Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Proteome in Two Canine Breeds: Dalmatians and Weimaraners
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
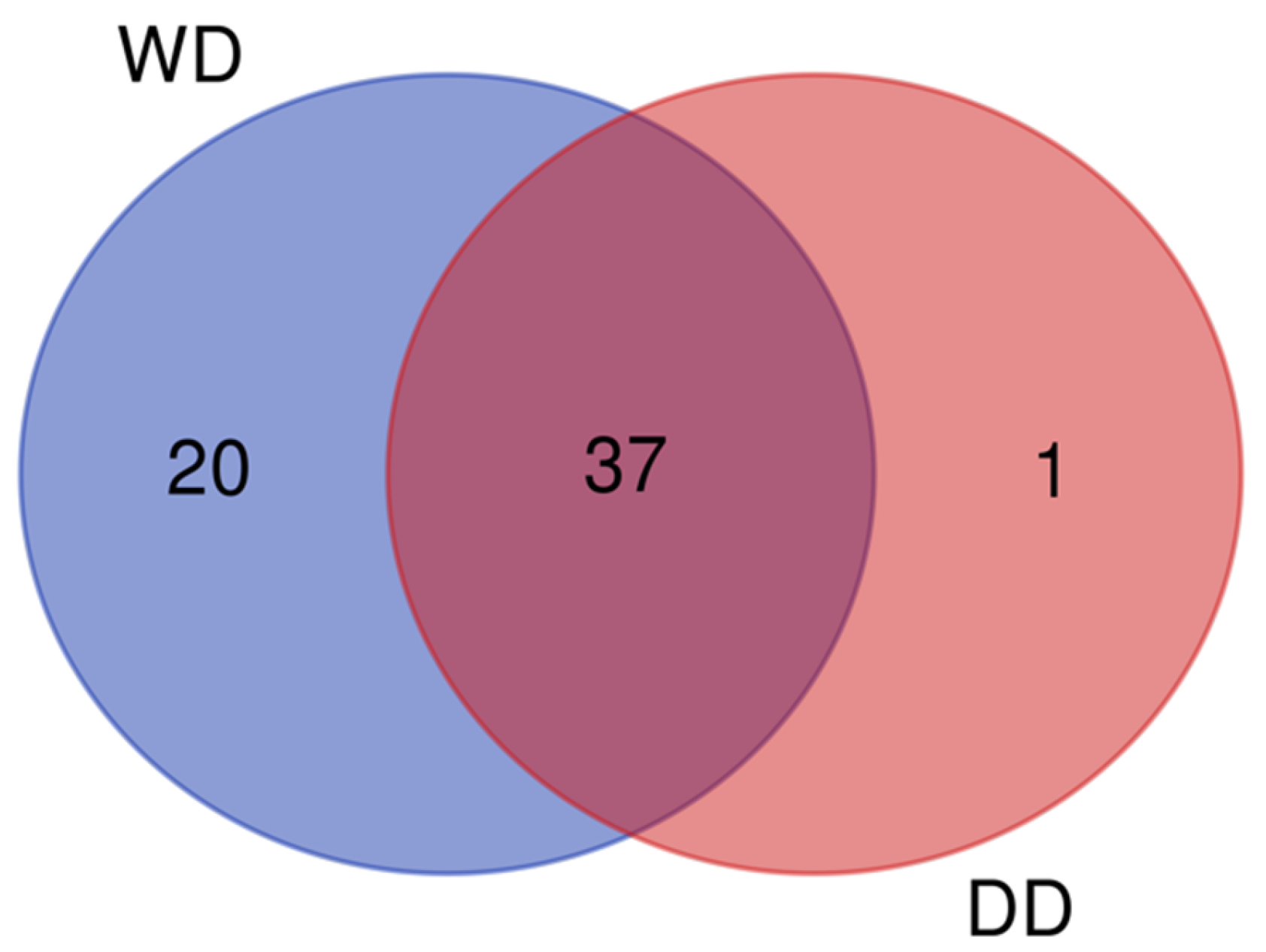
2.1. General Profile of the Fecal Proteome
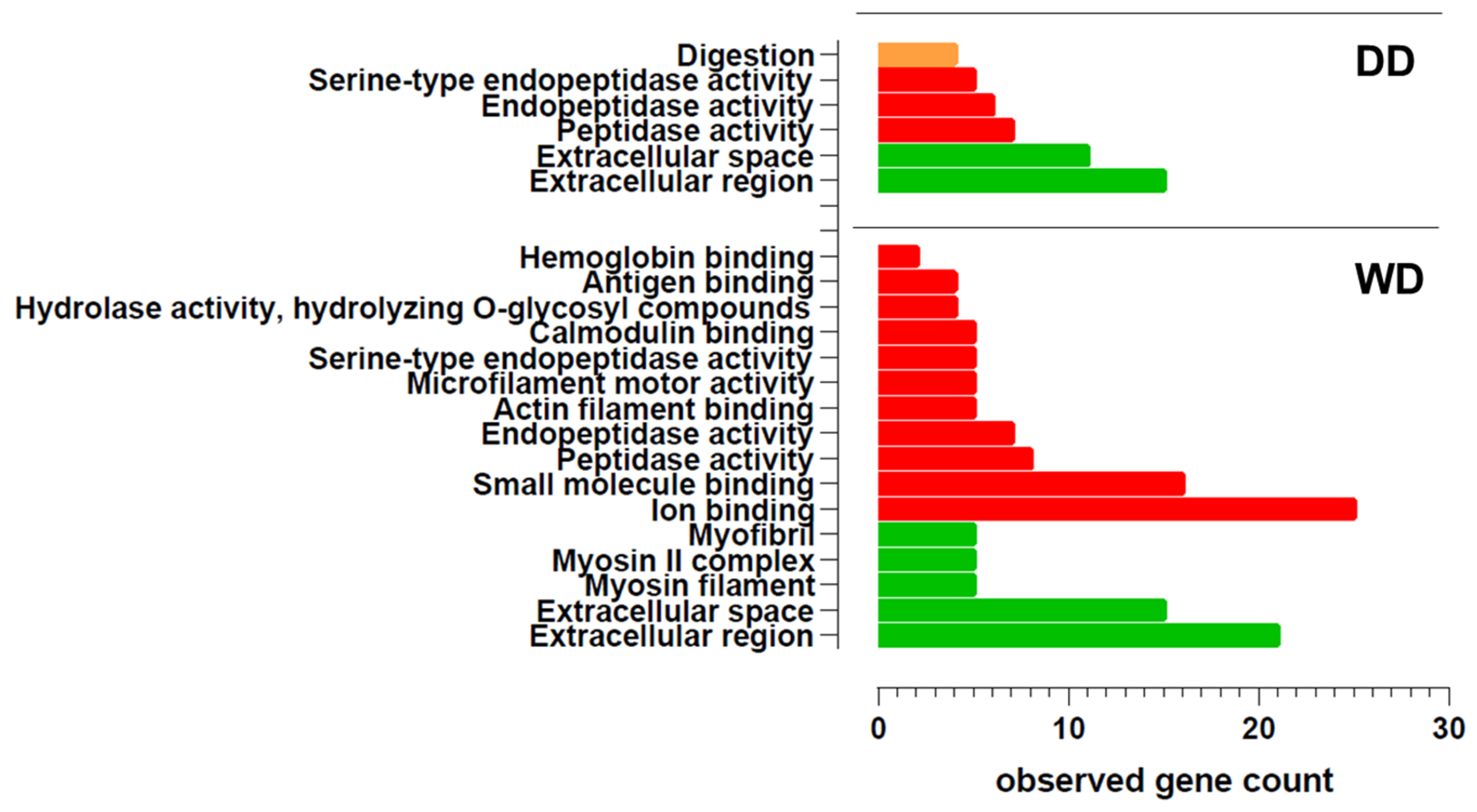
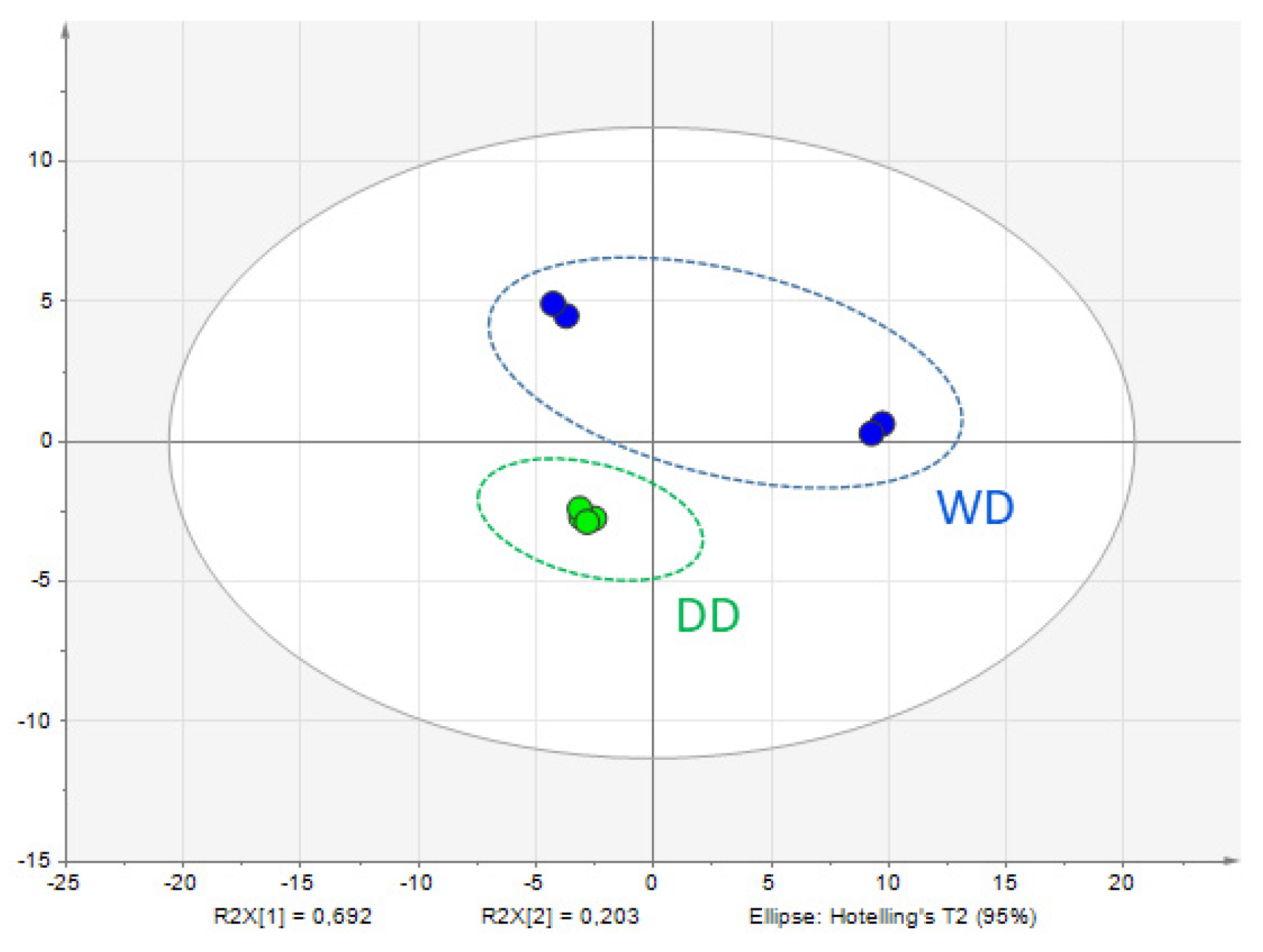
2.2. Comparative Fecal Proteomics Analysis Between Dalmatian and Weimaraner
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Dogs Included in This Study
4.2. Samplings and Protein Extraction, Digestion, and Purification
4.3. LC-MS/MS Analysis
4.4. Data Analysis
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis of Omics Data
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerquetella, M.; Rossi, G.; Spaterna, A.; Tesei, B.; Gavazza, A.; Pengo, G.; Pucciarelli, S.; Scortichini, L.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; et al. Fecal Proteomic Analysis in Healthy Dogs and in Dogs Suffering from Food Responsive Diarrhea. Sci. World J. 2019, 2019, 2742401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cerquetella, M.; Marchegiani, A.; Mangiaterra, S.; Rossi, G.; Gavazza, A.; Tesei, B.; Spaterna, A.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Polzonetti, V.; et al. Faecal proteome in clinically healthy dogs and cats: Findings in pooled faeces from 10 cats and 10 dogs. Vet. Rec. Open 2021, 8, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rossi, G.; Gavazza, A.; Vincenzetti, S.; Mangiaterra, S.; Galosi, L.; Marchegiani, A.; Pengo, G.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Cerquetella, M. Clinicopathological and Fecal Proteome Evaluations in 16 Dogs Presenting Chronic Diarrhea Associated with Lymphangiectasia. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- O’Reilly, E.L.; Horvatić, A.; Kuleš, J.; Gelemanović, A.; Mrljak, V.; Huang, Y.; Brady, N.; Chadwick, C.C.; Eckersall, P.D.; Ridyard, A. Faecal proteomics in the identification of biomarkers to differentiate canine chronic enteropathies. J. Proteomics 2022, 254, 104452, Erratum in J. Proteomics 2022, 259, 104510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerquetella, M.; Mangiaterra, S.; Rossi, G.; Gavazza, A.; Marchegiani, A.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Angeloni, S.; Fioretti, L.; Marini, C.; et al. Fecal Protein Profile in Eight Dogs Suffering from Acute Uncomplicated Diarrhea before and after Treatment. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cerquetella, M.; Mangiaterra, S.; Pinnella, F.; Rossi, G.; Marchegiani, A.; Gavazza, A.; Serri, E.; Di Cerbo, A.; Marini, C.; Cecconi, D.; et al. Fecal Proteome Profile in Dogs Suffering from Different Hepatobiliary Disorders and Comparison with Controls. Animals 2023, 13, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heilmann, R.M.; Steiner, J.M. Clinical utility of currently available biomarkers in inflammatory enteropathies of dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1495–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Marsilio, S.; Dröes, F.C.; Dangott, L.; Chow, B.; Hill, S.; Ackermann, M.; Estep, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Characterization of the intestinal mucosal proteome in cats with inflammatory bowel disease and alimentary small cell lymphoma. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 179–189, Erratum in J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Albasan, H.; Lulich, J.P.; Osborne, C.A.; Lekcharoensuk, C. Evaluation of the association between sex and risk of forming urate uroliths in Dalmatians. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 227, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, M.; Simpson, J.W.; Ridyard, A.E.; Chandler, M.L. Canine inflammatory bowel disease: Retrospective analysis of diagnosis and outcome in 80 cases (1995–2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathrani, A.; Werling, D.; Allenspach, K. Canine breeds at high risk of developing inflammatory bowel disease in the south-eastern UK. Vet. Rec. 2011, 169, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, T.; Schallert, K.; Vilchez-Vargas, R.; Benndorf, D.; Püttker, S.; Sydor, S.; Schulz, C.; Bechmann, L.; Canbay, A.; Heidrich, B.; et al. Metaproteomics of fecal samples of Crohn’s disease and Ulcerative Colitis. J. Proteomics 2019, 201, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConnell, R.E.; Benesh, A.E.; Mao, S.; Tabb, D.L.; Tyska, M.J. Proteomic analysis of the enterocyte brush border. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G914–G926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Engevik, M.A.; Engevik, A.C. Myosins and membrane trafficking in intestinal brush border assembly. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2022, 77, 102117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, G.P.; Cutz, E.; Hamilton, J.R.; Gall, D.G. Familial enteropathy: A syndrome of protracted diarrhea from birth, failure to thrive, and hypoplastic villus atrophy. Gastroenterology 1978, 75, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanDussen, K.L.; Stojmirović, A.; Li, K.; Liu, T.C.; Kimes, P.K.; Muegge, B.D.; Simpson, K.F.; Ciorba, M.A.; Perrigoue, J.G.; Friedman, J.R.; et al. Abnormal Small Intestinal Epithelial Microvilli in Patients With Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yokoyama, M.; Kimura, M.Y.; Ito, T.; Hayashizaki, K.; Endo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yagi, R.; Nakagawa, T.; Kato, N.; Matsubara, H.; et al. Myosin Light Chain 9/12 Regulates the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 594297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heybrock, S.; Kanerva, K.; Meng, Y.; Ing, C.; Liang, A.; Xiong, Z.J.; Weng, X.; Ah Kim, Y.; Collins, R.; Trimble, W.; et al. Lysosomal integral membrane protein-2 (LIMP-2/SCARB2) is involved in lysosomal cholesterol export. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sturley, S.L.; Patterson, M.C.; Balch, W.; Liscum, L. The pathophysiology and mechanisms of NP-C disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1685, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larabi, A.; Barnich, N.; Nguyen, H.T.T. New insights into the interplay between autophagy, gut microbiota and inflammatory responses in IBD. Autophagy 2020, 16, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Du, X.; Kumar, J.; Ferguson, C.; Schulz, T.A.; Ong, Y.S.; Hong, W.; Prinz, W.A.; Parton, R.G.; Brown, A.J.; Yang, H. A role for oxysterol-binding protein-related protein 5 in endosomal cholesterol trafficking. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garver, W.S.; Krishnan, K.; Gallagos, J.R.; Michikawa, M.; Francis, G.A.; Heidenreich, R.A. Niemann-Pick C1 protein regulates cholesterol transport to the trans-Golgi network and plasma membrane caveolae. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitto, T.; Onodera, K. Linkage between coenzyme a metabolism and inflammation: Roles of pantetheinase. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Diepen, J.A.; Jansen, P.A.; Ballak, D.B.; Hijmans, A.; Hooiveld, G.J.; Rommelaere, S.; Galland, F.; Naquet, P.; Rutjes, F.P.; Mensink, R.P.; et al. PPAR-alpha dependent regulation of vanin-1 mediates hepatic lipid metabolism. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giessner, C.; Millet, V.; Mostert, K.J.; Gensollen, T.; Vu Manh, T.P.; Garibal, M.; Dieme, B.; Attaf-Bouabdallah, N.; Chasson, L.; Brouilly, N.; et al. Vnn1 pantetheinase limits the Warburg effect and sarcoma growth by rescuing mitochondrial activity. Life Sci. Alliance 2018, 1, e201800073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Casazza, A.; Di Conza, G.; Wenes, M.; Finisguerra, V.; Deschoemaeker, S.; Mazzone, M. Tumor stroma: A complexity dictated by the hypoxic tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millet, V.; Gensollen, T.; Maltese, M.; Serrero, M.; Lesavre, N.; Bourges, C.; Pitaval, C.; Cadra, S.; Chasson, L.; Vu Man, T.P.; et al. Harnessing the Vnn1 pantetheinase pathway boosts short chain fatty acids production and mucosal protection in colitis. Gut 2023, 72, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Tao, G.; Xu, B.; Wang, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, C.H.; Dunn, J.C.Y.; Currie, C.; Framroze, B.; Sylvester, K.G. Soluble Protein Hydrolysate Ameliorates Gastrointestinal Inflammation and Injury in 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-Induced Colitis in Mice. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Harder, B.J.; Lekkerkerker, A.N.; Casavant, E.P.; Hackney, J.A.; Nguyen, A.; McBride, J.M.; Mathews, W.R.; Anania, V.G. Comprehensive profiling of the human fecal proteome from IBD patients with DIA-MS enables evaluation of disease-relevant proteins. Proteomics Clin. Appl. 2024, 18, e2300075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablaoui, A.; Kriaa, A.; Mkaouar, H.; Akermi, N.; Soussou, S.; Wysocka, M.; Wołoszyn, D.; Amouri, A.; Gargouri, A.; Maguin, E.; et al. Fecal Serine Protease Profiling in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Al-Awami, H.M.; Raja, A.; Soos, M.P. Physiology, gastric intrinsic factor. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toresson, L.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Spillmann, T. Oral Cobalamin Supplementation in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies and Hypocobalaminemia. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mosnier, L.O.; Bouma, B.N. Regulation of fibrinolysis by thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor, an unstable carboxypeptidase B that unites the pathways of coagulation and fibrinolysis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Dai, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, F. Differential roles of highly expressed PFKFB4 in colon adenocarcinoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16284, Correction in Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mangiaterra, S.; Vincenzetti, S.; Rossi, G.; Marchegiani, A.; Gavazza, A.; Petit, T.; Sagratini, G.; Ricciutelli, M.; Cerquetella, M. Evaluation of the Fecal Proteome in Healthy and Diseased Cheetahs (Acinonyx jubatus) Suffering from Gastrointestinal Disorders. Animals 2022, 12, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Bandla, C.; Kundu, D.J.; Kamatchinathan, S.; Bai, J.; Hewapathirana, S.; John, N.S.; Prakash, A.; Walzer, M.; Wang, S.; et al. The PRIDE database at 20 years: 2025 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D543–D553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Carlo, C.; Sousa, B.C.; Manfredi, M.; Brandi, J.; Dalla Pozza, E.; Marengo, E.; Palmieri, M.; Dando, I.; Wakelam, M.J.O.; Lopez-Clavijo, A.F.; et al. Integrated lipidomics and proteomics reveal cardiolipin alterations, upregulation of HADHA and long chain fatty acids in pancreatic cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| N. | Protein Name [OS = Canis lupus familiaris] | DD Sequest Score HT | WD Sequest Score HT | Accession | MW [kDa] | Calc. pI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Actin, cytoplasmic 1 | 54.33 | 129.72 | O18840 | 41.7 | 5.48 |
| 2 | Albumin | 1077.47 | 1674.59 | P49822 | 68.6 | 5.69 |
| 3 | Aminopeptidase N | 1108.5 | 1540.75 | P79143 | 110.2 | 6.18 |
| 4 | Anionic trypsin | 302.7 | 638.78 | P06872 | 26.4 | 4.83 |
| 5 | Annexin A2 | - | 4.33 | Q6TEQ7 | 38.6 | 7.31 |
| 6 | Beta-glucuronidase | - | 28.99 | O18835 | 74.4 | 6.57 |
| 7 | Cadherin-1 | 481.75 | 574.79 | F1PAA9 | 97.7 | 4.81 |
| 8 | Carboxypeptidase B | 213.29 | 194.1 | P55261 | 47.6 | 6.6 |
| 9 | Cathepsin S | - | 20.7 | Q8HY81 | 37.2 | 8.13 |
| 10 | Serine protease 1 | 266.92 | 289.09 | P06871 | 26.2 | 8.07 |
| 11 | Chymotrypsin-like elastase fam. member 1 | 128.43 | 243.38 | Q867B0 | 27.9 | 8.46 |
| 12 | Chymotrypsinogen 2 | 195.17 | 172.94 | P04813 | 27.8 | 7.2 |
| 13 | Cobalamin binding intrinsic factor | 149.5 | 39.58 | Q5XWD5 | 45 | 5.78 |
| 14 | Collagen alpha-5(IV) chain | - | 24.04 | Q28247 | 162.1 | 8.24 |
| 15 | Cubilin | - | 77.81 | Q9TU53 | 397.2 | 5.44 |
| 16 | Cytochrome c | 165.24 | 116.71 | P00011 | 11.6 | 9.58 |
