Significant Interplay Between Lipids, Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Blood Cells in an Outpatient Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Cytokine Values Below the Assay’s Standard Curve Limits
2.3. Biomarkers vs. Cytokines
2.4. Biomarkers vs. Hematology
2.5. CCGF Correlations
3. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Population
4.2. Sampling Procedures
4.3. Ethics
4.4. Proximity Extension Assay
4.5. STRING Images
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nedkoff, L.; Briffa, T.; Zemedikun, D.; Herrington, S.; Wright, F.L. Global Trends in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaeian, B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and aetiology of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen Carlsson, K.; Nilsson, K.; Wolden, M.L.; Faurby, M. Economic burden of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: A matched case-control study in more than 450,000 Swedish individuals. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2023, 23, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Zeng, X.; Wang, H.; Yin, P.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; Ran, S.; et al. Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases in China, 1990-2016: Findings From the 2016 Global Burden of Disease Study. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennini, F.S.; Scortichini, M.; Colivicchi, F.; Maggioni, A.P.; Sciattella, P. The Economic Burden of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Italy. Clin. Drug Investig. 2024, 44, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joynt Maddox, K.E.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Aparicio, H.J.; Commodore-Mensah, Y.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dowd, W.N.; Hernandez, A.F.; Khavjou, O.; Michos, E.D.; Palaniappan, L.; et al. Forecasting the Burden of Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke in the United States Through 2050-Prevalence of Risk Factors and Disease: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e65–e88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, D.S.; Elkind, M.S.V.; Deutsch, A.; Dowd, W.N.; Heidenreich, P.; Khavjou, O.; Mark, D.; Mussolino, M.E.; Ovbiagele, B.; Patel, S.S.; et al. Forecasting the Economic Burden of Cardiovascular Disease and Stroke in the United States Through 2050: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2024, 150, e89–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bornfeldt, K.E.; Linton, M.F.; Fisher, E.A.; Guyton, J.R. JCL roundtable: Lipids and inflammation in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2021, 15, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyu, K.Y.; Dimayuga, P.C.; Shah, P.K. Immunogenetics of Atherosclerosis-Link between Lipids, Immunity, and Genes. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2020, 22, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäck, M.; Yurdagul, A., Jr.; Tabas, I.; Öörni, K.; Kovanen, P.T. Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: Mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 389–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xie, L.; Cheng, C.; Xue, F.; Sun, C. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and cardiovascular diseases. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1409653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dhalla, N.S. The Role of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henein, M.Y.; Vancheri, S.; Longo, G.; Vancheri, F. The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maeyer, R.P.H.; Chambers, E.S. The impact of ageing on monocytes and macrophages. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 230, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre-Roig, C.; Braster, Q.; Ortega-Gomez, A.; Soehnlein, O. Neutrophils as regulators of cardiovascular inflammation. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2020, 17, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Scarpa, E.S.; Magnani, M. Human Red Blood Cells Modulate Cytokine Expression in Monocytes/Macrophages Under Anoxic Conditions. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 632682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Dewald, O.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Inflammatory mechanisms in myocardial infarction. Curr. Drug Targets Inflamm. Allergy 2003, 2, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsten, E.; Herbert, B.R. The emerging role of red blood cells in cytokine signalling and modulating immune cells. Blood Rev. 2020, 41, 100644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakogiannis, C.; Sachse, M.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Stellos, K. Platelet-derived chemokines in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maouia, A.; Rebetz, J.; Kapur, R.; Semple, J.W. The Immune Nature of Platelets Revisited. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2020, 34, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.B.; Eriksson, M.B.; Gordh, T.; Larsson, A.O. Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and Plasma Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.B.; Eriksson, M.; Gordh, T.; Larsson, A. Significant Associations Between Blood Cell Counts and a Large Number of Salivary Cytokines, Chemokines, and Growth Factors. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2025, 45, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunalp, S.; Helvaci, D.G.; Oner, A.; Bursalı, A.; Conforte, A.; Güner, H.; Karakülah, G.; Szegezdi, E.; Sag, D. TRAIL promotes the polarization of human macrophages toward a proinflammatory M1 phenotype and is associated with increased survival in cancer patients with high tumor macrophage content. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1209249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, R.; Ren, W.; Ya, G.; Wang, B.; He, J.; Ren, S.; Jiang, L.; Zhao, S. Role of chemokines in the crosstalk between tumor and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 1359–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, W.; Yi, Q. 91 Circulating inflammatory proteins and the risk of age-related macular degeneration: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 139, 112678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelman, L.; Pivovarova-Ramich, O.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Grune, T.; Aleksandrova, K. Cytokines for evaluation of chronic inflammatory status in ageing research: Reliability and phenotypic characterisation. Immun. Ageing 2019, 16, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, M.; Nakajima, H.; Toh, R.; Hirata, K.I.; Ishida, T. Cardioprotective Effects of High-Density Lipoprotein Beyond its Anti-Atherogenic Action. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wei, B.; Luo, Z. Impacts of pro-inflammatory cytokines variant on cardiometabolic profile and premature coronary artery disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Guo, Y.; Sun, H.; Zhang, W.; Hou, S.; Guo, Y.; Ma, X.; Meng, H. Exploration of the causal associations between circulating inflammatory proteins, immune cells, and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study and mediation analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 16, 1394738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravalet, N.; Guermouche, H.; Hirsch, P.; Picou, F.; Foucault, A.; Gallay, N.; Martignoles, J.A.; Beaud, J.; Suner, L.; Deswarte, C.; et al. Modulation of bone marrow and peripheral blood cytokine levels by age and clonal hematopoiesis in healthy individuals. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 255, 109730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, S.L.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.C.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X.D.; Wang, Z.K.; Wang, Y.C.; Xue, C.S.; Li, B.; Gao, D.L. Anti-inflammatory activities of hepatocyte growth factor in post-ischemic heart failure. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Maratos-Flier, E. Understanding the Physiology of FGF21. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2016, 78, 223–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, D.; Sens, J.; Brennig, S.; Brand, D.; Philipp, F.; Vollmer Barbosa, P.; Kuehle, J.; Steinemann, D.; Lenz, D.; Buchegger, T.; et al. Genetic Correction of IL-10RB Deficiency Reconstitutes Anti-Inflammatory Regulation in iPSC-Derived Macrophages. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, E.; Andersen, B. FGF19 and FGF21 for the Treatment of NASH-Two Sides of the Same Coin? Differential and Overlapping Effects of FGF19 and FGF21 From Mice to Human. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 601349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-j.; Ji, Y.-w.; Chen, J.-w.; Li, D.; Zhou, T.; Qi, P.; Wang, X.; Li, X.-f.; Zhang, Y.-f.; Yu, X.; et al. Targeted VEGFA therapy in regulating early acute kidney injury and late fibrosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2023, 44, 1815–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yin, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Kong, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wu, R.; Wang, N.; et al. IL-17C has a pathogenic role in kidney ischemia/reperfusion injury. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yin, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Kong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Chen, X.; Wang, F. IL-17C neutralization protects the kidney against acute injury and chronic injury. eBioMedicine 2023, 92, 104607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Dolegowka, K.; Pawlik, A.; Safranow, K.; Stepniewska, J.; Wisniewska, M.; Malyszko, J.; Ciechanowski, K. Association of FGF19, FGF21 and FGF23 with carbohydrate metabolism parameters and insulin resistance in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Appl. Biomed. 2020, 18, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Blair, J.E.A.