B-Cell ST6Gal1/Neuraminidase 1 Ratios Inversely Predict the Combined Remission and Low-Disease-Activity Subgroup with DAS28-MCP-1 and SDAI Scores for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics
2.2. Correlations Betweeen SIA/Anti-CCP Ratios, B-Cell SIA-Related Enzymes, and DAS28 Score
2.3. Correlations Between Different B-Cell SIA-Related Enzymes
2.4. Correlation Between SIA/Anti-CCP Ratios and Plasma Neu1 Levels Across Different Disease Activity, Remission, and Non-Remission Categories
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Recruitment of Patients with RA and Clinical Assessment
4.2. Cell Staining and Flow Cytometric Analysis
4.3. The Measurement of Plasma ST6Gal1 and Neu1
4.4. The Determination of IgG Anti-CCP Antibodies and Their SIA Contents
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harduin-Lepers, A.; Vallejo-Ruiz, V.; Krzewinski-Recchi, M.A.; Samyn-Petit, B.; Julien, S.; Delannoy, P. The human sialyltransferases family. Biochimie 2001, 83, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain Lehoux, S.; Groux-Degroote, S.; Cazet, A.; Dhaenens, C.M.; Maurage, C.A.; Caillet-Boudin, M.L.; Delannoy, P.; Krzewinski-Recchi, M.A. Transcriptional regulation of the human ST6GAL2 gene in cerebral cortex and neuronal cells. Glycoconj. J. 2010, 27, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barb, A.W.; Brady, E.K.; Prestegard, J.H. Branch Specific Sialylation of IgG-Fc Glycans by ST6Gal-I. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 9705–9707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basset, C.; Durand, V.; Mimassi, N.; Pennec, Y.L.; Youinou, P.; Dueymes, M. Enhanced sialyltransferase activity in B lymphocytes from patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Scand. J. Immunol. 2000, 51, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.P.; Enioutina, E.Y.; Daynes, R.A. The control of IL-4 gene expression in activated murine T lymphocytes: A novel role for neu-1 sialidase. J. Immunol. 