Anti-HIV and Antimicrobial Activity of 7-Hydrazino-8-hydroxyquinoline-Based Aromatic Hydrazones
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
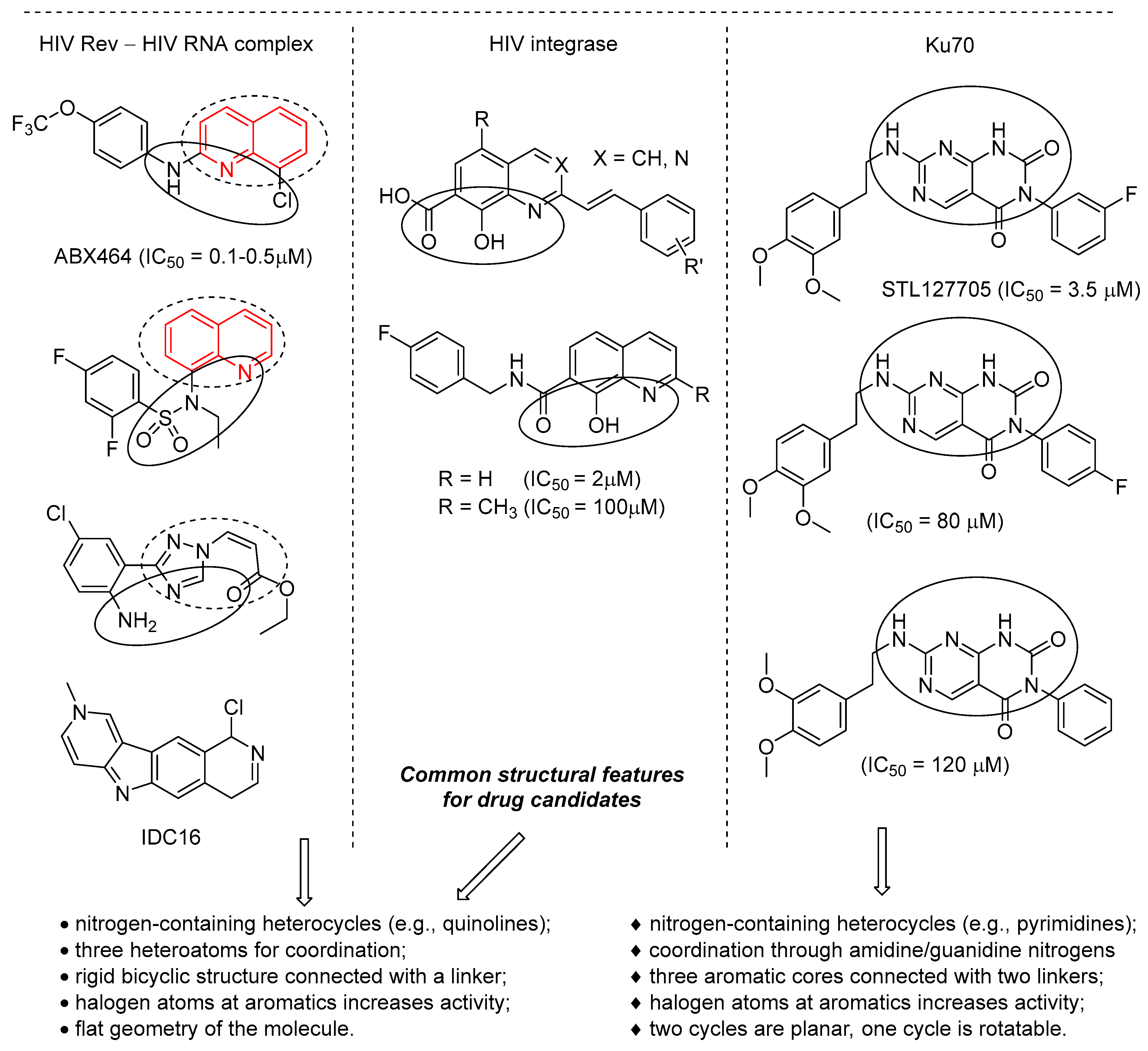
2.1. Compounds Selection
2.2. Anti-HIV Activity
2.2.1. Ability to Disrupt Formation of HIV Rev–RNA Complex
2.2.2. Activity Against HIV Integrase
2.2.3. Ability to Disrupt Formation of Ku70/Ku80–DNA Complex
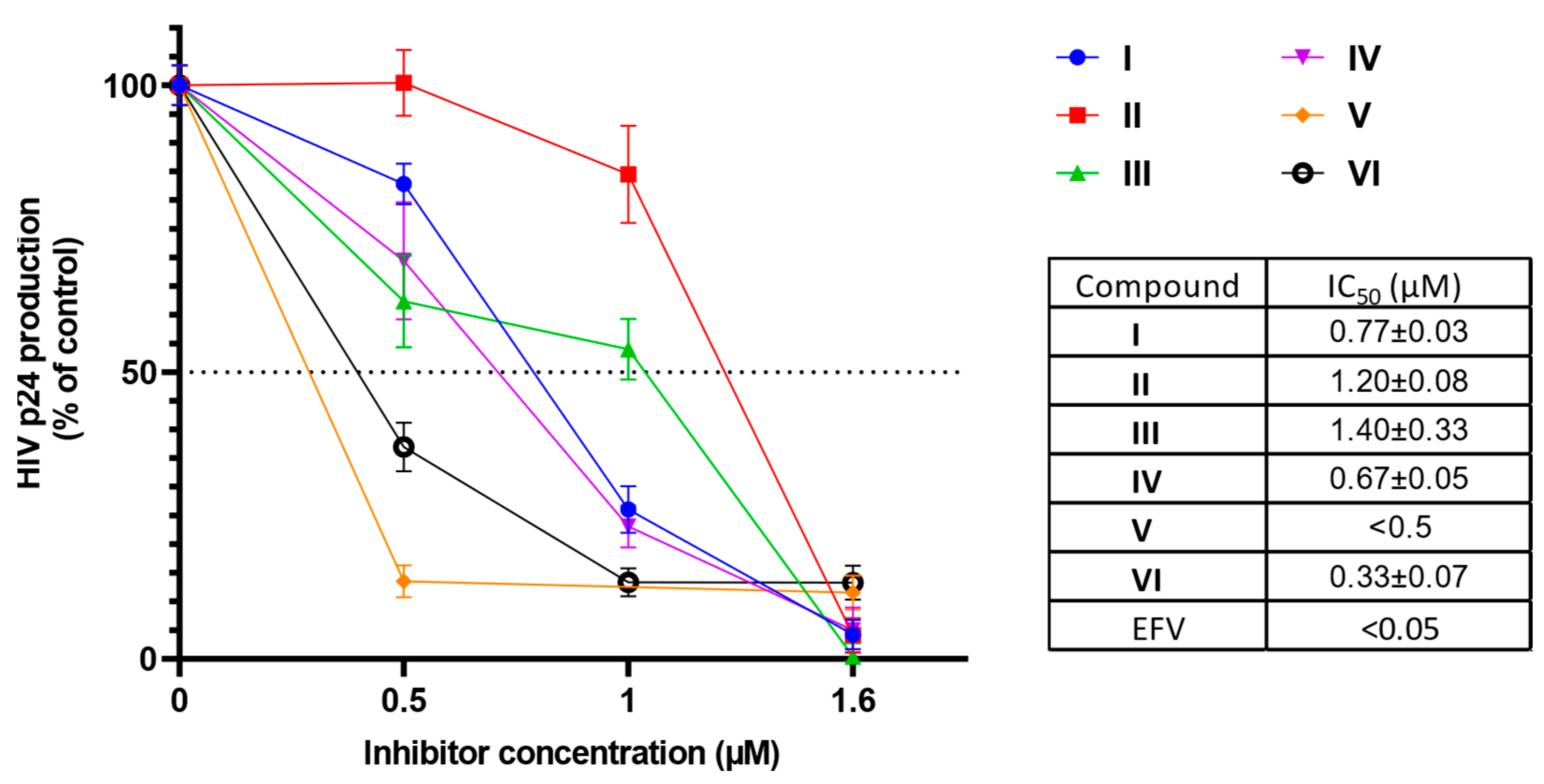
2.2.4. Antigen p24 Assay in HIV-Infected MT-4 Cells
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
2.4. Cytotoxicity
3. Materials and Methods
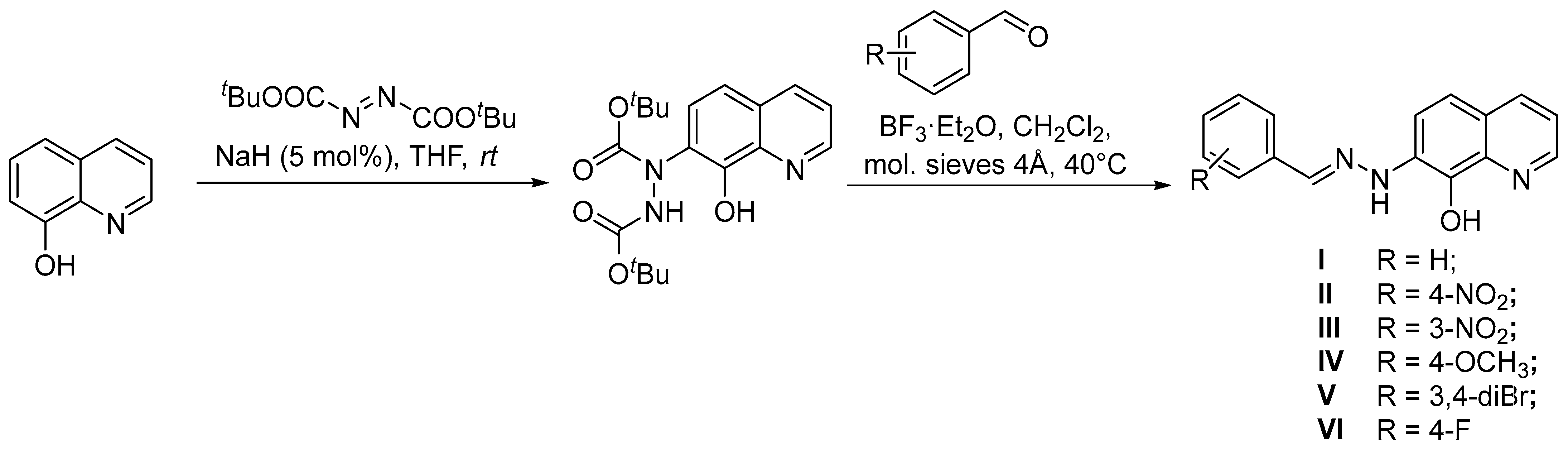
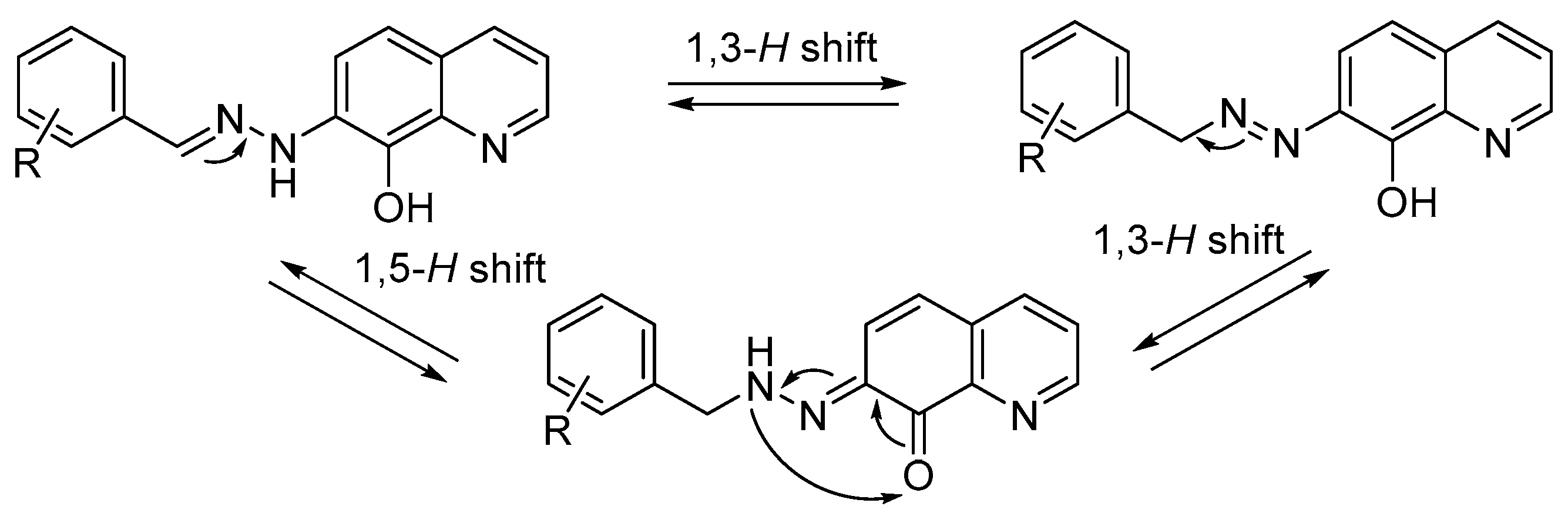
3.1. Chemical Synthesis
3.1.1. 7-(2-Benzylidenohydrazinyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline (I) (anti-isomer)
3.1.2. 7-(4-Nitrobenzylidenohydrazinyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline (II) (anti-isomer)
3.1.3. 7-(3-Nitrobenzylidenohydrazinyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline (III) (anti-isomer)
3.1.4. 7-(4-Methoxybenzylidenohydrazinyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline (IV) (anti-isomer)
3.1.5. 7-(3,4-Dibromobenzylidenohydrazinyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline (V) (anti-isomer)
3.1.6. 7-(4-Fluorobenzylidenohydrazinyl)-8-hydroxyquinoline (VI) (anti-isomer)
3.2. Compound Testing
3.3. Screening for HIV Integrase Activity
3.4. Ku Protein Assay
3.5. Screening Inhibition of HIV Rev–RNA Complex
3.6. Evaluation of the Compounds Activity Against Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV-1) Infected Cells
3.7. Bacterial and Fungi Culture
3.8. Antimicrobial Activity Evaluation
3.9. Microgel Formation
3.10. Cell Culture for Cytotoxicity Assays
3.11. MTT Assay
3.12. Neutral Red (NR) Assay
