Beyond the Biomarker: Monomeric CRP as a Driver of Multisystem Pathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CRP and mCRP in RA
2.1. Physiology of CRP and mCRP Conversion in Vascular Disease
2.2. The Dual Role of CRP-mCRP in Pathological Development of RA
2.3. CRP Signaling in RA Synovial Inflammation
2.4. Pro-Inflammatory Mechanisms of mCRP in RA
2.5. CRP in RA Under Treatment
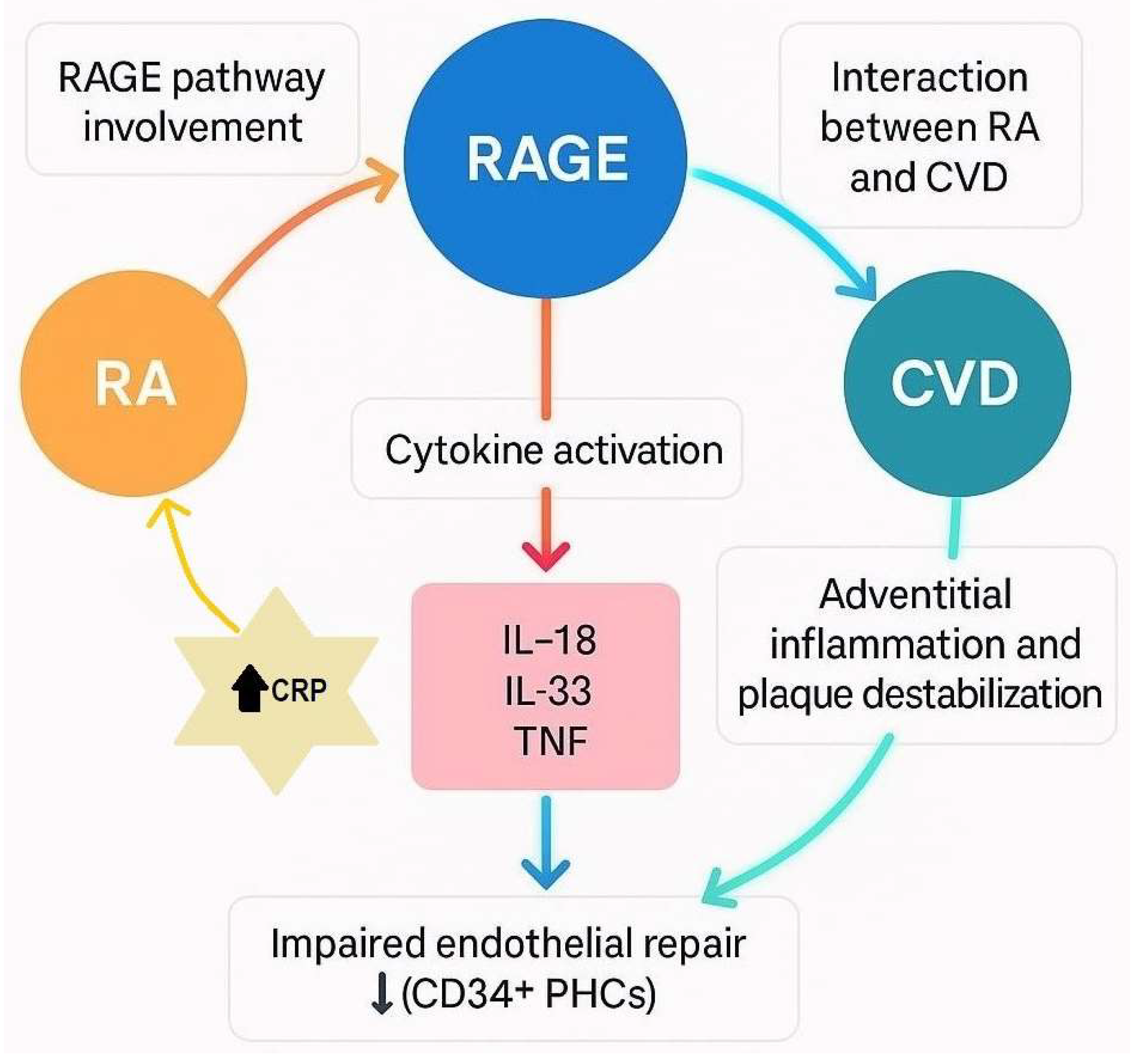
3. CRP Informs CVD Risk in RA Patients
3.1. Key Molecular Mechanisms of RA-Associated CVD
3.2. Role of Cytokines in RA-CVD
3.3. Endothelial Dysfunction in RA
3.4. Vascular Elasticity in RA
3.5. Atherosclerosis and Endothelial Repair in RA
3.6. CRP Implicated in Metabolic Syndrome
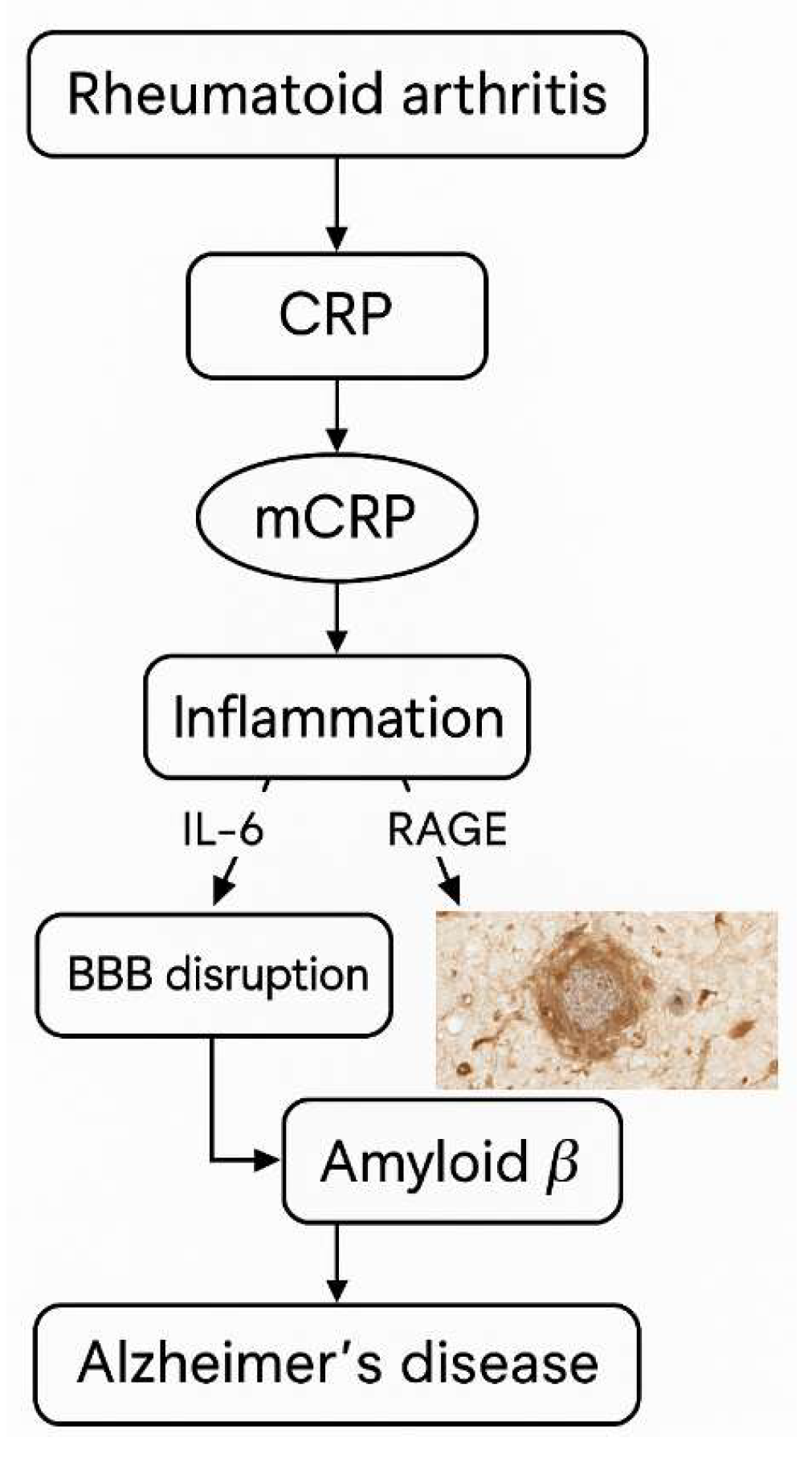
4. Neurocognitive Implications in RA Related to CRP
4.1. AD, Dementia, Stroke and CRP
4.2. Cognitive Dysfunction and CRP
4.3. Depression and CRP
5. Conclusions
6. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACPA | Anti-Citrullinated Peptide Antibody |
| ACS | Acute Coronary Syndrome |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ADNI | Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative |
| Aβ | Beta-Amyloid (Amyloid-beta) |
| Aβ42 | Amyloid-beta 1–42 |
| Abeta40 | Amyloid-beta 1–40 |
| Anti-CCP | Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide |
| Anti-Hsp60 | Antibodies Against 60 kDa Heat Shock Protein |
| BDI-II | Beck Depression Inventory-II |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| BNP | B-Type Natriuretic Peptide |
| BRASS | Brigham and Women’s Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study |
| C | Complement System |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| CHD | Coronary Heart Disease |
| CIA | Collagen-Induced Arthritis |
| CMD | Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| csDMARDs | Conventional Synthetic Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs |
| CV | Cardiovascular |
| CVD | Cardiovascular Disease |
| DAS28-CRP | Disease Activity Score 28 (or in 28 joints)-CRP |
| DBS | Dried Blood Spot |
| DMARDs | Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs |
| EC | Endothelial Cell |
| ECG | Electrocardiogram |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ESR | Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate |
| EV/EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| Fcγ receptors | Fc gamma receptors |
| FLS | Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| hscTnT | High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin T |
| hsCRP | High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1 beta |
| IL-2 | Interleukin-2 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-12 | Interleukin-12 |
| IL-18 | Interleukin-18 |
| IL-33 | Interleukin-33 |
| IMT | Intima-Media Thickness |
| JAKi | Janus Kinase Inhibitor |
| LDL-C | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| LpPLA2 | Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase |
| MAC | Membrane Attack Complex |
| MACE | Major Adverse Cardiac Events |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 |
| MDD | Major Depressive Disorder |
| MetS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| MFR | Myocardial Flow Reserve |
| MHC-II | Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| MPs | Microparticles |
| mCRP | Monomeric C-Reactive Protein |
| MVs | Microvesicles |
| nCRP | Native (Pentameric) C-Reactive Protein |
| NK | Natural Killer Cells |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor Kappa-light-chain-enhancer of Activated B cells |
| NFTs | Neurofibrillary Tangles |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database (Taiwan) |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| OPN | Osteopontin |
| PAD | Peripheral Artery Disease |
| PC | Phosphocholine |
| PE | Phosphoethanolamine |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| PHCs | Progenitor Hematopoietic Cells (CD34+ cells) |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
| pCRP/pCRP* | Pentameric C-Reactive Protein/Pentameric Symmetrical CRP (with neoepitope exposed)/Conformational Intermediate of CRP |
| PWV | Pulse Wave Velocity |
| RA | Rheumatoid Arthritis |