1997, 158, 3070–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seyrantepe, V.; Iannello, A.; Liang, F.; Kanshin, E.; Jayanth, P.; Samarani, S.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Ali Ahmad, A.; Pshezhetsky, A.V. Regulation of phagocytosis in macrophages by neuraminidase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naraparaju, V.R.; Yamamoto, N. Roles of beta-galactosidase of B lymphocytes and sialidase of T lymphocytes in inflammation-primed activation of macrophages. Immunol. Lett. 1994, 43, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yamaguchi, K.; Wada, T.; Hata, K.; Zhao, X.J.; Fujimoto, T.; Miyagi, T. A close association of the ganglioside-specific sialidase Neu3 with caveolin in membrane microdomains. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 26252–26259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makinen, H.; Kautianen, H.; Hannonen, P.; Sokka, T. Is DAS28 an appropriate tool to assess remission in rheumatoid arthritis? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2005, 64, 1410–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felson, D.T.; Smolen, J.S.; Wells, G.; Zhang, B.; van Tuyl, L.H.D.; Funovits, J.; Aletaha, D.; Allaart, C.F.; Bathon, J.; Bombardieri, S.; et al. American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism provisional definition of remission in rheumatoid arthritis for clinical trials. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 573–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, L.B.; Tsai, P.H.; Fang, Y.F.; Chen, Y.F.; Chen, C.C.; Lai, J.H. Sialic-acid-related enzymes of B cells and monocytes as novel markers to discriminate improvement categories and to fulfill two remission definitions in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmi, Y.; Ise, W.; Harazono, A.; Takakura, D.; Fukuyama, H.; Baba, Y.; Narazaki, M.; Shoda, H.; Takahashi, N.; Ohkawa, Y.; et al. Sialylation converts arthritogenic IgG into inhibitors of collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, L.B.; Huang, C.C. Reverse expression of α2,6-sialic acid ratios on IgG, IgM, and IgG/IgM autoantibodies correlates with mouse arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2020, 83, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, L.B.; Fang, Y.F.; Tan, C.F.; Lai, J.H.; Jang, S.S.; Tsai, P.H.; Yeh, T.C. A new laboratory surrogate (Monocyte Chemotactic Protein-1) for Disease Activity Score28: A favourable indicator for remission in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.B.; Oswald, D.M.; Joshi, S.; Whiteheart, S.W.; Orlando, R.; Cobb, B.A. B-cell-independent sialylation of IgG. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7207–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oswald, D.M.; Lehoux, S.D.; Zhou, J.Y.; Glendenning, L.M.; Cummings, R.D.; Cobb, B.A. ST6Gal1 in plasma is dispensable for IgG sialylation. Glycobiology 2022, 32, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Wu, K.C.H.; Bennett, A.N.; Fan, B.F.; Liu, J.D.; Huang, R.X.; Kong, A.P.S.; Tian, X.Y.; Kwok, M.K.M.; Chang, K.H.K. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug target gene associations with major depressive disorders: A Mendelian randomization study integrating GWAAS, eQTL and mQTL Data. Pharmocagenom. J. 2023, 23, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherer, H.U.; van der Woude, D.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; el Bannoudi, H.; Trouw, L.A.; Wang, J.; Haupl, T.; Burmester, G.R.; Deelder, A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; et al. Glycan Profiling of Anti–Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Isolated From Human Serum and Synovial Fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1620–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyebrovszki, B.; Ács, A.; Szabó, D.; Auer, F.; Novozánszki, S.; Rojkovich, B.; Magyar, A.; Hudecz, F.; Vékey, K.; Drahos, L.; et al. The Role of IgG Fc Region N-Glycosylation in the Pathomechanism