3.13. Sulforhodamine B (SRB) Assay
3.14. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveri, V.; Vecchio, G. 8-Hydroxyquinolines in medicinal chemistry: A structural perspective. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 120, 252–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almalki, Z.S.; Yue, X.; Xia, Y.; Wigle, P.R.; Guo, J.J. Utilization, Spending, and Price Trends for Quinolones in the US Medicaid Programs: 25 Years’ Experience 1991–2015. Pharmacoecon Open 2017, 1, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.; Pannecouque, C.; De Clercq, E.; Liu, X. Anti-HIV Drug Discovery and Development: Current Innovations and Future Trends. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2849–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solyev, P.N.; Sherman, D.K.; Novikov, R.A.; Levina, E.A.; Kochetkov, S.N. Hydrazo coupling: The efficient transition-metal-free C–H functionalization of 8-hydroxyquinoline and phenol through base catalysis. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 6381–6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thinnes, C.C.; Tumber, A.; Yapp, C.; Scozzafava, G.; Yeh, T.; Chan, M.C.; Tran, T.A.; Hsu, K.; Tarhonskaya, H.; Walport, L.J.; et al. Betti reaction enables efficient synthesis of 8-hydroxyquinoline inhibitors of 2-oxoglutarate oxygenases. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15458–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muruganantham, N.; Sivakumar, R.; Anbalagan, N.; Gunasekaran, V.; Leonard, J.T. Synthesis, anticonvulsant and antihypertensive activities of 8-substituted quinoline derivatives. