Specific Assay Protocols for Porcine Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Concerning Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
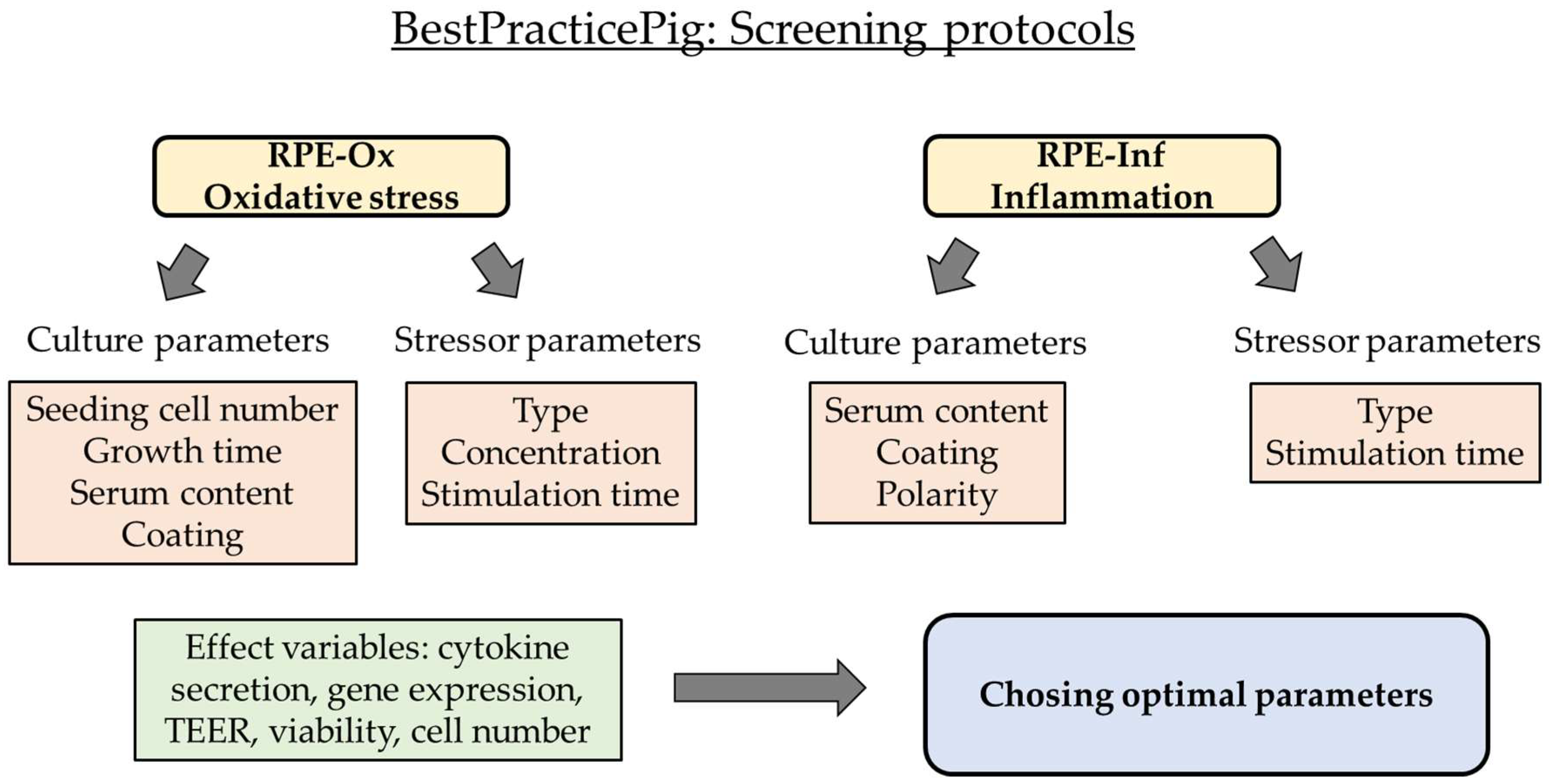
1. Introduction
2. Results
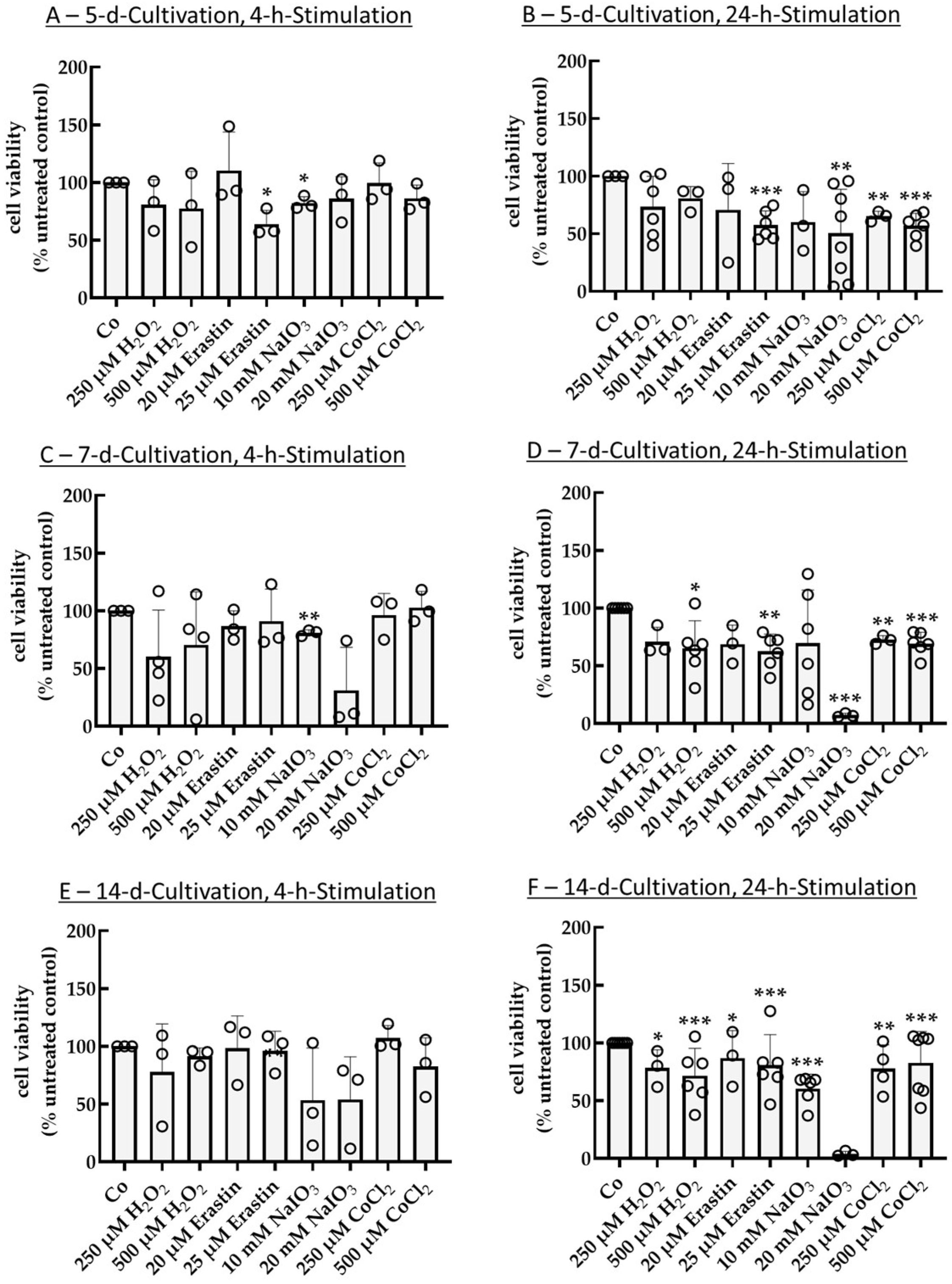
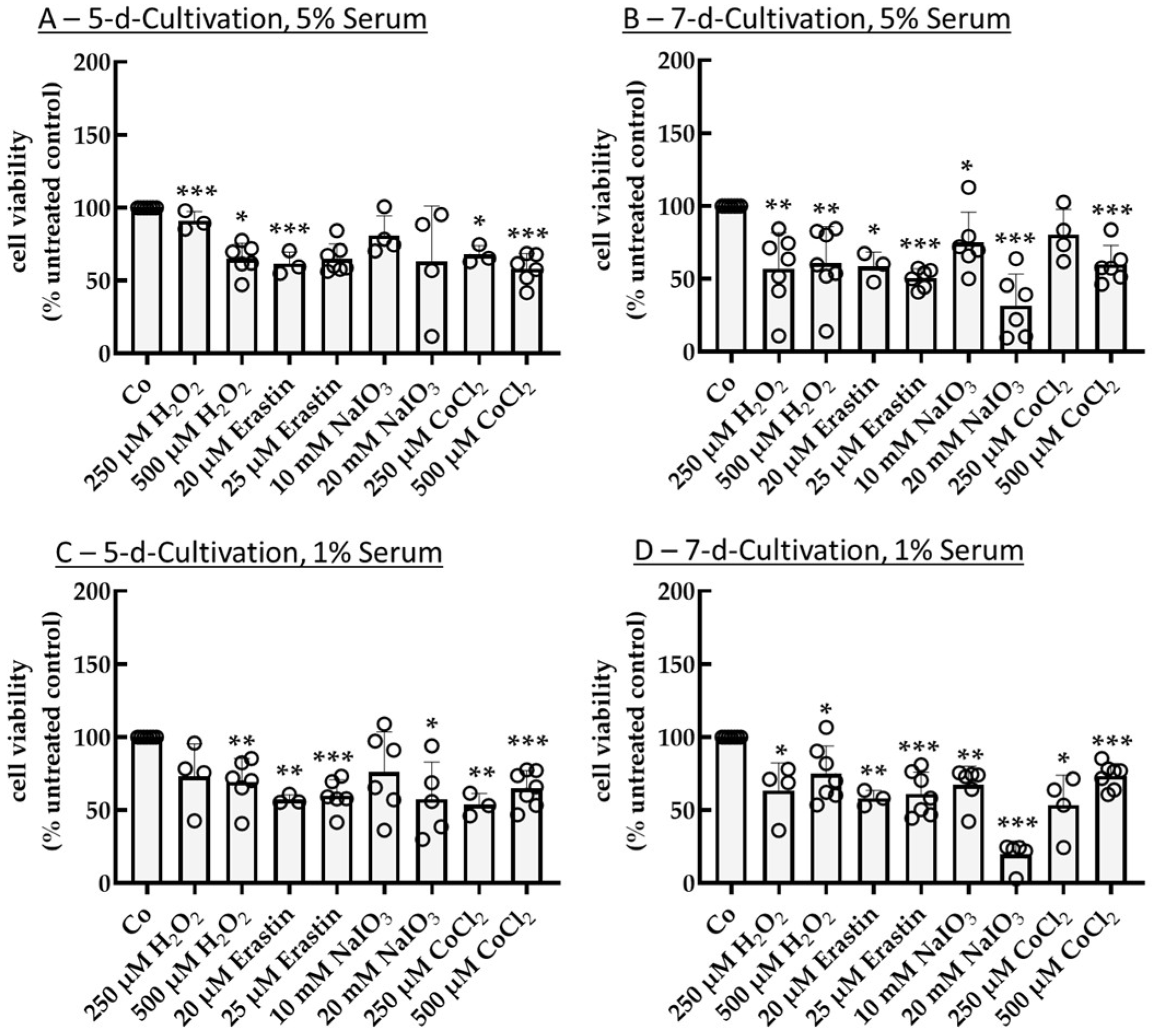
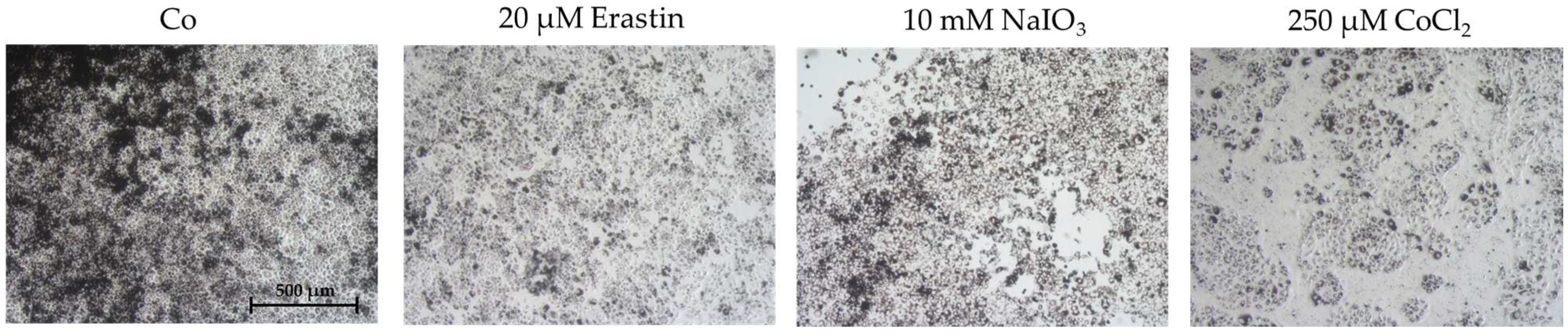
2.1. Establishing an Oxidative Stress Model with Single-Eye Cultures (RPE-Ox)
2.1.1. Optimal Conditions for Cell Survival Reduction (50%)
2.1.2. Expression of Oxidative Stress-Related Genes
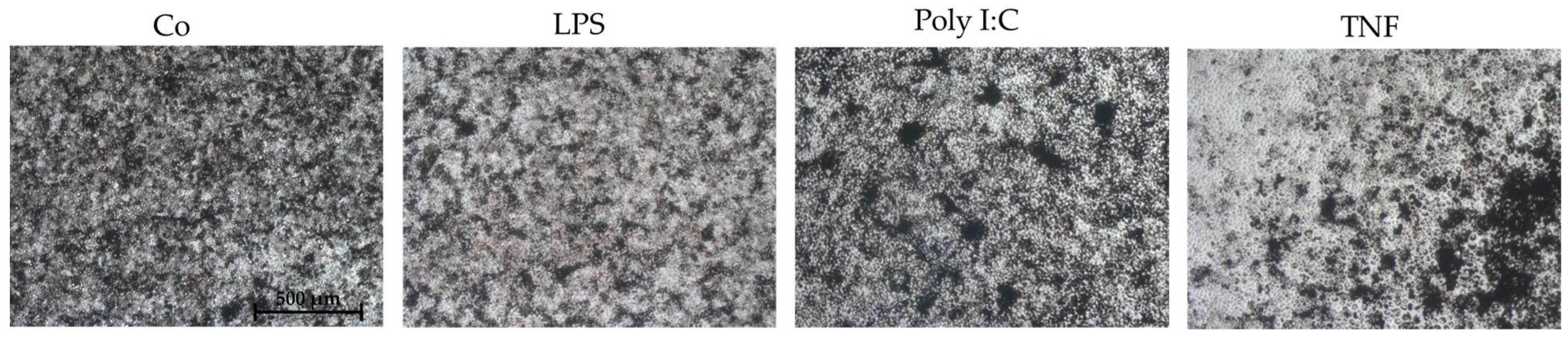
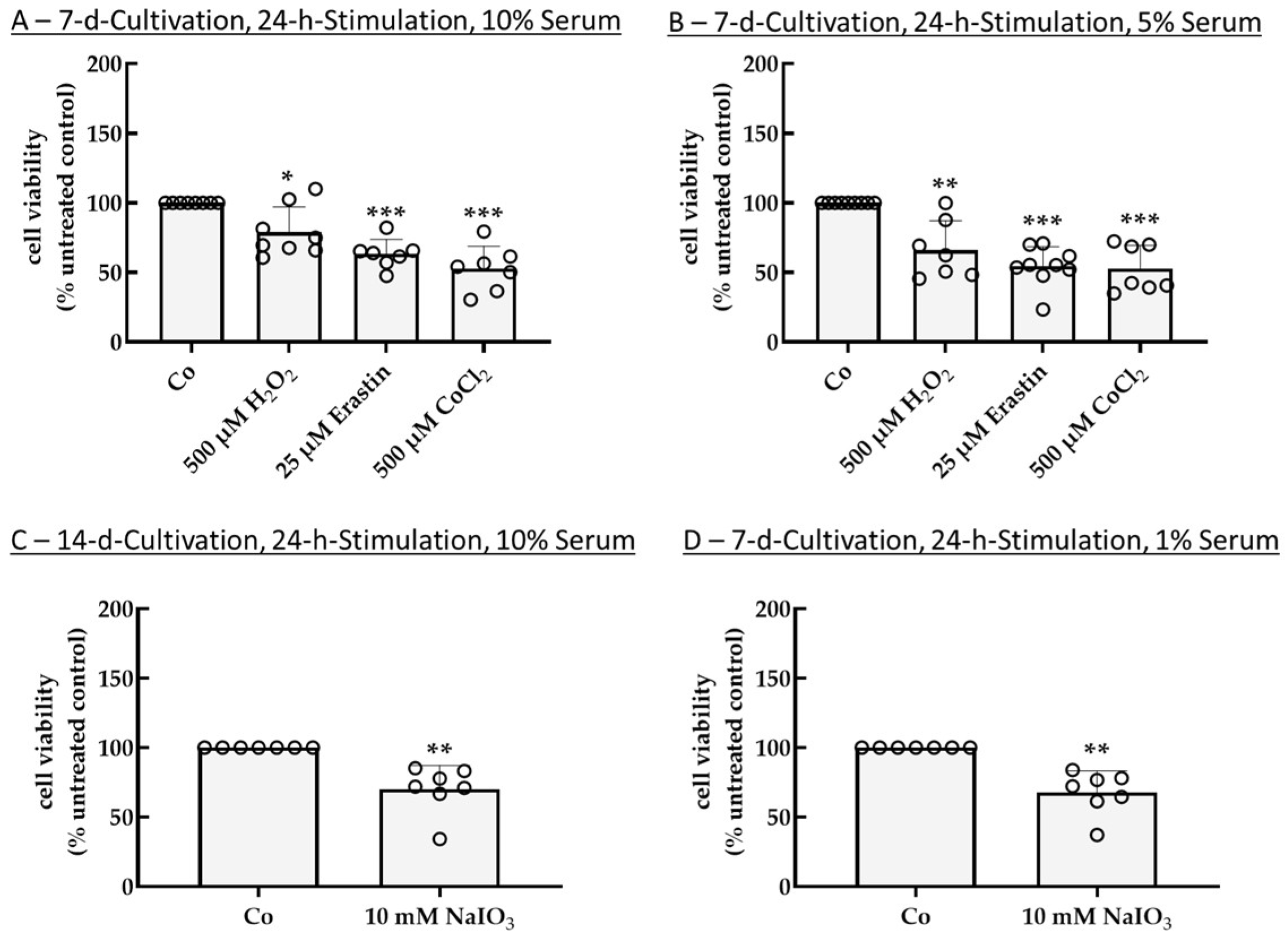
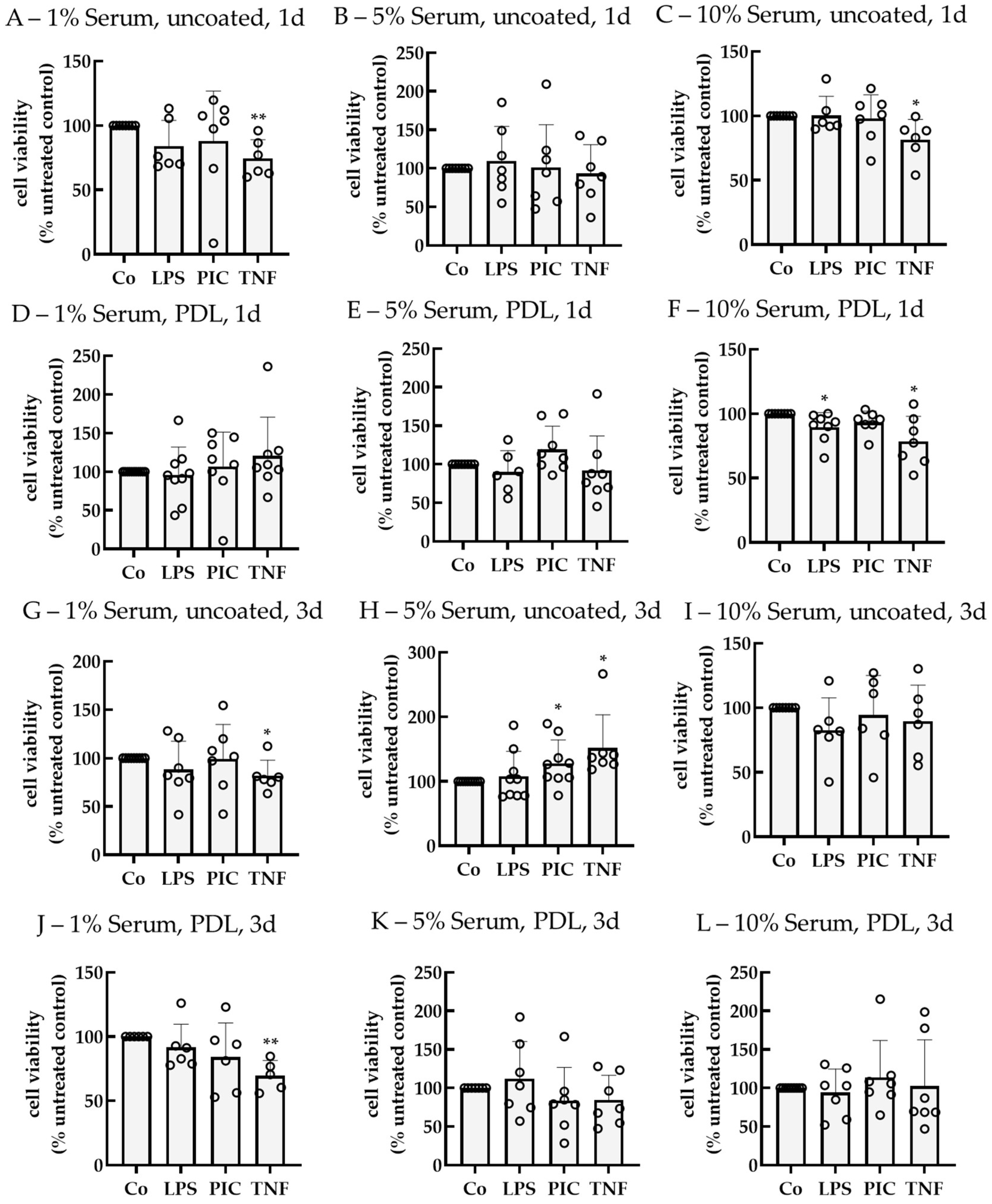
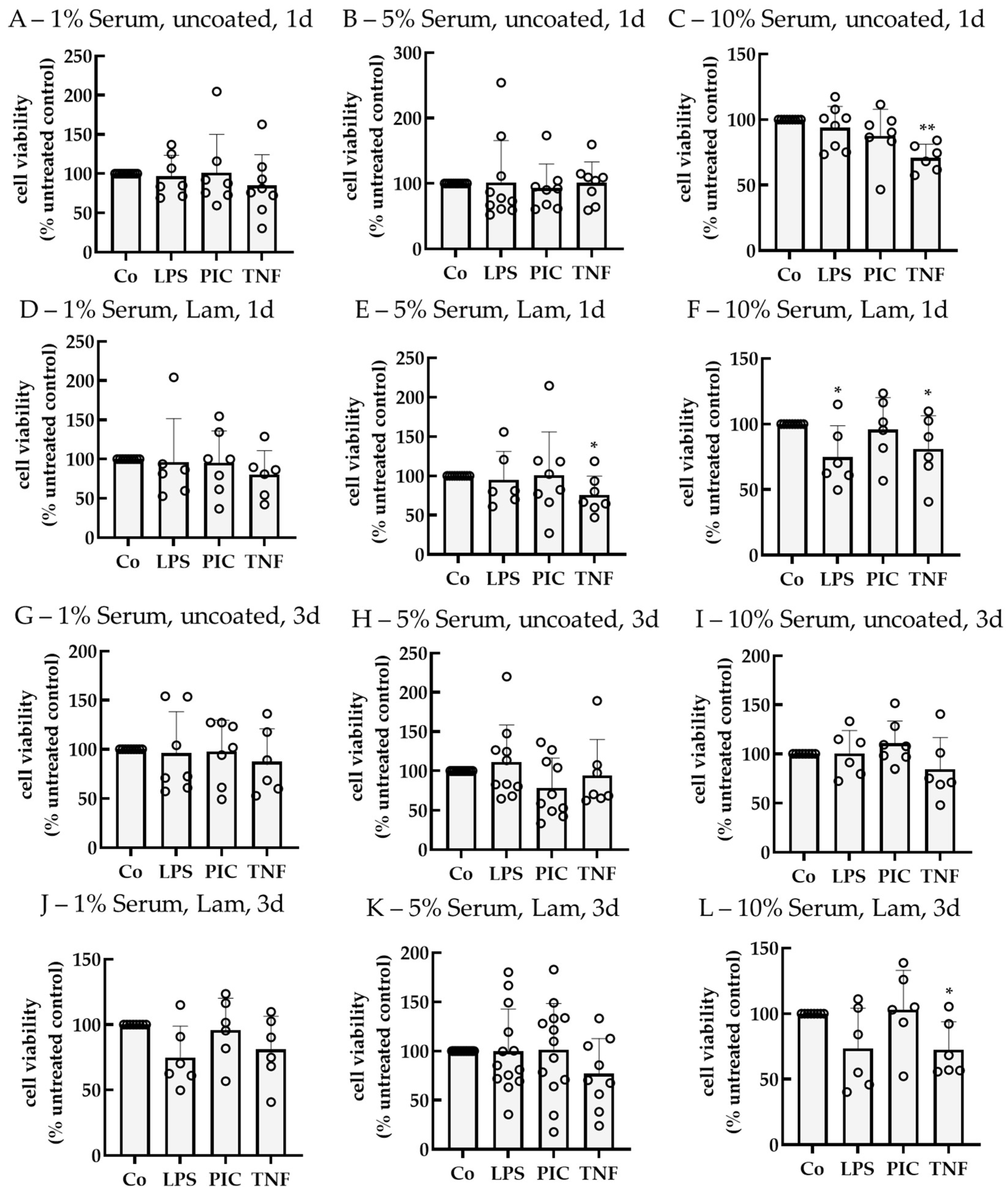
2.2. Establishing an Inflammation Model with Single-Eye Cultures (RPE-Inf)
2.2.1. Cell Viability
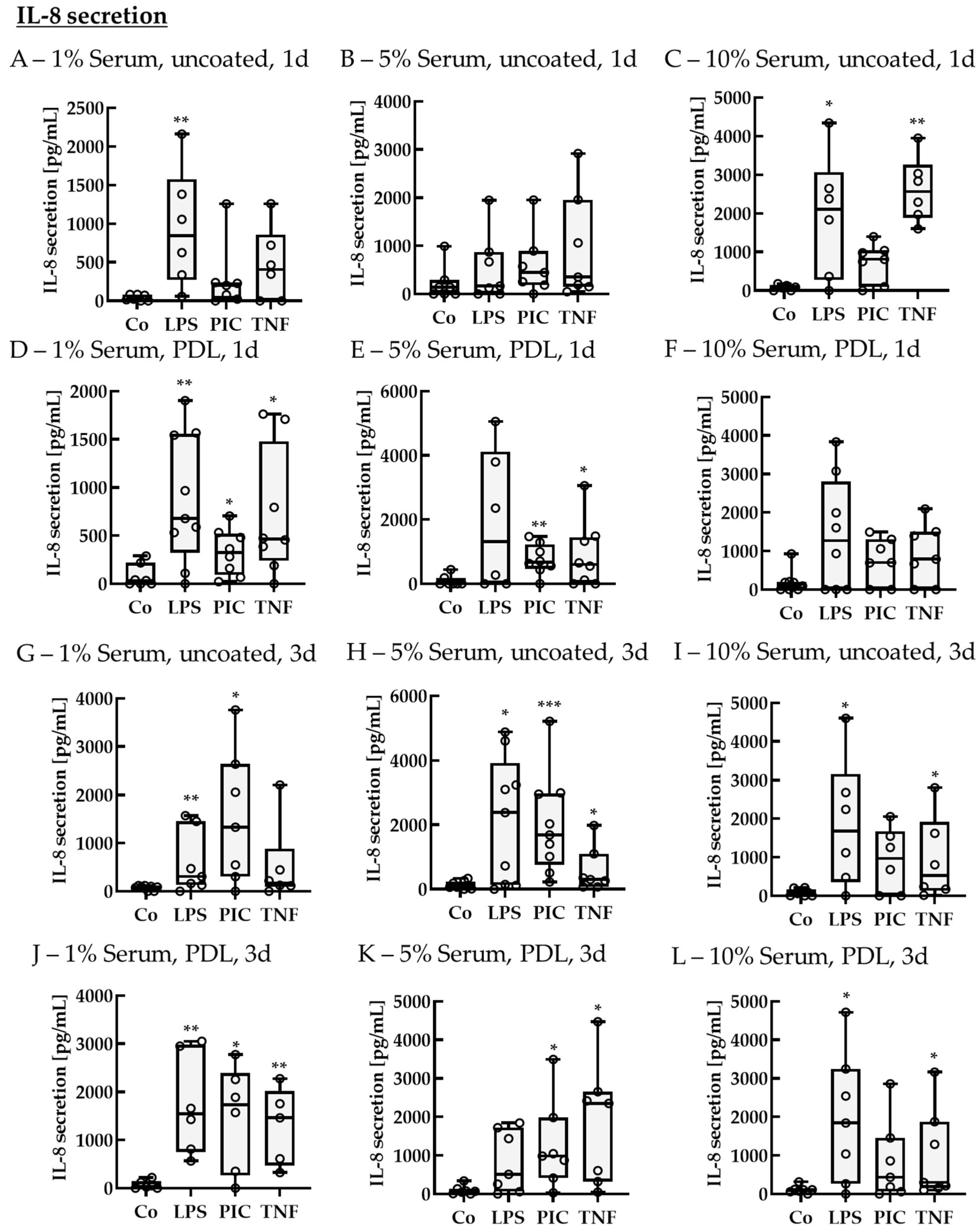
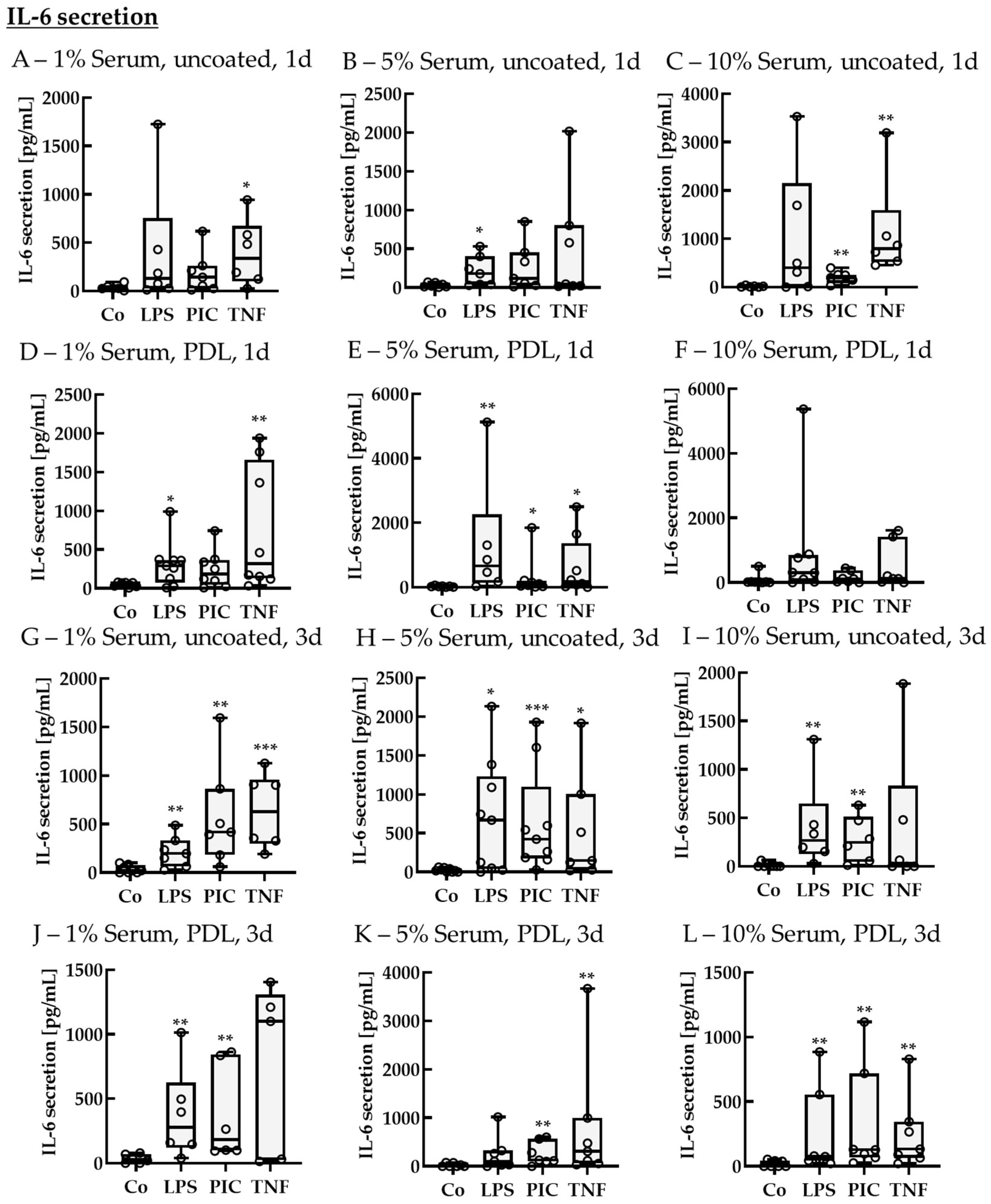
2.2.2. Cytokine Secretion—Non-Polar
IL-8 Secretion of Non-Polar Single-Eye Cultures
IL-6 Secretion of Non-Polar Single-Eye Cultures
TNF Secretion of Non-Polar Single-Eye Cultures
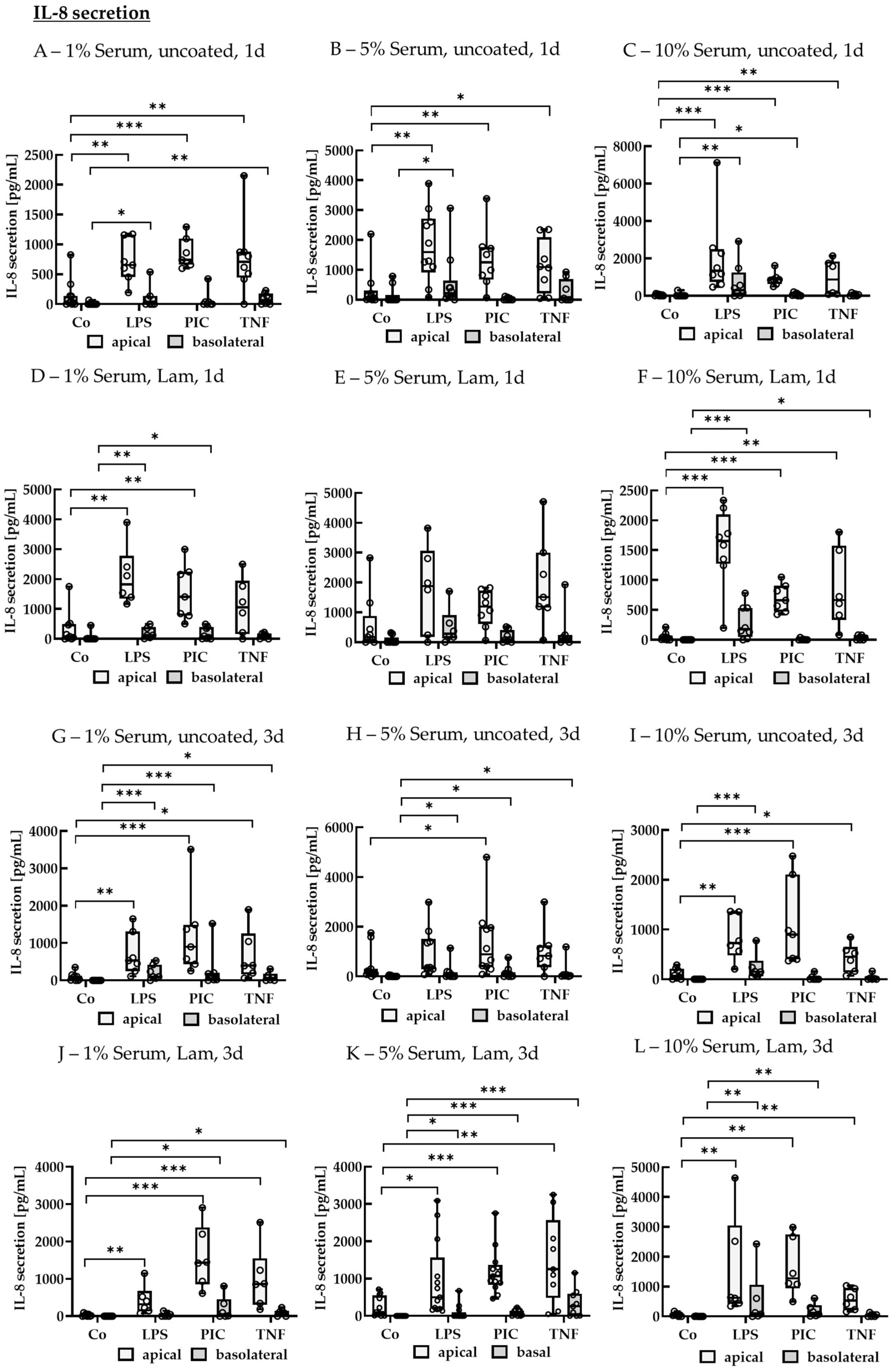
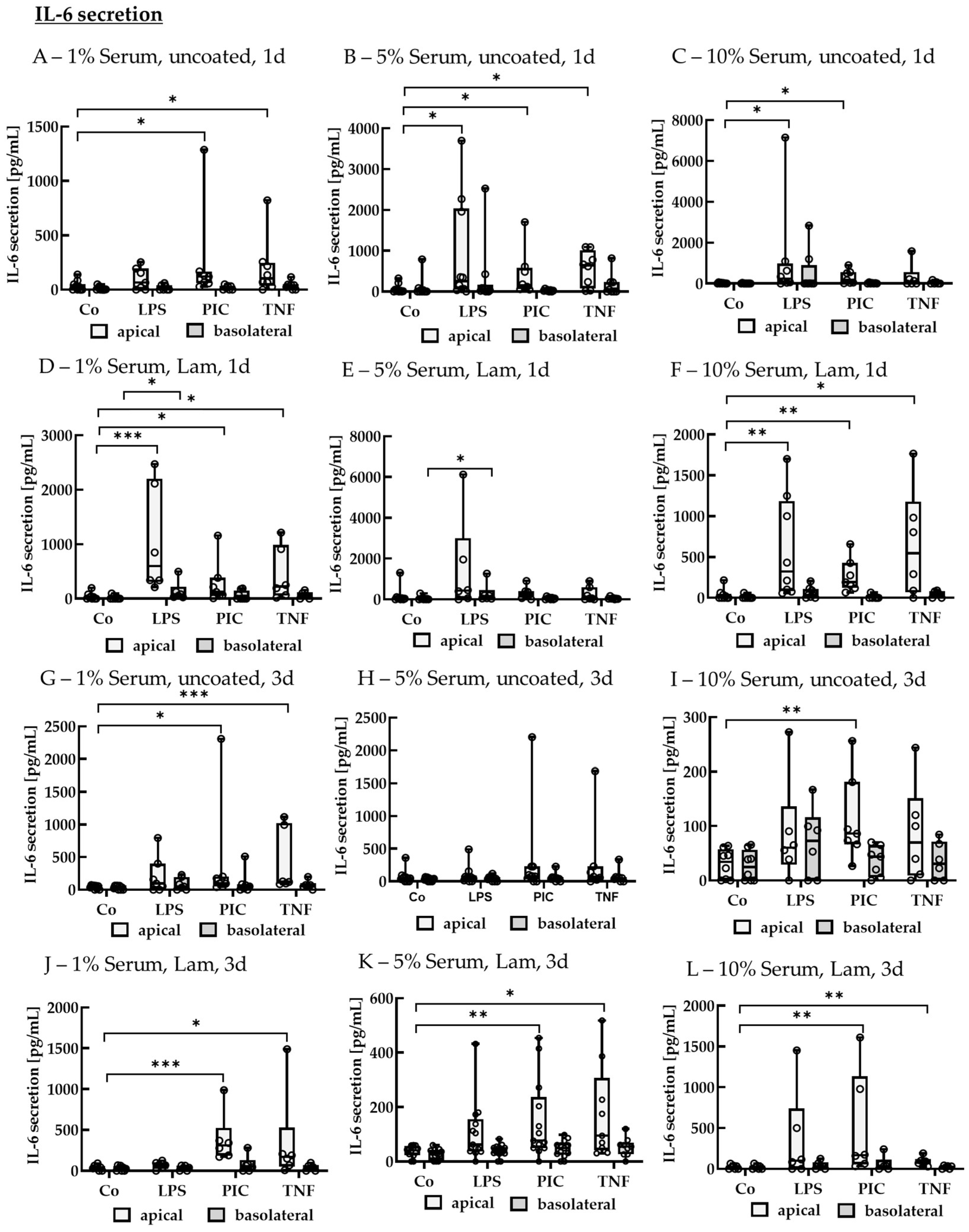
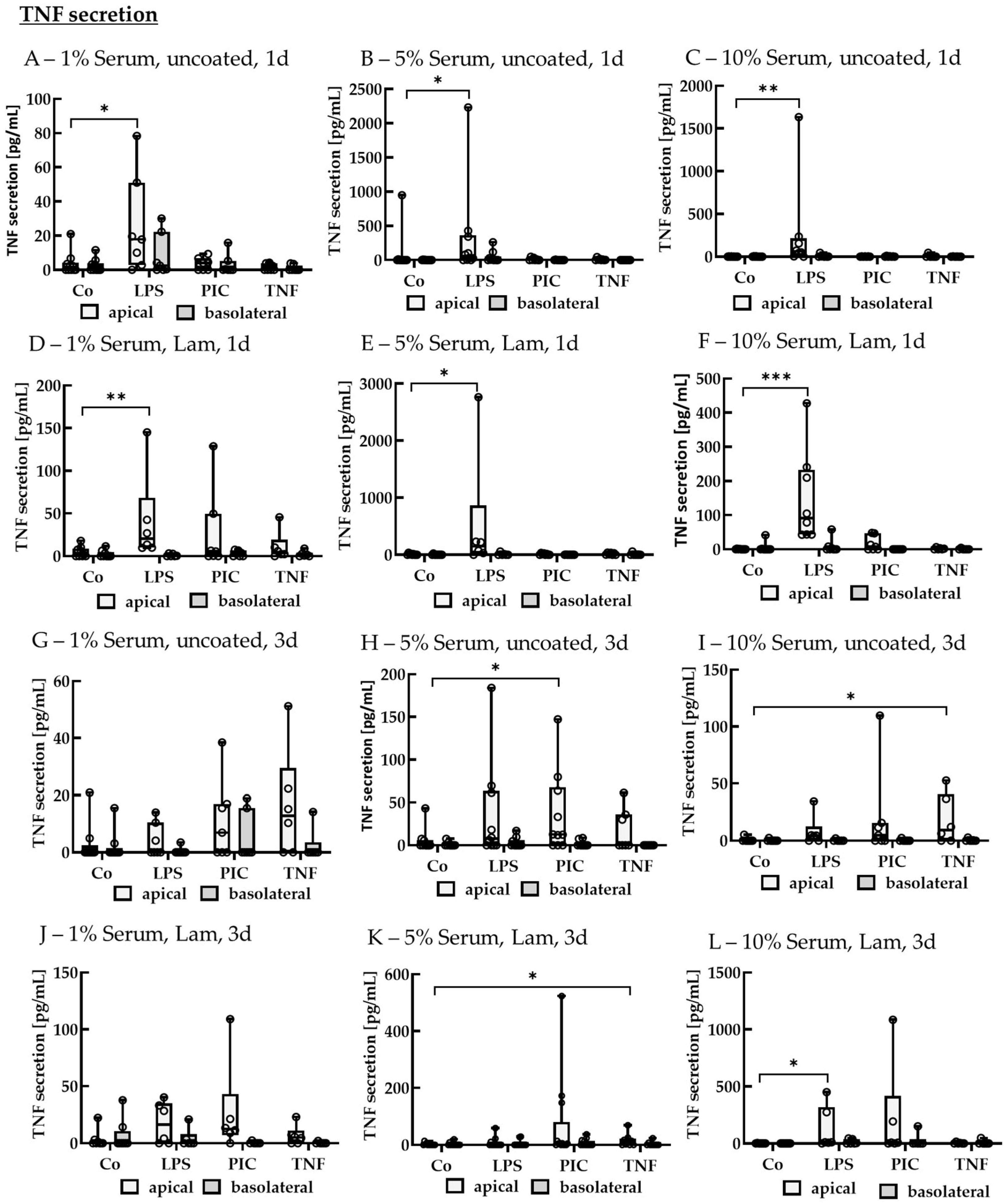
2.2.3. Cytokine Secretion—Polar
IL-8 Secretion of Polar Single-Eye Cultures
IL-6 Secretion of Polar Single-Eye Cultures
TNF Secretion of Polar Single-Eye Cultures
2.2.4. Gene Expression
2.2.5. Barrier
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Preparation
4.2. Coating of Microtiter Plates or Transwell Inserts
4.3. Stimulation Experiments
4.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Tetrazolium Assay
4.5. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Strauss, O. The retinal pigment epithelium in visual function. Physiol. Rev. 2005, 85, 845–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnichels, S.; Paquet-Durand, F.; Löscher, M.; Tsai, T.; Hurst, J.; Joachim, S.C.; Klettner, A. Retina in a dish: Cell cultures, retinal explants and animal models for common diseases of the retina. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 81, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dörschmann, P.; Wilke, J.; Tietze, N.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Single-Eye Porcine Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Cultures—A Validated and Reproducible Protocol. BioMed 2025, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; von der Weppen, S.; Koyama, E.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Porcine Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Culture for Barrier and Polarity Studies. Cells 2025, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzolo, L.J. Barrier properties of cultured retinal pigment epithelium. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 126, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, S. Porcine ophthalmology. Vet. Clin. North Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2010, 26, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, I.; Martin, R.; Ussa, F.; Fernandez-Bueno, I. The parameters of the porcine eyeball. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2011, 249, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grotz, S.; Schäfer, J.; Wunderlich, K.A.; Ellederova, Z.; Auch, H.; Bähr, A.; Runa-Vochozkova, P.; Fadl, J.; Arnold, V.; Ardan, T.; et al. Early disruption of photoreceptor cell architecture and loss of vision in a humanized pig model of usher syndromes. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 14, e14817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Hackam, A.S. Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) protects retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) cells from oxidative stress through a STAT3-dependent mechanism. Mol. Immunol. 2013, 54, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, S.; Cano, M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Wang, L.; Handa, J.T. The impact of oxidative stress and inflammation on RPE degeneration in non-neovascular AMD. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 60, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, P.X.; Stiles, T.; Douglas, C.; Ho, D.; Fan, W.; Du, H.; Xiao, X. Oxidative stress, innate immunity, and age-related macular degeneration. AIMS Mol. Sci. 2016, 3, 196–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tzekov, R.; Su, M.; Zhu, Y.; Han, A.; Li, W. Hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage and protective role of peroxiredoxin 6 protein via EGFR/ERK signaling pathway in RPE cells. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1169211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y. Glutathione depletion induces ferroptosis, autophagy, and premature cell senescence in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, M.; Dong, X.; Bai, J.; Shi, W.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yi, L.; Yin, X.; et al. Naringin Suppresses CoCl2-Induced Ferroptosis in ARPE-19 Cells. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klettner, A.; Brinkmann, A.; Winkelmann, K.; Käckenmeister, T.; Hildebrandt, J.; Roider, J. Effect of long-term inflammation on viability and function of RPE cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 200, 108214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanus, J.; Anderson, C.; Sarraf, D.; Ma, J.; Wang, S. Retinal pigment epithelial cell necroptosis in response to sodium iodate. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Retinal Diseases Associated with Oxidative Stress and the Effects of a Free Radical Scavenger (Edaravone). Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 9208489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.C.; Holm, M.; Austeng, D.; Morken, T.S.; Zhou, T.E.; Beaudry-Richard, A.; Sierra, E.M.; Dammann, O.; Chemtob, S. Retinopathy of prematurity: Inflammation, choroidal degeneration, and novel promising therapeutic strategies. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa Hernández, M.E.; Lewis-Luján, L.M.; Burboa Zazueta, M.G.; Del Castillo Castro, T.; de La Re Vega, E.; Gálvez-Ruiz, J.C.; Trujillo-López, S.; López Torres, M.A.; Iloki-Assanga, S.B. Role of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Age Related Macular Degeneration: Insights into the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koinzer, S.; Reinecke, K.; Herdegen, T.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Oxidative Stress Induces Biphasic ERK1/2 Activation in the RPE with Distinct Effects on Cell Survival at Early and Late Activation. Curr. Eye Res. 2015, 40, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.M.; Ji, X.; Ivanchenko, M.V.; Chung, M.; Piper, M.; Rana, P.; Wang, S.K.; Xue, Y.; West, E.; Zhao, S.R.; et al. Nrf2 overexpression rescues the RPE in mouse models of retinitis pigmentosa. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e145029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Wang, S. Not All Stressors Are Equal: Mechanism of Stressors on RPE Cell Degeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 591067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervellati, F.; Cervellati, C.; Romani, A.; Cremonini, E.; Sticozzi, C.; Belmonte, G.; Pessina, F.; Valacchi, G. Hypoxia induces cell damage via oxidative stress in retinal epithelial cells. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Averill-Bates, D. Reactive oxygen species and cell signaling. Review. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-J.; Ng, S.-C.; Ni, Y.-T.; Liu, J.-S.; Chen, C.-J.; Padma, V.V.; Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, W.-W. Protective effects of galangin against H2O2/UVB-induced dermal fibroblast collagen degradation via hsa-microRNA-4535-mediated TGFβ/Smad signaling. Aging 2021, 13, 25342–25364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhao, K.-K.; Tong, Y.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Wang, Y.-X.; Zhao, P.-Q.; Wang, Z.-Y. Exogenous NAD(+) decreases oxidative stress and protects H2O2-treated RPE cells against necrotic death through the up-regulation of autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Ye, M.; Zhang, L. Genipin protects against H2O2-induced oxidative damage in retinal pigment epithelial cells by promoting Nrf2 signaling. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yao, F.; Xu, J.-Y.; Chen, J.; Lu, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, J.; Mou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Pu, Z. The transcriptome profile of RPE cells by the fullerenol against hydrogen peroxide stress. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 996280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upadhyay, M.; Bonilha, V.L. Regulated cell death pathways in the sodium iodate model: Insights and implications for AMD. Exp. Eye Res. 2024, 238, 109728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Kannan, R.; Spee, C.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Dou, G.; Hinton, D.R. Protection of retina by αB crystallin in sodium iodate induced retinal degeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, J.; Ikeda, M.; Ide, T.; Griffin, C.T.; Ding, X.-Q.; Wang, S. Comparative mechanistic study of RPE cell death induced by different oxidative stresses. Redox Biol. 2023, 65, 102840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Pan, T.; Shen, H.; Xi, H.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Q. The rescue effect of mesenchymal stem cell on sodium iodate-induced retinal pigment epithelial cell death through deactivation of NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, W.; Shah, A.; Yu, M.; Liu, Y.; He, L.; Dang, J.; Yang, L.; Yan, M.; Ying, Y.; et al. Sodium iodate induces ferroptosis in human retinal pigment epithelium ARPE-19 cells. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; Li, X.; Lu, P. Assessing the protective effects of cryptotanshinone on CoCl2-induced hypoxia in RPE cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 24, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.-C.; Chiang, Y.-F.; Ali, M.; Hsia, S.-M. Oleocanthal mitigates CoCl2-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis via regulating MAPK pathway in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 180, 117582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.-R.; Zhang, Z.-Q.; Yao, J.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Duan, J.; Cao, C.; Jiang, Q. Ginsenoside Rg-1 protects retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells from cobalt chloride (CoCl2) and hypoxia assaults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, F.; Wang, T.; Jiao, Y. The Role of Erastin in Ferroptosis and Its Prospects in Cancer Therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 5429–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Du, T.; Yang, H.; Lei, L.; Guo, M.; Ding, H.-F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; et al. ATF3 promotes erastin-induced ferroptosis by suppressing system Xc. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.; Turnbull, T.; Sebastian, S.; Kempson, I. The MTT Assay: Utility, Limitations, Pitfalls, and Interpretation in Bulk and Single-Cell Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poltorak, A.; He, X.; Smirnova, I.; Liu, M.Y.; van Huffel, C.; Du, X.; Birdwell, D.; Alejos, E.; Silva, M.; Galanos, C.; et al. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: Mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science 1998, 282, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulou, L.; Holt, A.C.; Medzhitov, R.; Flavell, R.A. Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature 2001, 413, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörschmann, P.; Seeba, C.; Thalenhorst, T.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Anti-inflammatory properties of antiangiogenic fucoidan in retinal pigment epithelium cells. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, J.A.; Irlenbusch, L.; Hansen, U.; Himmler, M.; Zeng, C.; Eter, N.; Fuchsluger, T.; Heiduschka, P. Long-term cultivation of retinal pigment epithelium cells on nanofiber scaffolds. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2025, 263, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, J.; Lei, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Cellular and Molecular Signaling Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhutto, I.; Lutty, G. Understanding age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Relationships between the photoreceptor/retinal pigment epithelium/Bruch’s membrane/choriocapillaris complex. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 295–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhodapkar, R.M.; Martell, D.; Hafler, B.P. Glial-mediated neuroinflammatory mechanisms in age-related macular degeneration. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Lai, K. Role of immune inflammation regulated by macrophage in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2024, 239, 109770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riss, T.L.; Moravec, R.A.; Niles, A.L.; Duellman, S.; Benink, H.A.; Worzella, T.J.; Minor, L. Methods in Molecular Biology. In Assay Guidance Manual; Markossian, S., Grossman, A., Baskir, H., Eds.