TP53 Expression Status Alters Hemoglobinization and Ferroptosis Sensitivity in K-562 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
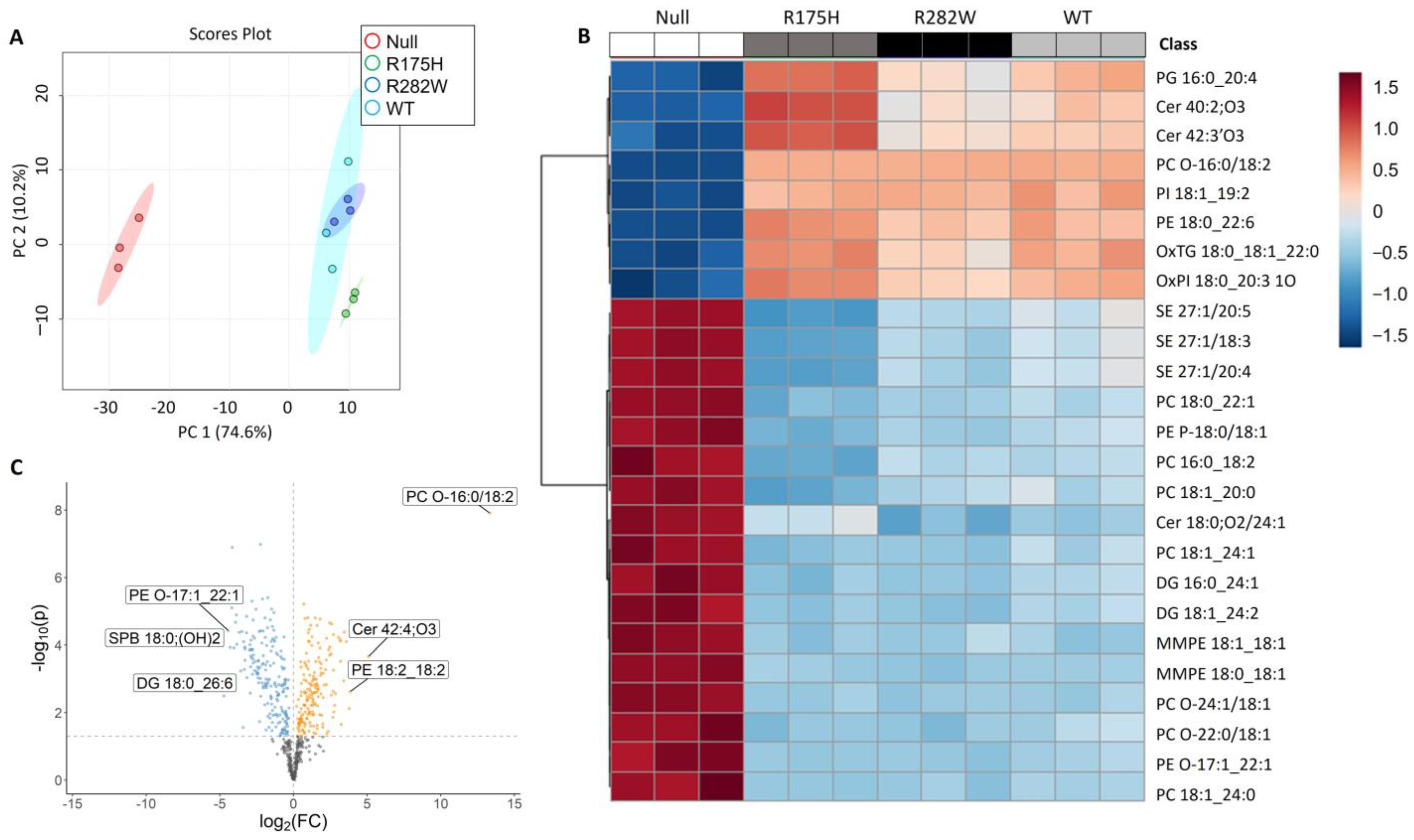
2.1. Induction of TP53 Expression Dramatically Alters K-562 Cell Lipid Composition
2.2. Lipids Involved in Choline Metabolism, Sphingolipid Metabolism, Glycerophospholipid Metabolism, and Ferroptosis, Among Others Differentially Expressed Following Induction of TP53
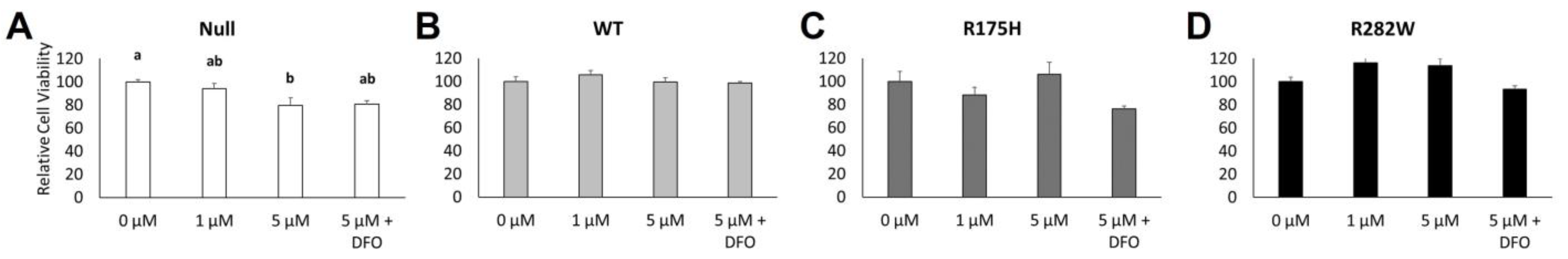
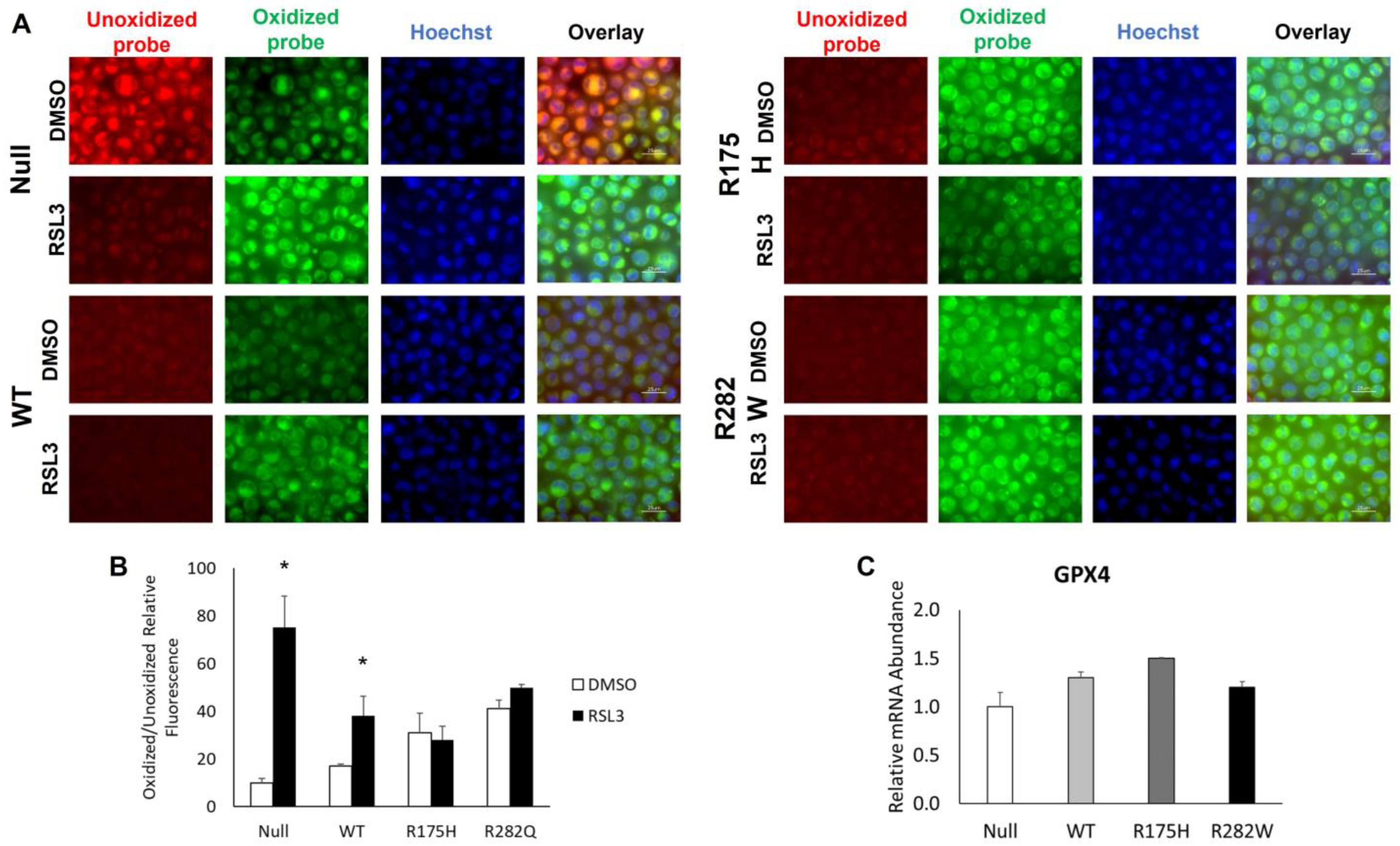
2.3. Induction of WT and Mutant TP53 Expression Increases Ferroptosis Resistance but Not GPX4 mRNA Expression in K-562 Cells
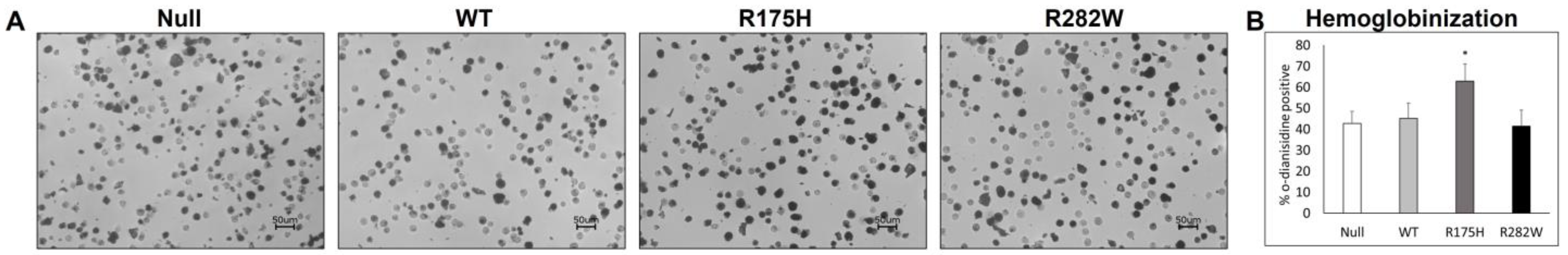
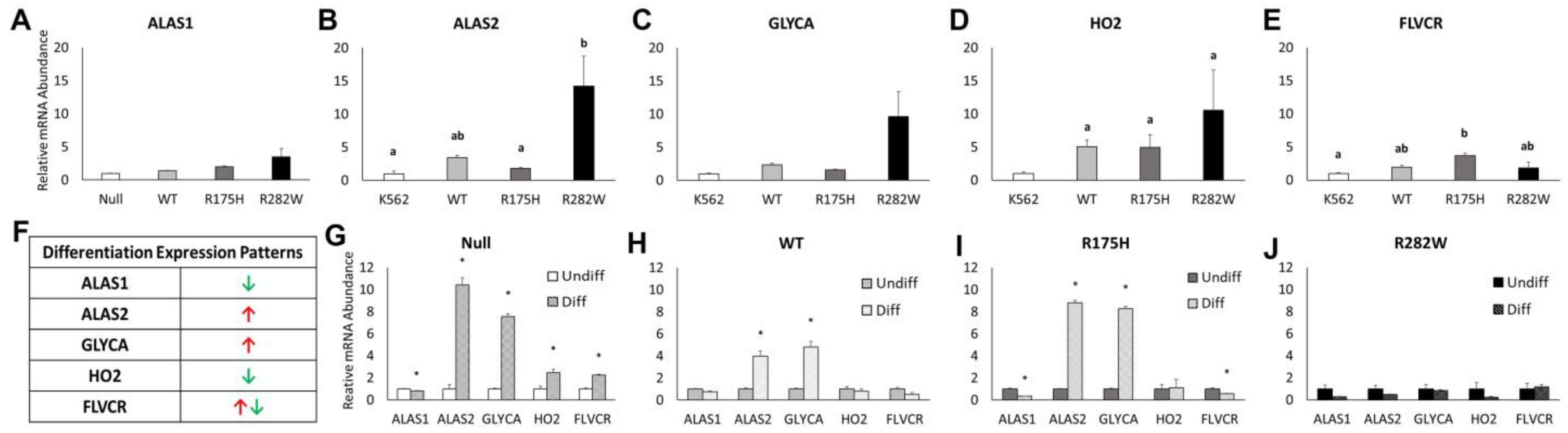
2.4. Hemoglobinization and Heme Metabolism-Related mRNA Expression Are Differentially Altered by Induction of WT and Mutant TP53 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Creation of Stable WT and Mutant TP53-Expressing Cell Lines
4.2. Lipid Extraction
4.3. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
4.4. Analysis of Lipidomics Data
4.5. Lipid Pathway Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Cell Proliferation and Viability Assays
4.7. Visualization and Quantification of Lipid Peroxidation
4.8. Differentiation and Assessment of Hemoglobinization
4.9. mRNA Expression Analysis
4.10. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DBA | Diamond-blackfan anemia |
| MDS | del(5q) myelodysplastic syndrome |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| WT | Wild-type |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit 8 |
| ALAS1 | 5-aminolevulinate synthase 1 |
| ALAS2 | 5-aminolevulinate synthase 2 |
| GLYCA | Glycophorin A |
| HO2 | Heme oxygenase 2 |
| FLVCR | Feline leukemia virus subgroup C receptor |
References