of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, L.B.; Huang, C.C. Sialyltransferase and Neuraminidase Levels/Ratios and Sialic Acid Levels in Peripheral Blood B Cells Correlate with Measures of Disease Activity in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Pilot Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, L.B.; Fang, Y.F.; Tsai, P.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Chang, C.T.; Chen, C.C.; Chiang, W.Y. Immunoregulatory cells and cytokines discriminate Disease Activity Score 28-remission statuses and ultrasound grades in rheumatoid arthritis patients with non-high disease activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean ± S.D. or Median | Range or 25th and 75th Percentiles | |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | F:M = 78:19 | Total number = 97 |
| Age | 57.5 ± 10.6 | 32–75 |
| Disease duration (months) | 87.4 | 41.65, 179.15 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 1.45 | 0.78, 3.61 |
| ESR (mm/hr) | 13.50 | 8.00, 26.50 |
| MCP-1 (pg/mL) | 95.62 | 51.42, 151.89 |
| RF (IU/mL) | 30.20 | 11.20, 110.50 |
| Anti-CCP (unit) | 183.32 | 139.54, 244.65 |
| SIA/anti-CCP ratios | 0.67 | 0.06, 1.38 |
| TJC | 2 | 0, 4.5 |
| SJC | 1 | 0, 3.0 |
| DAS28-ESR | 3.25 ± 1.40 | 0–6.62 |
| DAS28-CRP | 3.63 ± 1.16 | 1.40–6.59 |
| SDAI | 11.20 | 2.24, 17.10 |
| CDAI | 11.50 | 2.25, 16.75 |
| DAS28-MCP-1 | 3.46 | 2.14, 4.04 |
| HAQ-DI | 0 | 0, 0.5 |
| Enzymes in Subgroups | AUC | Asymptotic p-Values |
|---|---|---|
| B-cell ST6Gal1 via SDAI ≤ 11 | 0.566 | 0.100 |
| B-cell ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios via SDAI ≤ 11 | 0.616 | 0.004 |
| B-cell Neu1 via SDAI > 3.3 | 0.541 | 0.361 |
| B-cell ST6Gal1 via DAS28-MCP-1 ≤ 3.6 | 0.544 | 0.301 |
| B-cell ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios via DAS28-MCP-1 ≤ 3.6 | 0.600 | 0.018 |
| Rho | p-Values | Number of Visits | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DAS28-ESR | −0.236 | <0.001 | 215 |
| DAS28-CRP | −0.161 | 0.018 | 215 |