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 1601. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Bio Group Name | Cultivation Time | Serum Content | Coating | Target Name | Rq | Rq Min | Rq Max | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | none | CAT | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.54 | 0.023 * |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | none | GPX4 | 0.28 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.121 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | none | GSS | 0.39 | 0.11 | 1.35 | 0.137 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | none | NFE2L2 | 0.11 | 0.00 | 3.17 | 0.177 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | none | SOD1 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 2.41 | 0.610 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | PDL | CAT | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.21 | <0.001 *** |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | PDL | GPX4 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 0.61 | 0.045 * |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | PDL | GSS | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.72 | 0.226 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | PDL | NFE2L2 | 0.22 | 0.11 | 0.45 | 0.021 * |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 7 d | 1% | PDL | SOD1 | 0.37 | 0.29 | 0.48 | 0.088 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | none | CAT | 1.65 | 0.33 | 8.32 | 0.504 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | none | CAT | 0.38 | 0.11 | 1.31 | 0.132 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | none | GPX4 | 1.03 | 0.23 | 4.67 | 0.976 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | none | GPX4 | 0.87 | 0.26 | 2.98 | 0.877 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | none | GSS | 4.93 | 1.54 | 15.74 | 0.075 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | none | GSS | 0.90 | 0.34 | 2.36 | 0.889 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | none | NFE2L2 | 5.14 | 0.82 | 32.20 | 0.085 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | none | NFE2L2 | 1.87 | 0.74 | 4.72 | 0.223 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | none | SOD1 | 0.95 | 0.18 | 4.96 | 0.945 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | none | SOD1 | 0.85 | 0.25 | 2.87 | 0.784 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | PDL | CAT | 0.92 | 0.37 | 2.30 | 0.865 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | PDL | CAT | 0.36 | 0.12 | 1.06 | 0.063 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | PDL | GPX4 | 0.68 | 0.25 | 1.83 | 0.568 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | PDL | GPX4 | 0.96 | 0.30 | 3.10 | 0.948 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | PDL | GSS | 1.12 | 0.42 | 2.99 | 0.876 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | PDL | GSS | 0.62 | 0.09 | 4.37 | 0.605 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | PDL | NFE2L2 | 1.35 | 0.36 | 5.07 | 0.697 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | PDL | NFE2L2 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 1.25 | 0.270 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 