Calix[4]resorcinarene Amide Derivative: Thermodynamics of Cation Complexation Processes and Its Remarkable Properties for the Removal of Calcium (II) from Water
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Synthesis and structural characterization of a new calix[4]resorcinarene derivative, L containing amide pendant arms.
- 1H NMR studies on the interaction of L with metal cations in CD3CN and CD3OD. These are limited to assess whether the receptor interacts with the cations and, if possible, to identify the sites of ligand–metal cation interaction. For this work, these measurements are useful to avoid proceeding with detailed thermodynamic studies for those cations for which the NMR data shows no interaction with the ligand in the appropriate solvent.
- Conductometric studies to determine the composition of the complex in acetonitrile and methanol.
- A detailed thermodynamic study for the complexation of L and metal cations in acetonitrile and methanol to obtain quantitative information on the stability of the complexes and therefore the selectivity of L for a given cation relative to others. This information is of utmost importance for the selection of the receptor in the removal of cations from water.
- Extraction of Ca(II) from water by L under optimal experimental conditions.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. 1H NMR Characterization of L in Different Deuterated Solvents at 298 K
2.2. 1H NMR Investigations on the Complexation of L with Metal Cations in CD3CN and CD3OD at 298 K
2.3. Thermodynamic Parameters of Complexation of L with Metal Cations in CH3CN and CH3OH at 298.15 K
2.4. Calcium, Mercury, and Lead Ions Interaction with L Using Molecular Simulation
2.5. Extraction of Calcium Ion from Water Using L
2.5.1. Determination of Optimum Amount of L for the Removal of Calcium from Water at 298 K
2.5.2. The pH Effect on the Uptake of Calcium from Water by L at 298 K
2.5.3. Calcium Uptake Capacity of L at 298 K
2.5.4. Kinetics of Calcium Ion Uptake by L from Aqueous Solution at 298 K
2.5.5. Effect of Interfering Cations on Calcium Uptake from Aqueous Solution by L at 298 K
2.6. Recycling of L Ligand for Calcium Removal via pH-Switching Mechanism
2.7. Comparison with Other Materials
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of 5,11,17,23-Tetra-Tert-Butylcalix[4]arene-25, 26, 27, 28-Tetrol; 1
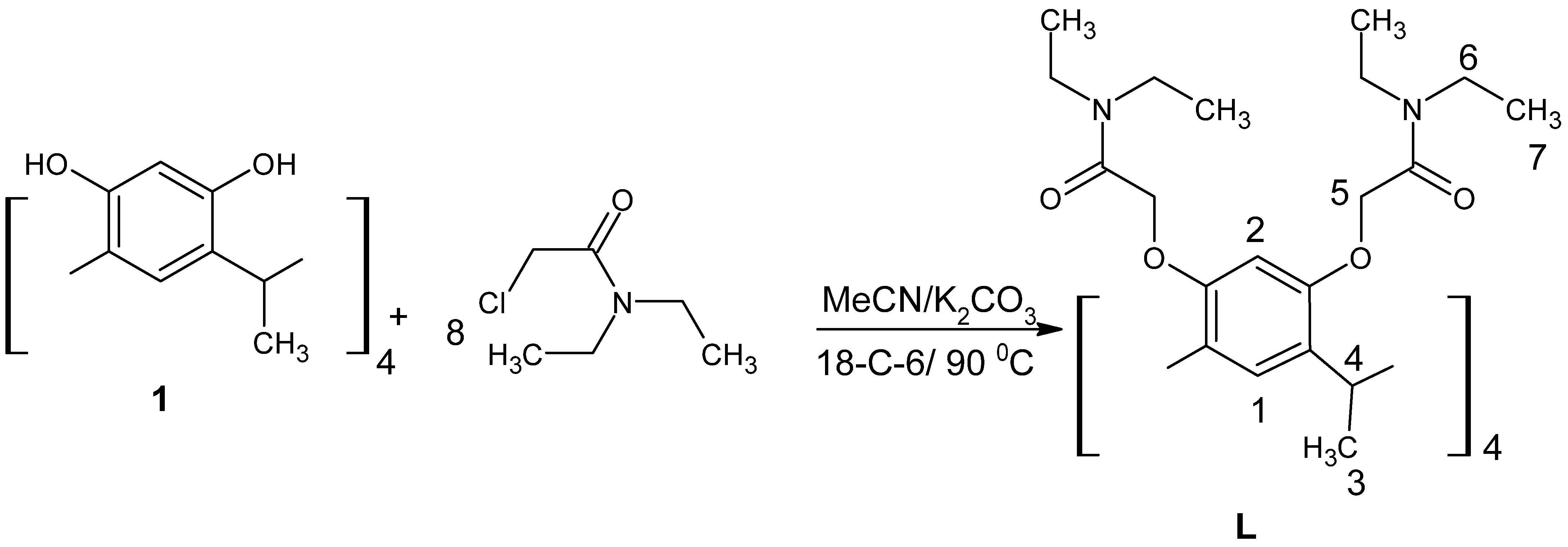
3.3. Synthesis of 4,6,10,12,16,18,22,24 Diethyl Amino Carbonyl Methoxy Calix[4]resorcinarene, L
3.4. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Measurements
1H NMR Measurements
3.5. Conductometric Measurements
3.6. Titration Calorimetric Measurements
3.7. Potentiometric Titrations for the Determination of Stability Constants
3.8. Molecular Simulation Studies
3.9. Calcium Uptake from Aqueous Solution by Calix[4]resorcinarene Amide, L
3.10. Optimum Mass of L for the Removal of Calcium from Aqueous Solutions
3.11. The Effect of pH Solution of the Aqueous Solution on the Extraction Process
3.12. Uptake Capacity of L for Calcium Ion
3.13. Kinetics of Calcium Extraction Processes from Aqueous Solutions by L
3.14. Effect of Interfering Cations on the Uptake of Calcium by L
