Unraveling Evolutionary Insights into AVT Peptide Conservation and Antimicrobial Motif Prediction Across Taxa
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence Retrieval
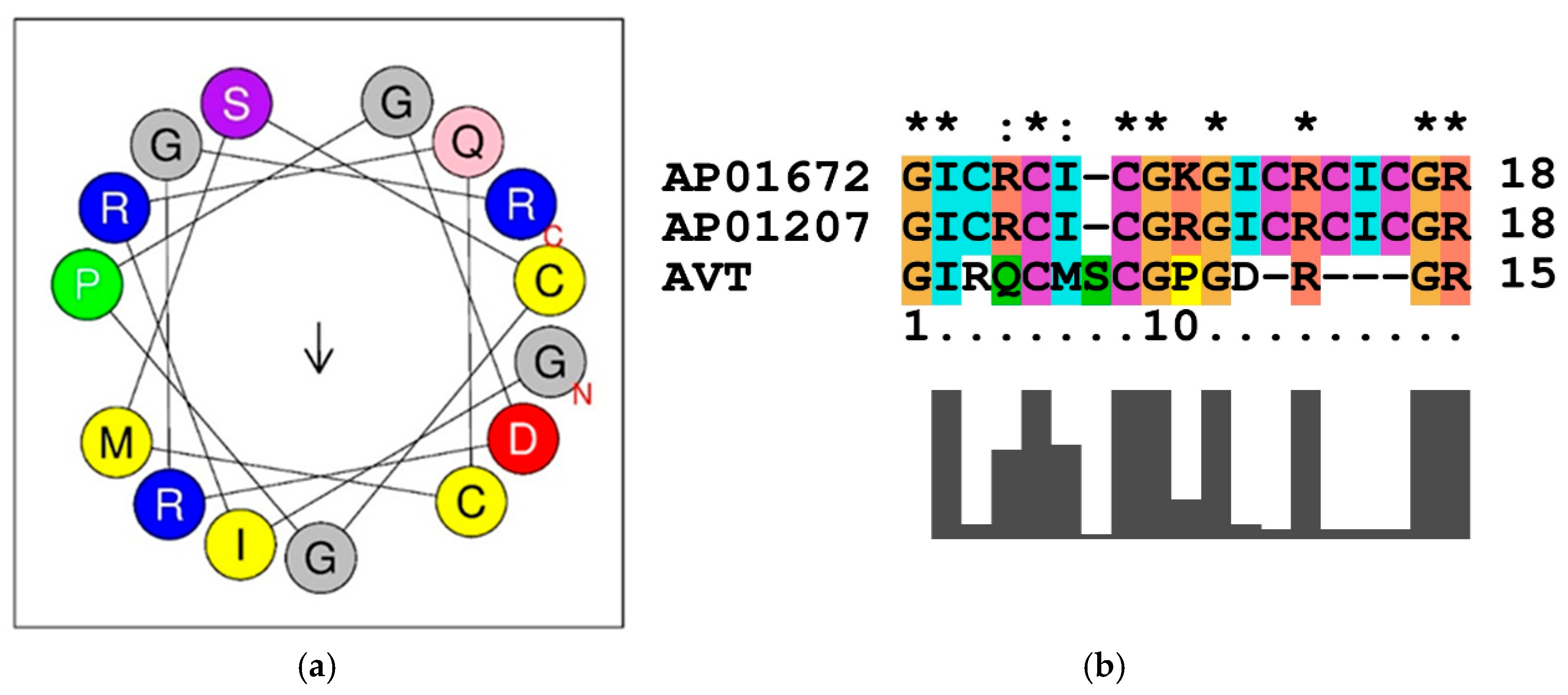
2.2. Prediction and Analyses of Antimicrobial Peptide (AMP)
2.3. Motif Prediction in AMP Sequence
2.4. Sequence Similarity Analyses
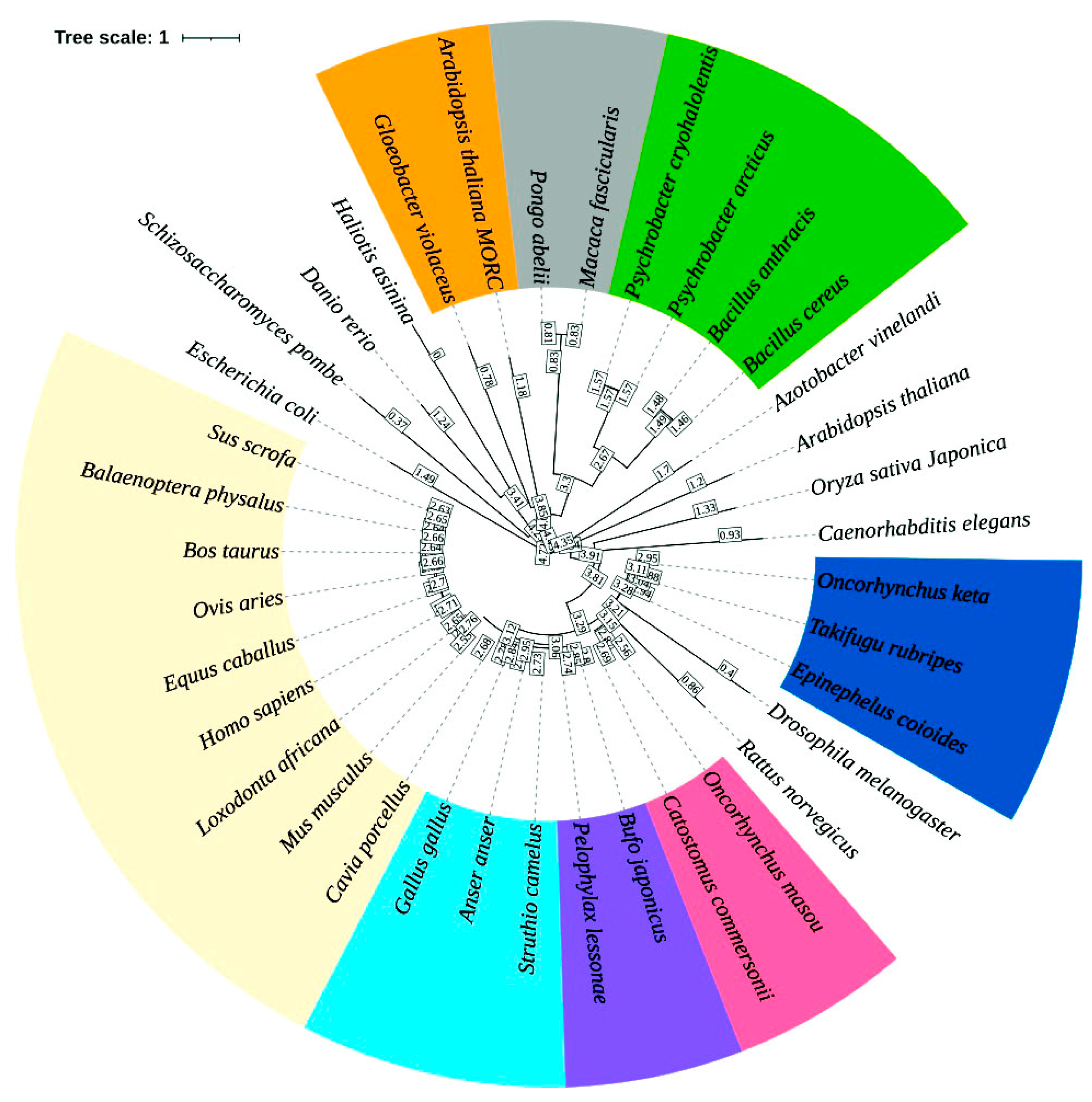
2.5. Phylogenetic Analyses
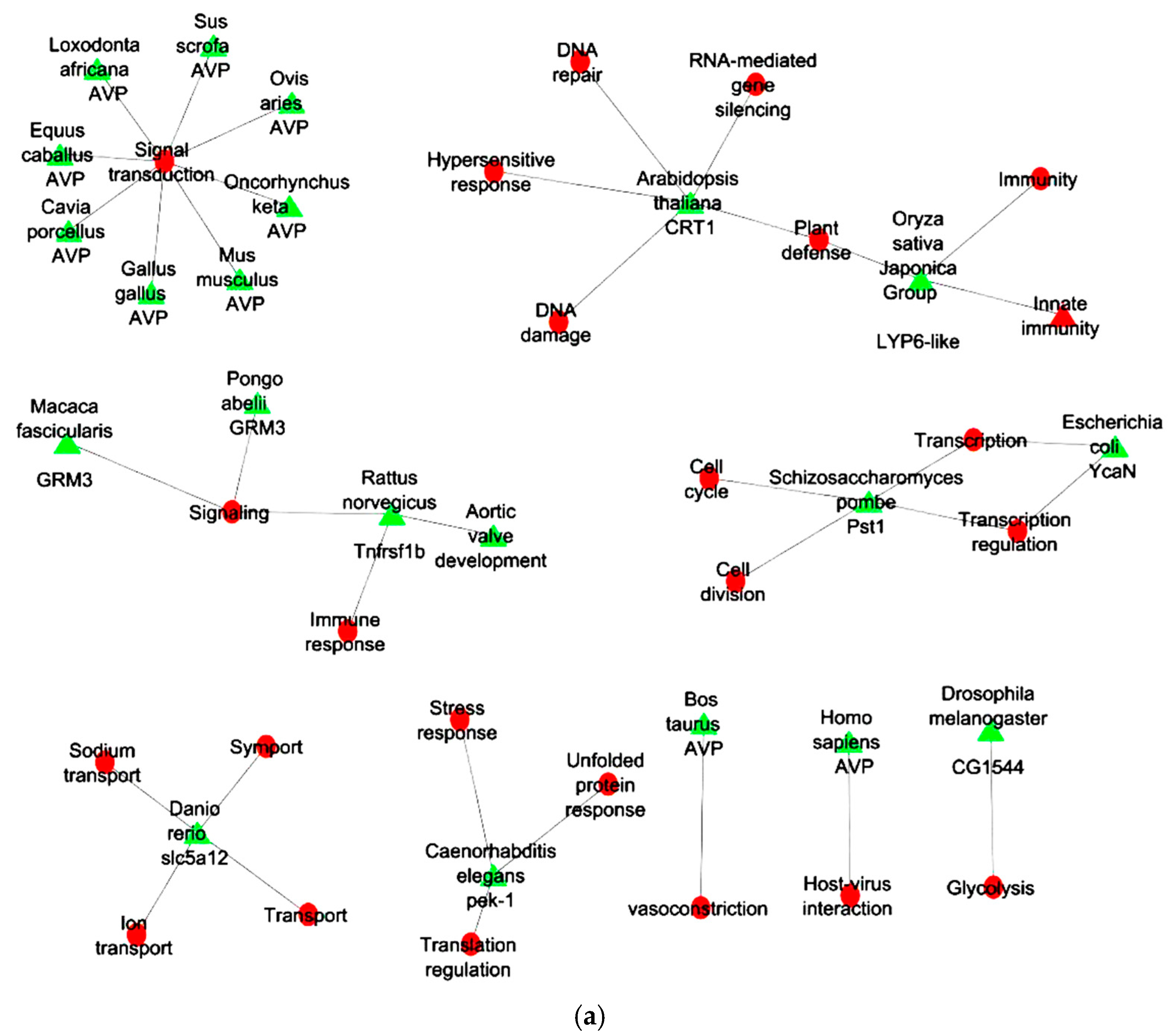
2.6. Gene Ontology Analyses
2.7. KEGG Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sequence Retrieval
4.2. Prediction and Analyses of Antimicrobial Peptide
4.3. Domain Identification and Functional Annotation
4.4. Multiple Sequence Alignment (MSA)
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.6. Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AVT | Arginine vasotocin |
| AVP | Arginine vasopressin |
| IT-1 | Isotocin-neurophysin |
| GH3.1 | Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase |
| BioD | Dethiobiotin synthetase |
| LYP6 | LysM domain-containing GPI-anchored |
| MORC1 | Protein MICRORCHIDIA 1 |
| PST1 | Paired amphipathic helix protein |
| YcaN | HTH-type transcriptional regulator |
| ArgD | Arginine decarboxylase |
| VNVT | Vasotocin-neurophysin VT |
| VN2C | Vasopressin-neurophysin 2-copeptin |
| Tnfrsf1b | TNF receptor superfamily member 1B |
| GRM3 | Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 |
| OC | Ovarian cancer |
| AGA | Androgenetic alopecia |
| slc5a12 | Sodium-coupled monocarboxylate transporter 2 |
| SBNN | Social behavior neural network |
| OT | AVP/oxytocin |
| AMP | Antimicrobial peptide |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| iTOL | Tree of life |
| NJ | Neighbor-joining |
| MEME | Multiple Em for Motif Elicitation |
References
- Albers, H.E. The regulation of social recognition, social communication and aggression: Vasopressin in the social behavior neural network. Horm. Behav. 2012, 61, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Santiago, M.; Nguyen, J.; Winton, L.S.; Weitekamp, C.A.; Hofmann, H.A. Arginine Vasotocin Preprohormone Is Expressed in Surprising Regions of the Teleost Forebrain. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, J.L.; Bass, A.H. Social behavior functions and related anatomical characteristics of vasotocin/vasopressin systems in vertebrates. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 35, 246–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, H.K.; Lee, H.J.; Macbeth, A.H.; Young, W.S., 3rd. Vasopressin: Behavioral roles of an “original” neuropeptide. Prog. Neurobiol. 