Nuclear Roles of Spliceosome-Associated microRNAs in Neuronal Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
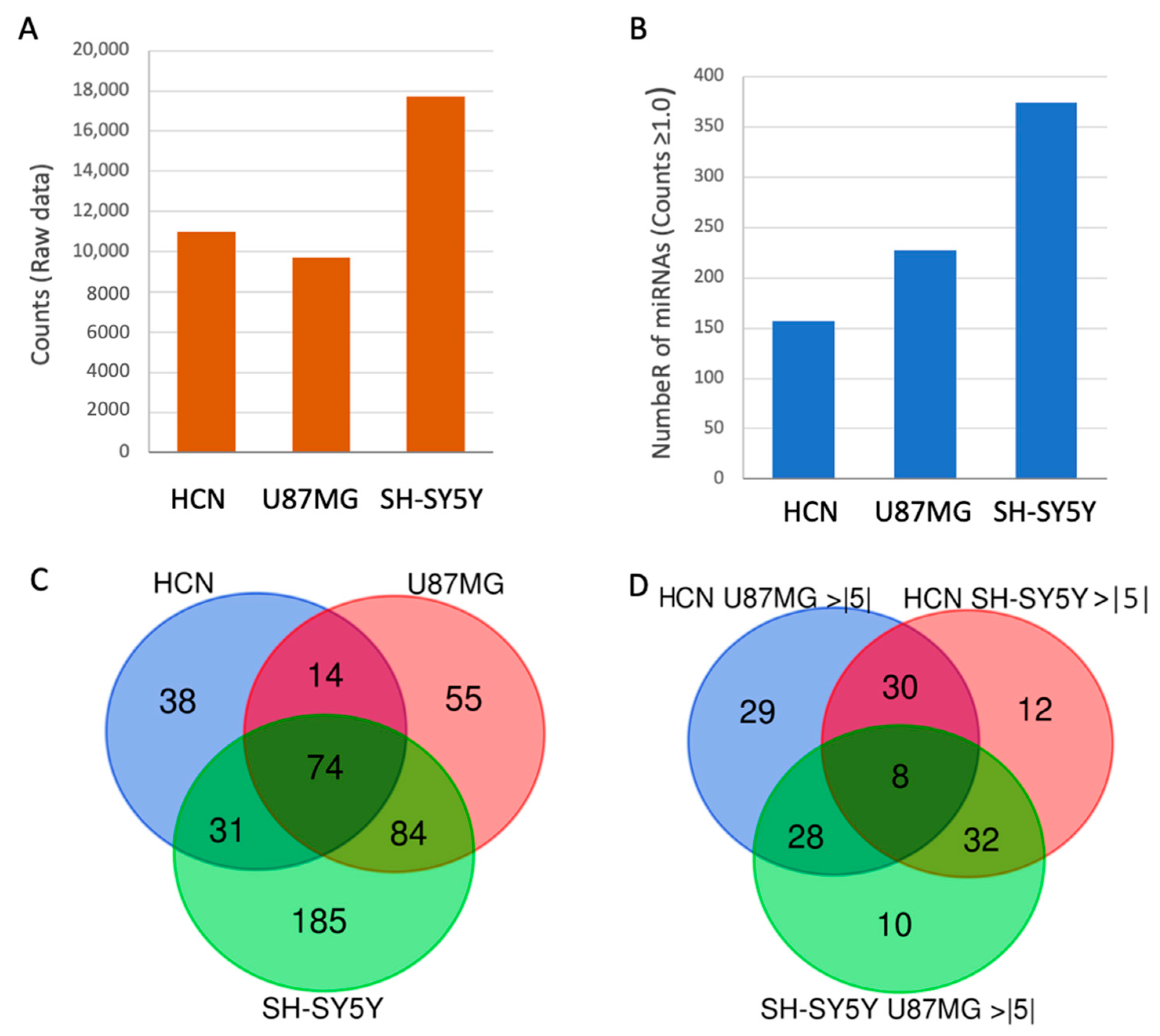
2.1. Isolation and Sequencing of Spliceosomal RNA from Neuronal Cell Lines
2.2. Changes in Expression of SF-miRNA Sequences in Neuronal Cancer Cells
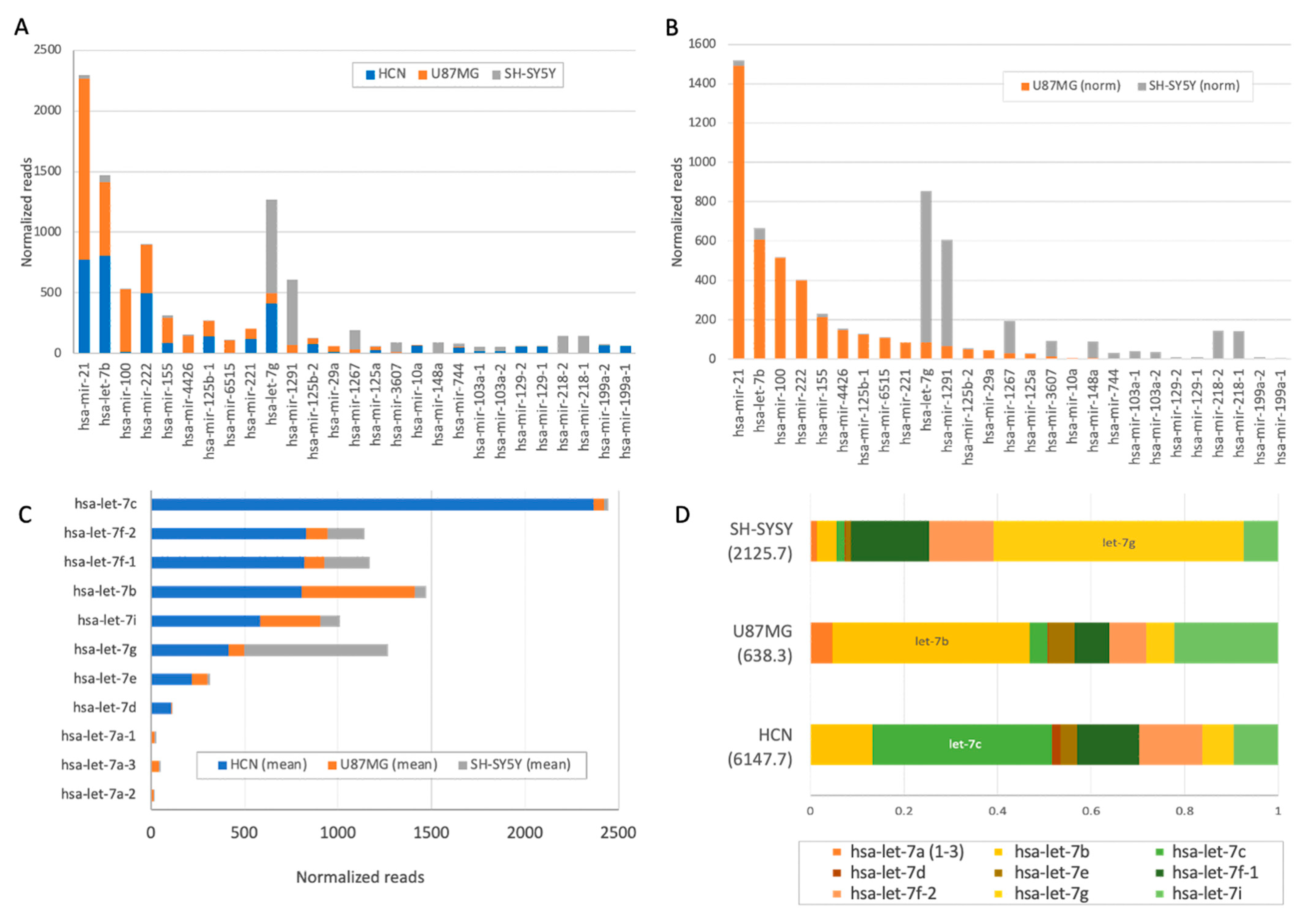
2.3. Comparison of the Differential Expression of SF-miRNAs in the Neuronal Cell Lines
2.4. Glioma and Glioblastoma Expression Trends
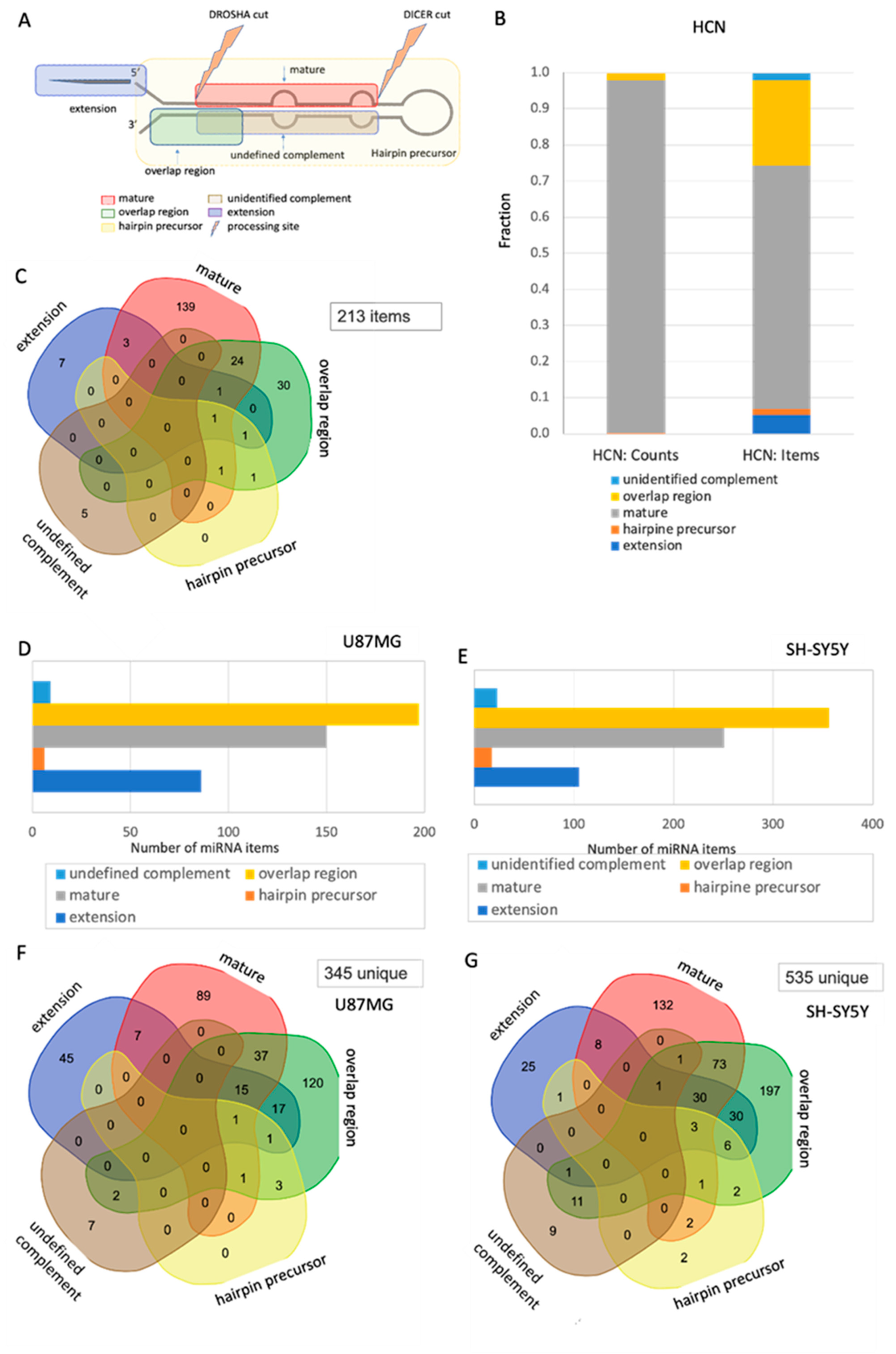
2.5. Changes in the Segmental Regions of SF-miRNA in Neuronal Cancer Cell Lines
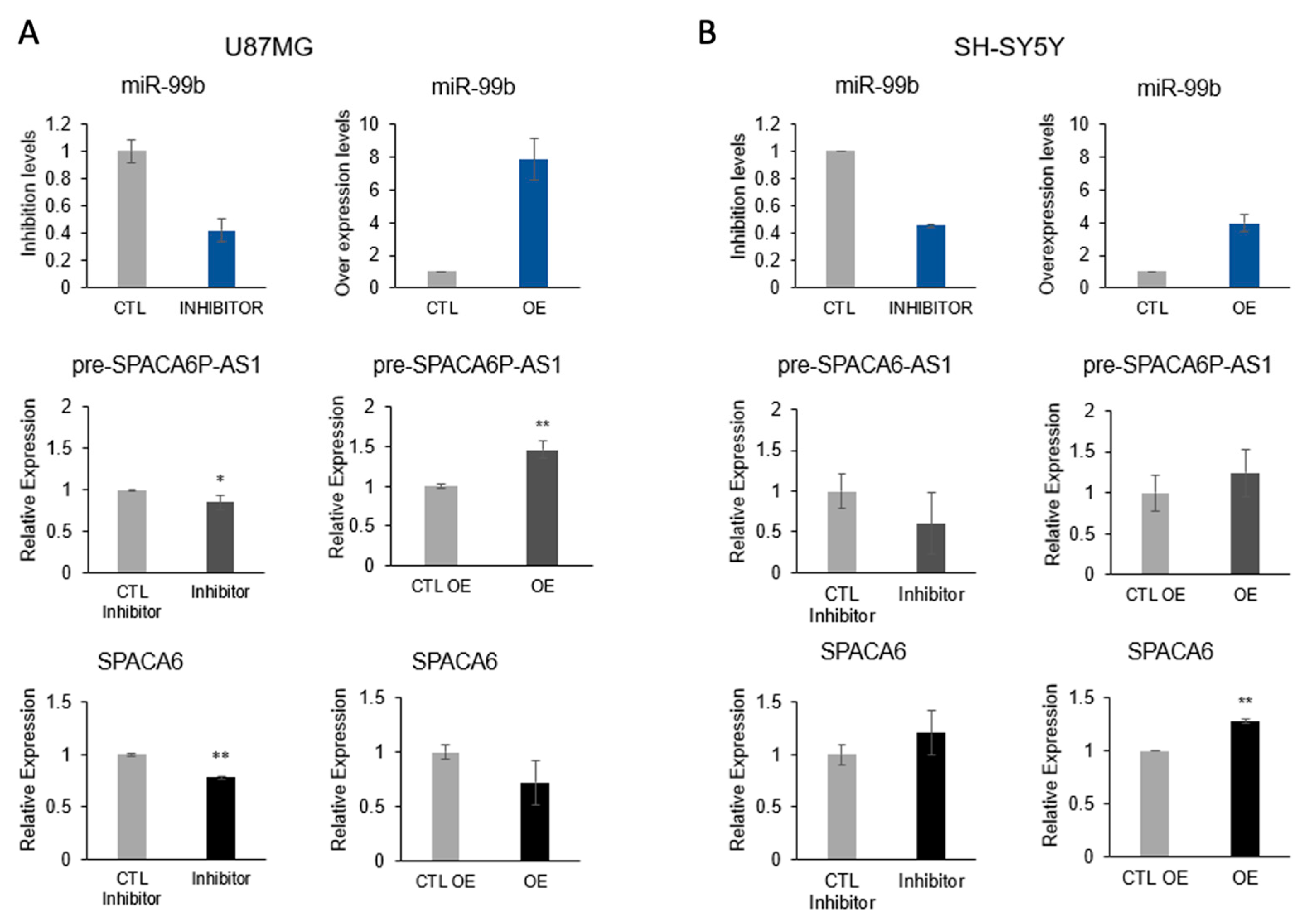
2.6. Spliceosomal miR-99b Inhibits Splicing of the lncRNA SPACA6-AS1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Isolation of Supraspliceosomes
4.3. Protein Detection
4.4. RNA Isolation from Supraspliceosomes and Deep Sequencing
4.5. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Analysis
4.6. Validation of Gene Expression of SPACA6 and SPACA6-AS1 Pre-mRNA
4.6.1. RT-PCR
4.6.2. RNA Isolation from Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Fractions
4.7. Quantitative PCR
4.7.1. Transfection
4.7.2. TaqMan microRNA Assay
4.7.3. RT of mRNA
4.7.4. Quantitative PCR Reaction
4.8. Statistical and Analytical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| SNORD | Small nucleolar RNA |
| FDR | False discover rate |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| HP | Hairpin precursor miRNA |
| lncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| PCR | False discover rate |
| RISC | RNA-induced silencing complex |
| RT | Reverse transcription |
| SF | Spliceosomal fraction |
| WB | Western blot |
References
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. microRNA in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, H.Y.; Norman, B.P.; Lai, K.S.; Rahman, N.; Alitheen, N.B.M.; Osman, M.A. The Regulatory Role of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabian, M.R.; Sonenberg, N. The mechanics of miRNA-mediated gene silencing: A look under the hood of miRISC. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, J.; Loedige, I.; Filipowicz, W. The widespread regulation of microRNA biogenesis, function and decay. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018, 173, 20–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, R.I.; Yan, K.P.; Amuthan, G.; Chendrimada, T.; Doratotaj, B.