The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Skin of Aged Female Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Effects of MR and GR Antagonists on mRNA Expression of MR/GR Markers in Skin Isolated from Vehicle or RELA-, EPL-, or MIRI-Treated Mice
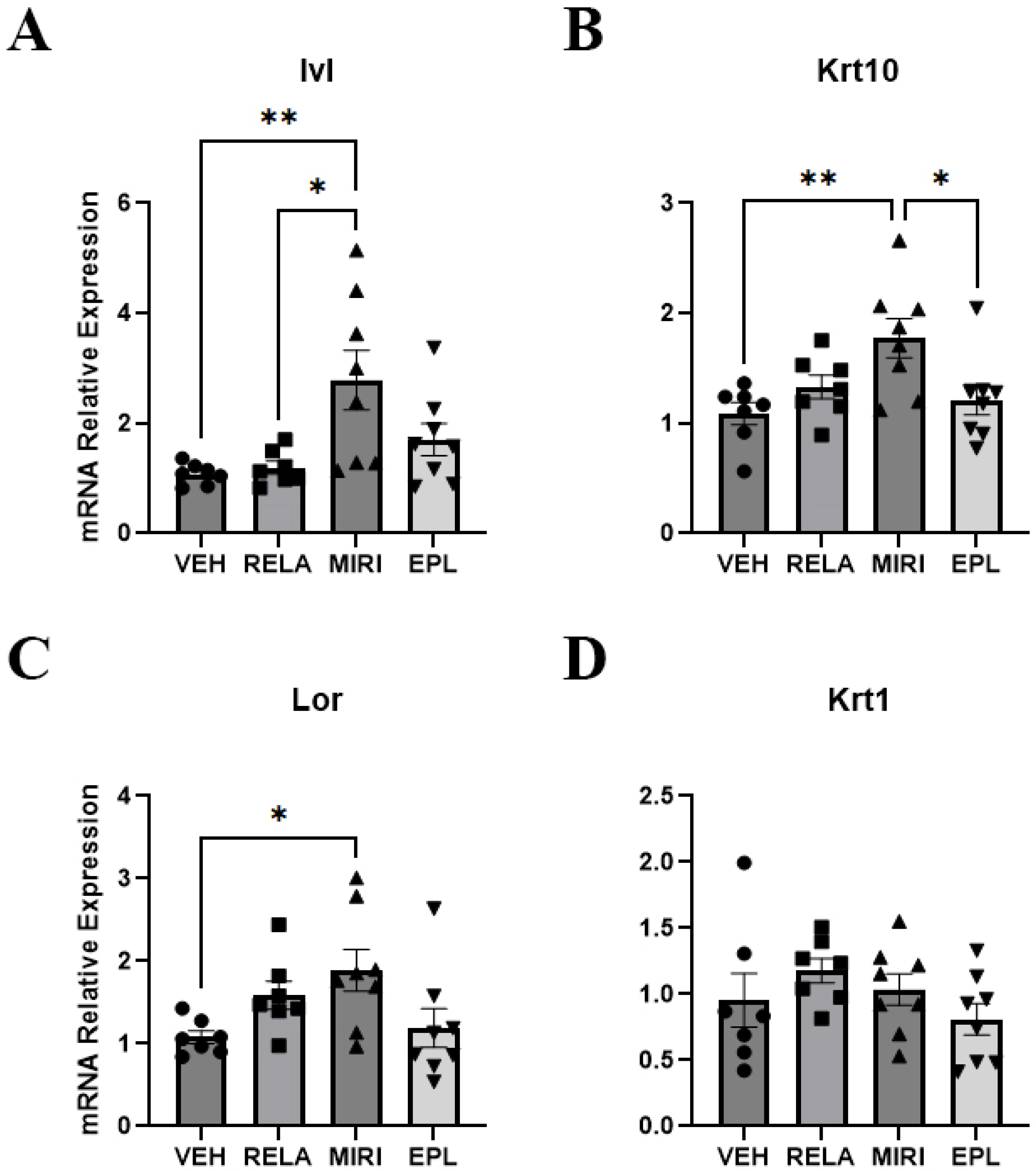
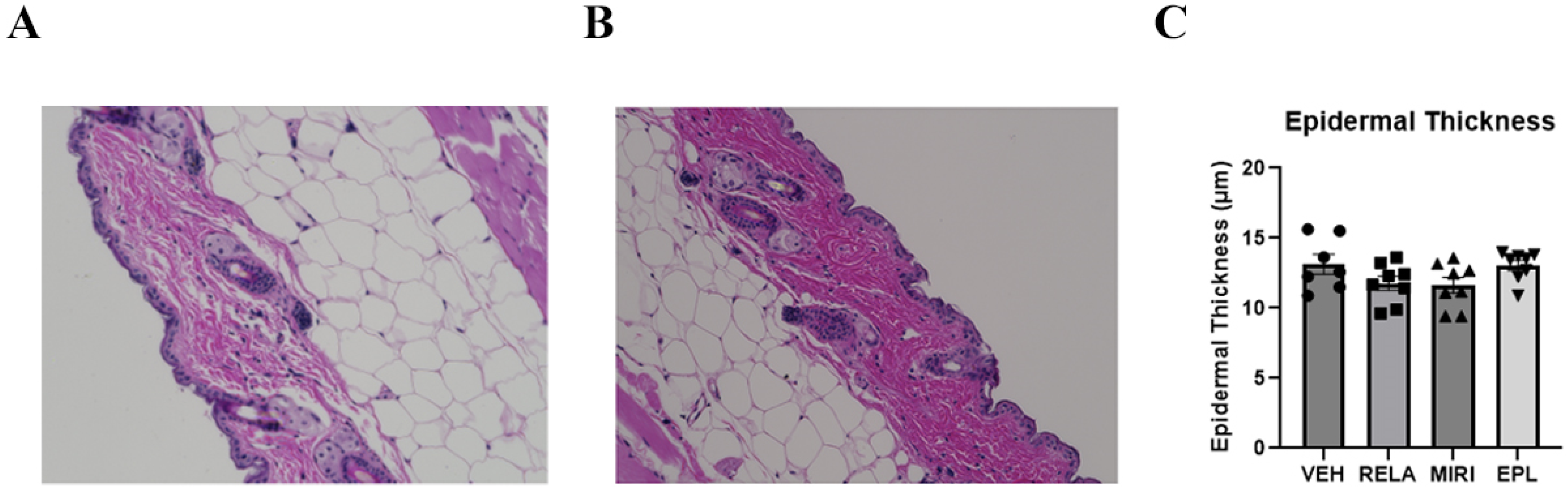
2.2. The Effects of MR and GR Antagonists on mRNA Expression of Keratinocyte Proliferation and Differentiation Markers and Epidermal Thickness in Skin Isolated from Vehicle- or RELA-, EPL, or MIRI-Treated Mice
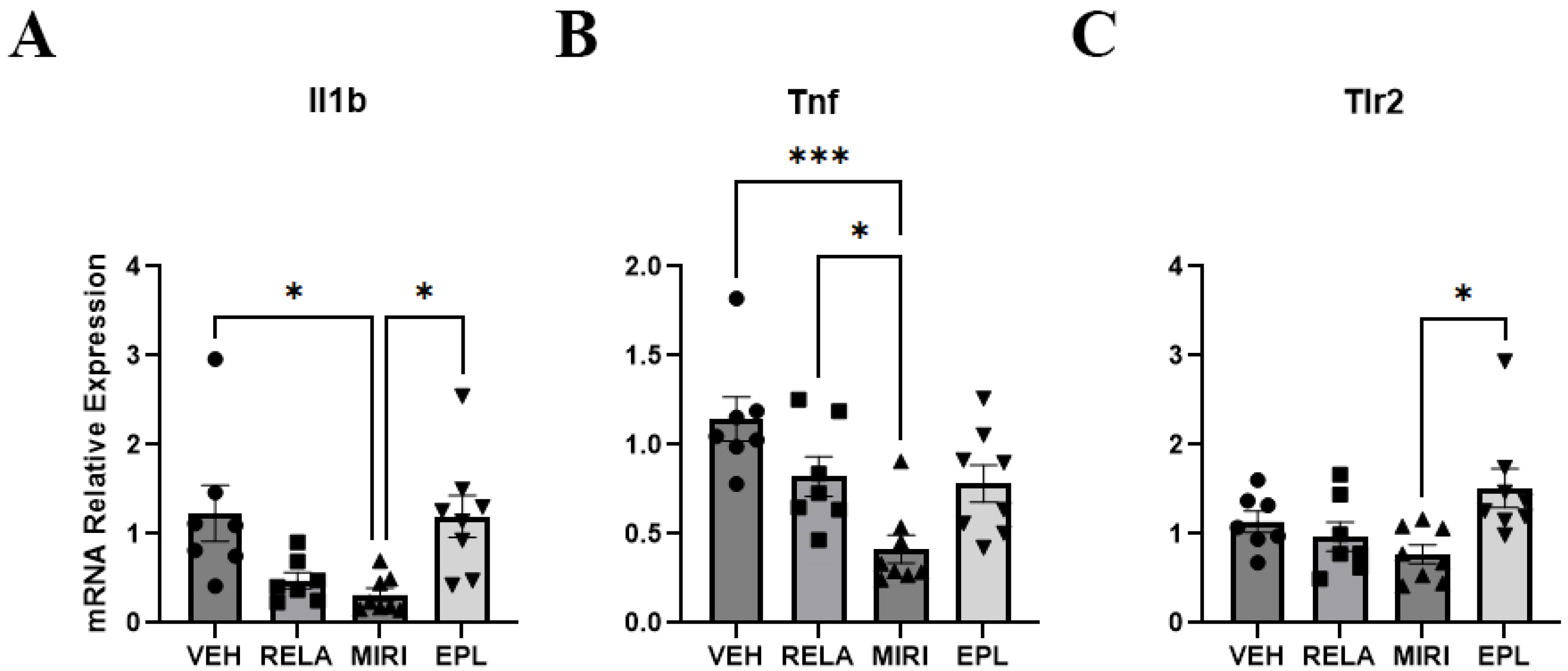
2.3. The Effects of MR and GR Antagonists on mRNA Expression of Inflammation Markers in the Skin Isolated from Vehicle-, RELA-, EPL-, or MIRI-Treated Mice
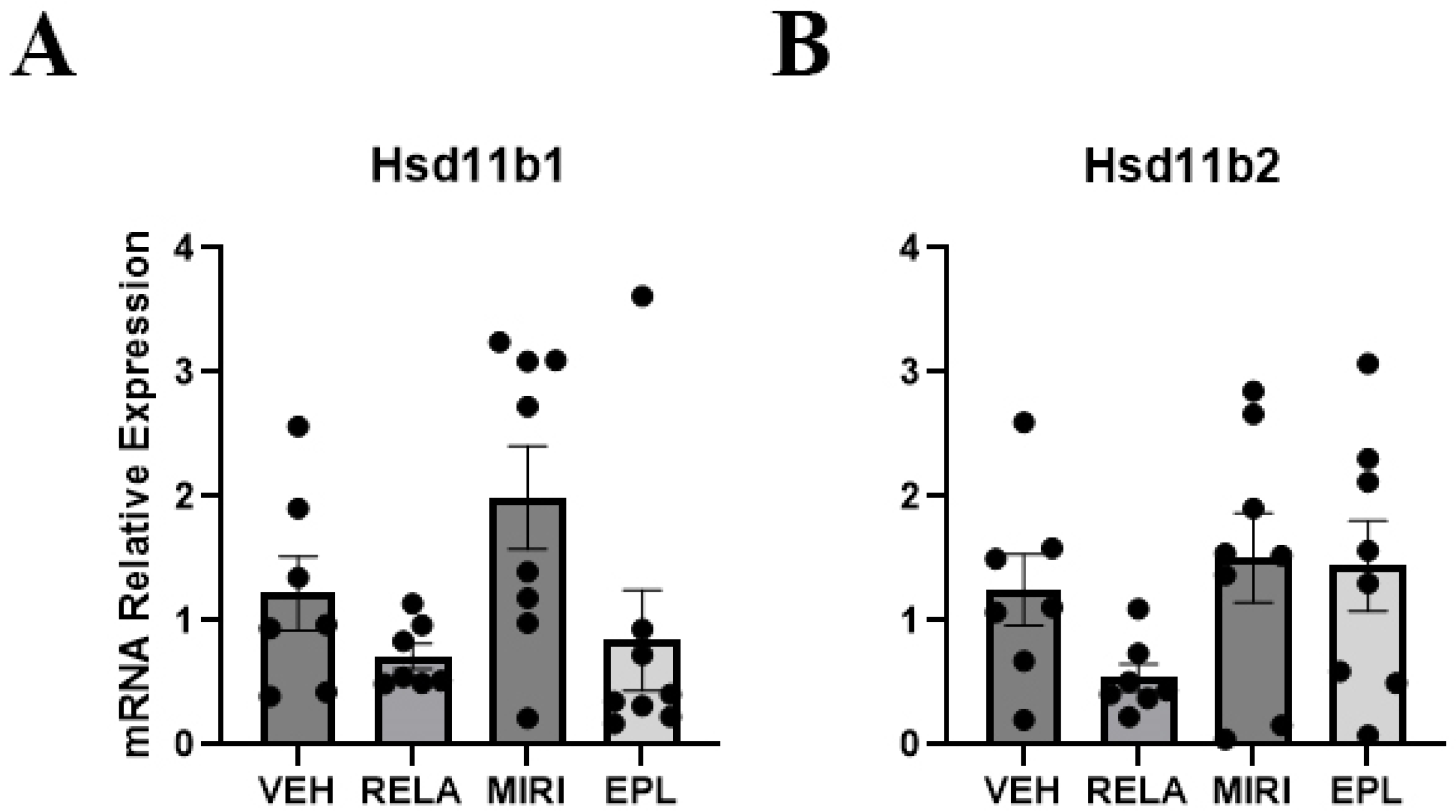
2.4. The Effects of MR and GR Antagonists on mRNA Expression of MR/GR Activity Regulators in Skin Isolated from Vehicle- or RELA-, EPL-, or MIRI-Treated Mice
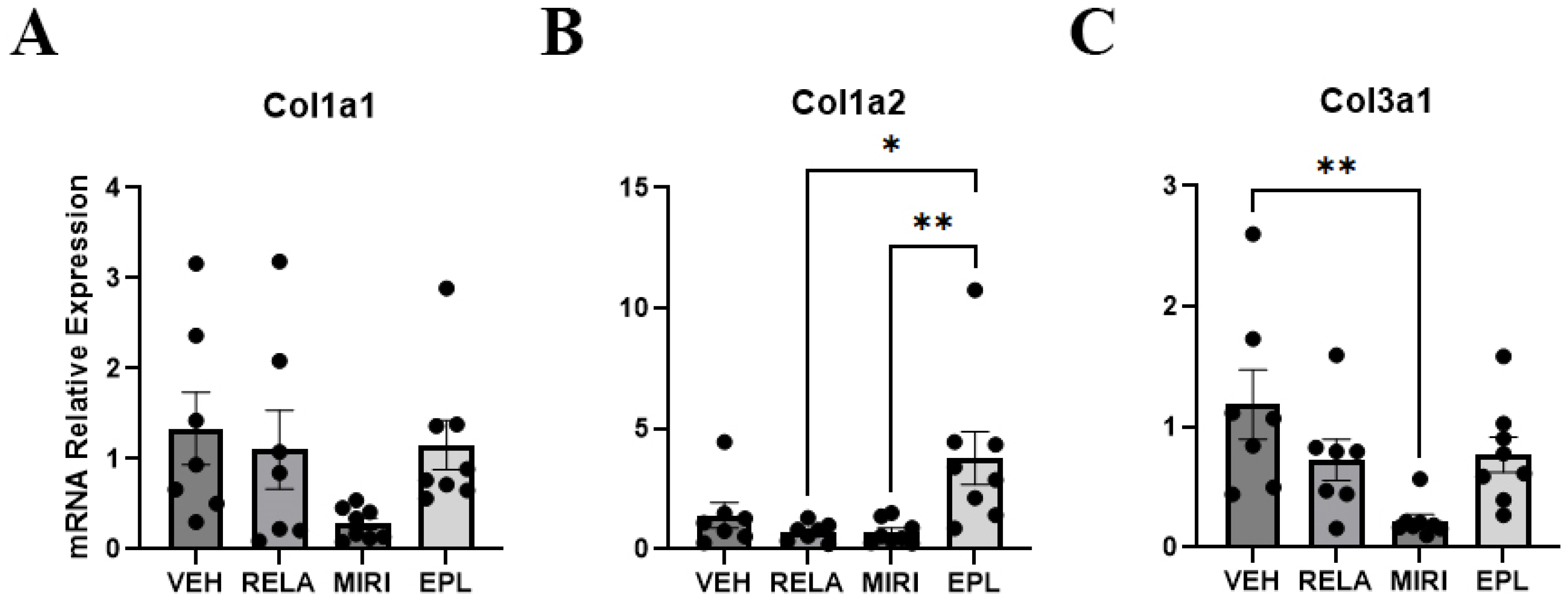
2.5. The Effects of MR and GR Antagonists on mRNA Expression of Dermal Extracellular Matrix Markers in Skin Isolated from Vehicle-, RELA-, EPL-, or MIRI-Treated Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. Sample Preparation
4.3. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR
4.4. Determination of Epidermal Thickness
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dąbrowska, A.K.; Spano, F.; Derler, S.; Adlhart, C.; Spencer, N.D.; Rossi, R.M. The relationship between skin function, barrier properties, and body-dependent factors. Skin Res. Technol. 2018, 24, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Bejaoui, M.; Isoda, H. Regulation of keratinocyte proliferation and differentiation by secoiridoid oleacein in monoculture and fibroblast co-culture models. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 185, 117985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, S. Anatomy, skin (integument), epidermis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/nbk/nbk470464 (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Chourpiliadis, C.; Aeddula, N.R. Physiology, glucocorticoids. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023; Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/NBK/nbk560897 (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Bigas, J.; Sevilla, L.M.; Carceller, E.; Boix, J.; De Felipe, B.; Pérez, P. Epidermal glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors act cooperatively to regulate epidermal development and counteract skin inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-κB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, L.M.; Pérez, P. Roles of the glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in skin pathophysiology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boix, J.; Sevilla, L.M.; Sáez, Z.; Carceller, E.; Pérez, P. Epidermal mineralocorticoid receptor plays beneficial and adverse effects in skin and mediates glucocorticoid responses. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2417–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagase, T.; Akase, T.; Sanada, H.; Minematsu, T.; Ibuki, A.; Huang, L.; Asada, M.; Yoshimura, K.; Nagase, M.; Shimada, T.; et al. Aging-like skin changes in metabolic syndrome model mice are mediated by mineralocorticoid receptor signaling. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitts, T.F.; Bunda, S.; Wang, Y.; Hinek, A. Aldosterone and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists modulate elastin and collagen deposition in human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2396–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, A.; Kratschmar, D.V. Tissue-specific modulation of mineralocorticoid receptor function by 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: An overview. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2012, 350, 168–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayo, P.; Sanchis, A.; Bravo, A.; Cascallana, J.L.; Buder, K.; Tuckermann, J.; Schütz, G.; Pérez, P. Glucocorticoid receptor is required for skin barrier competence. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevilla, L.M.; Latorre, V.; Sanchis, A.; Boix, J.; Ferrer, A.; Pérez, P. Epidermal inactivation of the glucocorticoid receptor triggers skin barrier defects and cutaneous inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Menuet, D.; Viengchareun, S.; Muffat-Joly, M.; Zennaro, M.C.; Lombès, M. Expression and function of the human mineralocorticoid receptor: Lessons from transgenic mouse models. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2004, 217, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carceller-Zazo, E.; Sevilla, L.M.; Pons-Alonso, O.; Chiner-Oms, Á.; Amazit, L.; Vu, T.A.; Vitellius, G.; Viengchareun, S.; Comas, I.; Jaszczyszyn, Y.; et al. The mineralocorticoid receptor modulates timing and location of genomic binding by glucocorticoid receptor in response to synthetic glucocorticoids in keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.T.; Farman, N.; Maubec, E.; Nassar, D.; Desposito, D.; Waeckel, L.; Aractingi, S.; Jaisser, F. Re-epithelialization of pathological cutaneous wounds is improved by local mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2080–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maubec, E.; Laouénan, C.; Deschamps, L.; Nguyen, V.T.; Scheer-Senyarich, I.; Wackenheim-Jacobs, A.C.; Steff, M.; Duhamel, S.; Tubiana, S.; Brahimi, N.; et al. Topical mineralocorticoid receptor blockade limits glucocorticoid-induced epidermal atrophy in human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollag, W.B.; Aitkens, L.; White, J.; Hyndman, K.A. Aquaporin-3 in the epidermis: More than skin deep. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2020, 318, C1144–C1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara-Chikuma, M.; Verkman, A.S. Roles of aquaporin-3 in the epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 2145–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: Molecular mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 1998, 94, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belden, Z.; Deiuliis, J.A.; Dobre, M.; Rajagopalan, S. The role of the mineralocorticoid receptor in inflammation: Focus on kidney and vasculature. Am. J. Nephrol. 