- Le Goff, S.; Boussaid, I.; Floquet, C.; Raimbault, A.; Hatin, I.; Andrieu-Soler, C.; Salma, M.; Leduc, M.; Gautier, E.F.; Guyot, B.; et al. P53 Activation during Ribosome Biogenesis Regulates Normal Erythroid Differentiation. Blood 2021, 137, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, V.; Quintas-Cardama, A.; Lozano, G. The P53 Pathway in Hematopoiesis: Lessons from Mouse Models, Implications for Humans. Blood 2012, 120, 5118–5127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Mohandas, N. Disorders of Red Cell Membrane. Br. J. Haematol. 2008, 141, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; McGraw, K.L.; Sallman, D.A.; List, A.F. The Role of P53 in Myelodysplastic Syndromes and Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Molecular Aspects and Clinical Implications. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 1777–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, W.; Tsuji, Y.; Torti, S.V.; Torti, F.M. Post-Transcriptional Modulation of Iron Homeostasis during P53-Dependent Growth Arrest. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 33911–33918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.L.; Thompson, L.R.; Dandekar, E.; Srinivasan, A.; Montgomery, M.R. Distinct TP53 Mutation Subtypes Differentially Influence Cellular Iron Metabolism. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Q.; Niu, H.; Yue, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, C.; Jiang, H.; Dong, S.; Shao, Z.; Xing, L.; et al. Abnormal Ferroptosis in Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarangelo, A.; Magtanong, L.; Bieging-Rolett, K.T.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Attardi, L.D.; Dixon, S.J. P53 Suppresses Metabolic Stress-Induced Ferroptosis in Cancer Cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Keel, S.B.; Shimamura, A.; Liu, L.; Gerds, A.T.; Li, H.Y.; Wood, B.L.; Scott, B.L.; Abkowitz, J.L. Delayed Globin Synthesis Leads to Excess Heme and the Macrocytic Anemia of Diamond Blackfan Anemia and Del(5q) Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 338ra67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Stockwell, B.R. The Hallmarks of Ferroptosis. Annu. Rev. Cancer Biol. 2019, 3, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, C.J.; Hermann, E.R.; Kouplen, K.N.; Hartson, S.D.; Montgomery, M.R. Differences in Antioxidant and Lipid Handling Protein Expression Influence How Cells Expressing Distinct Mutant TP53 Subtypes Maintain Iron Homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, L.R.; Oliveira, T.G.; Hermann, E.R.; Chowanadisai, W.; Clarke, S.L.; Montgomery, M.R. Distinct TP53 Mutation Types Exhibit Increased Sensitivity to Ferroptosis Independently of Changes in Iron Regulatory Protein Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamura, S.; Vegi, N.M.; Hoppe, P.S.; Schroeder, T.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Okreglicka, K.; Hultner, L.; Schneider, M.; Ladinig, C.; et al. Glutathione Peroxidase 4 and Vitamin E Control Reticulocyte Maturation, Stress Erythropoiesis and Iron Homeostasis. Haematologica 2020, 105, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouled-Haddou, H.; Messaoudi, K.; Demont, Y.; Lopes Dos Santos, R.; Carola, C.; Caulier, A.; Vong, P.; Jankovsky, N.; Lebon, D.; Willaume, A.; et al. A New Role of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 during Human Erythroblast Enucleation. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5666–5680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademacher, M.; Kuhn, H.; Borchert, A. Expression Silencing of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 in Mouse Erythroleukemia Cells Delays In Vitro Erythropoiesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Cho, E.; Wong, J. A Critical Role for the Co-Repressor N-CoR in Erythroid Differentiation and Heme Synthesis. Cell Res. 2007, 17, 804–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.C.; Ritke, M.K.; Yalowich, J.C.; Leder, G.H.; Ferrell, R.E. Mutational Inactivation of the P53 Gene in the Human Erythroid Leukemic K562 Cell Line. Leuk. Res. 1993, 17, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freed-Pastor, W.A.; Prives, C. Mutant P53: One Name, Many Proteins. Genes. Dev. 2012, 26, 1268–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stengel, A.