2008, 84, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haramura, T.; Ikegami, T.; Wong, M.K.S.; Takei, Y. Preparatory Mechanisms for Salinity Tolerance in Two Congeneric Anuran Species Inhabiting Distinct Osmotic Habitats. Zool. Sci. 2019, 36, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilczynski, W.; Quispe, M.; Munoz, M.I.; Penna, M. Arginine Vasotocin, the Social Neuropeptide of Amphibians and Reptiles. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruberto, T.; Swaney, W.T.; Reddon, A.R. Dominance and aggressiveness are associated with vasotocin neuron numbers in a cooperatively breeding cichlid fish. Horm. Behav. 2025, 168, 105677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouso, P.; Cabana, A.; Francia, V.; Silva, A. Vasotocin but not isotocin is involved in the emergence of the dominant-subordinate status in males of the weakly electric fish, Gymnotus omarorum. Horm. Behav. 2024, 158, 105446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, G.; Aruna, A.; Chang, C.F. Neuropeptide Arginine Vasotocin Positively Affects Neurosteroidogenesis in the Early Brain of Grouper, Epinephelus coioides. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 718–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, S.C.; Sanders, K.E.; Walti, K.A. Arginine vasotocin, isotocin and nonapeptide receptor gene expression link to social status and aggression in sex-dependent patterns. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 142–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, T.; Liang, X.; Lou, B. Metabonomics and Transcriptomics Analyses Reveal the Underlying HPA-Axis-Related Mechanisms of Lethality in Larimichthys polyactis Exposed to Underwater Noise Pollution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, A.; Lin, C.J.; Nagarajan, G.; Chang, C.F. Neurohypophysial Hormones Associated with Osmotic Challenges in the Brain and Pituitary of the Euryhaline Black Porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegelii. Cells 2021, 10, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, G.; Adimoolam, A.; Alkhamis, Y.A.; Mathew, R.T.; Chang, C.F. Localization of the Neuropeptide Arginine Vasotocin and Its Receptor in the Osmoregulatory Organs of Black Porgy, Acanthopagrus schlegelii: Gills, Kidneys, and Intestines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanardini, M.; Zhang, W.; Habibi, H.R. Arginine Vasotocin Directly Regulates Spermatogenesis in Adult Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Testes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lema, S.C.; Washburn, E.H.; Crowley, M.E.; Carvalho, P.G.; Egelston, J.N.; McCormick, S.D. Evidence for a role of arginine vasotocin receptors in the gill during salinity acclimation by a euryhaline teleost fish. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2019, 316, R735–R750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasunuma, I.; Toyoda, F.; Okada, R.; Yamamoto, K.; Kadono, Y.; Kikuyama, S. Roles of arginine vasotocin receptors in the brain and pituitary of submammalian vertebrates. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2013, 304, 191–225. [Google Scholar]
- Kline, R.J.; Holt, G.J.; Khan, I.A. Arginine vasotocin V1a2 receptor and GnRH-I co-localize in preoptic neurons of the sex changing grouper, Epinephelus adscensionis. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2016, 225, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, S.C.; Paitio, J.R.; Oliveira, R.F.; Bshary, R.; Soares, M.C. Arginine vasotocin reduces levels of cooperative behaviour in a cleaner fish. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 139, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yan, Y.; Cai, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Cui, H.; Wang, P.; Qin, Q. Transcriptome analysis of orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides) spleen in response to Singapore grouper iridovirus. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, G.; Aruna, A.; Chang, C.F. Neurosteroidogenic enzymes and their regulation in the early brain of the protogynous grouper Epinephelus coioides during gonadal sex differentiation. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2013, 181, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, G.; Tsai, Y.J.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, C.F. Developmental expression of genes involved in neural estrogen biosynthesis and signaling in the brain of the orange-spotted grouper Epinephelus coioides during gonadal sex differentiation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvillo-Robledo, A.; Ramirez-Farias, C.; Valdez-Urias, F.; Huerta-Carreon, E.P.; Quintanar-Stephano, A. Arginine vasopressin hormone receptor antagonists in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis rodent models: A new approach for human multiple sclerosis treatment. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1138627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, R.P.; Eade, C.R.; Waring, A.J.; Cole, A.L.; Cole, A.M. Characterization of the retrocyclin analogue RC-101 as a preventative of Staphylococcus aureus nasal colonization. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5338–5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, S.M.; Rudolph, D.L.; Wang, W.; Cole, A.M.; Waring, A.J.; Lal, R.B.; Lehrer, R.I. RC-101, a retrocyclin-1 analogue with enhanced activity against primary HIV type 1 isolates. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2004, 20, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, A.B.; Cost, M.R.; Cole, A.L.; Cole, A.M.; Patton, D.L.; Gupta, P.; Rohan, L.C. Formulation development of retrocyclin 1 analog RC-101 as an anti-HIV vaginal microbicide product. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 2282–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, R.; Yan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Nurmamat, A.; Zhang, S.; Xiu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Pang, Y.; Li, D.; Zhao, L.; et al. Evolutionary and functional analysis of metabotropic glutamate receptors in lampreys. Fish Physiol Biochem 2024, 50, 1861–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Yan, Z.B.; Meng, Y.M.; Hong, X.Y.; Shao, G.; Ma, J.J.; Cheng, X.R.; Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Fu, C.Y. Antimicrobial peptides: Mechanism of action, activity and clinical potential. Mil. Med. Res. 2021, 8, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khemaissa, S.; Walrant, A.; Sagan, S. Tryptophan, more than just an interfacial amino acid in the membrane activity of cationic cell-penetrating and antimicrobial peptides. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2022, 55, e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, A.F.; Kerscher, B.; Dall’Angelo, S.; Sani, M.; Longhi, R.; Baloban, M.; Wilson, H.M.; Mergaert, P.; Zanda, M.; Ferguson, G.P. Role of cysteine residues and disulfide bonds in the activity of a legume root nodule-specific, cysteine-rich peptide. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10791–10798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, K.; Nandy, J.; Hoernke, M. Strong Membrane Permeabilization Activity Can Reduce Selectivity of Cyclic Antimicrobial Peptides. J. Phys. Chem. B 2025, 129, 2446–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wright, B.; Allen-Vercoe, E.; Gu, H.; Beiko, R. Phylogenetic Clustering of Genes Reveals Shared Evolutionary Trajectories and Putative Gene Functions. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 2255–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, H.E. Species, sex and individual differences in the vasotocin/vasopressin system: Relationship to neurochemical signaling in the social behavior neural network. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 36, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennigen, J.A.; Ramachandran, D.; Shaw, K.; Chaube, R.; Joy, K.P.; Trudeau, V.L. Reproductive roles of the vasopressin/oxytocin neuropeptide family in teleost fishes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1005863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavas, M.; Gitlin-Domagalska, A.; Debowski, D.; Ptaszynska, N.; Legowska, A.; Rolka, K. Vasopressin and Its Analogues: From Natural Hormones to Multitasking Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhao, H.; Yao, M.; He, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, J.; Li, Z.; Su, S.; Liu, T.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomics identify TNFRSF1B as a novel T-cell exhaustion marker for ovarian cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; He, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Hu, Z. The TNFRSF1B Connection: Implications for Androgenetic Alopecia Pathogenesis and Treatment. FASEB J. 2025, 39, e70553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lata, S.; Sharma, B.K.; Raghava, G.P. Analysis and prediction of antibacterial peptides. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the Expasy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Cao, M.; Xiu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Yang, N.; Su, B.; Li, C. Identification of Antimicrobial Peptide Genes in Black Rockfish Sebastes schlegelii and Their Responsive Mechanisms to Edwardsiella tarda Infection. Biology 2021, 10, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dibbisa, D.; Daba, T.; Mohammed, S. Regulatory Element Analysis and Comparative Genomics Study of Heavy Metal-Resistant Genes in the Complete Genome of Cupriavidus gilardii CR3. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2024, 18, 11779322241299905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Wilm, A.; Dineen, D.; Gibson, T.J.; Karplus, K.; Li, W.; Lopez, R.; McWilliam, H.; Remmert, M.; Soding, J.; et al. Fast, scalable generation of high-quality protein multiple sequence alignments using Clustal Omega. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, M.A.; Blackshields, G.; Brown, N.P.; Chenna, R.; McGettigan, P.A.; McWilliam, H.; Valentin, F.; Wallace, I.M.; Wilm, A.; Lopez, R.; et al. Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2947–2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Quan, C.; Zhou, S.