Clonal Dissemination of Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST392KL27 in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients and Microbiological Identification of Isolates
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Profile
2.3. Genomic Collection and Clonal Analysis
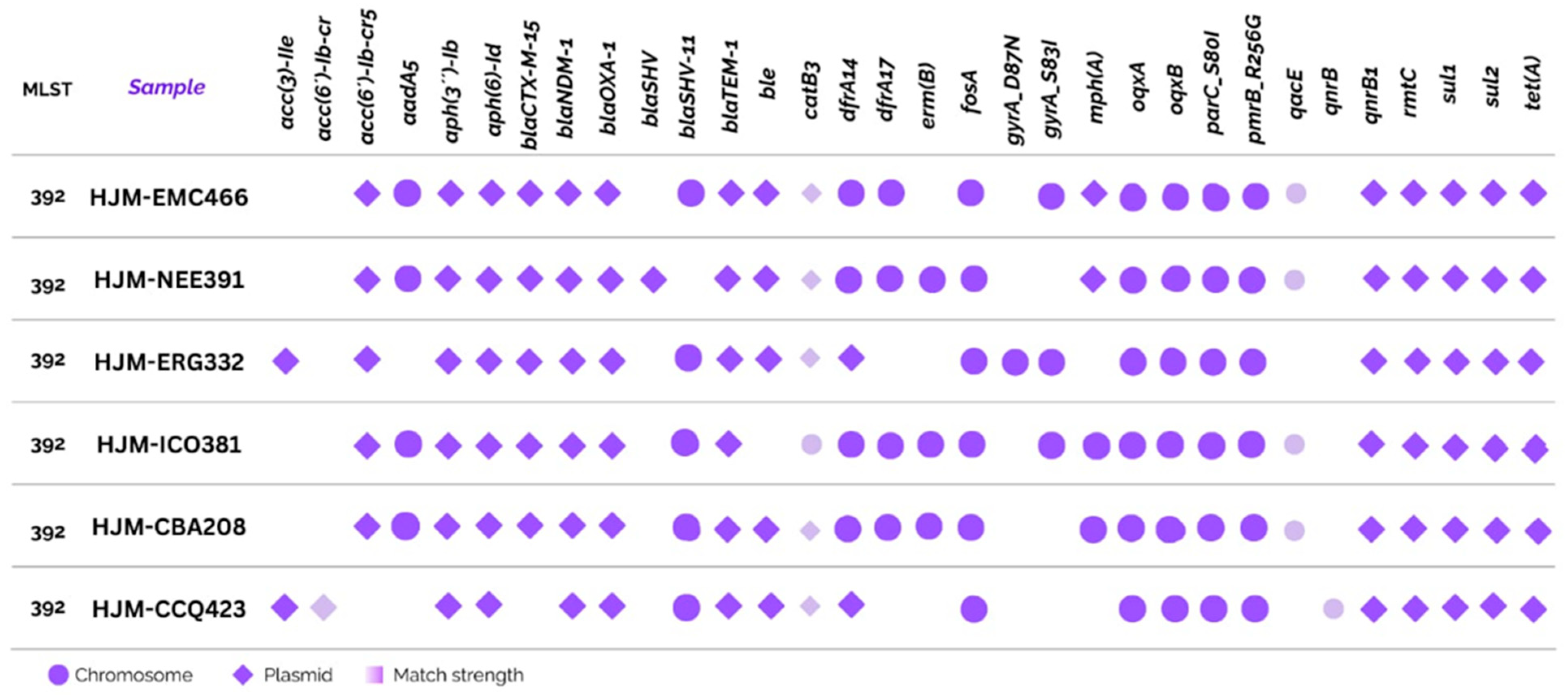
2.4. Resistome and Mobile Genetic Elements
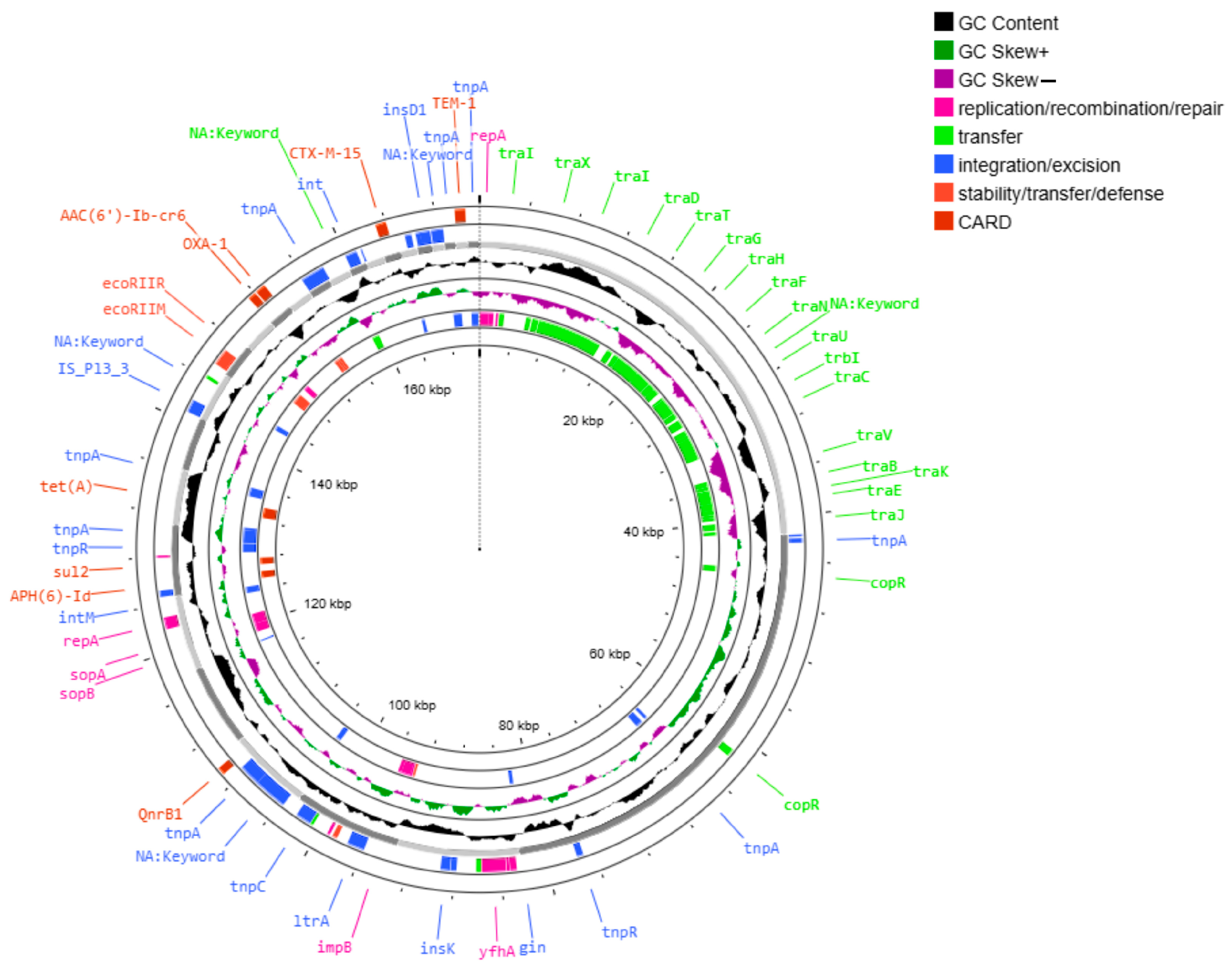
2.5. Genomic Resistance and Mobile Genetic Elements
2.6. CRISPR-Cas Loci Characterization
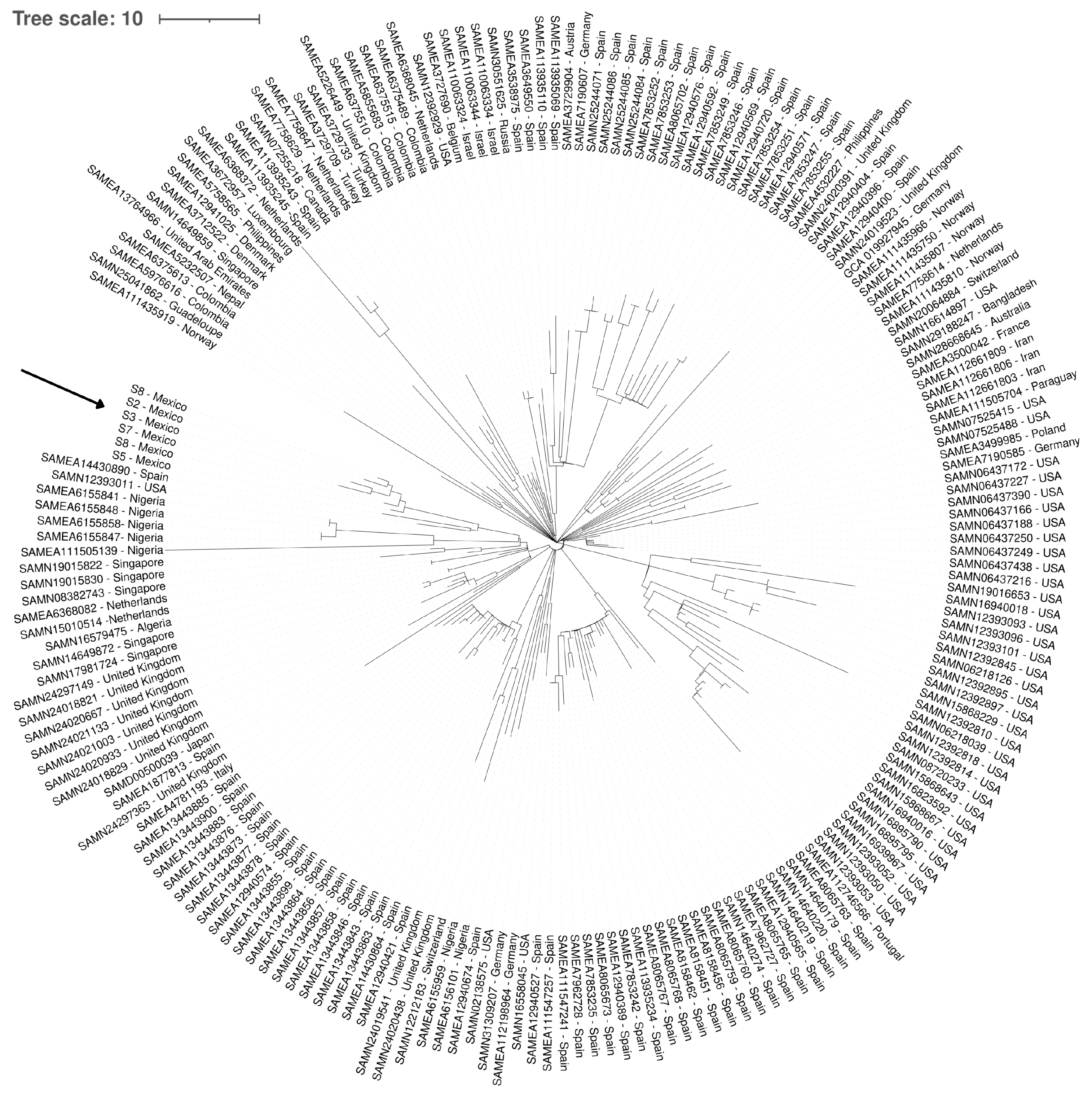
2.7. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Virulence Analysis
2.9. Global cgMLST Phylogeny
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Isolation and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
4.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDR | Pandrug-resistant |
| MDR | Multidrug-resistant |
| AMR | Antimicrobial resistance |
| AST | Antimicrobial susceptibility testing |
| CARD | Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database |
| Cas | CRISPR-associated proteins |
| CC | Clonal complex |
| cgMLST | Core genome multilocus sequence typing |
| CLSI | Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute |
| CRISPR | Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| ESBL | Extended-spectrum β-lactamase |
| In0 | Integron type 0 |
| Inc | Incompatibility group |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| KpSC | Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex |
| KL | Capsular locus |
| MGEs | Mobile genetic elements |
| MLST | Multilocus sequence typing |
| NCBI | National Center for Biotechnology Information |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| ORF | Open reading frame |
| PHOENIX | Automated microbial identification system |
| scgST | Subclonal genotype |
| SPAdes | St. Petersburg genome assembler |
| ST | Sequence type |
| TLA | Three letter acronyms |
| UTI | Urinary tract infection |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| wzi | Capsule-associated gene in K. pneumoniae |
References
- Gazerani, G.; Piercey, L.R.; Reema, S.; Wilson, K.A. Examining the Biophysical Properties of the Inner Membrane of Gram-Negative ESKAPE Pathogens. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2025, 65, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.P.; Kapoor, A.; Sinha, A.; Ma, Y.; Shankar, M. Virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumoniae: Insights into canonical and emerging mechanisms driving pathogenicity and drug resistance. Microbe 2025, 7, 100289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Imani, S.; Zhou, A.; Zhao, Y.; Du, L.; Deng, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Q. Combatting resistance: Understanding multi-drug resistant pathogens in intensive care units. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 167, 115564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza-Gonzalez, E.; Morfin-Otero, R.; Mendoza-Olazaran, S.; Bocanegra-Ibarias, P.; Flores-Trevino, S.; Rodriguez-Noriega, E.; Ponce-de-Leon, A.; Sanchez-Francia, D.; Franco-Cendejas, R.; Arroyo-Escalante, S.; et al. A snapshot of antimicrobial resistance in Mexico. Results from 47 centers from 20 states during a six-month period. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0209865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anantharajah, A.; Goormaghtigh, F.; Nguvuyla, M.E.; Guler, B.; Bearzatto, B.; Momal, A.; Werion, A.; Hantson, P.; Kabamba-Mukadi, B.; Van Bambeke, F.; et al. Long-term intensive care unit outbreak of carbapenemase-producing organisms associated with contaminated sink drains. J. Hosp. Infect. 2024, 143, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormala-Tiznado, A.M.; Allander, L.; Maatallah, M.; Kabir, M.H.; Brisse, S.; Sandegren, L.; Patpatia, S.; Coorens, M.; Giske, C.G. Molecular characteristics, fitness, and virulence of high-risk and non-high-risk clones of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0403622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boralli, C.; Paganini, J.A.; Meneses, R.S.; Mata, C.; Leite, E.M.M.; Schurch, A.C.; Paganelli, F.L.; Willems, R.J.L.; Camargo, I. Characterization of bla(KPC-2) and bla(NDM-1) Plasmids of a K. pneumoniae ST11 Outbreak Clone. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Chitnis, N.; Monos, D.; Dinh, A. Next-generation sequencing technologies: An overview. Hum Immunol. 2021, 82, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Song, G.; Xu, Y. Association of CRISPR/Cas System with the Drug Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Androsiuk, L.; Maane, S.; Tal, S. CRISPR spacers acquired from plasmids primarily target backbone genes, making them valuable for predicting potential hosts and host range. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0010424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roach, D.; Waalkes, A.; Abanto, J.; Zunt, J.; Cucho, C.; Soria, J.; Salipante, S.J. Whole Genome Sequencing of Peruvian Klebsiella pneumoniae Identifies Novel Plasmid Vectors Bearing Carbapenem Resistance Gene NDM-1. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada-Aguiluz, M.; Opazo-Capurro, A.; Lincopan, N.; Esposito, F.; Fuga, B.; Mella-Montecino, S.; Riedel, G.; Lima, C.A.; Bello-Toledo, H.; Cifuentes, M.; et al. Novel Megaplasmid Driving NDM-1-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae ST1588 in South America. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Samudio, V.; Pimentel-Peralta, G.; Herrera, M.; Pecchio, M.; Quintero, J.; Landires, I. Molecular Genetic Epidemiology of an Emerging Antimicrobial-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Clone (ST307) Obtained from Clinical Isolates in Central Panama. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saavedra, S.Y.; Bernal, J.F.; Montilla-Escudero, E.; Arevalo, S.A.; Prada, D.A.; Valencia, M.F.; Moreno, J.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Garcia-Vega, A.S.; Abrudan, M.; et al. Complexity of Genomic Epidemiology of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates in Colombia Urges the Reinforcement of Whole Genome Sequencing-Based Surveillance Programs. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, S290–S299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta-Macotela, P.; Flores-Monzon, B.; Lira de Leon, K.I.; Sanchez-Tusie, A.A.; Rodriguez-Medina, N.; Alvarado-Delgado, A.; Aguilar-Vera, E.; Zumaya-Estrada, F.; Garza-Ramos, U.; Garcia-Gutierrez, M.C. Complete genome sequences of Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella quasipneumoniae, and Klebsiella variicola clinical isolates from an epidemiology study. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2025, 14, e0106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, F.F.; Silva, D.; Rodrigues, A.; Pina-Vaz, C. Colistin Update on Its Mechanism of Action and Resistance, Present and Future Challenges. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, P.S.; Cheng, W.H.; Chang, S.K.; Lim, S.E.; Lai, K.S. MgrB Mutations and Altered Cell Permeability in Colistin Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Cells 2022, 11, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.D.; Groisman, E.A. The biology of the PmrA/PmrB two-component system: The major regulator of lipopolysaccharide modifications. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 67, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayol, A.; Nordmann, P.; Brink, A.; Poirel, L. Heteroresistance to colistin in Klebsiella pneumoniae associated with alterations in the PhoPQ regulatory system. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 2780–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaitan, A.O.; Morand, S.; Rolain, J.M. Mechanisms of polymyxin resistance: Acquired and intrinsic resistance in bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannatelli, A.; Giani, T.; D’Andrea, M.M.; Di Pilato, V.; Arena, F.; Conte, V.; Tryfinopoulou, K.; Vatopoulos, A.; Rossolini, G.M.; Group, C.S. MgrB inactivation is a common mechanism