| 17 | Dihydrolipoyl dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | 112.53 | 162.47 | P49819 | 54.1 | 7.84 |
| 18 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 1 | 240.81 | 414.86 | O97578 | 49.4 | 7.03 |
| 19 | DLA class I histocompatibility antigen, A9/A9 alpha chain | 48.96 | 55.73 | P18466 | 40.4 | 5.87 |
| 20 | DLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR-1 beta chain | 89.52 | 62.49 | P18470 | 30.1 | 6.15 |
| 21 | Double-headed protease inhibitor, submandibular gland | 26.47 | 53.34 | P01002 | 12.8 | 7.93 |
| 22 | Epididymal secretory glutathione peroxidase | - | 3.1 | O46607 | 25.3 | 8.91 |
| 23 | Ferritin heavy chain | - | 343.06 | Q95MP7 | 21.3 | 5.88 |
| 24 | Ferritin light chain | - | 165.13 | Q53VB8 | 20.1 | 6 |
| 25 | Fibronectin | 37.4 | 94.47 | Q28275 | 243.1 | 5.99 |
| 26 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | 44.69 | 27.51 | Q28259 | 35.8 | 8.12 |
| 27 | Haptoglobin | 19.08 | 252.56 | P19006 | 36.4 | 6.09 |
| 28 | Hemoglobin subunit alpha [OS = Canis latrans] | - | 83.61 | P60530 | 15.4 | 8.06 |
| 29 | Hemoglobin subunit beta | - | 84.53 | P60524 | 16 | 8.05 |
| 30 | Ig heavy chain V region GOM | 188.5 | 258.07 | P01784 | 12.4 | 5.4 |
| 31 | Ig heavy chain V region MOO | - | 67.5 | P01785 | 12.7 | 4.72 |
| 32 | Ig kappa chain V region GOM | 87.19 | 46.27 | P01618 | 12 | 6.61 |
| 33 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 10 | 150.23 | 153.13 | Q6EIZ0 | 57.7 | 5.15 |
| 34 | Keratin, type I cytoskeletal 9 | 9.54 | 13.88 | O18740 | 76.3 | 5.95 |
| 35 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 1 | 148.26 | 121.34 | Q6EIY9 | 63.8 | 7.84 |
| 36 | Keratin, type II cytoskeletal 2 epidermal | 43.31 | 37.37 | Q6EIZ1 | 64.5 | 7.74 |
| 37 | Lysozyme C, milk isozyme | 39.31 | 34.15 | P81708 | 14.5 | 8.29 |
| 38 | Lysozyme C, spleen isozyme | - | 15.41 | P81709 | 14.6 | 8.81 |
| 39 | Myosin-2 | - | 127.86 | Q076A7 | 223.1 | 5.81 |
| 40 | Myosin-4 | - | 175.55 | Q076A5 | 222.9 | 5.76 |
| 41 | Myosin-7 | - | 87.9 | P49824 | 222.8 | 5.73 |
| 42 | Myosin-13 | - | 20.54 | Q076A3 | 223.2 | 5.68 |
| 43 | Myosin-16 | - | 26.91 | F1PT61 | 222.5 | 6.02 |
| 44 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 | 48.56 | 63.39 | Q28895 | 16 | 8.02 |
| 45 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase A | 40.31 | 58.11 | Q50KA9 | 17.2 | 6.01 |
| 46 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B | 50.71 | 61.42 | Q50KA8 | 17.4 | 7.99 |
