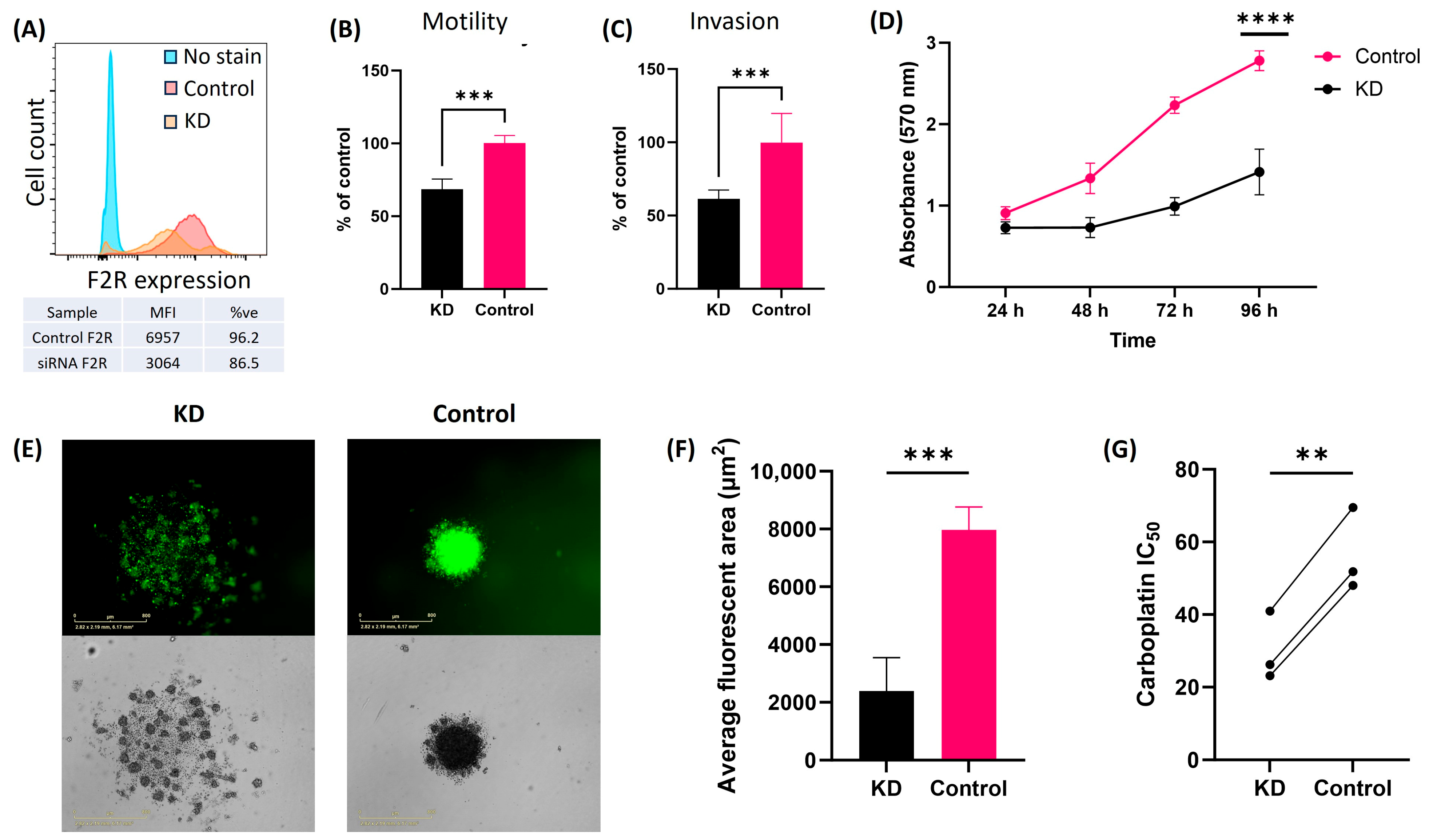
2.5. F2R Knockdown in Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines Alters the Tumor Cell Biology
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Public Data
4.3. Patient Tissue Cohorts
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Cell Culture and Patient-Derived Samples
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. siRNA Gene Knockdown and RT-qPCR
4.9. Motility and Invasion Assay
4.10. Cell Metabolism Assay
4.11. Carboplatin Response Assay
4.12. Spheroid Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGRF | Australian Genome Research Facility |
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| F2R | Coagulation factor II receptor |
| FACS | Fluorescence-activated cell sorting |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| FT | Fallopian tube |
| GPCRs | G-protein coupled receptors |
| GSEs | Genomic spatial events |
| HGSOC | High-grade serous ovarian cancer |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| KM Plot | Kaplan–Meier plot |
| LGSOC | Low-grade serous ovarian cancer |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| ns | Non-significant |
| OS | Overall survival |
| OSE | Ovarian surface epithelium |
| PAR1 | Protease-activated receptor 1 |
| PARs | Protease-activated receptors |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| RAH | Royal Adelaide Hospital |
| Rap1/MAPK | Ras-associated protein 1/Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| RT-qPCR | Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| SDHA | Succinate dehydrogenase complex flavoprotein subunit A |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TMA | Tissue microarray |
References
- Khetan, R.; Dharmayanti, C.; Gillam, T.A.; Kubler, E.; Klingler-Hoffmann, M.; Ricciardelli, C.; Oehler, M.K.; Blencowe, A.; Garg, S.; Albrecht, H. Using GPCRs as Molecular Beacons to Target Ovarian Cancer with Nanomedicines. Cancers 2022, 14, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulonis, U.A.; Sood, A.K.; Fallowfield, L.; Howitt, B.E.; Sehouli, J.; Karlan, B.Y. Ovarian cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khetan, R.; Eldi, P.; Lokman, N.A.; Ricciardelli, C.; Oehler, M.K.; Blencowe, A.; Garg, S.; Pillman, K.; Albrecht, H. Unveiling G-protein coupled receptors as potential targets for ovarian cancer nanomedicines: From RNA sequencing data analysis to in vitro validation. J. Ovarian Res. 2024, 17, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boire, A.; Covic, L.; Agarwal, A.; Jacques, S.; Sherifi, S.; Kuliopulos, A. PAR1 is a matrix metalloprotease-1 receptor that promotes invasion and tumorigenesis of breast cancer cells. Cell 2005, 120, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, D.; Hirono, Y.; Goi, T.; Katayama, K.; Matsukawa, S.; Yamaguchi, A. The activation of proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR1) promotes gastric cancer cell alteration of cellular morphology related to cell motility and invasion. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Gangadharan, B.; Brass, L.F.; Ruf, W.; Mueller, B.M. Protease-activated receptors (PAR1 and PAR2) contribute to tumor cell motility and metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2004, 2, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Ricks, T.K.; Trejo, J. Protease-activated receptor signalling, endocytic sorting and dysregulation in cancer. J. Cell Sci. 2007, 120, 921–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleiban, A.; Faxalv, L.; Claesson, K.; Jonsson, J.I.; Osman, A. miR-20b regulates expression of proteinase-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1) thrombin receptor in melanoma cells. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedda, S.; Marafini, I.; Caruso, R.; Pallone, F.; Monteleone, G. Proteinase activated-receptors-associated signaling in the control of gastric cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11977–11984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, T.; Yang, H.; Han, Z.; Zhang, P. Endothelial cell protein C receptor promotes MGC803 gastric cancer cells proliferation and migration by activating ERK1/2. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigler, M.; Kamiya, T.; Brantley, E.C.; Villares, G.J.; Bar-Eli, M. PAR-1 and thrombin: The ties that bind the microenvironment to melanoma metastasis. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6561–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Tao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhu, M.; Ji, W.; Liu, X.; Li, T.; Hu, X. Exosomal MMP-1 transfers metastasis potential in triple-negative breast cancer through PAR1-mediated EMT. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 193, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shi, Y.; Lu, Q.; Huang, D. F2RL3 Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Angiogenesis in Gastric Cancer through the Rap1/MAPK Signaling Pathway. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2024, 29, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinovitch, E.; Mihara, K.; Sananes, A.; Zaretsky, M.; Heyne, M.; Shifman, J.; Aharoni, A.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Papo, N. A KLK4 proteinase substrate capture approach to antagonize PAR1. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, A.; Covic, L.; Sevigny, L.M.; Kaneider, N.C.; Lazarides, K.; Azabdaftari, G.; Sharifi, S.; Kuliopulos, A. Targeting a metalloprotease-PAR1 signaling system with cell-penetrating pepducins inhibits angiogenesis, ascites, and progression of ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Chen, X.; Li, R.; Zheng, R.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y. A prognostic risk model for ovarian cancer based on gene expression profiles from gene expression omnibus database. Biochem. Genet. 2023, 61, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grisaru-Granovsky, S.; Salah, Z.; Maoz, M.; Pruss, D.; Beller, U.; Bar-Shavit, R. Differential expression of protease activated receptor 1 (Par1) and pY397FAK in benign and malignant human ovarian tissue samples. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 113, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreienbring, K.; Franz, A.; Richter, R.; Dragun, D.; Heidecke, H.; Muller, D.; Mentze, M.; Dechend, R.; Sehouli, J.; Braicu, E.I. The Role of PAR1 Autoantibodies in Patients with Primary Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2018, 38, 3619–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Yan, M.; Min, Y.; Pan, Z.; Qiu, S.; Xia, S.; Yu, J.; et al. Identifying miRNA-mRNA regulation network of major depressive disorder in ovarian cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5375–5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Yoon, B.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, S.Y. GENT2: An updated gene expression database for normal and tumor tissues. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartha, A.; Gyorffy, B. TNMplot.com: A Web Tool for the Comparison of Gene Expression in Normal, Tumor and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosti, I.; Jain, N.; Aran, D.; Butte, A.J.; Sirota, M. Cross-tissue Analysis of Gene and Protein Expression in Normal and Cancer Tissues. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Ngan, H.Y.S.; Chan, K.K.L. Molecular Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, N.A.; Correa, E.; Avila, E.P.; Vela, T.A.; Perez, V.M. PAR1 is selectively over expressed in high grade breast cancer patients: A cohort study. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, D.; Zeeh, F.; Gadeken, T.; Gieseler, F.; Rauch, B.H.; Settmacher, U.; Kaufmann, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. Proteinase-Activated Receptor 2 Is a Novel Regulator of TGF-beta Signaling in Pancreatic Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Boire, A.; Agarwal, A.; Nguyen, N.; O’Callaghan, K.; Tu, P.; Kuliopulos, A.; Covic, L. Blockade of PAR1 signaling with cell-penetrating pepducins inhibits Akt survival pathways in breast cancer cells and suppresses tumor survival