Distinct Gut Microbiota Signatures Are Associated with Severity of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in People with HIV
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
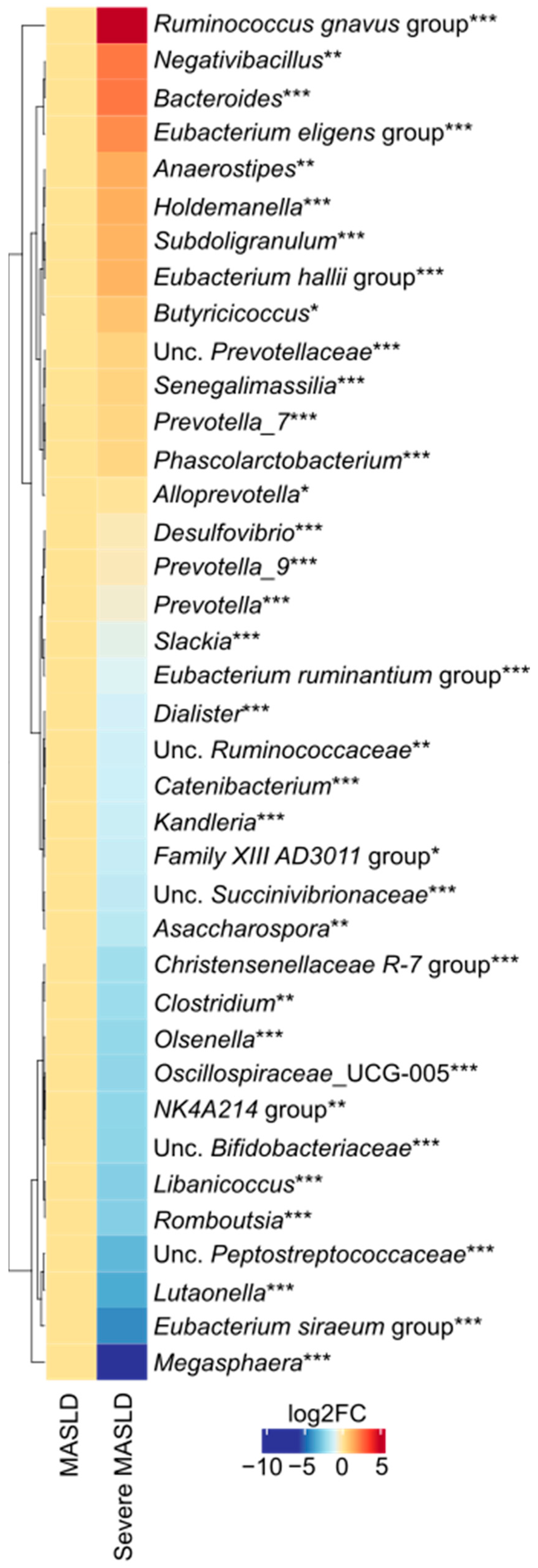
2.1. Microbiota Diversity and Taxonomic Differences
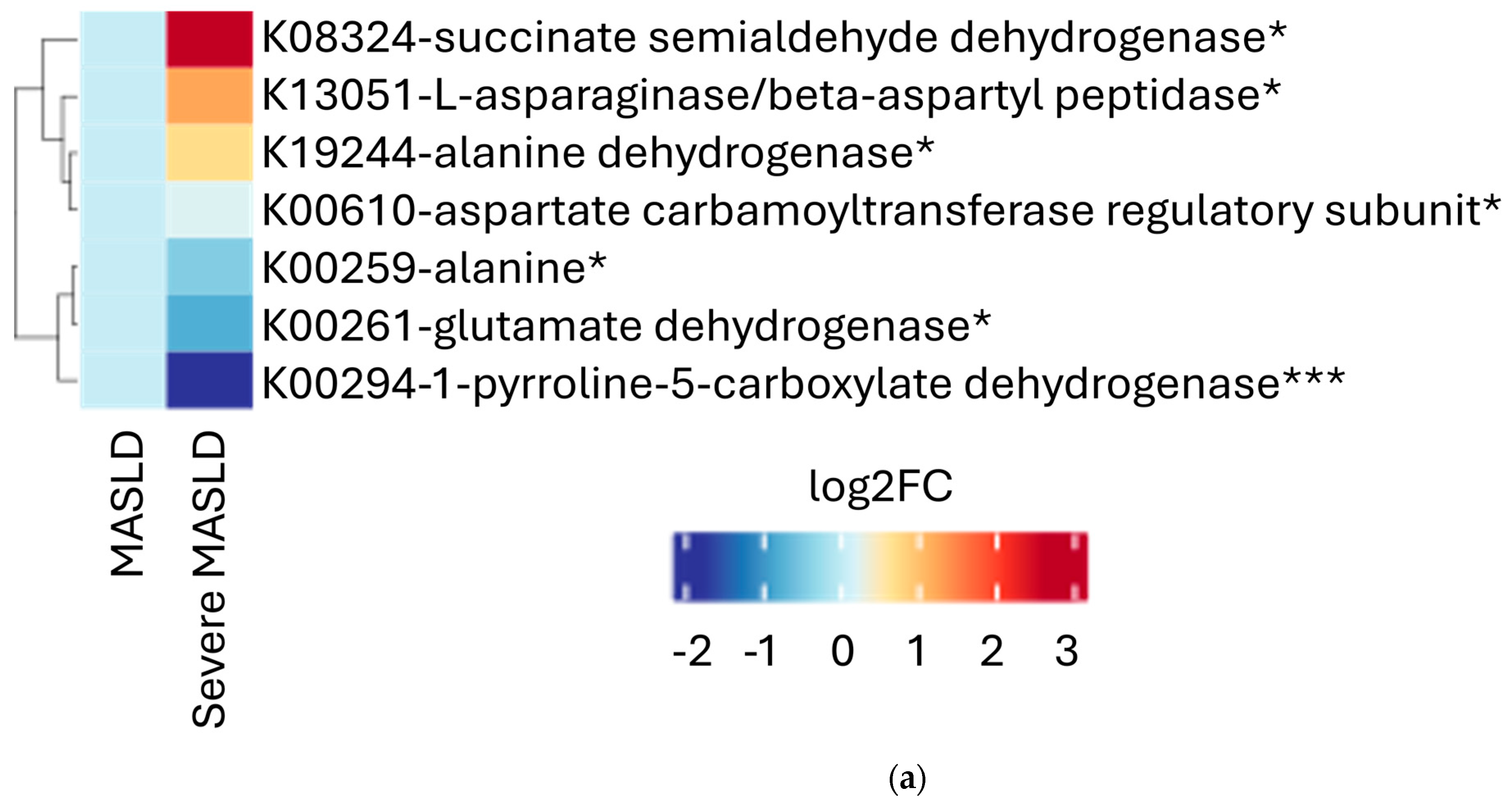
2.2. Microbial Functional Pathways
2.3. Integration with Clinical Features
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
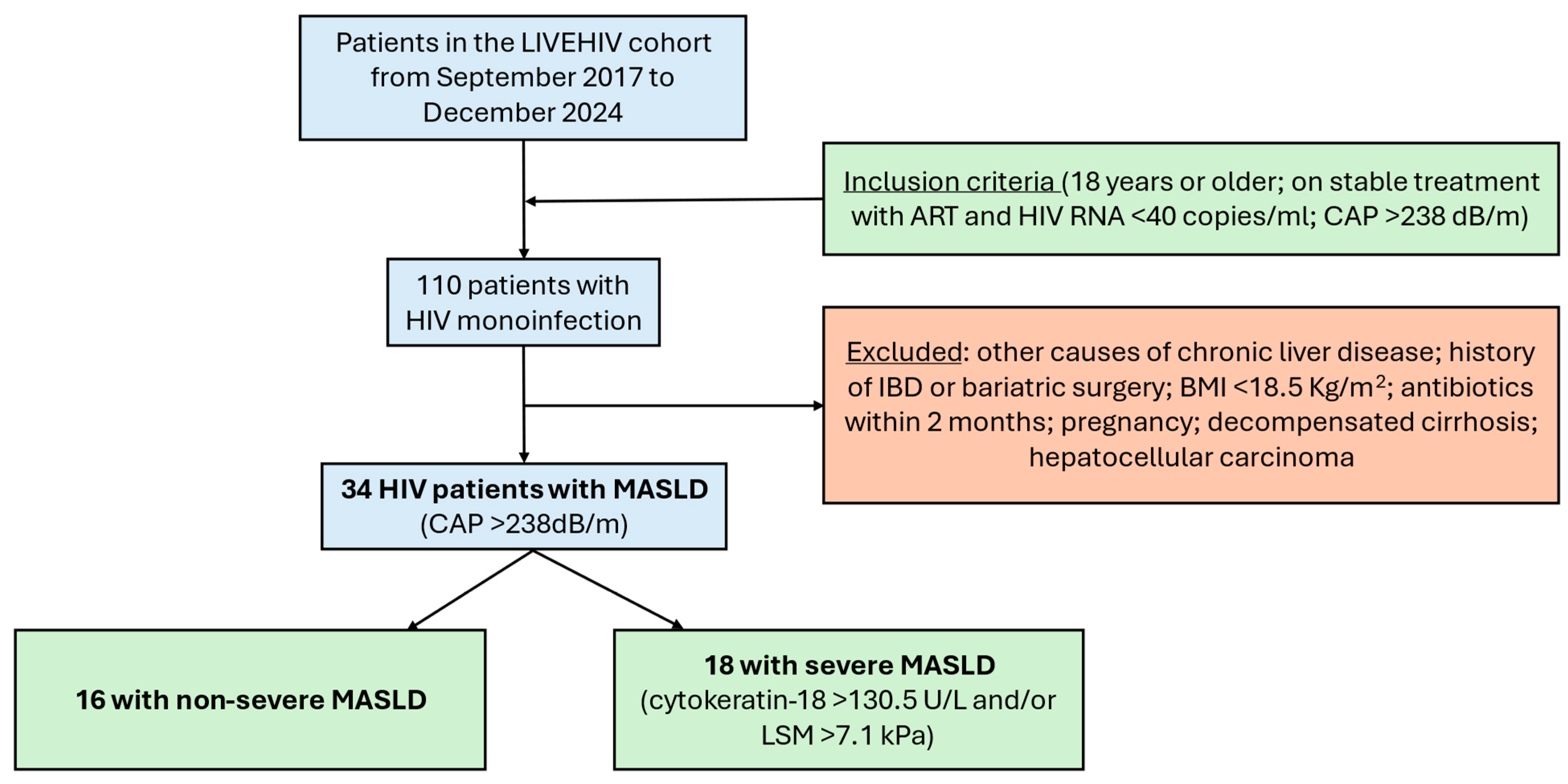
4.1. Study Design and Participants
4.2. Ethics
4.3. Transient Elastography Examination with CAP
4.4. Clinical and Biological Parameters
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collins, L.F.; Palella, F.J.; Mehta, C.C.; Holloway, J.; Stosor, V.; Lake, J.E.; Brown, T.T.; Topper, E.F.; Naggie, S.; Anastos, K.; et al. Aging-Related Comorbidity Burden Among Women and Men with or At-Risk for HIV in the US, 2008–2019. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2327584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trickey, A.; McGinnis, K.; Gill, M.J.; Abgrall, S.; Berenguer, J.; Wyen, C.; Hessamfar, M.; Reiss, P.; Kusejko, K.; Silverberg, M.J.; et al. Longitudinal trends in causes of death among adults with HIV on antiretroviral therapy in Europe and North America from 1996 to 2020: A collaboration of cohort studies. Lancet HIV 2024, 11, e176–e185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawrieh, S.; Vilar-Gomez, E.; Woreta, T.A.; Lake, J.E.; Wilson, L.A.; Price, J.C.; Naggie, S.; Sterling, R.K.; Heath, S.; Corey, K.E.; et al. Prevalence of steatotic liver disease, MASLD, MetALD and significant fibrosis in people with HIV in the United States. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 59, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; E Underwood, F.; A King, J.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.-A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the clinical assessment and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervo, A.; Shengir, M.; Patel, K.; Sebastiani, G. NASH in HIV. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2020, 17, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.G.; Kounatidis, D.; Psallida, S.; Vythoulkas-Biotis, N.; Adamou, A.; Zachariadou, T.; Kargioti, S.; Karampela, I.; Dalamaga, M. NAFLD/MASLD and the Gut–Liver Axis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment Options. Metabolites 2024, 14, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, M.J.; Tien, P.C.; Somsouk, M.; Price, J.C. The human microbiome and gut–liver axis in people living with HIV. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. 2023, 20, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Sanz, J.; Talavera-Rodríguez, A.; Díaz-Álvarez, J.; Cancio-Suárez, M.R.