Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Proton Pump Inhibitors by Targeting GRP78 and V-ATPase: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, PCA, and MM-GBSA Calculations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Molecular Docking and Interactions
2.2. Molecular Dynamics Simulation
2.2.1. RMSD Analysis
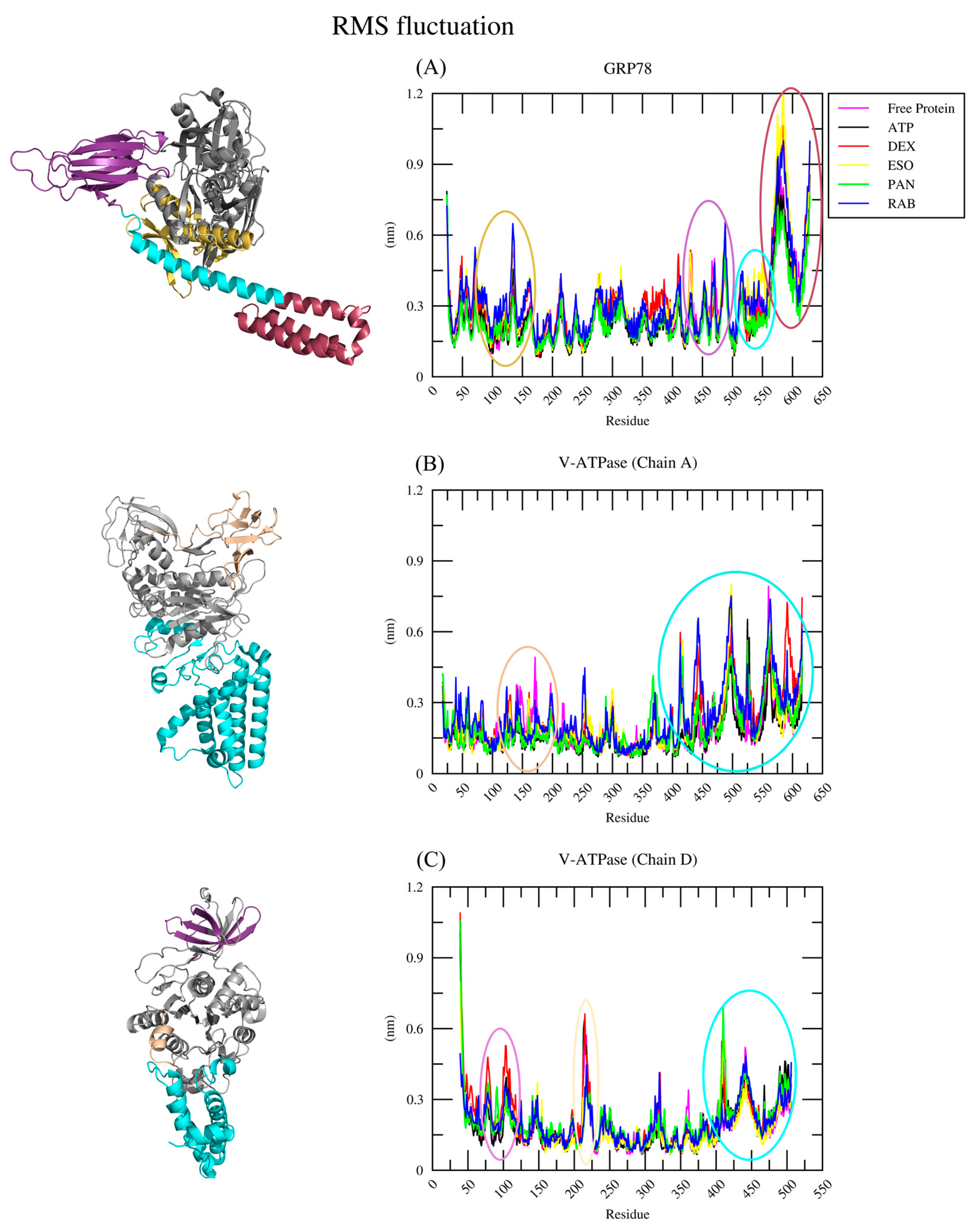
2.2.2. RMSF Analysis
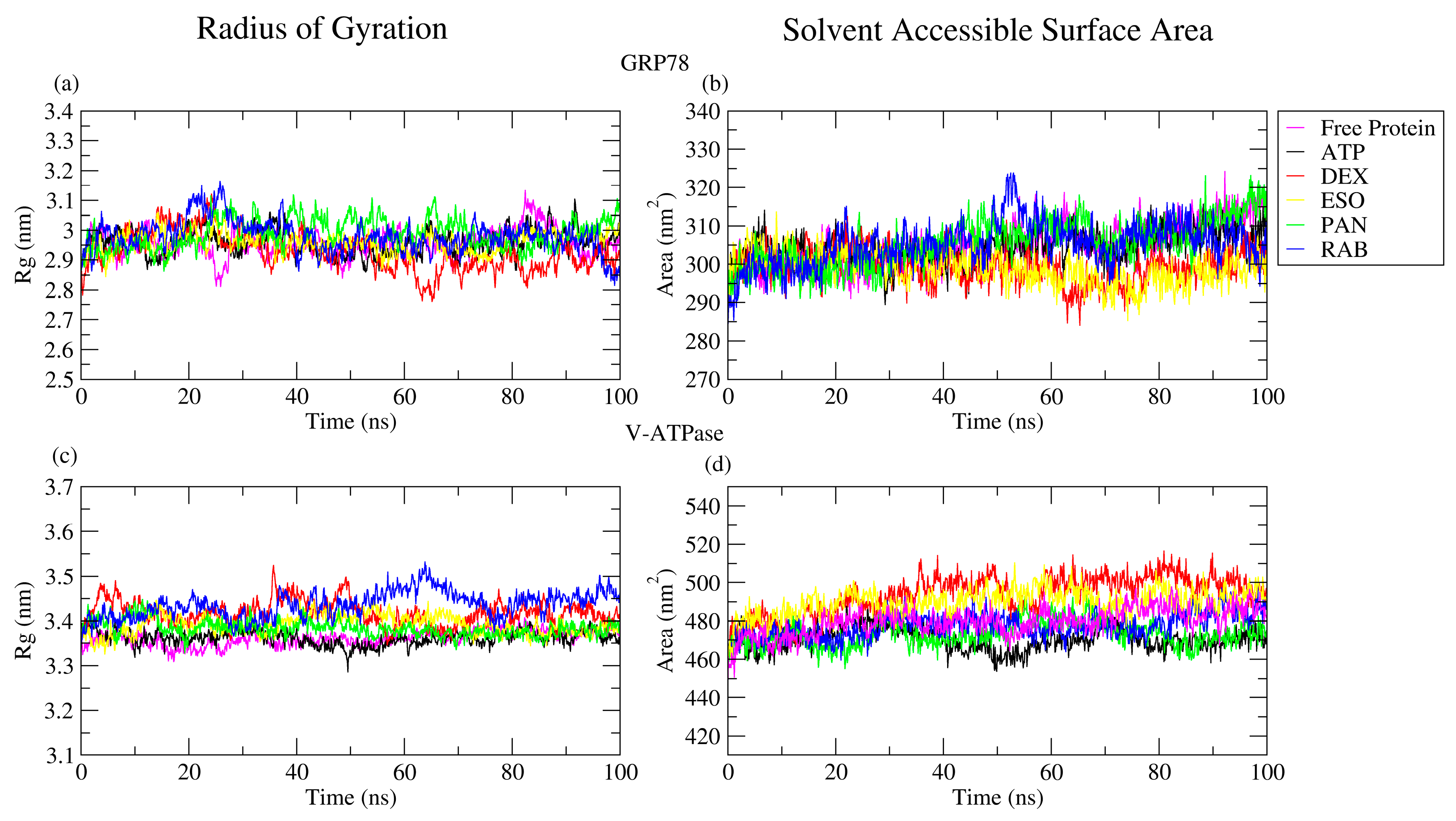
2.2.3. RoG and SASA Analyses
2.2.4. Hydrogen Bond Analysis
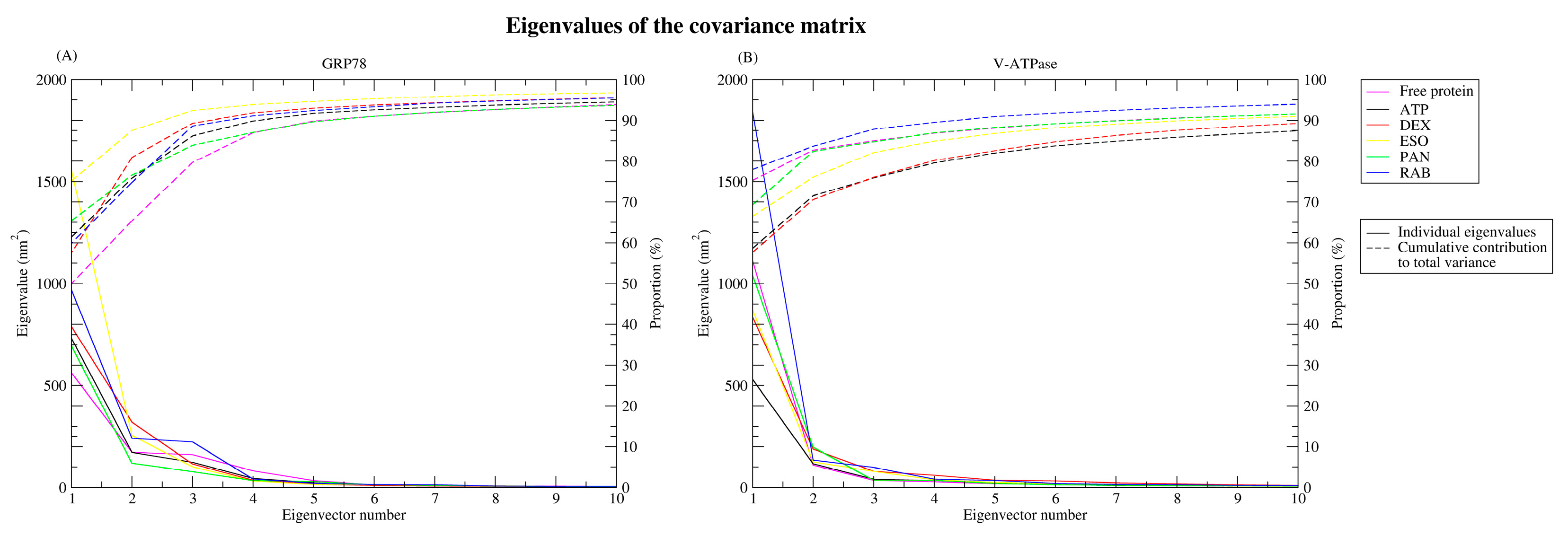
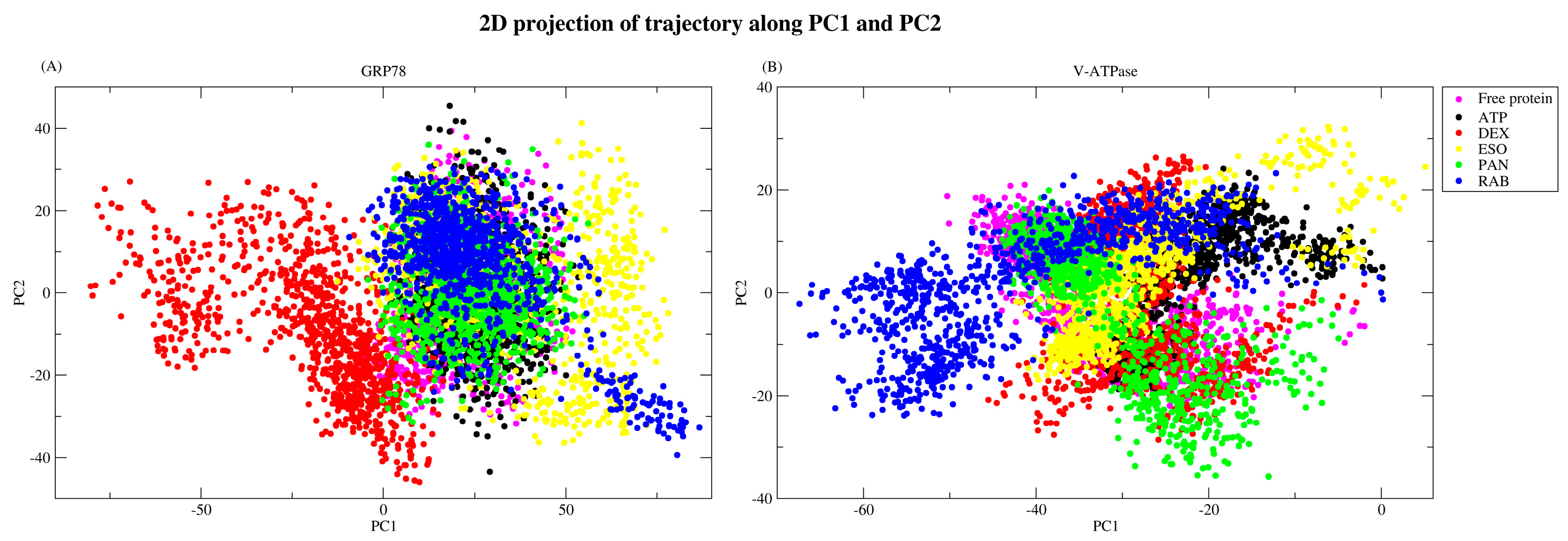
2.2.5. Principal Component Analysis
2.2.6. Free-Energy Landscape
2.2.7. Binding Free Energy
2.2.8. Amino Acid Contribution
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Structural Retrieval of Proteins and Ligands
3.2. Molecular Docking
3.3. Molecular Dynamics (MD) Simulations
3.4. Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Free-Energy-Landscape Analysis
3.5. Binding Free Energy Calculations
3.6. Visualization and Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADP | Adenine diphosphate |
| ATF6 | activating transcription factor 6 |
| ATP | Adenine triphosphate |
| CGenFF | CHARMM general force field |
| DEX | Dexlansoprazole |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ESO | Esomeprazole |
| FEL | Free-energy landscape |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| IRE1 | Inositol-requiring kinase 1 |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| MM-GBSA | Molecular mechanics–generalized Born surface area |
| NBD | Nucleotide-binding domain |
| PAN | Pantoprazole |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PERK | PKR-like eukaryotic initiation factor 2α kinase |
| PPIs | Proton pump inhibitors |
| RAB | Rabeprazole |
| RMSD | Root mean square deviation |
| RMSF | Root mean square fluctuation |
| RoG | Radius of gyration |
| SASA | Solvent-accessible surface area |
| SBD | Substrate-binding domain |
| UPR | Unfolded protein response |
| V-ATPse | Vacuolar-type H+-ATPase |
| VMD | Visual Molecular Dynamics |
References
