CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Overexpression of HGF Potentiates Tarim Red Deer Antler MSCs into Osteogenic Differentiation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Analysis
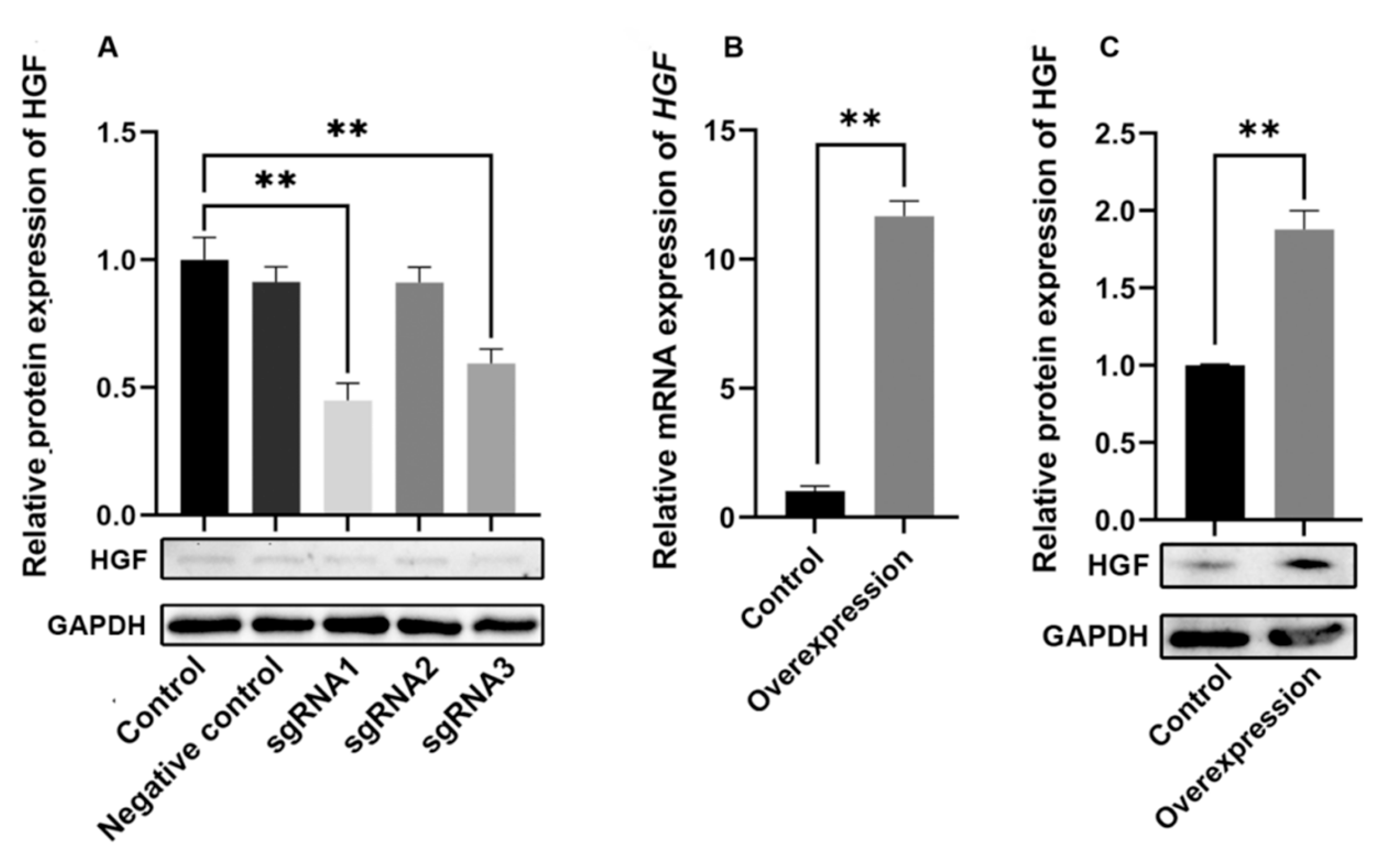
2.1. Efficiency Assay of Knockdown and Overexpression of HGF Gene in Antler MSCs
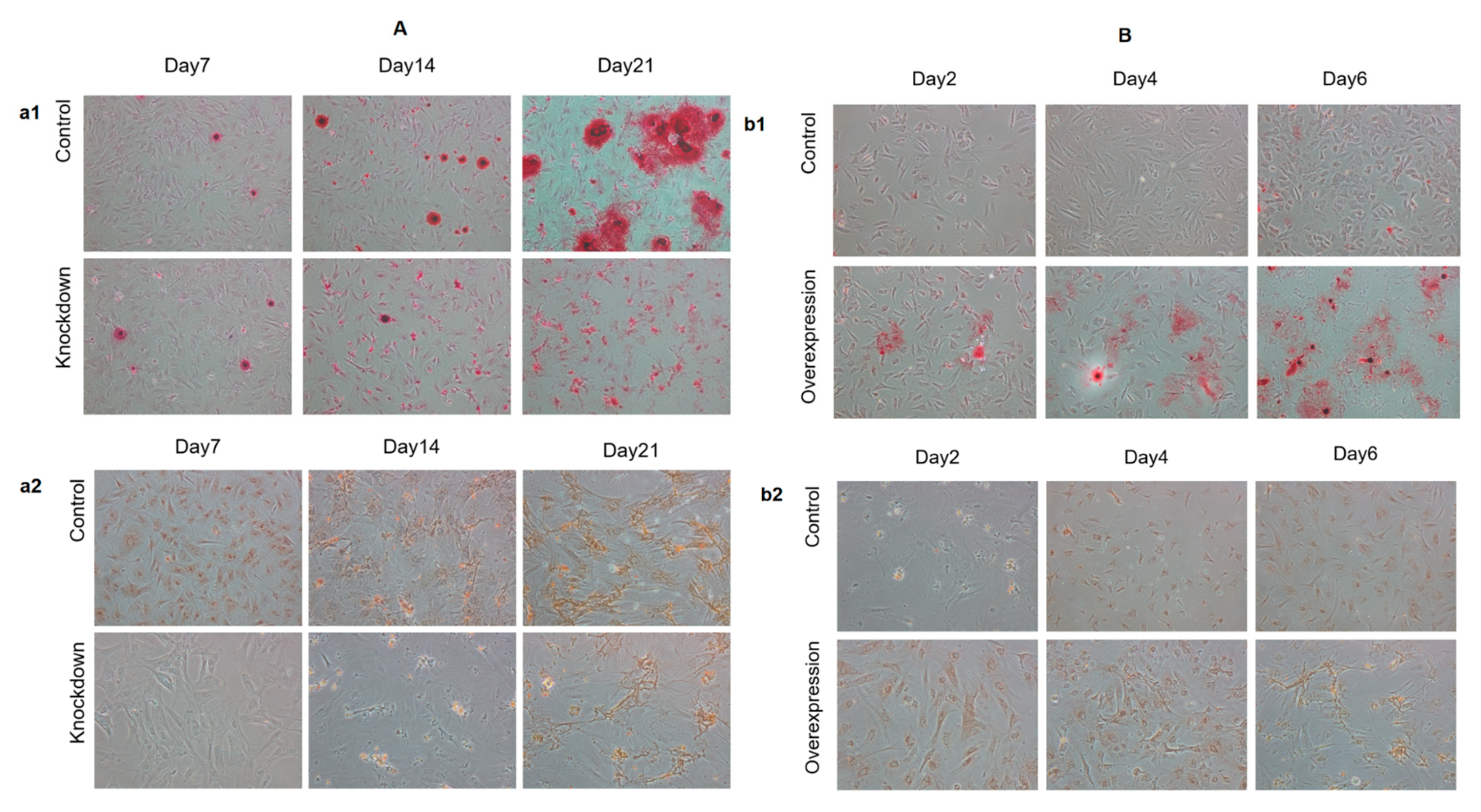
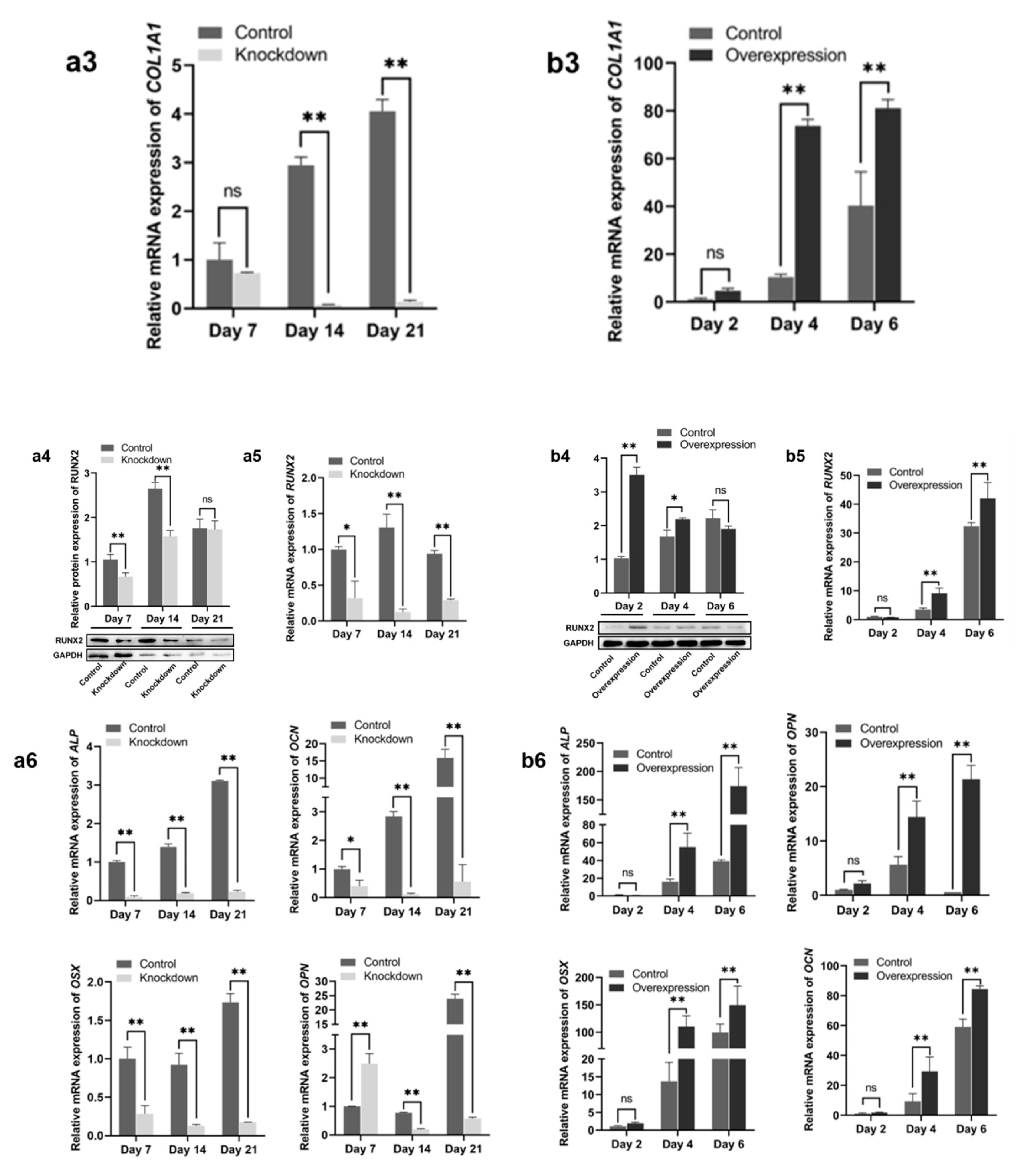
2.2. Effect of HGF Gene on Osteogenic Differentiation of Antler MSCs
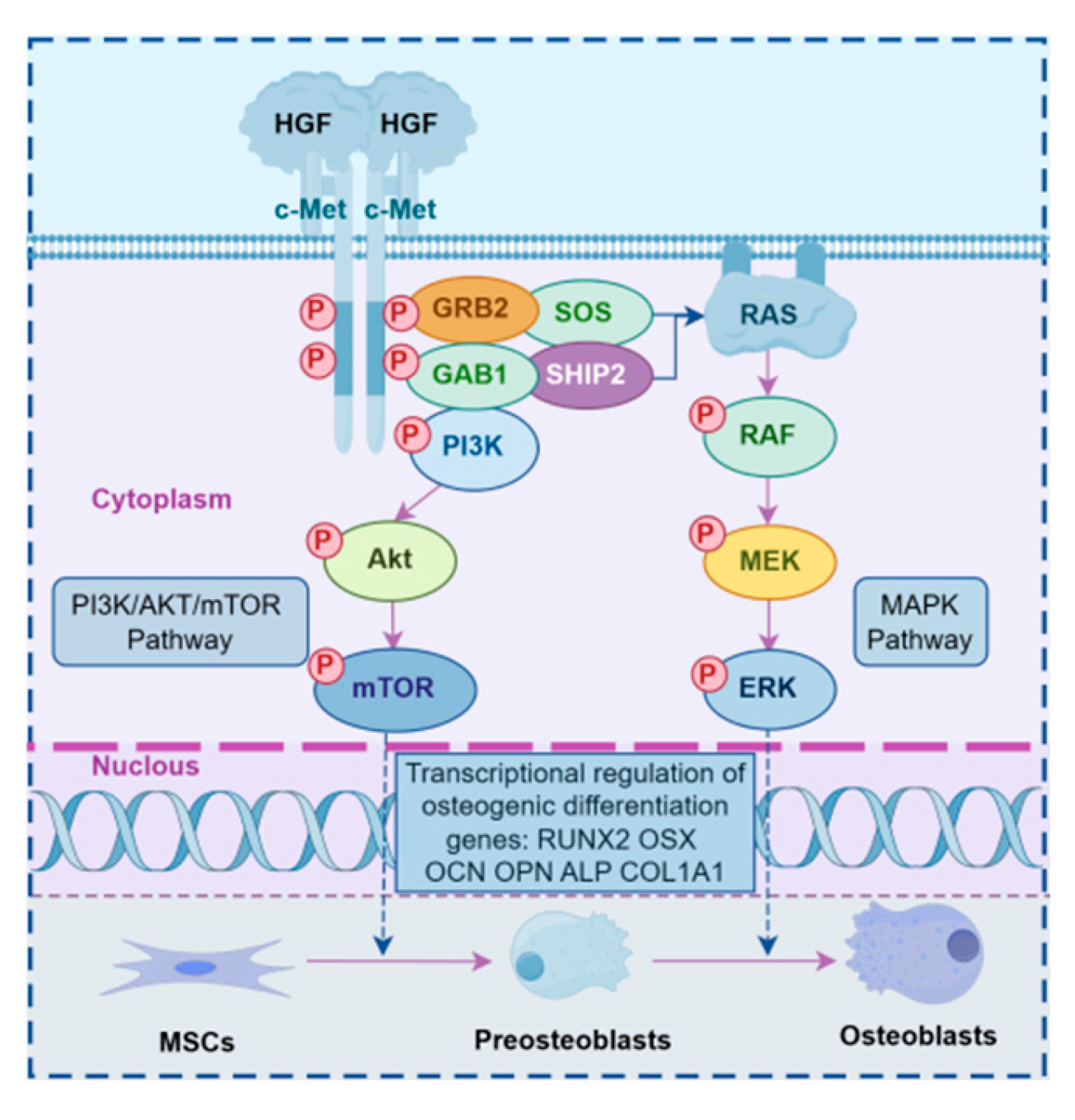
2.3. Expression of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Signaling Pathway Genes During sgRNA1 Group and Overexpression of Constitutive Bone Differentiation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Material
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. CRISPR/Cas9 Knockdown of HGF Gene in Deer Antler MSCs
4.2.2. Tissue RNA and Protein Extraction
4.2.3. Real-Time Fluorescence Quantitative PCR
4.2.4. Inducible Expression of pX330-HGF Protein
4.2.5. In Vitro Induction of Osteogenic Differentiation by Antler MSCs
4.2.6. Alizarin Red Staining to Identify the Effects of Osteogenic Differentiation
4.2.7. Immunohistochemical Identification of Osteogenic Differentiation Effects
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Landete-Castillejos, T.; Kierdorf, H.; Gomez, S.; Luna, S.; García, A.; Cappelli, J.; Pérez-Serrano, M.; Pérez-Barbería, J.; Gallego, L.; Kierdorf, U. Antlers—Evolution, development, structure, composition, and biomechanics of an outstanding type of bone. Bone 2019, 128, 115046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Mackintosh, C.G.; Martin, S.K.; Clark, D.E. Identification of key tissue type for antler regeneration through pedicle periosteum deletion. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 328, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Yang, F.; Li, G.; Gao, X.; Xing, X.; Wei, H.; Deng, X.; Clark, D.E. Antler regeneration: A dependent process of stem tissue primed via interaction with its enveloping skin. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2007, 307, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, D.; Jia, X.; Liu, J.; Hou, Z.; Han, C. Comparison of biological characteristics of mouse bone marrow with deer antler mesenchymal stem cells. J. Tarim Univ. 2023, 35, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yang, F.; Sheppard, A. Adult stem cells and mammalian epimorphic regeneration-insights from studying annual renewal of deer antlers. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2009, 4, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Sun, S.; Guo, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, M.; Peng, Y. Comparison between UC Method and ExoEasy Method for Extracting Exosomes from Antler Mesenchymal Stem cells. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2024, 46, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aenlle, K.K.; Curtis, K.M.; Roos, B.A.; Howard, G.A. Hepatocyte Growth Factor and p38 Promote Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 722–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, R.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, Y.; Ma, G.; Yang, B. Hepatocyte growth factor improves bone regeneration via the bone morphogenetic protein-2-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 6045–6053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, M.N.; Jeong, B.C.; Oh, S.H.; Kook, M.S.; Koh, J.T. Chemical inhibitors of c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase stimulate osteoblast differentiation and bone regeneration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 806, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, R.N.; Curtis, K.M.; Aenlle, K.K.; Howard, G.A. Hepatocyte growth factor and alternative splice variants—Expression, regulation and implications in osteogenesis and bone health and repair. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2016, 20, 1087–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, C.; Wang, S.; Gao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, Q. TGF-β1-Induced Differentiation of Wapiti Antler Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Cartilage and Expression Profile of Gene c-myc. Biotechnol. Bull. 2016, 32, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Kesari, K.K.; Kumar, A.; Rathi, B.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, P.K.; Jha, S.K.; Jha, N.K.; Slama, P.; Roychoudhury, S.; et al. Molecular mechanism(s) of regulation(s) of c-MET/HGF signaling in head and neck cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, J.; Yu, Z.; Xiong, C.; Zhang, J.; Gong, J.; Yu, C.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, X. Resistin targets TAZ to promote osteogenic differentiation through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. iScience 2023, 26, 107025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Guo, S.; Hong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Ma, C.; Ma, J. Pax2 is essential for proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells via Runx2. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 371, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.G.; Deng, Y.X.; Ke, K.X.; Cao, X.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Luo, H.H.; Yao, X.T.; Gao, X.; Du, Y.; et al. Matricellular Protein SMOC2 Potentiates BMP9-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation in Mesenchymal Stem Cells through the Enhancement of FAK/PI3K/AKT Signaling. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 5915988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, T.; Shi, H. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK pathways for cancer therapy. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Sequence(5′-3′) | Annealing Temperature/℃ | Fragment Length/bp | Accession Numbe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | F: TGTTTGTGATGGGCGTGAACCA R: ATGGCGTGGACAGTGGTCATAA | 61 | 154 | NM_001034034.2 |
| ALP | F:ACATCGAGGTGATCATGGGC R:GATCAGTGCGGTTCCAGACA | 60 | 183 | XM_043909115.1 |
| COL1A1 | F:CCAATGGCGCTCCTGGTATT R:ACCAGGTTCACCGCTGTTAC | 60 | 116 | XM_043904209.1 |
| OCN | F:GAAGAGACTCAGGCGCTACC R:GCTAGCTCGTCACAGTCAGG | 60 | 114 | XM_043878504.1 |
| OSX | F:TCCCTGCTTGAGGAGGAAG R:GGCTTCTTTGTGCCTGCTTT | 59 | 131 | XM_043882724.1 |
| OPN | F:CCTCCGCCCTTCCAGTTAAA R:CTGCTTCTGAGATGGGTCAGG | 60 | 116 | XM_043871261.1 |
| RUNX2 | F:CAAGGTGGTAGCCCTTGGAG R:AACAGCAGAGGCATTTCGGA | 60 | 103 | XM_043907628.1 |
| PI3K | F:GCAGACTGGAGGGAGGTGA R:TCCGCAAGGTCAAAGTGTAA | 59 | 280 | XM_043876754.1 |