| RAGE/RAGEs | Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products |
| RF | Rheumatoid Factor |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| sPLA2 | Secretory Phospholipase A2 |
| sRAGE | Soluble Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products |
| SA | Stable Angina |
| S100A8/A9 | Calprotectin |
| SLE | Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
| SSc | Systemic Sclerosis |
| SPs | Senile Plaques |
| ST2 | Suppression of Tumorigenicity 2 (soluble form often denoted as sST2) |
| STCS | Speckle Tracking Carotid Strain |
| suPAR | Soluble Urokinase Plasminogen Activator Receptor |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha |
| TGF-β | Transforming Growth Factor Beta |
| VAS | Visual Analog Scale |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
References
- Fujita, C.; Sakurai, Y.; Yasuda, Y.; Homma, R.; Huang, C.-L.; Fujita, M. mCRP as a Biomarker of Adult-Onset Still’s Disease: Quantification of mCRP by ELISA. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 938173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Choy, E.H. C-reactive protein and implications in rheumatoid arthritis and associated comorbidities. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-W.; Kim, B.-M.; Moon, H.-W.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, H.-R. Role of C-reactive protein in osteoclastogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-S.; Yan, W.; Geczy, C.L.; Brown, M.A.; Thomas, R. Serum levels of soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products and of S100 proteins are associated with inflammatory, autoantibody, and classical risk markers of joint and vascular damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-K.; Chiang, E.-P.I.; Chang, K.-H.; Tang, K.-T.; Chen, P.-K.; Yip, H.-T.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, D.-Y. The Sizes and Composition of HDL-Cholesterol Are Significantly Associated with Inflammation in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzichi, L.; Ghiadoni, L.; Rossi, A.; Bernardini, M.; Lanza, M.; De Feo, F.; Giacomelli, C.; Mencaroni, I.; Raimo, K.; Rossi, M.; et al. Osteopontin Is Associated with Increased Arterial Stiffness in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Med. 2009, 15, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Gullo, A.; Mandraffino, G.; Imbalzano, E.; Mamone, F.; Aragona, C.O.; D’Ascola, A.; Loddo, S.; Cinquegrani, A.; Alibrandi, A.; Mormina, E.; et al. Toll-like receptor 3 and interleukin 1β expression in CD34+ cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Association with inflammation and vascular involvement. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, 922–929. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, B.-T.; Lin, H.-B.; Cheng, Y.-F.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T.; Zhang, M.-Z.; Li, T.-J.; Xu, J.-P. Promotion of β-amyloid production by C-reactive protein and its implications in the early pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 60, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanimozhi; Aishwarya, K.; Yadav, S.; Chandy, A.A.; Muralikrishna, R.; Shinkre, R. Exploring the Link between Periodontal Disease and Systemic Conditions: Implications for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2024, 16, S3775–S3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, M.J.; Williams, A.L.; O’Sullivan, M.M.; Lewis, P.A.; Coles, E.C.; Jessop, J.D. Relationship between time-integrated C-reactive protein levels and radiologic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 1473–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, L.; van der Horst-Bru, I.E.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Bezemer, P.; Dijkmans, B. Predictors of radiographic joint damage in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2001, 60, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, J.; Gough, A.; Huissoon, A.; Perkins, P.; Holder, R.; Reece, R.; Arthur, V.; Emery, P. The acute phase and function in early rheumatoid arthritis. C-reactive protein levels correlate with functional outcome. J. Rheumatol. 1997, 24, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Braig, D.; Nero, T.L.; Koch, H.