Biomarkers in Heart Failure: A Review and a Wish
Abstract
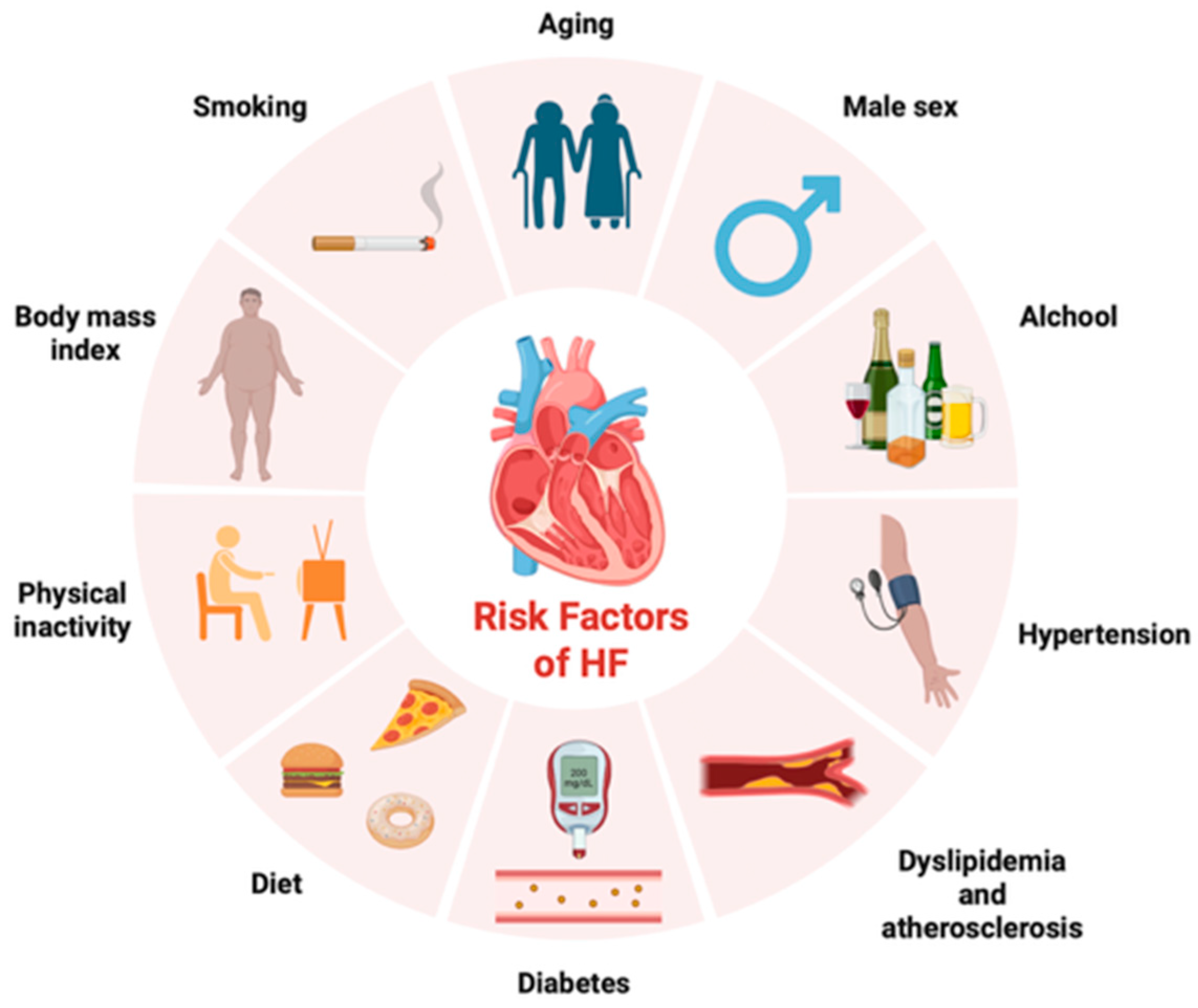
1. Introduction
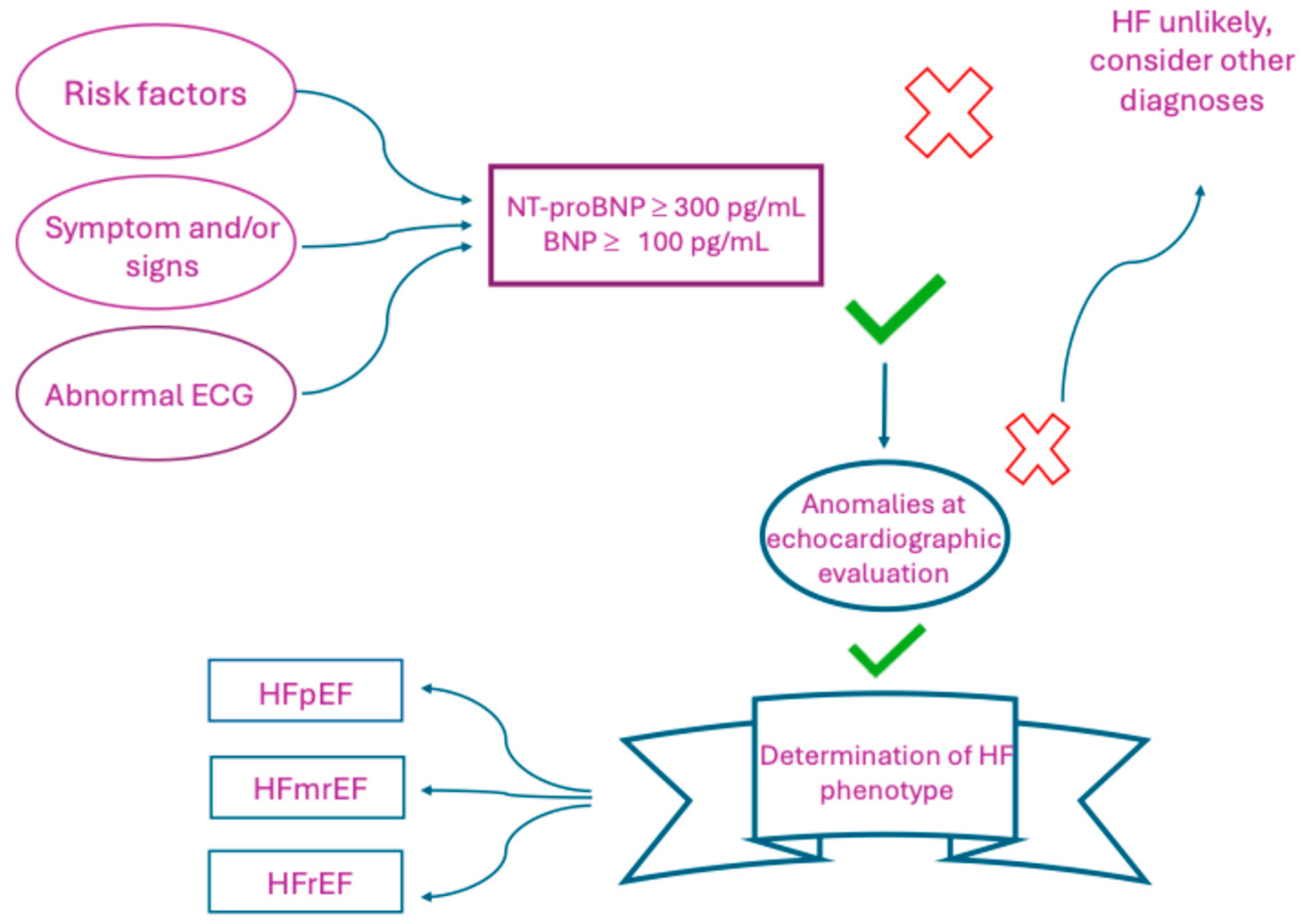
2. Management of HF: From Symptoms and Physical Examination to Advanced Imaging and Biomarkers
3. Biomarkers in HF: From the Traditional Biomarkers, BNP and NT-proBNP, with Their Advantages and Limitations, to Emerging Biomarkers
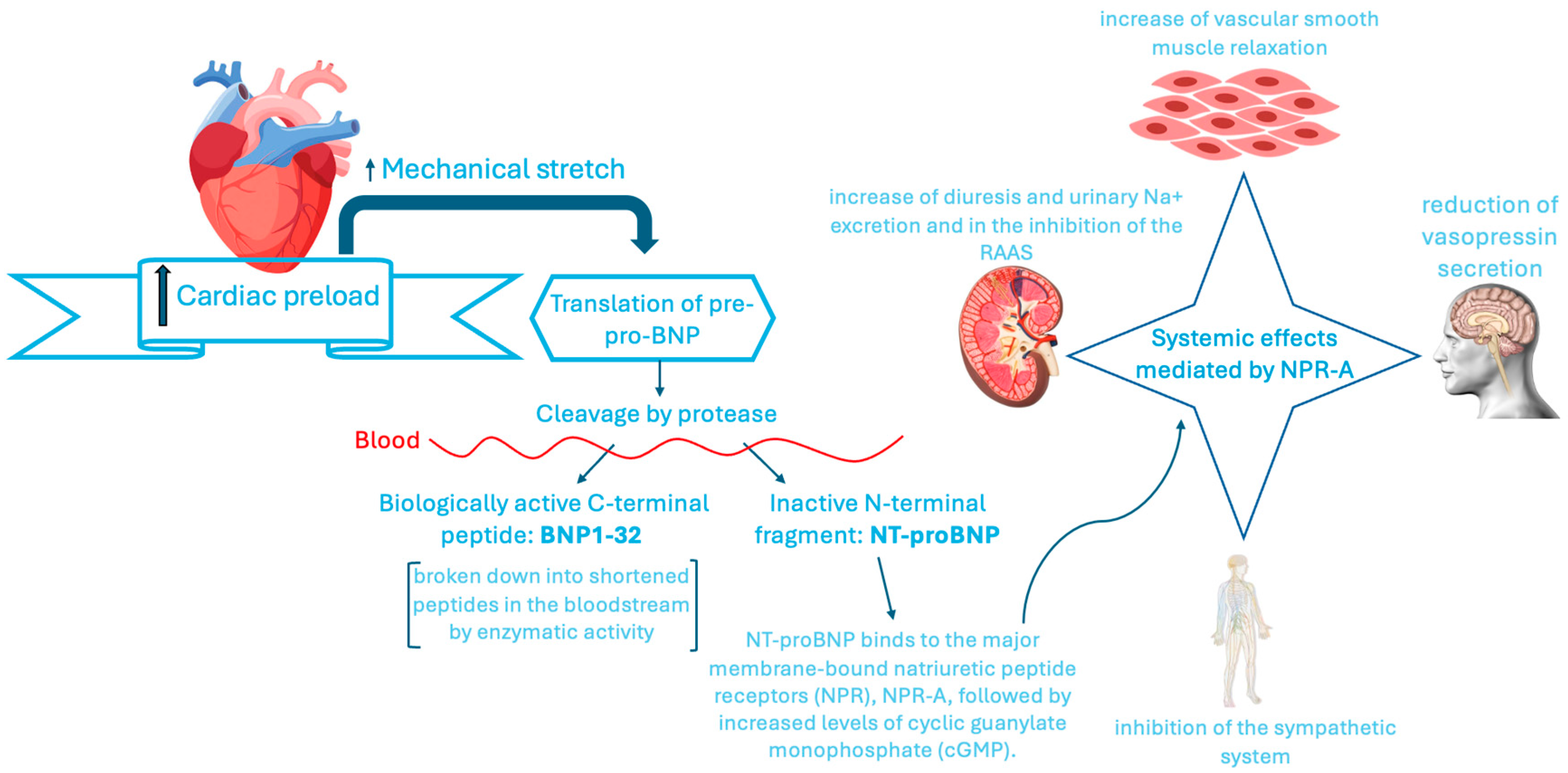
3.1. Traditional Biomarkers: BNP and NT-proBNP with Their Advantages and Limitations
3.1.1. NTproBNP and HF
3.1.2. MR-pro-ANP: Another Biomarker Prevalently Associated with the HF Diagnosis
3.2. Troponins as Myocardial Damage Biomarker
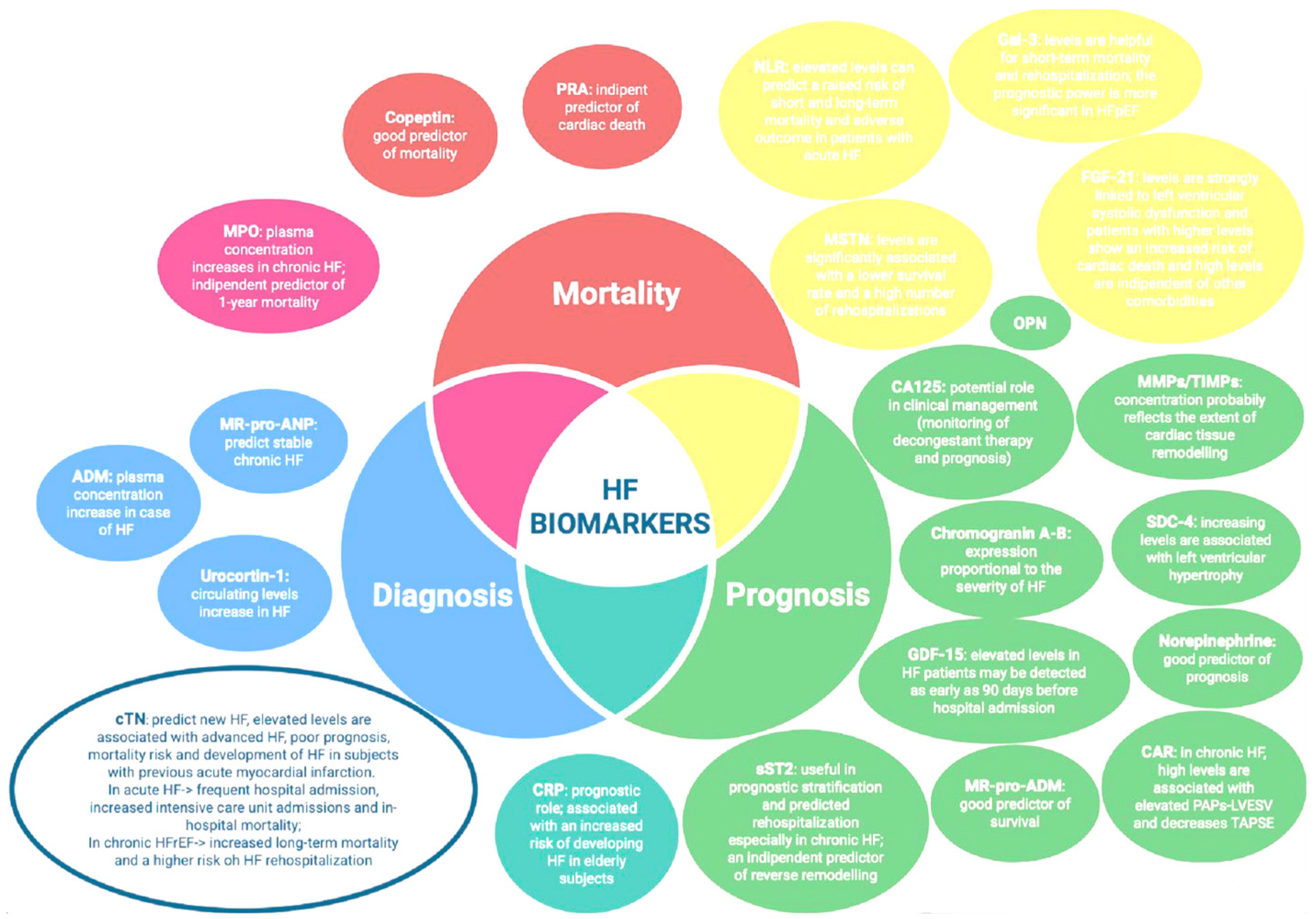
4. Emerging Biomarkers: From Diagnostic to Prognostic and Therapeutic Purpose
4.1. Biomarkers of Neuro-Hormonal Activation
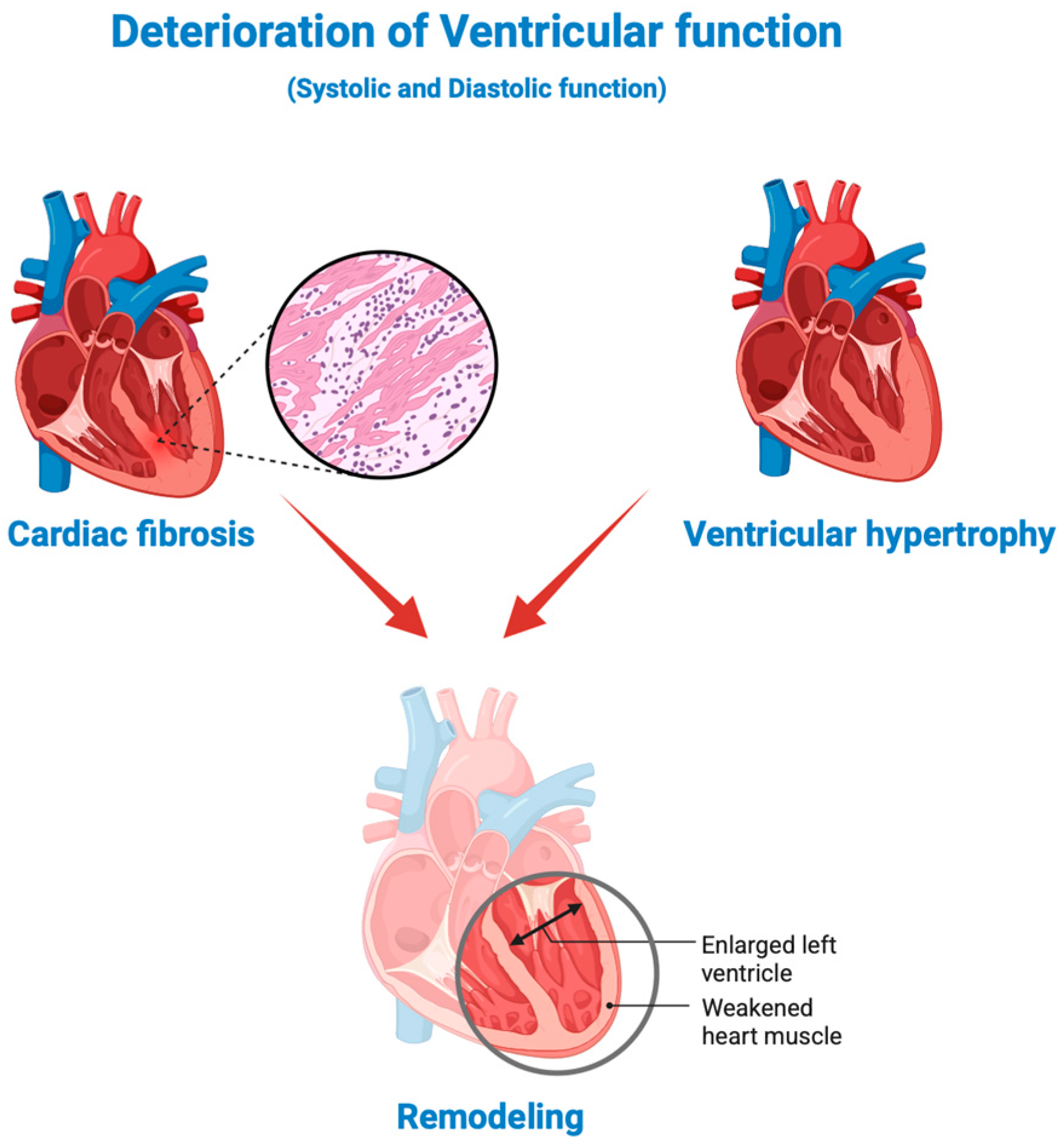
4.2. Biomarkers of Fibrosis and Cardiac Remodeling
4.3. Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
4.4. Clinical Viewpoint: Considerations and Limitations
5. Other Promising Biomarkers: Biomarkers of Negative HF Outcomes
5.1. Iron Deficiency
5.1.1. ID Blood Biomarkers
5.1.2. Clinical Viewpoint: Considerations and Limitations
5.2. Altered Renal Function: Related Biomarkers
Clinical Viewpoint: Considerations and Limitations
5.3. Altered Hepatic Function: Related Biomarkers
5.4. Endocrine–Metabolic Changes
5.5. Bone Marrow Alterations: Decreased Levels of Circulating Endothelial Cells (CECs) and Endothelial Progenitor Cells (EPCs) in HF as Biomarkers of Negative Outcomes
5.6. Another Bone Marrow Alteration: Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential (CHIP) as Additional HF Biomarker
6. Considerations: Towards the Development of Multi-Biomarkers Panels Through Artificial Intelligence and Multi-Omics?
From the Application of Multi-Omics to the Identification of Further Emerging Biomarkers: Genetic, Genomic and Transcriptome Biomarkers
7. From Identifying New Molecules as Emerging Biomarkers to Applying Them as Targets for Innovative Treatments in HF
7.1. Molecular Targeted Therapies
Challenges and Future Directions
7.2. Regenerative Therapy: EPCS as Promising Candidates of Progenitor Stem Cells Therapy
8. Discussions and Conclusions: Considerations and Suggestions on the Evidence Described
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozkurt, B.; Coats, A.J.S.; Tsutsui, H.; Abdelhamid, C.M.; Adamopoulos, S.; Albert, N.; Anker, S.D.; Atherton, J.; Böhm, M.; Butler, J.; et al. Universal definition and classification of heart failure: A report of the Heart Failure Society of America, Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, Japanese Heart Failure Society and Writing Committee of the Universal Definition. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 352–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) with the special contributio. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. (Engl. Ed.) 2022, 75, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, W.T.; Psotka, M.A.; Fiuzat, M.; Filippatos, G.; Lindenfeld, J.; Mehran, R.; Ambardekar, A.V.; Carson, P.E.; Jacob, R.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; et al. Standardized definitions for evaluation of heart failure therapies: Scientific expert panel from the Heart Failure Collaboratory and Academic Research Consortium. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2175–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulus, W.J.; Tschöpe, C.; Sanderson, J.E.; Rusconi, C.; Flachskampf, F.A.; Rademakers, F.E.; Marino, P.; Smiseth, O.A.; De Keulenaer, G.; Leite-Moreira, A.F.; et al. How to diagnose diastolic heart failure: A consensus statement on the diagnosis of heart failure with normal left ventricular ejection fraction by the Heart Failure and Echocardiography Associations of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2539–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Park, S.M. Sex differences in diagnosis and treatment of heart failure: Toward precision medicine. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2025, 40, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, C.W.; Aday, A.W.; Almarzooq, Z.I.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C.L.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Beaton, A.Z.; Boehme, A.K.; Buxton, A.E.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virani, S.S.; Alonso, A.; Benjamin, E.J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Delling, F.N.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2020, 141, e139–e596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasalam, R.; Sindone, A.; Deed, G.; Audehm, R.G.; Atherton, J.J. State of precision medicine for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a new therapeutic age. ESC Heart Fail. 2025, 12, 1544–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.L.; Carvalho, R.R.; Santos, L.G.; Sá, F.M.; Ruivo, C.; Mendes, S.L.; Martins, H.; Morais, J.A. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction: State of the Art and Prospects for the Future. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2020, 114, 120–129. [Google Scholar]
- Achten, A.; Weerts, J.; van Koll, J.; Ghossein, M.; Mourmans, S.G.J.; Aizpurua, A.B.; van Stipdonk, A.M.W.; Vernooy, K.; Prinzen, F.W.; Rocca, H.B.; et al. Prevalence and prognostic value of ventricular conduction delay in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2025, 57, 101622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogheim, G.M.; Amralla, M.T.; Werida, R.H. Role of neopterin as an inflammatory biomarker in congestive heart failure with insights on effect of drug therapies on its level. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachakis, P.K.; Theofilis, P.; Kachrimanidis, I.; Giannakopoulos, K.; Drakopoulou, M.; Apostolos, A.; Kordalis, A.; Leontsinis, I.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. The Role of Inflammasomes in Heart Failure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccardi, M.; Sammartino, A.M.; Piepoli, M.; Adamo, M.; Pagnesi, M.; Rosano, G.; Metra, M.; von Haehling, S.; Tomasoni, D. Heart failure: An update from the last years and a look at the near future. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 3667–3693, Erratum in ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, F.; Lund, L.H.; Benson, L.; Dahlström, U.; Karlström, P.; Linde, C.; Rosano, G.; Savarese, G. Trajectories in New York Heart Association functional class in heart failure across the ejection fraction spectrum: Data from the Swedish Heart Failure Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 2093–2104, Erratum in Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, B.; Aimo, A.; Al-Mohammad, A.; Keramida, K.; Ben Gal, T.; Dorbala, S.; Todiere, G.; Cameli, M.; Barison, A.; Bayes-Genis, A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of patients with left ventricular hypertrophy: Role of multimodality cardiac imaging. A scientific statement of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, M.; Carnovali, M.; Mastromarino, V. The natriuretic peptides system in the pathophysiology of heart failure: From molecular basis to treatment. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisel, A.S.; Duran, J.M.; Wettersten, N. Natriuretic Peptides in Heart Failure: Atrial and B-type Natriuretic Peptides. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudoh, T.; Maekawa, K.; Kojima, M.; Minamino, N.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding a precursor for human brain natriuretic peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1989, 159, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrath, M.F.; de Bold, M.L.; de Bold, A.J. The endocrine function of the heart. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, M.; Cannistraci, R.; Perseghin, G.; Ciardullo, S. The Role of Natriuretic Peptides in the Management of Heart Failure with a Focus on the Patient with Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, M.; Yasue, H.; Morita, E.; Sakaino, N.; Jougasaki, M.; Kurose, M.; Mukoyama, M.; Saito, Y.; Nakao, K.; Imura, H. Hemodynamic, renal, and hormonal responses to brain natriuretic peptide infusion in patients with congestive heart failure. Circulation 1991, 84, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, O.; Ogawa, Y.; Itoh, H.; Suga, S.; Komatsu, Y.; Kishimoto, I.; Nishino, K.; Yoshimasa, T.; Nakao, K. Rapid transcriptional activation and early mRNA turnover of brain natriuretic peptide in cardiocyte hypertrophy. Evidence for brain natriuretic peptide as an “emergency” cardiac hormone against ventricular overload. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1280–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.W.; Espiner, E.A.; Yandle, T.G.; Charles, C.J.; Richards, A.M. Delayed metabolism of human brain natriuretic peptide reflects resistance to neutral endopeptidase. J. Endocrinol. 2000, 167, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels, L.B.; Maisel, A.S. Natriuretic peptides. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 50, 2357–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, S.; Price, C.P.; John, R.I.; Abbas, N.A.; Webb, M.C.; Kempson, M.E.; Lamb, E.J. B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and amino-terminal proBNP in patients with CKD: Relationship to renal function and left ventricular hypertrophy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C.; McDonald, K.; de Boer, R.A.; Maisel, A.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Kozhuharov, N.; Coats, A.J.S.; Metra, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Ruschitzka, F.; et al. Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology practical guidance on the use of natriuretic peptide concentrations. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 715–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Wang, D.; Tang, O.; McEvoy, J.W.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Christenson, R.H.; Selvin, E. Subclinical Cardiovascular Disease in US Adults with and Without Diabetes. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e029083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natriuretic Peptides Studies Collaboration; Willeit, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Welsh, P.; Butterworth, A.S.; Chowdhury, R.; Spackman, S.A.; Pennells, L.; Gao, P.; Burgess, S.; et al. Natriuretic peptides and integrated risk assessment for cardiovascular disease: An individual-participant-data meta-analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventoulis, I.; Kamperidis, V.; Abraham, M.R.; Abraham, T.; Boultadakis, A.; Tsioukras, E.; Katsiana, A.; Georgiou, K.; Parissis, J.; Polyzogopoulou, E. Differences in Health-Related Quality of Life among Patients with Heart Failure. Medicina 2024, 60, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, J.G.F.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Clark, A.L.; Januzzi, J.L.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Mueller, C.; Pellicori, P.; Richards, M.; Teerlink, J.R.; Zannad, F.; et al. The struggle towards a Universal Definition of Heart Failure-how to proceed? Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 2331–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Berry, J.D.; Drazner, M.H.; Fang, J.C.; Tang, W.H.W.; Grodin, J.L. Body Mass Index, Natriuretic Peptides, and Risk of Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure and Preserved Ejection Fraction: Analysis from the TOPCAT Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e009664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Matsushita, K.; Sang, Y.; Lazo, M.; Agarwal, S.K.; Nambi, V.; Deswal, A.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Coresh, J.; et al. N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Heart Failure Risk Among Individuals with and Without Obesity: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study. Circulation 2016, 133, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obokata, M.; Reddy, Y.N.V.; Pislaru, S.V.; Melenovsky, V.; Borlaug, B.A. Evidence Supporting the Existence of a Distinct Obese Phenotype of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Circulation 2017, 136, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, P.; Campbell, R.T.; Mooney, L.; Kimenai, D.M.; Hayward, C.; Campbell, A.; Porteous, D.; Mills, N.L.; Lang, N.N.; Petrie, M.C.; et al. Reference Ranges for NT-proBNP (N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide) and Risk Factors for Higher NT-proBNP Concentrations in a Large General Population Cohort. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e009427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Docherty, K.F.; Petrie, M.C.; Januzzi, J.L.; Mueller, C.; Anderson, L.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Chioncel, O.; Cleland, J.G.F.; et al. Practical algorithms for early diagnosis of heart failure and heart stress using NT-proBNP: A clinical consensus statement from the Heart Failure Association of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2023, 25, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Chen-Tournoux, A.A.; Christenson, R.H.; Doros, G.; Hollander, J.E.; Levy, P.D.; Nagurney, J.T.; Nowak, R.M.; Pang, P.S.; Patel, D.; et al. N-Terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in the Emergency Department: The ICON-RELOADED Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1191–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianos, R.D.; Iancu, M.; Pop, C.; Lucaciu, R.L.; Hangan, A.C.; Rahaian, R.; Cozma, A.; Negrean, V.; Mercea, D.; Procopciuc, L.M. Predictive Value of NT-proBNP, FGF21, Galectin-3 and Copeptin in Advanced Heart Failure in Patients with Preserved and Mildly Reduced Ejection Fraction and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Medicina 2024, 60, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.V.; Nguyen, S.V.; Pham, A.L.; Nguyen, B.T.; Hoang, S.V. Prognostic value of NT-proBNP in the new era of heart failure treatment. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0309948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, L.A.; Massoud, G.P.; Chidiac, C.; Booz, G.W.; Altara, R.; Zouein, F.A. BNP and NT-proBNP as prognostic biomarkers for the prediction of adverse outcomes in HFpEF patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2025, 30, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goetze, J.P.; Bruneau, B.G.; Ramos, H.R.; Ogawa, T.; de Bold, M.K.; de Bold, A.J. Cardiac natriuretic peptides. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 698–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisel, A.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Landsberg, J.W.