| AKT | F:CGCACCGCTCCAAAGAAA R:ACGGCTGCACGTAGACACC | 59 | 199 | XM_043898476.1 |
| mTOR | F:CGTCTGTCGGTGGTCTTTG R:CGGAGGTTCCCATCTTTC | 57 | 169 | XM_043915272.1 |
| RAS | F:CCAGTGGAGGATGACGAG R:CCCATAGGCAGGAGTGAA | 56 | 183 | XM_043924996.1 |
| MEK | F:CGAAAGGCAAGAAGCGAAAC R:TCCACGATGGGCTCCAGGTC | 61 | 163 | XM_043905687.1 |
| ERK | F:AGACGCAACACCTCAGCA R:GCCAAGCCAAAGTCACAGA | 59 | 163 | XM_043901129.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, Y.; Jia, X.; Lin, C.; Qian, W.; Chen, H.; Fang, D.; Han, C. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Overexpression of HGF Potentiates Tarim Red Deer Antler MSCs into Osteogenic Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178273
Qi Y, Jia X, Lin C, Qian W, Chen H, Fang D, Han C. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Overexpression of HGF Potentiates Tarim Red Deer Antler MSCs into Osteogenic Differentiation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178273
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Yujiao, Xiaodong Jia, Chuan Lin, Wenxi Qian, Hong Chen, Di Fang, and Chunmei Han. 2025. "CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Overexpression of HGF Potentiates Tarim Red Deer Antler MSCs into Osteogenic Differentiation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178273
APA StyleQi, Y., Jia, X., Lin, C., Qian, W., Chen, H., Fang, D., & Han, C. (2025). CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Overexpression of HGF Potentiates Tarim Red Deer Antler MSCs into Osteogenic Differentiation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178273







