Opioid Affinity of Diazacyclic Peptidomimetic Compounds Derived from Reduced Polyamides
Abstract
1. Introduction
- The opioid receptor triple agonist (Delta, Mu, and Kappa receptor) DPI-125. The abuse liability of DPI-125 was evaluated with a self-administration model in rhesus monkeys. The observed agonist potencies of DPI-125 for Delta, Mu, and Kappa opioid receptors were 4.29 ± 0.36, 11.10 ± 3.04, and 16.57 ± 4.14 nmol/L, respectively. DPI-125 exhibited a high respiratory safety profile, clearly related to its high Delta receptor potency. The ratio of the EC50 potencies for the Mu and Delta receptors was found to be positively correlated with the respiratory safety ratio. DPI-125 has similar potencies for Mu and Kappa receptors, which is likely the reason for its reduced abuse potential [26].
- The dual opioid/NOP receptor agonist analgesic cebranopadol. The preclinical testing of cebranopadol has characterized it as a dual opioid and NOP receptor agonist that displays antinociceptive and antihyperalgesic action in a variety of acute and chronic pain models in animals. Unlike most current traditional opioids, it is generally more potent against neuropathic than nociceptive pain. Several phase 2 clinical trials have been completed and have moved to phase 3 clinical trials [27].
- The triple agonist DPI-125 is a preclinical-stage opioid drug that acts as a triple agonist at opioid receptors (δ, μ, and κ). It is being developed with the goal of providing effective pain relief with potentially reduced risks of respiratory depression and abuse liability compared to traditional Mu opioid agonists. [26].
- The dual Mu/Delta opioid receptor agonist N-phenethyl substituted 14-O-methylmorphinan-6-ones, which, contrary to N-methylmorphinans, produce effective and potent antinociception without motor impairment in mice [28].
- The dual Mu opioid receptor/nociception–orphanin FQ peptide receptor agonist BPR1M97. It is a potent, rapid analgesic with improved side effects in comparison to morphine. Its novel chemical structure provides novel insights into opioid-managed pain and may be used as a prototype of dual MOP/NOP full agonists [29].
- The dual Mu/Delta opioid agonist RV-Jim-C3, which demonstrated potent efficacious activity in several in vivo pain models, including inflammatory pain, antihyperalgesia, and antiallodynic with no significant motor impairment [30].
- The dual Kappa and Mu opioid receptor agonists. In vivo studies of salvinorin-based compound 10 showed that it produced analgesic activity while avoiding anxiogenic effects in murine models, thus providing further strong evidence for the therapeutic advantages of dual opioid receptor agonists over selective opioid receptor agonists [31].
- The Mu/Delta opioid agonist SRI-22141, which displays enhanced efficacy in neuropathic pain. It displays greatly reduced tolerance and dependence versus morphine. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect in chemotherapy-induced neuropathy. The efficacy and anti-inflammatory effects are mediated by the delta opioid receptor [32].
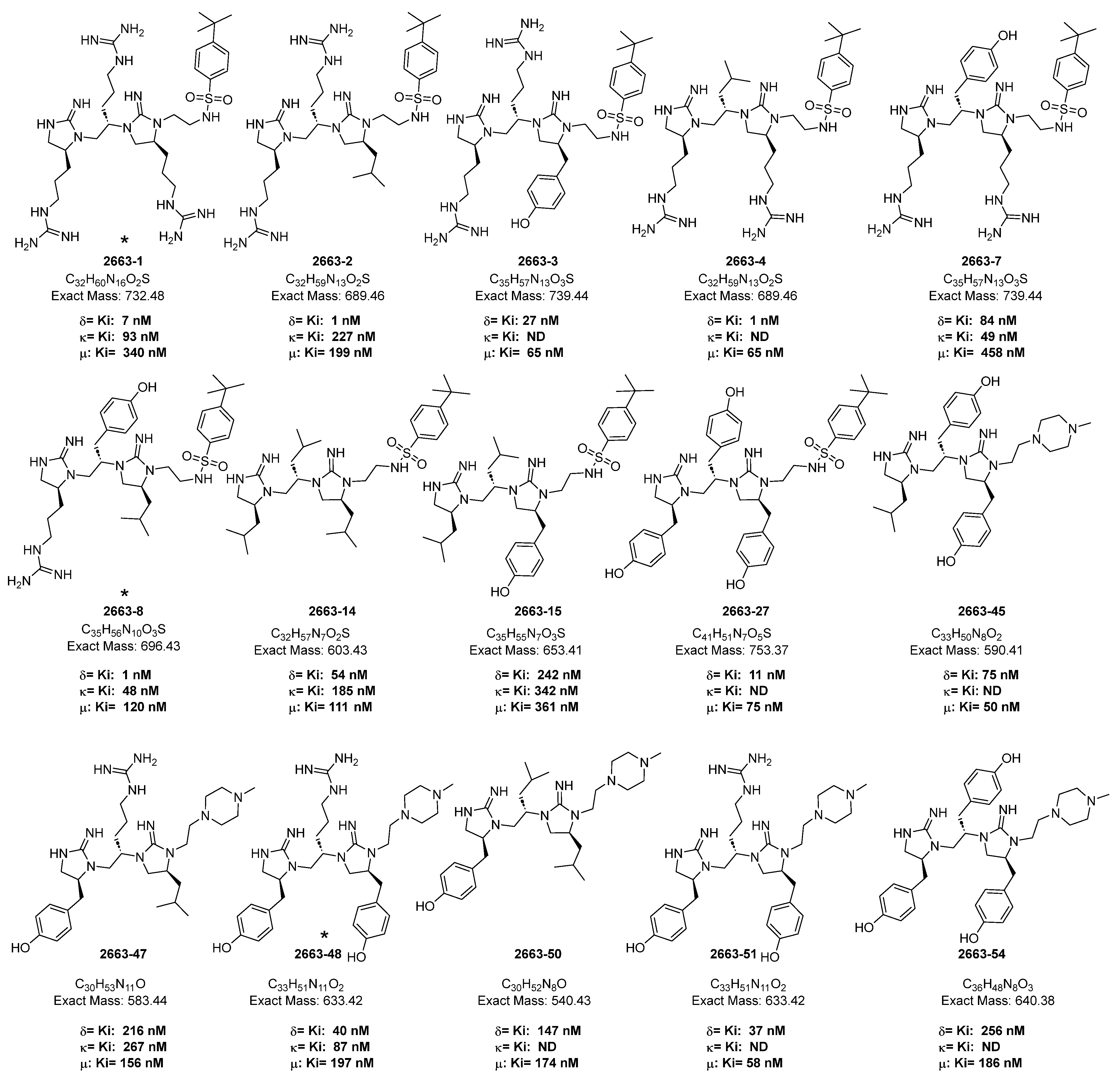
2. Results and Discussion
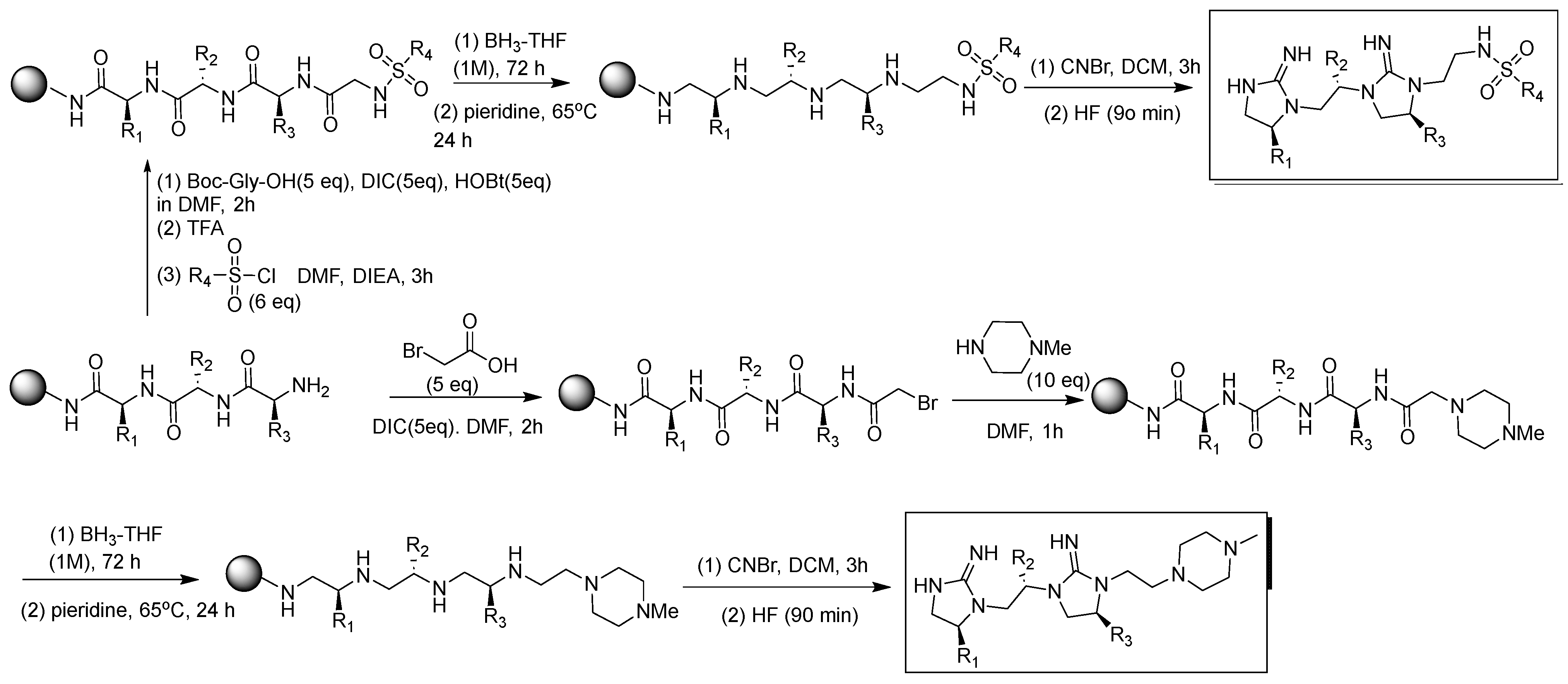
3. Methods and Materials
