Postbiotic pA1c®HI for Preventing Insulin Resistance and Obesity in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Prediabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
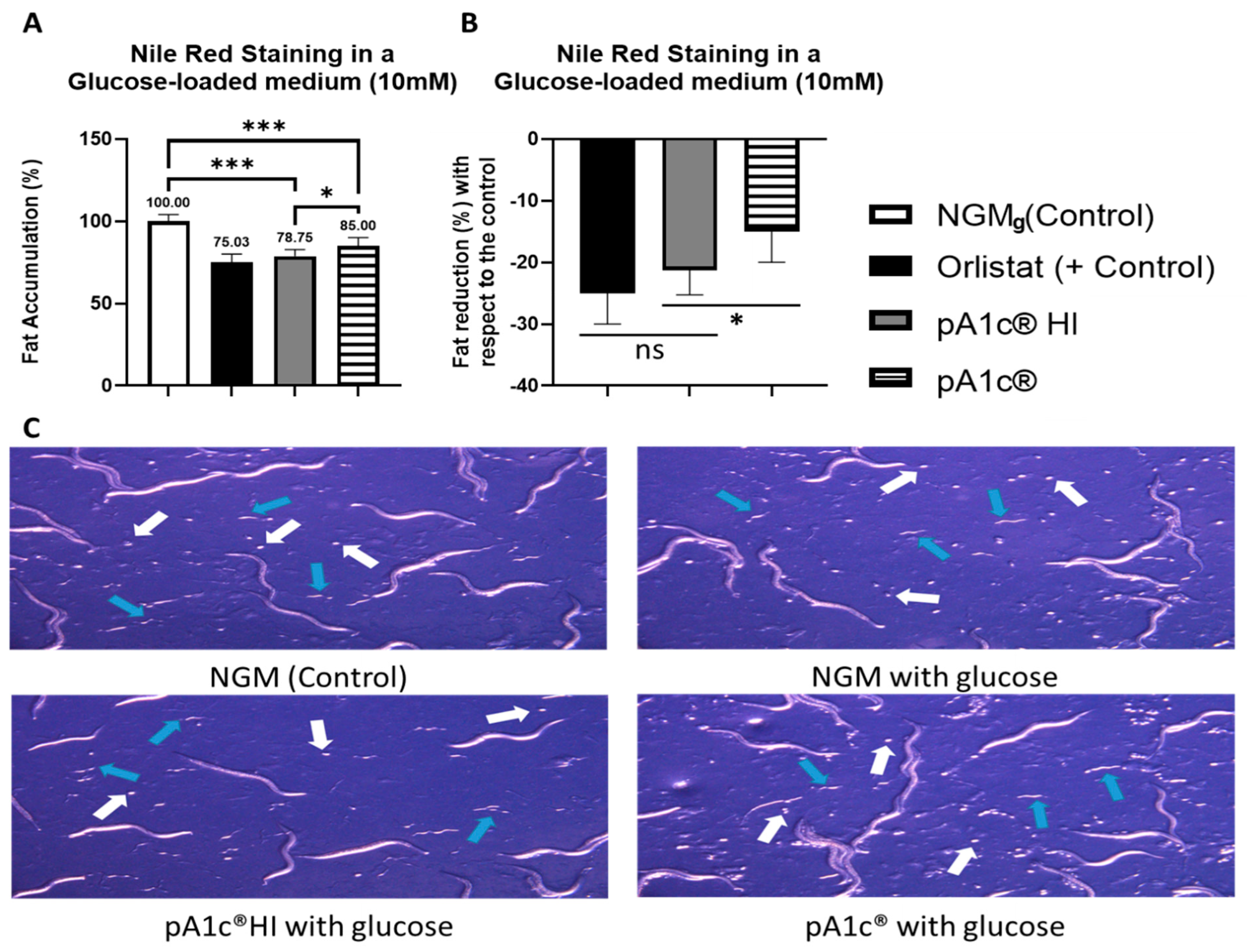
2.1. pA1c®HI Postbiotic Counteracts Glucose-Induced Fat Accumulation with Effectiveness Comparable to the Anti-Obesity Drug Orlistat
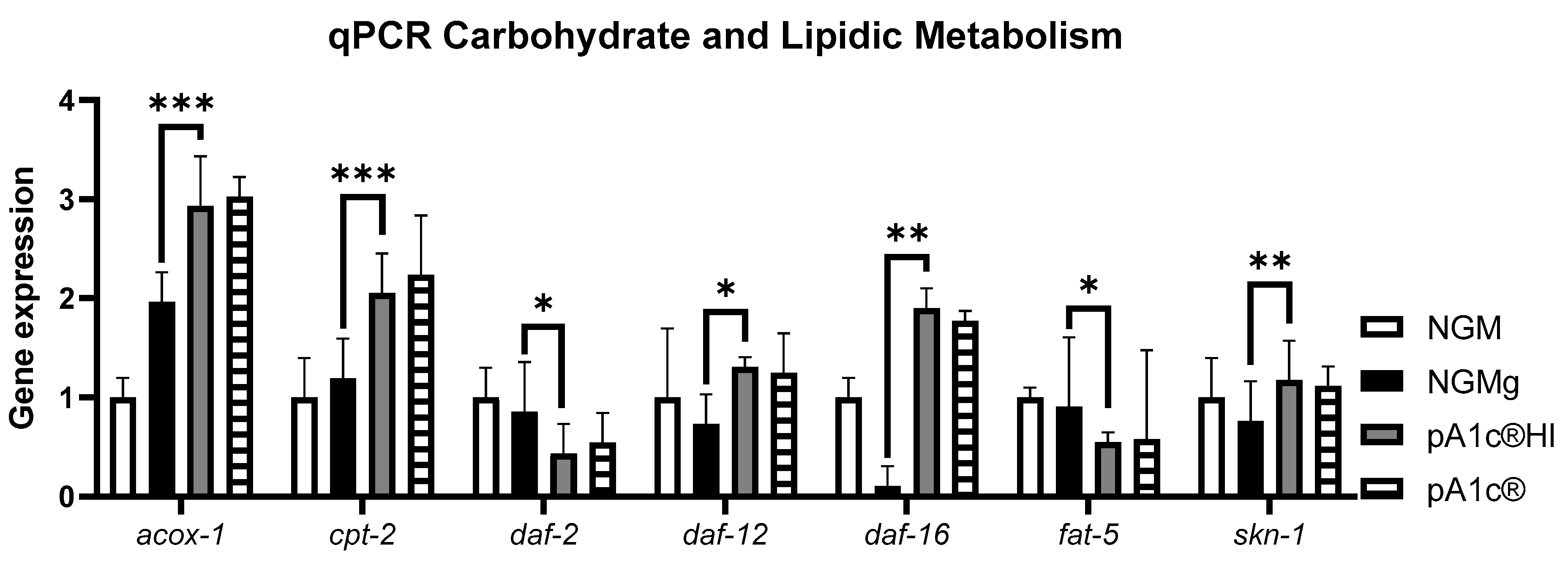
2.2. pA1c®HI Regulates the Insulin Signaling Pathway, Inhibits Fatty Acid Biosynthesis, and Activates the Fatty Acid β-Oxidation Process
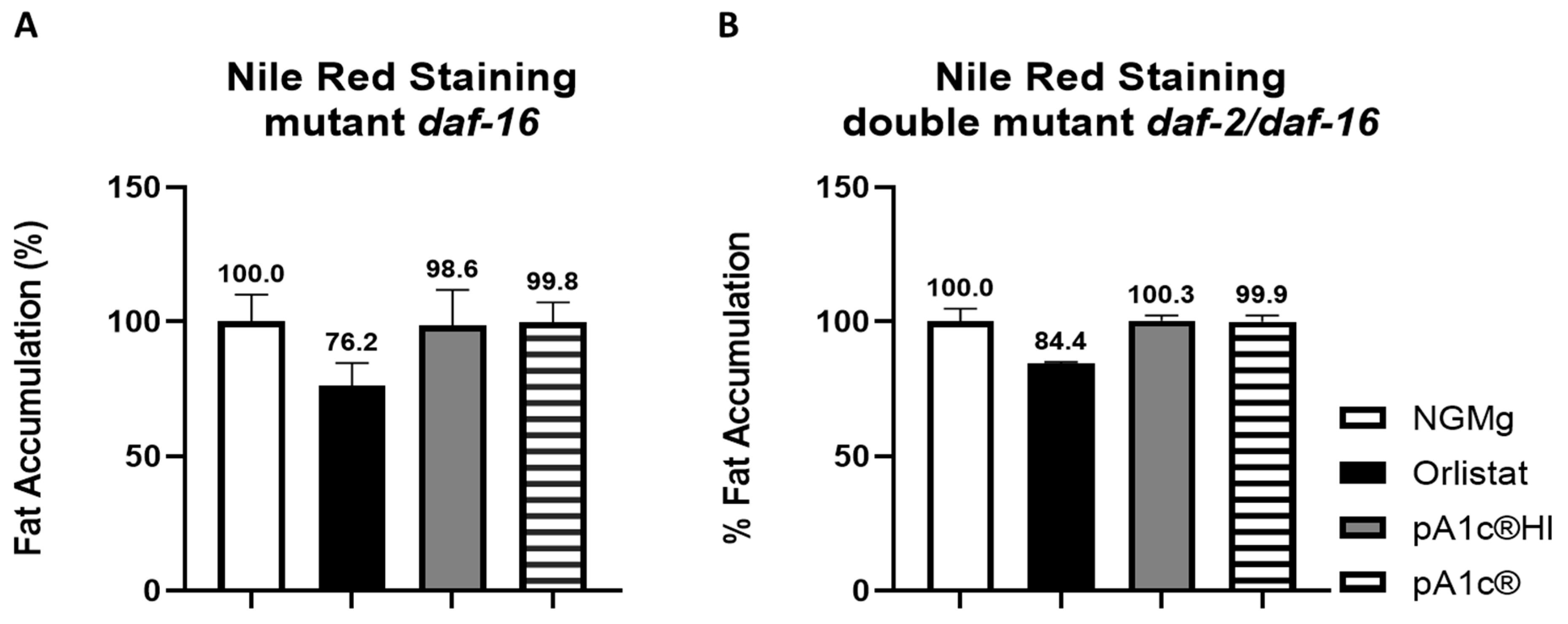
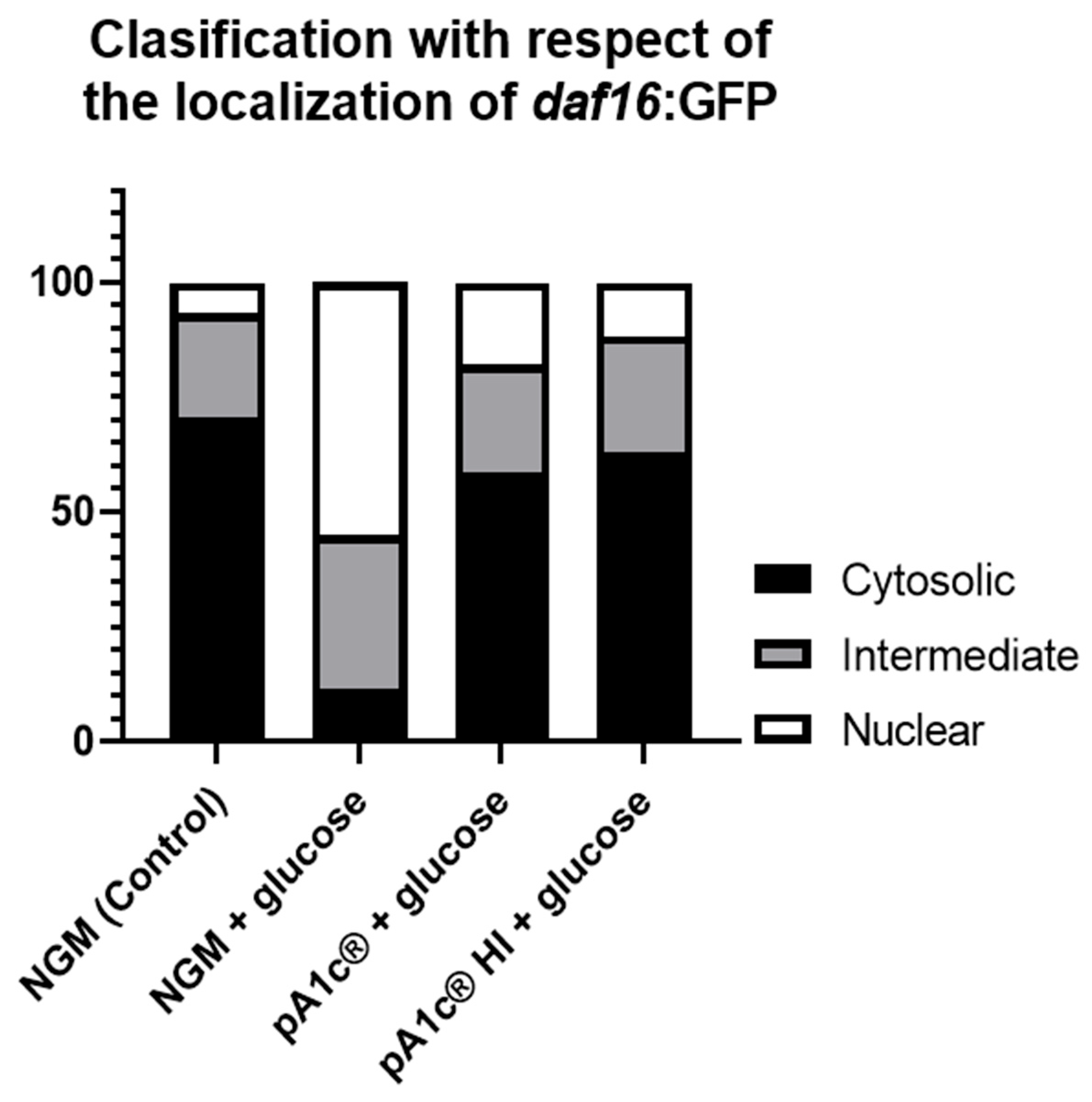
2.3. pA1c®HI Counteracts the High-Glucose-Induced Nuclear Localization of daf-16 More Effectively than the Alive pA1c®
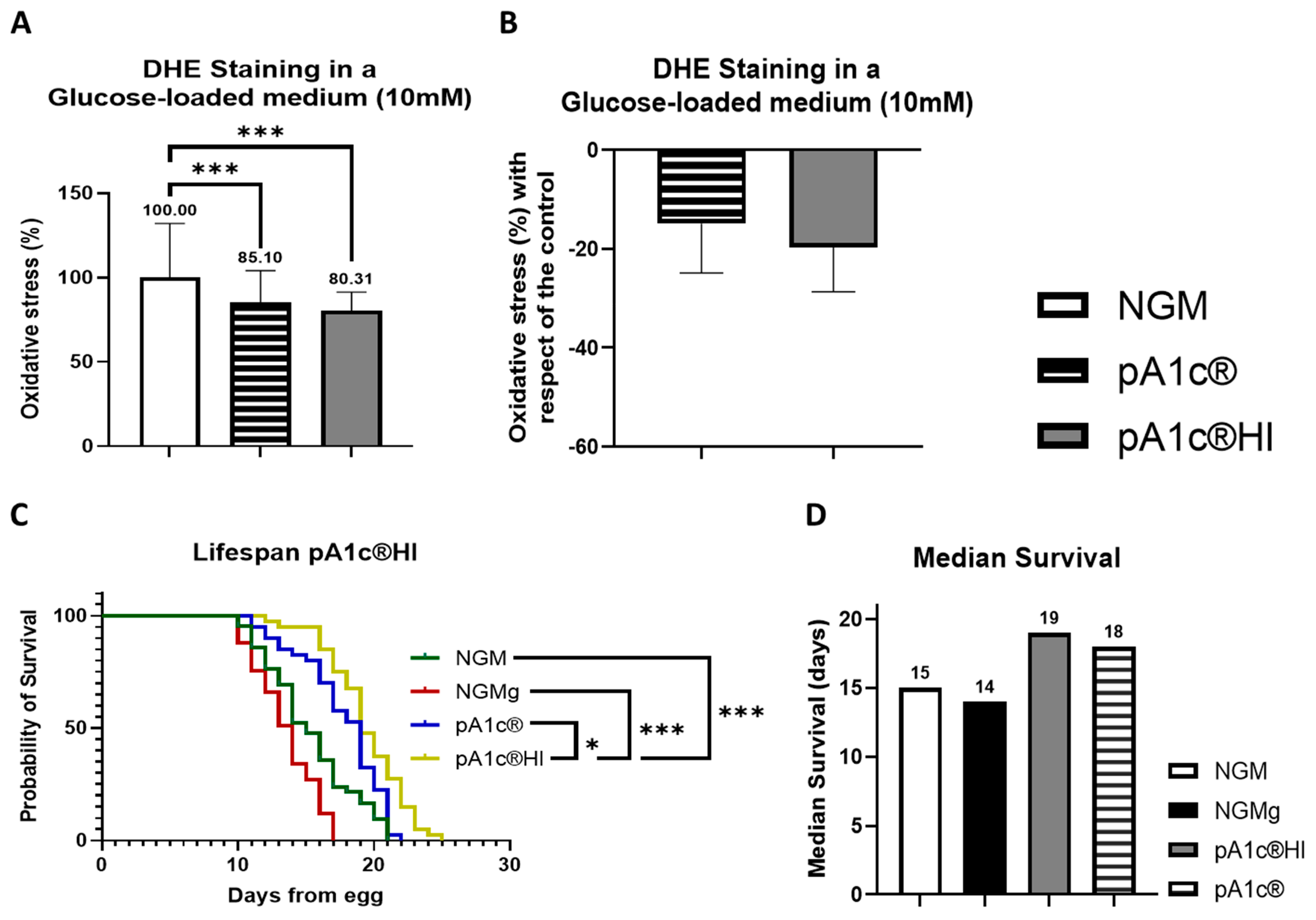
2.4. The Postbiotic pA1c®HI Enhances Oxidative Stress Response and Lifespan
2.5. Heat Stability of pA1c®HI
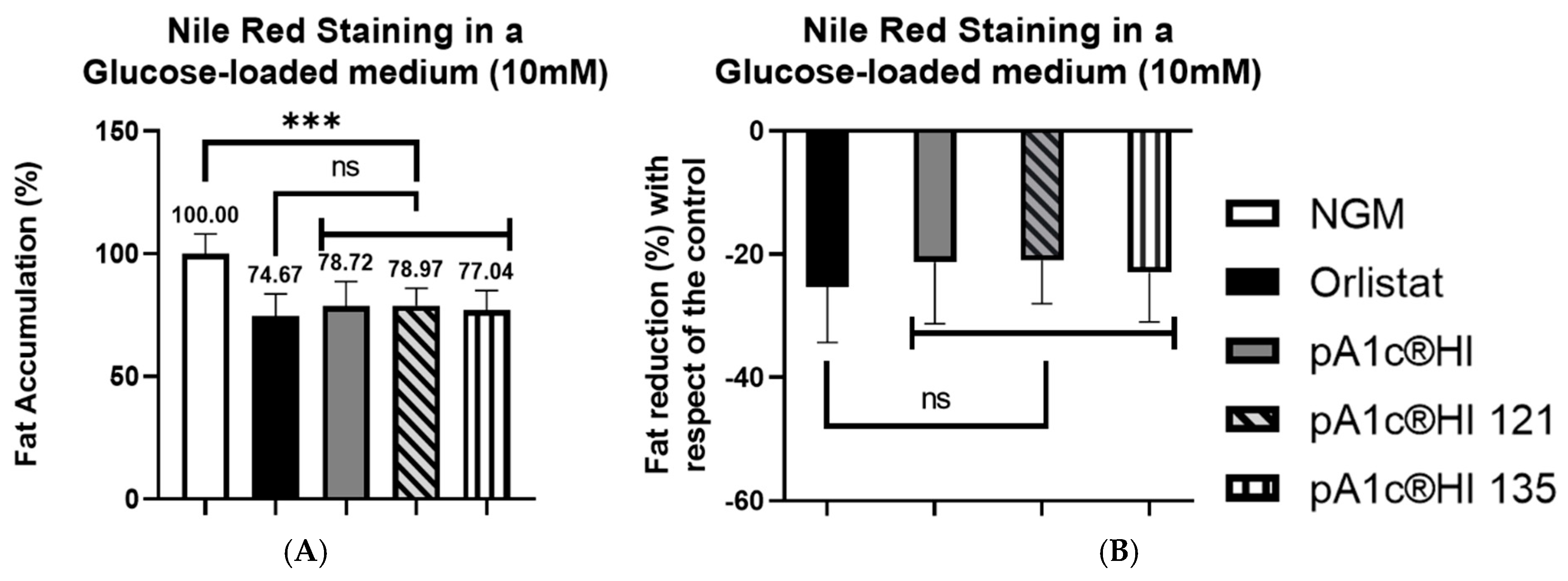
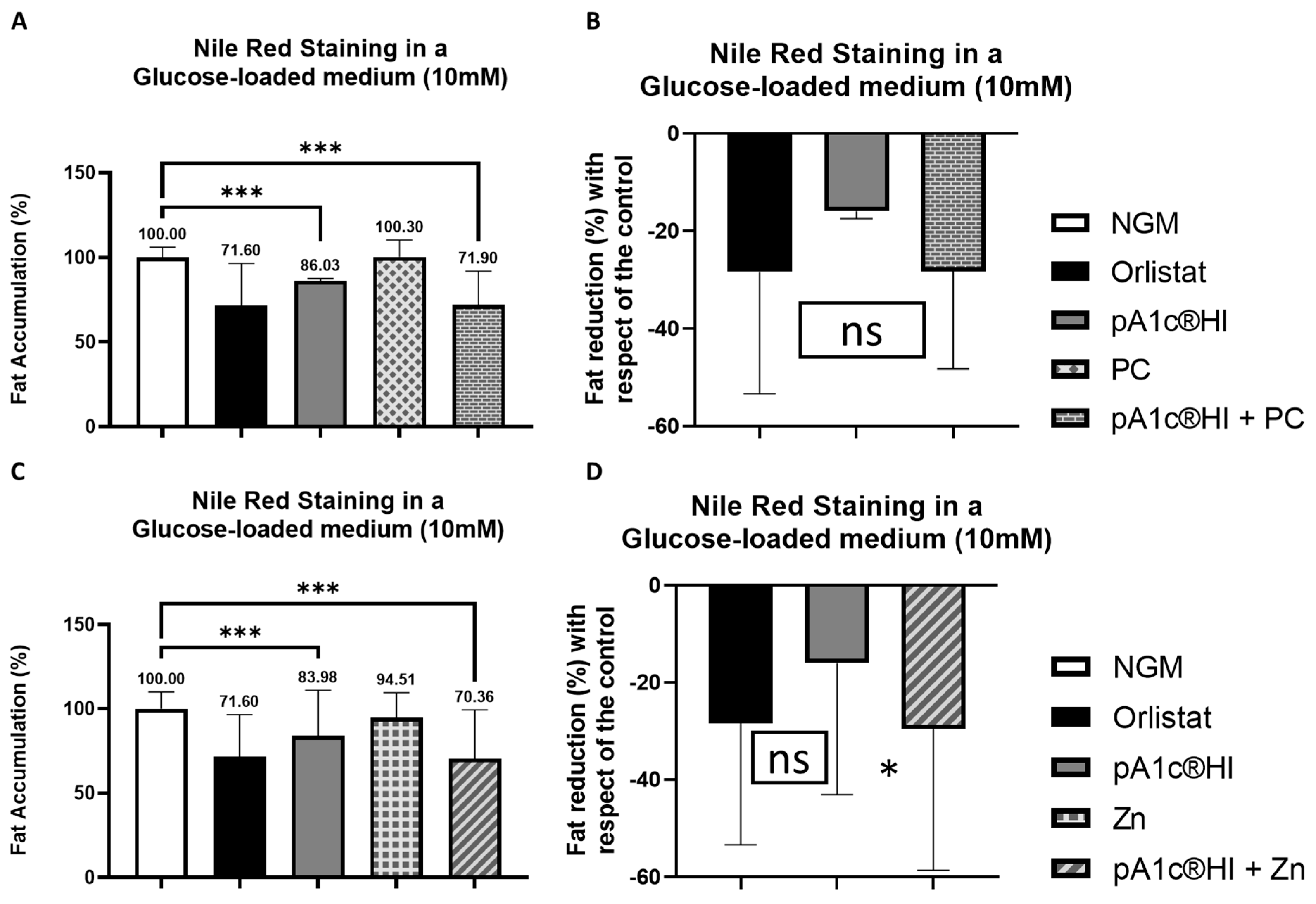
2.6. Synergistic Effects of pA1c®HI Combined with Chromium Picolinate and Zinc on Glucose Counteraction and Fat Reduction
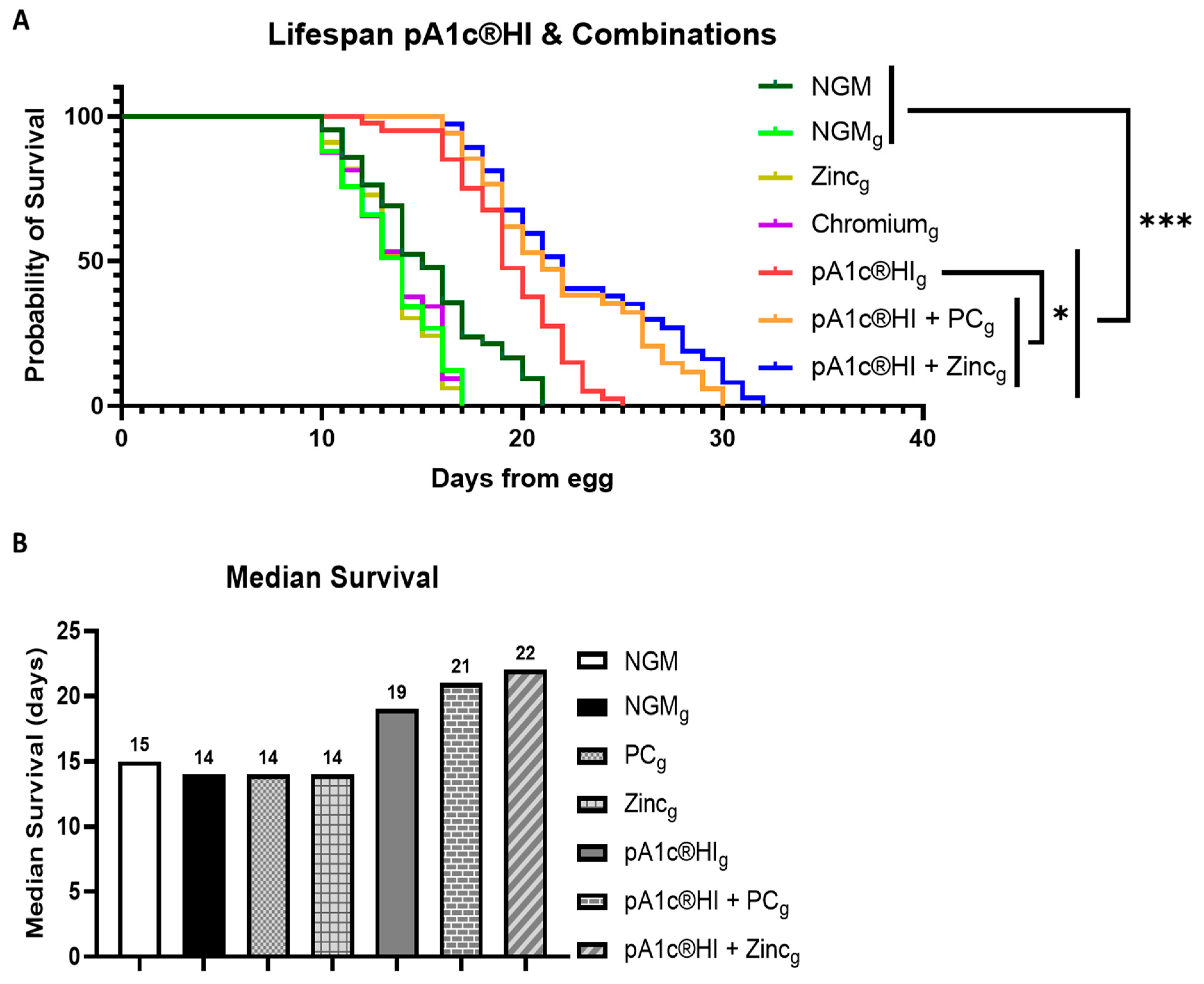
2.7. Synergistic Effects of pA1c®HI Combined with Chromium Picolinate and Zinc on Longevity and Lifespan
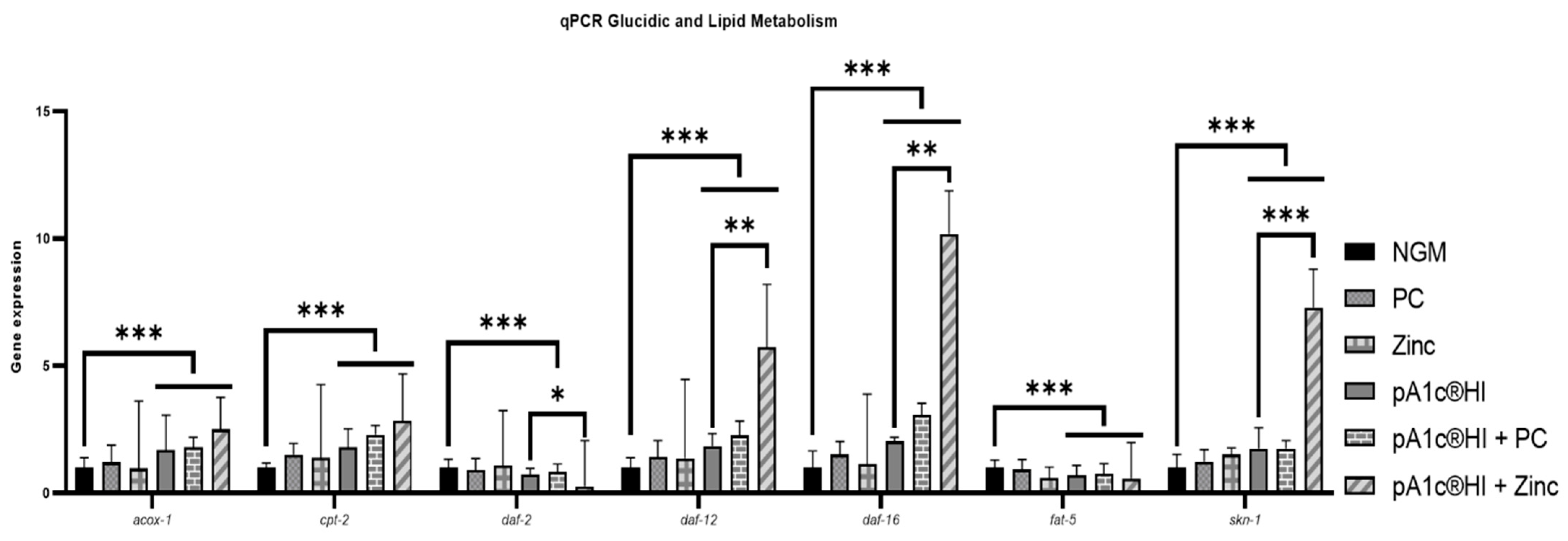
2.8. Combinations Containing pA1c®HI Modulated Glucose and Lipid Metabolism in a More Effective Way than pA1c®HI Alone
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains and Culture
4.2. C. elegans Experimental Design
4.3. Nile Red Staining
4.4. Localization of daf-16 Gene