5% | PDL | SOD1 | 3.04 | 1.73 | 5.34 | 0.011 * |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 5% | PDL | SOD1 | 1.86 | 0.59 | 5.86 | 0.230 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | none | CAT | 1.90 | 1.05 | 3.42 | 0.427 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | none | CAT | 1.46 | 0.22 | 9.61 | 0.717 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | none | GPX4 | 0.45 | 0.29 | 0.70 | 0.078 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | none | GPX4 | 0.54 | 0.06 | 4.57 | 0.502 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | none | GSS | 1.04 | 0.29 | 3.78 | 0.963 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | none | GSS | 1.10 | 0.03 | 36.92 | 0.949 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | none | NFE2L2 | 1.68 | 0.51 | 5.53 | 0.345 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | none | NFE2L2 | 1.58 | 0.25 | 9.93 | 0.538 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | none | SOD1 | 0.79 | 0.37 | 1.70 | 0.530 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | none | SOD1 | 1.43 | 0.19 | 10.69 | 0.662 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | PDL | CAT | 1.44 | 0.53 | 3.94 | 0.422 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | PDL | CAT | 0.39 | 0.18 | 0.84 | 0.088 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | PDL | GPX4 | 0.44 | 0.12 | 1.66 | 0.194 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | PDL | GPX4 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 1.74 | 0.250 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | PDL | GSS | 2.31 | 1.03 | 5.19 | 0.056 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | PDL | GSS | 0.70 | 0.40 | 1.22 | 0.321 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | PDL | NFE2L2 | 2.84 | 1.31 | 6.17 | 0.036 * |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | PDL | NFE2L2 | 1.32 | 0.67 | 2.63 | 0.554 |
| 25 µM erastin | 7 d | 10% | PDL | SOD1 | 2.45 | 1.38 | 4.34 | 0.126 |
| 500 µM CoCl2 | 7 d | 10% | PDL | SOD1 | 1.00 | 0.55 | 1.81 | 0.996 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | none | CAT | 0.21 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 0.024 * |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | none | GPX4 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 1.84 | 0.528 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | none | GSS | 0.99 | 0.36 | 2.71 | 0.993 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | none | NFE2L2 | 1.21 | 0.50 | 2.91 | 0.763 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | none | SOD1 | 1.14 | 0.39 | 3.28 | 0.842 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | PDL | CAT | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 0.003 ** |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | PDL | GPX4 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.37 | 0.015 * |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | PDL | GSS | 0.64 | 0.08 | 5.30 | 0.728 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | PDL | NFE2L2 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 0.53 | 0.074 |
| 10 mM NaIO3 | 14 d | 10% | PDL | SOD1 | 0.31 | 0.07 | 1.40 | 0.145 |