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, V.K.; Kanaiya, P.H. Chemistry of Calix[4]resorcinarene. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2011, 80, 75–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddaif, L.; Trif, L.; Telegdi, J.; Shaban, A.; Egyed, O. Calix[4]arene Macrocycles: Synthesis, Thermal Behavior, and Crystalline Characterisation. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 137, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Yamanaka, M. Self-Assembled Capsules Based on Tetrafunctionalized Calix[4]resorcinarene Cavitands. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozova, J.E.; Myaldzina, C.R.; Voloshina, A.D.; Lyubina, A.P.; Amerhanova, S.K.; Syakaev, V.V.; Ziganshina, A.Y.; Antipin, I.S. Calixresorcinarene Cavitants Bearing Lipophilic Cationic Fragments in the Construction of Mitochondrial-Targeting Supramolecular Nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 642, 128622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasat, A.; Sherman, J.C. Carceplexes and Hemicarceplexes. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 931–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannivasan, G.; Elambalassery, J.G.; Haridas, S. Calix[4]resorcinarenes as Stable, Metal-Free, Unexplored and Unfathomed Material for Iodine Capture: Experimental and Theoretical Insights. ACS Chem. Health Saf. 2024, 31, 414–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çapan, R.; Çapan, I.; Davis, F.; Ray, A.K. Spin-Coated Films of Calix[4]resorcinarenes as Sensors for Chlorinated Solvent Vapors. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumina, J.; Siswanta, D.; Zulkamain, K.; Triono, S.; Priatmoko, P.; Yuanita, E.; Fatmasari, N.; Nursalim, I. Development of C-Arylcalix[4]resorcinarenes and C-Arylcalix[4]pyrogallolarenes as Antioxidant and UV-B Protector. Indones. J. Chem. 2019, 19, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangemi, C.M.A.; Pappalardo, A.; Sfrazzetto, G.T. Applications of Supramolecular Capsules Derived from Resorcin[4]arenes, Calix[4]arenes, and Metallo-Ligands: From Biology to Catalysis. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51919–51933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Mozafari, R.; Ghadermazi, M. Phosphomolybdic Acid Supported in Magnetic Polycalix[4]resorcinarene-EDTA-Chitosane Network as a Recyclable Catalyst for the Synthesis of 5-Aroyl-NH-1,3-Oxazalidine-2-ones. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransen, J.R.; Dutton, P.J.J. Cation Binding and Conformation of Octafunctionalized Calix[4]resorcinarenes. Can. J. Chem. 1995, 73, 2217–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Cleverley, R.M.; Zapata Ormachea, M.L. Thermodynamics of Calixarene Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 2495–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafina, A.R.; Skripacheva, V.V.; Gubaidullin, A.T.; Konovalov, A.I. Structural and Thermodynamic Aspects of Complexation of a Calix[4]resorcinarene with Diverse Cations in Water-Organic Media. J. Struct. Chem. 2005, 46, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Chaaban, J.K.; Piro, O.E.; Castellano, E.E. A Resorcinarene-Based Receptor: Versatile Behavior in Its Interaction with Heavy and Soft Metal Cations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 2442–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Chaaban, J. A Partially Substituted Calix[4]resorcinarene Receptor and Its Selective Recognition for Soft Metal Cations (Silver and Mercury). J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Aparicio Aragon, W.; Nwogu, N.; El Gamouz, A.; Piro, O.E.; Castellano, E.E. Calixarene and Resorcinarene-Based Receptors: From Structural and Thermodynamic Studies to the Synthesis of a New Mercury(II)-Selective Material. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 6922–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riveros, D.C.; Martínez, F.; Vargas, E.F. Enthalpies of Solution of Methylcalix[4]resorcinarene in Nonaqueous Solvents as a Function of Concentration and Temperature. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 548, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, D.M.; Hefter, G.; Vargas, E.R. Thermodynamic Evidence for Nano-Heterogeneity in Solutions of the Macrocycle C-Butyl Resorcin[4]arene in Nonaqueous Solvents. J. Chem. Thermodyn. 2018, 125, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, D.M.; Hefter, G.; Vargas, E.R.M. Enthalpies of Solution of C-Alkyl Resorcin[4]arenes in Water and Acetonitrile: Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Effects. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 3763–3768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Ghousseini, L. Thermodynamics of Metal-Ion Cryptates and Cryptand 222 in N,N-Dimethylformamide and Dimethylsulphoxide. J. Chem. Soc. 1984, 80, 2843–2848. [Google Scholar]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Ghousseini, L. Enthalpies and Entropies of Complexation of Cryptand 222 and Metal Ions in Propylene Carbonate: Derived Thermodynamic Parameters for the Transfer of Metal-Ion Cryptates. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 1985, 81, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F. Linear Correlation Between Entropies of Cryptand 222 with Metal Ions in Nonaqueous Solvents and Entropies of Solvation of These Ions in These Solvents. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. I 1988, 84, 2241–2244. [Google Scholar]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Llosa Tanco, M.A.; Salomon, M.; Ng, C.Y. Thermodynamic, Structural, and Conductance Studies of Lithium Coronand Electrolytes Relevant to Lithium Battery Technology. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11796–11802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Llosa Tanco, M.A.; Ng, C.Y.; Salomon, M. Lithium-Coronand Electrolytes: Thermodynamic and Electrochemical Aspects. Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Chahine, S.; Castellano, E.E.; Piro, O.E.; Jenkins, H.D.B. A Preliminary Observation of Additive Thermodynamic Contribution of Pendant Arms to the Complexation of Calixarene Derivatives with Mercury(II). Chem. Commun. 2005, 30, 3844–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Alharthi, S.; El Gamouz, A.; Al Hakawati, N.; Cox, B.G. Calix[4]-Based Hg(II) Ion Selective Electrodes: A Thermodynamic Protocol to Address the Selectivity Versus Hosting Capacity Paradigm in the Selection of the Carrier. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 290, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hakawati, N.; Alharthi, S.; Danil de Namor, A.F. Thermodynamics: A Suitable Reporter in the Design of Mercury(II) Ion Selective Electrodes. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 8671–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danil de Namor, A.F.; Castellano, E.E.; Pulcha Salazar, L.E.; Piro, O.E. Thermodynamics of Cation Complexation by a Pyridylmethyl-Substituted Calix[4]arene. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 1999, 1, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, B.G.; Schneider, H. Coordination and Transport Properties of Macrocyclic Compounds in Solution; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, J. Metal Ions in Solution; Ellis Horwood Ltd.: Hemstead, UK, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Applications. Ion Exchange Resins. Classification and Properties. SigmaAldrich.com. Merck/Sigma-Aldrich. (n.d.). Applications. Ion Exchange Resins. Classification and Properties [PDF]. 2025. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/marketing/global/documents/638/232/ion_exchange_resins.pdf (accessed on 13 August 2025).
