Abstract
NIN-like proteins (NLPs) are conserved, plant-specific transcription factors that play crucial roles in the nitrate signaling response, plant growth and development, and abiotic stress responses. However, their functions have not been explored in sweet potato. In this study, we identified 7 NLPs in cultivated hexaploid sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas, 2n = 6x = 90), 9 NLPs in the diploid relative Ipomoea trifida (2n = 2x = 30), and 12 NLPs in Ipomoea triloba (2n = 2x = 30) via genome structure analysis and phylogenetic characterization, respectively. The protein physiological properties, chromosome localization, phylogenetic relationships, syntenic analysis maps, gene structure, promoter cis-acting regulatory elements, and protein interaction networks were systematically investigated to explore the possible roles of homologous NLPs in the nitrate signaling response, growth and development, and abiotic stress responses in sweet potato. The expression profiles of the identified NLPs in different tissues and treatments revealed tissue specificity and various expression patterns in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives, supporting differences in the evolutionary trajectories of the hexaploid sweet potato. These results are a critical first step in understanding the functions of sweet potato NLPs and offer more candidate genes for improving nitrogen use efficiency and increasing yield in cultivated sweet potato.
1. Introduction
Nitrogen (N), the main limiting factor for plant growth, is fundamental to agricultural productivity, animal and human nutrition, and sustainable ecosystems [1,2,3,4]. N is also an important component of biological macromolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, coenzymes, and chlorophyll in plants [5]. The availability of N in agricultural fields significantly affects crop yields [6]. In plants, nitrogen uptake and utilization from the soil is mainly through two forms—nitrate (NO3−) and ammonia (NH4+). In terrestrial plants, nitrate is the main source of nitrogen [7]. Over the past 60 years, the use of nitrogen fertilizer per unit of arable land has increased approximately eightfold in order to increase food production, resulting in significant soil, water, and air pollution [8]. Therefore, it is critically important to study the molecular mechanisms of crop nitrogen uptake and utilization and to improve crop nitrogen use efficiency to protect food and environmental security. Meanwhile, nitrate is also an important signaling molecule for lateral root development, flowering, and synergistic absorption of other nutrients [9]. Crucially, this nitrate signaling is perceived and transduced by NODULE INCEPTION-like proteins (NIN-like proteins/NLPs), which serve as pivotal transcription factors and central regulators. NLPs coordinate transcription, transport, metabolism, and systemic growth programs in response to nitrate [10,11,12,13,14,15,16].
Numerous studies have demonstrated that NLPs are central regulators of nitrate signaling and nitrogen uptake and utilization. The number of NLPs varied among different species, including 9 in Arabidopsis, 6 in rice, 9 in maize, 6 in tomato, 33 in tea plant, 18 in wheat, 31 in Brassica, 5 in apple, and 7 in Foxtail Millet [5,10,17,18,19,20,21,22,23]. Despite this diversity across the plant kingdom, NLPs were first identified not in these model crops but in the legume Lotus japonicus, where they regulate symbiotic root nodule formation [24]. In Arabidopsis, AtNLP6/7 were phosphorylated by AtCPK10/30/32 to ensure their localization in the nucleus for transcriptional activation of the primary nitrate response genes [12]. Furthermore, NLP6/7 interacts with TCP transcription factors to promote root meristem elongation under nitrogen starvation [15]. Crucially, NLP7 functions as a primary nitrate sensor in plants and plays an important role in the absorption and utilization of nitrogen [4]. NLP8 was reported as a key regulator of nitrate-promoted seed germination in Arabidopsis [25]. In rice, OsNLP3/4 regulates nitrogen nutrient signaling to promote panicle development [26], and OsNLP4 plays a pivotal role in rice nitrogen use efficiency (NUE) and provides insight into crop NUE improvement [27]. In maize, ZmNLP6 and ZmNLP8 restore nitrate signaling and assimilation [28]. In Medicago truncatula, NLP1 is required for the expression of nitrate-responsive genes [29]. Additionally, NLP1 was reported to regulate NRT2.1 to mediate root nodule formation across nitrate concentrations [30]. However, there is no advanced research about NLPs in sweet potato.
Nitrogen is vital for plant development, yet both deficiency and excess application compromise sweet potato yields. While nitrogen supply influences carbon metabolism in storage organs, few investigations have explored its impact on non-structural carbohydrate accumulation during sweet potato storage root development. Therefore, it is pivotal to explore the key genes regulating nitrogen uptake and utilization in sweet potato to improve nitrogen use efficiency and increase yield.
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam., 2n = 6x = 90) is an economically important root crop that is widely used as an industrial and bioenergy resource worldwide [31]. It possesses a sizable and intricate genome, resulting from polyploidy and high heterozygosity. In recent years, genome assemblies of the hexaploid cultivar Taizhong 6 [32], along with two closely related diploid relatives—Ipomoea trifida NCNSP0306 (2n = 2x = 30) and Ipomoea triloba NCNSP0323 (2n = 2x = 30) [33]—have been published. The assemblies of hexaploid and diploid genomes make it possible to identify and analyze important gene families at the whole-genome level in sweet potato.
In this study, a total of 28 NLPs were identified in I. batatas (7), Ipomoea trifida (9), and Ipomoea triloba (12). They were classified into four subgroups. We systematically investigated the protein physicochemical properties, chromosome localization, syntenic analysis maps, phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, promoter cis-elements, and protein interaction networks of NLPs in sweet potato. Furthermore, tissue specificity and expression pattern analyses of tuberous root development in different accessions and nitrate induction of NLPs were analyzed using qRT-PCR and RNA-seq. Differences in evolution and functions related to development, nitrate signaling response, and abiotic stress response were identified between sweet potato and its two diploid relatives.
2. Results
2.1. Identification and Characteristics of NLPs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
To comprehensively identify all NLPs in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives, we employed three typical strategies, as follows: BLASTP, HMMER search, and CD-Search database screening. A total of 28 NLPs were identified in I. batatas (7), I. trifida (9), and I. triloba (12) (Table 1 and Table S1), which were named after “Ib”, “Itf”, and “Itb”, respectively. The physicochemical properties were analyzed using the sequence of IbNLPs (Table 1). The CDS length varied from 714 bp (IbNLP1) to 2823 bp (IbNLP7). The amino acid lengths of IbNLPs ranged from 237 aa (IbNLP1) to 940 aa (IbNLP7), with molecular weight (MW) varying from 36.67 kDa (IbNLP1) to 109.26 kDa (IbNLP4). The pI of other NLPs ranged from 5.26 (IbNLP5) to 8.43 (IbNLP1), suggesting that they were basic proteins. All IbNLPs contained Ser, Thr, and Tyr phosphorylation sites. The grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) value of all IbNLPs proteins varied from −0.67 (IbNLP1) to −0.36 (IbNLP4), indicating that they were hydrophobic. Subcellular localization prediction assays showed that most of the IbNLPs were located in the nucleus, except for IbNLP2, which was located in the nucleus and mitochondrion.

Table 1.
Characterization of IbNLPs in sweet potato.