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, T.; Meggendorfer, M.; Fasan, A.; Haferlach, C. The Impact of TP53 Mutations and TP53 Deletions on Survival Varies between AML, ALL, MDS and CLL: An Analysis of 3307 Cases. Leukemia 2017, 31, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cao, L.; Yang, L.; Yang, M.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. The Ferroptosis Inducer Erastin Enhances Sensitivity of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells to Chemotherapeutic Agents. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2015, 2, e1054549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascon, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.R.; Costa, E.S.; Sorgine, M.H.F.; Nascimento-Silva, M.C.L.; Teodosio, C.; Bárcena, P.; Castro-Faria-Neto, H.C.; Bozza, P.T.; Orfao, A.; Oliveira, P.L.; et al. Heme-Oxygenases during Erythropoiesis in K562 and Human Bone Marrow Cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Keel, S.B.; Wood, B.L.; Scott, B.L.; Abkowitz, J.L. Pathophysiology of Macrocytic Anemia in Diamond Blackfan Anemia and Del(5q) Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Blood 2015, 126, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.-J.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Pishesha, N.; Lewis, C.A.; Freinkman, E.; Farquharson, C.; Millán, J.L.; Lodish, H. Enhanced Phosphocholine Metabolism Is Essential for Terminal Erythropoiesis. Blood 2018, 131, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L.; Wang, W.-J. P53 Regulates Lipid Metabolism in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 192, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calzada, E.; Onguka, O.; Claypool, S.M. Phosphatidylethanolamine Metabolism in Health and Disease. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 321, 29–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.W.; Manning, N. Abnormal Phospholipid Metabolism in Spur Cell Anemia: Decreased Fatty Acid Incorporation Into Phosphatidylethanolamine and Increased Incorporation Into Acylcarnitine in Spur Cell Anemia Erythrocytes. Blood 1994, 84, 1283–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Gong, H.-B.; Gao, H.-Y.; Wu, Y.-P.; Sun, W.-Y.; Li, Z.-Q.; Wang, G.; Liu, B.; Liang, L.; Kurihara, H.; et al. Oxygenated Phosphatidylethanolamine Navigates Phagocytosis of Ferroptotic Cells by Interacting with TLR2. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1971–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a P53-Mediated Activity during Tumour Suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, W. P53 in Ferroptosis Regulation: The New Weapon for the Old Guardian. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, S.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhong, M.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L.; Billiar, T.R.; et al. The Tumor Suppressor P53 Limits Ferroptosis by Blocking DPP4 Activity. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1692–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. Targeting Mutant P53 Stabilization for Cancer Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1215995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Li, D.; Ou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, W. Acetylation Is Crucial for P53-Mediated Ferroptosis and Tumor Suppression. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid Extraction by Methyl-Tert-Butyl Ether for High-Throughput Lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Kroeger, N.M.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Bowden, J.A.; Patterson, R.E.; Cochran, J.A.; Beecher, C.W.W.; Garrett, T.J.; Yost, R.A. LipidMatch: An Automated Workflow for Rule-Based Lipid Identification Using Untargeted High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry Data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, M. lipidmapsR: Lipid Maps Rest Service, version 1.0.4; LIPID MAPS: Wales, UK, 2022.