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Alba, C.; Montes, M.L.; Martín-Mateos, R.; Burgos-Santamaría, D.; Moreno, S.; et al. A gut microbiome signature for HIV and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1297378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanavich, C.; Perazzo, H.; Li, F.; Tobin, N.; Lee, D.; Zabih, S.; Morata, M.; Almeida, C.; Veloso, V.G.; Grinsztejn, B.; et al. A pilot study of microbial signatures of liver disease in those with HIV mono-infection in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. AIDS 2021, 36, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Vitetta, L. Gut Microbiota Metabolites in NAFLD Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, E.E.; Canfora, E.E.; Theis, S.; Frost, G.; Groen, A.K.; Mithieux, G.; Nauta, A.; Scott, K.; Stahl, B.; Van Harsselaar, J.; et al. Short chain fatty acids in human gut and metabolic health. Benef. Microbes 2020, 11, 411–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.; Nuñez-García, M.; Fernández-Tussy, P.; Barbier-Torres, L.; Fernández-Ramos, D.; Gómez-Santos, B.; Buqué, X.; Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Serrano-Macia, M.; et al. Targeting Hepatic Glutaminase 1 Ameliorates Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Restoring Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein Triglyceride Assembly. Cell Metab. 2020, 31, 605–622.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Cao, J.-C.; Liu, F.-R.; Deng, Z.; Chen, C.-J.; Sun, Y.-Y. Folate intake and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in US adults. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 32, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Hernández-Rocha, C.; Morales, C.; Vargas, J.I.; Solís, N.; Pizarro, M.; Robles, C.; Sandoval, D.; Ponthus, S.; Benítez, C.; et al. Serum cytokeratin-18 fragment levels as noninvasive marker of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the Chilean population. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 40, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoine, M.; Assoumou, L.; De Wit, S.; Girard, P.-M.; Valantin, M.A.; Katlama, C.; Necsoi, C.; Campa, P.; Huefner, A.D.; Wiesch, J.S.Z.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Noninvasive Markers of Steatosis, NASH, and Liver Fibrosis in HIV-Monoinfected Individuals at Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Results From the ECHAM Study. Am. J. Ther. 2019, 80, e86–e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Cai, D.; Zhou, S.; Li, A.; Xie, J.; Zhang, J. Uncovering a causal connection between the Lachnoclostridium genus in fecal microbiota and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1276790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, T.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yi, F.; Chen, Y. Impact of gut microbiota on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Insights from a leave-one-out cross-validation study. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1320279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanthier, N.; Rodriguez, J.; Nachit, M.; Hiel, S.; Trefois, P.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Cani, P.D.; Bindels, L.B.; Thissen, J.