2.2. Chromosomal Distribution and Syntenic Analysis of IbNLP Genes
The NLPs were distributed across 5, 5, and 6 chromosomes of I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba (Figure 1). In I. batatas, two IbNLPs were detected on LG2 and LG9, and one each on LG1, LG5, and LG14. In I. trifida, three ItfNLPs were detected on Chr10, two on Chr01 and Chr15, and one each on Chr09 and Chr12. In I. triloba, five ItbNLPs were detected on Chr04, three on Chr10, and one each on Chr05, Chr09, Chr12, and Chr15.
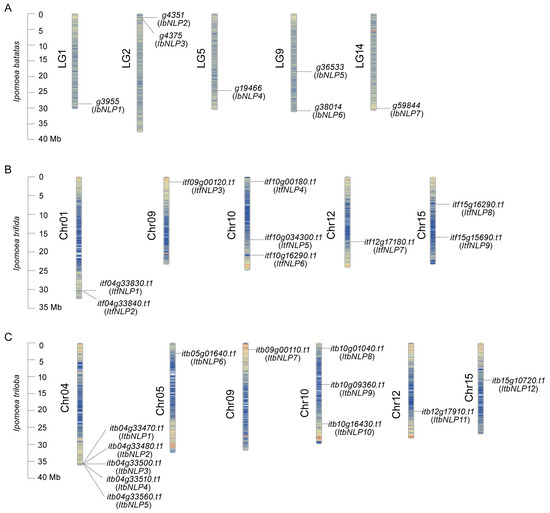
Figure 1.
Chromosomal localization and distribution of NLPs in I. batatas (A), I. trifida (B), and I. triloba (C). The bars in the left margin represent chromosomes. The chromosome numbers are displayed on the left side of the chromosomes, and the gene names are displayed on the right side. Detailed chromosomal location information is listed in Table S1.
Furthermore, four syntenic analysis maps—between I. batatas and each of its two diploid relatives, Arabidopsis, Zea mays, and Oryza sativa—were constructed to analyze the phylogenetic mechanisms of IbNLPs (Figure 2). Cultivated hexaploid sweet potato IbNLPs showed 7 syntenic gene pairs with I. triloba, 4 with I. trifida, 7 with Arabidopsis, 3 with Zea mays, and 0 with Oryza sativa. Most background collinear blocks associated with NLP pairs, identified between I. batatas and its two diploid relatives/the dicotyledon Arabidopsis, contained more genes than those between I. batatas and the monocotyledon rice/maize. NLPs showed no collinearity between sweet potato and rice, indicating different paths in their evolutionary history. IbNLP6 and IbNLP7 were found in the other three comparative syntenic maps, suggesting that these orthologous pairs might have already existed before the evolutionary divergence of monocotyledons and dicotyledons. In addition, these two genes might have played fundamental roles in the NLP family.
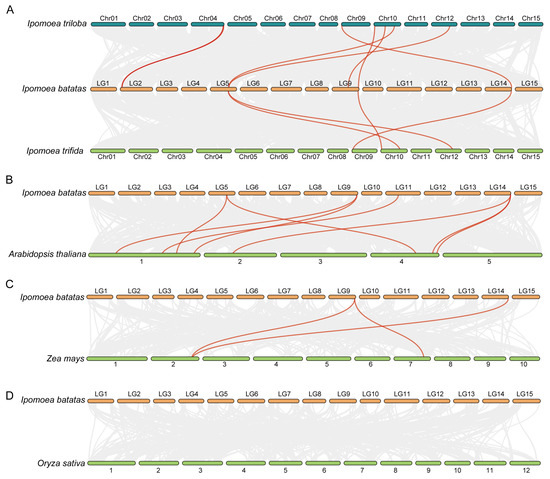
Figure 2.
Syntenic NLP gene pairs between I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba in (A), I. batatas and Arabidopsis in (B), I. batatas and Zea mays in (C), and I. batatas and Oryza sativa in (D). Gray lines indicate all the collinear blocks in the genome, and the red lines indicate the syntenic NLP gene pairs.
2.3. Phylogenetic Relationships of NLPs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
To study the evolutionary relationships of NLPs in I. batatas, I. trifida, I. triloba, and Arabidopsis, we constructed a phylogenetic tree for 37 NLPs from these four species (i.e., 7 in I. batatas, 9 in I. trifida, 12 in I. triloba, and 9 in Arabidopsis) (Figure 3). All NLPs were unevenly distributed on each branch of the phylogenetic tree. Interestingly, NLPs in I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba were divided into four subgroups (Group I to IV, Figure 3), but those in Arabidopsis were divided into three subgroups (Group I to III). The specific distribution of NLPs was as follows (total: I. batatas, I. trifida, I. triloba, Arabidopsis): Group I (13:2,3,3,5), Group II (7:1,2,2,2), Group III (5:1,1,1,2), and Group IV (12:3,6,3,0) (Figure 3; Table S1). We named IbNLPs, ItfNLPs, and ItbNLPs based on the order in which they appeared on the chromosomes. Only AtNLP4/5/6/9 from Arabidopsis had homologous proteins in I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba. These results indicate that the number and types of NLPs distributed in each subgroup of sweet potato differed from those in its two diploid relatives and Arabidopsis.
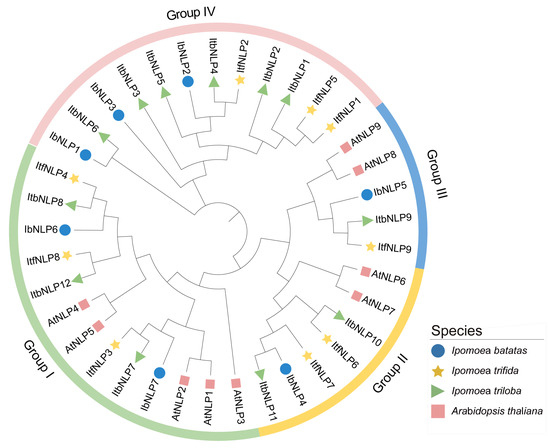
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of the NLPs in I. batatas, I. trifida, I. triloba, and Arabidopsis. A total of 37 NLPs were divided into our subgroups (Groups I to IV) according to the evolutionary distance. The blue circles, yellow pentagrams, green triangles, and pink squares represent IbNLPs in I. batatas, ItfNLPs in I. trifida, ItbNLPs in I. triloba, and AtNLPs in Arabidopsis, respectively.
2.4. Conserved Domain and Exon–Intron Structure Analysis of NLPs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
Protein domains and gene structure are important in analyzing gene functions. We analyzed conserved domains in the 7 IbNLPs, 9 ItfNLPs, and 12 ItbNLPs (Figure 4A). All NLPs contain two conserved domains: an RWP-RK domain, which can bind nitrate-response elements to regulate gene expression, and a PB1 domain, which determines protein interactions. Especially, in Group IV, IbNLP2, ItfNLP2, ItbNLP4, and ItbNLP1 contain 2 RWP-RK domains. ItbNLP1 contains 2 PB1 domains. Notably, IbNLP1 and ItbNLP6 contain another NAM domain, suggesting that they may possess some functions of the NAC transcription factor.
