Immunological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: From Inflammatory Response to Neurorepair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Sequential Role of the Immune System in CIRI
2.1. Acute Phase
2.2. Subacute Phase
2.3. Chronic Phase
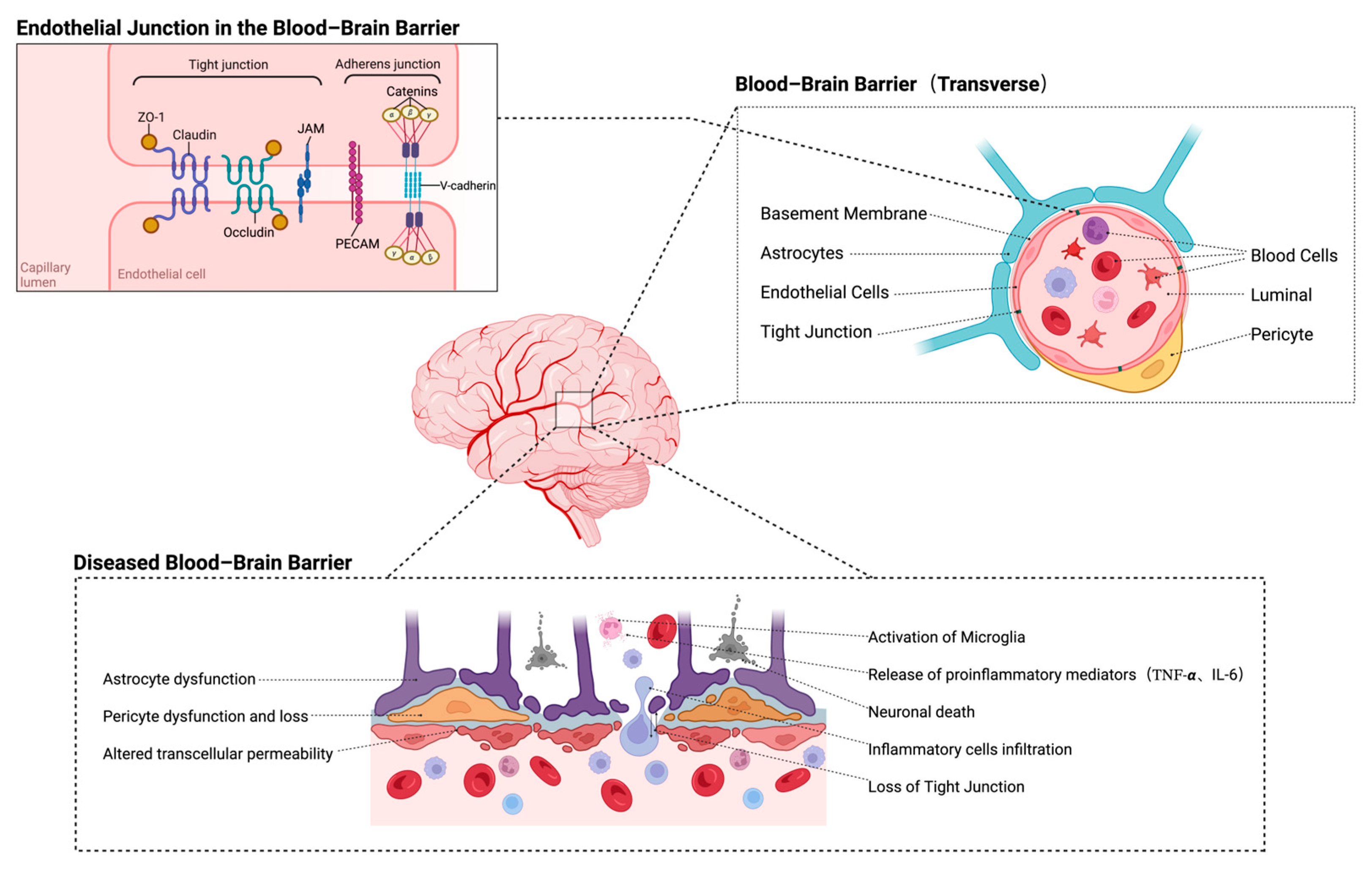
3. The Interaction Between the BBB and Immune Regulatory Mechanisms
4. Resident Immune Cells and Astrocytes in CIRI
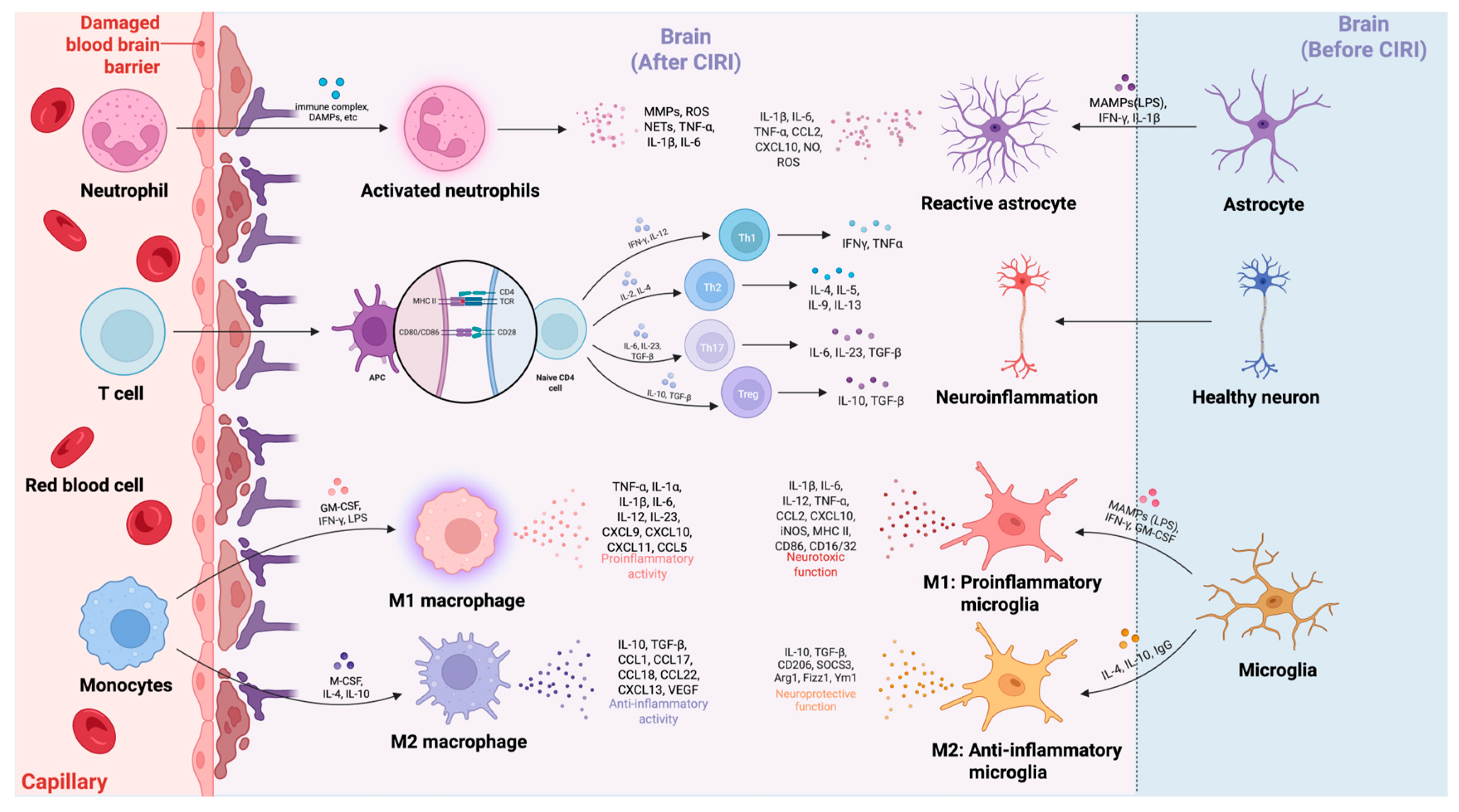
4.1. Microglia
4.1.1. Physiological Role of Microglia in the CNS
4.1.2. Microglia in CIRI
4.2. Astrocytes
4.2.1. The Physiological Roles of Astrocytes in the CNS
4.2.2. Astrocytes in CIRI
5. Peripheral Immune Cells and Platelets in CIRI
5.1. Neutrophils
5.2. MoDMs
5.3. T Cells
5.4. Platelets
6. The Interaction Between Cerebral Cellular and Peripheral Immune Cells in Driving Inflammatory Cascade Responses
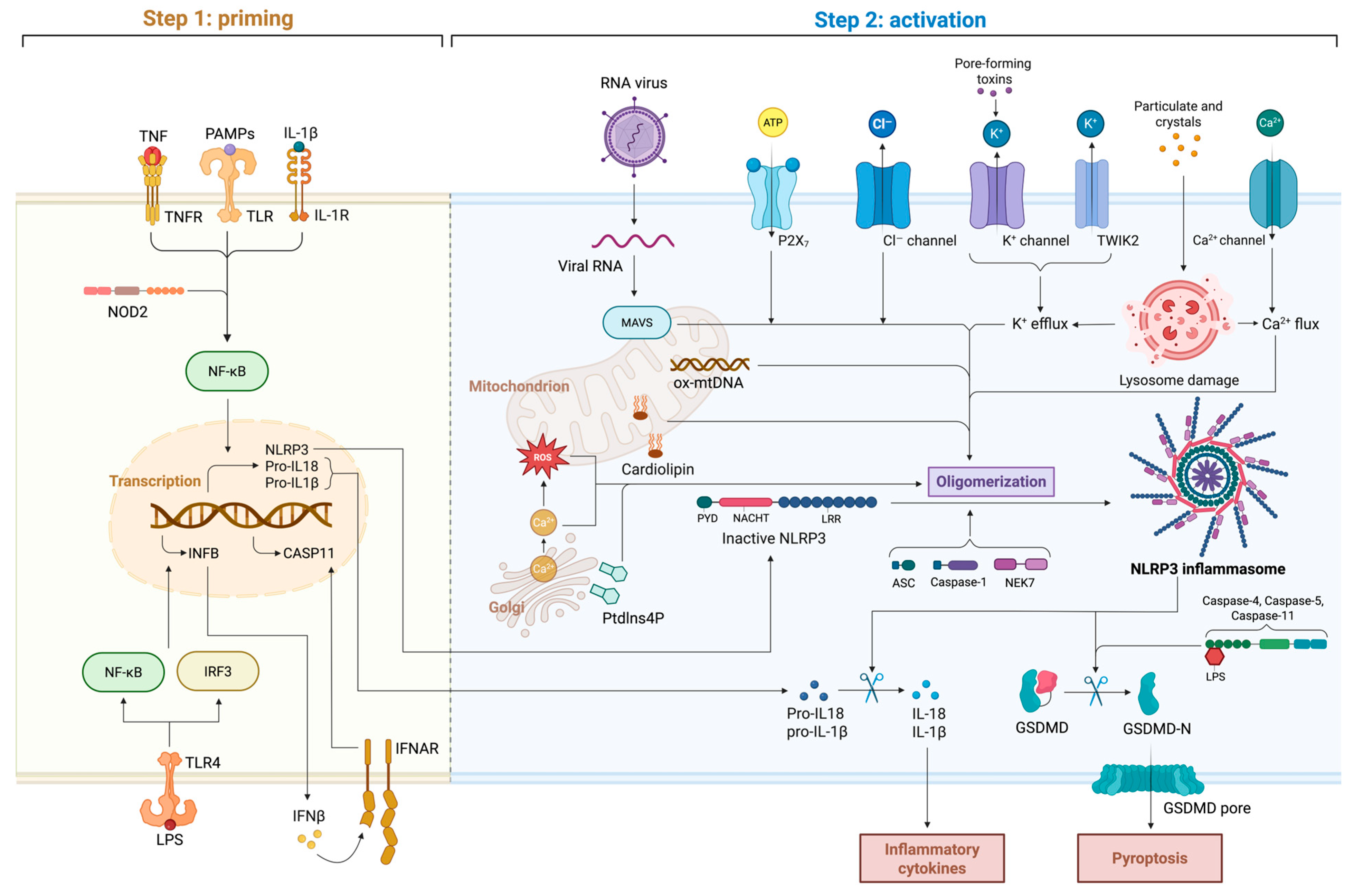
7. The Involvement of the Complement System and Inflammasomes in CIRI
7.1. The Complement System
7.2. Inflammasomes
8. Therapeutic Strategies and Clinical Applications of Immune Regulation in CIRI
9. Future Perspectives and Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jurcau, A.; Simion, A. Neuroinflammation in Cerebral Ischemia and Ischemia/Reperfusion Injuries: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Wei, Y. Neuronal Injuries in Cerebral Infarction and Ischemic Stroke: From Mechanisms to Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herpich, F.; Rincon, F. Management of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Animal Models of Stroke. Anim. Models Exp. Med. 2021, 4, 204–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, X.; Xu, T.; Ruan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Q. Tissue Kallikrein Supplementation in Ischemic Phase Protects the Neurovascular Unit and Attenuates Reperfusion-Induced Injury in Ischemic Stroke. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 209, 107435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Hou, S.; Xia, Y.; Wang, Y.-Q. Influence of the Brain-Gut Axis on Neuroinflammation in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2024, 53, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; You, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhu, C.; Hai, D.; Cai, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, J.; et al. Isoliquiritigenin Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Ameliorating Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Activating the Nrf2 Pathway. Redox Biol. 2024, 77, 103406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Wu, W.; Zhou, W.; Yan, K.; Liu, Z.; Yan, L.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. RNF13 Protects Neurons against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Stabilizing P62-Mediated Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Saini, S.; Singh, D. Mitochondrial Mechanisms in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Unravelling the Intricacies. Mitochondrion 2024, 77, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, B.; Ghildiyal, S.; Kharkwal, H. ML218 Modulates Calcium Binding Protein, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation during Ischemia-Reperfusion Brain Injury in Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 982, 176919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Yang, X.-Y.; Liu, H.-Q.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, C.-P.; Peng, J.; Luo, X.-J. The Weakened Interaction Between HECTD4 and GluN2B in Ischemic Stroke Promotes Calcium Overload and Brain Injury Through a Mechanism Involving the Decrease of GluN2B and MALT1 Ubiquitination. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 1563–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhu, R.; He, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Liang, D.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury-Induced Neuroinflammation and Pyroptosis by Modulating Microglia M1/M2 Phenotypes. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 341, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Lv, C.; Bao, S.; Gao, P.; He, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, C. Targeting TNF-α: The Therapeutic Potential of Certolizumab Pegol in the Early Period of Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 137, 112498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yan, L.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Xia, Q.; Zheng, L.; Shao, B.; Gao, Q.; Sun, N.; Shi, J. Tat-NTS Peptide Protects Neurons against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via ANXA1 SUMOylation in Microglia. Theranostics 2023, 13, 5561–5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zheng, L.; Geng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; You, G.; Cai, M.; Li, M.; Cheng, X.; Zan, J. FTO Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Neuroinflammation by Decreasing cGAS mRNA Stability in an m6A-Dependent Manner. Cell. Signal. 2023, 109, 110751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-F.; Pan, M.-X.; Tang, J.-C.; Cheng, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liao, H.-B.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, Z.-F.; et al. Arginine Is Neuroprotective through Suppressing HIF-1α/LDHA-Mediated Inflammatory Response after Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Mol. Brain 2020, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, S.; Huang, L.; Peng, Z.; Lu, H.; He, Q.; Chen, R.; Hu, L.; Wang, B.; Sun, B.; et al. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of Peripheral Blood Reveals That Monocytes with High Cathepsin S Expression Aggravate Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 107, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Yao, K.; Syeda, M.Z.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, Z.; et al. Ligustrazine Nanoparticle Hitchhiking on Neutrophils for Enhanced Therapy of Cerebral Ischemia-reperfusion Injury. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2301348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Ge, A.; Wang, S.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, X.; Mei, Z.; Wang, G.; Ge, J. A Systematic Review of the Research Progress of Non-Coding RNA in Neuroinflammation and Immune Regulation in Cerebral Infarction/Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maida, C.D.; Norrito, R.L.; Daidone, M.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Pinto, A. Neuroinflammatory Mechanisms in Ischemic Stroke: Focus on Cardioembolic Stroke, Background, and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.; Kong, Y.; Yang, S.; Lu, F.; Gong, Z.; Zhan, S.; Liu, M. Dynamic Changes of Inflammation and Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice Investigated by Ferumoxytol-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Santo, C.; La Russa, D.; Greco, R.; Persico, A.; Zanaboni, A.M.; Bagetta, G.; Amantea, D. Characterization of the Involvement of Tumour Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α-Stimulated Gene 6 (TSG-6) in Ischemic Brain Injury Caused by Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Mouse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.; Scofield, B.A.; Yu, I.; Chang, F.; Ganea, D.; Yen, J. Interferon-β Modulates Inflammatory Response in Cerebral Ischemia. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e002610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buizza, C.; Enström, A.; Carlsson, R.; Paul, G. The Transcriptional Landscape of Pericytes in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Transl. Stroke Res. 2024, 15, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Jian, Z.; Jin, T.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xiong, X.; Gu, L. NOX2-Mediated Reactive Oxygen Species Are Double-Edged Swords in Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekhon, M.S.; Stukas, S.; Hirsch-Reinshagen, V.; Thiara, S.; Schoenthal, T.; Tymko, M.; McNagny, K.M.; Wellington, C.; Hoiland, R. Neuroinflammation and the Immune System in Hypoxic Ischaemic Brain Injury Pathophysiology after Cardiac Arrest. J. Physiol. 2024, 602, 5731–5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Chen, M.; Zhu, D. Reperfusion and Cytoprotective Agents Are a Mutually Beneficial Pair in Ischaemic Stroke Therapy: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Pharmacological Targets and Candidate Drugs Focusing on Excitotoxicity and Free Radical. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2023, 9, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Q.-Q.; Zheng, Z.-Q.; Liao, J.; Li, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Wang, T.-Y.; Yuan, G.-Q.; Wang, Z.; Xue, Q. SPP1/AnxA1/TIMP1 as Essential Genes Regulate the Inflammatory Response in the Acute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 4873–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Chu, M.; Liu, Y.; Mao, X.; Wu, D.; Xu, D.; et al. Anti-Ferroptosis Exosomes Engineered for Targeting M2 Microglia to Improve Neurological Function in Ischemic Stroke. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rust, R.; Nih, L.R.; Liberale, L.; Yin, H.; El Amki, M.; Ong, L.K.; Zlokovic, B.V. Brain Repair Mechanisms after Cell Therapy for Stroke. Brain 2024, 147, 3286–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Jo, H.; Sonn, S.-K.; Jeong, S.-J.; Seo, S.; Suh, J.; Jin, J.; Kweon, H.Y.; Kim, T.K.; et al. The Antioxidant Enzyme Peroxiredoxin-1 Controls Stroke-Associated Microglia against Acute Ischemic Stroke. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M.; Feng, J. Roles of Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Chen, L.; Tang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. The Role of CCL2/CCR2 Axis in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Treatment: From Animal Experiments to Clinical Trials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamud Yusuf, A.; Hagemann, N.; Ludewig, P.; Gunzer, M.; Hermann, D.M. Roles of Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils in Ischemic Brain Injury and Post-Ischemic Brain Remodeling. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 825572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellut, M.; Bieber, M.; Kraft, P.; Weber, A.N.R.; Stoll, G.; Schuhmann, M.K. Delayed NLRP3 Inflammasome Inhibition Ameliorates Subacute Stroke Progression in Mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-T.; Huang, H.-C.; Kao, S.-T.; Chang, T.-T.; Cheng, C.-Y. Neuroprotective Effects of Alpinia Oxyphylla Miq against Mitochondria-Related Apoptosis by the Interactions between Upregulated P38 MAPK Signaling and Downregulated JNK Signaling in the Subacute Phase of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion in Rats. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2022, 50, 2057–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, H.; Cai, W.; Cai, M.; Ji, X.; Leak, R.K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J.; et al. Interleukin-4 Is Essential for Microglia/Macrophage M2 Polarization and Long-Term Recovery after Cerebral Ischemia. Stroke 2016, 47, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, L.; Du, Y.; Fan, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, N. P-Hydroxy Benzaldehyde Revitalizes the Microenvironment of Peri-Infarct Cortex in Rats after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion. Phytomedicine 2022, 105, 154379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Liao, X.; Xie, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, R. The Role of Neuroglial Cells Communication in Ischemic Stroke. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 209, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Lu, D.; Yuan, J.; Ren, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, J. L-Borneol Promotes Neurovascular Unit Protection in the Subacute Phase of Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Rats: P38-MAPK Pathway Activation, Anti-Inflammatory, and Anti-Apoptotic Effect. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4166–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; He, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, G.; Du, X.; Du, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Galectin-3 Mediated Inflammatory Response Contributes to Neurological Recovery by QiShenYiQi in Subacute Stroke Model. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 588587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawoot, N.; Sengking, J.; Wicha, P.; Govitrapong, P.; Tocharus, C.; Tocharus, J. Melatonin Attenuates Reactive Astrogliosis and Glial Scar Formation Following Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury Mediated by GSK-3β and RIP1K. J. Cell. Physiol. 2022, 237, 1818–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Ren, J.; Luo, Y.; He, Q.; Zhao, R.; Chang, J.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.-N. T Cell Response in Ischemic Stroke: From Mechanisms to Translational Insights. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 707972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, M.; Komai, K.; Nakamura, T.; Srirat, T.; Yoshimura, A. Tissue Regulatory T Cells and Neural Repair. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Li, F.; Shi, J.; Yang, D.; Deng, Y.; Gong, Q. Gastrodin Ameliorates Subacute Phase Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Inflammation and Apoptosis in Rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 4144–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghatge, S.B.; Surya, N.; Modi, D. Rapid Recovery from Subacute to Chronic Ischemic Stroke Following Revascularization by Carotid Stenting: Preliminary Findings. Neurol. India 2022, 70, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Jia, S.; Sun, Y.; Pang, M.; Lv, E.; Li, X.; Meng, Q.; Wang, Y. Docosahexaenoic Acid Promotes M2 Microglia Phenotype via Activating PPARγ-Mediated ERK/AKT Pathway against Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 199, 110660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boese, A.C.; Le, Q.-S.E.; Pham, D.; Hamblin, M.H.; Lee, J.-P. Neural Stem Cell Therapy for Subacute and Chronic Ischemic Stroke. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Du, G. Baicalein Administered in the Subacute Phase Ameliorates Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Brain Injury by Reducing Neuroinflammation and Neuronal Damage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Chen, J.; Fan, H.-D.; Wang, W.; Wang, B.; Ma, J.-Y.; Li, P.-P.; Pu, H.-W.; Guo, X.-Y.; et al. Maintaining Moderate Levels of Hypochlorous Acid Promotes Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation in the Recovery Phase of Stroke. Neural Regener. Res. 2024, 20, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, T.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, X.; Huang, D.; Pan, T.; Zhou, L. Platelet Glycoprotein Receptor Ib Blockade Ameliorates Experimental Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Strengthening the Blood–Brain Barrier Function and Anti-Thrombo-Inflammatory Property. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 69, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.T.; Ong, L.K.; Gyawali, P.; Nassir, C.M.N.C.M.; Mustapha, M.; Nandurkar, H.H.; Sashindranath, M. Role of Purinergic Signalling in Endothelial Dysfunction and Thrombo-Inflammation in Ischaemic Stroke and Cerebral Small Vessel Disease. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, S.; Zhang, H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, Y.; Won, M.-H.; Kim, Y.-M.; Kwon, Y.-G. CLEC14A Deficiency Exacerbates Neuronal Loss by Increasing Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Inflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.N.; Bix, G.J. Roles of Blood-Brain Barrier Integrins and Extracellular Matrix in Stroke. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2019, 316, C252–C263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhou, W.; Wen, L.; Jin, X.; Meng, T.; Li, S.; Hong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, H.; Hu, F. The Protective Effects of Axitinib on Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction and Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 379, 114870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, R.; Jia, M.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J. Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Induced Blood Brain Barrier Dysfunction and the Involved Molecular Mechanism. Neurochem. Res. 2023, 48, 2320–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Keep, R.F.; Ye, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; et al. Endothelial Peroxiredoxin-4 Is Indispensable for Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity and Long-Term Functional Recovery after Ischemic Stroke. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2400272121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Ban, W.; Liu, H.; Lv, L.; Zhang, B.; Liu, A.; Hou, Z.; Lu, J.; Chen, X.; et al. Pterostilbene Alleviated Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction via Inhibiting Early Endothelial Cytoskeleton Reorganization and Late Basement Membrane Degradation. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 8291–8308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, W.; Chen, H.; Li, M.; Fan, X.; Jiang, F.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Song, J.; Zhong, D.; et al. NRF2 Activation Ameliorates Blood–Brain Barrier Injury after Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Regulating Ferroptosis and Inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, F.; Xu, C.; Fan, X.; Yang, S.; Fan, W.; Li, M.; Song, J.; Wei, W.; Chen, H.; Zhong, D.; et al. MyD88 Inhibition Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Regulating the Inflammatory Response and Reducing Blood–Brain Barrier Damage. Neuroscience 2024, 549, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, S.; Aruga, J. Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Signaling Is Involved in Impaired Blood–Brain Barrier Function in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Luo, Y.; Han, Z. Crosstalk between Inflammation and the BBB in Stroke. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Mu, H.; Liu, L.; Jiang, X.; Wu, D.; Shi, Y.; Leak, R.K.; Ji, X. Transient Selective Brain Cooling Confers Neurovascular and Functional Protection from Acute to Chronic Stages of Ischemia/Reperfusion Brain Injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 39, 1215–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Hao, X.; Dou, H.; Zou, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, B.; Yue, H.; Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte Growth Factor-Modified Hair Follicle Stem Cells Ameliorate Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2023, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Bian, H.; Shu, S.; Xia, S.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xu, Y.; Cao, X. AIM2 Deletion Enhances Blood-brain Barrier Integrity in Experimental Ischemic Stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 1224–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic-Djergovic, D.; Goonewardena, S.N.; Pinsky, D.J. Inflammatory Disequilibrium in Stroke. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 142–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-Y.; Wu, M.-H.; Hu, M.-L. Therapeutic Treatment with Vitamin C Reduces Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Brain Infarction in Rats by Attenuating Disruptions of Blood Brain Barrier and Cerebral Neuronal Apoptosis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 155, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Barres, B.A. Microglia and Macrophages in Brain Homeostasis and Disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, M.; Butovsky, O. Microglia Function in the Central Nervous System During Health and Neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 35, 441–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borst, K.; Dumas, A.A.; Prinz, M. Microglia: Immune and Non-Immune Functions. Immunity 2021, 54, 2194–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Wang, Y.; Stetler, A.R.; Leak, R.K.; Hu, X.; Chen, J. Phagocytic Microglia and Macrophages in Brain Injury and Repair. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2022, 28, 1279–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voet, S.; Prinz, M.; Van Loo, G. Microglia in Central Nervous System Inflammation and Multiple Sclerosis Pathology. Trends Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butovsky, O.; Weiner, H.L. Microglial Signatures and Their Role in Health and Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 19, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Kong, X.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Yang, T.; Dong, Y.; Li, J.; et al. HDAC3 Inhibition Ameliorates Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Brain Injury by Regulating the Microglial cGAS-STING Pathway. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9644–9662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Zhan, G.; Mao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Li, X. TRIM45 Causes Neuronal Damage by Aggravating Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation upon Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Liu, M.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xie, H.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J.; et al. Intermittent Theta-Burst Stimulation Improves Motor Function by Inhibiting Neuronal Pyroptosis and Regulating Microglial Polarization via TLR4/NFκB/NLRP3 Signaling Pathway in Cerebral Ischemic Mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Jiang, W.; Yu, B.; Liang, H.; Mao, S.; Hu, X.; Feng, Y.; Xu, J.; Chu, L. Quercetin Improves Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Microglia/Macrophages M2 Polarization via Regulating PI3K/Akt/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 168, 115653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Peng, J.; Li, X.; Wang, H.; Rong, X.; Peng, Y. Transmission of NLRP3-IL-1β Signals in Cerebral Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury: From Microglia to Adjacent Neuron and Endothelial Cells via IL-1β/IL-1R1/TRAF6. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 2749–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.A.; Ibrahim, W.W.; Mohamed, A.F.; Abdelkader, N.F. Microglia Polarization in Nociplastic Pain: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Inflammopharmacology 2023, 31, 1053–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarchi, A.; Albi, E.; Arcuri, C. Microglia Signatures: A Cause or Consequence of Microglia-Related Brain Disorders? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Lo, R.Y.; Yang, F. Ultrasound Reduces Inflammation by Modulating M1/M2 Polarization of Microglia through STAT1/STAT6/PPARγ Signaling Pathways. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 4113–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Jia, H.-Y.; Li, R.; Ma, Z.; Si, M.; Qian, C.; Zhu, F.; Sheng-Yong, L. Downregulation of Nogo-B Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice through Regulating Microglia Polarization via TLR4/NF-kappaB Pathway. Neurochem. Int. 2023, 167, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in Biology and Targeted Therapy: New Insights and Translational Implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Chang, X.; Wang, H. Relationship between the cGAS−STING and NF-κB Pathways-Role in Neurotoxicity. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Dhapola, R.; Sharma, P.; Nagar, P.; Medhi, B.; HariKrishnaReddy, D. The Impact of Cytokines in Neuroinflammation-Mediated Stroke. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 78, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Jia, H.; Si, M.; Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhu, F.; Luo, S. Loureirin B Protects against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through Modulating M1/M2 Microglial Polarization via STAT6/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 953, 175860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Jiang, T.; Ma, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, M. Targeting PI3K/Akt in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Alleviation: From Signaling Networks to Targeted Therapy. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 7930–7949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, A.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Kim, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Y.; et al. Panax Notoginseng: Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Attenuate Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via Altering Microglia Polarization. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Seo, J.S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Ha, K.-T.; Choi, B.T.; Shin, Y.-I.; Yun, Y.J.; Shin, H.K. AIM2 Inflammasome Contributes to Brain Injury and Chronic Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment in Mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 87, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, L.; Kang, S.-W.; Baik, S.-H.; Ng, G.Y.Q.; She, D.T.; Balaganapathy, P.; Dheen, S.T.; Magnus, T.; Gelderblom, M.; Sobey, C.G.; et al. Evidence That NLRC4 Inflammasome Mediates Apoptotic and Pyroptotic Microglial Death Following Ischemic Stroke. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 75, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, N.; Jeltema, D.; Duan, Y.; He, Y. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: An Overview of Mechanisms of Activation and Regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wu, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Yue, J.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A Detrimental Role of Endothelial S1PR2 in Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Modulating Mitochondrial Dysfunction, NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation, and Pyroptosis. Redox Biol. 2024, 75, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Schardien, K.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonnemacher, M.R. Roles of Neuropathology-Associated Reactive Astrocytes: A Systematic Review. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.-Y.; Huo, J. A1/A2 Astrocytes in Central Nervous System Injuries and Diseases: Angels or Devils? Neurochem. Int. 2021, 148, 105080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Barres, B.A. Reactive Astrocytes: Production, Function, and Therapeutic Potential. Immunity 2017, 46, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnerbauer, M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Astrocyte Crosstalk in CNS Inflammation. Neuron 2020, 108, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, Y.J.; Zhao, A.; Jiang, X.; Gan, J. Astrocyte Modulation in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: A Promising Therapeutic Strategy. Exp. Neurol. 2024, 378, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, L.; Peng, Z.; Liu, W.; et al. Astrocytic A1/A2 Paradigm Participates in Glycogen Mobilization Mediated Neuroprotection on Reperfusion Injury after Ischemic Stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wu, X.; Luo, J.; Wang, X.; Guo, H.; Feng, D.; Zhao, L.; Bai, H.; Song, M.; Liu, X.; et al. Pterostilbene Attenuates Astrocytic Inflammation and Neuronal Oxidative Injury after Ischemia-Reperfusion by Inhibiting NF-κB Phosphorylation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Kong, T.; Shao, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, S.; Kong, Q.; Chen, J.; Cheng, B.; Wang, C. Orexin-a Alleviates Astrocytic Apoptosis and Inflammation via Inhibiting OX1R-Mediated NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Zha, J.; Wang, C.; An, J.; Xie, Z.; Qiao, S. Astrocyte-Derived TNF-α-Activated Platelets Promote Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Regulating the RIP1/RIP3/AKT Signaling Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2022, 59, 5734–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, H.; Xu, C.; Sun, H.; Wei, W.; Song, J.; Jia, F.; Zhong, D.; Li, G. A2 Reactive Astrocyte-derived Exosomes Alleviate Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury by Delivering miR-628. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Liang, X.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Z.; Luo, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Folic Acid Deficiency Exacerbates the Inflammatory Response of Astrocytes after Ischemia-reperfusion by Enhancing the Interaction between IL-6 and JAK-1/pSTAT3. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2023, 29, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Xu, X.; Kong, X.; Ren, J.; Yao, X.; Wen, Q.; et al. Microglia and Macrophage Exhibit Attenuated Inflammatory Response and Ferroptosis Resistance after RSL3 Stimulation via Increasing Nrf2 Expression. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.-Y.; Pan, X.-R.; Luo, X.-X.; Wang, Y.-F.; Zhang, X.-X.; Yang, S.-H.; Zhong, Z.-Q.; Liu, C.; Chen, Q.; Wang, P.-F.; et al. Astrocyte-Derived Lactate Aggravates Brain Injury of Ischemic Stroke in Mice by Promoting the Formation of Protein Lactylation. Theranostics 2024, 14, 4297–4317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Cao, J.; Fu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Lou, J.; et al. Cottonseed Oil Alleviates Ischemic Stroke Injury by Inhibiting the Inflammatory Activation of Microglia and Astrocyte. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Liang, J.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, Z.; Zhang, W. Metabolic Reprogramming in Gliocyte Post-Cerebral Ischemia/ Reperfusion: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2024, 22, 1672–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, T.