- Chavez, M.L.; de Pablo, L.; García, T.A. Adsorption of Ba(II) by Calcium-Exchange Clinoptilolite Tuff and Montmorillonite Clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Peng, X.; Pepe, F. Silica Modified Calcium-Alginate-Xanthan Gum Hybrid Bead Composites for the Removal and Recovery of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 234, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhefnawy, O.; Elabd, A.A. Natural Silica Sand Modified by Calcium Oxide as a New Adsorbent for Uranyl Ions Removal from Aqueous Solutions. Radiochim. Acta 2017, 105, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, D.D.; Amarego, W.L.F.; Perrin, D.R. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 2nd ed.; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Al Hakawati, N. Calix-Macrocycles: From Synthesis and Physico-Chemical Studies to Analytical and Biological Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Surrey, Guildford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, J.J.; Izatt, R.M.; Hansen, L.D. A Thermometric Titration Calorimeter. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1965, 36, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eatough, D.J.; Christensen, J.J.; Izatt, R.M. Experiments in Thermometric Titrimetry and Titration Calorimetry; Brigham Young University Press: Provo, UT, USA, 1974; vii; p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Suurkuusk, J.; Wadsö, I. A Flow-Mix Microcalorimeter for Studies of Fast Reactions. Chem. Scr. 1982, 20, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Briggner, L.E.; Wadsö, I. A New Calorimeter for Flowing Liquids and Gases. J. Biochem. Biophys. Methods 1991, 22, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanati, K.; Yamashita, J.; Sekine, T.; Itani, T. Study of Microcalorimetry in Analytical Chemistry. Jpn. Soc. Anal. Chem. 2003, 19, 775–779. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, M.A. ArgusLab, 4.0.1; Planaria Software LLC: Seattle, WA, USA, 2004.
- Rappé, A.K.; Casewit, C.J.; Colwell, K.S.; Goddard, W.A.; Skiff, W.M. UFF, a Full Periodic Table Force Field for Molecular Mechanics and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10024–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
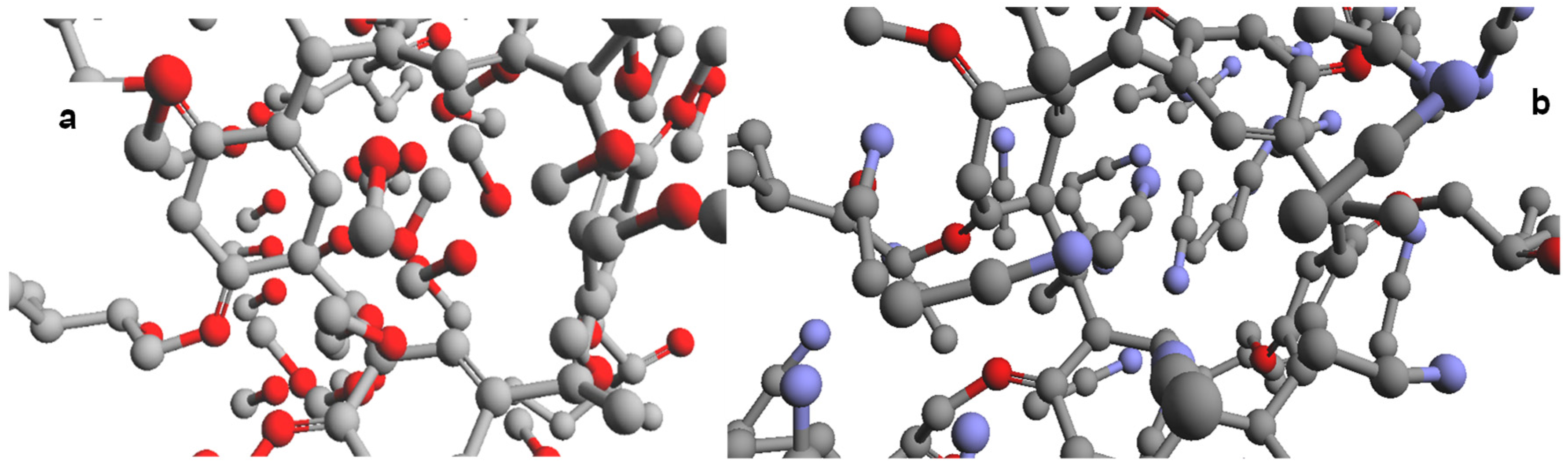








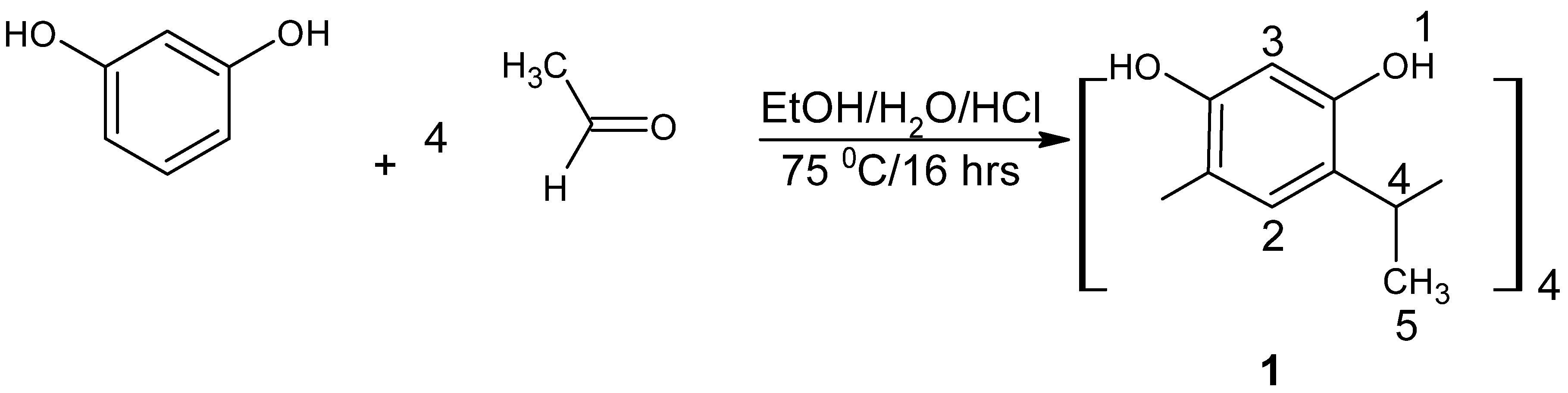
| Proton # | CD3CN δ (ppm) | CD3OD δ (ppm) | Δδ (ppm) (CD3CN-CD3OD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H-1 | 6.34 | -- | -- |
| H-2 | 6.73 | 6.47 | 0.26 |
| H-3 | 1.42 | 1.44 | −0.02 |
| H-4 | 4.70 | 4.70 | 0.00 |
| H-5 | 4.50 | 4.55 | −0.05 |
| H-6 | 1.10 | 1.14 | −0.04 |
| H-7 | 3.31 | 3.39 | −0.08 |
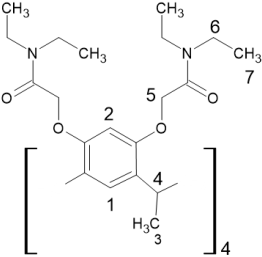 L | |||
 L L | |||||||
| . | H-1 | H-2 | H-3 | H-4 | H-5 | H-6 | H-7 |
| Solvent: CD3CN | |||||||
| δRef | 6.34 | 6.73 | 1.42 | 4.70 | 4.50 | 1.10 | 3.31 |
| Li(I) | 0.16 | −0.05 | 0.12 | 0.01 | −0.02 | 0.05 | 0.00 |
| Na(I) | 0.16 | --- | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.01 | −0.02 |
| K(I) | −0.10 | −0.23 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.14 | 0.00 | −0.01 |
| Rb(I) | −0.12 | −0.23 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.17 | 0.01 | −0.02 |
| Mg(II) | 0.16 | −0.11 | 0.08 | 0.17 | −0.03 | 0.04 | 0.08 |