- Yuan, Y.; Fan, J.; Liang, D.; Wang, S.; Luo, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, N.; Xiang, T.; Zhao, X. Cell Surface GRP78-Directed CAR-T Cells Are Effective at Treating Human Pancreatic Cancer in Preclinical Models. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 39, 101803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zong, Y.; Su, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Columbus, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Q. Conformation Transitions of the Polypeptide-Binding Pocket Support an Active Substrate Release from Hsp70s. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.M.; Abdelmalek, D.H.; Elfiky, A.A. GRP78: A Cell’s Response to Stress. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, R.J.; van Lidth de Jeude, J.F.; Heijmans, J. ER Stress and the Unfolded Protein Response in Gastrointestinal Stem Cells and Carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2024, 587, 216678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavilán, E.; Medina-Guzman, R.; Bahatyrevich-Kharitonik, B.; Ruano, D. Protein Quality Control Systems and ER Stress as Key Players in SARS-CoV-2-Induced Neurodegeneration. Cells 2024, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, D.; Robinson, C.V.; Wu, H.; Fu, T.-M. Structures of a Complete Human V-ATPase Reveal Mechanisms of Its Assembly. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 501–511.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Rubinstein, J.L. CryoEM of V-ATPases: Assembly, Disassembly, and Inhibition. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2023, 80, 102592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toei, M.; Toei, S.; Forgac, M. Definition of Membrane Topology and Identification of Residues Important for Transport in Subunit a of the Vacuolar ATPase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35176–35186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, R.; Mei, D.; Kerti-Szigeti, K.; Pepe, S.; Koenig, M.K.; Von Allmen, G.; Cho, M.T.; McDonald, K.; Baker, J.; Bhambhani, V.; et al. Phenotypic and Genetic Spectrum of ATP6V1A Encephalopathy: A Disorder of Lysosomal Homeostasis. Brain 2022, 145, 2687–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, G.; El Choubassi, N.; Herczegfalvi, Á.; Kölbel, H.; Lekaj, A.; Schara, U.; Holtgrewe, M.; Krause, S.; Horvath, R.; Schuelke, M.; et al. Expanding the Clinical and Molecular Spectrum of ATP6V1A Related Metabolic Cutis Laxa. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2021, 44, 972–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Matsukawa, R.; Takahashi, S.; Kudo, K.; Sun-Wada, G.