-G.; Kaiser, B.; Wang, X.; Thiele, J.R.; Morton, C.J.; Zeller, J.; Kiefer, J.; Potempa, L.A.; et al. Transitional changes in the CRP structure lead to the exposure of proinflammatory binding sites. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, S.; Kushner, I.; Samols, D. C-reactive Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48487–48490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sproston, N.R.; Ashworth, J.J. Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, J.R.; Habersberger, J.; Braig, D.; Schmidt, Y.; Goerendt, K.; Maurer, V.; Bannasch, H.; Scheichl, A.; Woollard, K.J.; von Dobschütz, E.; et al. Dissociation of Pentameric to Monomeric C-Reactive Protein Localizes and Aggravates Inflammation. Circulation 2014, 130, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M. C-reactive protein: A critical update. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.R.; Zeller, J.; Bannasch, H.; Stark, G.B.; Peter, K.; Eisenhardt, S.U. Targeting C-Reactive Protein in Inflammatory Disease by Preventing Conformational Changes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 372432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withrow, J.; Murphy, C.; Liu, Y.; Hunter, M.; Fulzele, S.; Hamrick, M.W. Extracellular vesicles in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloutier, N.; Tan, S.; Boudreau, L.H.; Cramb, C.; Subbaiah, R.; Lahey, L.; Albert, A.; Shnayder, R.; Gobezie, R.; Nigrovic, P.A.; et al. The exposure of autoantigens by microparticles underlies the formation of potent inflammatory components: The microparticle-associated immune complexes. EMBO Mol. Med. 2013, 5, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schioppo, T.; Ubiali, T.; Ingegnoli, F.; Bollati, V.; Caporali, R. The role of extracellular vesicles in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3481–3497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciurtin, C.; Helmy, G.A.; Ferreira, A.C.; Manson, J.J.; Jury, E.C.; McDonnell, T. A tale of two functions: C-reactive protein complement-ary structures and their role in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 265, 110281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.-K.; Li, H.-Y.; Liang, Y.-L.; Potempa, L.A.; Ji, S.-R.; Wu, Y. Monomeric C-Reactive Protein Binds and Neutralizes Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 234, (Erratum in “Monomeric C-Reactive Protein Binds and Neutralizes Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand-Induced Osteoclast Differentiation”, Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 619847. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.619847). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hawkins, P.N.; Kahan, M.C.; Tennent, G.A.; Gallimore, J.R.; Graham, D.; Sabin, C.A.; Zychlinsky, A.; de Diego, J. Pro-inflammatory Effects of Bacterial Recombinant Human C-Reactive Protein are Caused by Contamination with Bacterial Products not by C-Reactive Protein Itself. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, e97–e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, K.E.; van den Berg, C.W. Structural and functional comparison of native pentameric, denatured monomeric and biotinylated C-reactive protein. Immunology 2007, 120, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.R.; Zeller, J.; Kiefer, J.; Braig, D.; Kreuzaler, S.; Lenz, Y.; Potempa, L.A.; Grahammer, F.; Huber, T.B.; Huber-Lang, M.; et al. A Conformational Change in C-Reactive Protein Enhances Leukocyte Recruitment and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Kaptoge, S.; Angelantonio, E.D.; Lowe, G.; Pepys, M.B.; Thompson, S.G.; Collins, R.; Danesh, J. C-reactive protein concentration and risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, and mortality: An individual participant meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lill, R. From the discovery to molecular understanding of cellular iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. Biol. Chem. 2020, 401, 855–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, S.U.; Habersberger, J.; Murphy, A.; Chen, Y.