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.; Richards, M.; et al. Mid-region pro-hormone markers for diagnosis and prognosis in acute dyspnea: Results from the BACH (Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 2062–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.V.; Truong, Q.A.; Gaggin, H.K.; Pfannkuche, J.; Hartmann, O.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Mid-regional pro-atrial natriuretic peptide and pro-adrenomedullin testing for the diagnostic and prognostic evaluation of patients with acute dyspnoea. Eur. Heart J. 2012, 33, 2197–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Latini, R.; Carbonieri, E.; Moretti, L.; Rossi, M.G.; Ciricugno, S.; Milani, V.; Marchioli, R.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; et al. The predictive value of stable precursor fragments of vasoactive peptides in patients with chronic heart failure: Data from the GISSI-heart failure (GISSI-HF) trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 12, 338–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balistreri, C.R.; Magro, D.; Scola, L.; Aridon, P.; Ragonese, P.; Dos Santos Mendes, F.A.; Schirò, G.; D’Amelio, M. Shed Syndecans (1-3), ELA-32, BDNF, NLR, and hs-CRP in Parkinson’s Disease: Appropriate Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers When Combined in a Unique Panel. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wettersten, N. Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure: Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment. Int. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 3, 81–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.; Parashar, Y.; Bagchi, S.; Siddiqui, S.A.; Ajari, O.; deFilippi, C. Preclinical screening for cardiovascular disease with high-sensitivity cardiac troponins: Ready, set, go? Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1350573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netala, V.R.; Hou, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Teertam, S.K. Cardiovascular Biomarkers: Tools for Precision Diagnosis and Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breha, A.; Delcea, C.; Ivanescu, A.C.; Dan, G.A. The Prognostic Value of Troponin Levels Adjusted for Renal Function in Heart Failure—A Systematic Review. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2025, 63, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotfinaghsh, A.; Imam, A.; Pompian, A.; Stitziel, N.O.; Javaheri, A. Clinical Insights from Proteomics in Heart Failure. Curr. Heart Fail Rep. 2025, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.K.; McCarthy, C.P.; Jaffe, A.S.; Body, R.; Alotaibi, A.; Sandoval, Y.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Assays: From Implementation to Resource Utilization and Cost Effectiveness. J. Appl. Lab. Med. 2025, 10, 710–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber, I.; McCarthy, C.P.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. A Test in Context: Interpretation of High-Sensitivity Cardiac Troponin Assays in Different Clinical Settings. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Ahmad, J.; Abbas, M.; Zainullah Umar, Z.; Nasir, M.; Zain, K.; Ahmad, J.; Arshad, S.; Bashir, A.; Ullah, S.; et al. The Role of N-terminal Pro-B-Type Natriuretic Peptide, Troponins, and D-dimer in Acute Cardio-Respiratory Syndromes: A Multi-specialty Systematic Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e84460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, Y.; Wang, S.; Wei, Q. Heart failure, inflammation and exercise. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 3324–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylavarapu, M.; Kodali, L.S.M.; Vempati, R.; Nagarajan, J.S.; Vyas, A.; Desai, R. Circulating microRNAs in predicting fibrosis in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A systematic review. World J. Cardiol. 2025, 17, 106123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman-Pepine, D.; Serban, A.M.; Capras, R.D.; Cismaru, C.M.; Filip, A.G. A Comprehensive Review: Unraveling the Role of Inflammation in the Etiology of Heart Failure. Heart Fail Rev. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BaniHani, H.A.; Khaled, L.H.; Al Sharaa, N.M.; Al Saleh, R.A.; Bin Ghalaita, A.K.; Bin Sulaiman, A.S.; Holeihel, A. Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prognosis of Cardiac Fibrosis: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e81264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalmi, T.W.; Jensen, A.S.B.; Goetze, J.P. Cardiac natriuretic peptides. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2024, 122, 115–139. [Google Scholar]
- Giovou, A.E.; Gladka, M.M.; Christoffels, V.M. The Impact of Natriuretic Peptides on Heart Development, Homeostasis, and Disease. Cells 2024, 13, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Han, Y.; Zhang, M. NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis: Implications in inflammation and multisystem disorders. PeerJ 2025, 13, e19887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohn, J.N.; Levine, T.B.; Olivari, M.T.; Garberg, V.; Lura, D.; Francis, G.S.; Simon, A.B.; Rector, T. Plasma norepinephrine as a guide to prognosis in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabassi, A.; de Champlain, J.; Maggiore, U.; Parenti, E.; Coghi, P.; Vicini, V.; Tedeschi, S.; Cremaschi, E.; Binno, S.; Rocco, R.; et al. Prealbumin improves death risk prediction of BNP-added Seattle Heart Failure Model: Results from a pilot study in elderly chronic heart failure patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 3334–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceconi, C.; Ferrari, R.; Bachetti, T.; Opasich, C.; Volterrani, M.; Colombo, B.; Parrinello, G.; Corti, A. Chromogranin A in heart failure; a novel neurohumoral factor and a predictor for mortality. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 23, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Røsjø, H.; Husberg, C.; Dahl, M.B.; Stridsberg, M.; Sjaastad, I.; Finsen, A.V.; Carlson, C.R.; Oie, E.; Omland, T.; Christensen, G. Chromogranin B in heart failure: A putative cardiac biomarker expressed in the failing myocardium. Circ. Heart Fail. 2010, 3, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azuma, K.; Nishimura, K.; Min, K.D.; Takahashi, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Eguchi, A.; Okuhara, Y.; Naito, Y.; Suna, S.; Asakura, M.; et al. Plasma renin activity variation following admission predicts patient outcome in acute decompensated heart failure with reduced and mildly reduced ejection fraction. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaduganathan, M.; Cheema, B.; Cleveland, E.; Sankar, K.; Subacius, H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Solomon, S.D.; Lewis, E.F.; Greene, S.J.; Maggioni, A.P.; et al. Plasma renin activity, response to aliskiren, and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized for heart failure: The ASTRONAUT trial. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; Kremer, D.; Geven, C.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Pickkers, P.; Metra, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Düngen, H.D.; et al. Adrenomedullin in heart failure: Pathophysiology and therapeutic application. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, A.M.; Doughty, R.; Nicholls, M.G.; MacMahon, S.; Sharpe, N.; Murphy, J.; Espiner, E.A.; Frampton, C.; Yandle, T.G.; Australia-New Zealand Heart Failure Group. Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and adrenomedullin: Prognostic utility and prediction of benefit from carvedilol in chronic ischemic left ventricular dysfunction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 1781–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Haehling, S.; Filippatos, G.S.; Papassotiriou, J.; Cicoira, M.; Jankowska, E.A.; Doehner, W.; Rozentryt, P.; Vassanelli, C.; Struck, J.; Banasiak, W.; et al. Mid-regional pro-adrenomedullin as a novel predictor of mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2010, 2, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisel, A.; Xue, Y.; Shah, K.; Mueller, C.; Nowak, R.; Peacock, W.F.; Ponikowski, P.; Mockel, M.; Hogan, C.; Wu, A.H.; et al. Increased 90-day mortality in patients with acute heart failure with elevated copeptin: Secondary results from the Biomarkers in Acute Heart Failure (BACH) study. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, R.; Yan, L.; Lin, M.; Liu, X.; You, T. Copeptin in heart failure: Review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 475, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.L.; Xie, S.; Qiao, X.; An, Y.M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Guo, X.B.; Zhang, F.C.; Wu, L.L. Plasma endothelin-1-related peptides as the prognostic biomarkers for heart failure: A PRISMA-compliant meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, A.L.; Grodin, J.L.; Wu, Y.; Hernandez, A.F.; Butler, J.; Metra, M.; Felker, G.M.; Voors, A.A.; McMurray, J.J.; Armstrong, P.W.; et al. Increased mortality with elevated plasma endothelin-1 in acute heart failure: An ASCEND-HF biomarker substudy. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2016, 18, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, Y.; Ling, L.; Yang, Z.; Wan, L.; Yang, X.; Lei, M.; Guo, X.; Ren, Z. Molecular mechanisms and intervention approaches of heart failure (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 56, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.K.; Kinno, M.; Liebo, M.; Yu, M.D.; Syed, M. Evolving role of myocardial fibrosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2025, 12, 1573346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ververeli, C.L.; Dimitroglou, Y.; Soulaidopoulos, S.; Cholongitas, E.; Aggeli, C.; Tsioufis, K.; Tousoulis, D. Cardiac Remodeling and Arrhythmic Burden in Pre-Transplant Cirrhotic Patients: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Management Strategies. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergaro, G.; Prud’homme, M.; Fazal, L.; Merval, R.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M.; Samuel, J.L.; Cohen Solal, A.; Delcayre, C. Inhibition of Galectin-3 Pathway Prevents Isoproterenol-Induced Left Ventricular Dysfunction and Fibrosis in Mice. Hypertension 2016, 67, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijers, W.C.; Januzzi, J.L.; deFilippi, C.; Adourian, A.S.; Shah, S.J.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; de Boer, R.A. Elevated plasma galectin-3 is associated with near-term rehospitalization in heart failure: A pooled analysis of 3 clinical trials. Am. Heart J. 2014, 167, 853–860.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miró, Ò.; González de la Presa, B.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Fernández Bonifacio, R.; Möckel, M.; Mueller, C.; Casals, G.; Sandalinas, S.; Llorens, P.; Martín-Sánchez, F.J.; et al. The GALA study: Relationship between galectin-3 serum levels and short- and long-term outcomes of patients with acute heart failure. Biomarkers 2017, 22, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehlken, C.; Suthahar, N.; Meijers, W.C.; de Boer, R.A. Galectin-3 in Heart Failure: An Update of the Last 3 Years. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Vergaro, G.; Sciarrone, P.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. Clinical and Prognostic Significance of sST2 in Heart Failure: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdin, M.; Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Lupón, J.; Latini, R.; Meessen, J.; Anand, I.S.; Cohn, J.N.; Gravning, J.; et al. sST2 Predicts Outcome in Chronic Heart Failure Beyond NT-proBNP and High-Sensitivity Troponin T. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.M. ST2 and Prognosis in Chronic Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2321–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, J.J.; Digrajkar, A.; Das, B.; Bansal, M.; Toomu, A.; Maisel, A.S. ST2 elevation in heart failure, predictive of a high early mortality. Indian Heart J. 2018, 70, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Guan, J.; Qi, C.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; He, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Association of point-of-care testing for sST2 with clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2024, 11, 2857–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, L.; Tian, P.; Feng, J.; Huang, L.; Huang, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Guan, J.; et al. sST2 and Big ET-1 as Alternatives of Multi-Biomarkers Strategies for Prognosis Evaluation in Patients Hospitalized with Heart Failure. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2023, 16, 5003–5016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Vergaro, G.; Richards, A.M.; Lam, C.S.P.; Latini, R.; Anand, I.S.; Cohn, J.N.; Ueland, T.; Gullestad, L.; et al. Circulating levels and prognostic value of soluble ST2 in heart failure are less influenced by age than N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide and high-sensitivity troponin T. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 2078–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Maisel, A.S.; Castiglione, V.; Emdin, M. sST2 for Outcome Prediction in Acute Heart Failure: Which Is the Best Cutoff? J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 478–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, G.; Voors, A.A.; Prescott, M.F.; Felker, G.M.; Filippatos, G.; Greenberg, B.H.; Pang, P.S.; Ponikowski, P.; Milo, O.; Hua, T.A.; et al. Growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF-15) in patients admitted for acute heart failure: Results from the RELAX-AHF study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santema, B.T.; Chan, M.M.Y.; Tromp, J.; Dokter, M.; van der Wal, H.H.; Emmens, J.E.; Takens, J.; Samani, N.J.; Ng, L.L.; Lang, C.C.; et al. The influence of atrial fibrillation on the levels of NT-proBNP versus GDF-15 in patients with heart failure. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2020, 109, 331–338, Erratum in Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2021, 110, 1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zile, M.R.; Desantis, S.M.; Baicu, C.F.; Stroud, R.E.; Thompson, S.B.; McClure, C.D.; Mehurg, S.M.; Spinale, F.G. Plasma biomarkers that reflect determinants of matrix composition identify the presence of left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, E.M.; Chang, J.; González, A.; Genovese, F. Circulating collagen type I fragments as specific biomarkers of cardiovascular outcome risk: Where are the opportunities? Matrix Biol. 2025, 137, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, J.W.; Claggett, B.L.; O’Meara, E.; Prescott, M.F.; Pfeffer, M.A.; Shah, S.J.; Redfield, M.M.; Zannad, F.; Chiang, L.M.; Rizkala, A.R.; et al. Effect of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Biomarkers of Extracellular Matrix Regulation in Patients with HFpEF. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommakia, S.; Almaw, N.H.; Lee, S.H.; Ramadurai, D.K.A.; Taleb, I.; Kyriakopoulos, C.P.; Stubben, C.J.; Ling, J.; Campbell, R.A.; Alharethi, R.A.; et al. FGF21 (Fibroblast Growth Factor 21) Defines a Potential Cardiohepatic Signaling Circuit in End-Stage Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2022, 15, e008910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Gu, L.; Yao, Y.; Ma, G. Elevated Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is Relevant to Heart Failure Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction. Comput. Math Methods Med. 2022, 2022, 7138776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, R.; Yao, Y.; Ma, G. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Correlates with the Prognosis of Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Cardiology 2021, 146, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazal, R.; Wang, M.; Liu, D.; Tschumperlin, D.J.; Pereira, N.L. Cardiac Fibrosis in the Multi-Omics Era: Implications for Heart Failure. Circ. Res. 2025, 136, 773–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soejima, H.; Irie, A.; Fukunaga, T.; Oe, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kaikita, K.; Kawano, H.; Sugiyama, S.; Yoshimura, M.; Kishikawa, H.; et al. Osteopontin expression of circulating T cells and plasma osteopontin levels are increased in relation to severity of heart failure. Circ. J. 2007, 71, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Gu, R.; Xu, B. Syndecan-4 deficiency accelerates the transition from compensated hypertrophy to heart failure following pressure overload. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2017, 28, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; McMahon, C.D.; Matthews, K.G.; Devlin, G.P.; Elston, M.S.; Conaglen, J.V. Absence of Myostatin Improves Cardiac Function Following Myocardial Infarction. Heart Lung Circ. 2018, 27, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Liu, Z.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, S.; Pan, Y.; Lei, X.; Wu, D.; Xu, D. Predictive value of serum myostatin for the severity and clinical outcome of heart failure. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2019, 64, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Shang, R.; Chen, Y. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) as an important risk factor for the increased cardiovascular diseases and heart failure in chronic kidney disease. Nitric Oxide 2018, 78, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roumeliotis, S.; Veljkovic, A.; Georgianos, P.I.; Lazarevic, G.; Perisic, Z.; Hadzi-Djokic, J.; Liakopoulos, V.; Kocic, G. Association between Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress and Inflammation with Cardiac Necrosis and Heart Failure in Non-ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Patients and Various Degrees of Kidney Function. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 3090120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberale, L.; Duncker, D.J.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Kraler, S.; Bøtker, H.E.; Podesser, B.K.; Heusch, G.; Kleinbongard, P. Vascular (dys)function in the failing heart. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreadou, I.; Ghigo, A.; Nikolaou, P.E.; Swirski, F.K.; Thackeray, J.T.; Heusch, G.; Vilahur, G. Immunometabolism in heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nägele, H.; Bahlo, M.; Klapdor, R.; Schaeperkoetter, D.; Rödiger, W. CA 125 and its relation to cardiac function. Am. Heart J. 1999, 137, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J.; Miñana, G.; González, M.; Garcia-Ramón, R.; Sanchis, J.; Bodí, V.; Núñez, E.; Chorro, F.J.; Llàcer, A.; Miguel, A. Antigen carbohydrate 125 in heart failure: Not just a surrogate for serosal effusions? Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 146, 473–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinescu, M.C.; Oprea, V.D.; Munteanu, S.N.; Nechita, A.; Tutunaru, D.; Nechita, L.C.; Romila, A. Carbohydrate Antigen 125 (CA 125): A Novel Biomarker in Acute Heart Failure. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, M.; Magro, D.; Scola, L.; Pisano, C.; Guida, E.; Gervasi, F.; Giambanco, C.; Aronica, T.S.; Frati, G.; Balistreri, C.R. CAR, mGPS and hs-mGPS: What is among them the best gero-biomarker for age-related diseases? And for what clinical application? Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 220, 111952, Erratum in Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 221, 111977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rosa, M.; Sabbatinelli, J.; Giuliani, A.; Carella, M.; Magro, D.; Biscetti, L.; Soraci, L.; Spannella, F.; Fedecostante, M.; Lenci, F.; et al. Inflammation scores based on C-reactive protein and albumin predict mortality in hospitalized older patients independent of the admission diagnosis. Immun. Ageing. 2024, 21, 67, Erratum in Immun. Ageing. 2024, 21, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, R.B.; Oktafia, P.; Saputra, P.B.T.; Purwati, D.D.; Saputra, M.E.; Maghfirah, I.; Faizah, N.N.; Oktaviono, Y.H.; Alkaff, F.F. The roles of C-reactive protein-albumin ratio as a novel prognostic biomarker in heart failure patients: A systematic review. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A.; Soltani, S.; Asoudeh, F.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of omega-3 supplementation on serum albumin, pre-albumin and the CRP/albumin ratio in hospitalized patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 237–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento, D.M.; Bock, P.M.; Nemetz, B.; Goldraich, L.A.; Schaan, B.D. Meta-Analysis of Physical Training on Natriuretic Peptides and Inflammation in Heart Failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2022, 178, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, A.; Vyas, K. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Heart Failure Patients. Cureus 2025, 17, e83359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Du, Y. Prognostic value of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio for cardiovascular diseases: Research progress. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2025, 17, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, S.P.; Chia, J.E.; Jaiswal, V.; Hanif, M.; Iglesias, J. Prognostic Value of Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakhshoori, M.; Nemati, S.; Sabouhi, S.; Yavari, B.; Shakarami, M.; Bondariyan, N.; Emami, S.A.; Shafie, D. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) prognostic effects on heart failure; a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2023, 23, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadorozny, L.; Du, J.; Supanekar, N.; Annamalai, K.; Yu, Q.; Wang, M. Caveolin and oxidative stress in cardiac pathology. Front. Physiol. 2025, 16, 1550647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittipibul, V.; Ambrosy, A.P.; Greene, S.J. Myeloperoxidase inhibition in the landscape of anti-inflammatory therapies for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: The ENDEAVOR trial. Heart Fail Rev. 2025, 30, 735–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Zhao, H.; Luo, L.; Wu, W. Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Supplementation to Alleviate Heart Failure: A Mitochondrial Dysfunction Perspective. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, L.X.; Xie, S.P. Autophagy in cardiac pathophysiology: Navigating the complex roles and therapeutic potential in cardiac fibrosis. Life Sci. 2025, 123761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, I.; Trzaskalski, N.A.; Hsiao, Y.T.; Liu, P.P.; Shimizu, I.; Derumeaux, G.A. Aging at the Crossroads of Organ Interactions: Implications for the Heart. Circ. Res. 2025, 136, 1286–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Network pharmacology and bioinformatics analysis reveals: NXC improves cardiac lymphangiogenesis through miR-126-3p/SPRED1 regulating the VEGF-C axis to ameliorate post-myocardial infarction heart failure. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2025, 350, 119959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.L.; Lin, Y.N.; Xu, J.; Qiu, Y.X.; Wu, Y.H.; Qian, X.G.; Wu, Y.Q.; Wang, Z.N.; Zhang, W.W.; Li, Y.C. Macrophage-derived VEGF-C reduces cardiac inflammation and prevents heart dysfunction in CVB3-induced viral myocarditis via remodeling cardiac lymphatic vessels. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143 Pt 1, 113377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mericskay, M.; Zuurbier, C.J.; Heather, L.C.; Karlstaedt, A.; Inserte, J.; Bertrand, L.; Kararigas, G.; Ruiz-Meana, M.; Maack, C.; Schiattarella, G.G. Cardiac intermediary metabolism in heart failure: Substrate use, signalling roles and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auerbach, M.; DeLoughery, T.G.; Tirnauer, J.S. Iron Deficiency in Adults: A Review. JAMA 2025, 333, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anghel, L.; Dinu, C.; Patraș, D.; Ciubară, A.; Chiscop, I. Iron Deficiency Treatment in Heart Failure-Challenges and Therapeutic Solutions. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maidana, D.; Arroyo-Álvarez, A.; Barreres-Martín, G.; Arenas-Loriente, A.; Cepas-Guillen, P.; Brigolin Garofo, R.T.; Caravaca-Pérez, P.; Bonanad, C. Targeting Inflammation and Iron Deficiency in Heart Failure: A Focus on Older Adults. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maack, C. Metabolic alterations in heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.; Takamatsu, C.; Alabagi, A.; Pham, H.N.; Thajudeen, B.; Demirjian, S.; Tang, W.H.W.; William, P. Kidney Replacement Therapies in Advanced Heart Failure: Timing, Modalities and Clinical Considerations. J. Card Fail. 2025, 31, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangregorio, F.; Mosconi, E.; Debellis, M.G.; Provini, S.; Esposito, C.; Garolfi, M.; Oraka, S.; Kaloudi, O.; Mustafazade, G.; Marín-Baselga, R.; et al. A Systematic Review of Metabolic Syndrome: Key Correlated Pathologies and Non-Invasive Diagnostic Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, B.; Lajeunesse-Trempe, F.; Keshvani, N.; Lavie, C.J.; Pandey, A. Impact of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Steatotic Liver Disease on Cardiovascular Structure, Function, and the Risk of Heart Failure. Can. J. Cardiol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, J.; Galli, L.; Speidl, W.S.; Krychtiuk, K.A. Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2025, 27, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarese, G.; von Haehling, S.; Butler, J.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Ponikowski, P.; Anker, S.D. Iron deficiency and cardiovascular disease. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 14–27, Erratum in Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafourian, K.; Shapiro, J.S.; Goodman, L.; Ardehali, H. Iron and Heart Failure: Diagnosis, Therapies, and Future Directions. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2020, 5, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.; Damy, T.; Doehner, W.; Lam, C.S.P.; Sindone, A.; van der Meer, P.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Kindermann, I.; Manito, N.; Pfister, O.; et al. Screening, diagnosis and treatment of iron deficiency in chronic heart failure: Putting the 2016 European Society of Cardiology heart failure guidelines into clinical practice. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2018, 20, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, C.S.P.; Doehner, W.; Comin-Colet, J.; IRON CORE Group. Iron deficiency in chronic heart failure: Case-based practical guidance. ESC Heart Fail. 2018, 5, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote Beverborg, N.; Klip, I.T.; Meijers, W.C.; Voors, A.A.; Vegter, E.L.; van der Wal, H.H.; Swinkels, D.W.; van Pelt, J.; Mulder, A.B.; Bulstra, S.K.; et al. Definition of Iron Deficiency Based on the Gold Standard of Bone Marrow Iron Staining in Heart Failure Patients. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e004519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, S.; Azzo, J.D.; Zhao, L.; Pourmussa, B.; Dib, M.J.; Salman, O.; Erten, O.; Ebert, C.; Richards, A.M.; Javaheri, A.; et al. Transferrin Saturation, Serum Iron, and Ferritin in Heart Failure: Prognostic Significance and Proteomic Associations. Circ. Heart Fail. 2025, 18, e011728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, F.J.; Guha, K.; Cleland, J.G.; Kalra, P.R. Treating iron deficiency in patients with heart failure: What, why, when, how, where and who. Heart 2024, 110, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Haehling, S.; Ebner, N.; Evertz, R.; Ponikowski, P.; Anker, S.D. Iron Deficiency in Heart Failure: An Overview. JACC Heart Fail. 2019, 7, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinatolo, E.; Dasseni, N.; Metra, M.; Lombardi, C.; von Haehling, S. Iron deficiency in heart failure. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2018, 19, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamage, M.; Manouras, A.; Hage, C.; Savarese, G.; Ljung, K.; Melin, M. Implementation of guidelines for intravenous iron therapy in heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindone, A.; Doehner, W.; Comin-Colet, J. Systematic review and meta-analysis of intravenous iron-carbohydrate complexes in HFrEF patients with iron deficiency. ESC Heart Fail. 2023, 10, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezel, T.; Audureau, E.; Mansourati, J.; Baudry, G.; Ben Driss, A.; Durup, F.; Fertin, M.; Godreuil, C.; Jeanneteau, J.; Kloeckner, M.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Iron Deficiency in Heart Failure: OFICSel study by the French Heart Failure Working Group. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 1509–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Houstis, N.E.; Cunningham, T.F.; Brooks, L.C.; Chen, K.; Slocum, C.L.; Ostrom, K.; Birchenough, C.; Moore, E.; Tattersfield, H.; et al. Transferrin Saturation Is a Better Predictor Than Ferritin of Metabolic and Hemodynamic Exercise Responses in HFpEF. JACC Heart Fail. 2025, 13, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboelsaad, I.A.F.; Claggett, B.L.; Arthur, V.; Dorbala, P.; Matsushita, K.; Lutsey, P.L.; Yu, B.; Lennep, B.W.; Ndumele, C.E.; Farag, Y.M.K.; et al. Hepcidin, Incident Heart Failure and Cardiac Dysfunction in Older Adults: The ARIC Study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2025, zwaf018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Busti, F.; Borella, N.; Scoccia, E.; Pecoraro, B.; Sani, E.; Morandin, R.; Csermely, A.; Piasentin, D.; Grespan, E.; et al. Elevated plasma hepcidin concentrations are associated with an increased risk of mortality and nonfatal cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, A.C.; Vitolo, M.; Imberti, J.F.; Malavasi, V.L.; Boriani, G. Red Cell Distribution Width: A Routinely Available Biomarker with Important Clinical Implications in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 3901–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Escobar, A.; Lázaro-García, R.; Goicolea-Ruigómez, J.; González-Casal, D.; Fontenla-Cerezuela, A.; Soto, N.; González-Panizo, J.; Datino, T.; Pizarro, G.; Moreno, R.; et al. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width is a Biomarker of Red Cell Dysfunction Associated with High Systemic Inflammation and a Prognostic Marker in Heart Failure and Cardiovascular Disease: A Potential Predictor of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. 2024, 31, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, G.; Graham, F.J.; Pellicori, P.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Cuthbert, J.J.; Kazmi, S.; Inciardi, R.M.; Clark, A.L. Criteria for Iron Deficiency in Patients with Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2022, 79, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsino, A.; Carey, M.R.; Husain, S.; Mohan, S.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Jennings, D.L.; Nguonly, A.S.; Ladanyi, A.; Braghieri, L.; Takeda, K.; et al. The Difference Between Cystatin C- and Creatinine-Based Estimated GFR in Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction: Insights From PARADIGM-HF. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 82, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łagosz, P.; Biegus, J.; Urban, S.; Zymliński, R. Renal Assessment in Acute Cardiorenal Syndrome. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M. Integrated Management of Cardiovascular-Renal-Hepatic-Metabolic Syndrome: Expanding Roles of SGLT2is, GLP-1RAs, and GIP/GLP-1RAs. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Lin, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, N.; Cai, K. Prognostic Value of Serum Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Acute Heart Failure: A Meta-Analysis. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 25, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodorakis, N.; Nikolaou, M. From Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Syndrome to Cardiovascular-Renal-Hepatic-Metabolic Syndrome: Proposing an Expanded Framework. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Pompilio, G.; Balistreri, C.R. Endothelial progenitor cells in ageing. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2016, 159, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balistreri, C.R. In reviewing the emerging biomarkers of human inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): Endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) and their vesicles as potential biomarkers of cardiovascular manifestations and targets for personalized treatments. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2024, 222, 112006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balistreri, C.R. Endothelial Progenitor Cells: A New Real Hope or Only an Unrealizable Dream? Springer International Publishing: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Samman Tahhan, A.; Hammadah, M.; Sandesara, P.B.; Hayek, S.S.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; Alkhoder, A.; Mohamed Kelli, H.; Topel, M.; Ghasemzadeh, N.; Chivukula, K.; et al. Progenitor Cells and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2017, 10, e004106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourek, C.; Karatzanos, E.; Psarra, K.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Delis, D.; Linardatou, V.; Gavrielatos, G.; Papadopoulos, C.; Nanas, S.; Dimopoulos, S. Endothelial progenitor cells mobilization after maximal exercise according to heart failure severity. World J. Cardiol. 2020, 12, 526–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelucci, A.; Cesari, F.; Ricciardi, G.; Attanà, P.; Pieragnoli, P.; Ristalli, F.; Padeletti, L.; Gori, A.M.; Gensini, G.F.; Abbate, R. Left ventricular mass and progenitor cells in chronic heart failure patients. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2015, 10, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsheimer, L.; Assmus, B.; Rasper, T.; Ortmann, C.A.; Ecke, A.; Abou-El-Ardat, K.; Schmid, T.; Brüne, B.; Wagner, S.; Serve, H.; et al. Association of Mutations Contributing to Clonal Hematopoiesis with Prognosis in Chronic Ischemic Heart Failure. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Díez-Díez, M.; Hernández-Vicente, Á.; Vázquez-Andrés, D.; de la Barrera, J.; Vazquez, E.; Quintas, A.; Zuriaga, M.A.; Asensio-López, M.C.; et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis and Risk of Progression of Heart Failure with Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1747–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assmus, B.; Cremer, S.; Kirschbaum, K.; Culmann, D.; Kiefer, K.; Dorsheimer, L.; Rasper, T.; Abou-El-Ardat, K.; Herrmann, E.; Berkowitsch, A.; et al. Clonal haematopoiesis in chronic ischaemic heart failure: Prognostic role of clone size for DNMT3A- and TET2-driver gene mutations. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, F.L.; Abelson, S.; Brahmbhatt, D.H.; Medeiros, J.J.F.; Fan, C.S.; Fung, N.L.; Mihajlovic, V.; Anker, M.S.; Otsuki, M.; Lawler, P.R.; et al. Clonal haematopoiesis is associated with higher mortality in patients with cardiogenic shock. Eur. J. Heart. Fail. 2022, 24, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuermans, A.; Honigberg, M.C.; Raffield, L.M.; Yu, B.; Roberts, M.B.; Kooperberg, C.; Desai, P.; Carson, A.P.; Shah, A.M.; Ballantyne, C.M.; et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis and Incident Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2353244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastos, J.M.; Colaço, B.; Baptista, R.; Gavina, C.; Vitorino, R. Innovations in heart failure management: The role of cutting-edge biomarkers and multi-omics integration. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. Plus 2025, 11, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaccesi, L.; Balistreri, C.R. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress in Acute and Chronic Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carella, M.; Porreca, A.; Piazza, C.; Gervasi, F.; Magro, D.; Venezia, M.; Verso, R.L.; Vitale, G.; Agnello, A.G.; Scola, L.; et al. Could the Combination of eGFR and mGPS Facilitate the Differential Diagnosis of Age-Related Renal Decline from Diseases? A Large Study on the Population of Western Sicily. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhene, M.; Wang, Y.; Wei, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, L.; Acheampong, E.; Zhengcan, Z.; Xiaoyan, Q.; Yunsheng, X.; et al. Biomarkers in heart failure: The past, current and future. Heart Fail. Rev. 2019, 24, 867–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.M.; Claggett, B.; Sweitzer, N.K.; Shah, S.J.; Anand, I.S.; O’Meara, E.; Desai, A.S.; Heitner, J.F.; Li, G.; Fang, J.; et al. Cardiac structure and function and prognosis in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: Findings from the echocardiographic study of the Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist (TOPCAT) Trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 740–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, J.; Seringa, J.; Magalhaes, T. Machine learning methods, applications and economic analysis to predict heart failure hospitalisation risk: A scoping review. BMJ Open 2025, 15, e093495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharda, M.; Sharma, S.; Raikar, S.; Verhagen, N.; Wagle, J.; Mathur, R.; Gowda, S.; Kommu, S.; Prasad, R.; Bhandari, S.; et al. The Role of Machine Learning in Predicting Hospital Readmissions Among General Internal Medicine Patients: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e84761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Loscalzo, J.; Mahmud, A.K.M.F.; Aly, D.M.; Rzhetsky, A.; Zitnik, M.; Benson, M. Digital twins as global learning health and disease models for preventive and personalized medicine. Genome Med. 2025, 17, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaparthi, E.C.; Aditya Reddy, P.; Padala, T.; Sri Venkata Mahi Karthika, K.; Paka, R.; Ami Reddy, V.; Ayub, S.; Khyati Sri, V.; Rebanth Nandan, V.; Patnaik, P.K.; et al. The Rise of Personalized Medicine in Heart Failure Management: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2025, 17, e83731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palaparthi, E.C.; Padala, T.; Singamaneni, R.; Manaswini, R.; Kantula, A.; Aditya Reddy, P.; Chandini, P.; Sathwika Eliana, A.; Siri Samhita, P.; Patnaik, P.K. Emerging Therapeutic Strategies for Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Review of Novel Pharmacological and Molecular Targets. Cureus 2025, 17, e81573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magro, D.; Venezia, M.; Balistreri, C.R. The omics technologies and liquid biopsies: Advantages, limitations, applications. Med. Omics 2024, 11, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, H.; Colleran, R.; Cassese, S.; Joner, M.; Kastrati, A.; Byrne, R.A. Association of interleukin 6 -174 G/C polymorphism with coronary artery disease and circulating IL-6 levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 70, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrink, K.A.; Lymperopoulos, A. β1-adrenoceptor Arg389Gly polymorphism and heart disease: Marching toward clinical practice integration. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 1035–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.K. ACE insertion/deletion polymorphism and diabetic nephropathy: Clinical implications of genetic information. J. Diabetes Res. 2024, 2014, 846068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.M.; Cardone, K.M.; Zhang, D.Y.; Tsao, N.L.; Abramowitz, S.; Sharma, P.; DePaolo, J.S.; Conery, M.; Aragam, K.G.; Biddinger, K.; et al. Common-variant and rare-variant genetic architecture of heart failure across the allele-frequency spectrum. Nat. Genet. 2025, 57, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, R.F.; Cretoiu, S.M. MicroRNAs as monitoring markers for right-sided heart failure and congestive hepatopathy. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Li, J.L.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, S.X.; Jiao, Z.H.; Li, S.Q.; Liu, J.; Ding, J. miR-208a in Cardiac Hypertrophy and Remodeling. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 773314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asjad, E.; Dobrzynski, H. MicroRNAs: Midfielders of Cardiac Health, Disease and Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsen, A.J.; Pinto, Y.M.; Creemers, E.E. Circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 303, H1085-95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colpaert, R.M.W.; Calore, M. MicroRNAs in Cardiac Diseases. Cells 2019, 8, 737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, A.; Khoshniyat, S.; Nzeako, T.; Khazeei Tabari, M.A.; Olanisa, O.O.; Tabbaa, K.; Alkowati, H.; Askarianfard, M.; Daoud, D.; Oyesanmi, O.; et al. The Future of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)-Cas9 Gene Therapy in Cardiomyopathies: A Review of Its Therapeutic Potential and Emerging Applications. Cureus 2025, 17, e79372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balistreri, C.R.; De Falco, E.; Bordin, A.; Maslova, O.; Koliada, A.; Vaiserman, A. Stem cell therapy: Old challenges and new solutions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3117–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulak, J.; Zieliński, T.; Józkowicz, A.; Łoboda, A. Pluripotent Stem Cell-Based Approaches for Heart Repair and the Potential of Genetic Modifications. Mol. Ther. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Shi, Y.; Han, S.; Yang, X. Efficacy and clinical outcomes of bone-marrow mononuclear cell therapy in chronic heart failure: A systemic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2025, 25, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|
| Early diagnosis marker in patients with diabetes in the absence of a clear clinical expression of heart failure. | The increase in BNPs and NT-proBNPs may also depend on other comorbidities such as chronic renal failure or atrial fibrillation. |
| In the absence of a defined cardiovascular pathology, the dosage of NT-proBNP values could predict the onset of heart failure, coronary artery disease and stroke. | The value of NT-proBNPs should also be correlated with age, sex, and BMI. |
| NT-proBNP values are significantly associated with increased odds of advanced HF. | There is a significant “gray area” in which the diagnosis is rather indeterminate. |
| Correlation between NT-proBNP values and the risk of adverse events in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. |
| HF Phenotype | Typical Diagnostic Biomarker | Atypical Diagnostic Biomarker |
|---|---|---|
| HFpEF | NT-proBNP, MR-pro-ANP | MR-proADM, Gal-3, sST2, GDF-15, MMPs/TIMPs, FGF21, CRP |
| HFmrEF | NT-proBNP, MR-pro-ANP | chromogranin A, copeptin, sST2, CA125, CAR |
| HFrEF | NT-proBNP, MR-pro-ANP, cTn | chromogranin A, copeptin, sST2, CA125, CAR |
| miRNA | Role |
|---|---|
| mir-22 |
|
| miR-133/miR-223-3p |
|
| miR-21 |
|
| miR-1 |
|
| miR-212/132 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Asta, L.; Pisano, C.; Sbrigata, A.; Raffa, G.M.; Scola, L.; Balistreri, C.R. Biomarkers in Heart Failure: A Review and a Wish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168046
Asta L, Pisano C, Sbrigata A, Raffa GM, Scola L, Balistreri CR. Biomarkers in Heart Failure: A Review and a Wish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168046
Chicago/Turabian StyleAsta, Laura, Calogera Pisano, Adriana Sbrigata, Giuseppe Maria Raffa, Letizia Scola, and Carmela Rita Balistreri. 2025. "Biomarkers in Heart Failure: A Review and a Wish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168046
APA StyleAsta, L., Pisano, C., Sbrigata, A., Raffa, G. M., Scola, L., & Balistreri, C. R. (2025). Biomarkers in Heart Failure: A Review and a Wish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8046. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168046