| SDAI | −0.180 | 0.008 | 215 |
| CDAI | −0.187 | 0.006 | 217 |
| DAS28-MCP-1 | −0.147 | 0.036 | 205 |
| Plasma Enzymes in Subgroups | AUC | Asymptotic p-Values |
|---|---|---|
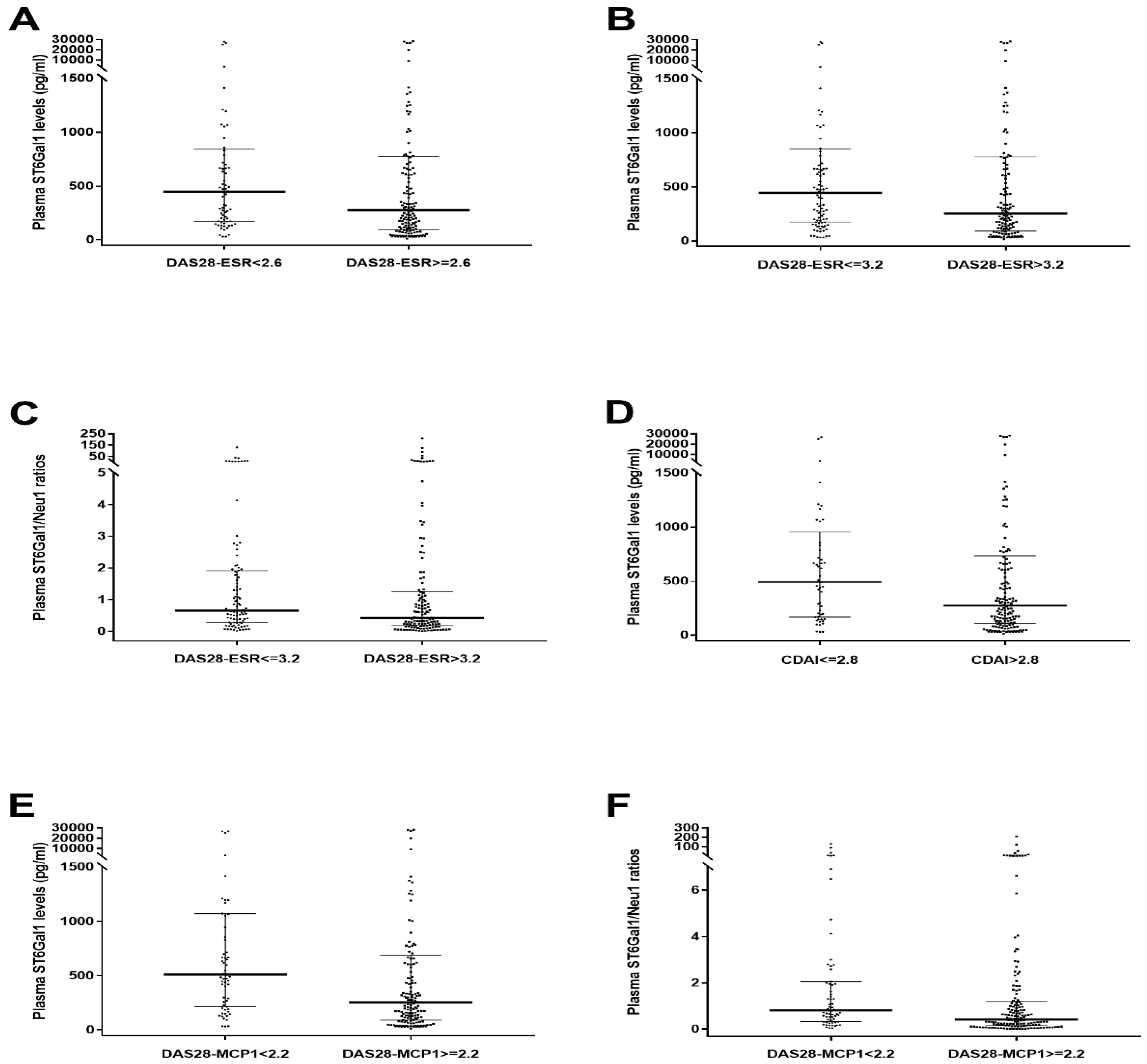
| Plasma ST6Gal1 via DAS28-ESR < 2.6 | 0.582 | 0.046 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1 via DAS28-ESR ≤ 3.2 | 0.588 | 0.024 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios via DAS28-ESR ≤ 3.2 | 0.580 | 0.039 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1 via CDAI ≤ 2.8 | 0.593 | 0.041 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1 via DAS28-MCP-1 < 2.2 | 0.642 | 0.001 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios via DAS28-MCP-1 < 2.2 | 0.628 | 0.003 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1 via modified 2005 ARA remission | 0.619 | 0.012 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios via modified 2005 ARA remission | 0.590 | 0.056 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1 via 2011 ACR/EULAR remission | 0.567 | 0.152 |
| Plasma ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios via 2011 ACR/EULAR remission | 0.549 | 0.295 |
| Correlation Pairs | Non-Interfering Independent Variables (p-Values < 0.05) | Interfering Independent Variables (p-Values ≥ 0.05) |
|---|---|---|
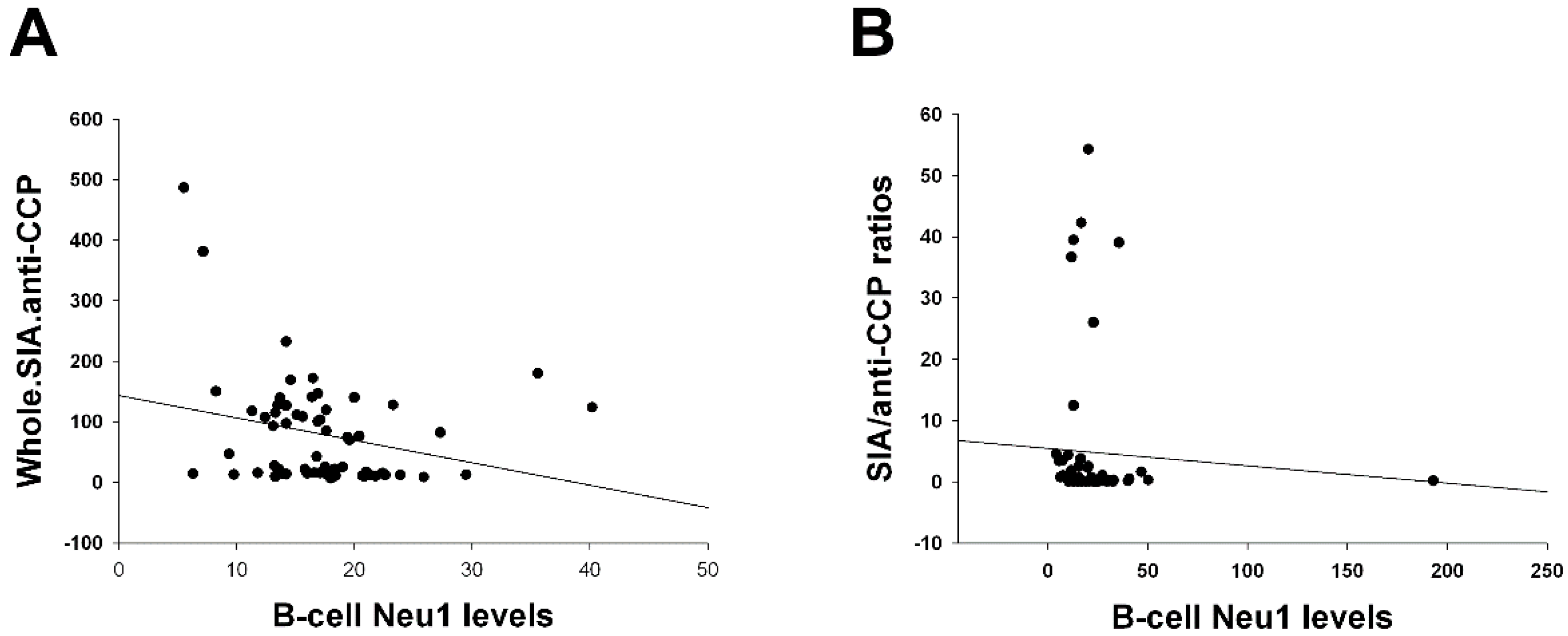
| Total SIA contents of IgG anti-CCP antibodies vs. B-cell Neu1 levels (Figure 1A) | Age, IgG anti-CCP, HCQ, biologics, CRP, and MCP-1. | Disease duration, MTX, sulfasa, and ESR. |
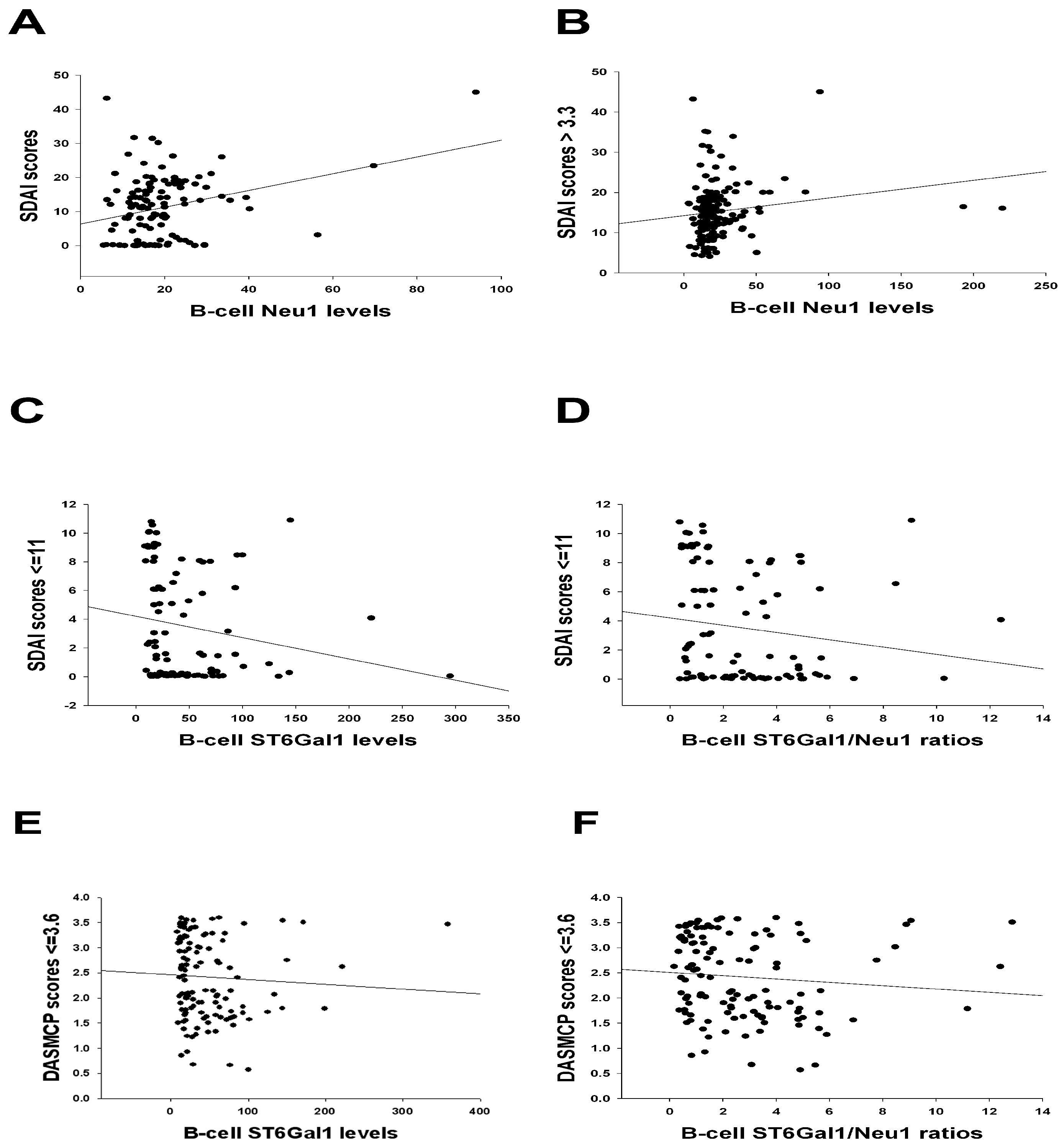
| SDAI scores > 3.3 vs. Ln(B-cell Neu1 levels (Figure 2B) | Sulfasa, HCQ, biologics, CRP, and ESR. | Age, disease duration, IgG anti-CCP, MTX, and MCP-1. |
| SDAI scores ≤ 11 vs. Ln(B-cell ST6Gal1 levels (Figure 2C) | Age, disease duration, IgG anti-CCP, MTX, sulfasa, and HCQ. | Biologics, CRP, ESR, and MCP-1. |
| SDAI scores ≤ 11 vs. Ln(B-cell ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios (Figure 2D) | Age, disease duration, IgG anti-CCP, MTX, sulfasa, and HCQ. | Biologics, CRP, ESR, and MCP-1. |