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. The Microprocessor complex mediates the genesis of microRNAs. Nature 2004, 432, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lee, Y.; Yeom, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jin, H.; Kim, V.N. The Drosha-DGCR8 complex in primary microRNA processing. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 3016–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lee, Y.; Yeom, K.H.; Nam, J.W.; Heo, I.; Rhee, J.K.; Sohn, S.Y.; Cho, Y.; Zhang, B.T.; Kim, V.N. Molecular basis for the recognition of primary microRNAs by the Drosha-DGCR8 complex. Cell 2006, 125, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landthaler, M.; Yalcin, A.; Tuschl, T. The human DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 and Its D. melanogaster homolog are required for miRNA biogenesis. Curr. Biol. 2004, 14, 2162–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Han, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Yim, J.; Lee, J.; Provost, P.; Radmark, O.; Kim, S.; et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 2003, 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.K.; Kim, V.N. Processing of intronic microRNAs. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, G.; Veneziano, D.; Acunzo, M.; Croce, C.M. Small non-coding RNA and cancer. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Shi, S.; Xie, H.; Peng, X.; Yin, W.; Tao, Y.; et al. miRNA-based biomarkers, therapies, and resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriely, G.; Wurdinger, T.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.C.; Burchard, J.; Linsley, P.S.; Krichevsky, A.M. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriely, G.; Yi, M.; Narayan, R.S.; Niers, J.M.; Wurdinger, T.; Imitola, J.; Ligon, K.L.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.; Stephens, R.M.; et al. Human glioma growth is controlled by microRNA-10b. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3563–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guessous, F.; Zhang, Y.; Dipierro, C.; Kefas, B.; Johnson, E.; Marcinkiewicz, L.; Jiang, J.; Yang, Y.; Schmittgen, T.D.; et al. MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting multiple oncogenes. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7569–7576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wijk, N.; Zohar, K.; Linial, M. Challenging Cellular Homeostasis: Spatial and Temporal Regulation of miRNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciafre, S.A.; Galardi, S. microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins: A complex network of interactions and reciprocal regulations in cancer. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, T.C. The MicroRNA Biology of the Mammalian Nucleus. Mol. Ther. 2014, 3, e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guil, S.; Esteller, M. RNA-RNA interactions in gene regulation: The coding and noncoding players. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2015, 40, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, V.; Li, L.C. miRNA goes nuclear. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, C.; He, Q.; Pan, Z.; Xiao, D.; Tao, Y. Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation, immunity and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in Control of Gene Expression: An Overview of Nuclear Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.Y.; Ma, L.M.; Guo, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Zhou, H.; Shao, P.; Chen, Y.Q.; Qu, L.H. Deep sequencing of human nuclear and cytoplasmic small RNAs reveals an unexpectedly complex subcellular distribution of miRNAs and tRNA 3′ trailers. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffries, C.D.; Fried, H.M.; Perkins, D.O. Nuclear and cytoplasmic localization of neural stem cell microRNAs. RNA 2011, 17, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohrt, T.; Mutze, J.; Staroske, W.; Weinmann, L.; Hock, J.; Crell, K.; Meister, G.; Schwille, P. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and fluorescence cross-correlation spectroscopy reveal the cytoplasmic origination of loaded nuclear RISC in vivo in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6439–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameyar-Zazoua, M.; Rachez, C.; Souidi, M.; Robin, P.; Fritsch, L.; Young, R.; Morozova, N.; Fenouil, R.; Descostes, N.; Andrau, J.C.; et al. Argonaute proteins couple chromatin silencing to alternative splicing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasanaro, P.; Greco, S.; Lorenzi, M.; Pescatori, M.; Brioschi, M.; Kulshreshtha, R.; Banfi, C.; Stubbs, A.; Calin, G.A.; Ivan, M.; et al. An integrated approach for experimental target identification of hypoxia-induced miR-210. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35134–35143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucci, E.; Patella, F.; Waage, J.; Holmstrom, K.; Lindow, M.; Porse, B.; Kauppinen, S.; Lund, A.H. microRNA-9 targets the long non-coding RNA MALAT1 for degradation in the nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Wiklund, E.D.; Bramsen, J.B.; Villadsen, S.B.; Statham, A.L.; Clark, S.J.; Kjems, J. miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, L.; Zhu, D.; Hou, D.; Cao, T.; Gu, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Zen, K. Mouse miRNA-709 directly regulates miRNA-15a/16-1 biogenesis at the posttranscriptional level in the nucleus: Evidence for a microRNA hierarchy system. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 504–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, K.; Nishi, A.; Nagasawa, T.; Ui-Tei, K. Human TNRC6A is an Argonaute-navigator protein for microRNA-mediated gene silencing in the nucleus. RNA 2013, 19, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Saetrom, P.; Snove, O., Jr.; Rossi, J.J. MicroRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 16230–16235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younger, S.T.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Corey, D.R. Predicting potential miRNA target sites within gene promoters. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 3791–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.V.; Santoso, S.; Turner, A.M.; Pastori, C.; Hawkins, P.G. Bidirectional transcription directs both transcriptional gene activation and suppression in human cells. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Kim, D.; Morris, K.V. Promoter-associated RNA is required for RNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12422–12427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.C.; Younger, S.T.; Nguyen, N.B.; Hardy, D.B.; Monia, B.P.; Corey, D.R.; Janowski, B.A. Antisense transcripts are targets for activating small RNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2008, 15, 842–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Schwartz, J.C.; Chu, Y.; Younger, S.T.; Gagnon, K.T.; Elbashir, S.; Janowski, B.A.; Corey, D.R. Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs at sequences downstream from 3’ gene termini. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S.W.; Zang, J.B.; Mele, A.; Darnell, R.B. Argonaute HITS-CLIP decodes microRNA-mRNA interaction maps. Nature 2009, 460, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomron, N.; Levy, C. MicroRNA-biogenesis and Pre-mRNA splicing crosstalk. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2009, 2009, 594678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattioli, C.; Pianigiani, G.; Pagani, F. Cross talk between spliceosome and microprocessor defines the fate of pre-mRNA. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2014, 5, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, N.; Fujita, M.; Ohno, M. Functional association of the Microprocessor complex with the spliceosome. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3243–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiohama, A.; Sasaki, T.; Noda, S.; Minoshima, S.; Shimizu, N. Nucleolar localization of DGCR8 and identification of eleven DGCR8-associated proteins. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 4196–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janas, M.M.; Khaled, M.; Schubert, S.; Bernstein, J.G.; Golan, D.; Veguilla, R.A.; Fisher, D.E.; Shomron, N.; Levy, C.; Novina, C.D. Feed-forward microprocessing and splicing activities at a microRNA-containing intron. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1002330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allo, M.; Buggiano, V.; Fededa, J.P.; Petrillo, E.; Schor, I.; de la Mata, M.; Agirre, E.; Plass, M.; Eyras, E.; Elela, S.A.; et al. Control of alternative splicing through siRNA-mediated transcriptional gene silencing. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2009, 16, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agranat-Tamir, L.; Shomron, N.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Interplay between pre-mRNA splicing and microRNA biogenesis within the supraspliceosome. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4640–4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnal, S.C.; Lopez-Oreja, I.; Valcarcel, J. Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer—Implications for care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ule, J.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative Splicing Regulatory Networks: Functions, Mechanisms, and Evolution. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marasco, L.E.; Kornblihtt, A.R. The physiology of alternative splicing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2023, 24, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. RNA Splicing by the Spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, J.; Azubel, M.; Sperling, R. Structure and Function of the Pre-mRNA Splicing Machine. Structure 2008, 16, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperling, R. The nuts and bolts of the endogenous spliceosome. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2017, 8, e1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azubel, M.; Habib, N.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Native spliceosomes assemble with pre-mRNA to form supraspliceosomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 356, 955–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Krausz, S.; Sperling, R.; Sperling, J. Exploring the architecture of the intact supraspliceosome using electron microscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlab-Aviv, S.; Boulos, A.; Peretz, A.R.; Eliyahu, T.; Carmel, L.; Sperling, R.; Linial, M. Small RNA sequences derived from pre-microRNAs in the supraspliceosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 11014–11029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahlab-Aviv, S.; Zohar, K.; Cohen, Y.; Peretz, A.R.; Eliyahu, T.; Linial, M.; Sperling, R. Spliceosome-Associated microRNAs Signify Breast Cancer Cells and Portray Potential Novel Nuclear Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R. Small non-coding RNA within the endogenous spliceosome and alternative splicing regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafat, M.; Sperling, R. Crosstalk between Long Non-Coding RNA and Spliceosomal microRNA as a Novel Biomarker for Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spann, P.; Feinerman, M.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Isolation and visualization of large compact ribonucleoprotein particles of specific nuclear RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, B.; Zhang, Z.; Raitskin, O.; Hiller, M.; Benderska, N.; Hartmann, A.M.; Bracco, L.; Elliott, D.; Ben-Ari, S.; Soreq, H.; et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein G regulates splice site selection by binding to CC(A/C)-rich regions in pre-mRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14303–14315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raitskin, O.; Angenitzki, M.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Large nuclear RNP particles-the nuclear pre-mRNA processing machine. J. Struct. Biol. 2002, 140, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotzer-Nevo, H.; de Lima Alves, F.; Rappsilber, J.