IL-15 Promotes the Survival of Anti-Inflammatory (M2), Immunoinhibitory (IL-10+) Dermal Macrophages in Human Eyelid Skin Under IFNγ-Dominated Inflammatory Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
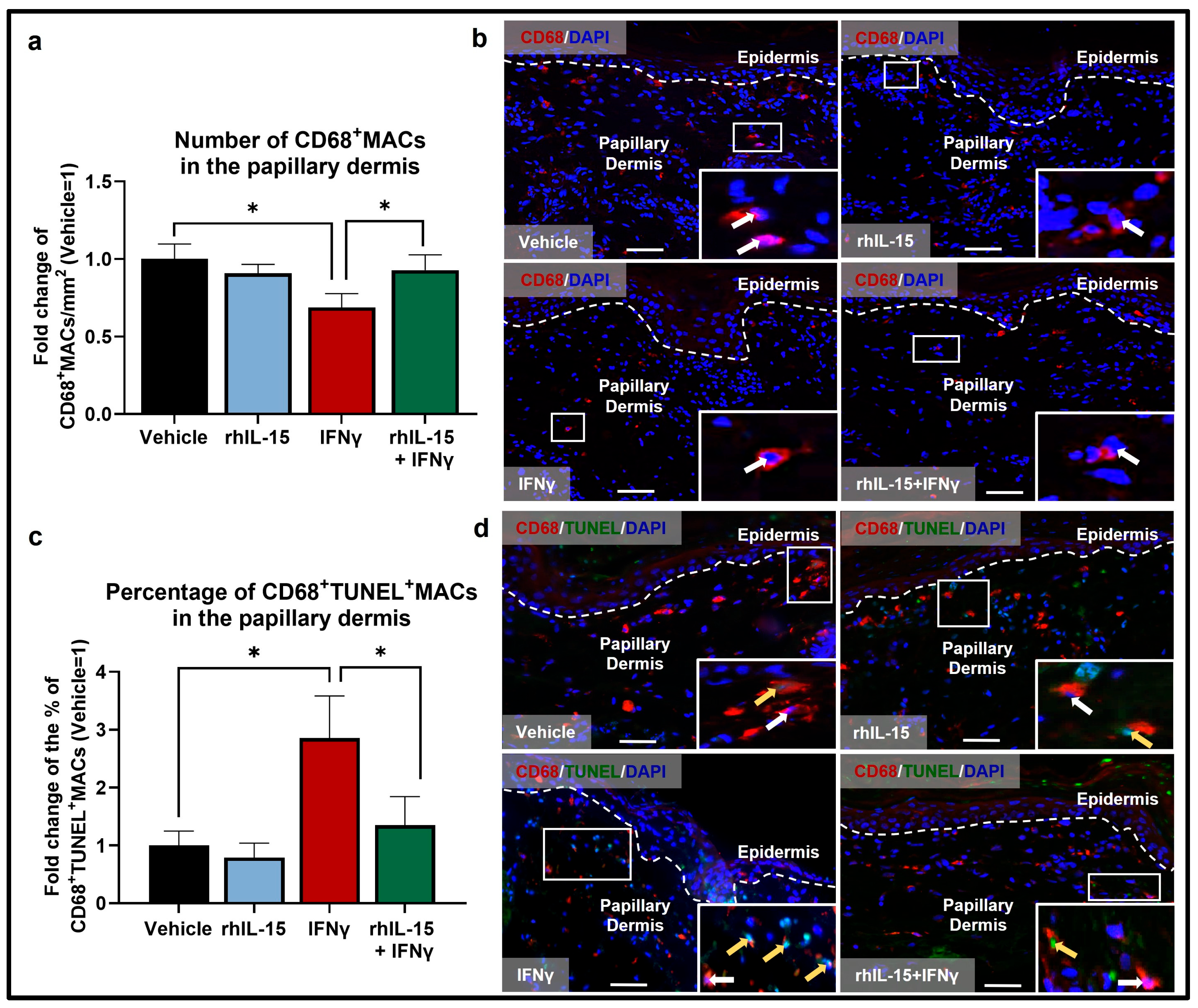
2.1. IFNγ Reduces the Total Pool of Human Dermal MACs Ex Vivo
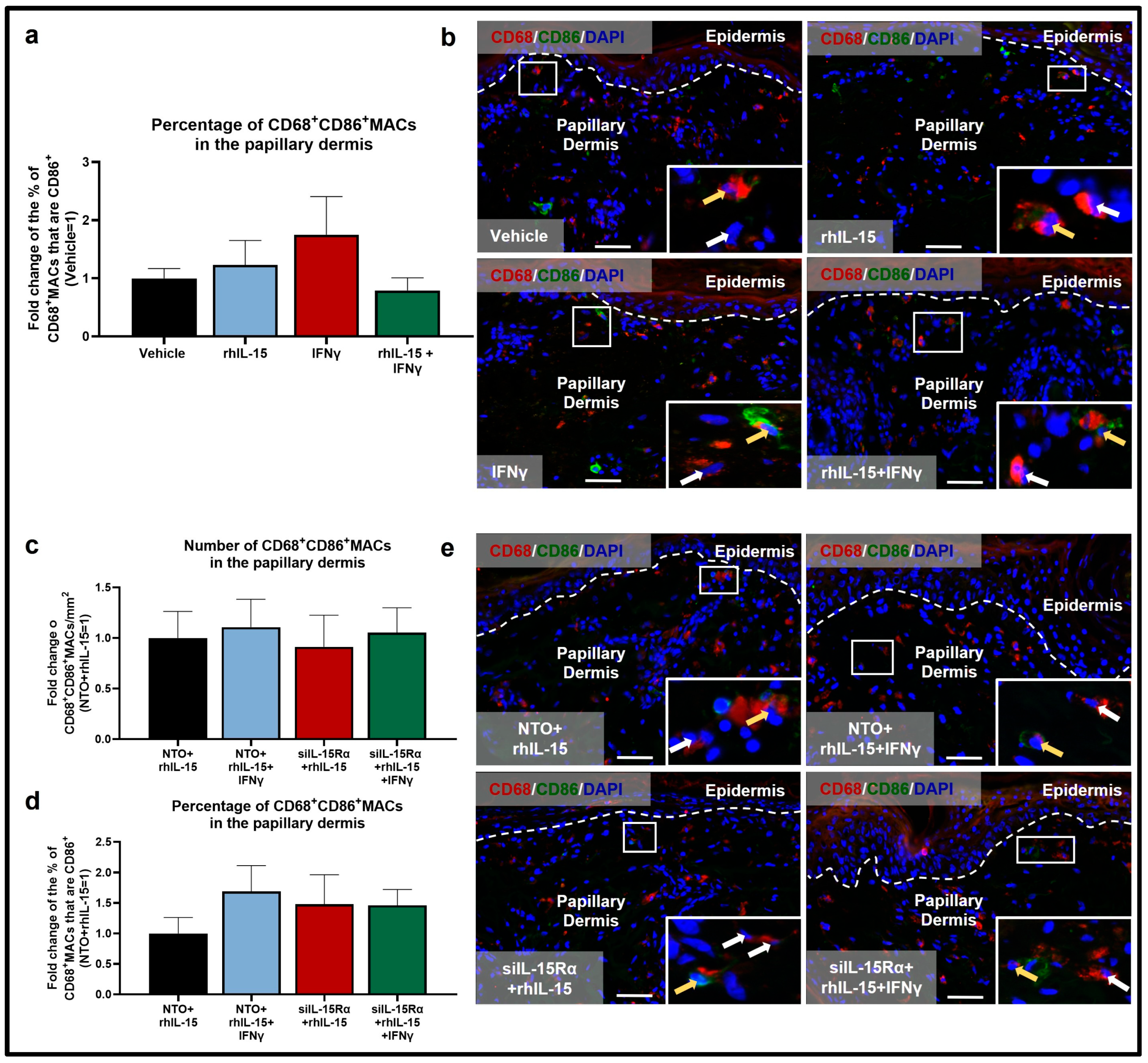
2.2. rhIL-15 Reverses the IFNγ-Induced Reduction in M2 CD206+MACs
2.3. Human Dermal M2 CD206+MAC Survival Depends on IL-15Rα-Mediated Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Eyelid Skin Samples
4.2. Eyelid Skin Organ Culture
4.3. IL-15Rα Silencing Ex Vivo
4.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.5. Immunofluorescence Microscopy and Quantitative Immunohistomorphometry
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CD68 | Cluster of differentiation 68 |
| CD86 | Cluster of differentiation 86 |
| CD206 | Cluster of differentiation 206 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IL-15 | Interleukin-15 |
| IL-15Rα | Interleukin-15 receptor alpha |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| IFNγ | Interferon gamma |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| MAC | Macrophage |
| qIHM | Quantitative immunohistomorphometry |
| iNKT10 | IL-10-secreting inhibitory natural killer T |
| siIL-15Rα | Small interfering RNA interleukin-15 receptor alpha |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| TUNEL | TdT-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end labeling |
| N/A | Not applicable |
References
- He, X.; Gao, X.; Xie, W. Research Progress in Skin Aging and Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apeku, E.; Tantuoyir, M.M.; Zheng, R.; Tanye, N. Exploring the Polarization of M1 and M2 Macrophages in the Context of Skin Diseases. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Xu, L.; Huang, B.; Xiong, K.; Yang, X.; Ye, J. Decoding Macrophage Dynamics: A Pathway to Understanding and Treating Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, T.; Fu, S.; Yang, R.; Yang, K.; Lei, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, J.; Yu, L.; et al. Advances in the Study of Macrophage Polarization in Inflammatory Immune Skin Diseases. J. Inflamm. 2023, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, J.A. Recently Discovered Roles for Macrophages in Human Skin Development. Br. J. Dermatol. 2025, 192, 371–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherardini, J.; Uchida, Y.; Hardman, J.A.; Chéret, J.; Mace, K.; Bertolini, M.; Paus, R. Tissue-Resident Macrophages Can Be Generated de Novo in Adult Human Skin from Resident Progenitor Cells during Substance P-Mediated Neurogenic Inflammation Ex Vivo. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Tripathi, A. Biology of Macrophage Fate Decision: Implication in Inflammatory Disorders. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 1539–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Wu, S. B Cells Recruitment Promotes M2 Macrophage Polarization to Inhibit Inflammation during Wound Healing. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2025, 219, uxaf002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolliniati, O.; Ieronymaki, E.; Vergadi, E.; Tsatsanis, C. Metabolic Regulation of Macrophage Activation. J. Innate Immun. 2022, 14, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Fu, S.; Zhao, Q. 2022 Update on the Scientific Premise and Clinical Trials for IL-15 Agonists as Cancer Immunotherapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2022, 112, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Jagannath, C. Crosstalk between Metabolism and Epigenetics during Macrophage Polarization. Epigenetics Chromatin 2025, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.-H.; Lai, C.-Y.; Yeh, D.-W.; Liu, Y.-L.; Su, Y.-W.; Hsu, L.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Catherine Jin, S.-L.; Chuang, T.-H. Involvement of M1 Macrophage Polarization in Endosomal Toll-Like Receptors Activated Psoriatic Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3523642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Sacks, D.L. Resilience of Dermis Resident Macrophages to Inflammatory Challenges. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 2105–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behr, N.J.; Pierre, S.; Ickelsheimer, T.; Ziegler, N.; Luckhardt, S.; Kannt, A.; Pinter, A.; Geisslinger, G.; Schäfer, S.M.G.; König, A.; et al. High Content Imaging Shows Distinct Macrophage and Dendritic Cell Phenotypes for Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasraie, S.; Werfel, T. Role of Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 942375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, M.; Tada, Y. Dendritic Cells and Macrophages in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 941071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Jang, J.; Lee, E.-H.; Jung, S.; Roh, J.Y.; Jung, Y. Decreased Expression of Response Gene to Complement 32 in Psoriasis and Its Association with Reduced M2 Macrophage Polarization. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 166–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Benedetti, F.; Prencipe, G.; Bracaglia, C.; Marasco, E.; Grom, A.A. Targeting Interferon-γ in Hyperinflammation: Opportunities and Challenges. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 678–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orzan, O.A.; Tutunaru, C.V.; Ianoși, S.L. Understanding the Intricate Pathophysiology of Psoriasis and Related Skin Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha Ray, A.; Odum, O.P.; Wiseman, D.; Weinstock, A. The Diverse Roles of Macrophages in Metabolic Inflammation and Its Resolution. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1147434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchin, I.; Bourcier, M. The Role of Interleukins in the Pathogenesis of Dermatological Immune-Mediated Diseases. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 4474–4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieminska, I.; Pieniawska, M.; Grzywa, T.M. The Immunology of Psoriasis-Current Concepts in Pathogenesis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2024, 66, 164–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Chéret, J.; Scala, F.D.; Rajabi-Estarabadi, A.; Akhundlu, A.; Demetrius, D.-L.; Gherardini, J.; Keren, A.; Harries, M.; Rodriguez-Feliz, J.; et al. Interleukin-15 Is a Hair Follicle Immune Privilege Guardian. J. Autoimmun. 2024, 145, 103217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulfone-Paus, S. Exploring the Role of IL-15 in the Skin Immune System. Exp. Dermatol. 2002, 11, 481–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappl, G.; Kapsokefalou, A.; Heuser, C.; Rössler, M.; Ugurel, S.; Tilgen, W.; Reinhold, U.; Abken, H. Dermal Fibroblasts Sustain Proliferation of Activated T Cells via Membrane-Bound Interleukin-15 upon Long-Term Stimulation with Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2001, 116, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabri, B.; Abadie, V. IL-15 Functions as a Danger Signal to Regulate Tissue-Resident T Cells and Tissue Destruction. Nat. Reviews Immunol. 2015, 15, 771–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldmann, T.A.; Waldmann, R.; Lin, J.-X.; Leonard, W.J. The Implications of IL-15 Trans-Presentation on the Immune Response. Adv. Immunol. 2022, 156, 103–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skariah, N.; James, O.J.; Swamy, M. Signalling Mechanisms Driving Homeostatic and Inflammatory Effects of Interleukin-15 on Tissue Lymphocytes. Discov. Immunol. 2024, 3, kyae002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villadsen, L.S.; Schuurman, J.; Beurskens, F.; Dam, T.N.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Skov, L.; Rygaard, J.; Voorhorst-Ogink, M.M.; Gerritsen, A.F.; van Dijk, M.A.; et al. Resolution of Psoriasis upon Blockade of IL-15 Biological Activity in a Xenograft Mouse Model. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1571–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückert, R.; Asadullah, K.; Seifert, M.; Budagian, V.M.; Arnold, R.; Trombotto, C.; Paus, R.; Bulfone-Paus, S. Inhibition of Keratinocyte Apoptosis by IL-15: A New Parameter in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis? J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 2240–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlen, H.; Yousefi, S.; Simon, H.-U.; Simon, D. IL-15 Expression Pattern in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 181, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Carmona, A.; Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Corell, A. Role of Interleukins in Dermatology: Exploring the Immune Mechanisms in Skin Diseases. JEADV Clin. Pract. 2024, 3, 1381–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneat, A.; Rueda, V.; Patel, H.; Brune, Z.; Sherry, B.; Shih, A.; Kaplan, S.; Rao, A.; Lee, A.; Varghese, A.; et al. Elevation of Plasma IL-15 and RANTES as Potential Biomarkers of Healing in Chronic Venous Ulcerations: A Pilot Study. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mack, M.R.; Brestoff, J.R.; Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; Trier, A.M.; Yang, T.-L.B.; McCullen, M.; Collins, P.L.; Niu, H.; Bodet, N.D.; Wagner, J.A.; et al. Blood Natural Killer Cell Deficiency Reveals an Immunotherapy Strategy for Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020, 12, eaay1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchaud, G.; Gehrke, S.; Krieg, C.; Kolios, A.; Hafner, J.; Navarini, A.A.; French, L.E.; Boyman, O. Epidermal IL-15Rα Acts as an Endogenous Antagonist of Psoriasiform Inflammation in Mouse and Man. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghraieb, A.; Keren, A.; Ginzburg, A.; Ullmann, Y.; Schrum, A.G.; Paus, R.; Gilhar, A. iNKT Cells Ameliorate Human Autoimmunity: Lessons from Alopecia Areata. J. Autoimmun. 2018, 91, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Kwon, H.-Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, H.-G.; Kang, N.-Y.; Chang, Y.-T. Development of a Fluorescent Probe for M2 Macrophages via Gating-Oriented Live-Cell Distinction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 2951–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Hu, K.H.; Kersten, K.; Courau, T.; Kuhn, N.F.; Zaleta-Linares, I.; Samad, B.; Combes, A.J.; Krummel, M.F. Critical Role of CD206+ Macrophages in Promoting a cDC1-NK-CD8 T Cell Anti-Tumor Immune Axis. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, A.; Matsuguchi, T.; Yamaki, K.; Hayakawa, T.; Yoshikai, Y. Interleukin-15 Prevents Mouse Mast Cell Apoptosis through STAT6-Mediated Bcl-xL Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26107–26113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meghnem, D.; Maillasson, M.; Barbieux, I.; Morisseau, S.; Keita, D.; Jacques, Y.; Quéméner, A.; Mortier, E. Selective Targeting of IL-15Rα Is Sufficient to Reduce Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 886213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Scala, F.; Demetrius, D.-L.; Gherardini, J.; Rodriguez-Feliz, J.; Kuka-Epstein, G.; Chéret, J.; Paus, R. IL-15 Prolongs Anagen, Stimulates Proliferation, and Suppresses Apoptosis in the Hair Matrix of Human Scalp Hair Follicles. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 165–170.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Mommaas, M.; Oppel, T.; Schottdorf, E.-M.; Günther, S.; Moderer, M. Expression and Function of the Mannose Receptor CD206 on Epidermal Dendritic Cells in Inflammatory Skin Diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard-Chamard, H.; Mishra, H.K.; Nandi, M.; Mayhue, M.; Menendez, A.; Ilangumaran, S.; Ramanathan, S. Interleukin-15 in Autoimmunity. Cytokine 2020, 136, 155258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmberg, C.S.; Levinger, C.; Abongwa, M.; Ceriani, C.; Archin, N.M.; Siegel, M.; Ghosh, M.; Bosque, A. HIV-1 Latency Reversal and Immune Enhancing Activity of IL-15 Is Not Influenced by Sex Hormones. JCI Insight 2024, 9, e180609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.E.; Burrack, K.S.; Jameson, S.C.; Hamilton, S.E.; Lenz, L.L. NK Cell IL-10 Production Requires IL-15 and IL-10 Driven STAT3 Activation. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafei, H.; Basar, R.; Acharya, S.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Liu, P.; Zhang, D.; Bohn, T.; Liang, Q.; Mohanty, V.; Upadhyay, R.; et al. CREM Is a Regulatory Checkpoint of CAR and IL-15 Signalling in NK Cells. Nature 2025, 643, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Buhtoiarov, I.N.; Guo, H.; Cheung, N.-K.V. A Novel Multimeric IL15/IL15Rα-Fc Complex to Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1893500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, C.; Just, H.; Baumgartner Nielsen, J.; Thestrup-Pedersen, K.; Deleuran, M. Expression of CCR2 on Monocytes and Macrophages in Chronically Inflamed Skin in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2004, 84, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, M.; Yang, H.; Qu, R.; Qiu, Y.; Hao, J.; Bi, H.; Guo, D. Regulatory Mechanism of M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization in the Development of Autoimmune Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2023, 2023, 8821610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhode, P.R.; Egan, J.O.; Xu, W.; Hong, H.; Webb, G.M.; Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, X.; Wen, J.; You, L.; et al. Comparison of the Superagonist Complex, ALT-803, to IL15 as Cancer Immunotherapeutics in Animal Models. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevilla, A.; Chéret, J.; Lee, W.; Paus, R. Concentration-Dependent Stimulation of Melanin Production as Well as Melanocyte and Keratinocyte Proliferation by Melatonin in Human Eyelid Epidermis. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samra, T.; Gomez-Gomez, T.; Linowiecka, K.; Akhundlu, A.; Lopez de Mendoza, G.; Gompels, M.; Lee, W.W.; Gherardini, J.; Chéret, J.; Paus, R. Melatonin Exerts Prominent, Differential Epidermal and Dermal Anti-Aging Properties in Aged Human Eyelid Skin Ex Vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, T.; Park, S.B.; Inuzuka, T.; Zhang, M.; Allen, J.N.; Chayama, K.; Liang, T.J. Genetically Edited Hepatic Cells Expressing the NTCP-S267F Variant Are Resistant to Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 23, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Hasse, S.; Bodo, E.; Rose, C.; Funk, W.; Paus, R. Towards the Development of a Simplified Long-Term Organ Culture Method for Human Scalp Skin and Its Appendages under Serum-Free Conditions. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, M.; Pretzlaff, M.; Sulk, M.; Bähr, M.; Gherardini, J.; Uchida, Y.; Reibelt, M.; Kinori, M.; Rossi, A.; Bíró, T.; et al. Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide, Whose Receptor-Mediated Signalling May Be Defective in Alopecia Areata, Provides Protection from Hair Follicle Immune Privilege Collapse. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Gu, B.-H.; Park, S.Y.; Park, D.S.; Hwang, S.M.; Ji, W.; Kim, S.B.; Kim, M. Topical Administration of Coumarin Derivatives Alleviates Skin Inflammatory Symptoms in Atopic Dermatitis Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 186, 118004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, T.; Feng, S.; Zhu, H.; Bai, R.; Gan, X.; He, K.; Du, W.; Cheng, B.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Plasma-Treated Solutions in Atopic Dermatitis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 225, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zima, K.; Purzycka-Bohdan, D.; Szczerkowska-Dobosz, A.; Gabig-Cimińska, M. Keratinocyte-Mediated Antigen Presentation in Psoriasis: Preliminary Insights from In Vitro Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Li, X.; Huang, X.; Lin, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, X.; Chu, C.; Han, J.; Wang, F. Translation-Dependent Skin Hyperplasia Is Promoted by Type 1/17 Inflammation in Psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2023, 110, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson-Huang, L.M.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Pierson, K.C.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Cueto, I.; Lentini, T.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Krueger, J.G.; Haider, A.S.; et al. A Single Intradermal Injection of IFN-γ Induces an Inflammatory State in Both Non-Lesional Psoriatic and Healthy Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1177–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Chéret, J.; Scala, F.D.; Akhundlu, A.; Gherardini, J.; Demetrius, D.-L.; O’Sullivan, J.D.B.; Kuka Epstein, G.; Bauman, A.J.; Demetriades, C.; et al. mTORC1 Activity Negatively Regulates Human Hair Follicle Growth and Pigmentation. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e56574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardman, J.A.; Muneeb, F.; Pople, J.; Bhogal, R.; Shahmalak, A.; Paus, R. Human Perifollicular Macrophages Undergo Apoptosis, Express Wnt Ligands, and Switch Their Polarization during Catagen. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2543–2546.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkshaw, N.J.; Hardman, J.A.; Haslam, I.S.; Shahmalak, A.; Gilhar, A.; Lim, X.; Paus, R. Identifying Novel Strategies for Treating Human Hair Loss Disorders: Cyclosporine A Suppresses the Wnt Inhibitor, SFRP1, in the Dermal Papilla of Human Scalp Hair Follicles. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2003705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, S.-E.; Jeong, I.-H.; Lee, S.E. Mechanism Underlying Pruritus in Recessive Dystrophic Epidermolysis Bullosa: Role of Interleukin-31 from Mast Cells and Macrophages. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, P.B.; McDonald, E.; Bravo-Blas, A.; Baer, H.M.; Heawood, A.; Bain, C.C.; Mowat, A.M.; Clay, S.L.; Robertson, E.V.; Morton, F.; et al. The Mannose Receptor (CD206) Identifies a Population of Colonic Macrophages in Health and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani-Arabshahi, R.; Leboeuf, C.; Rivet, J.; Pisonero, H.; Zhao, W.