-H.; Wada, Y.; Nakanishi-Matsui, M. V-ATPase A3 Isoform Mutations Identified in Osteopetrosis Patients Abolish Its Expression and Disrupt Osteoclast Function. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 389, 111901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, H.; Han, L.; Zou, X.; Shen, W. Expression and Role of V1A Subunit of V-ATPases in Gastric Cancer Cells. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 20, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Kang, R.; Liu, J.; Tang, D. The V-ATPases in Cancer and Cell Death. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1529–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratto, E.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Siefert, N.S.; Schneider, M.; Wittmann, M.; Helm, D.; Palm, W. Direct Control of Lysosomal Catabolic Activity by MTORC1 through Regulation of V-ATPase Assembly. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, T.; Duchi, S.; Cortese, K.; Tacchetti, C.; Bilder, D. The Vacuolar ATPase Is Required for Physiological as Well as Pathological Activation of the Notch Receptor. Development 2010, 137, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Stratton, S.A.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, M.; Jun, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, B.; Cervantes, C.L.; Cha, J.; Barton, M.C.; et al. TMEM9-v-ATPase Activates Wnt/Β-Catenin Signaling Via APC Lysosomal Degradation for Liver Regeneration and Tumorigenesis. Hepatology 2021, 73, 776–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, M.P.; Forgac, M. Regulation and Function of V-ATPases in Physiology and Disease. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshbaf, M.; Khosroushahi, A.Y.; Mojarad-Jabali, S.; Zarebkohan, A.; Valizadeh, H.; Walker, P.R. Cell Surface GRP78: An Emerging Imaging Marker and Therapeutic Target for Cancer. J. Control. Release 2020, 328, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S. GRP78 Induction in Cancer: Therapeutic and Prognostic Implications. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3496–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal, U.; Pizzo, S.V. Cell Surface GRP78 Signaling: An Emerging Role as a Transcriptional Modulator in Cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2021, 236, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, I.; Cohen, M. Linking Cell-Surface GRP78 to Cancer: From Basic Research to Clinical Value of GRP78 Antibodies. Cancer Lett. 