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 27, 1683–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, L.E.; De Sousa, P.T., Jr.; Joussef, A.C. Investigation of Chemoselective Reaction of 2-Amino-8-hydroxyquinoline with Arylsulfonylchloride Derivatives. Synth. Comm. 2009, 39, 1378–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motati, D.R.; Uredia, D.; Watkins, E.B. A general method for the metal-free, regioselective, remote C-H halogenation of 8-substituted quinolines. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 1782–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, J.; Raines, R.T. Hydrolytic stability of hydrazones and oximes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 7523–7526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrahman, M.A.; Salama, I.; Gomaa, M.S.; Elaasser, M.M.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Soliman, D.H. Design, synthesis and 2D QSAR study of novel pyridine and quinolone hydrazone derivatives as potential antimicrobial and antitubercular agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 138, 698–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Luxami, V.; Paul, K. Insights of 8-hydroxyquinolines: A novel target in medicinal chemistry. Bioorg. Chem. 2021, 108, 104633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reference Data from the Open Sources. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov (accessed on 6 June 2025).
- Carcelli, M.; Rogolino, D.; Gatti, A.; Pala, N.; Corona, A.; Caredda, A.; Tramontano, E.; Pannecouque, C.; Naesens, L.; Esposito, F. Chelation Motifs Affecting Metal-dependent Viral Enzymes: N′-acylhydrazone Ligands as Dual Target Inhibitors of HIV-1 Integrase and Reverse Transcriptase Ribonuclease H Domain. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musiol, R. Quinoline-based HIV integrase inhibitors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, F.; Geng, G.; Chen, B.; Pan, T.; Li, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bai, C. Identification of benzenesulfonamide quinoline derivatives as potent HIV-1 replication inhibitors targeting Rev protein. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkour, N.; Lin, Y.; Maire, S.; Ayadi, L.; Mahuteau-Betzer, F.; Nguyen, C.; Mettling, C.; Portales, P.; Grierson, D.; Chabot, B.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of HIV pre-mRNA splicing as a novel antiretroviral therapy to overcome drug resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2007, 3, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weterings, E.; Gallegos, A.C.; Dominick, L.N.; Cooke, L.S.; Bartels, T.N.; Vagner, J.; Matsunaga, T.O.; Mahadevan, D. A novel small molecule inhibitor of the DNA repair protein Ku70/80. DNA Repair 2016, 43, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, N.; Myburgh, R.; Garcel, A.; Vautrin, A.; Lapasset, L.; Nadal, E.S.; Mahuteau-Betzer, F.; Najman, R.; Fornarelli, P.; Tantale, K.; et al. Long lasting control of viral rebound with a new drug ABX464 targeting Rev–mediated viral RNA biogenesis. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemskaya, A.S.; Arutyunyan, A.F.; Sherman, D.K.; Yanvarev, D.V.; Shuvalov, A.V.; Kalnina, L.B.; Kaluzhny, D.N.; Novikov, R.A.; Solyev, P.N.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T. Isolation of recombinant HIV-1 Rev protein and investigation of a new class of benzimidazole inhibitors capability to disrupt Rev-RRE complex. Bioorg. Chem. 2025, 161, 108487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluymers, W.; Pais, G.; Van Maele, B.; Pannecouque, C.; Fikkert, V.; Burke, T.R., Jr.; De Clercq, E.; Witvrouw, M.; Neamati, N.; Debyser, Z. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integration by diketo derivatives. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 3292–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisenko, A.N.; Knyazhanskaya, E.S.; Zatsepin, T.S.; Gottikh, M.B. Human Ku70 protein binds hairpin RNA and double stranded DNA through two different sites. Biochimie 2017, 132, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fell, V.L.; Schild-Poulter, C. The Ku heterodimer: Function in DNA repair and beyond. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 763, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadrina, O.A.; Knyazhanskaya, E.S.; Korolev, S.P.; Gottikh, M.B. Host Proteins Ku and HMGA1 As Participants of HIV-1 Transcription. Acta Naturae 2016, 8, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostyushev, D.; Kostyusheva, A.; Brezgin, S.; Zarifyan, D.; Utkina, A.; Goptar, I.; Chulanov, V. Suppressing the NHEJ pathway by DNA-PKcs inhibitor NU7026 prevents degradation of HBV cccDNA cleaved by CRISPR/Cas9. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-I.; Hsu, Y.-K.; Chou, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-H.; Hsu, S.-T.; Liou, Y.-S.; Dai, Y.-C.; Chang, M.-F.; Chang, S.C. Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protein Plays a Dual Role in WRN-Mediated Repair of Nonhomologous End Joining. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01273-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisenko, A.; Galkin, S.; Mikhaylov, A.A.; Khrenova, M.G.; Agapkina, Y.; Korolev, S.; Garkul, L.; Shirokova, V.; Ikonnikova, V.A.; Korlyukov, A.; et al. KuINins as a New Class of HIV-1 Inhibitors That Block Post-Integration