| 47 | Pancreatic secretory granule membrane major glycoprotein GP2 | 20.86 | 68.68 | P25291 | 56.7 | 5.62 |
| 48 | Pantetheinase | - | 5.39 | Q9TSX8 | 57.4 | 6.65 |
| 49 | Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | 107.81 | 58.74 | Q3YIX4 | 20.9 | 7.49 |
| 50 | Proteasome subunit beta type-8 | - | 8.11 | Q5W416 | 30.5 | 7.72 |
| 51 | Sodium/calcium exchanger 1 | - | 28.99 | P23685 | 107.9 | 4.96 |
| 52 | Superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn] | 306.13 | 291.48 | Q8WNN6 | 15.9 | 6.11 |
| 53 | Tissue alpha-L-fucosidase | 51.38 | 253.61 | P48300 | 53.7 | 6.74 |
| 54 | Trefoil factor 2 | 62.11 | 64.23 | Q863J2 | 14.1 | 7.65 |
| 55 | Trefoil factor 3 | 187.7 | 203.52 | Q863B4 | 8.9 | 4.94 |
| 56 | Triosephosphate isomerase | 221.29 | 162.87 | P54714 | 26.7 | 7.33 |
| 57 | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 | 29.11 | 33.4 | P63050 | 14.7 | 9.83 |
| 58 | WAP four-disulfide core domain protein 2 | 47.9 | - | A0A8I3NWP8 | 63.8 | 7.84 |
| Tot. 38 | Tot. 57 |
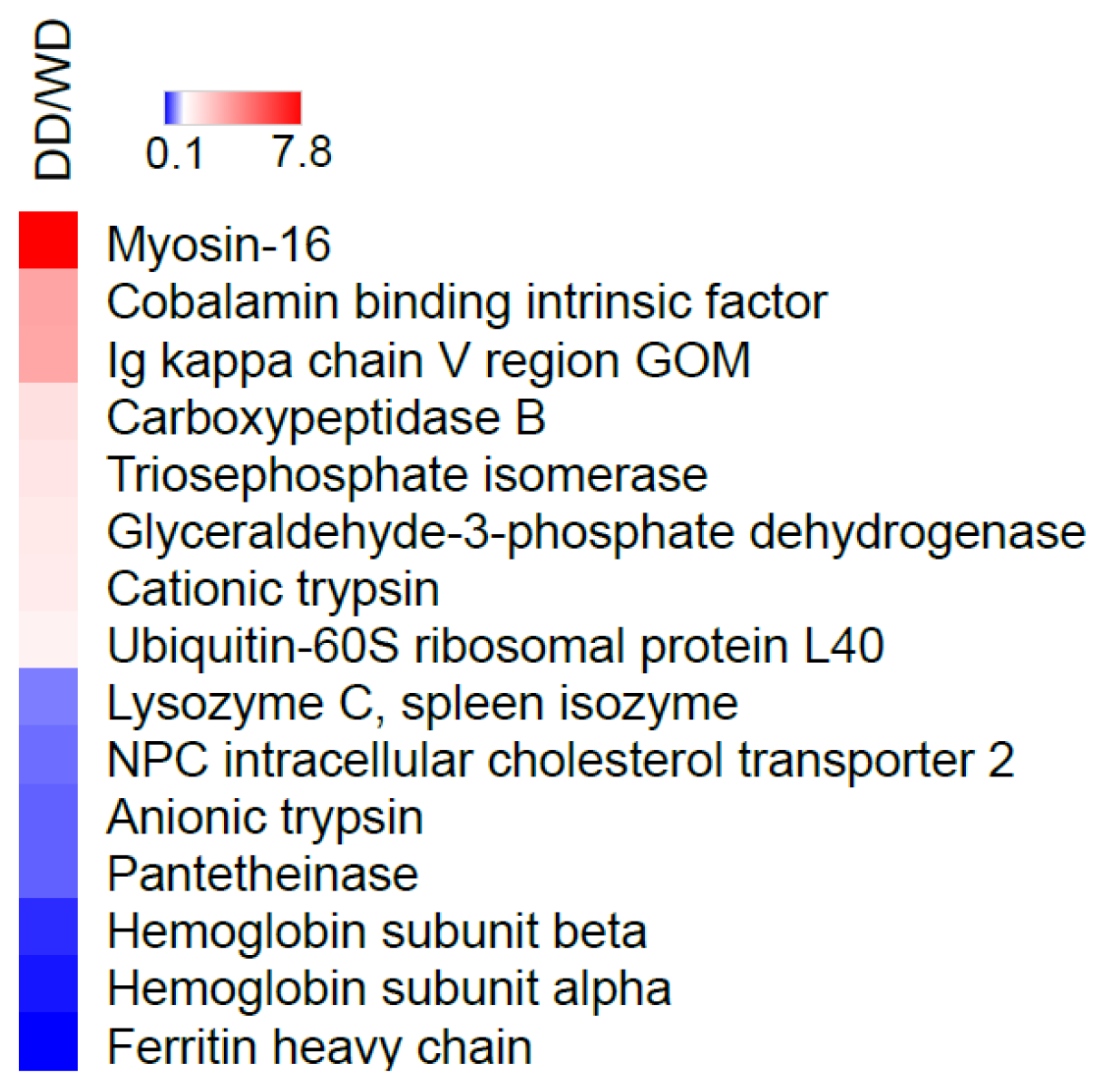
| Gene Name | Protein Name | Protein ID | Sequence Coverage | Score Sequest HT | N. Peptides | Fold Change (DD/WD) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYH16 | Myosin-16 | F1PT61 | 2 | 36.66 | 3 | 7.80 | 0.0000 |
| CBLIF | Cobalamin binding intrinsic factor | Q5XWD5 | 24 | 189.08 | 9 | 3.58 | 0.0008 |
| Ig kappa chain V region GOM | P01618 | 34 | 131.02 | 2 | 3.51 | 0.0008 | |
| CPB1 | Carboxypeptidase B | P55261 | 42 | 405.24 | 14 | 2.02 | 0.0105 |
| TPI1 | Triosephosphate isomerase | P54714 | 78 | 384.16 | 14 | 1.90 | 0.0118 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Q28259 | 24 | 72.2 | 5 | 1.78 | 0.0298 |
| PRSS1 | Serine protease 1 | P06871 | 81 | 556.01 | 12 | 1.74 | 0.0342 |
| UBA52 | Ubiquitin-60S ribosomal protein L40 | P63050 | 27 | 54.1 | 3 | 1.56 | 0.0209 |
| LYZ | Lysozyme C, spleen isozyme | P81709 | 38 | 15.41 | 3 | 0.67 | 0.0321 |
| NPC2 | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 | Q28895 | 42 | 111.95 | 5 | 0.60 | 0.0223 |
| PRSS2 | Anionic trypsin | P06872 | 60 | 969.67 | 8 | 0.55 | 0.0264 |
| VNN1 | Pantetheinase | Q9TSX8 | 5 | 5.39 | 2 | 0.55 | 0.0013 |
| HBB | Hemoglobin subunit beta | P60524 | 66 | 88.01 | 11 | 0.32 | 0.0007 |
| HBA | Hemoglobin subunit alpha | P60530 | 62 | 94.38 | 6 | 0.23 | 0.0121 |
| FTH1 | Ferritin heavy chain | Q95MP7 | 85 | 348.38 | 16 | 0.14 | 0.0535 |