2022, 524, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemailem, K.S.; Almatroudi, A.; Alrumaihi, F.; Almatroodi, S.A.; Alkurbi, M.O.; Basfar, G.T.; Rahmani, A.H.; Khan, A.A. Novel Approaches of Dysregulating Lysosome Functions in Cancer Cells by Specific Drugs and Its Nanoformulations: A Smart Approach of Modern Therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 5065–5098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, R.K.; Chae, S.-W.; Kim, H.-R.; Chae, H.J. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Cancer. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 19, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, J. The Proton-Pump Inhibitors: Similarities and Differences. Clin. Ther. 2000, 22, 266–280, discussion 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orel, R.; Benninga, M.A.; Broekaert, I.J.; Gottrand, F.; Papadopoulou, A.; Ribes-Koninckx, C.; Thomson, M.; Wilschanski, M.; Thapar, N. Drugs in Focus: Proton Pump Inhibitors. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2021, 72, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Zhu, X.; Lu, X. Exploration of the Binding of Proton Pump Inhibitors to Human P450 2C9 Based on Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulation. J. Mol. Model. 2011, 17, 1941–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumz, M.L.; Lynch, I.J.; Greenlee, M.M.; Cain, B.D.; Wingo, C.S. The Renal H+-K+-ATPases: Physiology, Regulation, and Structure. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2009, 298, F12–F21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-P. Suppression of Vacuolar-Type ATPase and Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Proton Pump Inhibitors. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2022, 85, 915–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Fatima, K.; Aisha, S.; Malik, F. Unveiling the Mechanisms and Challenges of Cancer Drug Resistance. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, G.; Ha, D.P.; Wang, J.; Xiong, M.; Lee, A.S. ER Chaperone GRP78/BiP Translocates to the Nucleus under Stress and Acts as a Transcriptional Regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2303448120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfiky, A.A.; Baghdady, A.M.; Ali, S.A.; Ahmed, M.I. GRP78 Targeting: Hitting Two Birds with a Stone. Life Sci. 2020, 260, 