of colistin resistance in KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae of clinical origin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5696–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akintayo, I.; Siroglavic, M.; Frolova, D.; Silva, M.B.; Grundmann, H.; Iqbal, Z.; Budimir, A.; Reuter, S. Tracking clonal and plasmid transmission in colistin- and carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSystems 2025, 10, e0112824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, E.; Bonnin, R.A.; Rocha, E.P.C. Phage-Plasmids Spread Antibiotic Resistance Genes through Infection and Lysogenic Conversion. mBio 2022, 13, e0185122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Wu, F.; Chai, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Tian, S.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, H.; et al. A new plasmid carrying mphA causes prevalence of azithromycin resistance in enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli serogroup O6. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, H.; Huang, B.; Hu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, L.; Yang, L.; Deng, J.; Wang, Q. Characterization of resistance genes and plasmids from sick children caused by Salmonella enterica resistance to azithromycin in Shenzhen, China. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1116172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Huang, M.; Mei, Y.; Gu, B.; Wu, R.; Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wang, T. Analysis of antimicrobial resistance and class 1 integrons among strains from upper respiratory tract of healthy adults. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firoozeh, F.; Mahluji, Z.; Khorshidi, A.; Zibaei, M. Molecular characterization of class 1, 2 and 3 integrons in clinical multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadkhoda, H.; Gholizadeh, P.; Ghotaslou, R.; Nabizadeh, E.; Pirzadeh, T.; Ahangarzadeh Rezaee, M.; Feizi, H.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Aghazadeh, M. Role of CRISPR-cas system on virulence traits and carbapenem resistance in clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 199, 107151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Lin, J.; Gu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hu, J. Detection of CRISPR–Cas and type I R-M systems in Klebsiella pneumoniae of human and animal origins and their relationship to antibiotic resistance and virulence. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e0000924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Y.; Kao, C.Y.; Lin, W.H.; Zheng, P.X.; Yan, J.J.; Wang, M.C.; Teng, C.H.; Tseng, C.C.; Wu, J.J. Characterization of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates Uncovers Its Potential Association with Antibiotic Susceptibility. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkompoz, A.K.; Hamed, S.M.; Zaid, A.S.A.; Almangour, T.A.; Al-Agamy, M.H.; Aboshanab, K.M. Correlation of CRISPR/Cas and Antimicrobial Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates Recovered from Patients in Egypt Compared to Global Strains. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek-Davenet, S.; Criscuolo, A.; Ailloud, F.; Passet, V.; Jones, L.; Delannoy-Vieillard, A.S.; Garin, B.; Le Hello, S.; Arlet, G.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H.; et al. Genomic definition of hypervirulent and multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae clonal groups. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.; Cardoso, B.; Fontana, H.; Esposito, F.; Cortopassi, S.R.G.; Sellera, F.P.; Lincopan, N. Human pandemic K27-ST392 CTX-M-15 extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-positive Klebsiella pneumoniae: A one health clone threatening companion animals. One Health 2022, 15, 100414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Ma, M.; Geng, X.; Zhang, J. Recent advances in small molecule LpxC inhibitors against gram-negative bacteria (2014–2024). Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1541379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Han, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Nang, S.C.; Zhai, Y.; Yuan, L.; et al. Revisiting therapeutic options against resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae infection: Phage therapy is key. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 293, 128083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volozhantsev, N.V.; Makarova, M.A.; Kartseva, A.S.; Silkina, M.V.; Krasilnikova, V.M.; Denisenko, E.A.; Borzilov, A.I.; Firstova, V.V. Immunomodulatory Effect of Phage Depolymerase Dep_kpv74 with Therapeutic Potential Against K2-Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsels, K.A.; Mastro, K.A.; Steele, J.M.; Thomas, S.J.; Kufel, W.D. Cefiderocol: A novel siderophore cephalosporin for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacterial infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 31st ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2021; CLSI supplement M100; Volume 41. [Google Scholar]