2017, 46, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelse, K.; Pöschl, E.; Aigner, T. Collagens—Structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2003, 55, 1531–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Stournaras, C.; Zacharopoulou, N.; Voelkl, J.; Alesutan, I. Serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 and the response to cell stress. Cell Stress 2019, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tak, P.P.; Firestein, G.S. NF-κB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 107, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, N.F.; Bollag, W.B. The role of the mineralocorticoid receptor in skin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2025, 608, 112628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Bai, M.; Guo, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Fan, X.; Sun, R.; Yang, X.; Yuan, D.; Shi, Y.; et al. Inhibition of serum- and glucocorticoid-regulated protein kinase-1 aggravates imiquimod-induced psoriatic dermatitis and enhances proinflammatory cytokine expression through the NF-κB pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 143, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Lin, J.-M.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lin, L.; Xu, J.; Du, J. Exploring the common pathogenic mechanisms of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis: The interaction between SGK1 and TIGIT signaling pathways. Inflammation 2025, 48, 1257–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuller, P.J.; Yang, J.; Young, M.J.; Cole, T.J. Mechanisms of ligand-mediated modulation of mineralocorticoid receptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2025, 600, 112504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tsoi, L.C.; Billi, A.C.; Ward, N.L.; Harms, P.W.; Zeng, C.; Maverakis, E.; Kahlenberg, J.M.; Gudjonsson, J.E. Cytokinocytes: The diverse contribution of keratinocytes to immune responses in skin. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e142067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koning, A.-S.C.A.M.; Buurstede, J.C.; van Weert, L.T.C.M.; Meijer, O.C. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptors in the brain: A transcriptional perspective. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1917–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casamassimi, A.; Ciccodicola, A. Transcriptional regulation: Molecules, involved mechanisms, and misregulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, J.; Bajaj, T.; Klengel, C.; Chatzinakos, C.; Ebert, T.; Dedic, N.; McCullough, K.M.; Lardenoije, R.; Joëls, M.; Meijer, O.C.; et al. Mineralocorticoid receptors dampen glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity to stress via regulation of FKBP5. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Rosa, D.A.; Ramos-Hernandez, Z.; Weller-Perez, J.; Johnson, T.A.; Hager, G.L. The impact of mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor interaction on corticosteroid transcriptional outcomes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2024, 594, 112389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D regulated keratinocyte differentiation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keidar, S.; Hayek, T.; Kaplan, M.; Pavlotzky, E.; Hamoud, S.; Coleman, R.; Aviram, M. Effect of eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, on blood pressure, serum and macrophage oxidative stress, and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 41, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Saito, Y.; Naya, N.; Imagawa, K.; Somekawa, S.; Kawata, H.; Takeda, Y.; Uemura, S.; Kishimoto, I.; Nakao, K. The specific mineralocorticoid receptor blocker eplerenone