4.5. DHE Staining
4.6. Image Acquisition and Quantification
4.7. Lifespan Analysis
4.8. Egg Laying and Development Analysis
4.9. RNA Extraction and Quantitative PCR Analyses
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Sala, L.; Pontiroli, A.E. Prevention of Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease in Obesity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Yang, X.; Qin, P.; Chen, C.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; et al. Consumption of Dairy Products and the Risk of Overweight or Obesity, Hypertension, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Dose-Response Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Cohort Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousri, N.A.; Suhre, K.; Yassin, E.; Al-Shakaki, A.; Robay, A.; Elshafei, M.; Chidiac, O.; Hunt, S.C.; Crystal, R.G.; Fakhro, K.A. Metabolic and Metabo-Clinical Signatures of Type 2 Diabetes, Obesity, Retinopathy, and Dyslipidemia. Diabetes 2022, 71, 184–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.J.; Lin, T.L.; Tsai, Y.L.; Wu, T.R.; Lai, W.F.; Lu, C.C.; Lai, H.C. Next Generation Probiotics in Disease Amelioration. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) Consensus Statement on the Definition and Scope of Postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Tu, H.; Chen, T. Postbiotics in Human Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Wang, B.; Bai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Suo, H.; Wang, C. Postbiotics Are a Candidate for New Functional Foods. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B.; Verbeke, K. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Microbiota–Gut–Brain Communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, T.; Luo, R.; Liu, J.; Jin, R.; Peng, X. Recent Advances and Potentiality of Postbiotics in the Food Industry: Composition, Inactivation Methods, Current Applications in Metabolic Syndrome, and Future Trends. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 5768–5792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.O.; Box, A.C.; Xu, N.; Men, J.L.; Yu, J.; Guo, F.; Trimble, R.; Mak, H.Y. Genetic and Dietary Regulation of Lipid Droplet Expansion in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4640–4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Habsi, N.; Al-Khalili, M.; Haque, S.A.; Elias, M.; Olqi, N.A.; Al Uraimi, T. Health Benefits of Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.L.; Ristow, M. Lipid and Carbohydrate Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 2017, 207, 413–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Goyache, I.; López-Yoldi, M.; Aranaz, P. Glucose-Lowering Effects of a Synbiotic Combination Containing Pediococcus acidilactici in C. elegans and Mice. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 2117–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyache, I.; Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Aranaz, P. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Screening Model for Probiotics with Properties against Metabolic Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; López-Yoldi, M.; Clemente, I.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Aranaz, P. Pediococcus acidilactici (PA1c®) Alleviates Obesity-Related Dyslipidemia and Inflammation in Wistar Rats by Activating Beta-Oxidation and Modulating the Gut Microbiota. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10855–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorov-dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Aranaz, P. Pediococcus acidilactici CECT9879 (PA1c) Counteracts the Effect of a High-Glucose Exposure in C. elegans by Affecting the Insulin Signaling Pathway (IIS). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Milagro, F.I.; Ayo, J.; Oneca, M.; Goyache, I.; López-Yoldi, M.; FitzGerald, J.A.; Crispie, F.; Cotter, P.D.; Aranaz, P. Pediococcus acidilactici CECT 9879 (PA1c®) and Heat Inactivated PA1c® (PA1c® HI) Ameliorate Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Mice. Life Sci. 2025, 362, 123359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello-Olmo, M.; Oneca, M.; Urtasun, R.; Pajares, M.J.; Goñi, S.; Riezu-Boj, J.I.; Milagro, F.I.; Ayo, J.; Encio, I.J.; Barajas, M.; et al. Pediococcus acidilactici PA1c® Improves the Beneficial Effects of Metformin Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes by Controlling Glycaemia and Modulating Intestinal Microbiota. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabello-Olmo, M.; Oneca, M.; Pajares, M.J.; Jiménez, M.; Ayo, J.; Encío, I.J.; Barajas, M.; Araña, M. Antidiabetic Effects of Pediococcus acidilactici PA1c on HFD-Induced Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorcia, W.; Ruter, D.L.; Nhan, J.; Curran, S.P. Quantification of Lipid Abundance and Evaluation of Lipid Distribution in Caenorhabditis elegans by Nile Red and Oil Red O Staining. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 133, e57352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Li, S.; Shen, P.; Park, Y. Caenorhabditis elegans as a Model for Obesity Research. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 692–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Juárez, B.; Gómez-Manzo, S.; Hernández-Ochoa, B.; Cárdenas-Rodríguez, N.; Arreguin-Espinosa, R.; de la Cruz, V.P.; Ortega-Cuellar, D. Effects of High Dietary Carbohydrate and Lipid Intake on the Lifespan of C. elegans. Cells 2021, 10, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, E.; Olsen, L.; Mörck, C.; Brackmann, C.; Enejder, A.; Faergeman, N.J.; Pilon, M. The Adiponectin Receptor Homologs in C. elegans Promote Energy Utilization and Homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.T.; Hu, P.J. Insulin/Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling in C. elegans. In WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology; WormBook: Pasadena, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.D.; Tissenbaum, H.A.; Liu, Y.; Ruvkun, G. Daf-2, an Insulin Receptor-like Gene That Regulates Longevity and Diapause in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 1997, 277, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tissenbaum, H.A. DAF-16: FOXO in the Context of C. elegans. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2018, 127, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zečić, A.; Braeckman, B.P. DAF-16/FoxO in Caenorhabditis elegans and Its Role in Metabolic Remodeling. Cells 2020, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Ji, S.; Zheng, S. Glucose and Cholesterol Induce Abnormal Cell Divisions via DAF-12 and MPK-1 in C. elegans. Aging 2020, 12, 16255–16269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, H.D.; Nguyen, T.T.M.; Lee, S.; Seo, M.; An, Y.J.; de Guzman, A.C.V. The Metabolic Contribution of SKN-1/Nrf2 to the Lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Metabolomics 2023, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Chen, S.; Zhang, C.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Zhou, H.; Jin, L.; Qian, X.; Jin, J.; Lyu, J. Enhanced ROS Production Leads to Excessive Fat Accumulation through DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 112, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, F.; Zhou, J.; Yao, C.; Ma, G.; et al. Acyl-CoA Oxidase ACOX-1 Interacts with a Peroxin PEX-5 to Play Roles in Larval Development of Haemonchus Contortus. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; King, M.L.; Fitzpatrick, Z.L.; Wei, W.; King, J.F.; Wang, M.; Greenway, F.L.; Finley, J.W.; Burton, J.H.; Johnson, W.D.; et al. Prowashonupana Barley Dietary Fibre Reduces Body Fat and Increases Insulin Sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans Model. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 18, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.L.; Meng, X.; Wang, C.; Dai, W.; Luo, Z.; Yin, Z.; Ju, Z.; Fu, X.; Yang, J.; Ye, Q.; et al. Histone H3K4me3 Modification Is a Transgenerational Epigenetic Signal for Lipid Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.A.; Stolzing, A. The Role of Lipid Metabolism in Aging, Lifespan Regulation, and Age-Related Disease. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e13048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, A.S.; Duffy, J.; Wang, M.C. Lipid Metabolism and Lipid Signals in Aging and Longevity. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 1394–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Dong, H.H. FoxO Integration of Insulin Signaling with Glucose and Lipid Metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, R67–R79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, H.; Lin, D.; Guo, W.; Xu, Z.; Wang, L.; Guan, S. Ginsenoside Prolongs the Lifespan of C. elegans via Lipid Metabolism and Activating the Stress Response Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, B.H.; Ali, S.A.; Behare, P.V.; Yadav, H. Postbiotics-Parabiotics: The New Horizons in Microbial Biotherapy and Functional Foods. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savova, M.S.; Todorova, M.N.; Binev, B.K.; Georgiev, M.I.; Mihaylova, L.V. Curcumin Enhances the Anti-Obesogenic Activity of Orlistat through SKN-1/NRF2-Dependent Regulation of Nutrient Metabolism in Caenorhabditis elegans. Int. J. Obes. 2025, 49, 516–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenspan, P.; Mayer, E.P.; Fowler, S.D. Nile Red: A Selective Fluorescent Stain for Intracellular Lipid Droplets. J. Cell Biol. 1985, 100, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yavorov-Dayliev, D.; Iturria, I.; Iriarte, L.; Araña, M.; Barajas, M.; Ayo, J. Postbiotic pA1c®HI for Preventing Insulin Resistance and Obesity in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Prediabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168094
Yavorov-Dayliev D, Iturria I, Iriarte L, Araña M, Barajas M, Ayo J. Postbiotic pA1c®HI for Preventing Insulin Resistance and Obesity in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Prediabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168094
Chicago/Turabian StyleYavorov-Dayliev, Deyan, Iñaki Iturria, Leyre Iriarte, Miriam Araña, Miguel Barajas, and Josune Ayo. 2025. "Postbiotic pA1c®HI for Preventing Insulin Resistance and Obesity in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Prediabetes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168094
APA StyleYavorov-Dayliev, D., Iturria, I., Iriarte, L., Araña, M., Barajas, M., & Ayo, J. (2025). Postbiotic pA1c®HI for Preventing Insulin Resistance and Obesity in a Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Prediabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8094. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168094