- Carattoli, A.; Hasman, H. PlasmidFinder and In Silico pMLST: Identification and Typing of Plasmid Replicons in Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2075, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.L.; Mullet, J.; Hindi, F.; Stoll, J.E.; Gupta, S.; Choi, M.; Keenum, I.; Vikesland, P.; Pruden, A.; Zhang, L. mobileOG-db: A Manually Curated Database of Protein Families Mediating the Life Cycle of Bacterial Mobile Genetic Elements. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 88, e0099122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neron, B.; Littner, E.; Haudiquet, M.; Perrin, A.; Cury, J.; Rocha, E.P.C. IntegronFinder 2.0: Identification and Analysis of Integrons across Bacteria, with a Focus on Antibiotic Resistance in Klebsiella. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, J.R.; Enns, E.; Marinier, E.; Mandal, A.; Herman, E.K.; Chen, C.Y.; Graham, M.; Van Domselaar, G.; Stothard, P. Proksee: In-depth characterization and visualization of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W484–W492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded curation, support for machine learning, and resistome prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Neron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stothard, P.; Grant, J.R.; Van Domselaar, G. Visualizing and comparing circular genomes using the CGView family of tools. Brief. Bioinform. 2019, 20, 1576–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argimon, S.; David, S.; Underwood, A.; Abrudan, M.; Wheeler, N.E.; Kekre, M.; Abudahab, K.; Yeats, C.A.; Goater, R.; Taylor, B.; et al. Rapid Genomic Characterization and Global Surveillance of Klebsiella Using Pathogenwatch. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, S325–S335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Suleski, M.; Sanderford, M.; Sharma, S.; Tamura, K. MEGA12: Molecular Evolutionary Genetic Analysis Version 12 for Adaptive and Green Computing. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2024, 41, msae263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Patient Gender | Age | Isolation Source | Patient Survival | Diagnostic | Treatment Before Detection | Treatment After Detection | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HJM-EMC466 | Female | 81 | Expectoration | No | Liver abscess and pneumoniae | Levofloxacin, metronidazole, cefepime, and ciprofloxacin | Colistin |
| HJM-NEE391 | Female | 45 | Catheter | Yes | Subarachnoid hemorrhage | Ceftriaxone, piperacillin tazobactam and vancomycin | Colistin |
| HJM-ERG332 | Male | 28 | Urine | No | Testicular cancer and pulmonary metastasis | Ciprofloxacin, ceftazidime, and amikacin | Colistin |
| HJM-ICO381 | Male | 34 | Purulent wound | No | Gastric G1 neuroendocrine tumor and septic shock | Piperacillin tazobactam, vancomycin, and imipenem | Colistin |
| HJM-CBA208 | 32 | Blood | No | Soft tissue sepsis, pneumonia, and urinary tract infection | Levofloxacin, metronidazole, meropenem, ceftazidime, and cefepime | Colistin | |
