Molecular Iodine Induces Anti- and Pro-Neoplastic Effects in Prostate Cancer Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. I2 Decreases Cell Viability and Invasive Capacity in Prostate Cancer Cell Lines
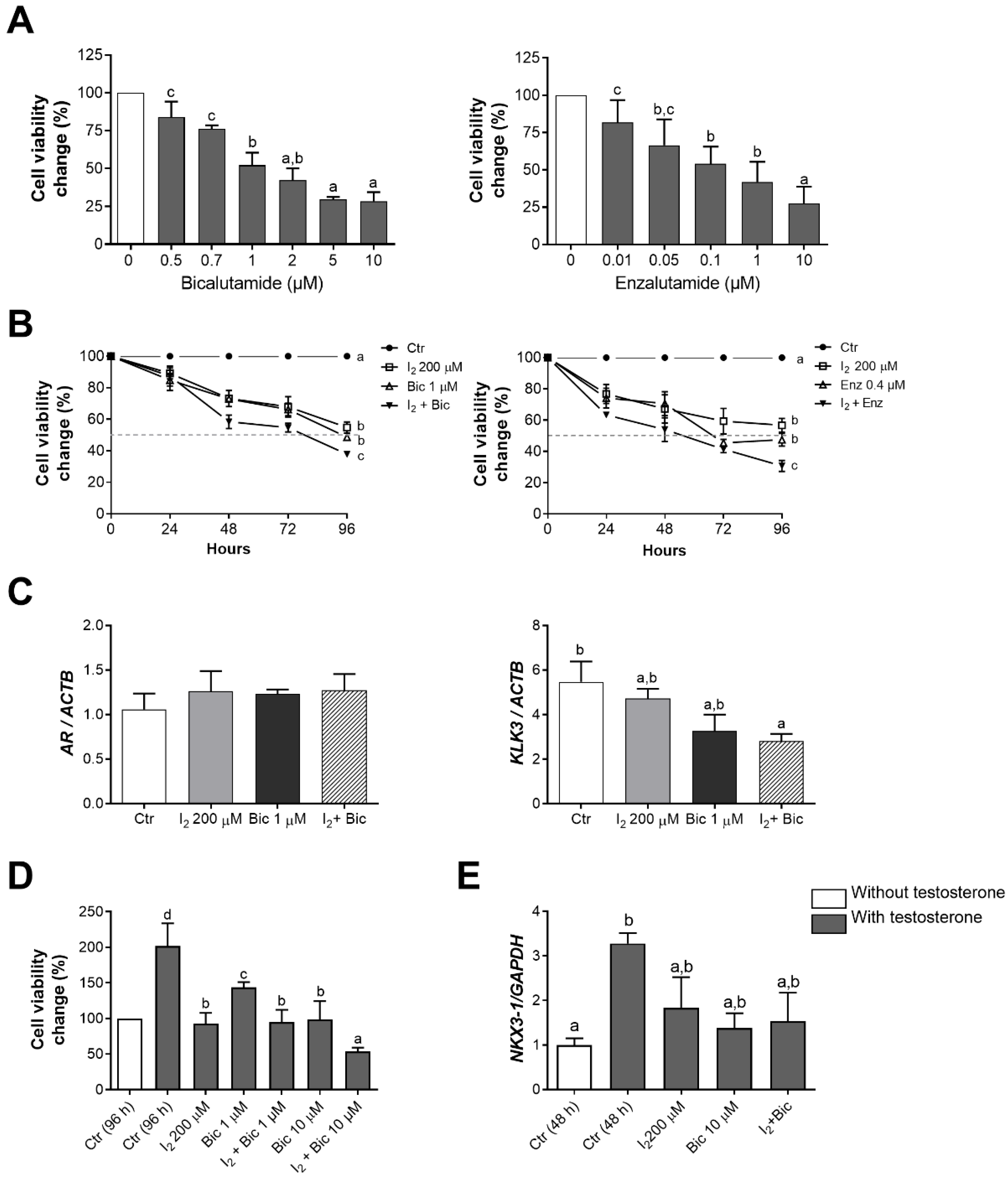
2.2. The Effects of I2 and Androgen Antagonists on the Loss of Cell Viability in LNCaP Cells
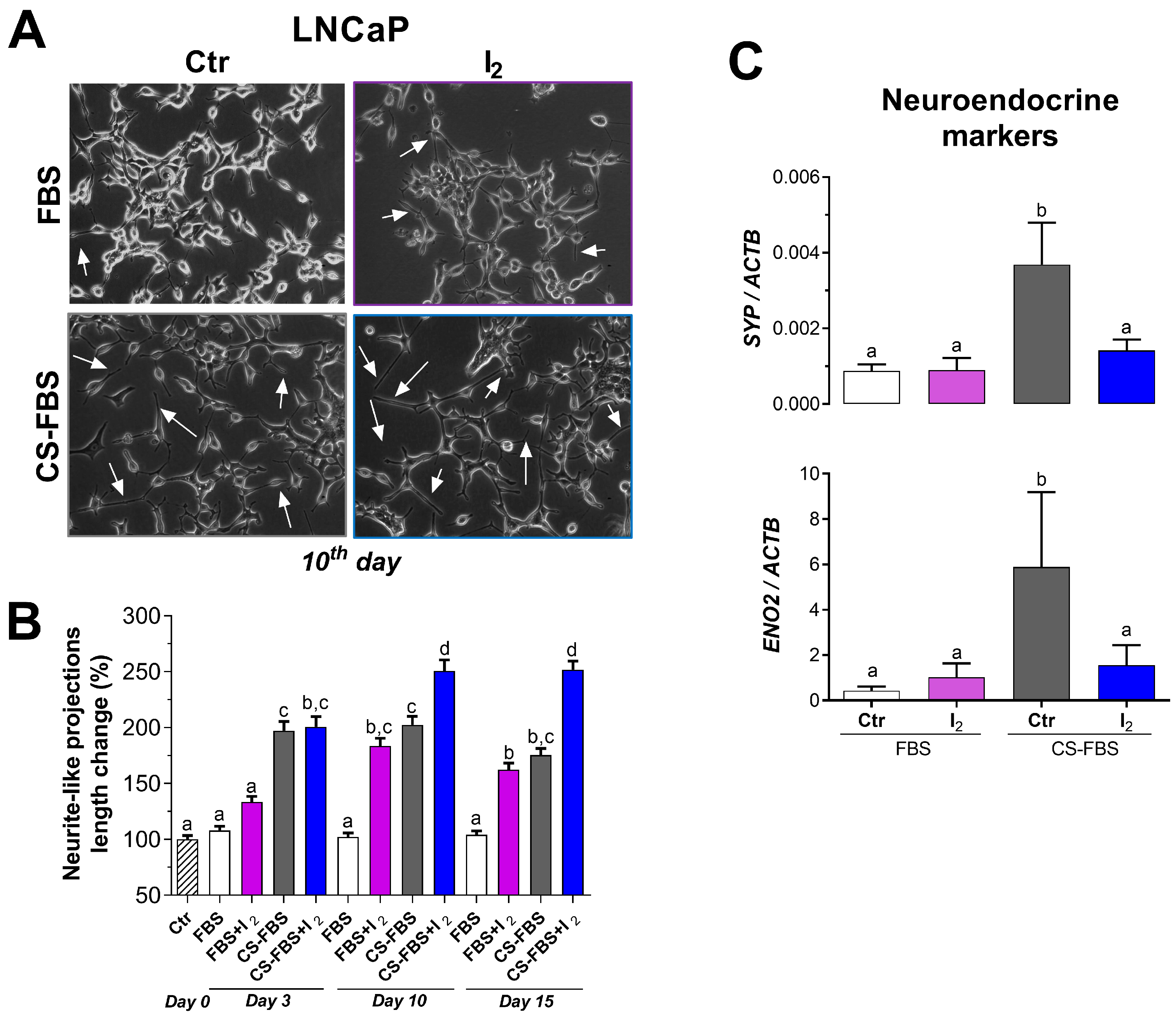
2.3. I2 Enhanced the Outgrowth of Neurite-like Projections Induced by Androgen Deficiency
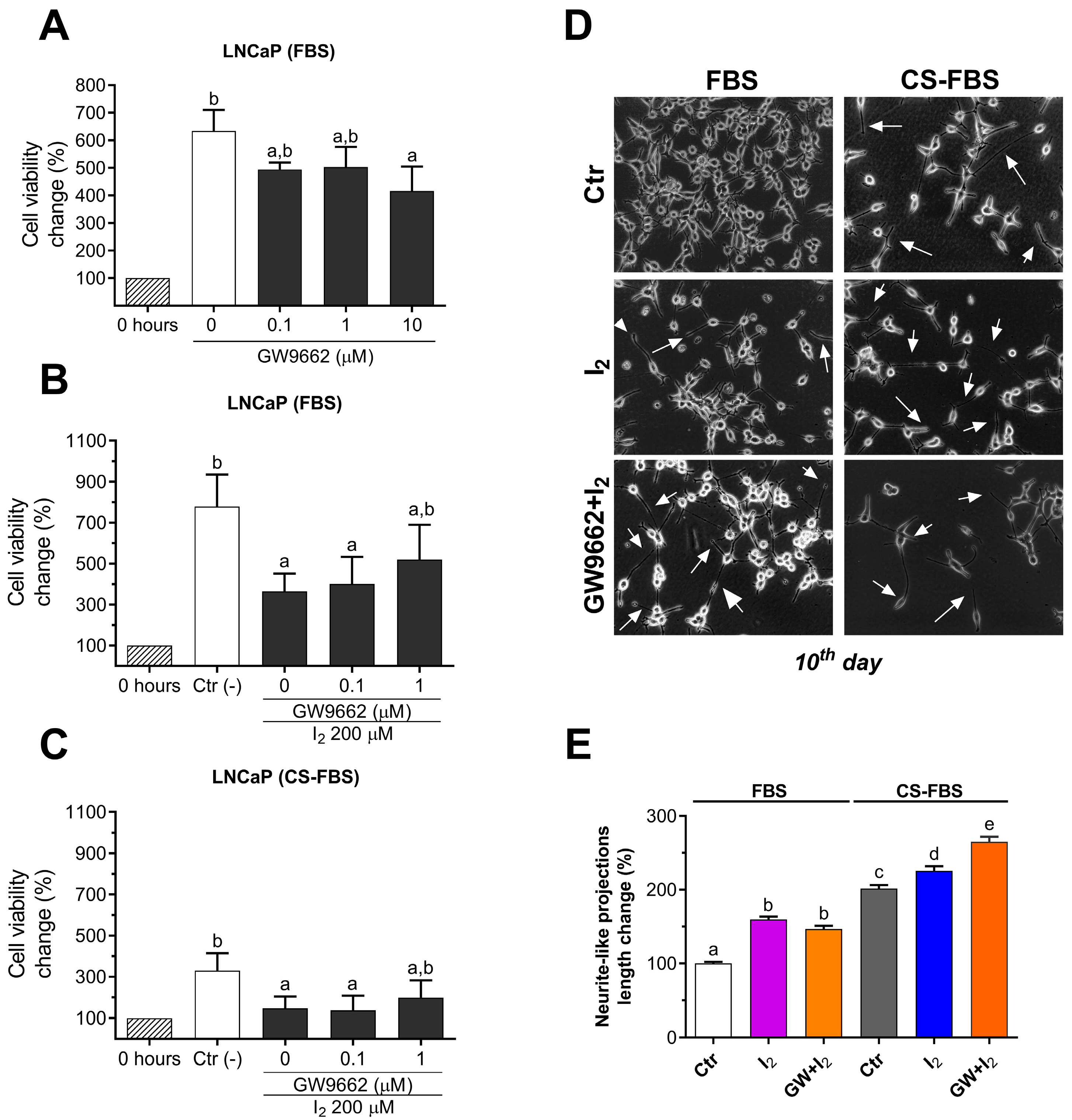
2.4. I2 Effects Are Not Mediated by PPARG in the LNCaP Cell Line
2.5. The Lipidic Response by Iodine Is Not Mediated by PPARG
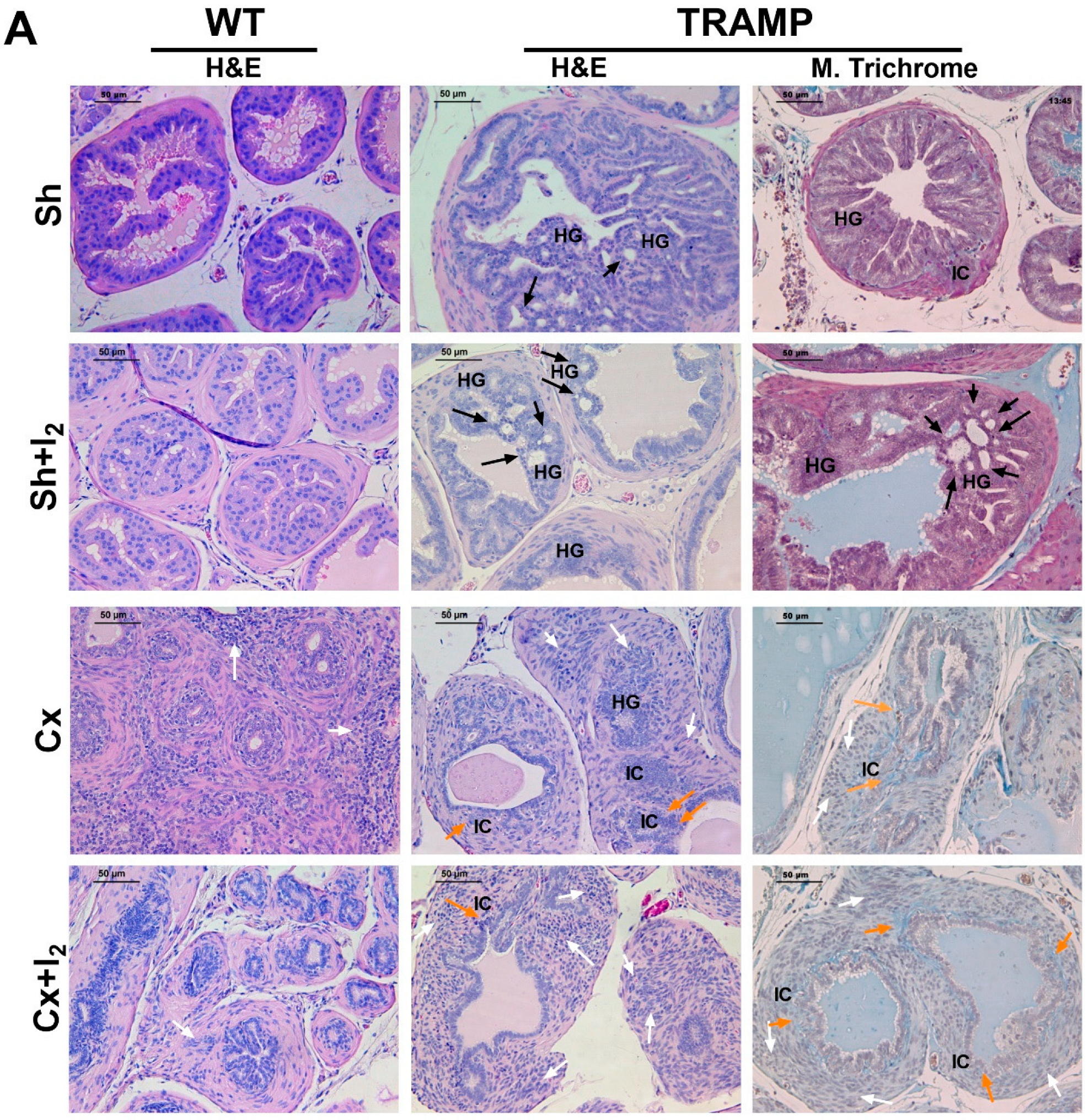
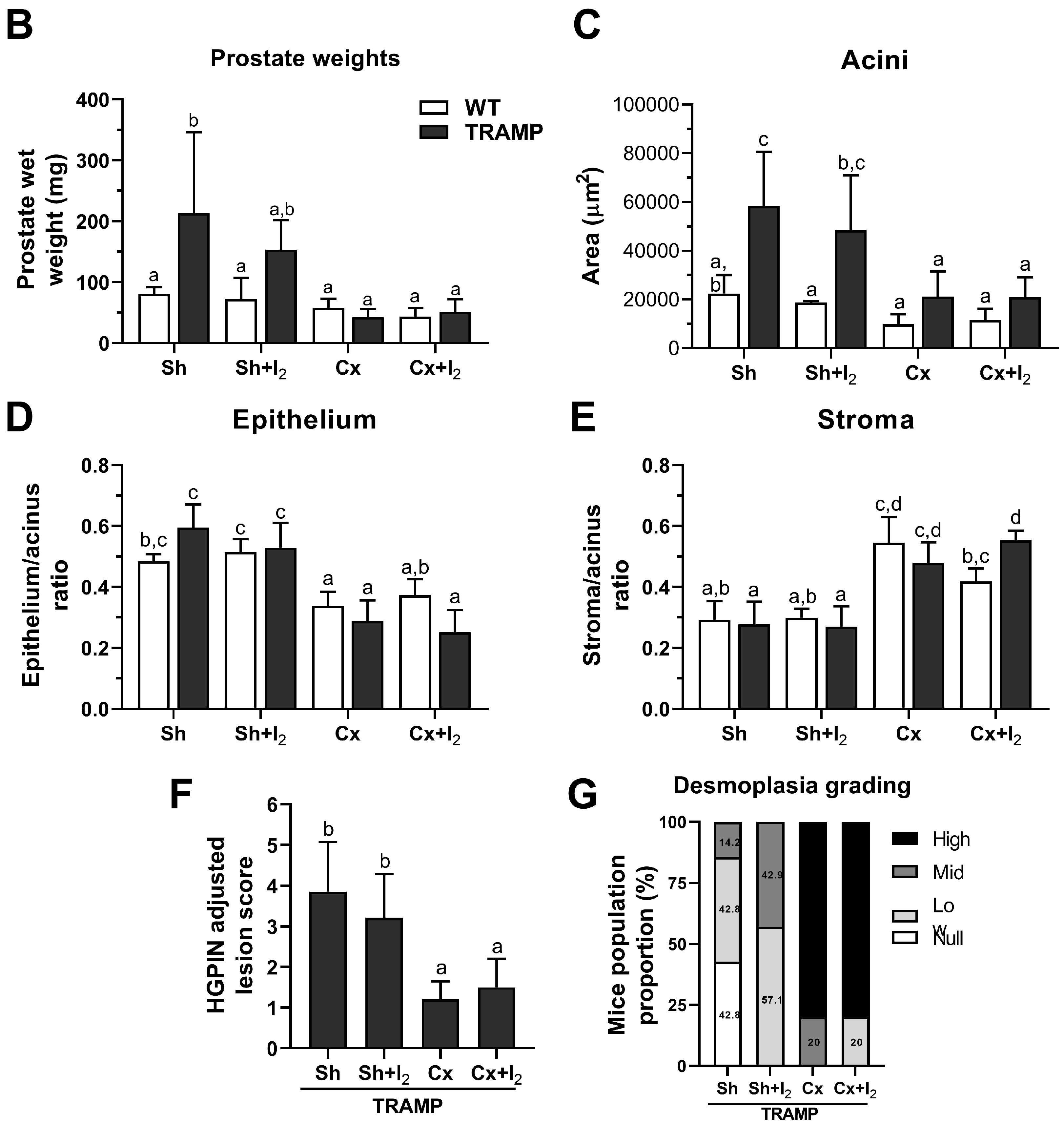
2.6. Effects of I2 and/or Castration on Histology and Prostate Pathology
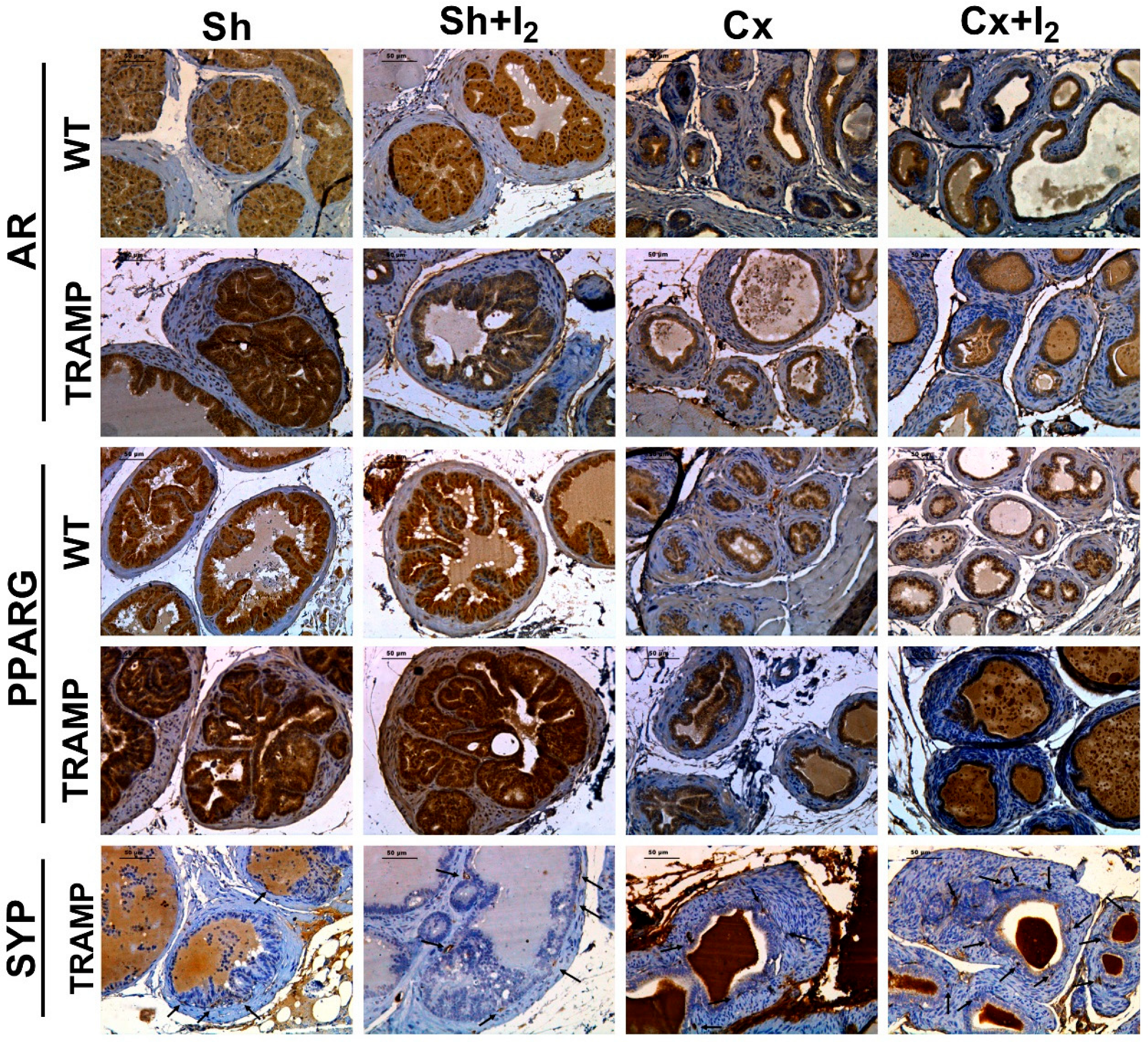
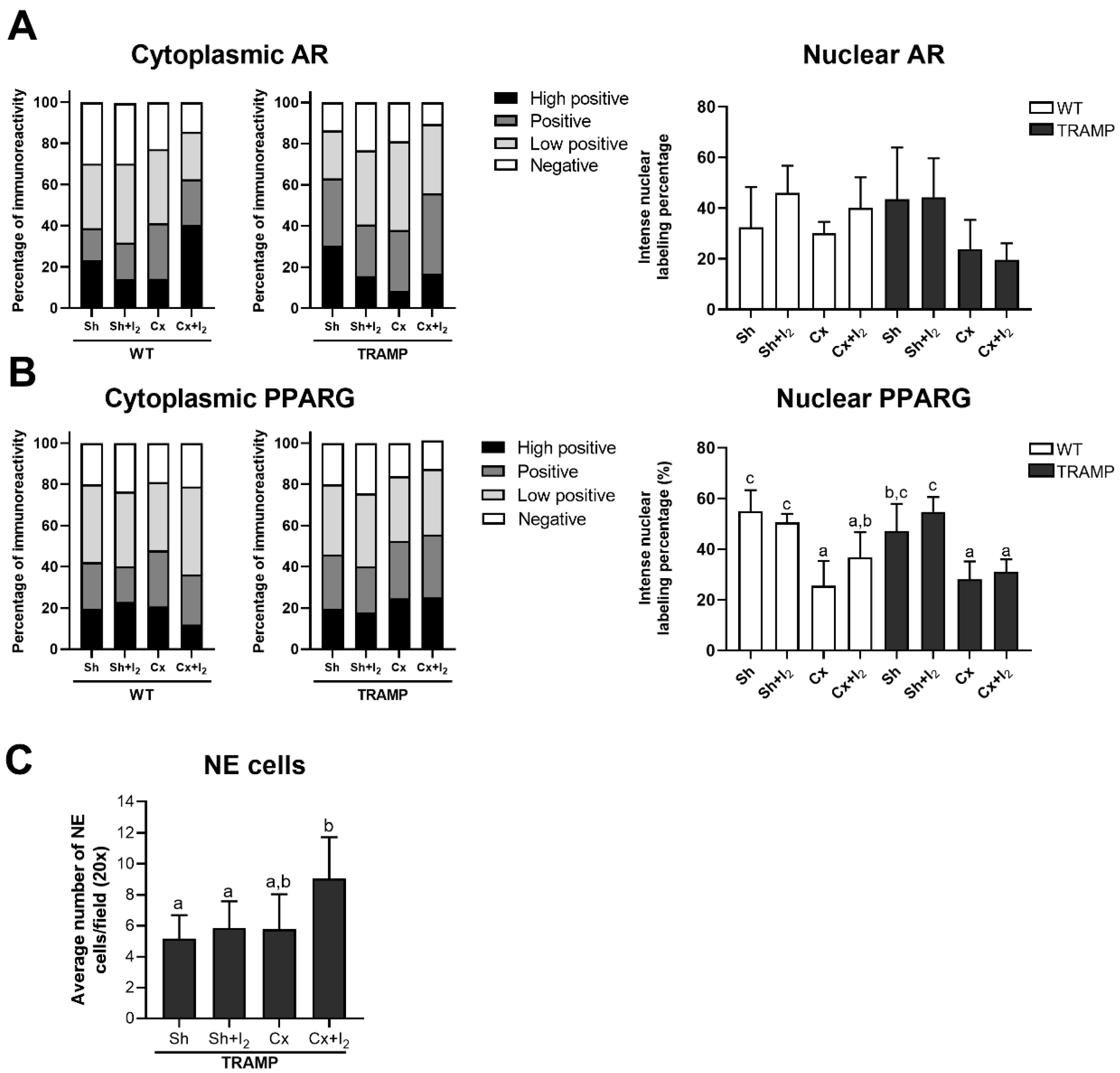
2.7. Effects of I2 and/or Castration on Immunopositivity for SYP, AR, and PPARG
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Models
4.2. Androgen and PPARG Inhibition
4.3. Research Design
4.3.1. Effects of I2 on Cell Viability and Invasive Capacity
4.3.2. Effects of I2 on the Androgen Antagonist Response
4.3.3. The Effects of I2 on the Acquisition of a NE-like Phenotype Induced by Androgen Deprivation in LNCaP Cells
4.3.4. Influence of Androgenic Status and Contribution of PPARG to I2 Effects
4.3.5. The Effects of I2 and Androgen Deficiency on the Prostatic Regulation of AR and PPARG and Cancer NE Progression in TRAMP Mice
4.4. Analytical Methods
4.4.1. Cell Viability
4.4.2. Intracellular Lipid Content
4.4.3. Gene Expression
4.4.4. Invasion Assays
4.4.5. Histopathology Analysis
4.4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.4.7. IHC Immunolabeling Quantification
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTB | Beta-actin |
| AR | Androgen Receptor |
| ENO2 | Enolase 2 |