and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6223–6231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Tan, Y.; Zhou, D.; Bai, Y.; Cao, T.; Zhong, C.; Huang, W.; Ou, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Atlas Reveals the Tumor Microenvironment of Metastatic High-Grade Serous Ovarian Carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 923194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, L.; Cheng, H.; Wang, S.; Luan, W.; Cai, E.; Ye, X.; Zhu, H.; Cui, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Characterization of candidate factors associated with the metastasis and progression of high-grade serous ovarian cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 2974–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, K.M.; Covic, L.; Kuliopulos, A. Matrix metalloproteases and PAR1 activation. Blood 2013, 121, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallyas, F., Jr.; Sumegi, B.; Szabo, C. Role of Akt Activation in PARP Inhibitor Resistance in Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, A.; Burikhanov, R.; de Thonel, A.; Fujita, N.; Goswami, M.; Zhao, Y.; Eriksson, J.E.; Tsuruo, T.; Rangnekar, V.M. Binding and phosphorylation of par-4 by akt is essential for cancer cell survival. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.C.; Chou, Y.T.; Fu, H.W. Protease-activated receptor 2 induces migration and promotes Slug-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 486–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Cisowski, J.; Nguyen, N.; O’Callaghan, K.; Xu, J.; Agarwal, A.; Kuliopulos, A.; Covic, L. Dysregulated protease activated receptor 1 (PAR1) promotes metastatic phenotype in breast cancer through HMGA2. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtukiewicz, M.Z.; Hempel, D.; Sierko, E.; Tucker, S.C.; Honn, K.V. Protease-activated receptors (PARs)—biology and role in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardelli, C.; Lokman, N.A.; Pyragius, C.E.; Ween, M.P.; Macpherson, A.M.; Ruszkiewicz, A.; Hoffmann, P.; Oehler, M.K. Keratin 5 overexpression is associated with serous ovarian cancer recurrence and chemotherapy resistance. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17819–17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokman, N.A.; Price, Z.K.; Hawkins, E.K.; Macpherson, A.M.; Oehler, M.K.; Ricciardelli, C. 4-Methylumbelliferone Inhibits Cancer Stem Cell Activation and Overcomes Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, J.; Shames, B.; Johnson, C.P.; Nilakantan, V. MnTMPyP, a superoxide dismutase/catalase mimetic, decreases inflammatory indices in ischemic acute kidney injury. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khetan, R.; Lokman, N.A.; Eldi, P.; Price, Z.K.; Oehler, M.K.; Brooks, D.A.; Blencowe, A.; Garg, S.; Ricciardelli, C.; Albrecht, H. Protease-Activated Receptor F2R Is a Potential Target for New Diagnostic/Prognostic and Treatment Applications for Patients with Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178529
Khetan R, Lokman NA, Eldi P, Price ZK, Oehler MK, Brooks DA, Blencowe A, Garg S, Ricciardelli C, Albrecht H. Protease-Activated Receptor F2R Is a Potential Target for New Diagnostic/Prognostic and Treatment Applications for Patients with Ovarian Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178529
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhetan, Riya, Noor A. Lokman, Preethi Eldi, Zoe K. Price, Martin K. Oehler, Doug A. Brooks, Anton Blencowe, Sanjay Garg, Carmela Ricciardelli, and Hugo Albrecht. 2025. "Protease-Activated Receptor F2R Is a Potential Target for New Diagnostic/Prognostic and Treatment Applications for Patients with Ovarian Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178529
APA StyleKhetan, R., Lokman, N. A., Eldi, P., Price, Z. K., Oehler, M. K., Brooks, D. A., Blencowe, A., Garg, S., Ricciardelli, C., & Albrecht, H. (2025). Protease-Activated Receptor F2R Is a Potential Target for New Diagnostic/Prognostic and Treatment Applications for Patients with Ovarian Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8529. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178529