DNA Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korolev, S.P.; Kondrashina, O.V.; Druzhilovsky, D.S.; Starosotnikov, A.M.; Dutov, M.D.; Bastrakov, M.A.; Dalinger, I.L.; Filimonov, D.A.; Shevelev, S.A.; Poroikov, V.V.; et al. Structural-Functional Analysis of 2,1,3-Benzoxadiazoles and Their N-oxides as HIV-1 Integrase Inhibitors. Acta Naturae 2013, 5, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrina, O.; Garaniba, I.; Korolev, S.; Zatsepin, T.; Van Asseche, J.; Daouad, F.; Wallwt, C.; Rohr, O.; Gottikh, M. Analysis of RNA binding properties of human Ku protein reveals its interactions with 7SK snRNA and protein components of 7SK snRNP complex. Biochimie 2020, 171–172, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadrina, O.; Knyazhanskaya, E.; Korolev, S. The optimization of the production of human protein Ku in Escherichia coli. Univers. Chem. Biol. 2016, 10, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, A.V.; Korovina, A.N.; Tunitskaya, V.L.; Kostyuk, D.A.; Rechinsky, V.O.; Kukhanova, M.K.; Kochetkov, S.N. Development of the system ensuring a high-level expression of hepatitis C virus nonstructural NS5B and NS5A proteins. Protein Expr. Purif. 2006, 48, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arutyunyan, A.F.; Kostyukov, A.A.; Korolev, S.P.; Gottikh, M.B.; Kaluzhny, D.N.; Susova, O.Y.; Zhuze, A.L. DNA Sequence-Specific Ligands. 19. Synthesis, Spectral Properties, Virological and Biochemical Studies of DB3(n) Fluorescent Dimeric Trisbenzimidazoles. Mol. Biol. 2023, 57, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Document M27-A3; Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts; Approved Standard (3rd ed.). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008.
- CLSI Document M07-A11; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard (11th ed.). Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018.