| FASN | Fatty Acid Synthase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| HGPIN | High-Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia |
| KLK3 | Kallikrein-related peptidase 3 |
| NE | Neuroendocrine |
| NKX3-1 | NK3 homeobox 1 |
| PCNA | Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen |
| PPARG | Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma |
| SREBF1 | Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Transcription |
| SYP | Synaptophysin |
| TRAMP | Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of the Mouse Prostate |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, W.; Huang, J. Neuroendocrine Cells of the Prostate: Histology, Biological Functions, and Molecular Mechanisms. Precis. Clin. Med. 2021, 4, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.K.; Chugh, N.; Tripathi, M. Neuroendocrine Differentiation of Prostate Cancer—An Intriguing Example of Tumor Evolution at Play. Cancers 2019, 11, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.H.; Beltran, H.; Zoubeidi, A. Cellular Plasticity and the Neuroendocrine Phenotype in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2018, 15, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.D.; Choo, R.; Huang, J. Neuroendocrine Differentiation in Prostate Cancer: A Mechanism of Radioresistance and Treatment Failure. Front. Oncol. 2015, 5, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrenti, S.; Baldini, E.; Pironi, D.; Lauro, A.; D’orazi, V.; Tartaglia, F.; Tripodi, D.; Lori, E.; Gagliardi, F.; Praticò, M.; et al. Iodine: Its Role in Thyroid Hormone Biosynthesis and Beyond. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendieta, I.; Nuñez-Anita, R.E.; Nava-Villalba, M.; Zambrano-Estrada, X.; Delgado-González, E.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C. Molecular Iodine Exerts Antineoplastic Effects by Diminishing Proliferation and Invasive Potential and Activating the Immune Response in Mammary Cancer Xenografts. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-León, W.; Mendieta, I.; Delgado-González, E.; Aceves, C.; Anguiano, B. Molecular Iodine/Cyclophosphamide Synergism on Chemoresistant Neuroblastoma Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigoni-Ordóñez, G.D.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E.; Rosendo-Chalma, P.; Valencia-González, H.A.; Aceves, C.; García-Carrancá, A. Molecular Iodine Inhibits the Expression of Stemness Markers on Cancer Stem-like Cells of Established Cell Lines Derived from Cervical Cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava-Villalba, M.; Nuñez-Anita, R.E.; Bontempo, A.; Aceves, C. Activation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Is Crucial for Antitumoral Effects of 6-Iodolactone. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olvera-Caltzontzin, P.; Delgado, G.; Aceves, C.; Anguiano, B. Iodine Uptake and Prostate Cancer in the TRAMP Mouse Model. Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintero-García, M.; Delgado-González, E.; Sánchez-Tusie, A.; Vázquez, M.; Aceves, C.; Anguiano, B. Iodine Prevents the Increase of Testosterone-Induced Oxidative Stress in a Model of Rat Prostatic Hyperplasia. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 115, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, N.; Sosa, S.; Delgado, G.; Aceves, C.; Anguiano, B. Uptake and Antitumoral Effects of Iodine and 6-Iodolactone in Differentiated and Undifferentiated Human Prostate Cancer Cell Lines. Prostate 2013, 73, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anguiano, B.; Álvarez, L.; Delgado-González, E.; Ortiz-Martínez, Z.; Montes de Oca, C.; Morales, G.; Aceves, C. Protective Effects of Iodine on Rat Prostate Inflammation Induced by Sex Hormones and on the DU145 Prostate Cancer Cell Line Treated with TNF. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2023, 572, 111957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elix, C.C.; Salgia, M.M.; Otto-Duessel, M.; Copeland, B.T.; Yoo, C.; Lee, M.; Tew, B.Y.; Ann, D.; Pal, S.K.; Jones, J.O. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Controls Prostate Cancer Cell Growth through AR-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms. Prostate 2020, 80, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Mui, E.; Galbraith, L.; Patel, R.; Tan, E.H.; Salji, M.; Rust, A.G.; Repiscak, P.; Hedley, A.; Markert, E.; et al. Sleeping Beauty Screen Reveals Pparg Activation in Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 8290–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lu, T.; Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, F. Upregulated PPARG2 Facilitates Interaction with Demethylated AKAP12 Gene Promoter and Suppresses Proliferation in Prostate Cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, D.W.; Jiang, M.; Murphy, T.A.; Yi, Y.; Konvinse, K.C.; Franco, O.E.; Wang, Y.; Young, J.D.; Hayward, S.W. PPARγ Isoforms Differentially Regulate Metabolic Networks to Mediate Mouse Prostatic Epithelial Differentiation. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokpa, E.; Moss, P.E.; Stewart, L.M.V. Crosstalk between the Androgen Receptor and PPAR Gamma Signaling Pathways in the Prostate. PPAR Res. 2017, 2017, 9456020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, P.E.; Lyles, B.E.; Stewart, L.M.V. The PPARγ Ligand Ciglitazone Regulates Androgen Receptor Activation Differently in Androgen-Dependent versus Androgen-Independent Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 3478–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.C.; Gao, A.C.; Lai, C.H.; Hsieh, J.T.; Lin, H. Induction of Neuroendocrine Differentiation in Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer Cells by Adipocyte Differentiation-Related Protein (ADRP) Delivered by Exosomes. Cancer Lett. 2017, 391, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, S.W.; Cunha, G.R. The Prostate: Development and Physiology. Radiol. Clin. North. Am. 2000, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, J.V.; Van Veldhoven, P.P.; Esquenet, M.; Heyns, W.; Verhoeven, G. Androgens Markedly Stimulate the Accumulation of Neutral Lipids in the Human Prostatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Line LNCaP. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 4468–4474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, J.V.; Verhoeven, G. Androgens and the Control of Lipid Metabolism in Human Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 65, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoykova, G.E.; Schlaepfer, I.R. Lipid Metabolism and Endocrine Resistance in Prostate Cancer, and New Opportunities for Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, P.P.; Banerjee, S.; Brown, T.R.; Zirkin, B.R. Androgen Action in Prostate Function and Disease. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2018, 6, 62–77. [Google Scholar]
- Buttyan, R.; Ghafar, M.A.; Shabsigh, A. The Effects of Androgen Deprivation on the Prostate Gland: Cell Death Mediated by Vascular Regression. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2000, 10, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkenburg, K.C.; Amend, S.R.; Pienta, K.J. Murine Prostate Micro-Dissection and Surgical Castration. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 2016, 53984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta, I.; Rodríguez-Gómez, G.; Rueda-Zarazúa, B.; Rodríguez-Castelán, J.; Álvarez-León, W.; Delgado-González, E.; Anguiano, B.; Vázquez-Martínez, O.; Díaz-Muñoz, M.; Aceves, C. Molecular Iodine Synergized and Sensitized Neuroblastoma Cells to the Antineoplastic Effect of ATRA. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2020, 27, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.A.; Iversen, P.; Schwier, P.; Corn, A.L.; Sandusky, G.; Graff, J.; Neubauer, B.L. Castration Triggers Growth of Previously Static Androgen-Independent Lesions in the Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of the Mouse Prostate (TRAMP) Model. Prostate 2005, 62, 322–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiwara, S.; Ishii, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kato, M.; Nishikawa, K.; Kanda, H.; Arima, K.; Watanabe, M.; Sugimura, Y. Castration-Induced Stromal Remodeling Disrupts the Reconstituted Prostate Epithelial Structure. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 670–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, S.; Abate-Shen, C. Modeling Prostate Cancer in Mice: Something Old, Something New, Something Premalignant, Something Metastatic. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013, 32, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceves, C.; Anguiano, B.; Delgado, G. The Extrathyronine Actions of Iodine as Antioxidant, Apoptotic, and Differentiation Factor in Various Tissues. Thyroid 2013, 23, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Vega, A.; Vega-Riveroll, L.; Ayala, T.; Peralta, G.; Torres-Martel, J.M.; Rojas, J.; Mondragón, P.; Domínguez, A.; De Obaldía, R.; Avecilla-Guerrero, C.; et al. Adjuvant Effect of Molecular Iodine in Conventional Chemotherapy for Breast Cancer. Randomized Pilot Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano-Estrada, X.; Landaverde-Quiroz, B.; Dueñas-Bocanegra, A.A.; De Paz-Campos, M.A.; Hernández-Alberto, G.; Solorio-Perusquia, B.; Trejo-Mandujano, M.; Pérez-Guerrero, L.; Delgado-González, E.; Anguiano, B.; et al. Molecular Iodine/Doxorubicin Neoadjuvant Treatment Impair Invasive Capacity and Attenuate Side Effect in Canine Mammary Cancer. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Micó, O.; Delgado-González, E.; Anguiano, B.; Vaca-Paniagua, F.; Medina-Rivera, A.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M.; Aceves, C. Effects of Molecular Iodine/Chemotherapy in the Immune Component of Breast Cancer Tumoral Microenvironment. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, Y.; Delgado, G.; Cárabez, A.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C. Iodine and Doxorubicin, a Good Combination for Mammary Cancer Treatment: Antineoplastic Adjuvancy, Chemoresistance Inhibition, and Cardioprotection. Mol. Cancer 2013, 12, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, K.; Kishore, U.; Metkari, S.M.; Madan, T. Immunomodulatory Role of Surfactant Protein-D in a Transgenic Adenocarcinoma of Mouse Prostate (TRAMP) Model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 930449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.H.; Izumi, K.; Lee, S.O.; Lin, W.J.; Yeh, S.; Chang, C. Anti-Androgen Receptor ASC-J9 versus Anti-Androgens MDV3100 (Enzalutamide) or Casodex (Bicalutamide) Leads to Opposite Effects on Prostate Cancer Metastasis via Differential Modulation of Macrophage Infiltration and STAT3-CCL2 Signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.; Song, L.; Wang, B.Y.; Rezazadeh Kalebasty, A.; Uchio, E.; Zi, X. Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy: A Review of Recent Advancements with Novel Treatment Methods and Efficacy. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2022, 10, 210–233. [Google Scholar]
- Frohlich, D.A.; McCabe, M.T.; Arnold, R.S.; Day, M.L. The Role of Nrf2 in Increased Reactive Oxygen Species and DNA Damage in Prostate Tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 4353–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendieta, I.; Leon-Pichardo, J.; Orizaga-Osti, G.; Juvera-Avalos, E.R.; Rangel-Chavez, U.; Delgado-Gonzalez, E.; Anguiano, B.; Aceves, C. Molecular Iodine Exhibited Differential Antiproliferative Actions in Progenitor and Stem Populations from Chemoresistant Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, C.S.; Pipas, J.M. T Antigens of Simian Virus 40: Molecular Chaperones for Viral Replication and Tumorigenesis. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2002, 66, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowska, M.M.; Degraff, D.J.; Yu, X.; Jin, R.J.; Chen, Z.; Borowsky, A.D.; Matusik, R.J. Mouse Models of Prostate Cancer: Picking the Best Model for the Question. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikkeland, J.; Jin, Y.; Saatcioglu, F. Methods to Assess Lipid Accumulation in Cancer Cells. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 542, 407–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttie, A.; Nyska, A.; Haseman, J.K.; Moser, G.J.; Hackett, T.R.; Goldsworthy, T.L. A Grading Scheme for the Assessment of Proliferative Lesions of the Mouse Prostate in the TRAMP Model. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, F.; Bukhari, A.B.; Malhotra, R.; De, A. IHC Profiler: An Open Source Plugin for the Quantitative Evaluation and Automated Scoring of Immunohistochemistry Images of Human Tissue Samples. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Montes de Oca, C.; Álvarez, L.; Aceves, C.; Anguiano, B. Molecular Iodine Induces Anti- and Pro-Neoplastic Effects in Prostate Cancer Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167800
Montes de Oca C, Álvarez L, Aceves C, Anguiano B. Molecular Iodine Induces Anti- and Pro-Neoplastic Effects in Prostate Cancer Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167800
Chicago/Turabian StyleMontes de Oca, Carlos, Lourdes Álvarez, Carmen Aceves, and Brenda Anguiano. 2025. "Molecular Iodine Induces Anti- and Pro-Neoplastic Effects in Prostate Cancer Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167800
APA StyleMontes de Oca, C., Álvarez, L., Aceves, C., & Anguiano, B. (2025). Molecular Iodine Induces Anti- and Pro-Neoplastic Effects in Prostate Cancer Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7800. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167800