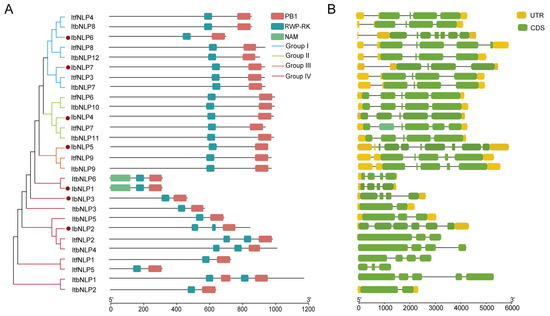
Figure 4.
The phylogenetic tree shows that NLPs are distributed into four groups on the left. The red dots represent the IbNLPs. (A) Conserved domain structure of NLPs in I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba. The pink, blue, and yellow boxes represent the PB1 domain, RWP-RK domain, and NAM domain, respectively; and (B) Exon–intron structure of NLPs in I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba. The yellow boxes, green boxes, and grey lines represent the UTR, exons, and introns, respectively.
To better understand the structural diversity among NLPs, the exon–intron structures were analyzed (Figure 4B). The number of exons in the NLPs ranged from two to eight. In more detail, the NLPs of Group I contained four to seven exons; the NLPs of Group II contained five or six exons; the NLPs of Group III contained five or eight exons, and the NLPs of Group IV contained two to six exons (Figure 4B). The exon–intron structures of some homologous NLPs were different in I. batatas compared to those in I. trifida and I. triloba, such as IbNLP5 (containing 8 exons), ItfNLP9 (containing five exons), and ItbNLP9 (containing five exons) in Group III, and IbNLP4 (containing five exons), ItfNLP7 (containing six exons) and ItbNLP11 (containing five exons) in Group II (Figure 4B). These results indicated that the NLP family may have undergone a lineage-specific differentiation event in the sweet potato genome.
2.5. cis-Element Analysis in the Promoter of IbNLPs in Sweet Potato
NLPs are involved in light, development, and abiotic/biotic response, and cis-elements in the promoter region play a key role in the expression of NLPs. We analyzed the 2000 bp upstream promoter sequences of NLPs from I. batatas to predict gene function. We divided the elements into four categories: core, light-responsive elements, development regulation, and abiotic/biotic stress-responsive (Figure 5). A large number of core elements were identified in the 7 IbNLPs (CAAT-box and TATA-box) (Figure 5). Most of the IbNLPs contained light-responsive elements such as the GT1 motif, which is believed to affect the growth and development of plants (found in IbNLP1, IbNLP2, IbNLP3, IbNLP4, IbNLP5, and IbNLP7). All IbNLPs contained many development elements, such as the AT-rich element, which plays a key role in the structure and function of the eukaryotic genome (found in IbNLP1 and IbNLP2), CAT-box, which is involved in meristem formation (found in IbNLP4, IbNLP5, and IbNLP6), and the circadian element, which is the core regulator of the circadian clock (found in IbNLP2 and IbNLP3).
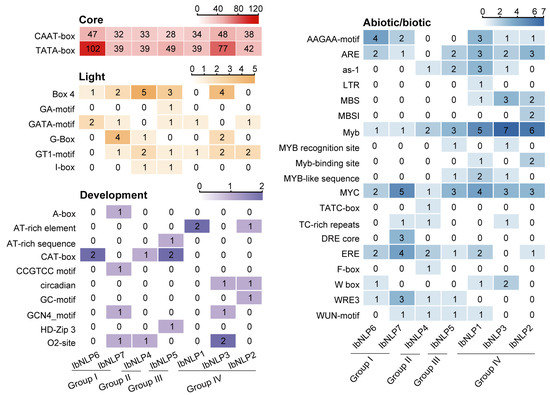
Figure 5.
Cis-elements analysis of IbNLPs in I. batatas. The cis-elements were divided into four categories. The degree of different colors represents the number of cis-elements in the IbNLPs promoters.
Crucially, all IbNLPs contained drought-responsive elements MYB and MYC elements, which indicated that they may be involved in the drought response (Figure 5). Meanwhile, IbNLP1, IbNLP2, and IbNLP3 contained the salt-responsive element MBS and W box. Furthermore, Most NLPs contained AAGAA-motif, ARE, ERE, and WUN-motif elements, which are involved in abiotic/biotic stress-response. In summary, IbNLPs are involved in light response, plant growth and development, and abiotic stress adaptation in sweet potato.
2.6. Protein Interaction Network of IbNLPs in Sweet Potato
To explore the potential regulatory network of IbNLPs, we constructed an IbNLPs interaction network based on Arabidopsis orthologous proteins (Figure 6). Protein interaction predictions indicated that some IbNLPs (IbNLP4, IbNLP5, IbNLP6, and IbNLP7) could interact with each other to form a heterodimer. In addition, NLPs could interact with the transcription factor HRS1, which can integrate nitrate and phosphate starvation responses and adaptation of root architecture depending on nutrient availability [34]. NLPs could interact with MOB1A/B, which play critical roles in plant development [35,36]. NLPs could interact with ROPGEF14, which is involved in the response to complex environmental signals [37]. These results indicated that IbNLPs were involved in the regulation of nitrate signaling response, plant growth and development, and stress adaptation in sweet potato.
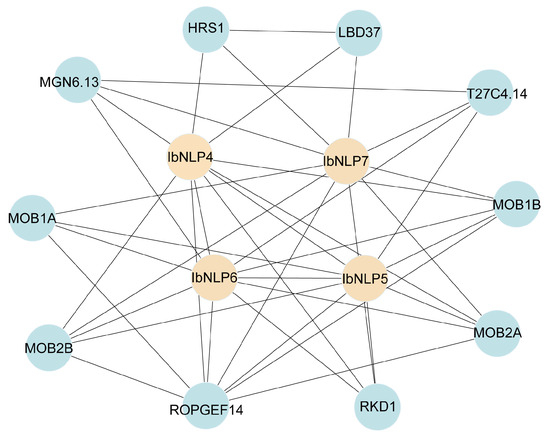
Figure 6.
Functional interaction networks of IbNLPs in I. batatas according to orthologs in Arabidopsis. Network nodes represent proteins, and lines represent protein-protein associations.
2.7. Expression Analysis of NLPs in Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
2.7.1. Expression Analysis in Different Tissues
To investigate the potential biological function of IbNLPs in growth and development, we measured the expression of IbNLPs in six tissues (i.e., bud, petiole, leaf, stem, fibrous root, and tuberous root) (Figure 7A). In Group I, IbNLP6 was highly expressed in the fibrous root, indicating that IbNLP6 may be involved in nitrogen uptake in the fibrous root. Meanwhile, IbNLP7 and IbNLP4 were highly expressed in the bud and stem. IbNLP5 in Group III showed higher expression levels in all tissues than in other subgroups. In Group IV, IbNLP1, IbNLP2, and IbNLP3 were lowly expressed in all tissues.