| Ca(II) | 0.16 | −0.17 | 0.03 | 0.15 | −0.04 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Sr(II) | 0.16 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.14 | −0.03 | 0.06 | 0.03 |
| Ba(II) | 0.16 | −0.05 | 0.06 | −0.10 | --- | 0.07 | −0.08 |
| Zn(II) | 0.16 | −0.16 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.05 | −0.03 |
| Pb(II) | 0.16 | −0.14 | 0.12 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.01 |
| Cd(II) | 0.16 | −0.16 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.26 | 0.05 | −0.03 |
| Hg(II) | 0.16 | −0.10 | 0.08 | 0.14 | −0.02 | −0.01 | −0.02 |
| Solvent: CD3OD | |||||||
| δRef | ---- | 6.47 | 1.44 | 4.75 | 4.55 | 1.14 | 3.39 |
| Ca(II) | ---- | 0.22 | 0.07 | −0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Sr(II) | ---- | 0.23 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.06 |
| Ba(II) | ---- | 0.17 | 0.03 | −0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Ag(I) | ---- | −0.17 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.06 |
| Pb(II) | ---- | ---- | 0.11 | −0.10 | ---- | 0.07 | 0.04 |
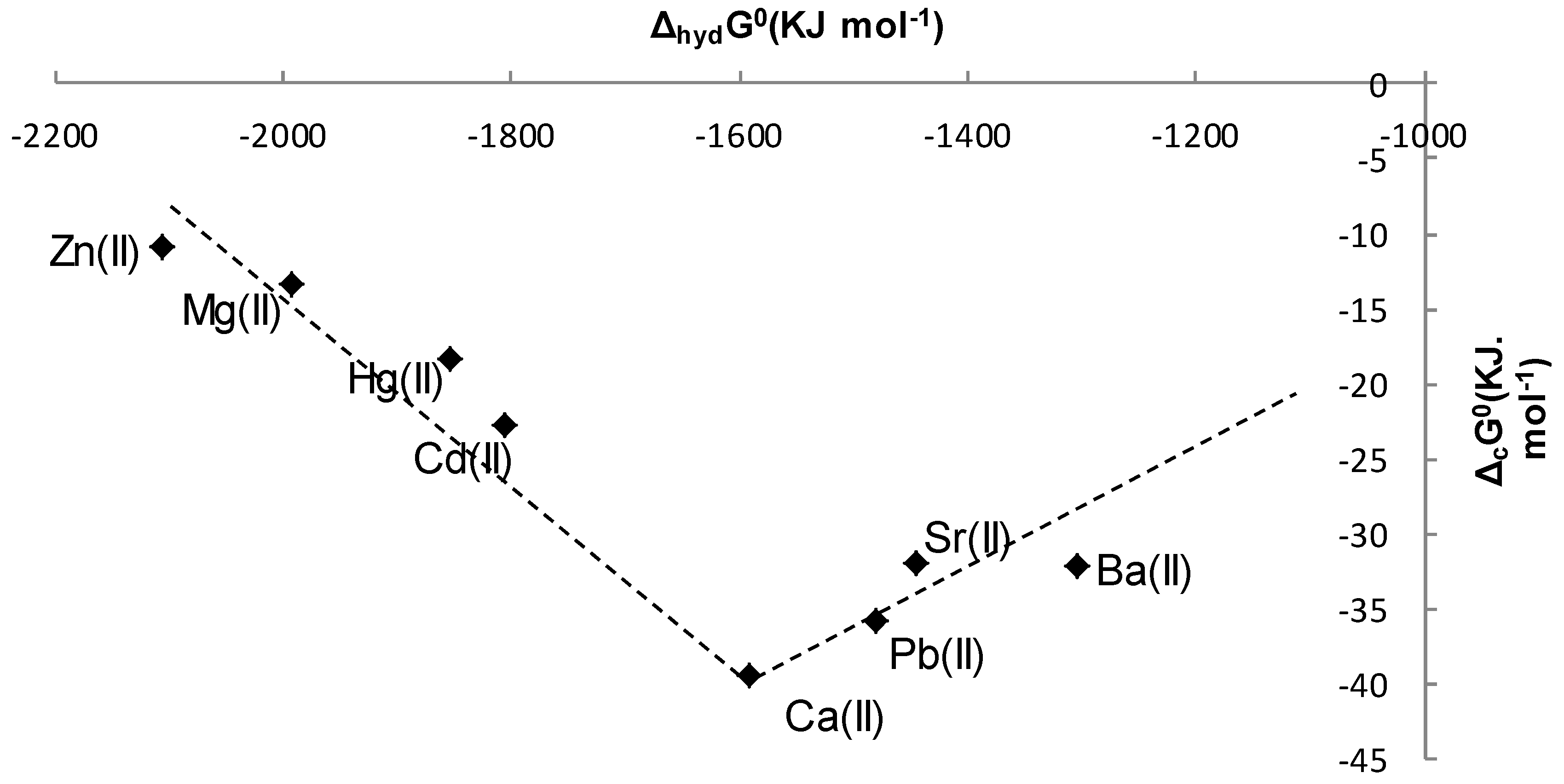
| Cation (L:M) (1:1) | Log Ks | ΔcG0 (kJ.mol−1) | ΔcH0 (kJ.mol−1) | ΔcS0 (J.K−1.mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent: MeCN | ||||
| Na(I) | 2.5 ± 0.1 a | −14.3 ± 0.3 | −70.7 ± 0.5 a | −190 |
| Mg(II) | 2.34 ± 0.02 a | −13.4 ± 0.1 | −24.2 ± 0.4 a | −36 |
| Ca(II) | 6.92 ± 0.02 b | −39.51 ± 0.02 | −126.2 ± 0.3 b | −291 |
| Sr(II) | 5.58 ± 0.09 a | −31.9 ± 0.5 | −31.6 ± 0.2 a | 1 |
| Ba(II) | 5.64 ± 0.03 a | −32.2 ± 0.2 | −29.9 ± 0.6 a | 8 |
| Cd(II) | 4.0 ± 0.1 a | −22.8 ± 0.5 | −29.3 ± 0.1 a | −22 |