118317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stransky, L.; Cotter, K.; Forgac, M. The Function of V-ATPases in Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1071–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edache, E.I.; Uzairu, A.; Mamza, P.A.; Shallangwa, G.A.; Yagin, F.H.; Abdel Samee, N.; Mahmoud, N.F. Combining Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulations, AD-MET Pharmacokinetics Properties, and MMGBSA Calculations to Create Specialized Protocols for Running Effective Virtual Screening Campaigns on the Autoimmune Disorder and SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1254230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargolzaei, M. Effect of Nelfinavir Stereoisomers on Coronavirus Main Protease: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation and MM/GBSA Study. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2021, 103, 107803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, E.; Dorr, B.; Woetzel, N.; Staritzbichler, R.; Meiler, J. Solvent Accessible Surface Area Approximations for Rapid and Accurate Protein Structure Prediction. J. Mol. Model. 2009, 15, 1093–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, P.P.; Singh, A.K.; Bansal, T.; Yadav, A.; Prajapati, K.S.; Shuaib, M.; Kumar, S. Identification of Natural Inhibitors Against SARS-CoV-2 Drugable Targets Using Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics Simulation, and MM-PBSA Approach. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 730288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Greene, D.; Xiao, L.; Qi, R.; Luo, R. Recent Developments and Applications of the MMPBSA Method. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U. The MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA Methods to Estimate Ligand-Binding Affinities. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2015, 10, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version~3.0.3; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
- Yuriev, E.; Ramsland, P.A. Latest Developments in Molecular Docking: 2010–2011 in Review. J. Mol. Recognit. 2013, 26, 215–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated Docking with Selective Receptor Flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, M.F. Python: A Programming Language for Software Integration and Development. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1999, 17, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the Speed and Accuracy of Docking with a New Scoring Function, Efficient Optimization, and Multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Cheng, X.; Swails, J.M.; Yeom, M.S.; Eastman, P.K.; Lemkul, J.A.; Wei, S.; Buckner, J.; Jeong, J.C.; Qi, Y.; et al. CHARMM-GUI Input Generator for NAMD, GROMACS, AMBER, OpenMM, and CHARMM/OpenMM Simulations Using the CHARMM36 Additive Force Field. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, S.; Kim, T.; Iyer, V.G.; Im, W. CHARMM-GUI: A Web-Based Graphical User Interface for CHARMM. J. Comput. Chem. 2008, 29, 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; Hatcher, E.; Acharya, C.; Kundu, S.; Zhong, S.; Shim, J.; Darian, E.; Guvench, O.; Lopes, P.; Vorobyov, I.; et al. CHARMM General Force Field: A Force Field for Drug-like Molecules Compatible with the CHARMM All-Atom Additive Biological Force Fields. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 671–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanommeslaeghe, K.; MacKerell, A.D.J.r. Automation of the CHARMM General Force Field (CGenFF) I: Bond Perception and Atom Typing. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 3144–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl; Abraham; Hess; Van Der Spoel. GROMACS 2021.3 Source Code; Zenodo: Genève, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Rauscher, S.; Nawrocki, G.; Ran, T.; Feig, M.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; MacKerell, A.D. CHARMM36m: An Improved Force Field for Folded and Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 71–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.A.M.; Loccisano, A.E.; Firestine, S.M.; Evanseck, J.D. Chapter 13 Principal Components Analysis: A Review of Its Application on Molecular Dynamics Data. Annu. Rep. Comput. Chem. 2006, 2, 233–261. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, F.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, T.; Cao, Z. Identification of Novel PI3Kα Inhibitor Against Gastric Cancer: QSAR-, Molecular Docking–, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation–Based Analysis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 196, 7233–7246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamad, S.; Gupta, D.; Kumar, V. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Oligomerization: Insights from Molecular Docking and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 2430–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollman, P.A.; Massova, I.; Reyes, C.; Kuhn, B.; Huo, S.; Chong, L.; Lee, M.; Lee, T.; Duan, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Calculating Structures and Free Energies of Complex Molecules: Combining Molecular Mechanics and Continuum Models. Acc. Chem. Res. 2000, 33, 889–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.R.I.I.I.; McGee, T.D., Jr.; Swails, J.M.; Homeyer, N.; Gohlke, H.; Roitberg, A.E. MMPBSA.Py: An Efficient Program for End-State Free Energy Calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2012, 8, 3314–3321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. Gmx_MMPBSA: A New Tool to Perform End-State Free Energy Calculations with GROMACS. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2021, 17, 6281–6291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual Molecular Dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
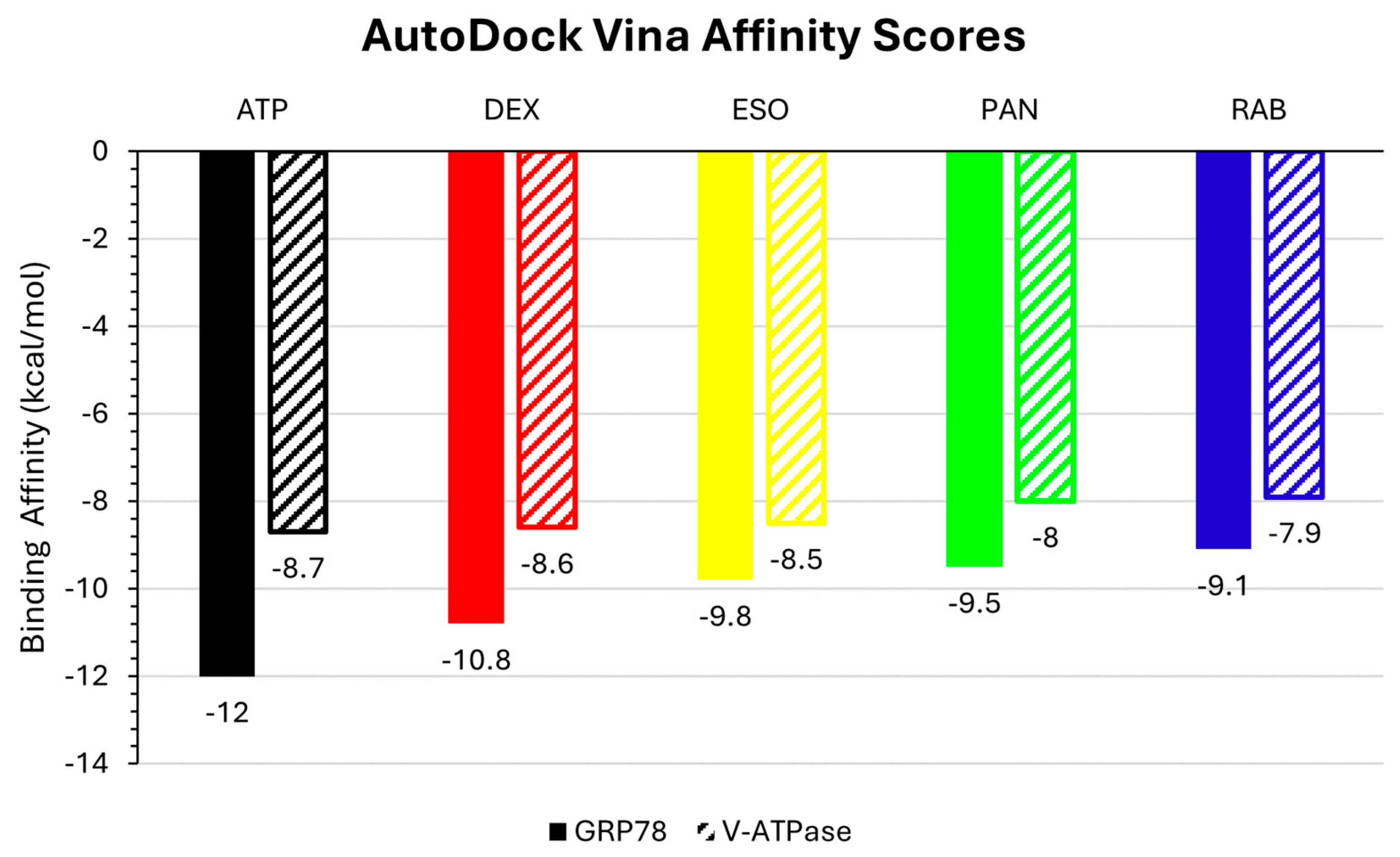
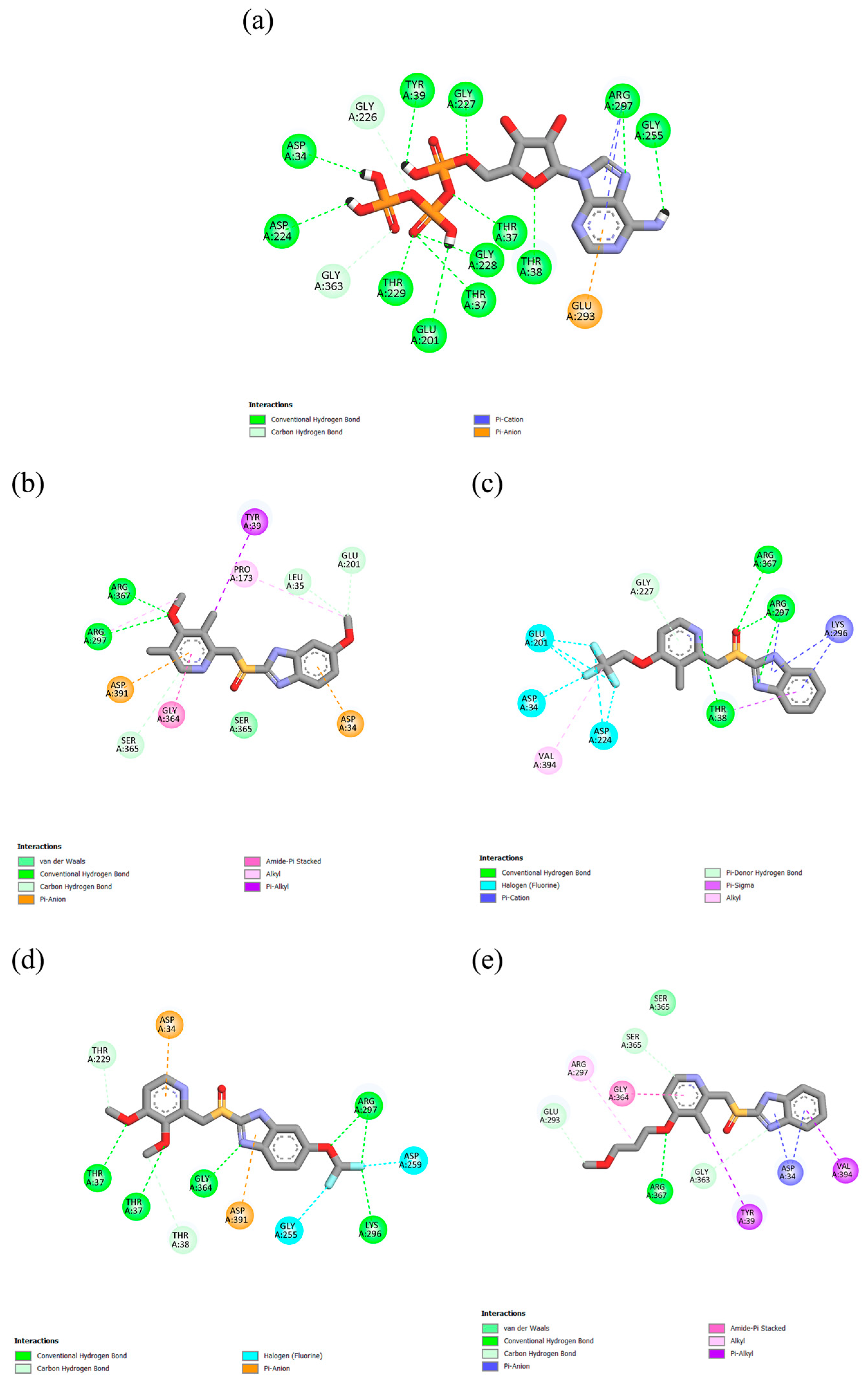
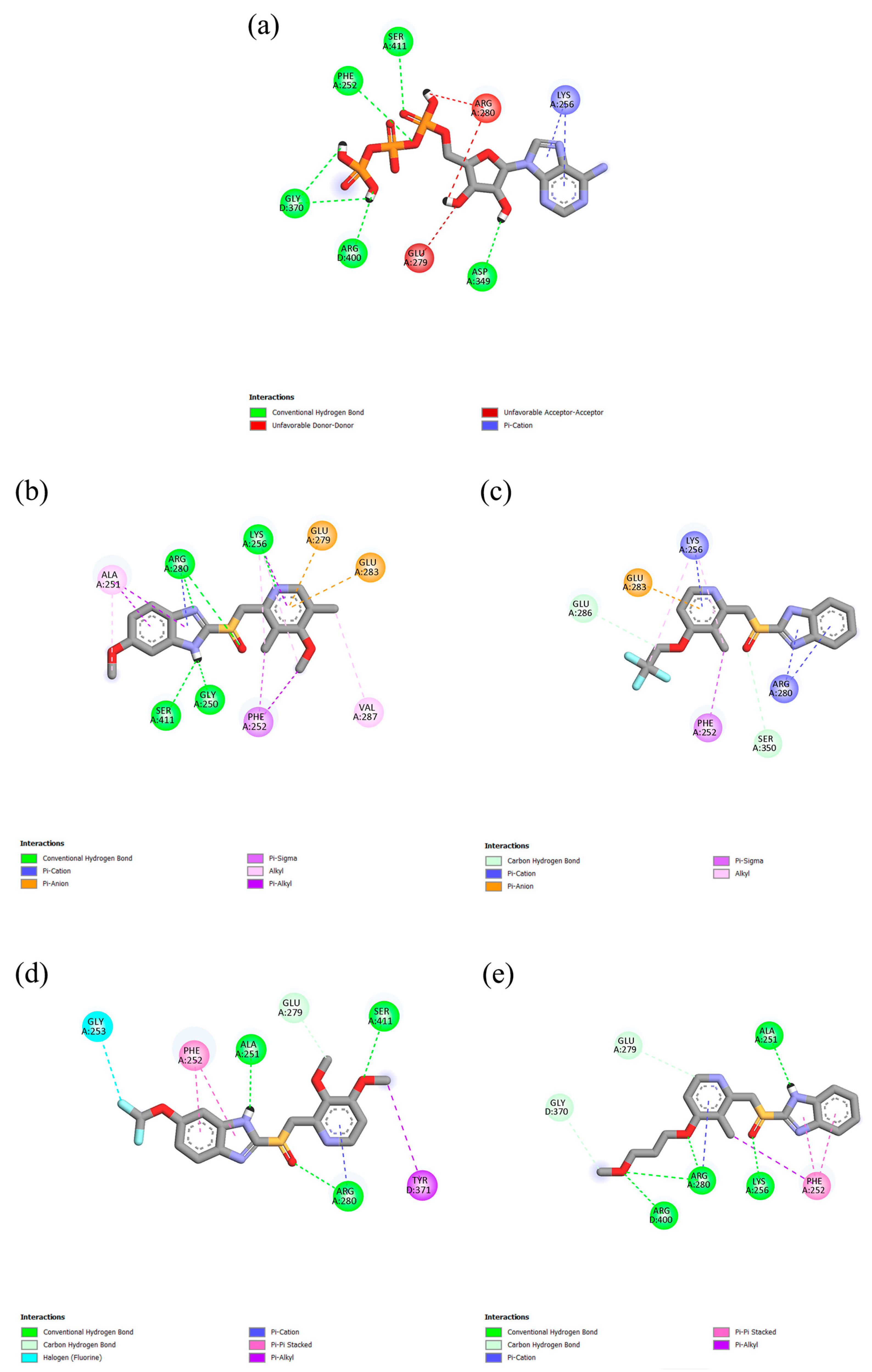
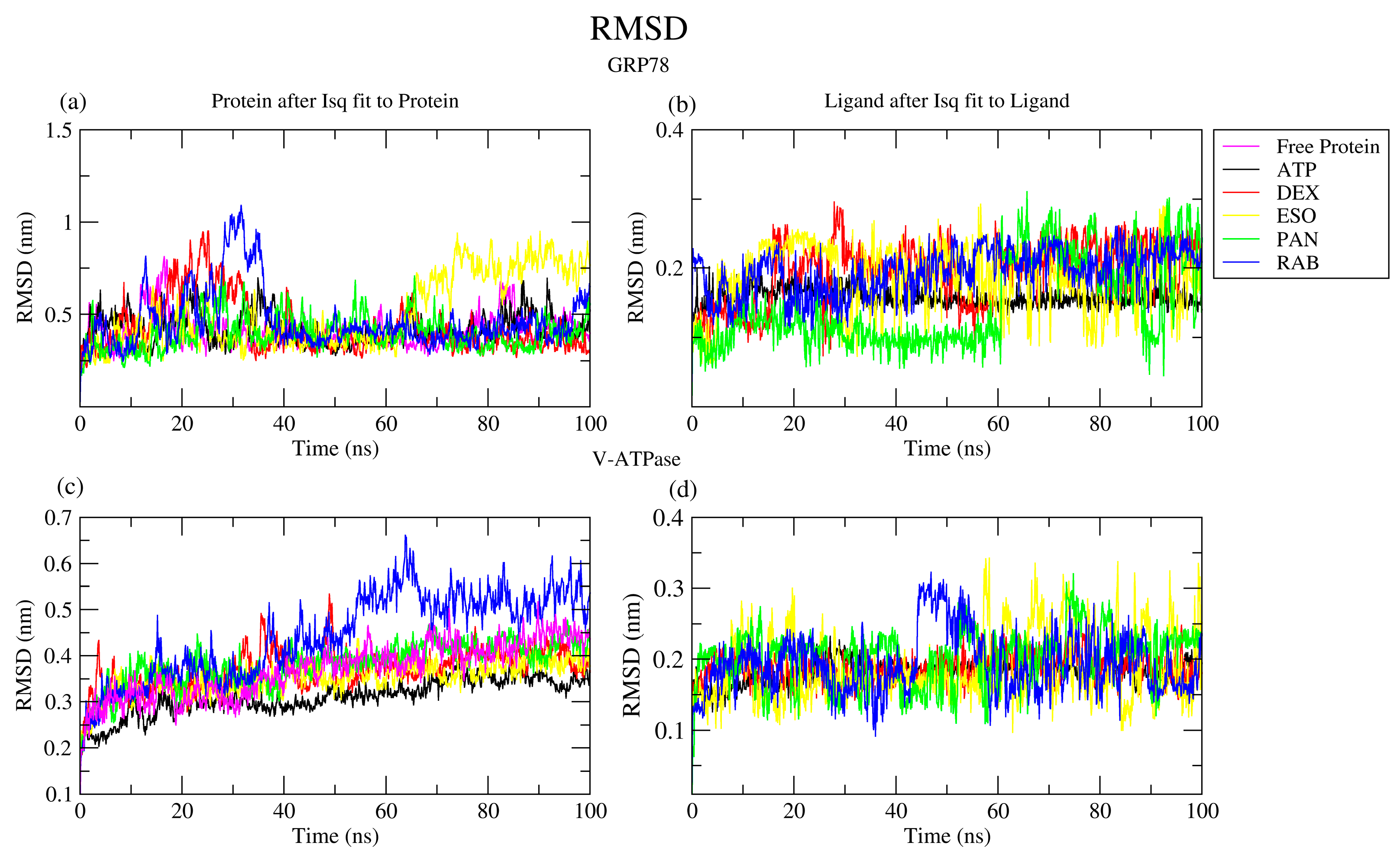



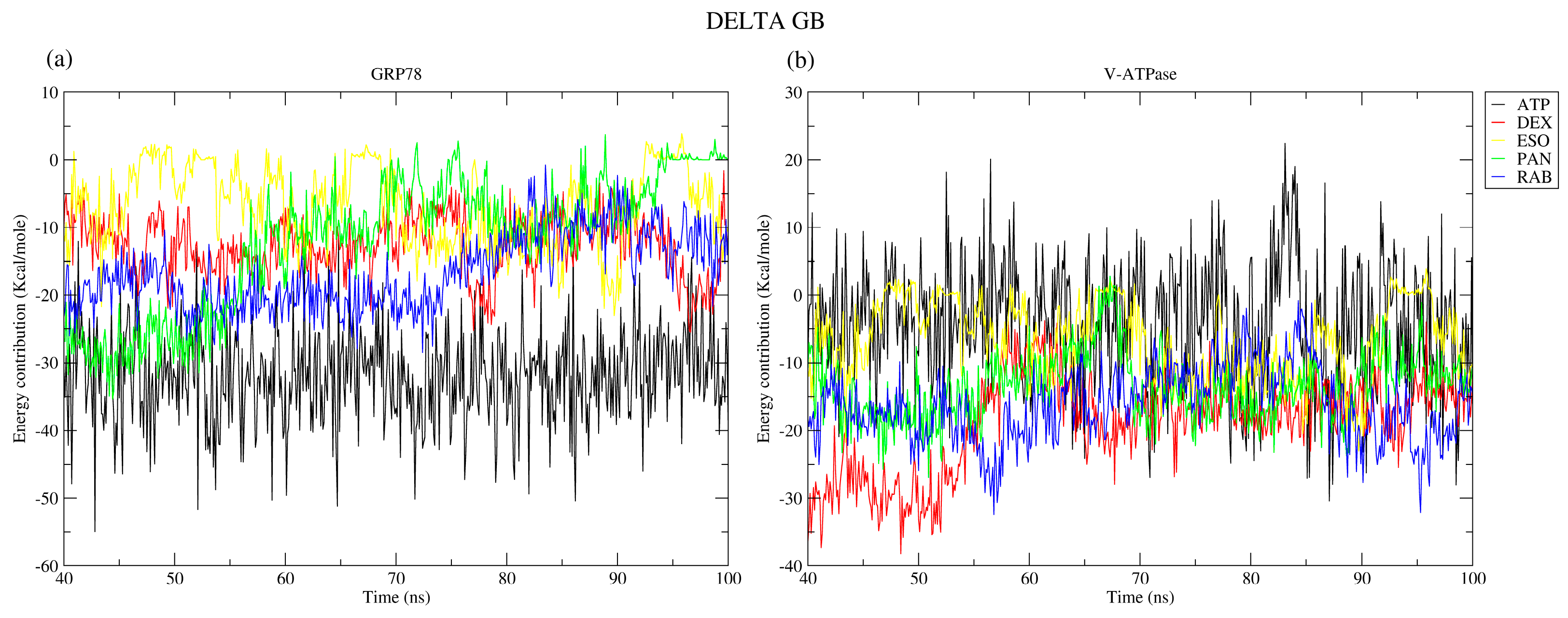
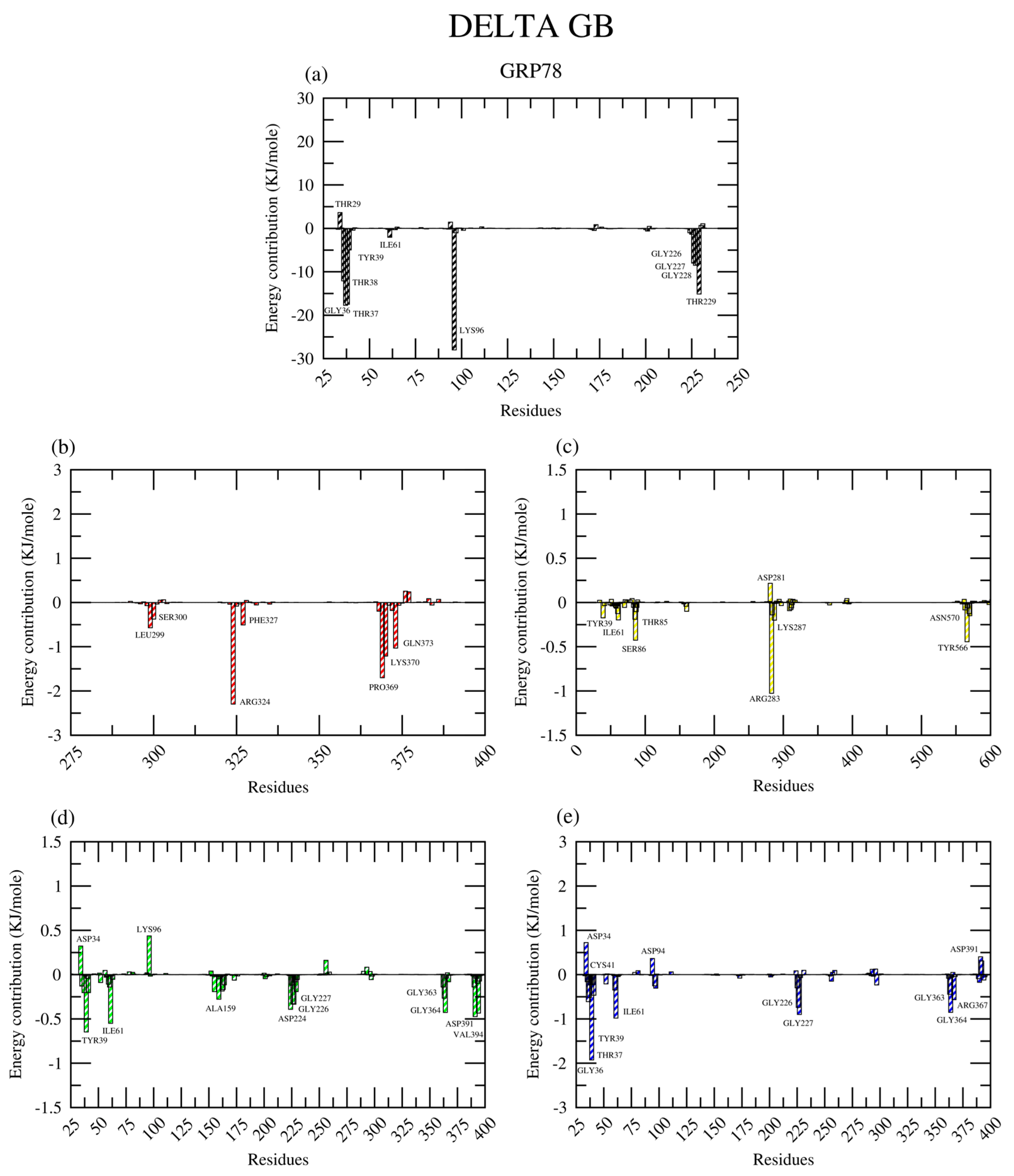
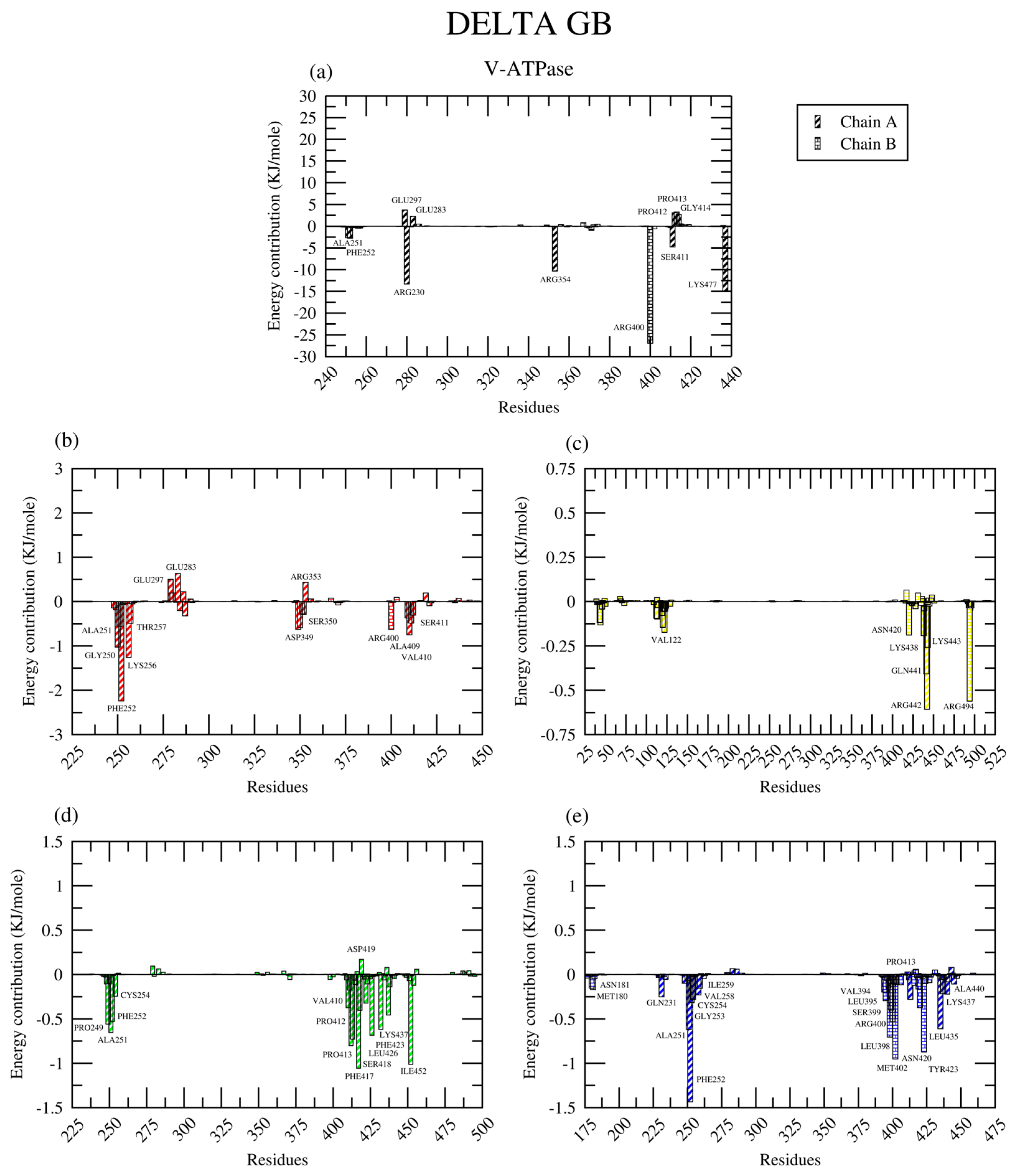
| Protein | Ligand | RMSD (nm) | Ligand RMSD (nm) | RMSF (nm) | RoG (nm) | SASA (nm2) | H-Bond |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRP78 | - | ~0.41 | - | ~0.17 | ~2.96 | ~304.84 | - |
| ATP | ~0.42 | ~0.16 | ~0.15 | ~2.96 | ~304.43 | ~11.9 | |
| DEX | ~0.43 | ~0.20 | ~0.22 | ~2.93 | ~299.27 | ~0.62 | |
| ESO | ~0.51 | ~0.19 | ~0.20 | ~2.96 | ~298.94 | ~0.97 | |
| PAN | ~0.40 | ~0.15 | ~0.16 | ~2.99 | ~305.74 | ~1.66 | |
| RAB | ~0.47 | ~0.19 | ~0.21 | ~2.98 | ~305.21 | ~1.29 | |
| V-ATPase | - | ~0.37 | - | ~0.14 | ~3.36 | ~479.68 | - |
| ATP | ~0.31 | ~0.18 | ~0.12 | ~3.36 | ~470.65 | ~8.83 | |
| DEX | ~0.37 | ~0.19 | ~0.17 | ~3.42 | ~493.87 | ~1.08 | |
| ESO | ~0.35 | ~0.18 | ~0.18 | ~3.39 | ~473.29 | ~0.42 | |
| PAN | ~0.38 | ~0.20 | ~0.16 | ~3.38 | ~477.53 | ~0.66 | |
| RAB | ~0.44 | ~0.19 | ~0.22 | ~3.44 | ~489.77 | ~0.78 |
| Protein | Ligand | VDWAALS | EEL | EGB | ESURF | GGAS | GSOLV | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRP78 | ATP | −32.64 ± 0.17 | −573.43 ±1.84 | 579.06 ±1.78 | −5.02 ±0.01 | −606.07 ±1.84 | 574.04 ±1.78 | −32.03 ±0.28 |