-P.; Delzenne, N.M. Microbiota analysis and transient elastography reveal new extra-hepatic components of liver steatosis and fibrosis in obese patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 659, Erratum in Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korobeinikova, A.V.; Zlobovskaya, O.A.; Sheptulina, A.F.; Ashniev, G.A.; Bobrova, M.M.; Yafarova, A.A.; Akasheva, D.U.; Kabieva, S.S.; Bakoev, S.Y.; Zagaynova, A.V.; et al. Gut Microbiota Patterns in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Assessment Using Three Analysis Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahnemo, L.; Nethander, M.; Coward, E.; Gabrielsen, M.E.; Sree, S.; Billod, J.-M.; Engstrand, L.; Abrahamsson, S.; Langhammer, A.; Hveem, K.; et al. Cross-sectional associations between the gut microbe Ruminococcus gnavus and features of the metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 481–483, Erratum in Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, H.; Yang, X.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lu, D.; Ye, L.; Cui, P.; et al. The role of gut microbiota in the occurrence and progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1257903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, J.; Yang, L.; Hu, Q.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Pan, D.; Zhao, Q. Altered gut microbial profile accompanied by abnormal short chain fatty acid metabolism exacerbates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Qin, Q.; Chen, J.; Yan, S.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, A.; Ding, S. Gut Microbiome Alterations in Patients with Visceral Obesity Based on Quantitative Computed Tomography. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 823262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlano, R.; Martinez-Gili, L.; Takis, P.; Miguens-Blanco, J.; Liu, T.; Triantafyllou, E.; Skinner, C.; Loomba, R.; Thursz, M.; Marchesi, J.R.; et al. Disruption of gut barrier integrity and host–microbiome interactions underlie MASLD severity in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2304157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, H.; Shen, L.; Ni, Y.; Fang, Q.; Wu, G.; Qian, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Metabolic phenotypes and the gut microbiota in response to dietary resistant starch type 2 in normal-weight subjects: A randomized crossover trial. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Zhang, K.; Liang, L.; Yang, Y.; Lu, D.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, T.; Fan, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; et al. Multi-omics analyses of the gut microbiota and metabolites in children with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. mSystems 2025, 10, e0114824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.S.; Luu, K.; Lagishetty, V.; Sedighian, F.; Woo, S.