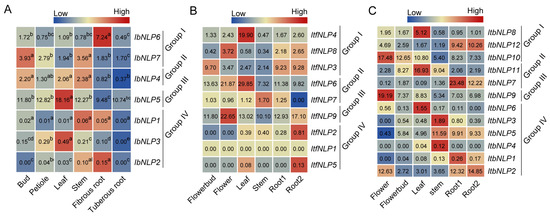
Figure 7.
Gene expression patterns of NLPs in different tissues of I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba. (A) Expression analysis in bud, petiole, leaf, stem, fibrous root, and tuberous root of I. batatas. RT-qPCR determined the values from three biological replicates consisting of pools of three plants, and the results were analyzed using the comparative CT method. The expression of IbNLP6 in the leaf was considered as “1”. The fold change was shown in the boxes. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference in each IbNLP at p < 0.05 based on the Student’s t-test. (B) Gene expression patterns of ItfNLPs in flower bud, flower, leaf, stem, root1, and root2 of I. trifida as determined by RNA-seq. Log2 (FPKM) was shown in the boxes. (C) Gene expression patterns of ItbNLPs in flower bud, flower, leaf, stem, root1, and root2 of I. triloba as determined by RNA-seq. Log2 (FPKM) was shown in the boxes.
In addition, we used RNA-seq data of six tissues (i.e., flower bud, flower, leaf, stem, root1, and root2) to study the expression patterns of NLPs in I. trifida and I. triloba [33] (Figure 7B,C). In I. trifida, ItfNLP9 in Group III was highly expressed in six tissues. ItfNLP3 was highly expressed in the flower bud, root1, and root2. ItfNLP6 was highly expressed in the flower and leaf (Figure 7B). ItfNLPs in Group IV were lowly expressed in all tissues. In I. triloba, ItbNLP10 and ItbNLP11 were highly expressed in the flower bud and leaf; ItbNLP2, ItbNLP9, and ItbNLP10 were highly expressed in the flower; ItbNLP5 and ItbNLP11 were highly expressed in the stem (Figure 7C). Therefore, we observed that ItbNLP2, ItbNLP7, and ItbNLP12 were highly expressed in the root1 and root2, which suggested that they may regulate root development by regulating nutrient uptake (Figure 7C). Those results showed that NLPs exhibit different expression patterns and play important roles in the growth and development of sweet potato and the two diploids.
2.7.2. Expression Analysis in Different Development Stages
We further performed qRT-PCR to evaluate the expression levels of IbNLPs in different development stages of sweet potato roots (i.e., 10 d, 20 d, 30 d, 40 d, 50 d, 60 d, 70 d, 80 d, 100 d, and 120 d) (Figure 8). All IbNLPs were highly expressed in the early stages of sweet potato root development (i.e., 10 d), suggesting that they may be involved in the initial expansion of sweet potato roots. IbNLP6 was extremely highly expressed in the early stage of root development, and its expression reached 33-fold at 10 d. IbNLP7 was highly expressed in the late stage of root development (i.e., 80 d, 100 d). In Group II, IbNLP4 was expressed highly with 2.75-fold in the early stage. Especially, IbNLP5 showed a high expression level in all stages of root development, notably, 80 d and 100 d of tuberous root development. Interestingly, IbNLP1, IbNLP2, and IbNLP3 in Group IV were all expressed less than 0.5-fold in all stages.
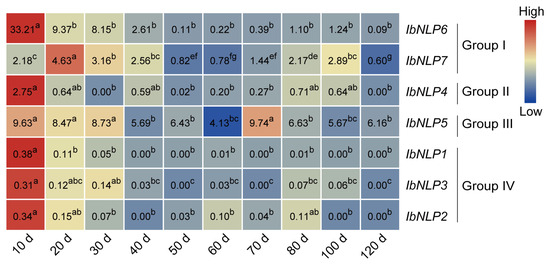
Figure 8.
Gene expression patterns of IbNLPs in different root development stages (i.e., 10 d, 20 d, 30 d, 40 d, 50 d, 60 d, 70 d, 80 d, 100 d, and 120 d). The values were determined by RT-qPCR from three biological replicates consisting of pools of three plants, and the results were analyzed using the comparative CT method. The expression of IbNLP6 at 80 d was considered as “1”. The fold changes were shown in the boxes. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference for each IbNLP at p < 0.05 based on Student’s t-test.
2.7.3. Expression Analysis in Sweet Potato Starch Transcriptome
As a root crop, the most important product of the sweet potato is starch. We analyzed the expression of IbNLPs using two published starch-related transcriptomes (Figure 9) [38,39]. The expression level of IbNLP2, IbNLP5, and IbNLP7 in the four high-starch accessions (H8, H21, H42, H74) was higher than that in the four low-starch accessions (L4, L18, L118, L123) (Figure 9A). Moreover, the expression of IbNLP5 in high-starch cultivar H283 was higher than in low-starch cultivar L423 at three different root development stages in tuberous roots (Figure 9B). Notably, all NLPs showed high expression levels in high starch, except IbNLP4 and IbNLP3 (Figure 9A). However, in Group IV, all NLPs were highly expressed at 60 d in L423, which was a low-starch accession (Figure 9B). Those results showed that NLPs exhibit different expression patterns, and IbNLP5 may play an important role in starch synthesis in sweet potato.
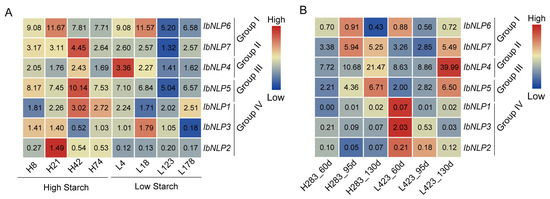
Figure 9.
Gene expression of IbNLPs in starch-related transcriptomes. (A) Expression analysis of IbNLPs in high-starch accessions (H8, H21, H42, H74) and low-starch accessions (L4, L18, L118, L123). (B) Expression analysis of IbNLPs in high-starch accession H283 and low-starch accession L423 at 60, 95, and 130 d after planting. Log2 (FPKM) was shown in the boxes.
2.7.4. Expression Analysis in Nitrate Induction
Nitrogen is a limiting factor for plant growth and has an important impact on sweet potato yields [1,40,41]. NLPs are the key transcription factors in nitrate signaling to regulate nitrogen uptake and utilization in crops. To obtain evidence of possible roles of IbNLPs in root nitrate absorption regulation during nitrogen deficiency, the transcript abundance of IbNLPs in roots was examined by qRT-PCR after N starvation (Figure 10). We found that all NLPs responded quickly to nitrogen-induced expression at 0.5 h after treatment. In particular, we noted that IbNLP6 was up-regulated by up to 29-fold and IbNLP4 was up-regulated by up to 15-fold, which suggests that they may be key regulators of the nitrogen signaling pathway. Notably, some IbNLPs were also induced at other times, such as IbNLP6 (1 h), IbNLP4 (3 h and 6 h), IbNLP3, and IbNLP2 (24 h). In summary, NLPs are involved in nitrate signaling response and nitrogen uptake and utilization in sweet potato.