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Kong, X.; Kulyar, M.F.; et al. Genetic Characterization and Phylogenetic Analysis of Fasciola Species Isolated from Yaks on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 824785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, G., Jr.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimand, J.; Isserlin, R.; Voisin, V.; Kucera, M.; Tannus-Lopes, C.; Rostamianfar, A.; Wadi, L.; Meyer, M.; Wong, J.; Xu, C.; et al. Pathway enrichment analysis and visualization of omics data using g:Profiler, GSEA, Cytoscape and EnrichmentMap. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 482–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Property | Value | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1592.83 Da | |
| Theoretical Isoelectric Point (pI) | 9.02 | |
| Net Charge (z) | 2 | |
| Positively Charged Residues | 3 | Arg(3) |
| Negatively Charged Residues | 1 | Asp(1) |
| Mean Hydrophobicity (⟨H⟩) | 0.185 | Mildly hydrophobic |
| Hydrophobic Moment (⟨µH⟩) | 0.21 | Low amphipathicity |
| Polar Residues + Glycine | 10 (66.67%) | GLN(1), SER(1), GLY(4), Arg(3), Asp(1) |
| Nonpolar Residues | 5 (33.33%) | LEU(1), VAL(1), ALA(1), ILE(1), MET(1) |
| Protein Name | Scientific Name | Common Name | Percent Identity | Accession ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isotocin-neurophysin (IT-1) | Catostomus commersonii | White sucker | 100.00% | P15210 |
| Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase (GH3.1) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Thale cress | 100.00% | O82333 |
| Dethiobiotin synthetase (BioD) | Gloeobacter violaceus | Cyanobacterium | 100.00% | Q7NFL5 |
| Collagen alpha-1 (Col4A1) | Drosophila melanogaster | Fruit fly | 100.00% | P08120.3 |
| NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit C/D | Psychrobacter arcticus | Arctic bacterium | 100.00% | Q4FU62 |
| NADH-quinone oxidoreductase subunit C/D | P. cryohalolentis | Cold-tolerant bacterium | 100.00% | Q1QD95 |
| Vasotocin-neurophysin VT 1 | Takifugu rubripes | Japanese pufferfish | 93.33% | O42499 |
| IT 1 | Oncorhynchus masou | Masu salmon | 92.31% | Q07663 |
| LysM domain-containing GPI-anchored (LYP6) | Oryza sativa Japonica | Rice | 88.89% | Q69T51 |
| Sodium-coupled monocarboxylate transporter 2 (slc5a12) | Danio rerio | Zebrafish | 87.50% | Q7T384 |
| Protein MICRORCHIDIA 1 (MORC1) | Arabidopsis thaliana | Thale cress | 85.71% | Q84WV6 |
| Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (GRM3) | Macaca fascicularis | Crab-eating macaque | 85.71% | Q1ZZH1 |
| GRM3 | Pongo abelii | Sumatran orangutan | 85.71% | Q5RAL3 |