-L.; Dreskin, B.W.; Katzka, W.; Chang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Arias-Jayo, N.; et al. Gut microbiome profiles associated with steatosis severity in metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Hepatoma Res. 2021, 7, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas-Pinto, A.; Bakewell, N.; Milinkovic, A.; Williams, I.; Vera, J.; Post, F.A.; Anderson, J.; Beynon, M.; O’Brien, A.; Doyle, N.; et al. Hepatic steatosis in people older and younger than fifty who are living with HIV and HIV-negative controls: A cross-sectional study nested within the POPPY cohort. HIV Med. 2023, 25, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.; Xu, W.; Tong, B.; Wang, S.; Ji, R.; Tan, Y.; Zhu, Y. Characteristics of gut microbiota in patients with metabolic associated fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Pareja, I.; Amiar, M.R.; Ocaña-Wilhelmi, L.; Soler-Humanes, R.; Arranz-Salas, I.; Garrido-Sánchez, L.; Gutiérrez-Repiso, C.; Tinahones, F.J. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with morbid obesity: The gut microbiota axis as a potential pathophysiology mechanism. J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 59, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caussy, C.; Tripathi, A.; Humphrey, G.; Bassirian, S.; Singh, S.; Faulkner, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Rizo, E.; Richards, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; et al. A gut microbiome signature for cirrhosis due to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isnard, S.; Lin, J.; Fombuena, B.; Ouyang, J.; Varin, T.V.; Richard, C.; Marette, A.; Ramendra, R.; Planas, D.; Marchand, L.R.; et al. Repurposing Metformin in Nondiabetic People With HIV: Influence on Weight and Gut Microbiota. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Feng, A.; Luo, D.; Wu, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, L.; Zou, H. Altered gut microbiota is associated with different immunologic responses to antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected men who have sex with men. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Sortino, O.; Verheij, E.; Sklar, J.; Wit, F.W.; Kootstra, N.A.; Sellers, B.; Brenchley, J.M.; Ananworanich, J.; Van Der Loeff, M.S.; et al. HIV-associated gut dysbiosis is independent of sexual practice and correlates with noncommunicable diseases. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, S.; Sheng, S.; Qin, Q.; Chen, J.; Li, W.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Wang, L.; Ang, L.; et al. Comparison of gut microbiota in male MAFLD patients with varying liver stiffness. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 873048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; He, Z.; Li, H. Bacteroides and NAFLD: Pathophysiology and therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1288856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zi, L.; Kuang, T.; Wang, K.; Qiu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, R.; Wang, P.; Wang, W. Investigating causal associations among gut microbiota, metabolites, and liver diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1159148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, C.; Endo, T.; Iino, K.; Tateda, T.; Sato, S.; Igarashi, G.; Mikami, K.; Sakuraba, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; Nakaji, S.; et al. Reduced Equol Production and Gut Microbiota Features in Men with Lean Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Men’s Health 2022, 16, 15579883221115598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Faraci, G.; Nanda, S.; Ter-Saakyan, S.; Love, T.M.; Mack, W.J.; Dubé, M.P.; Lee, H.Y. Gut microbiome in people living with HIV is associated with impaired thiamine and folate syntheses. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 160, 105209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batool, T.; Makky, E.A.; Jalal, M.; Yusoff, M.M. A Comprehensive Review on l-Asparaginase and Its Applications. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 178, 900–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Koh, C.; Samala, N.; Fontana, R.J.; Stolz, A.; Durazo, F.; Hayashi, P.H.; Phillips, E.; Wang, T.; Hoofnagle, J.H.; et al. Asparaginase-induced hepatotoxicity: Rapid development of cholestasis and hepatic steatosis. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajaz, S.; McPhail, M.J.; Gnudi, L.; Trovato, F.M.; Mujib, S.; Napoli, S.; Carey, I.; Agarwal, K. Mitochondrial dysfunction as a mechanistic biomarker in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Mitochondrion 2021, 57, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, J.M.; Pandhare, J.; Liu, Y. The Metabolism of Proline as Microenvironmental Stress Substrate. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2008S–2015S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Levy, C.; Angulo, P.; Keach, J.; Jorgensen, R.; Lindor, K.D. Open-label pilot study of folic acid in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Liver Int. 2007, 27, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, K.E.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Deng, L.; Caudill, M.A.; Rozen, R. Steatosis in mice is associated with gender, folate intake, and expression of genes of one-carbon metabolism. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sid, V.; Wu, N.; Sarna, L.K.; Siow, Y.L.; House, J.D.; O, K. Folic acid supplementation during high-fat diet feeding restores AMPK activation via an AMP-LKB1-dependent mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2015, 309, R1215–R1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, L.K.; Wu, N.; Wang, P.; Hwang, S.-Y.; Siow, Y.L.; O, K. Folic acid supplementation attenuates high fat diet induced hepatic oxidative stress via regulation of NADPH oxidase. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 90, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischoff, J.; Gu, W.; Schwarze-Zander, C.; Boesecke, C.; Wasmuth, J.