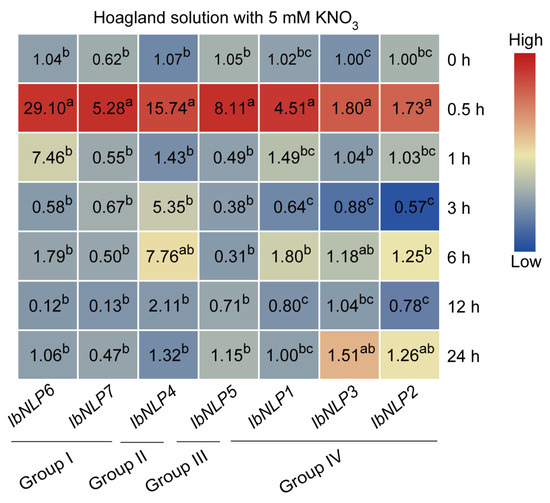
Figure 10.
Gene expression of IbNLPs after N starvation treatment. Log2 (FPKM) was shown in the boxes. The values were determined by RT-qPCR from three biological replicates consisting of pools of three plants, and the results were analyzed using the comparative CT method. The expression of IbNLP6 at 0 h was considered as “1”. The fold changes were shown in the boxes. Different lowercase letters indicate a significant difference for each IbNLP at p < 0.05 based on Student’s t-test.
2.7.5. Expression Analysis Under Abiotic Stresses
A large number of stress-related elements were found in the promoter regions of NLPs, indicating that they could participate in the stress-related processes in sweet potato. We analyzed the expression patterns of IbNLPs using the RNA-seq data of a drought-tolerant variety Xu55-2 under drought stress, and the RNA-seq data of a salt-sensitive variety Lizixiang and a salt-tolerant line ND98 under salt stress [42,43]. IbNLP4 was induced by both PEG and NaCl treatments in Xu55-2, Lizixiang, and ND98 (Figure 11). In Group I, IbNLP6 and IbNLP7 were inhibited by PEG treatments in Xu55-2. In Group IV, IbNLP3 was up-regulated to 174-fold by PEG at 48 h in Xu55-2, and was induced 5-fold in Lizixiang by NaCl treatment. IbNLP1 and IbNLP5 showed no significant change in expression levels in Xu55-2, Lizixiang, and ND98. IbNLP2 and IbNLP7 were slightly inhibited by PEG in Xu55-2.
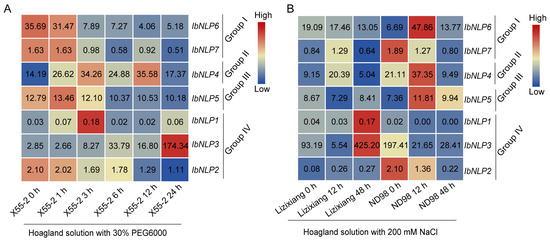
Figure 11.
Gene expression of IbNLPs under drought and salt stresses as determined by RNA-seq. (A) Expression analysis of IbNLPs under PEG treatment in a drought-tolerant variety Xu55-2. (B) Expression analysis of IbNLPs under NaCl treatment in a salt-sensitive variety, Lizixiang, and a salt-tolerant line, ND98. Log2 (FPKM) was shown in the boxes.
Further, we also analyzed the expression patterns of NLPs using the RNA-seq data of I. trifida and I. triloba under drought and salt treatments [33]. In I. trifida, ItfNLP8 and ItfNLP9 were induced by both drought and salt treatments, which indicated that they were involved in the response to drought stress. ItfNLP4, ItfNLP6, and ItfNLP7 were inhibited by both drought and salt treatments, which suggested that they may be involved in life activities inhibited by drought stress, such as nitrogen uptake and nitrate signaling response (Figure S1A). In I. triloba, ItbNLP9, ItbNLP3, and ItbNLP2 were induced by both drought and salt treatments; ItbNLP8, ItfNLP10, and ItfNLP11 were inhibited by both drought and salt treatments (Figure S1B). Taken together, these results indicated that NLPs were differentially expressed in response to various abiotic stresses between sweet potato and its two diploid relatives.
3. Discussion
Nitrogen (N) is an essential nutrient for photosynthetic plant growth in most soils and controls metabolic and developmental processes pivotal to plant vegetative and reproductive development [1,2,3,4,6,7,8,9]. NLPs are plant-specific transcription factors that play crucial roles in nitrate signaling response [5,10,11,12]. However, the functions and transcriptional regulatory mechanisms of NLPs remain largely unknown in sweet potato. The release of the sweet potato genome provides the possibility for genome-wide identification of NLPs. In this study, we systematically identified NLPs and compared their characteristics between the cultivated hexaploid sweet potato and its two diploid relatives based on their genome sequences. Our study provides insights into the function of NLPs in sweet potato.
3.1. Identification and Evolution of the NLP Family
In this study, a total of 28 NLPs were identified in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives. The number of NLPs was identified as 7 in I. batatas, 9 in I. trifida, and 12 in I. triloba. (Table 1 and Table S1). Fewer NLPs in hexaploid sweet potato than diploid relatives, suggesting that some NLPs (i.e., ItfNLP6 and ItfNLP8 in I. trifida; ItbNLP1, ItbNLP2, ItbNLP4, ItbNLP10, and ItbNLP12 in I. triloba) were lost during domestication. There may be functional redundancy between NLPs, such as in Group I, where ItfNLP8 and ItfNLP3 showed similar expression patterns in different tissues of I. trifida (Figure 7B). In I. triloba, ItbNLP1 and ItbNLP2 showed low expression (less than 0.3-fold) in all tissues, suggesting that they may not be functional (Figure 7C). The chromosome localization and distribution of NLPs were different between I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba; 6 chromosomes contained NLP genes in I. batatas and I. triloba, but only 5 in I. trifida (Figure 1). Moreover, collinearity analysis revealed that there are 7 syntenic gene pairs with I. triloba, but 4 with I. trifida (Figure 2A). Genomic alignment revealed differentiation and evolution of chromosomes. Based on the phylogenetic relationship, NLPs in I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba were divided into four subgroups (Groups I to IV, Figure 3), but AtNLPs were divided into three subgroups (Groups I to III). The number and types of NLPs distributed in each subgroup of sweet potato and its two diploid relatives were different from those of Arabidopsis and other plants. Moreover, only AtNLP4/5/6/9 from Arabidopsis have homologous proteins in I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba (Table 1; Figure 3). These results suggest that the NLP family might have undergone a lineage-specific differentiation event in the terrestrial plant genome.