-C.; Woollard, K.J.; Bassler, N.; Qian, H.; von zur Muhlen, C.; Hagemeyer, C.E.; Ahrens, I.; et al. Dissociation of Pentameric to Monomeric C-Reactive Protein on Activated Platelets Localizes Inflammation to Atherosclerotic Plaques. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.; Pepys, M.B.; Wood, S.P. The physiological structure of human C-reactive protein and its complex with phosphocholine. Structure 1999, 7, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srirangan, S.; Choy, E.H. The Role of Interleukin 6 in the Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2010, 2, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.R.; Pegues, M.A.; McCrory, M.A.; Kerr, S.W.; Jiang, H.; Sellati, R.; Berger, V.; Villalona, J.; Parikh, R.; McFarland, M.; et al. Collagen-Induced Arthritis is Exacerbated in C-Reactive Protein Deficient Mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, M.E.; Hornick, M.G.; Stefanski, A.; Albanna, H.R.; Gjoni, A.; Hall, G.D.; Hart, P.C.; Rajab, I.M.; Potempa, L.A. A biofunctional review of C-reactive protein (CRP) as a mediator of inflammatory and immune responses: Differentiating pentameric and modified CRP isoform effects. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1264383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasu, E.; Halbgebauer, R.; Schütte, L.; Greven, J.; Bläsius, F.M.; Zeller, J.; Winninger, O.; Braig, D.; Messerer, D.A.C.; Berger, B.; et al. A conformational change of C-reactive protein drives neutrophil extracellular trap formation in inflammation. BMC Biol. 2025, 23, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-González, D.; García-González, M.; Gómez-Bernal, F.; Quevedo-Abeledo, J.C.; González-Rivero, A.F.; Fernández-Cladera, Y.; González-López, E.; Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G.; Jiménez-Sosa, A.; González-Toledo, B.; et al. Complete Description of the Three Pathways of the Complement System in a Series of 430 Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bemis, E.A.; Norris, J.M.; Seifert, J.; Frazer-Abel, A.; Okamoto, Y.; Feser, M.L.; Demoruelle, M.K.; Deane, K.D.; Banda, N.K.; Holers, V.M. Complement and its Environmental Determinants in the Progression of Human Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molenaar, E.T.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Familian, A.; van Mierlo, G.J.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Hack, C.E. Complement activation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis mediated in part by C-reactive protein. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 997–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biró, É.; Nieuwland, R.; Tak, P.P.; Pronk, L.M.; Schaap, M.C.L.; Sturk, A.; Hack, C.E. Activated complement components and complement activator molecules on the surface of cell-derived microparticles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy individuals. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadyen, J.D.; Kiefer, J.; Braig, D.; Loseff-Silver, J.; Potempa, L.A.; Eisenhardt, S.U.; Peter, K. Dissociation of C-Reactive Protein Localizes and Amplifies Inflammation: Evidence for a Direct Biological Role of C-Reactive Protein and Its Conformational Changes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Lv, J.; Wang, J.; Qin, Q.; He, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, G.; Liu, G.; Zhong, F.; Zheng, Y.; et al. C-Reactive Protein Promotes the Activation of Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes From Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomé, J.; Limmer, J.; Brose, T.Z.; Zeller, J.; Chevalier, N.; Schäfer, A.-L.; Schneider, L.; Lind, M.; Christmann, T.; Dreck, M.; et al. C-reactive protein induced T cell activation is an indirect monocyte-dependent mechanism involving the CD80/CD28 pathway. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1622865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gershov, D.; Kim, S.; Brot, N.; Elkon, K.B. C-Reactive Protein Binds to Apoptotic Cells, Protects the Cells from Assembly of the Terminal Complement Components, and Sustains an Antiinflammatory Innate Immune Response. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Fernández, C.; Gonzalez-Rodríguez, M.; Francisco, V.; Rajab, I.M.; Gómez, R.; Conde, J.; Lago, F.; Pino, J.; Mobasheri, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; et al. Monomeric C reactive protein (mCRP) regulates inflammatory responses in human and mouse chondrocytes. Lab. Investig. 2021, 101, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozijn, A.E.; Tartjiono, M.T.; Ravipati, S.; Ham, F.v.d.; Barrett, D.A.; Mastbergen, S.C.; Korthagen, N.M.; Lafeber, F.P.J.G.; Zuurmond, A.M.; Bobeldijk, I.; et al. Human C-reactive protein aggravates osteoarthritis development in mice on a high-fat diet. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2019, 27, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajab, I.M.; Hart, P.C.; Potempa, L.A. How C-Reactive Protein Structural Isoforms With Distinctive Bioactivities Affect Disease Progression. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouki, C.; Haas, B.; Chan, J.S.; Potempa, L.A.; Filep, J.G. Loss of pentameric symmetry of C-reactive protein is associated with promotion of neutrophil-endothelial cell adhesion. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 5355–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filep, J.G.; Potempa, L.A. Topological Localization of Monomeric C-reactive Protein Determines Proinflammatory Endothelial Cell Responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14283–14290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, S.U.; Habersberger, J.; Oliva, K.; Lancaster, G.I.; Ayhan, M.; Woollard, K.J.; Bannasch, H.; Rice, G.E.; Peter, K. A proteomic analysis of C-reactive protein stimulated THP-1 monocytes. Proteome Sci. 2011, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, J.; Wetterö, J.; Potempa, L.A.; Fernandez-Botran, R.; O’Neill, Y.; Wirestam, L.; Mobarrez, F.; Sjöwall, C. Extracellular vesicles opsonized by monomeric C-reactive protein (CRP) are accessible as autoantigens in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and associate with autoantibodies against CRP. J. Autoimmun. 2023, 139, 103073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Cruz, L.G.; McEleney, K.G.; Cochrane, C.; Tan, K.B.C.; Shukla, P.; Gardiner, P.V.; Small, D.; Zhang, S.-D.; Gibson, D.S. Assessment of a dried blood spot C-reactive protein method to identify disease flares in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xu, K.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Yuan, P.; Xu, P.; Li, H. Monomeric C-reactive protein level is associated with osteoarthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- England, B.R.; Thiele, G.M.; Anderson, D.R.; Mikuls, T.R. Increased cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: Mechanisms and implications. Br. Med. J. 2018, 361, k1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, N.J.; Symmons, D.P.M.; Scott, D.G.I.; Bunn, D.; Lunt, M.; Silman, A.J. Baseline levels of C-reactive protein and prediction of death from cardiovascular disease in patients with inflammatory polyarthritis: A ten-year followup study of a primary care-based inception cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2293–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Doornum, S.; McColl, G.; Wicks, I. Atorvastatin reduces arterial stiffness in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 1571–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, M.A.; Danielson, E.; Rifai, N.; Ridker, P.M.; PRINCE Investigators. Effect of Statin Therapy on C-Reactive Protein LevelsThe Pravastatin Inflammation/CRP Evaluation (PRINCE): A Randomized Trial and Cohort Study. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2001, 286, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterö, J.; Nilsson, L.; Jonasson, L.; Sjöwall, C. Reduced serum levels of autoantibodies against monomeric C-reactive protein (CRP) in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2009, 400, 128–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusztai, A.; Hamar, A.; Horváth, Á.; Gulyás, K.; Végh, E.; Bodnár, N.; Kerekes, G.; Czókolyová, M.; Szamosi, S.; Bodoki, L.; et al. Soluble Vascular Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis: Effects of 1-year Antitumor Necrosis Factor-α Therapy. J. Rheumatol. 