-C.; van Bremen, K.; Dold, L.; Rockstroh, J.K.; Trebicka, J. Stratifying the risk of NAFLD in patients with HIV under combination antiretroviral therapy (cART). eClinicalMedicine 2021, 40, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaraldi, G.; Milic, J.; Renzetti, S.; Motta, F.; Cinque, F.; Bischoff, J.; Desilani, A.; Conti, J.; Medioli, F.; del Monte, M.; et al. The effect of weight gain and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease on liver fibrosis progression and regression in people with HIV. AIDS 2024, 38, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Cardoso, S.; Klatt, N.R.; Reyes-Terán, G. Impact of antiretroviral drugs on the microbiome: Unknown answers to important questions. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2018, 13, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, F.; Saeed, S.; Kablawi, D.; Ballesteros, L.R.; Elgretli, W.; Moodie, E.E.M.; Price, C.; Monteith, K.; Cooper, C.; Walmsley, S.L.; et al. Role of fatty liver in the epidemic of advanced chronic liver disease among people with HIV: Protocol for the Canadian LIVEHIV multicentre prospective cohort. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e076547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías, J.; González, J.; Tural, C.; Ortega-González, E.; Pulido, F.; Rubio, R.; Cifuentes, C.; Díaz-Menéndez, M.; Jou, A.; Rubio, P.; et al. Prevalence and factors associated with liver steatosis as measured by transient elastography with controlled attenuation parameter in HIV-infected patients. AIDS 2014, 28, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, J.; Zarski, J.; de Ledinghen, V.; Rousselet, M.; Sturm, N.; Lebail, B.; Fouchard-Hubert, I.; Gallois, Y.; Oberti, F.; Bertrais, S.; et al. Determination of reliability criteria for liver stiffness evaluation by transient elastography. Hepatology 2012, 57, 1182–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiani, G.; Saeed, S.; Lebouche, B.; de Pokomandy, A.; Szabo, J.; Haraoui, L.-P.; Routy, J.-P.; Wong, P.; Deschenes, M.; Ghali, P.; et al. Vitamin E is an effective treatment for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in HIV mono-infected patients. AIDS 2020, 34, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shengir, M.; Lebouche, B.; Elgretli, W.; Saeed, S.; Ramanakumar, A.V.; Giannakis, A.; De Pokomandy, A.; Cox, J.; Costiniuk, C.; Routy, J.; et al. Switch to a raltegravir-based antiretroviral regimen in people with HIV and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. HIV Med. 2023, 25, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Kawashima, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D457–D462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mallick, H.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Benson, A.K.; Yi, N. Negative binomial mixed models for analyzing microbiome count data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Package ‘Emmeans’ Type Package. Estimated Marginal Means, aka Least-Squares Means. 2025. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/emmeans/emmeans.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2025).