-L.; Bachelez, H.; Ameisen, J.C.; Janin, A. Bcl-xL Gene Expression Correlated with Lower Apoptotic Cell Numbers and Shorter Progression-Free Survival in PCFCL. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 1703–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Lotti, R.; Kimura, H.; Hasegawa, A.; Bennett, B.; Amato, A.; Pincelli, C.; Abe, R. Advancements in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Treatment: Utilizing Fas-FasL Inhibition to Target Cell Death Signaling Pathways for Practical Human Application. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2025, 145, 962–965.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Antigen | Blocking | Primary Antibody | Secondary Antibody | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD68 | N/A | Rabbit anti-human CD68 [EPR23917-164] Abcam, ab213363 1:50 | Goat anti-rabbit IgG-Alexa Fluor® 555 Life Technology 1:400 | [6] |
| CD86 | 5% BSA in TBS | Mouse anti-human CD86 Novus Biologicals, NBP2-25208 1:50 | Goat anti-mouse IgG FITC Jackson ImmunoResearch 1:200 | [62] |
| CD206 | N/A | Rabbit anti-mannose receptor CD206 Abcam, ab64693 1:50 | Goat anti-rabbit IgG FITC Life Technology 1:200 | [38,62,65] |
| IL-10 | N/A | Mouse anti-human IL-10 R&D systems, MAB217 1:50 | Goat anti-mouse- Rhodamine Jackson ImmunoResearch 1:200 | [23,36] |
| IL-15Rα | 5% BSA in PBS | Mouse anti-IL-15Rα Abcam, ab91270, clone JM7A4 1:100 | Goat anti-mouse Alexa Fluor® 594 Life Technology 1:400 | [23,41] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Demetrius, D.-L.; Perez, S.M.; Suzuki, T.; Gherardini, J.; Lee, W.; Chéret, J.; Paus, R. IL-15 Promotes the Survival of Anti-Inflammatory (M2), Immunoinhibitory (IL-10+) Dermal Macrophages in Human Eyelid Skin Under IFNγ-Dominated Inflammatory Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167811
Demetrius D-L, Perez SM, Suzuki T, Gherardini J, Lee W, Chéret J, Paus R. IL-15 Promotes the Survival of Anti-Inflammatory (M2), Immunoinhibitory (IL-10+) Dermal Macrophages in Human Eyelid Skin Under IFNγ-Dominated Inflammatory Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167811
Chicago/Turabian StyleDemetrius, Dana-Lee, Sofia M. Perez, Takahiro Suzuki, Jennifer Gherardini, Wendy Lee, Jérémy Chéret, and Ralf Paus. 2025. "IL-15 Promotes the Survival of Anti-Inflammatory (M2), Immunoinhibitory (IL-10+) Dermal Macrophages in Human Eyelid Skin Under IFNγ-Dominated Inflammatory Conditions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167811
APA StyleDemetrius, D.-L., Perez, S. M., Suzuki, T., Gherardini, J., Lee, W., Chéret, J., & Paus, R. (2025). IL-15 Promotes the Survival of Anti-Inflammatory (M2), Immunoinhibitory (IL-10+) Dermal Macrophages in Human Eyelid Skin Under IFNγ-Dominated Inflammatory Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7811. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167811