2021, 48, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Hollan, I.; Curran, S.A.; Kitson, S.M.; Riggio, M.P.; Mikkelsen, K.; Almdahl, S.M.; Aukrust, P.; McInnes, I.B.; Goodyear, C.S. Brief Report: Proatherogenic Cytokine Microenvironment in the Aortic Adventitia of Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1361–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchester, R.; Giles, J.T.; Nativ, S.; Downer, K.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Bag-Ozbek, A.; Zartoshti, A.; Bokhari, S.; Bathon, J.M. Association of Elevations of Specific T Cell And Monocyte Subpopulations in Rheumatoid Arthritis with Subclinical Coronary Artery Atherosclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Södergren, A.; Karp, K.; Boman, K.; Eriksson, C.; Lundström, E.; Smedby, T.; Söderlund, L.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Wållberg-Jonsson, S. Atherosclerosis in early rheumatoid arthritis: Very early endothelial activation and rapid progression of intima media thickness. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, J.R.; Trial, J.; Nambi, V.; Hoogeveen, R.C.; Taffet, G.E.; Entman, M.L. Plasma Levels of Endothelial Microparticles Bearing Monomeric C-reactive Protein Are Increased in Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2016, 9, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, C.R.; Stock, R.E.; Flanagan, S.S.; Darling, C.E.; Smith, C.S.; Snyder, L.M. Early verification of myocardial ischemia with a novel biomarker of acute tissue damage: C-reactive protein fractional forms. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2012, 413, 1536–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozos, I.; Malainer, C.; Horbańczuk, J.; Gug, C.; Stoian, D.; Luca, C.T.; Atanasov, A.G. Inflammatory Markers for Arterial Stiffness in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasci, V.; Tekin, A.F.; Baygin, H.; Unsal, A.; Gok, M. Assessment of Carotid Stiffness and Strain Parameters Using Speckle Tracking Strain Ultrasonography in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 26, 27092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinkema, H.J.; Nienhuis, H.L.A.; Groot, L.d.; Smit, A.J.; Roon, A.M.v.; Bijl, M.; Posthumus, M.D. Is Small Artery Elasticity Decreased Prior to Intima-Media Thickening in Patients with Longstanding Rheumatoid Arthritis? J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2133–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucer, M.; Cengiz, B.; Taylan Sahin, S.; Yavuz, S.; Yilmaz, N. Decreased Aortic Elasticity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Early Sign of Atherosclerosis and Predictive Factors. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2024, 11, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, B.; Weisenfeld, D.; Massarotti, E.; Seyok, T.; Cremone, G.; Lam, E.; Golnik, C.; Brownmiller, S.; Liu, F.; Huang, S.; et al. Interplay Between Systemic Inflammation, Myocardial Injury, and Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results From the LiiRA Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. Cardiovasc. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2024, 13, e030387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giles, J.T.; Post, W.S.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Polak, J.; Petri, M.; Gelber, A.C.; Szklo, M.; Bathon, J.M. Longitudinal Predictors of Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3216–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.P.; Myasoedova, E.; Crowson, C.S.; Davis, J.M.; Roger, V.L.; Karon, B.L.; Borgeson, D.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Rodeheffer, R.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Increased Prevalence of Diastolic Dysfunction in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1665–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Rincón, I.; Polak, J.F.; O’Leary, D.H.; Battafarano, D.F.; Erikson, J.M.; Restrepo, J.F.; Molina, E.; Escalante, A. Systemic inflammation and cardiovascular risk factors predict rapid progression of atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1118–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Qadir Nawabi, A.; Feng, Y.; Ma, G.; Tong, J.; Shen, C.; Liu, N. Coronary tortuosity is associated with an elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein concentration and increased risk of ischemic stroke in hypertensive patients. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Buring, J.E.; Cook, N.R.; Rifai, N. C-Reactive Protein, the Metabolic Syndrome, and Risk of Incident Cardiovascular Events. Circulation 2003, 107, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danesh, J.; Wheeler, J.G.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Eda, S.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Rumley, A.; Lowe, G.D.O.; Pepys, M.B.; Gudnason, V. C-Reactive Protein and Other Circulating Markers of Inflammation in the Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, K.I.; Hopstock, L.A.; Cook, S. Association of C-reactive protein with future development of diabetes: A population-based 7-year cohort study among Norwegian adults aged 30 and older in the Tromsø Study 2007–2016. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e070284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethorst, C.D.; Bernstein, I.; Trivedi, M.H. Inflammation, obesity and metabolic syndrome in depression: Analysis of the 2009–2010 National Health and Nutrition Survey (NHANES). J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, e1428–e1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trzeciak, P.; Herbet, M.; Dudka, J. Common Factors of Alzheimer’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis—Pathomechanism and Treatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 6038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, F.; Scheichl, A.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Htun, N.; Bassler, N.; Eisenhardt, S.U.; Habersberger, J.; Peter, K. Amyloid plaques dissociate pentameric to monomeric C-reactive protein: A novel pathomechanism driving cortical inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease? Brain Pathol. 2011, 22, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatelopoulos, K.; Sibbing, D.; Rallidis, L.S.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Stakos, D.; Braun, S.; Gatsiou, A.; Sopova, K.; Kotakos, C.; Varounis, C.; et al. Amyloid-Beta (1-40) and the Risk of Death From Cardiovascular Causes in Patients With Coronary Heart Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slevin, M.; Matou, S.; Zeinolabediny, Y.; Corpas, R.; Weston, R.; Liu, D.; Boras, E.; Di Napoli, M.; Petcu, E.; Sarroca, S.; et al. Monomeric C-reactive protein-a key molecule driving development of Alzheimer’s disease associated with brain ischaemia? Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slevin, M.; Matou-Nasri, S.; Turu, M.; Luque, A.; Rovira, N.; Badimon, L.; Boluda, S.; Potempa, L.; Sanfeliu, C.; De Vera, N.; et al. Modified C-Reactive Protein Is Expressed by Stroke Neovessels and Is a Potent Activator of Angiogenesis In Vitro. Brain Pathol. 2009, 20, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oláh, C.; Kardos, Z.; Andrejkovics, M.; Szarka, E.; Hodosi, K.; Domján, A.; Sepsi, M.; Sas, A.; Kostyál, L.; Fazekas, K.; et al. Assessment of cognitive function in female rheumatoid arthritis patients: Associations with cerebrovascular pathology, depression and anxiety. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, B.; Marr, C.; Holmes, C.; Edwards, C.J.; Cardwell, C.; McHenry, M.; Meenagh, G.; McGuinness, B. Prevalence of cognitive impairment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A cross sectional study. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tachibana, A.; Iga, J.; Ozaki, T.; Yoshida, T.; Yoshino, Y.; Shimizu, H.; Mori, T.; Furuta, Y.; Shibata, M.; Ohara, T.; et al. Serum high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and dementia in a community-dwelling Japanese older population (JPSC-AD). Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, G.; Clouston, S.A.P.; Smith, D.M. Elevated C-Reactive Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease Without Depression in Older Adults: Findings From the Health and Retirement Study. J. Gerontol. A. Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 77, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-M.; Chen, W.-S.; Sheu, J.-J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, J.-H.; Chang, C.-C. Autoimmune rheumatic diseases increase dementia risk in middle-aged patients: A nationwide cohort study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0186475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, K.; Solomon, A.; Kåreholt, I.; Tuomilehto, J.; Soininen, H.; Kivipelto, M. Midlife rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of cognitive impairment two decades later: A population-based study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourida, I.; Hannon, E.; Littlejohns, T.J.; Langa, K.M.; Hyppönen, E.; Kuźma, E.; Llewellyn, D.J. Association of Lifestyle and Genetic Risk With Incidence of Dementia. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 322, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, K.A.; Sharrett, A.R.; Wu, A.; Schneider, A.L.C.; Albert, M.; Lutsey, P.L.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Coresh, J.; Gross, A.L.; Windham, B.G.; et al. Association of Midlife to Late-Life Blood Pressure Patterns With Incident Dementia. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019, 322, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, C.; Cunningham, C.; Zotova, E.; Woolford, J.; Dean, C.; Kerr, S.; Culliford, D.; Perry, V.H. Systemic inflammation and disease progression in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2009, 73, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, K.; Pasinska, P.; Klimiec-Moskal, E.; Pera, J.; Slowik, A.; Klimkowicz-Mrowiec, A.; Dziedzic, T. C-reactive protein and post-stroke depressive symptoms. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Kojima, T.; Suzuki, S.; Oguchi, T.; Oba, M.; Tsuchiya, H.; Sugiura, F.; Kanayama, Y.; Furukawa, T.A.; Tokudome, S.; et al. Depression, inflammation, and pain in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 61, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, A.; Calabrese, P. Comparing underlying mechanisms of depression in multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2021, 20, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain, S.R.; Cavanagh, J.; de Boer, P.; Mondelli, V.; Jones, D.N.C.; Drevets, W.C.; Cowen, P.J.; Harrison, N.A.; Pointon, L.; Pariante, C.M.; et al. Treatment-resistant depression and peripheral C-reactive protein. Br. J. Psychiatry 2019, 214, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caprio, V.; Badimon, L.; Di Napoli, M.; Fang, W.-H.; Ferris, G.R.; Guo, B.; Iemma, R.S.; Liu, D.; Zeinolabediny, Y.; Slevin, M. pCRP-mCRP Dissociation Mechanisms as Potential Targets for the Development of Small-Molecule Anti-Inflammatory Chemotherapeutics. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepys, M.B.; Hirschfield, G.M.; Tennent, G.A.; Gallimore, J.R.; Kahan, M.C.; Bellotti, V.; Hawkins, P.N.; Myers, R.M.; Smith, M.D.; Polara, A.; et al. Targeting C-reactive protein for the treatment of cardiovascular disease. Nature 2006, 440, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeller, J.; Cheung Tung Shing, K.S.; Nero, T.L.; McFadyen, J.D.; Krippner, G.; Bogner, B.; Kreuzaler, S.; Kiefer, J.; Horner, V.K.; Braig, D.; et al. A novel phosphocholine-mimetic inhibits a pro-inflammatory conformational change in C-reactive protein. EMBO Mol. Med. 2022, 15, e16236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lazarut-Nistor, A.; Slevin, M. Beyond the Biomarker: Monomeric CRP as a Driver of Multisystem Pathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178227
Lazarut-Nistor A, Slevin M. Beyond the Biomarker: Monomeric CRP as a Driver of Multisystem Pathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178227
Chicago/Turabian StyleLazarut-Nistor, Andreea, and Mark Slevin. 2025. "Beyond the Biomarker: Monomeric CRP as a Driver of Multisystem Pathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178227
APA StyleLazarut-Nistor, A., & Slevin, M. (2025). Beyond the Biomarker: Monomeric CRP as a Driver of Multisystem Pathology in Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8227. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178227