| HJM-CCQ423 | Male | 53 | Expectoration | No | Soft tissue infection and uncontrolled diabetes mellitus | Imipenem, clindamycin, levofloxacin, ceftriaxone, and metronidazole | Colistin |
| Isolate | Mob Cluster | Size (BP) | Amr Gene | Replicon Types | Relaxase Types | Mash Nearest Neighbor | Mash Neighbor Distance | Mobility |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HJM-EMC466 | AA276 | 1,171,674 | 10 | IncFIB, IncFII | MOBF | CP010390 | 0.00243596 | Conjugative |
| AA046 | 93,728 | 4 | IncFIB, IncFII, | MOBF | CP022350 | 0.00227104 | Conjugative | |
| AA103 | 4171 | - | ColRNAI | - | CP024435 | 0.000215742 | Non-mobilizable | |
| AC249 | 6894 | 1 | - | - | KU254581 | 0.0588483 | Non-mobilizable | |
| HJM-NEE391 | AA276 | 172,586 | 10 | IncFIB, IncFII | MOBF | CP010390 | 0.00240836 | Conjugative |
| AA046 | 96,552 | 5 | IncFIB, IncFII, | MOBF | CP022350 | 0.00360762 | Conjugative | |
| AA103 | 4167 | - | ColRNAI | - | CP024435 | 0.000312573 | Non-mobilizable | |
| AB749 | - | - | - | - | LR134256 | 0.0350415 | Non-mobilizable | |
| ADO94 | 12,963 | 1 | - | - | CP015133 | 0.0437856 | Non-mobilizable | |
| HJM-ERG332 | AA276 | 174,011 | 12 | IncFIB, IncFII | MOBF | CP010390 | 0.0025468 | Conjugative |
| AA046 | 92,509 | 4 | IncFIB, IncFII, | MOBF | CP022350 | 0.00366686 | Conjugative | |
| AA103 | 4168 | - | ColRNAI | - | CP024435 | 0.000264084 | Non-mobilizable | |
| HJM-ICO381 | AA276 | 167,036 | 9 | IncFIB, IncFII | MOBF | CP010390 | 0.00340187 | Conjugative |
| AA046 | 87,014 | 4 | IncFIB, IncFII, | MOBF | CP022350 | 0.00448671 | Conjugative | |
| AA103 | 4167 | - | ColRNAI | - | CP024435 | 0.000239895 | Non-mobilizable | |
| HJM-CBA208 | AA276 | 170,592 | 10 | IncFIB, IncFII | MOBF | CP010390 | 0.00268639 | Conjugative |
| AA046 | 93,856 | 4 | IncFIB, IncFII, | MOBF | CP022350 | 0.00249129 | Conjugative | |
| AA103 | 4167 | - | ColRNAI | CP024435 | 0.000483446 | Non-mobilizable | ||
| HJM-CCQ423 | AA046 | 95,436 | 4 | IncFIB, IncFII, | MOBF | CP022350 | 0.00369655 | conjugative |
| AA276 | 172,300 | 11 | IncFIB, IncFII | MOBF | CP010390 | 0.00218918 | conjugative | |
| AB749 | 14,407 | - | - | - | LR134256 | 0.0350415 | non-mobilizable | |
| AA103 | 4170 | - | ColRNAI | - | CP024435 | 0.000191626 | non-mobilizable |
| Strain | CRISPR-Cas Subtype | Consensus Repeat (5′-3′) | N Repeats | Repeat Length (bp) | Avg. Spacer Length (bp) | Repeat Identity (%) | Spacer Identity (%) | Spacer Length SEM | Cas Genes | Trusted |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 466 | I-E | GTGTTCCCCGCGCCAGCGGGGATAAACCG | 11 | 29 | 32 | 100 | 42.4 | 0.1 | Yes (complete) | TRUE |