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.; Zuo, W.; Wang, P.; Zhao, G.; et al. Dysfunction of Astrocytic Glycophagy Exacerbates Reperfusion Injury in Ischemic Stroke. Redox Biol. 2024, 74, 103234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoll, G.; Nieswandt, B. Thrombo-Inflammation in Acute Ischaemic Stroke—Implications for Treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lv, M.; Zhou, X.; Cui, Y. Roles of Peripheral Immune Cells in the Recovery of Neurological Function after Ischemic Stroke. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1013905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhang, X. Regulatory T Cells in Ischemic Stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2021, 27, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fang, C.; Feng, Z.; Yin, M.; Huang, J.; Ma, Y.; Mo, Z. Advancing Stroke Therapy: A Deep Dive into Early Phase of Ischemic Stroke and Recanalization. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamchai, S.; Chumboatong, W.; Hata, J.; Tocharus, C.; Suksamrarn, A.; Tocharus, J. Morin Protects the Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion through Anti-Inflammatory Actions in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Weng, Y.-C.; Chiang, I.-C.; Huang, Y.-T.; Liao, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Kao, C.-Y.; Liu, Y.-L.; Lee, T.-H.; Chou, W.-H. Neutralization of Lipocalin-2 Diminishes Stroke-Reperfusion Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Guo, Y.; Xie, W.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Huang, D.; Li, P. Brain Border-derived CXCL2 + Neutrophils Drive NET Formation and Impair Vascular Reperfusion Following Ischemic Stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Guo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Fang, R.; Zhang, W.; Mei, Z. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Friend and Foe. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 2079–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Zhang, H.-N.; Gao, T.; Wang, X.-S.; Wang, X.; Yu, M.-Y.; Li, M.-K.; Huang, J. Upregulation of TRPC1 in Microglia Promotes Neutrophil Infiltration after Ischemic Stroke. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 208, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frieler, R.A.; Chung, Y.; Ahlers, C.G.; Gheordunescu, G.; Song, J.; Vigil, T.M.; Shah, Y.M.; Mortensen, R.M. Genetic Neutrophil Deficiency Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 298, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jin, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, X.; Yu, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Dong, X.; Cao, X.; et al. Microglial Lnc-U90926 Facilitates Neutrophil Infiltration in Ischemic Stroke via MDH2/CXCL2 Axis. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2873–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzmann, G.; Kargaran, S.; Engelhardt, B. Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury in Stroke: Impact of the Brain Barriers and Brain Immune Privilege on Neutrophil Function. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2018, 11, 1756286418794184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holloway, P.M.; Durrenberger, P.F.; Trutschl, M.; Cvek, U.; Cooper, D.; Orr, A.W.; Perretti, M.; Getting, S.J.; Gavins, F.N.E. Both MC1 and MC3 Receptors Provide Protection from Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Induced Neutrophil Recruitment. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2015, 35, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.N.; Mohan, E.C.; Pandya, G.; Ali, U.; Tan, C.; Kofler, J.K.; Shapiro, L.; Marrelli, S.P.; Chauhan, A. CD13 Facilitates Immune Cell Migration and Aggravates Acute Injury but Promotes Chronic Post-Stroke Recovery. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Wang, Z.; Huang, X.; Xue, J.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Zhou, S. Bacteria-Derived Outer-Membrane Vesicles Hitchhike Neutrophils to Enhance Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.; Cho, S. Microglia and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages in Stroke. Neurotherapeutics 2016, 13, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicks, E.E.; Ran, K.R.; Kim, J.E.; Xu, R.; Lee, R.P.; Jackson, C.M. The Translational Potential of Microglia and Monocyte-Derived Macrophages in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 897022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhai, X.; Han, D.; Xiong, X.; Wang, T.; Zeng, X.; He, S.; Liu, R.; Miyata, M.; Xu, B.; et al. CCR2-Dependent Monocytes/Macrophages Exacerbate Acute Brain Injury but Promote Functional Recovery after Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3530–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.X.; Broughton, B.R.S.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, S.; Drummond, G.R.; Sobey, C.G. Evidence That Ly6Chi Monocytes Are Protective in Acute Ischemic Stroke by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization. Stroke 2015, 46, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, R.; Jiang, M.; Ye, Q.; Smith, A.D.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y. Macrophages Reprogram after Ischemic Stroke and Promote Efferocytosis and Inflammation Resolution in the Mouse Brain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2019, 25, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Song, P.; Gu, X.; Liang, W.; Sun, W.; Hua, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, Z. Comprehensive Landscape of Immune Infiltration and Aberrant Pathway Activation in Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 766724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Lee, R.P.; Yazigi, E.; Atta, L.; Feghali, J.; Pant, A.; Jain, A.; Levitan, I.; Kim, E.; Patel, K.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 Reprograms Blood Monocytes to Prevent Cerebral Edema and Facilitate Recovery after Ischemic Stroke. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 116, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-G.; Ren, J.-X.; Chen, Y.; Tian, M.-F.; Zhou, L.; Wen, J.; Song, X.-S.; Wu, Y.-L.; Yang, Q.-H.; Jiang, P.-R.; et al. M2 Macrophages Mediate Fibrotic Scar Formation in the Early Stages after Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 2208–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaviglio, E.A.; Peralta Ramos, J.M.; Arroyo, D.S.; Bussi, C.; Iribarren, P.; Rodriguez-Galan, M.C. Systemic Sterile Induced-Co-Expression of IL-12 and IL-18 Drive IFN-γ-Dependent Activation of Microglia and Recruitment of MHC-II-Expressing Inflammatory Monocytes into the Brain. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 105, 108546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohme, M.; Sauvigny, T.; Mader, M.M.-D.; Schweingruber, N.; Maire, C.L.; Rünger, A.; Ricklefs, F.; Regelsberger, J.; Schmidt, N.O.; Westphal, M.; et al. Immune Characterization in Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Reveals Distinct Monocytic Activation and Chemokine Patterns. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 1348–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesselingh, R.; Griffith, S.; Broadley, J.; Tarlinton, D.; Buzzard, K.; Seneviratne, U.; Butzkueven, H.; O’BRien, T.J.; Monif, M. Peripheral Monocytes and Soluble Biomarkers in Autoimmune Encephalitis. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 135, 103000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, A.; De Feo, D.; Friebel, E.; Ingelfinger, F.; Anderfuhren, C.D.; Krishnarajah, S.; Andreadou, M.; Welsh, C.A.; Liu, Z.; Ginhoux, F.; et al. IFNγ and GM-CSF Control Complementary Differentiation Programs in the Monocyte-to-Phagocyte Transition during Neuroinflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhu, X.; Smerin, D.; Zhong, Y.; Gu, L.; Fang, W.; Xiong, X. The Involvement and Therapy Target of Immune Cells after Ischemic Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and Foe for Ischemic Stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Jian, Z.; Stary, C.; Xiong, X. T Cells and Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Ye, J.; Cui, L.; Chu, S.; Chen, N. Regulatory T Cells in Ischemic Stroke. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, A.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, B. Immune Cells in the BBB Disruption After Acute Ischemic Stroke: Targets for Immune Therapy? Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 678744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.A.; Lin, T.-N.; Chen, C.-Y.; Mau, S.-Y.; Huang, W.-Z.; Kao, Y.-C.; Ma, R.; Liao, N.-S. Interleukin 15 Blockade Protects the Brain from Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 562–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-R.; Cui, W.-Q.; Wu, H.-Y.; Xu, X.-D.; Xu, X.-Q. The Role of T Cells in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Brain Res. Bull. 2023, 196, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegner, D.; Klaus, V.; Nieswandt, B. Platelets as Modulators of Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denorme, F.; Manne, B.K.; Portier, I.; Eustes, A.S.; Kosaka, Y.; Kile, B.T.; Rondina, M.T.; Campbell, R.A. Platelet Necrosis Mediates Ischemic Stroke Outcome in Mice. Blood 2020, 135, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawish, E.; Nording, H.; Münte, T.; Langer, H.F. Platelets as Mediators of Neuroinflammation and Thrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 548631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szepanowski, R.D.; Haupeltshofer, S.; Vonhof, S.E.; Frank, B.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Casas, A.I. Thromboinflammatory Challenges in Stroke Pathophysiology. Semin. Immunopathol. 2023, 45, 389–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Li, H.; Chen, Z.; Dong, T.; He, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, Z.; Duan, J.; Cao, T.; Chen, Q.; et al. Thrombo-Inflammation and Immunological Response in Ischemic Stroke: Focusing on Platelet-Tregs Interaction. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 955385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, N.F.; Regan, R.F.; Naik, U.P. Platelets as Drivers of Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury after Stroke. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1576–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Wang, M.; Jin, R.; Li, G. Blocking of PI3-Kinase Beta Protects against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Reducing Platelet Activation and Downstream Microvascular Thrombosis in Rats. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, X.; Wu, X.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Chen, D.; Li, G.; Tang, Z. Cell Polarization in Ischemic Stroke: Molecular Mechanisms and Advances. Neural Regener. Res. 2024, 20, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Ye, D.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, K.; Weng, Y.; Xiong, X.; Zhan, R.; Shen, J. Systemic Immune Responses after Ischemic Stroke: From the Center to the Periphery. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 911661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candelario-Jalil, E.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Magnus, T. Neuroinflammation, Stroke, Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction, and Imaging Modalities. Stroke 2022, 53, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yue, X.; Jia, M.; Wang, J. Neuroinflammation and Anti-Inflammatory Therapy for Ischemic Stroke. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontiers|Single-Cell Analyses Reveal the Dynamic Functions of Itgb2+ Microglia Subclusters at Different Stages of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Transient Middle Cerebral Occlusion Mice Model. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1114663/full (accessed on 18 August 2025).