| Bio Group Name | Serum Content | Coating | Target Name | Rq | Rq Min | Rq Max | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | IL1B | 2.49 | 1.16 | 5.36 | 0.158 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | IL1B | 0.32 | 0.08 | 1.28 | 0.164 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | IL6 | 0.68 | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.248 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | IL6 | 0.44 | 0.25 | 0.80 | 0.048 * |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | CXCL8 | 1.33 | 0.48 | 3.65 | 0.599 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | CXCL8 | 0.40 | 0.26 | 0.61 | 0.036 * |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | NOS2 | 0.55 | 0.28 | 1.04 | 0.148 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | NOS2 | 0.72 | 0.38 | 1.34 | 0.400 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | IL1B | 8.04 | 3.35 | 19.29 | 0.035 * |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | IL1B | 2.09 | 0.87 | 5.01 | 0.392 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | IL6 | 1.85 | 0.87 | 3.94 | 0.208 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | IL6 | 0.90 | 0.40 | 2.02 | 0.829 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | CXCL8 | 2.07 | 1.29 | 3.34 | 0.060 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | CXCL8 | 1.15 | 0.48 | 2.80 | 0.760 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | NOS2 | 1.10 | 0.81 | 1.48 | 0.706 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | NOS2 | 0.69 | 0.44 | 1.09 | 0.201 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | PDL | IL1B | 3.00 | 1.48 | 6.11 | 0.230 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | PDL | IL1B | 0.70 | 0.19 | 2.62 | 0.716 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | PDL | IL6 | 1.78 | 0.86 | 3.68 | 0.343 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | PDL | IL6 | 1.10 | 0.81 | 1.50 | 0.853 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | PDL | CXCL8 | 2.19 | 0.60 | 8.05 | 0.352 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | PDL | CXCL8 | 1.09 | 0.50 | 2.40 | 0.901 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | PDL | NOS2 | 0.64 | 0.24 | 1.71 | 0.341 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | PDL | NOS2 | 0.90 | 0.65 | 1.25 | 0.662 |
| Bio Group Name | Serum Content | Coating | Target Name | Rq | Rq Min | Rq Max | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | IL1B | 2.53 | 1.19 | 5.36 | 0.242 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | IL1B | 0.23 | 0.02 | 2.78 | 0.258 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | IL6 | 1.14 | 0.65 | 1.98 | 0.718 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | IL6 | 0.33 | 0.13 | 0.85 | 0.042 * |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | CXCL8 | 1.60 | 0.86 | 2.99 | 0.204 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | CXCL8 | 0.78 | 0.55 | 1.10 | 0.388 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | none | NOS2 | 1.84 | 1.29 | 2.64 | 0.122 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | none | NOS2 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.81 | 0.040 * |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | IL1B | 0.77 | 0.27 | 2.19 | 0.636 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | IL1B | 0.41 | 0.18 | 0.96 | 0.088 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | IL6 | 0.87 | 0.65 | 1.17 | 0.548 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | IL6 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 1.44 | 0.318 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | CXCL8 | 1.39 | 0.46 | 4.25 | 0.545 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | CXCL8 | 0.94 | 0.44 | 2.02 | 0.888 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 10% | none | NOS2 | 1.11 | 0.69 | 1.79 | 0.662 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 10% | none | NOS2 | 0.95 | 0.63 | 1.42 | 0.792 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | Lam | IL1B | 1.20 | 0.35 | 4.05 | 0.758 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | Lam | IL1B | 0.30 | 0.06 | 1.62 | 0.151 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | Lam | IL6 | 1.13 | 0.68 | 1.88 | 0.659 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | Lam | IL6 | 0.75 | 0.44 | 1.25 | 0.313 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | Lam | CXCL8 | 2.84 | 1.79 | 4.52 | 0.006 ** |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | Lam | CXCL8 | 0.58 | 0.25 | 1.36 | 0.223 |
| 1 µg/mL LPS | 5% | Lam | NOS2 | 0.93 | 0.34 | 2.59 | 0.882 |
| 10 µg/mL PIC | 5% | Lam | NOS2 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.65 | 0.022 * |
| 1% Serum | 5% Serum | 10% Serum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 199.31 Ω·cm2 | 247.01 Ω·cm2 | 316.74 Ω·cm2 |
| STD | 137.36 Ω·cm2 | 181.18 Ω·cm2 | 251.39 Ω·cm2 |
| + Lam | + Lam | + Lam | |
| Mean | 193.18 Ω·cm2 | 248.81 Ω·cm2 | 212.00 Ω·cm2 |
| STD | 126.24 Ω·cm2 | 205.89 Ω·cm2 | 158.88 Ω·cm2 |
| Gene | Product | Assay ID |
|---|---|---|
| CAT | Catalase | Ss04323025_m1 |
| CXCL8 | Interleukin 8 | Ss03392437_m1 |
| GPX4 | Glutathione Peroxidase 4 | Ss03384646_u1 |
| GSS | Glutathione Synthetase | Ss04328106_m1 |
| GUSB | Glucuronidase Beta | Ss03387751_u1 |
| IL1B | Interleukin 1 Beta | Ss03393804_m1 |
| IL6 | Interleukin 6 | Ss07308316_g1 |
| NFE2L2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2) | Ss06886076_m1 |
| NOS2 | Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 | Ss03374608_u1 |
| SOD1 | Superoxide Dismutase 1 | Ss03375614_u1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dörschmann, P.; Prinz, M.; Schmitkall, G.; Roider, J.; Klettner, A. Specific Assay Protocols for Porcine Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Concerning Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178434
Dörschmann P, Prinz M, Schmitkall G, Roider J, Klettner A. Specific Assay Protocols for Porcine Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Concerning Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178434
Chicago/Turabian StyleDörschmann, Philipp, Marie Prinz, Greta Schmitkall, Johann Roider, and Alexa Klettner. 2025. "Specific Assay Protocols for Porcine Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Concerning Oxidative Stress and Inflammation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178434
APA StyleDörschmann, P., Prinz, M., Schmitkall, G., Roider, J., & Klettner, A. (2025). Specific Assay Protocols for Porcine Single-Eye Retinal Pigment Epithelium Concerning Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8434. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178434