| I-E | CGGTTTATCCCCGCTGGCGCGGGGAACAC | 34 | 29 | 31.9 | 93.1 | 39.5 | 0.1 | No (Orphan) | TRUE | |
| 391 | I-E | GTGTTCCCCGCGCCAGCGGGGATAAACCG | 44 | 29 | 32 | 98.7 | 40.9 | 0.7 | Yes (complete) | TRUE |
| 219 | I-E | GTGTTCCCCGCGCCAGCGGGGATAAACCG | 44 | 29 | 32 | 98.7 | 40.9 | 0.1 | Yes (complete) | TRUE |
| 381 | I-E | CGGTTTATCCCCGCTGGCGCGGGGAACAC | 30 | 29 | 31.9 | 93.1 | 42.7 | 0.1 | No (Orphan) | TRUE |
| I-E | CGGTTTATCCCCGCTGGCGCGGGGAACAC | 10 | 29 | 32 | 100 | 40.5 | 0.0 | No (Orphan | TRUE | |
| 208 | I-E | CGGTTTATCCCCGCTGGCGCGGGGAACAC | 44 | 29 | 32 | 100 | 41.8 | 0.1 | Yes (complete) | TRUE |
| 423 | I-E | CGGTTTATCCCCGCTGGCGCGGGGAACAC | 44 | 29 | 32 | 100 | 41.8 | 0.1 | Yes (complete) | TRUE |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cortés-Ortíz, I.A.; Cortés-Malagón, E.M.; García-Moncada, E.; Acosta-Altamirano, G.; Pineda-Migranas, J.A.; García-Prudencio, K.L.; Mendieta-Condado, E.; Araiza-Rodríguez, A.; Bonilla-Cortés, A.Y.; Sierra-Martínez, M.; et al. Clonal Dissemination of Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST392KL27 in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mexico. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168047
Cortés-Ortíz IA, Cortés-Malagón EM, García-Moncada E, Acosta-Altamirano G, Pineda-Migranas JA, García-Prudencio KL, Mendieta-Condado E, Araiza-Rodríguez A, Bonilla-Cortés AY, Sierra-Martínez M, et al. Clonal Dissemination of Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST392KL27 in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mexico. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168047
Chicago/Turabian StyleCortés-Ortíz, Iliana Alejandra, Enoc Mariano Cortés-Malagón, Eduardo García-Moncada, Gustavo Acosta-Altamirano, Jesús Alejandro Pineda-Migranas, Karen Lizzet García-Prudencio, Edgar Mendieta-Condado, Adnan Araiza-Rodríguez, Alejandra Yareth Bonilla-Cortés, Mónica Sierra-Martínez, and et al. 2025. "Clonal Dissemination of Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST392KL27 in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mexico" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168047
APA StyleCortés-Ortíz, I. A., Cortés-Malagón, E. M., García-Moncada, E., Acosta-Altamirano, G., Pineda-Migranas, J. A., García-Prudencio, K. L., Mendieta-Condado, E., Araiza-Rodríguez, A., Bonilla-Cortés, A. Y., Sierra-Martínez, M., & Bravata-Alcántara, J. C. (2025). Clonal Dissemination of Pandrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST392KL27 in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Mexico. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8047. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168047