All NLPs contain two conserved domains, an RWP-RK domain and a PB1 domain (Figure 4A). The RWP-RK domain recognizes nitrate-responsive cis-elements (NREs), thereby mediating DNA binding and regulating gene expression in midstream and downstream nitrogen pathways. The PB1 domain determines protein interactions [17]. The two domains are key to NLPs’ roles in plant growth and development, stress response, and nitrogen regulation [13,14,15,16]. Introns typically function as mutation-resistant buffer zones, minimizing deleterious mutations and insertions. Furthermore, they play essential roles in regulating mRNA export, facilitating transcriptional coupling, enabling alternative splicing, modulating gene expression, and other fundamental cellular processes. The exon–intron structures of some homologous NLPs were different in I. batatas compared to those in I. trifida and I. triloba, such as IbNLP5 (containing 8 exons), ItfNLP9 (containing five exons), and ItbNLP9 (containing five exons) in Group III, IbNLP4 (containing five exons), ItfNLP7 (containing six exons) and ItbNLP11 (containing five exons) in Group II (Figure 4B). These differences in the exon–intron structures in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives might lead NLPs to be involved in different growth and development processes in sweet potato.
3.2. Different Functions of NLPs in Tuberous Root Development and Starch Synthesis in Sweet Potato
Nitrate acts as a signal and nutrient to regulate root growth and development [44,45]. In Arabidopsis, NLP6/7 interact with TCP20 to promote root meristem elongation under nitrogen starvation [15]; furthermore, overexpression of AtNLP7 promotes primary and lateral root growth [46]. In rice, the root length of nlp1 mutants is shorter than that of the wild type, and overexpression of OsNLP1 significantly increases root length [47]. As the key regulators in this process in plants, NLPs play vital roles in the tuberous root development of sweet potato. In this study, in the N starvation experiment, all NLPs responded quickly to nitrogen-induced expression at 0.5 h after treatment in sweet potato. In particular, we noted that IbNLP6, which is conserved in different plants (Figure 4), was up-regulated by up to 29-fold, which suggests that it may be a key regulator of the nitrogen signaling pathway.
For sweet potato, the formation and development of tuberous roots are critical to its yield and quality. Meanwhile, the development of the root system and nitrogen uptake and utilization directly affect the yield of tuberous roots [40,41]. Most of the IbNLPs were highly expressed in the early stage of root development. Notably, we found that IbNLP6, which is highly induced by N, showed the highest expression level in the early stage of root development. This result suggests that it may be involved in the uptake and utilization of nitrogen in sweet potato fibrous roots.
As a food crop, the most important component of sweet potato is starch. The expression levels of IbNLP2, IbNLP5, and IbNLP7 in the four high-starch accessions (H8, H21, H42, H74) were higher than those in the four low-starch accessions (L4, L18, L118, L123) (Figure 9A) [38]. Moreover, the expression of IbNLP5 in high-starch cultivar H283 was higher than in low-starch cultivar L423 at three different root development stages in tuberous roots (Figure 9B) [39]. These results suggest that NLPs may play an important role in starch synthesis in sweet potato.
3.3. Different Functions of NLPs on Abiotic Stress Response Between Sweet Potato and Its Two Diploid Relatives
The NLPs have been reported to participate in the abiotic stress response in plants. AtNLP7 in Arabidopsis may be involved in stomatal movement and drought resistance [11]. The NLPs of Poncirus Trifoliata were expressed differently under different water conditions. NLPs in roots continued to downregulate under drought stress [48]. Under drought stress, the expression levels of MdNLP2, MdNLP3, and MdNLP5 in apple showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing [49]. In this study, we found NLPs were differentially expressed in response to various abiotic stresses between sweet potato and its two diploid relatives. IbNLP4 was induced by both PEG and NaCl treatments in Xu55-2, Lizixiang, and ND98 (Figure 11). IbNLP6 was inhibited by PEG and NaCl treatments in Xu55-2 and Lizixiang. Moreover, diploid I. trifida and I. triloba represent valuable resources for identifying functional genes—particularly those conferring resistance or tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses—that may have been lost during sweet potato domestication. ItfNLP8, ItfNLP9, ItbNLP9, ItbNLP3, and ItbNLP2 were induced by both drought and salt treatments, suggesting that they are involved in the response to drought stress. Taken together, these results indicate that NLPs can be candidate genes to improve abiotic stress tolerance in sweet potato.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of NLPs
The whole genome sequences of I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba were downloaded from Ipomoea Genome Hub (https://ipomoea-genome.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2025)) and Sweetpotato Genomics Resource (http://sweetpotato.plantbiology.msu.edu/ (accessed on 15 June 2025)). To accurately identify all NLP family members, three different screening methods were combined. First, the BLAST (https://www.arabidopsis.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2025)) algorithm was used to identify predicted NLPs using all AtNLPs from the Arabidopsis genome database (https://www.arabidopsis.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2025)) as queries (BLASTP, E value ≤ 1 × 10−5). Next, the HMMER 3.0 software was used to identify potential NLPs through the Hidden Markov Model profiles (HMMER search, E value ≤ 1 × 10−5) of PF02042 and PB1 domains (hmm, PF00564, which were extracted from the Pfam databases (http://pfam.xfam.org/ (accessed on 15 June 2025)). Finally, all putative NLPs were verified using SMART (http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/ (accessed on 15 June 2025)) and CD-Search (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi (accessed on 15 June 2025)).
4.2. Chromosomal Distribution of NLPs and Syntenic Analysis
The IbNLPs, ItfNLPs, and ItbNLPs were separately mapped to the I. batatas, I. trifida, and I. triloba chromosomes based on the chromosomal location provided in the Ipomoea Genome Hub (https://ipomoea-genome.org/ (accessed on 16 June 2025)) and Sweetpotato Genomics Resource (http://sweetpotato.plantbiology.msu.edu/ (accessed on 16 June 2025)). The visualization was generated using the TBtools-II software (v.2.315) (South China Agricultural University, Guangzhou, China) [50]. The syntenic analysis maps of orthologous NLP genes were constructed using the Dual Synteny Plotter software (v2.0)) [50].
4.3. Protein Properties Prediction of NLPs
The phosphorylation sites of NLPs were predicted using GPS 5.0 [51]. The MW, theoretical pI, and hydropathy of NLPs were calculated with ExPASy (https://www.expasy.org/ (accessed on 18 June 2025)). The subcellular localization of NLPs was predicted using Plant-mPLoc (http://www.csbio.sjtu.edu.cn/bioinf/plant-multi/ (accessed on 18 June 2025)).
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of NLPs
The phylogenetic analysis of NLPs from I. batatas, I. trifida, I. triloba, and Arabidopsis was performed using ClustalW (v2.0.11) in MEGA 7.0 [52] with default parameters. The maximum likelihood method and the Poisson correction model were used. Bootstrapping was performed 1000 times. Then, the phylogenetic tree was constructed using iTOL (http://itol.embl.de/ (accessed on 16 June 2025) v7.2.1).
4.5. Domain Identification Analysis of NLPs
The conserved domains of NLPs were analyzed using NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/cdd/wrpsb.cgi (accessed on 16 June 2025) (v2.1)).
4.6. Exon–Intron Structures and Promoter Analysis of NLPs
The exon–intron structures of NLPs were obtained using GSDS 2.0 (http://gsds.gao-lab.org/) and were visualized using the TBtools-II software. cis-elements in the approximately 2000 bp promoter regions of NLPs were predicted using PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/ (accessed on 18 June 2025)) [53].