| DEX | −25.26 ± 0.18 | −15.33 ±0.50 | 31.37 ±0.39 | −3.49 ±0.03 | −40.59 ±0.51 | 27.89 ±0.38 | −12.70 ±0.18 | |
| ESO | −13.83 ± 0.33 | −5.97 ±0.32 | 15.08 ±0.41 | −1.95 ±0.05 | −19.80 ±0.55 | 13.13 ±0.37 | −6.67 ±0.23 | |
| PAN | −23.35 ± 0.54 | −16.24 ±0.56 | 30.94 ±0.73 | −3.36 ±0.07 | −39.60 ±1.03 | 27.58 ±0.66 | −12.02 ±0.40 | |
| RAB | −34.61 ± 0.24 | −19.35 ±0.37 | 42.38 ±0.37 | −5.00 ±0.03 | −53.96 ±0.52 | 37.37 ±0.35 | −16.59 ±0.22 | |
| V-ATPase | ATP | −31.89 ± 0.21 | −500.3 ±1.81 | 534.4 ±1.69 | −6.35 ±0.01 | −532.26 ±1.78 | 528.11 ±1.69 | −4.16 ±0.37 |
| DEX | −32.58 ± 0.17 | −28.44 ±0.50 | 46.93 ±0.37 | −4.88 ±0.02 | −61.02 ±0.60 | 42.05 ±0.36 | −18.97 ±0.28 | |
| ESO | −12.42 ± 0.40 | −5.30 ±0.32 | 14.02 ±0.48 | −1.65 ±0.05 | −17.72 ±0.63 | 12.36 ±0.43 | −5.35 ±0.23 | |
| PAN | −25.29 ± 0.22 | −16.60 ±0.46 | 32.20 ±0.47 | −3.74 ±0.03 | −41.89 ±0.57 | 28.46 ±0.45 | −13.43 ±0.20 | |
| RAB | −28.78 ± 0.22 | −11.08 ±0.30 | 27.83 ±0.30 | −4.16 ±0.03 | −39.86 ±0.43 | 23.67 ±0.28 | −16.19 ±0.22 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elfiky, A.A.; Mansour, K.R.; Mohamed, Y.; Abdelaziz, Y.K.; Nicholls, I.A. Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Proton Pump Inhibitors by Targeting GRP78 and V-ATPase: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, PCA, and MM-GBSA Calculations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178170
Elfiky AA, Mansour KR, Mohamed Y, Abdelaziz YK, Nicholls IA. Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Proton Pump Inhibitors by Targeting GRP78 and V-ATPase: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, PCA, and MM-GBSA Calculations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178170
Chicago/Turabian StyleElfiky, Abdo A., Kirolos R. Mansour, Yousef Mohamed, Yomna Kh. Abdelaziz, and Ian A. Nicholls. 2025. "Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Proton Pump Inhibitors by Targeting GRP78 and V-ATPase: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, PCA, and MM-GBSA Calculations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178170
APA StyleElfiky, A. A., Mansour, K. R., Mohamed, Y., Abdelaziz, Y. K., & Nicholls, I. A. (2025). Exploring the Anticancer Potential of Proton Pump Inhibitors by Targeting GRP78 and V-ATPase: Molecular Docking, Molecular Dynamics, PCA, and MM-GBSA Calculations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178170