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Supraspliceosomes at Defined Functional States Portray the Pre-Assembled Nature of the pre-mRNA Processing Machine in the Cell Nucleus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11637–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falaleeva, M.; Pages, A.; Matsuzek, Z.; Hidmi, S.; Agranat-Tamir, L.; Korotkov, K.; Nevo, Y.; Eyras, E.; Sperling, R.; Stamm, S. dual function of C/d box snoRNAs in rRNA modification and alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1625–E1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Ding, Q.; Han, H.; Wu, D. miRCancer: A microRNA-cancer association database constructed by text mining on literature. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Chen, Z.; Lin, B.; Zhang, S.; Qu, J. A seven-lncRNA signature for predicting prognosis in breast carcinoma. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 4033–4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Palo, A.; Siniscalchi, C.; Mosca, N.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. A Novel ceRNA Regulatory Network Involving the Long Non-Coding Antisense RNA SPACA6P-AS, miR-125a and its mRNA Targets in Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Falaleeva, M.; Agranat-Tamur, L.; Pages, A.P.; Eyras, E.E.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R.; Stamm, S. The 5’ untranslated region of the serotonin receptor 2C pre-mRNA generates miRNAs and is expressed in non-neuronal cells. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 230, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Khoshbakht, T.; Hussen, B.M.; Taheri, M.; Samadian, M. A Review on the Role of miR-1246 in the Pathoetiology of Different Cancers. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 771835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yitzhaki, S.; Miriami, E.; Sperling, J.; Sperling, R. Phosphorylated Ser/Arg-rich proteins: Limiting factors in the assembly of 200S large nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8830–8835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SF-miRNA | HCN (%) | U87MG (%) | SH-SY5Y (%) | Total Counts | Function in CNS Cancer a |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-mir-1246 | 3.27 | 24.73 | 72.00 | 5963.50 | OncomiR: exosome, regulates Wnt/β-catenin and TP53 |
| hsa-mir-21 | 33.77 | 64.92 | 1.32 | 2294.20 | OncomiR: cell proliferation, invasion |
| hsa-mir-222 | 55.32 | 44.66 | 0.02 | 898.40 | cell cycle progression |
| hsa-mir-20a | 0.77 | 59.41 | 39.81 | 816.70 | miR-17-92 cluster: oncogenic: proliferation, invasion, |
| hsa-mir-7704 | 5.84 | 72.12 | 22.04 | 792.60 | U.D., regulating HAGLR |
| hsa-mir-19b-1 | 0.25 | 60.57 | 39.18 | 788.50 | miR-17-92 cluster: oncogenic: proliferation, invasion, |