- Repetto, G.; Peso, A.; Zurita, J.L. Neutral red uptake assay for the estimation of cell viability/cytotoxicity. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichai, V.; Kirtikara, K. Sulforhodamine B colorimetric assay for cytotoxicity screening. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1112–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Compound | I | II | III | IV | V | VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50, μM | 160 ± 50 | >200 | 190 ± 60 | 150 ± 50 | >200 | 40 ± 10 |
| Compound | I | II | III | IV | V | VI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50, μM | 40 ± 10 | 50 ± 20 | 60 ± 20 | 80 ± 30 | 25 ± 8 | >250 |
| Compounds | MIC (Mean ± SE) * | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans ATCC 10231 | S. aureus ATCC 29213 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | ||||
| μg/mL | μM | μg/mL | μM | μg/mL | μM | |
| I | 4.0 | 15.2 | 52.0 ± 5.9 | 197.5 ± 22.3 | >64 | >243 |
| II | 4.0 | 13.0 | 14.0 ± 1.9 | 45.4 ± 6.2 | >64 | >208 |
| III | 11.3 ± 1.2 | 36.8 ± 3.9 | 18.0 ± 4.8 | 58.4 ± 15.6 | >64 | >208 |
| IV | 8.0 | 27.3 | 64.0 | 218.2 | >64 | >218 |
| V | 15.3 ± 0.7 | 36.3 ± 1.7 | 36.3 ± 10.3 | 86.1 ± 24.5 | >64 | >152 |
| VI | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 13.6 ± 0.6 | ≥64 | ≥227.5 | >64 | >228 |
| Amphotericin B | 0.4 | 0.4 | n/d | n/d | n/d | n/d |
| Gentamicin | n/d ** | n/d | 0.6 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.3 | 4.2 ± 0.6 |
| Compound | MTT | NR | SRB |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | 50.5 ± 2.5 | 14.5 ± 3.5 | 59.5 ± 12.5 |
| II | 123.0 ± 13.2 | 21.0 ± 4.0 | 8.0 ± 0.1 |
| III | 38.0 ± 9.1 | 7.1 ± 0.7 | 7.1 ± 0.4 |
| IV | 47.0 ± 3.2 | 9.1 ± 1.5 | 40.0 ± 0.2 |
| V | 120.5 ± 7.5 | 8.6 ± 0.1 | 6.9 ± 0.3 |
| VI | 45.5 ± 3.6 | 6.7 ± 0.2 | 7.0 ± 0.2 |
| I in alginate microgel | >150 | >150 | >150 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozmenko, Y.V.; Khisamov, M.M.; Revtovich, S.V.; Korolev, S.P.; Sherman, D.K.; Spiridonov, V.V.; Kalnina, L.B.; Valuev-Elliston, V.T.; Gottikh, M.B.; Kochetkov, S.N.; et al. Anti-HIV and Antimicrobial Activity of 7-Hydrazino-8-hydroxyquinoline-Based Aromatic Hydrazones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178402
Kozmenko YV, Khisamov MM, Revtovich SV, Korolev SP, Sherman DK, Spiridonov VV, Kalnina LB, Valuev-Elliston VT, Gottikh MB, Kochetkov SN, et al. Anti-HIV and Antimicrobial Activity of 7-Hydrazino-8-hydroxyquinoline-Based Aromatic Hydrazones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178402
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozmenko, Yaroslav V., Marat M. Khisamov, Svetlana V. Revtovich, Sergey P. Korolev, Daria K. Sherman, Vasiliy V. Spiridonov, Lyudmila B. Kalnina, Vladimir T. Valuev-Elliston, Marina B. Gottikh, Sergey N. Kochetkov, and et al. 2025. "Anti-HIV and Antimicrobial Activity of 7-Hydrazino-8-hydroxyquinoline-Based Aromatic Hydrazones" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178402
APA StyleKozmenko, Y. V., Khisamov, M. M., Revtovich, S. V., Korolev, S. P., Sherman, D. K., Spiridonov, V. V., Kalnina, L. B., Valuev-Elliston, V. T., Gottikh, M. B., Kochetkov, S. N., Zemskaya, A. S., & Solyev, P. N. (2025). Anti-HIV and Antimicrobial Activity of 7-Hydrazino-8-hydroxyquinoline-Based Aromatic Hydrazones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8402. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178402