| ID | Term | Term p-Value Corrected with Bonferroni Step Down | Group p-Value Corrected with Bonferroni Step Down | % Associated Genes | Nr. Genes | Associated Genes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KEGG:00010 | Glycolysis/gluconeogenesis | 0.0075 | 0.0050 | 2.30 | 2 | GAPDH, TPI1 |
| KEGG:04972 | Pancreatic secretion | 0.0055 | 0.0094 | 2.20 | 2 | CPB1, PRSS2 |
| KEGG:04974 | Protein digestion and absorption | 0.0033 | 0.0094 | 2.00 | 2 | CPB1, PRSS2 |
| Variable | Weimaraner Dogs (WDs, n = 13) | Dalmatian Dogs (DDs, n = 13) |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Health Status | Healthy | Healthy |
| Medication Status | No medications | No medications |
| Diarrhea (last month) | None reported | None reported |
| Other Clinical Signs (last month) | None reported | None reported |
| Parasite Treatments | Regular treatments | Regular treatments |
| Diet | Maintenance kibble | Maintenance kibble |
| Percentage of Male/Female Dogs | 46%/54 | 38%/62% |
| Age (mean ± SD, years) | 5.5 ± 2.9 | 7.5 ± 3.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cerquetella, M.; Pinnella, F.; Morazzini, R.; Rossi, G.; Marchegiani, A.; Gavazza, A.; Mangiaterra, S.; Di Cerbo, A.; Sorio, D.; Brandi, J.; et al. Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Proteome in Two Canine Breeds: Dalmatians and Weimaraners. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178247
Cerquetella M, Pinnella F, Morazzini R, Rossi G, Marchegiani A, Gavazza A, Mangiaterra S, Di Cerbo A, Sorio D, Brandi J, et al. Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Proteome in Two Canine Breeds: Dalmatians and Weimaraners. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178247
Chicago/Turabian StyleCerquetella, Matteo, Francesco Pinnella, Rachele Morazzini, Giacomo Rossi, Andrea Marchegiani, Alessandra Gavazza, Sara Mangiaterra, Alessandro Di Cerbo, Daniela Sorio, Jessica Brandi, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Proteome in Two Canine Breeds: Dalmatians and Weimaraners" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178247
APA StyleCerquetella, M., Pinnella, F., Morazzini, R., Rossi, G., Marchegiani, A., Gavazza, A., Mangiaterra, S., Di Cerbo, A., Sorio, D., Brandi, J., Cecconi, D., & Vincenzetti, S. (2025). Comparative Analysis of the Fecal Proteome in Two Canine Breeds: Dalmatians and Weimaraners. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8247. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178247