| Zn(II) | 1.89 ± 0.01 a | −10.79 ± 0.03 | −16.41 ± 0.02 a | −19 |
| Hg(II) | 3.2 ± 0.1 a | −18.37 ± 0.01 | −85.1 ± 0.1 a | −224 |
| Pb(II) | 6.3 ± 0.1 b | −35.8 ± 0.3 | −99.9 ± 0.3 b | −215 |
| Solvent: MeOH | ||||
| Ca(II) | 4.0 ± 0.2 a | −22.9 ± 0.2 | −1.9 ± 0.5 | 71 |
| Ba(II) | 0.8 ± 0.1 a | −4.7 ± 0.4 | −62.9 ± 0.3 | −195 |
| Pb(II) | 1.5 ± 0.1 a | −8.5 ± 0.3 | −136.4 ± 0.4 | −429 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Namor, A.F.D.; Jumaa, A.; Al Hakawati, N. Calix[4]resorcinarene Amide Derivative: Thermodynamics of Cation Complexation Processes and Its Remarkable Properties for the Removal of Calcium (II) from Water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168043
de Namor AFD, Jumaa A, Al Hakawati N. Calix[4]resorcinarene Amide Derivative: Thermodynamics of Cation Complexation Processes and Its Remarkable Properties for the Removal of Calcium (II) from Water. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168043
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Namor, Angela F. Danil, Ahmad Jumaa, and Nawal Al Hakawati. 2025. "Calix[4]resorcinarene Amide Derivative: Thermodynamics of Cation Complexation Processes and Its Remarkable Properties for the Removal of Calcium (II) from Water" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168043
APA Stylede Namor, A. F. D., Jumaa, A., & Al Hakawati, N. (2025). Calix[4]resorcinarene Amide Derivative: Thermodynamics of Cation Complexation Processes and Its Remarkable Properties for the Removal of Calcium (II) from Water. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8043. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168043