4.7. Protein Interaction Network of NLPs
Protein interaction networks of NLPs were predicted using STRING (https://cn.string-db.org/ (v12.0)), based on Arabidopsis homologous proteins. The network map was built using Cytoscape software (v3.0) [54].
4.8. qRT-PCR Analysis of NLPs
The sweet potato (I. batatas) variety ‘Xushu18’ was used for qRT-PCR analysis in this study. In vitro-grown Xushu18 plants were cultured on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium at 27 ± 1 °C under a photoperiod consisting of 13 h of cool-white fluorescent light at 54 μmol m−2 s−1 and 11 h of darkness. Sweet potato plants were cultivated in a field on the campus of China Agricultural University, Beijing, China. For expression analysis in various tissues, total RNA was extracted from the bud, leaves, petioles, stems, fibrous root, and tuberous root tissues of 3-month-old field-grown Xushu18 plants; different tuberous root tissues of Xushu18 at different developmental stages (10 d, 20 d, 30 d, 40 d, 50 d, 60 d, 80 d, 100 d, 120 d) were collected using the TRIzol method (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). For expression analysis of nitrate response, 1-month-old in vitro Xushu18 seedlings were subjected to N starvation (0.15 mM KNO3) for 2 weeks and then supplied with nitrate (5 mM KNO3). A modified Hoagland nutrient solution was employed, with 5 mM KNO3 as a sufficient nitrogen solution and 0.15 mM KNO3 as an N starvation solution. The differences in potassium supply were balanced with KCl. The solutions were changed every 2 days. The roots were sampled at 0, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, 12, and 24 h after being treated. Three independent biological replicates were taken, each with three plants. qRT-PCR was conducted using the SYBR detection protocol (TaKaRa, Kyoto, Japan) on a 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). The reaction mixture was composed of first-strand cDNA, primer mix, and SYBR Green M Mix (TaKaRa; code RR420A) in a final volume of 20 μL. The sweet potato actin gene (GenBank AY905538) was used as the internal control. The relative gene expression levels were quantified using the comparative CT method [55]. The specific primers used for qRT-PCR analysis are listed in Table S2. The heat maps of gene expression profiles were constructed using TBtools-II software (v.2.315) [50].
4.9. Transcriptome Analysis
The RNA-seq data of ItfNLPs and ItbNLPs in I. trifida and I. triloba were downloaded from the Sweetpotato Genomics Resource (http://sweetpotato.plantbiology.msu.edu/ (accessed on 18 June 2025)). The RNA-seq data of IbNLPs in I. batatas were obtained from related research in our laboratory [44,45]. The expression levels of NLPs were calculated as fragments per kilobase of exon per million fragments mapped (FPKM). The heat maps were constructed using TBtools-II software (v.2.315) [50].
5. Conclusions
In this study, we systematically investigated the protein physicochemical properties, chromosome localization, phylogenetic relationships, syntenic analysis maps, gene structure, cis-elements of promoters, and protein interaction networks of NLPs in sweet potato. In addition, tissue specificity and expression pattern analyses of tuberous root development in different accessions and nitrate induction of NLPs were analyzed using qRT-PCR and RNA-seq. We discovered the evolution and different functions in development, nitrate signaling response, and abiotic stress response of NLPs in sweet potato and its two diploid relatives. In summary, this study is a critical first step in understanding the functions of sweet potato NLPs and offers more candidate genes for improving nitrogen use efficiency and increasing yield in cultivated sweet potato.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms26178435/s1.
Author Contributions
H.Z. (Huan Zhang) and S.H. conceived and designed the research. K.P. and W.W. analyzed the data. K.P., W.W., Z.D. and M.S. performed the experiments. H.Z. (Huan Zhang) and K.P. wrote the paper. Q.L., H.Z. (Hong Zhai), N.Z. and S.G. revised the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 32472157), the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFD1200700/2023YFD1200703), the Beijing Food Crops Innovation Consortium Program (BAIC02-2025), the Earmarked Fund for CARS-10-Sweetpotato, the 2115 Talent Development Program of China Agricultural University, and the Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (2025TC141).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are openly available at reference number [32,33,38,39].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bloom, A.R. The increasing importance of distinguishing among plant nitrogen sources. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 25, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.E.; Craine, J.M.; Lany, N.K.; Jonard, M.; Ollinger, S.V.; Groffman, P.M.; Fulweiler, R.W.; Angerer, J.; Read, Q.D.; Reich, P.B.; et al. Evidence, causes, and consequences of declining nitrogen availability in terrestrial ecosystems. Science 2022, 376, eabh3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, N.M.; Forde, B.G. Molecular and developmental biology of inorganic nitrogen nutrition. Arab. Book 2002, 1, e0011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Liu, M.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Liu, C.; Guo, A.; Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S.; Wagner, G.; et al. NIN-like protein 7 transcription factor is a plant nitrate sensor. Science 2022, 377, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhi, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Genome-wide survey and expression analysis of NIN-like Protein (NLP) genes reveals its potential roles in the response to nitrate signaling in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.J.; Cramer, M.D. Root nitrogen acquisition and assimilation. Plant Soil 2005, 274, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forde, B.G.; Clarkson, D.T. Nitrate and ammonium nutrition of plants: Physiological and molecular perspectives. Adv. Bot. Res. 1999, 30, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Tian, H. Global nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer use for agriculture production in the past half century: Shifted hot spots and nutrient imbalance. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, E.A.; Alvarez, J.M.; Araus, V.; Riveras, E.; Brooks, M.D.; Krouk, G.; Ruffel, S.; Lejay, L.; Crawford, N.M.; Coruzzi, G.M.; et al. Nitrate in 2020: Thirty years from transport to signaling networks. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 2094–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S. Arabidopsis NIN-like transcription factors have a central role in nitrate signalling. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaings, L.; Camargo, A.; Pocholle, D.; Gaudon, V.; Texier, Y.; Boutet-Mercey, S.; Taconnat, L.; Renou, J.P.; Daniel-Vedele, F.; Fernandez, E.; et al. The nodule inception-like protein 7 modulates nitrate sensing and metabolism in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 57, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Niu, Y.; Konishi, M.; Wu, Y.; Du, H.; Chung, H.S.; Li, L.; Boudsocq, M.; McCormack, M.; Maekawa, S.; et al. Discovery of nitrate-CPK-NLP signalling in central nutrient growth networks. Nature 2017, 545, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchive, C.; Roudier, F.; Castaings, L.; Bréhaut, V.; Blondet, E.; Colot, V.; Meyer, C.; Krapp, A. Nuclear retention of the transcription factor NLP7 orchestrates the early response to nitrate in plants. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; He, B.; Ning, L.; Du, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, L.; Lin, F.; et al. The NIN-like protein 5 (ZmNLP5) transcription factor is involved in modulating the nitrogen response in maize. Plant J. 2020, 102, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Ripoll, J.J.; Wang, R.; Vuong, L.; Bailey-Steinitz, L.J.; Ye, D.; Crawford, N.M. Interacting TCP and NLP transcription factors control plant responses to nitrate availability. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, P. Dancing with Hormones: A current perspective of nitrate signaling and regulation in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadhesan, B.; Sathee, L.; Meena, H.S.; Jha, S.K.; Chinnusamy, V.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Genome wide analysis of NLP transcription factors reveals their role in nitrogen stress tolerance of rice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liang, S.; Bao, H.; Zhao, H. Genome-wide analysis of maize NLP transcription factor family revealed the roles in nitrogen response. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 84, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jin, Y.; Lu, Q.; Ren, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of NIN-like protein (NLP) genes: Exploring their potential roles in nitrate response in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 207, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Singroha, G.; Tiwari, R.; Sharma, P. Comprehensive genome-wide expression analysis of NLP transcription factors elucidates their crucial role in enhancing nitrogen response in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Curr. Plant Biol. 2025, 42, 100463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chang, W.; Fan, Y.; Sun, W.; Qu, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of NODULE-INCEPTION-Like protein (NLP) family genes in Brassica napus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hou, Q.; Nie, X.; Shang, C.; Dong, Q.; Wang, Q. Genome-wide identification of the apple NLP (NIN-like proteins) family and their potential role under abiotic stress. 3 Biotech 2025, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Tang, W.; Sun, D.; Wang, S.; Chen, K.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of NLP Gene Families and Haplotype Analysis of SiNLP2 in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauser, L.; Roussis, A.; Stiller, J.; Stougaard, J. A plant regulator controlling development of symbiotic root nodules. Nature 1999, 402, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Easwaran, V.; Chau, V.; Okamoto, M.; Ierullo, M.; Kimura, M.; Endo, A.; Yano, R.; Pasha, A.; Gong, Y.; et al. NIN-like protein 8 is a master regulator of nitrate-promoted seed germination in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Sun, L.Q.; Song, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wan, G.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Xia, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zhao, Z.; et al. The OsNLP3/4-OsRFL module regulates nitrogen-promoted panicle architecture in rice. New Phytol. 2023, 240, 2404–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.S.; Xia, J.Q.; Alfatih, A.; Song, Y.; Huang, Y.J.; Wan, G.Y.; Sun, L.Q.; Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; et al. Rice NIN-LIKE PROTEIN 4 plays a pivotal role in nitrogen use efficiency. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Qi, S.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Crawford, N.M.; Wang, Y. Overexpression of the maize ZmNLP6 and ZmNLP8 can complement the Arabidopsis nitrate regulatory mutant nlp7 by restoring nitrate signaling and assimilation. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Mysore, K.S.; Wen, J.; Xie, F. NIN interacts with NLPs to mediate nitrate inhibition of nodulation in Medicago truncatula. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Lu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Fu, M.; Mysore, K.S.; Wen, J.; Gong, J.; Murray, J.; et al. The small peptide CEP1 and the NIN-like protein NLP1 regulate NRT2.1 to mediate root nodule formation across nitrate concentrations. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 776–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q. Improvement for agronomically important traits by gene engineering in sweetpotato. Breed Sci. 2017, 67, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Moeinzadeh, M.H.; Kuhl, H.; Helmuth, J.; Xiao, P.; Haas, S.; Liu, G.L.; Zheng, J.L.; Sun, Z.; Fan, W.; et al. Haplotype-resolved sweet potato genome traces back its hexaploidization history. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Lau, K.H.; Cao, Q.; Hamilton, J.P.; Sun, H.; Zhou, C.; Eserman, L.; Gemenet, D.C.; Olukolu, B.A.; Wang, H.; et al. Genome sequences of two diploid wild relatives of cultivated sweetpotato reveal targets for genetic improvement. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Gao, Y. Plant NIGT1/HRS1/HHO transcription factors: Key regulators with multiple roles in plant growth, development, and stress responses. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Guo, Z.; Song, L.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, Y. NCP1/AtMOB1A plays key roles in auxin-mediated Arabidopsis development. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Yue, X.; Cui, X.; Song, L.; Cheng, Y. AtMOB1 genes regulate jasmonate accumulation and plant development. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgues, L.; Smokvarska, M.; Mercier, C.; Igisch, C.P.; Crabos, A.; Dongois, A.; Bayle, V.; Fiche, J.B.; Nacry, P.; Nollmann, M.; et al. GEF14 acts as a specific activator of the plant osmotic signaling pathway by controlling ROP6 nanodomain formation. EMBO Rep. 2025, 26, 2146–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Li, A.; Dong, S.; Wang, Q.; Hou, F.; Zhang, H. Comparative transcriptome analysis of hybrid population provides insights into starch content in sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) storage root. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 39, 673–684, Correction in Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 39, 685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11105-021-01296-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhu, H.; Zhai, H.; He, S.; Gao, S.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H.; et al. Source-sink synergy is the key unlocking sweet potato starch yield potential. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Cheng, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. Meta-analysis on the effect and influence factors of nitrogen application on tuber yield of sweet potato in China. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 1606–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xie, B.; Li, A.; Hou, F.; Dong, S.; Wang, B.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, L. Differences between nitrogen-tolerant and nitrogen-susceptible sweetpotato cultivars in photosynthate distribution and transport under different nitrogen conditions. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, H.; He, S.; Zhao, N.; Liu, Q. Transcriptome profiling reveals insights into the molecular mechanism of drought tolerance in sweetpotato. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhai, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; He, S. Transcript profile analysis reveals important roles of jasmonic acid signalling pathway in the response of sweet potato to salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Hsu, P.K.; Tsay, Y.F. Uptake, allocation and signaling of nitrate. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 458–467, Erratum in Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.08.007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Naz, M.; Fan, X.; Xuan, W.; Miller, A.J.; Xu, G. Plant nitrate transporters: From gene function to application. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2463–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Wu, J.; Tang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Li, S.; Xiang, C. Overexpression of Arabidopsis NLP7 improves plant growth under both nitrogen-limiting and -sufficient conditions by enhancing nitrogen and carbon assimilation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfatih, A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xia, J.; Jan, S.; Yu, L.; Xiang, C. Rice NIN-LIKE PROTEIN 1 rapidly responds to nitrogen deficiency and improves yield and nitrogen use efficiency. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 6032–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Lu, X.; Xiong, J.; Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, F.; Xie, S. Cloning and expression of Poncirus Trifoliata (L.) Raf. NIN- Like transcription factors under different water conditions. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, X.; Han, Y.; Wang, X.; Hao, Y. Genome-wide identification and expression pattern analysis of NLP (NIN-Like Protein) transcription factor gene family in apple. Sci. Agri. Sin. 2019, 52, 4333–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, H.; Lin, S.; Deng, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Peng, D.; Xue, Y. GPS 5.0: An update on the prediction of kinase-specific phosphorylation sites in proteins. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2020, 18, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for Bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids. Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, M.; Wiese, S.; Warscheid, B. Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Data Min. Proteom. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 696, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).