| Whole Study Population (n = 34) | Severe MASLD (n = 18) | Non-Severe MASLD (n = 16) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 51 (10) | 53 (10) | 49 (11) | 0.293 |
| Male sex (%) | 31 (91) | 17 (94) | 14 (88) | 0.476 |
| Ethnicity (%) | ||||
| White | 21 (62) | 13 (72) | 8 (50) | 0.286 |
| Hispanic | 9 (26) | 2 (11) | 6 (38) | |
| Black non-Hispanic | 3 (9) | 1 (6) | 2 (13) | |
| MSM (%) | 21 (62) | 12 (67) | 9 (56) | 0.533 |
| IDU (%) | 1 (3) | 1 (6) | 0 | 0.325 |
| Current alcohol use (%) | 20 (59) | 11 (61) | 9 (56) | 0.773 |
| Current smoking (%) | 3 (9) | 1 (6) | 2 (13) | 0.476 |
| Hypertension (%) | 11 (32) | 7 (39) | 4 (25) | 0.387 |
| Diabetes (%) | 4 (12) | 5 (28) | 0 | 0.027 |
| History of cardiovascular event (%) | 4 (12) | 4 (22) | 1 (6) | 0.189 |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 28.9 (4) | 29.9 (5) | 28.0 (4) | 0.222 |
| Time since HIV diagnosis (years) | 16.3 (7) | 17.5 (8) | 15.1 (7) | 0.388 |
| CD4 cell count (cells/μL) | 581 (248) | 680 (249) | 488 (213) | 0.028 |
| CD4/CD8 ratio | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 1 (0) | 0.714 |
| Current ART regimen (%) | ||||
| NRTIs | 28 (82) | 13 (72) | 15 (94) | 0.100 |
| NNRTIs | 9 (26) | 6 (33) | 3 (19) | 0.336 |
| Protease inhibitors | 11 (32) | 8 (44) | 3 (19) | 0.097 |
| Integrase inhibitors | 22 (65) | 10 (56) | 12 (75) | 0.236 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 27 (11) | 32 (9) | 23 (11) | 0.014 |
| AST (IU/L) | 25 (9) | 27 (8) | 23 (10) | 0.150 |
| GGT (IU/L) | 44 (24) | 51 (26) | 39 (22) | 0.112 |
| Platelets (109/L) | 215 (61) | 220 (68) | 210 (54) | 0.676 |
| Bilirubin (mmol/L) | 13 (10) | 15 (14) | 10 (9) | 0.171 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 43 (4) | 44 (3) | 42 (5) | 0.888 |
| Creatinine (mmol/L) | 83 (14) | 82 (13) | 84 (15) | 0.646 |
| Triglycerides (mmol/L) | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 2 (1) | 0.033 |
| Total cholesterol (mmol/L) | 5 (1) | 5 (1) | 5 (1) | 0.370 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 0.106 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 3 (1) | 2 (1) | 3 (1) | 0.099 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 6 (1) | 6 (1) | 6 (0) | 0.003 |
| Glycosylated Hemoglobin | 6 (1) | 6 (1) | 6 (0) | 0.407 |
| Statin use (%) | 13 (38) | 9 (50) | 4 (25) | 0.134 |
| LSM (kPa) | 7 (5) | 9 (6) | 5 (1) | 0.007 |
| CAP (dB/m) | 300 (48) | 319 (49) | 283 (41) | 0.031 |
| Cytokeratin-18 (U/L) | 185 (161) | 253 (177) | 81 (26) | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Righetti, R.; Cinque, F.; Lebouché, B.; Ramos Ballesteros, L.; Routy, J.-P.; Klein, M.B.; Szabo, J.; Cox, J.; Falutz, J.; Haraoui, L.-P.; et al. Distinct Gut Microbiota Signatures Are Associated with Severity of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in People with HIV. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178165
Righetti R, Cinque F, Lebouché B, Ramos Ballesteros L, Routy J-P, Klein MB, Szabo J, Cox J, Falutz J, Haraoui L-P, et al. Distinct Gut Microbiota Signatures Are Associated with Severity of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in People with HIV. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(17):8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178165
Chicago/Turabian StyleRighetti, Riccardo, Felice Cinque, Bertrand Lebouché, Luz Ramos Ballesteros, Jean-Pierre Routy, Marina B. Klein, Jason Szabo, Joseph Cox, Julian Falutz, Louis-Patrick Haraoui, and et al. 2025. "Distinct Gut Microbiota Signatures Are Associated with Severity of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in People with HIV" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 17: 8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178165
APA StyleRighetti, R., Cinque, F., Lebouché, B., Ramos Ballesteros, L., Routy, J.-P., Klein, M. B., Szabo, J., Cox, J., Falutz, J., Haraoui, L.-P., Costiniuk, C. T., De Pokomandy, A., Pembroke, T., Constante, M., Santos, M., & Sebastiani, G. (2025). Distinct Gut Microbiota Signatures Are Associated with Severity of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in People with HIV. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(17), 8165. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26178165