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stein, C. New concepts in opioid analgesia. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2018, 27, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busserolles, J.; Lolignier, S.; Kerckhove, N.; Bertin, C.; Authier, N.; Eschalier, A. Replacement of current opioid drugs focusing on MOR-related strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 210, 107519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machelska, H.; Celik, M. Advances in Achieving Opioid Analgesia Without Side Effects. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlbeck, K. Opioids: A two-faced Janus. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2011, 27, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khademi, H.; Kamangar, F.; Brennan, P.; Malekzadeh, R. Opioid Therapy and its Side Effects: A Review. Arch. Iran. Med. 2016, 19, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volkow, N.D.; Blanco, C. The changing opioid crisis: Development, challenges and opportunities. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnaturi, R.; Chiechio, S.; Salerno, L.; Rescifina, A.; Pittalà, V.; Cantarella, G.; Tomarchio, E.; Parenti, C.; Pasquinucci, L. Progress in the development of more effective and safer analgesics for pain management. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 183, 111701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corder, G.; Castro, D.C.; Bruchas, M.R.; Scherrer, G. Endogenous and Exogenous Opioids in Pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2018, 41, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inturrisi, C.E. Clinical pharmacology of opioids for pain. Clin. J. Pain. 2002, 18 (Suppl. S4), S3–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, N.P.; Sittampalam, G.S.; Jonson, S.G.; Hall, M.D.; Gorby, H.E.; Tamiz, A.P.; McManus, O.B.; Felder, C.C.; Rasmussen, K. The Opioid Crisis and the Future of Addiction and Pain Therapeutics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 371, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, A.T.; Kieffer, B.L.; Darcq, E. Current strategies toward safer mu opioid receptor drugs for pain management. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidlack, J.M. Mixed κ/μ partial opioid agonists as potential treatments for cocaine dependence. Adv. Pharmacol. 2014, 69, 387–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yan, Z.; Sromek, A.; Knapp, B.I.; Scrimale, T.; Bidlack, J.M.; Neumeyer, J.L. Aminothiazolomorphinans with mixed κ and μ opioid activity. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1903–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, M.; Szymaszkiewicz, A.; Jacenik, D.; Schodel, L.; Sałaga, M.; Zatorski, H.; Kordek, R.; Becker, C.; Krajewska, W.M.; Fichna, J. Cyclic derivative of morphiceptin Dmt-cyclo-(D-Lys-Phe-D-Pro-Asp)-NH2(P-317), a mixed agonist of MOP and KOP opioid receptors, exerts anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor activity in colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 885, 173463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzam, A.A.H.; McDonald, J.; Lambert, D.G. Hot topics in opioid pharmacology: Mixed and biased opioids. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 122, e136–e145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atigari, D.V.; Paton, K.F.; Uprety, R.; Váradi, A.; Alder, A.F.; Scouller, B.; Miller, J.H.; Majumdar, S.; Kivell, B.M. The mixed kappa and delta opioid receptor agonist, MP1104, attenuates chemotherapy-induced neuropathic pain. Neuropharmacology 2021, 185, 108445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattanzi, R.; Rief, S.; Schmidhammer, H.; Negri, L.; Spetea, M. In vitro and in vivo Pharmacological Activities of 14-O-Phenylpropyloxymorphone, a Potent Mixed Mu/Delta/Kappa-Opioid Receptor Agonist With Reduced Constipation in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, C.A.; Negus, S.S.; Zong, R.; Neumeyer, J.L.; Bidlack, J.M.; Mello, N.K. Effects of mixed-action kappa/mu opioids on cocaine self-administration and cocaine discrimination by rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1125–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mello, N.K.; Negus, S.S. Interactions between kappa opioid agonists and cocaine. Preclinical studies. Ann. N. Y Acad. Sci. 2000, 909, 104–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Váradi, A.; Marrone, G.F.; Eans, S.O.; Ganno, M.L.; Subrath, J.J.; Le Rouzic, V.; Hunkele, A.; Pasternak, G.W.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Majumdar, S. Synthesis and characterization of a dual kappa-delta opioid receptor agonist analgesic blocking cocaine reward behavior. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1813–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, C.L.; Honda, C.N. Co-administration of δ- and μ-opioid receptor agonists promotes peripheral opioid receptor function. Pain 2010, 151, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeHaven-Hudkins, D.L.; Burgos, L.C.; Cassel, J.A.; Daubert, J.D.; DeHaven, R.N.; Mansson, E.; Nagasaka, H.; Yu, G.; Yaksh, T. Loperamide (ADL 2-1294), an opioid antihyperalgesic agent with peripheral selectivity. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brice-Tutt, A.C.; Wilson, L.L.; Eans, S.O.; Stacy, H.M.; Simons, C.A.; Simpson, G.G.; Coleman, J.S.; Ferracane, M.J.; Aldrich, J.V.; McLaughlin, J.P. Multifunctional opioid receptor agonism and antagonism by a novel macrocyclic tetrapeptide prevents reinstatement of morphine-seeking behaviour. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4209–4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, D.J.; Peterson, C.D.; Kitto, K.F.; Akgün, E.; Lazzaroni, S.; Portoghese, P.S.; Fairbanks, C.A.; Wilcox, G.L. Combination of a δ-opioid Receptor Agonist and Loperamide Produces Peripherally-mediated Analgesic Synergy in Mice. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 649–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, C.; Clark, J.D.; Oh, U.; Vasko, M.R.; Wilcox, G.L.; Overland, A.C.; Vanderah, T.W.; Spencer, R.H. Peripheral mechanisms of pain and analgesia. Brain Res. Rev. 2009, 60, 90–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.P.; Kong, Q.H.; Li, Y.L.; Pan, C.L.; Yu, J.; Cui, B.Q.; Wang, Y.F.; Wang, G.L.; Zhou, P.L.; Wang, L.L.; et al. The opioid receptor triple agonist DPI-125 produces analgesia with less respiratory depression and reduced abuse liability. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 977–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffa, R.; Burdge, G.; Gambrah, J.; Kinecki, H.; Lin, F.; Lu, B.; Nguyen, J.; Phan, V.; Ruan, A.; Sesay, M. Cebranopadol: Novel dual opioid/NOP receptor agonist analgesic. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2017, 42, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumitrascuta, M.; Bermudez, M.; Ben Haddou, T.; Guerrieri, E.; Schläfer, L.; Ritsch, A.; Hosztafi, S.; Lantero, A.; Kreutz, C.; Massotte, D. N-Phenethyl substitution in 14-methoxy-N-methylmorphinan-6-ones turns selective µ opioid receptor ligands into dual µ/δ opioid receptor agonists. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, P.-K.; Chang, H.-F.; Chang, W.-T.; Yeh, T.-K.; Ou, L.-C.; Chuang, J.-Y.; Hsu, J.T.-A.; Tao, P.-L.; Loh, H.H.; Shih, C. BPR1M97, a dual mu opioid receptor/nociceptin-orphanin FQ peptide receptor agonist, produces potent antinociceptive effects with safer properties than morphine. Neuropharmacology 2020, 166, 107678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podolsky, A.T.; Sandweiss, A.; Hu, J.; Bilsky, E.J.; Cain, J.P.; Kumirov, V.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Hruby, V.J.; Vardanyan, R.S.; Vanderah, T.W. Novel fentanyl-based dual μ/δ-opioid agonists for the treatment of acute and chronic pain. Life Sci. 2013, 93, 1010–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akins, N.S.; Mishra, N.; Harris, H.M.; Dudhipala, N.; Kim, S.J.; Keasling, A.W.; Majumdar, S.; Zjawiony, J.K.; Paris, J.J.; Ashpole, N.M. 6, 5-Fused Ring, C2-Salvinorin Ester, Dual Kappa and Mu Opioid Receptor Agonists as Analgesics Devoid of Anxiogenic Effects. ChemMedChem 2022, 17, e202100684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Vekariya, R.H.; Ananthan, S.; Streicher, J.M. A novel mu-delta opioid agonist demonstrates enhanced efficacy with reduced tolerance and dependence in mouse neuropathic pain models. J. Pain 2020, 21, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, J.P.; Rayala, R.; Bunnell, A.J.; Tantak, M.P.; Eans, S.O.; Nefzi, K.; Ganno, M.L.; Dooley, C.T.; Nefzi, A. Bis-Cyclic Guanidine Heterocyclic Peptidomimetics as Opioid Ligands with Mixed μ-, κ- and δ-Opioid Receptor Interactions: A Potential Approach to Novel Analgesics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantak, M.P.; Rayala, R.; Chaudhari, P.; Danta, C.C.; Nefzi, A. Synthesis of Diazacyclic and Triazacyclic Small-Molecule Libraries Using Vicinal Chiral Diamines Generated from Modified Short Peptides and Their Application for Drug Discovery. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, H.R.; Chaudhari, P.; Bunnell, A.; Nefzi, K.; Chen, C.; Zhao, P.; Eans, S.O.; Masood, S.R.; Dooley, C.T.; Liu-Chen, L.-Y.; et al. Peripherally Restricted Fused Heterocyclic Peptidomimetic Multifunctional Opioid Agonists as Novel, Potent Analgesics. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2025, 16, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefzi, A.; Ostresh, J.M.; Yu, Y.; Houghten, R.A. Combinatorial chemistry: Libraries from libraries, the art of the diversity-oriented transformation of resin-bound peptides and chiral polyamides to low molecular weight acyclic and heterocyclic compounds. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 3603–3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghten, R.A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: Specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 5131–5135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eans, S.O.; Ganno, M.L.; Mizrachi, E.; Houghten, R.A.; Dooley, C.T.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Nefzi, A. Parallel Synthesis of Hexahydrodiimidazodiazepines Heterocyclic Peptidomimetics and Their in Vitro and in Vivo Activities at μ (MOR), δ (DOR), and κ (KOR) Opioid Receptors. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 4905–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nefzi, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Houghten, R.A. Solid-phase synthesis of bis-heterocyclic compounds from resin-bound orthogonally protected lysine. J. Comb. Chem. 2001, 3, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nefzi, A.; Ostresh, J.M.; Appel, J.R.; Bidlack, J.; Dooley, C.T.; Houghten, R.A. Identification of potent and highly selective chiral tri-amine and tetra-amine mu opioid receptors ligands: An example of lead optimization using mixture-based libraries. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4331–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, M.A.; Michaels, H.; Molina, B.; Toenjes, S.; Davis, J.; Marconi, G.D.; Hecht, D.; Gustafson, J.L.; Piedrafita, F.J.; Nefzi, A. Discovery of cyclic guanidine-linked sulfonamides as inhibitors of LMTK3 kinase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 30, 127108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.T.; Chung, N.N.; Wilkes, B.C.; Schiller, P.W.; Bidlack, J.M.; Pasternak, G.W.; Houghten, R.A. An all D-amino acid opioid peptide with central analgesic activity from a combinatorial library. Science 1994, 266, 2019–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.T.; Houghten, R.A. New opioid peptides, peptidomimetics, and heterocyclic compounds from combinatorial libraries. Biopolymers 1999, 51, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, C.T.; Ny, P.; Bidlack, J.M.; Houghten, R.A. Selective ligands for the mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors identified from a single mixture based tetrapeptide positional scanning combinatorial library. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 18848–18856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaudhari, P.; Bunnell, A.; Yegambaram, M.; Dooley, C.; Nefzi, A. Opioid Affinity of Diazacyclic Peptidomimetic Compounds Derived from Reduced Polyamides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178249
Chaudhari P, Bunnell A, Yegambaram M, Dooley C, Nefzi A. Opioid Affinity of Diazacyclic Peptidomimetic Compounds Derived from Reduced Polyamides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178249
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaudhari, Prakash, Ashley Bunnell, Manivannan Yegambaram, Colette Dooley, and Adel Nefzi. 2025. "Opioid Affinity of Diazacyclic Peptidomimetic Compounds Derived from Reduced Polyamides" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178249
APA StyleChaudhari, P., Bunnell, A., Yegambaram, M., Dooley, C., & Nefzi, A. (2025). Opioid Affinity of Diazacyclic Peptidomimetic Compounds Derived from Reduced Polyamides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178249