| Paired amphipathic helix protein (PST1) | Schizosaccharomyces pombe | Fission yeast | 85.71% | Q09750 |
| HTH-type transcriptional regulator (YcaN) | Escherichia coli K-12 | E. coli | 85.71% | P75836 |
| Vasotocin-neurophysin VT 2 | Oncorhynchus keta | Chum salmon | 80.00% | P16042 |
| Neurophysin 2 | Struthio camelus | Ostrich | 78.57% | P21916 |
| Arginine decarboxylase (ArgD) | Bacillus cereus | Bacillus cereus | 77.78% | Q819L4 |
| ArgD | Bacillus anthracis | Anthrax bacterium | 77.78% | Q81MS2 |
| TNF receptor superfamily member 1B (Tnfrsf1b) | Rattus norvegicus | Rat | 75.00% | Q80WY6 |
| Uncharacterized protein 5 | Haliotis asinina | Sea snail | 75.00% | P86728 |
| Protein FixB | Azotobacter vinelandii | Soil bacterium | 75.00% | P53574 |
| Translation initiation factor 2 kinase (pek1) | Caenorhabditis elegans | Nematode | 72.73% | Q19192 |
| Vasotocin-neurophysin VT (VNVT) | Pelophylax lessonae | Pool frog | 69.23% | P11858 |
| VNVT | Gallus gallus | Chicken | 66.67% | P24787 |
| Neurophysin 2 | Anser anser anser | Domestic goose | 66.67% | P19630 |
| VNVT | Bufo japonicus | Japanese toad | 64.29% | P08163 |
| Vasopressin-neurophysin 2-copeptin (VN2C) | Sus scrofa | Pig | 64.29% | P01183 |
| VN2C | Bos taurus | Cow | 64.29% | P01180 |
| VN2C | Homo sapiens | Human | 64.29% | P01185 |
| VN2C | Mus musculus | Mouse | 64.29% | P35455 |
| VN2C | Ovis aries | Sheep | 64.29% | P01181 |
| Neurophysin 2 | Loxodonta africana | African elephant | 64.29% | P81768 |
| VN2C | Cavia porcellus | Guinea pig | 64.29% | P10769 |
| Neurophysin 2 | Equus caballus | Horse | 64.29% | P01182 |
| VN2C | Balaenoptera physalus | Fin whale | 64.29% | P01184 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagarajan, G. Unraveling Evolutionary Insights into AVT Peptide Conservation and Antimicrobial Motif Prediction Across Taxa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168026
Nagarajan G. Unraveling Evolutionary Insights into AVT Peptide Conservation and Antimicrobial Motif Prediction Across Taxa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168026
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagarajan, Ganesan. 2025. "Unraveling Evolutionary Insights into AVT Peptide Conservation and Antimicrobial Motif Prediction Across Taxa" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168026
APA StyleNagarajan, G. (2025). Unraveling Evolutionary Insights into AVT Peptide Conservation and Antimicrobial Motif Prediction Across Taxa. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 8026. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26168026