- Conroy, M.J.; Andrews, R.M.; Andrews, S.; Cockayne, L.; Dennis, E.A.; Fahy, E.; Gaud, C.; Griffiths, W.J.; Jukes, G.; Kolchin, M.; et al. LIPID MAPS: Update to Databases and Tools for the Lipidomics Community. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1677–D1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebisch, G.; Fahy, E.; Aoki, J.; Dennis, E.A.; Durand, T.; Ejsing, C.S.; Fedorova, M.; Feussner, I.; Griffiths, W.J.; Köfeler, H.; et al. Update on LIPID MAPS Classification, Nomenclature, and Shorthand Notation for MS-Derived Lipid Structures. J. Lipid Res. 2020, 61, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Sud, M.; Cotter, D.; Subramaniam, S. LIPID MAPS Online Tools for Lipid Research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W606–W612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopczynski, D.; Hoffmann, N.; Peng, B.; Ahrends, R. Goslin: A Grammar of Succinct Lipid Nomenclature. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 10957–10960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooms, J. The Jsonlite Package: A Practical and Consistent Mapping Between JSON Data and R Objects. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1403.2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, R.A.M.; Chen, Z.J. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis (2nd ed.). Meas. Interdiscip. Res. Perspect. 2019, 17, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K.; Vaughan, D.; Software, P. PBC Dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. 2023. Available online: https://dplyr.tidyverse.org/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Graves, S.; Dorai-Raj, H.-P.P.; Selzer, L.; Dorai-Raj, S. Multcompview: Visualizations of Paired Comparisons. 2024. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/multcompView/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Vaughan, D.; Girlich, M.; Ushey, K.; Software, P. PBC Tidyr: Tidy Messy Data. 2024. Available online: https://tidyr.tidyverse.org/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Henry, L.; Software, P. PBC [cph; fnd Purrr: Functional Programming Tools. 2025. Available online: https://purrr.tidyverse.org/ (accessed on 26 August 2025).
- The R Core Team. R Core Team R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
| Pathway Name | Pathway Lipids | p-Value | Benjamini Correction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 26 | 0.000019862 | 0.000536263 |
| Ether lipid metabolism | 16 | 0.002329627 | 0.023079117 |
| Sphingolipid signaling pathway | 9 | 0.003733457 | 0.023079117 |
| Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor biosynthesis | 3 | 0.004273911 | 0.023079117 |
| Autophagy–animal | 4 | 0.008345775 | 0.028166992 |
| Necroptosis | 4 | 0.008345775 | 0.028166992 |
| Choline metabolism in cancer | 5 | 0.013581394 | 0.040744182 |
| Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling | 8 | 0.035407737 | 0.087988827 |
| Sphingolipid metabolism | 21 | 0.043529482 | 0.090407385 |
| Ferroptosis | 11 | 0.064784195 | 0.124940948 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cardona, C.; Young, M.; Montgomery, M. TP53 Expression Status Alters Hemoglobinization and Ferroptosis Sensitivity in K-562 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178359
Cardona C, Young M, Montgomery M. TP53 Expression Status Alters Hemoglobinization and Ferroptosis Sensitivity in K-562 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178359
Chicago/Turabian StyleCardona, Cameron, Madelyne Young, and McKale Montgomery. 2025. "TP53 Expression Status Alters Hemoglobinization and Ferroptosis Sensitivity in K-562 Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178359
APA StyleCardona, C., Young, M., & Montgomery, M. (2025). TP53 Expression Status Alters Hemoglobinization and Ferroptosis Sensitivity in K-562 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8359. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178359