- Kim, G.S.; Harmon, E.; Gutierrez, M.C.; Kim, S.; Vance, L.; Burrous, H.; Stephenson, J.M.; Chauhan, A.; Banerjee, A.; Wise, Z.; et al. Single-Cell Analysis Identifies Ifi27l2a as a Gene Regulator of Microglial Inflammation in the Context of Aging and Stroke in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Z.; Cao, G.; Qian, Y.; Fu, L.; Hu, J.; Xu, T.; Wu, Y.; Lv, Y. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Unveils Lrg1’s Role in Cerebral Ischemia–reperfusion Injury by Modulating Various Cells. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormann, D.; Knoflach, M.; Poreba, E.; Riedl, C.J.; Testa, G.; Orset, C.; Levilly, A.; Cottereau, A.; Jauk, P.; Hametner, S.; et al. Single-Nucleus RNA Sequencing Reveals Glial Cell Type-Specific Responses to Ischemic Stroke in Male Rodents. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 6232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Bonilla, L.; Shahanoor, Z.; Sciortino, R.; Nazarzoda, O.; Racchumi, G.; Iadecola, C.; Anrather, J. Analysis of Brain and Blood Single-Cell Transcriptomics in Acute and Subacute Phases after Experimental Stroke. Nat. Immunol. 2024, 25, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, F.H.; Lee, J.D.; Ruitenberg, M.J.; Woodruff, T.M. Therapeutic Targeting of Complement to Modify Disease Course and Improve Outcomes in Neurological Conditions. Semin. Immunol. 2016, 28, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Z.; Pan, J.; Shen, Q.; Li, M.; Peng, Y. Mitochondrial Dysfunction Induces NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation during Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.-Y.; Shen, S.; Wang, J. Protecting Neurons from Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of an siRNA to Inhibit Microglial Neurotoxicity. Biomaterials 2018, 161, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawieh, A.; Elvington, A.; Zhu, H.; Yu, J.; Kindy, M.S.; Atkinson, C.; Tomlinson, S. Modulation of Post-Stroke Degenerative and Regenerative Processes and Subacute Protection by Site-Targeted Inhibition of the Alternative Pathway of Complement. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Maihemuti, N.; Fang, Y.; Tan, J.; Jia, M.; Mu, Q.; Huang, K.; Gan, H.; Zhao, J. JR14a: A Novel Antagonist of C3aR Attenuates Neuroinflammation in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Brain Res. Bull. 2024, 213, 110986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, A.R.; Christophe, B.R.; Khahera, A.; Sim, J.L.; Connolly, E.S., Jr. Therapeutic Modulation of the Complement Cascade in Stroke. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiang, D.; Rosenkrans, Z.T.; Barnhart, T.E.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Ni, D.; Engle, J.W.; Cai, W. Aptamer-Conjugated Framework Nucleic Acids for the Repair of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 7334–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Jian, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, X.; Pu, B.; Gu, L.; Xiong, X. Janus Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Injury and Neuroinflammation Through Reducing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 714943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, M.; Bieber, M.; Kraft, P.; Weber, A.N.R.; Stoll, G.; Schuhmann, M.K. The NLRP3 Inflammasome Drives Inflammation in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury after Transient Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion in Mice. Brain Behav. Immun. 2021, 92, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Ren, W.; Wu, Q.; Liu, T.; Wei, Y.; Ding, J.; Zhou, C.; Xu, H.; Yang, S. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation: A Therapeutic Target for Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 847440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Jin, T.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Ye, B.; Wang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xiong, X.; Gu, L. Meisoindigo Protects Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Regulating Microglia/Macrophage Polarization via TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Luo, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y.; Tan, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, C.; Jiang, N.; Luo, Y. Intestinal Metabolite UroB Alleviates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Competition between TRIM65 and TXNIP for Binding to NLRP3 Inflammasome in Response to Neuroinflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2024, 1870, 167056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Xu, W.; Zhou, R. NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Cell Death. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2114–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Núñez, G. The NLRP3 Inflammasome: Activation and Regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 48, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, P.; Hong, Y.; Xie, Y.; Peng, M.; Sun, R.; Guo, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Lipocalin-2-Mediated Astrocyte Pyroptosis Promotes Neuroinflammatory Injury via NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2023, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Tan, J.; Ji, Y.; Luo, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J. BRCC3 Mediates Inflammation and Pyroptosis in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Activating the NLRP6 Inflammasome. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Dai, M.; Yao, S.; Lin, Y. CX3CL1 Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome-Induced Microglial Pyroptosis and Improves Neuronal Function in Mice with Experimentally-Induced Ischemic Stroke. Life Sci. 2022, 300, 120564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Ji, L.; Peng, B. METTL14 Regulates Microglia/Macrophage Polarization and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation after Ischemic Stroke by the KAT3B-STING Axis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 185, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, H.-X.; Shi, S.-T.; Bai, Y.-L.; Zhe, X.; Zhang, S.-J.; Li, Y.-J. Interleukin-11 Treatment Protected against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 115, 108816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Mao, J.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Wu, B.; Yuan, Y. Kaempferol Protects Against Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Through Intervening Oxidative and Inflammatory Stress Induced Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, J.; Xiong, L.; Xiao, Z.; Ye, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Huang, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, Z.-S.; et al. Stepwise Targeted Strategies for Improving Neurological Function by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress Levels and Inflammation Following Ischemic Stroke. J. Control. Release 2024, 368, 607–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Di, B.; Miao, J. Curcumol Ameliorates Neuroinflammation after Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury via Affecting Microglial Polarization and Treg/Th17 Balance through Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB Signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Lv, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q.; He, W.; Min, Z.; Teng, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, L.; Yin, J.; et al. Smart Liposomal Nanocarrier Enhanced the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke through Neutrophil Extracellular Traps and Cyclic Guanosine Monophosphate-Adenosine Monophosphate Synthase-Stimulator of Interferon Genes (cGAS-STING) Pathway Inhibition of Ischemic Penumbra. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 17845–17857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shi, X.; Xiong, T.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, K.; Nan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Ai, K. Inhibiting Mitochondrial Damage for Efficient Treatment of Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Through Sequential Targeting Nanomedicine of Neuronal Mitochondria in Affected Brain Tissue. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2409529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Cao, L.; He, C.; Ye, Q.; Liang, R.; You, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, J.; Ye, J.; Tannous, B.A.; et al. Targeted Delivery of Neural Progenitor Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Anti-Inflammation after Cerebral Ischemia. Theranostics 2021, 11, 6507–6521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, I.H.; Villa-González, M.; Martín, G.; Soto, M.; Pérez-Álvarez, M.J. Glial Cells as Therapeutic Approaches in Brain Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Cells 2021, 10, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Qiao, M.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wen, G.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y. Modulating the RPS27A/PSMD12/NF-κB Pathway to Control Immune Response in Mouse Brain Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.-D.; Ma, R.-Y.; Chen, Y.-J.; Xiang, X.-M.; Hou, D.-Y.; Li, X.-H.; Huang, H.; Li, T.; Duan, C.-Y. Activated Drp1 Regulates P62-Mediated Autophagic Flux and Aggravates Inflammation in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion via the ROS-RIP1/RIP3-Exosome Axis. Mil. Med. Res. 2022, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Huang, K.-Y.; Um, D.; Jung, Y.; Kong, H. Delivery-Mediated Exosomal Therapeutics in Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: Advances, Mechanisms, and Future Directions. Nano Converg. 2024, 11, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Duan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, J.; Bai, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Shao, J. Bioinformatics-Driven Identification and Validation of Diagnostic Biomarkers for Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion Injury. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.-E.; Wang, W.; Liu, A.-F.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, A.-P.; Lv, J.; et al. Identification of Key Transcription Factors Associated with Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Based on Gene-Set Enrichment Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 2429–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, M.; Fang, Z.; Wang, H. Immunological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: From Inflammatory Response to Neurorepair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178336
Li Z, Li M, Fang Z, Wang H. Immunological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: From Inflammatory Response to Neurorepair. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178336
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhendong, Man Li, Zhi Fang, and Haijun Wang. 2025. "Immunological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: From Inflammatory Response to Neurorepair" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178336
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, M., Fang, Z., & Wang, H. (2025). Immunological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies in Cerebral Ischemia–Reperfusion Injury: From Inflammatory Response to Neurorepair. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8336. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178336