| DAS28-MCP-1 scores ≤ 3.6 vs. Ln(B-cell ST6Gal1 levels (Figure 2E) | Age, disease duration, IgG anti-CCP, MTX, sulfasa, and HCQ. | Biologics, CRP, ESR, and MCP-1. |
| DAS28-ESR scores vs. Ln(B-cell ST6Gal1/Neu1 ratios (Table 3) | Age, disease duration, IgG anti-CCP, MTX, sulfasa, and HCQ. | Biologics, CRP, ESR, and MCP-1. |
| SIA/anti-CCP ratios vs. Ln(plasma Neu1 levels) in the DAS28-MCP-1 scores < 2.2 remission subgroup (Supplementary Figure S1) | Age. | Disease duration, IgG anti-CCP, MTX, sulfasa, HCQ, biologics, CRP, ESR, and MCP-1. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liou, L.-B.; Tsai, P.-H.; Fang, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-F.; Chang, C.-T.; Chen, C.-C.; Chiang, W.-Y. B-Cell ST6Gal1/Neuraminidase 1 Ratios Inversely Predict the Combined Remission and Low-Disease-Activity Subgroup with DAS28-MCP-1 and SDAI Scores for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178226
Liou L-B, Tsai P-H, Fang Y-F, Chen Y-F, Chang C-T, Chen C-C, Chiang W-Y. B-Cell ST6Gal1/Neuraminidase 1 Ratios Inversely Predict the Combined Remission and Low-Disease-Activity Subgroup with DAS28-MCP-1 and SDAI Scores for Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178226
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiou, Lieh-Bang, Ping-Han Tsai, Yao-Fan Fang, Yen-Fu Chen, Che-Tzu Chang, Chih-Chieh Chen, and Wen-Yu Chiang. 2025. "B-Cell ST6Gal1/Neuraminidase 1 Ratios Inversely Predict the Combined Remission and Low-Disease-Activity Subgroup with DAS28-MCP-1 and SDAI Scores for Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178226
APA StyleLiou, L.-B., Tsai, P.-H., Fang, Y.-F., Chen, Y.-F., Chang, C.-T., Chen, C.-C., & Chiang, W.-Y. (2025). B-Cell ST6Gal1/Neuraminidase 1 Ratios Inversely Predict the Combined Remission and Low-Disease-Activity Subgroup with DAS28-MCP-1 and SDAI Scores for Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178226