| hsa-mir-1291 | 0.28 | 11.01 | 88.72 | 610.60 | U.D. |
| hsa-mir-3198-2 | 0.00 | 54.17 | 45.83 | 593.90 | U.D. |
| hsa-mir-100 | 2.59 | 97.34 | 0.09 | 529.90 | tumor suppressor, targeting mTOR, FGFR3, and IGF1R. |
| hsa-mir-3687 | 0.87 | 41.31 | 57.84 | 423.60 | U.D. |
| hsa-mir-92a-1 | 13.35 | 51.31 | 35.36 | 417.10 | miR-17-92 cluster: oncogenic: proliferation, invasion, |
| hsa-mir-92a-2 | 14.68 | 50.37 | 34.92 | 374.60 | miR-17-92 cluster: oncogenic: proliferation, invasion, |
| hsa-mir-320a | 47.03 | 30.14 | 22.83 | 360.00 | tumor suppressor: inhibit angiogenesis and migration. |
| hsa-mir-155 | 26.82 | 67.58 | 5.60 | 314.30 | immune response, STAT3 signaling |
| hsa-mir-27b | 78.53 | 5.81 | 15.69 | 302.70 | conflict: anti-migration. apoptosis, stemness |
| hsa-mir-125b-1 | 52.31 | 45.70 | 1.99 | 270.90 | inhibiting proliferation and regulate apoptosis |
| hsa-mir-221 | 58.17 | 41.83 | 0.00 | 206.30 | driving proliferation, survival, invasion, apoptosis |
| hsa-mir-3064 | 7.24 | 41.43 | 51.33 | 203.00 | U.D. |
| hsa-mir-1267 | 0.00 | 16.05 | 83.95 | 195.00 | U.D. |
| hsa-mir-423 | 29.02 | 37.62 | 33.37 | 193.00 | cell growth via p21 and p53-related pathways |
| hsa-mir-24-2 | 81.85 | 5.85 | 12.30 | 182.90 | tumor-suppressive effects |
| hsa-mir-26a-1 | 73.28 | 11.12 | 15.67 | 158.30 | tumor-suppressive effects |
| hsa-mir-26a-2 | 71.48 | 12.16 | 16.36 | 157.10 | tumor-suppressive effects |
| hsa-mir-4426 | 0.00 | 95.90 | 4.10 | 153.80 | U.D. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mahlab-Aviv, S.; Swissa, K.O.; Arafat, M.; Zohar, K.; Peretz, A.R.; Linial, M.; Sperling, R. Nuclear Roles of Spliceosome-Associated microRNAs in Neuronal Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178349
Mahlab-Aviv S, Swissa KO, Arafat M, Zohar K, Peretz AR, Linial M, Sperling R. Nuclear Roles of Spliceosome-Associated microRNAs in Neuronal Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178349
Chicago/Turabian StyleMahlab-Aviv, Shelly, Keren Or Swissa, Maram Arafat, Keren Zohar, Ayelet Rachel Peretz, Michal Linial, and Ruth Sperling. 2025. "Nuclear Roles of Spliceosome-Associated microRNAs in Neuronal Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178349
APA StyleMahlab-Aviv, S., Swissa, K. O., Arafat, M., Zohar, K., Peretz, A. R., Linial, M., & Sperling, R. (2025). Nuclear Roles of Spliceosome-Associated microRNAs in Neuronal Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8349. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178349







