Circulating microRNAs as Early Biomarkers of Colon Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Within a Prospective Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
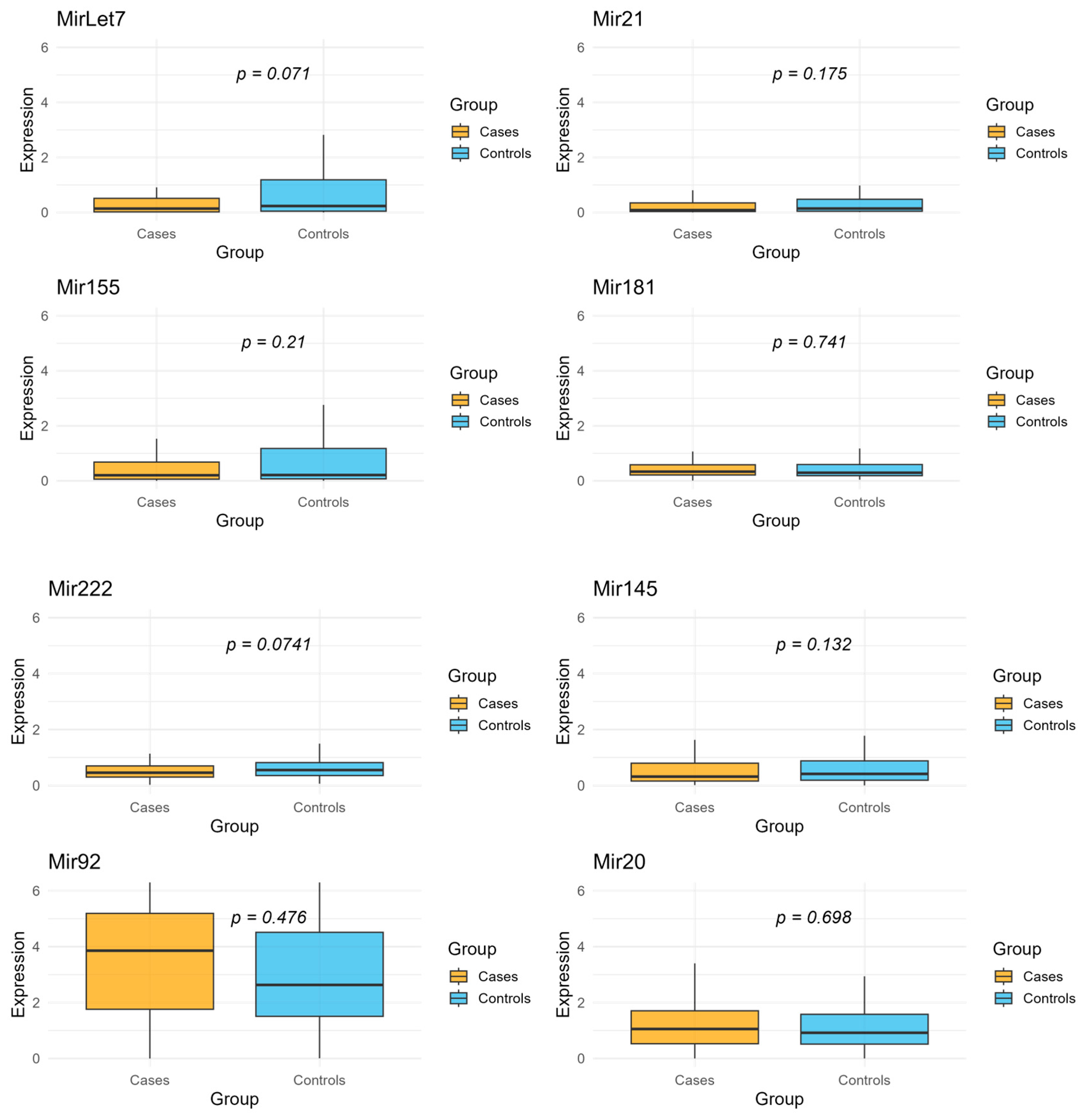
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Case and Control Selection
4.3. Selection of miRNAs
4.4. Laboratory Methods
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 522–531, Erratum in Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, F. MicroRNAs: Discovery, breakthrough, and innovation. Blood Sci. 2024, 6, e00210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vishnoi, A.; Rani, S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1509, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravorty, N. Non-coding RNAs: The silent regulators of health and diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 6971–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed Central]
- Strubberg, A.M.; Madison, B.B. MicroRNAs in the etiology of colorectal cancer: Pathways and clinical implications. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wang, T.; Wang, G.; Hao, D.; Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Ning, N.; Li, X. Aberrant regulation of the LIN28A/LIN28B and let-7 loop in human malignant tumors and its effects on the hallmarks of cancer. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, J.V.; Larsen, F.B.; Nielsen, B.S.; Brunner, N.; Madsen, C.; Bak, M.; Sorensen, F.B. MicroRNA let-7, T cells, and patient survival in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Han, H.; et al. Novel evidence for an oncogenic role of microRNA-21 in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Gut 2016, 65, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamichi, N.; Shimomura, R.; Inada, K.; Sakurai, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Fujita, S.; Mizutani, T.; Furukawa, C.; Fujishiro, M.; et al. Locked nucleic acid in situ hybridization analysis of miR-21 expression during colorectal cancer development. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4009–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Xiao, H.-X.; Tian, H.-P.; Liu, Z.-L.; Xia, S.-S.; Zhou, T. Upregulation of microRNA-155 promotes the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through the regulation of claudin-1 expression. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1375–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prossomariti, A.; Piazzi, G.; D’Angelo, L.; Miccoli, S.; Turchetti, D.; Alquati, C.; Montagna, C.; Bazzoli, F.; Ricciardiello, L. miR-155 is downregulated in familial adenomatous polyposis and modulates WNT signaling by targeting AXIN1 and TCF4. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1965–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Li, J.-W.; Zhang, B.-M.; Lv, J.-C.; Li, Y.-M.; Gu, X.-Y.; Yu, Z.-W.; Jia, Y.-H.; Bai, X.-F.; Li, L.; et al. The lncRNA CRNDE promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation and chemoresistance via miR-181a-5p-mediated regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhang, T.; Sun, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhu, X.; et al. Circulating miR-221/222 reduces CD4+T cells by inhibiting CD4 expression in colorectal cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2021, 53, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, Y.-T.; Li, X.-Y.; Li, H.-N.; Zhang, X.-P.; Long, J.-Y.; Lu, Y.-Q.; Liu, L.; Yang, G.; et al. Suppression of microRNA-222-3p ameliorates ulcerative colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer to protect against oxidative stress via targeting BRG1 to activate Nrf2/HO- 1 signaling pathway. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1089809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Rolle, A.-F.; Chiu, T.K.; Zeng, Z.; Shia, J.; Weiser, M.R.; Paty, P.B.; Chiu, V.K. Oncogenic KRAS activates an embryonic stem cell-like program in human colon cancer initiation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2159–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, A.; Nakagawa, Y.; Akao, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Nagasaka, M.; Shibata, T.; Tahara, T.; Hirata, I. Downregulation of anti-oncomirs miR-143/145 cluster occurs before APC gene aberration in the development of colorectal tumors. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2013, 46, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sehgal, P.; Lanauze, C.; Wang, X.; Hayer, K.E.; Torres-Diz, M.; Leu, N.A.; Sela, Y.; Stanger, B.Z.; Lengner, C.J.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A. MYC hyperactivates Wnt signaling in APC/CTNNB1-Mutated colorectal cancer cells through miR-92a- dependent repression of DKK3. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Peng, H.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Z.; Tian, H.; Hou, S.; Xie, X.; Peng, Q.; Zhou, T. Knockdown of miR-92a suppresses the stemness of colorectal cancer cells via mediating SOCS3. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 5613–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghofrani-Shahpar, M.; Pakravan, K.; Razmara, E.; Amooie, F.; Mahmoudian, M.; Heshmati, M.; Babashah, S. Cancer-associated fibroblasts drive colorectal cancer cell progression through exosomal miR-20a-5p-mediated targeting of PTEN and stimulating interleukin-6 production. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansero, L.; Ricceri, F.; De Marco, L.; Fiano, V.; Nesi, G.; Padroni, L.; Milani, L.; Caini, S.; Masala, G.; Agnoli, C.; et al. Investigating the Role of Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer: An Epidemiological Systematic Review. Biomedcines 2022, 10, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Longo, F.; Gattuso, G.; Spoto, G.; Ricci, D.; Venera Vitale, A.C.; Lavoro, A.; Candido, S.; Libra, M.; Falzone, L. The multifaceted role of microRNAs in colorectal cancer: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Non-Coding RNA Res. 2025, 14, 65–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mima, K.; Nishihara, R.; Nowak, J.A.; Kim, S.A.; Song, M.; Inamura, K.; Sukawa, Y.; Masuda, A.; Yang, J.; Dou, R.; et al. MicroRNA MIR21 and T Cells in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Nishida, N.; Calin, G.A.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of circulat-ing cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruštincová, A.; Votavová, H.; Dostálová Merkerová, M. Circulating MicroRNAs: Methodological Aspects in Detection of These Biomarkers. Folia Biol (Praha) 2015, 61, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Wang, H.; Yao, X.; Zhang, D.; Xie, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, X. Circulating MicroRNAs in Cancer: Potential and Challenge. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hur, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21 is a novel biomarker in patients with colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2465–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schetter, A.J.; Leung, S.Y.; Sohn, J.J.; Zanetti, K.A.; Bowman, E.D.; Yanaihara, N.; Yuen, S.T.; Chan, T.L.; Kwong, D.L.; Au, G.K.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colon adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5113–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okugawa, Y.; Toiyama, Y.; Hur, K.