attenuates left ventricular remodeling in mice lacking the gene encoding guanylyl cyclase-A. Hypertens. Res. 2008, 31, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zitt, E.; Eller, K.; Huber, J.M.; Kirsch, A.H.; Tagwerker, A.; Mayer, G.; Rosenkranz, A.R. The selective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist eplerenone is protective in mild anti-GBM glomerulonephritis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 606–615. [Google Scholar][Green Version]

| Markers of MR/GR | Proliferative KCs | Differentiative KCs | Inflammatory Markers | Regulators of MR/GR Activity | Dermal ECM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sgk1 (↑MIRI) | Aqp3 | Ivl (↑MIRI) | Il1a | Hsd11b1 | Col1a1 |
| Scnn1a | Krt5 | Krt1 | Il1b (↓MIRI) | Hsd11b2 | Col2a1 (EPL > MIRI, RELA) |
| Scnn1g (↓RELA) | Ccnd1 | Krt10 (↑MIRI) | Il6 | Col3a1 (↓MIRI) | |
| Nr3c1 (EPL > MIRI) | Lor (↑MIRI) | Tnf (↓MIRI) | |||
| Nr3c2 | Tlr4 | ||||
| Tlr2 (EPL > MIRI) |
| Primer Name | Source | Identifier |
|---|---|---|
| Sgk1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00441380_m1 |
| Scnn1a | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00803386_m1 |
| Scnn1g | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00441228_m1 |
| Nr3c1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00433832_m1 |
| Nr3c2 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01241596_m1 |
| Aqp3 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01208559_m1 |
| Krt5 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01305291_g1 |
| Ccnd1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00432359_m1 |
| Ivl | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00515219_s1 |
| Krt1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00492992_g1 |
| Krt10 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm03009921_m1 |
| Lor | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01219285_m1 |
| Il1a | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00439620_m1 |
| Il1b | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01336189_m1 |
| Il6 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm99999064_m1 |
| Tnf | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00443259_m1 |
| Tlr4 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00445273_m1 |
| Tlr2 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01213946_g1 |
| Hsd11b1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00476182_m1 |
| Hsd11b2 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm01251104_m1 |
| Col1a1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00801666_g1 |
| Col1a2 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm000483888_m1 |
| Col3a1 | ThermoFisher Scientific | Mm00802300_m1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, A.; Fossas De Mello, N.; Luo, Y.; Bensreti, H.; Melynk, S.; Shaver, J.C.; Choudhary, V.; McGee-Lawrence, M.E.; Bollag, W.B. The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Skin of Aged Female Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178346
Ali A, Fossas De Mello N, Luo Y, Bensreti H, Melynk S, Shaver JC, Choudhary V, McGee-Lawrence ME, Bollag WB. The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Skin of Aged Female Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178346
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, Ameena, Natalia Fossas De Mello, Yonghong Luo, Husam Bensreti, Samuel Melynk, Joseph C. Shaver, Vivek Choudhary, Meghan E. McGee-Lawrence, and Wendy B. Bollag. 2025. "The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Skin of Aged Female Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178346
APA StyleAli, A., Fossas De Mello, N., Luo, Y., Bensreti, H., Melynk, S., Shaver, J. C., Choudhary, V., McGee-Lawrence, M. E., & Bollag, W. B. (2025). The Effect of Glucocorticoid and Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists in the Skin of Aged Female Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8346. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178346