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21, miR-29a, and miR-125b are promising biomarkers for the early detection of colorectal neoplasia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4234–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, V.; Sengar, R.S. MicroRNAs Are Key Molecules Involved in the Gene Regulation of Colorectal Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 828128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, H.-R.; Yang, Y. Expression analysis of microRNA as prognostic biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15257–15273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidíková, P.; Herichová, I. miRNA Clusters with Up-Regulated Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Shirzad, S.; Eterafi, M.; Karimi, Z.; Barazesh, M. MicroRNAs involved in colorectal cancer: A rapid mini-systematic review. BMC Cancer 2024, 25, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palli, D.; Berrino, F.; Vineis, P.; Tumino, R.; Panico, S.; Masala, G.; Saieva, C.; Salvini, S.; Ceroti, M.; Pala, V.; et al. A molecular epidemiology project on diet and cancer: The EPIC-Italy prospective study. Tumori 2003, 89, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareham, N.J.; Jakes, R.W.; Rennie, K.L.; Schuit, J.; Mitchell, J.; Hennings, S.; Day, N.E. Validity and repeatability of a simple index derived from the short physical activity questionnaire used in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC) study. Public Health Nutr. 2003, 6, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Anatomy of health effects of Mediterranean diet: Greek EPIC prospective cohort study. BMJ 2009, 338, b2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sacerdote, C.; Ricceri, F.; Rolandsson, O.; Baldi, I.; Chirlaque, M.-D.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Bendinelli, B.; Ardanaz, E.; Arriola, L.; Balkau, B.; et al. Lower educational level is a predictor of incident type 2 diabetes in European countries: The EPIC-InterAct study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1162–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 4 August 2025).
| miRNA | Role in CC | Key Targets/Pathways | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Let7 | Tumor suppressor; promotes differentiation and inhibits proliferation. Suppressed by LIN28A/B. | LIN28A/B; regulates cell differentiation; anti-proliferative | [6,7] |
| Mir21 | Oncogenic; promotes proliferation, invasion, inflammation, and therapy resistance. | PDCD4, PTEN; Wnt/β-catenin and AKT pathways | [8,9] |
| Mir155 | Oncogenic; promotes migration, invasion, EMT, and inflammation. | AXIN1, TCF4; Wnt/β-catenin; CAF/TAM exosomal signaling | [10,11] |
| Mir181 | Promotes tumor progression and therapy resistance; involved in Wnt signaling. | Wnt/β-catenin; CYLD, modulated by lncRNAs | [12] |
| Mir222 | Oncogenic; promotes migration, invasion, metastasis, and immune escape. | MST3, SPINT1, ADAM-17, ATF3; chemoresistance | [13,14] |
| Mir145 | Tumor suppressor; downregulated in early CC; promotes differentiation. | OCT4, SOX2, EGFR, RREB1; Ras-MAPK and Wnt regulation | [15,16] |
| Mir92a | Oncogenic; member of Mir17~92 cluster; promotes proliferation and angiogenesis. | DKK3, SOCS3, NF2, KLF4 | [17,18] |
| Mir 20a | Oncogenic; part of Mir17~92 cluster; promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis. | ATG5, FIP200, CXCL8, PDCD4, MICA, FOXJ2, PTEN, SMAD4 | [19] |
| Characteristics | Cases N = 104 | Controls N = 104 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean ± SD) | 55.8 ± 6.0 | 54.5 ± 6.5 | 0.09 |
| Center | >0.90 | ||
| Florence | 53 (51%) | 53 (51%) | |
| Turin | 51 (49%) | 51 (49%) | |
| Smoking Status | 0.20 | ||
| Never smokers | 46 (44%) | 47 (45%) | |
| Former smokers | 38 (37%) | 28 (27%) | |
| Smokers | 20 (19%) | 29 (28%) | |
| Body Mass Index | 0.70 | ||
| Normal weight (BMI < 25) | 31 (31%) | 37 (37%) | |
| Overweight (25 < BMI < 30) | |||
| 55 (54%) | 51 (50%) | ||
| Obese (BMI > 30) | 15 (15%) | 13 (13%) | |
| Physical Activity | 0.50 | ||
| Active | 7 (6.7%) | 12 (12%) | |
| Moderately active | 38 (37%) | 41 (39%) | |
| Moderately inactive | 40 (38%) | 36 (35%) | |
| Inactive | 19 (18%) | 15 (14%) | |
| Mediterranean Score | >0.90 | ||
| 0–2 | 26 (25.5%) | 23 (22.6%) | |
| 3–5 | 60 (57.0%) | 59 (56.0%) | |
| 6–10 | 18 (17.5%) | 22 (21.4%) | |
| Socioeconomic Position | 0.80 | ||
| High | 35 (35%) | 30 (30%) | |
| Medium | 27 (27%) | 29 (29%) | |
| Low | 38 (38%) | 41 (41%) |
| miRNA | Mean Expression in Cases | Mean Expression in Controls | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Let7 | 0.68 | 2.63 | 0.26 |
| Mir21 | 0.41 | 1.96 | 0.21 |
| Mir155 | 0.56 | 1.50 | 0.37 |
| Mir181 | 0.47 | 0.87 | 0.54 |
| Mir222 | 0.57 | 1.52 | 0.38 |
| Mir145 | 0.63 | 1.73 | 0.36 |
| Mir92 | 3.91 | 3.36 | 1.16 |
| Mir20 | 1.37 | 2.53 | 0.54 |
| miRNA | OR | Low IC 95% | High IC 95% | p-Value | Bonferroni Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Let7 | 0.91 | 0.84 | 1.00 | 0.04 | 0.33 |
| Mir21 | 0.90 | 0.81 | 1.01 | 0.07 | 0.56 |
| Mir155 | 0.92 | 0.83 | 1.02 | 0.10 | 0.83 |
| Mir181 | 0.96 | 0.77 | 1.19 | 0.71 | 1.00 |
| Mir222 | 0.82 | 0.64 | 1.03 | 0.09 | 0.74 |
| Mir145 | 0.89 | 0.76 | 1.04 | 0.14 | 1.00 |
| Mir92 | 0.97 | 0.85 | 1.12 | 0.68 | 1.00 |
| Mir20 | 1.00 | 0.87 | 1.14 | 0.95 | 1.00 |
| miRNA | OR | Low IC 95% | High IC 95% | p-Value | Bonferroni Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Let7 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 0.06 | 0.48 |
| Mir21 | 0.92 | 0.81 | 1.04 | 0.18 | 1.00 |
| Mir155 | 0.93 | 0.83 | 1.04 | 0.20 | 1.00 |
| Mir181 | 0.97 | 0.75 | 1.25 | 0.83 | 1.00 |
| Mir222 | 0.75 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0.05 | 0.40 |
| Mir145 | 0.88 | 0.73 | 1.06 | 0.17 | 1.00 |
| Mir92 | 0.97 | 0.82 | 1.14 | 0.71 | 1.00 |
| Mir20 | 1.01 | 0.87 | 1.18 | 0.86 | 1.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Padroni, L.; Marmiroli, G.; De Marco, L.; Fiano, V.; Dansero, L.; Caini, S.; Masala, G.; Manfredi, L.; Milani, L.; Ricceri, F.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as Early Biomarkers of Colon Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Within a Prospective Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167893
Padroni L, Marmiroli G, De Marco L, Fiano V, Dansero L, Caini S, Masala G, Manfredi L, Milani L, Ricceri F, et al. Circulating microRNAs as Early Biomarkers of Colon Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Within a Prospective Cohort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167893
Chicago/Turabian StylePadroni, Lisa, Giorgia Marmiroli, Laura De Marco, Valentina Fiano, Lucia Dansero, Saverio Caini, Giovanna Masala, Luca Manfredi, Lorenzo Milani, Fulvio Ricceri, and et al. 2025. "Circulating microRNAs as Early Biomarkers of Colon Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Within a Prospective Cohort" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167893
APA StylePadroni, L., Marmiroli, G., De Marco, L., Fiano, V., Dansero, L., Caini, S., Masala, G., Manfredi, L., Milani, L., Ricceri, F., & Sacerdote, C. (2025). Circulating microRNAs as Early Biomarkers of Colon Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Within a Prospective Cohort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7893. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167893