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Lerma, E.V.; Mezue, K.; Molitch, M.; Mullens, W.; et al. Cardiorenal Syndrome: Classification, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawant, S.; Tucker, B.; Senanayake, P.; Waters, D.D.; Patel, S.; Rye, K.A.; Ong, K.L.; Cochran, B.J. The association between lipid levels and leukocyte count: A cross-sectional and longitudinal analysis of three large cohorts. Am. Heart J. Plus 2021, 4, 100024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkambule, B.B.; Chan, M.V.; Lachapelle, A.R.; Grech, J.; Thibord, F.; Chen, M.H.; Johnson, A.D. The association between platelet reactivity and lipoprotein levels in Framingham Heart Study participants. Thromb. Res. 2023, 225, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Autieri, M.V.; Scalia, R. Adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2021, 320, C375–C391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhangi, M.A.; Keshavarz, S.A.; Eshraghian, M.; Ostadrahimi, A.; Saboor-Yaraghi, A.A. White blood cell count in women: Relation to inflammatory biomarkers, haematological profiles, visceral adiposity, and other cardiovascular risk factors. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2013, 31, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, J.C.; Shatzel, J.J. The hematologic consequences of obesity. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, R.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Mirhosseini, N.; Lankarani, K.B.; Akbari, M.; Dadgostar, E.; Borhani-Haghighi, A.; Peymani, P.; Ahmadizar, F.; Asemi, Z. The effects of statin use on inflammatory markers among patients with metabolic syndrome and related disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 141, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, J.; Herre, M.; Dragomir, A.; Rabelo-Melo, F.; Svensson, A.; Thålin, C.; Rosell, A.; Hjalmar, V.; Wallén, H.; Lindman, H.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps promote cancer-associated inflammation and myocardial stress. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2049487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedervall, J.; Dragomir, A.; Saupe, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ärnlöv, J.; Larsson, E.; Dimberg, A.; Larsson, A.; Olsson, A.K. Pharmacological targeting of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 prevents cancer-associated kidney injury in mice. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1320009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastrocola, R.; Aragno, M.; Alloatti, G.; Collino, M.; Penna, C.; Pagliaro, P. Metaflammation: Tissue-Specific Alterations of the NLRP3 Inflammasome Platform in Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wu, H. Structural Mechanisms of NLRP3 Inflammasome Assembly and Activation. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 41, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennike, T.B. Advances in proteomics: Characterization of the innate immune system after birth and during inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1254948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, V.B.; Murphy, R.C.; Watson, S.P. Platelet lipidomics: Modern day perspective on lipid discovery and characterization in platelets. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1185–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, P.; Dahate, P.; Raghuwanshi, S.; Sharma, D.S.; Kovuru, N.; Gutti, U.; Yarla, N.S.; Gutti, R.K. Current Updates on Role of Lipids in Hematopoiesis. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, L.B.; Gordh, T.; Karlsten, R.; LoMartire, R.; Thor, A.; Tegelberg, Å. Intravenous S-ketamine’s analgesic efficacy in third molar surgery. A randomized placebo-controlled double-blind clinical trial. Br. J. Pain. 2024, 18, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.B.; Gordh, T.; Karlsten, R.; Thor, A.; Tegelberg, Å. Patient safety of adjunct pre-operative intravenous S-ketamine for pain relief in third molar surgery—A randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial. Br. J. Pain. 2024, 18, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, U.; Grubb, A.; Larsson, A.; Hansson, L.O.; Flodin, M.; Nordin, G.; Lindström, V.; Björk, J. The revised Lund-Malmö GFR estimating equation outperforms MDRD and CKD-EPI across GFR, age and BMI intervals in a large Swedish population. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 815–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMA Declaration of Helsinki—Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Available online: https://www.wma.net/policies-post/wma-declaration-of-helsinki-ethical-principles-for-medical-research-involving-human-subjects (accessed on 23 March 2022).
- What is PEA? Available online: https://olink.com/technology/what-is-pea (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Documents. User manual. Available online: https://olink.com/knowledge/documents?query=user%20manual (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Assarsson, E.; Lundberg, M.; Holmquist, G.; Björkesten, J.; Thorsen, S.B.; Ekman, D.; Eriksson, A.; Rennel Dickens, E.; Ohlsson, S.; Edfeldt, G.; et al. Homogenous 96-plex PEA immunoassay exhibiting high sensitivity, specificity, and excellent scalability. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skau, E.; Wagner, P.; Leppert, J.; Ärnlöv, J.; Hedberg, P. Are the results from a multiplex proteomic assay and a conventional immunoassay for NT-proBNP and GDF-15 comparable? Clin. Proteom. 2023, 20, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STRING: Functional Protein Association Networks. Available online: https://string-db.org (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
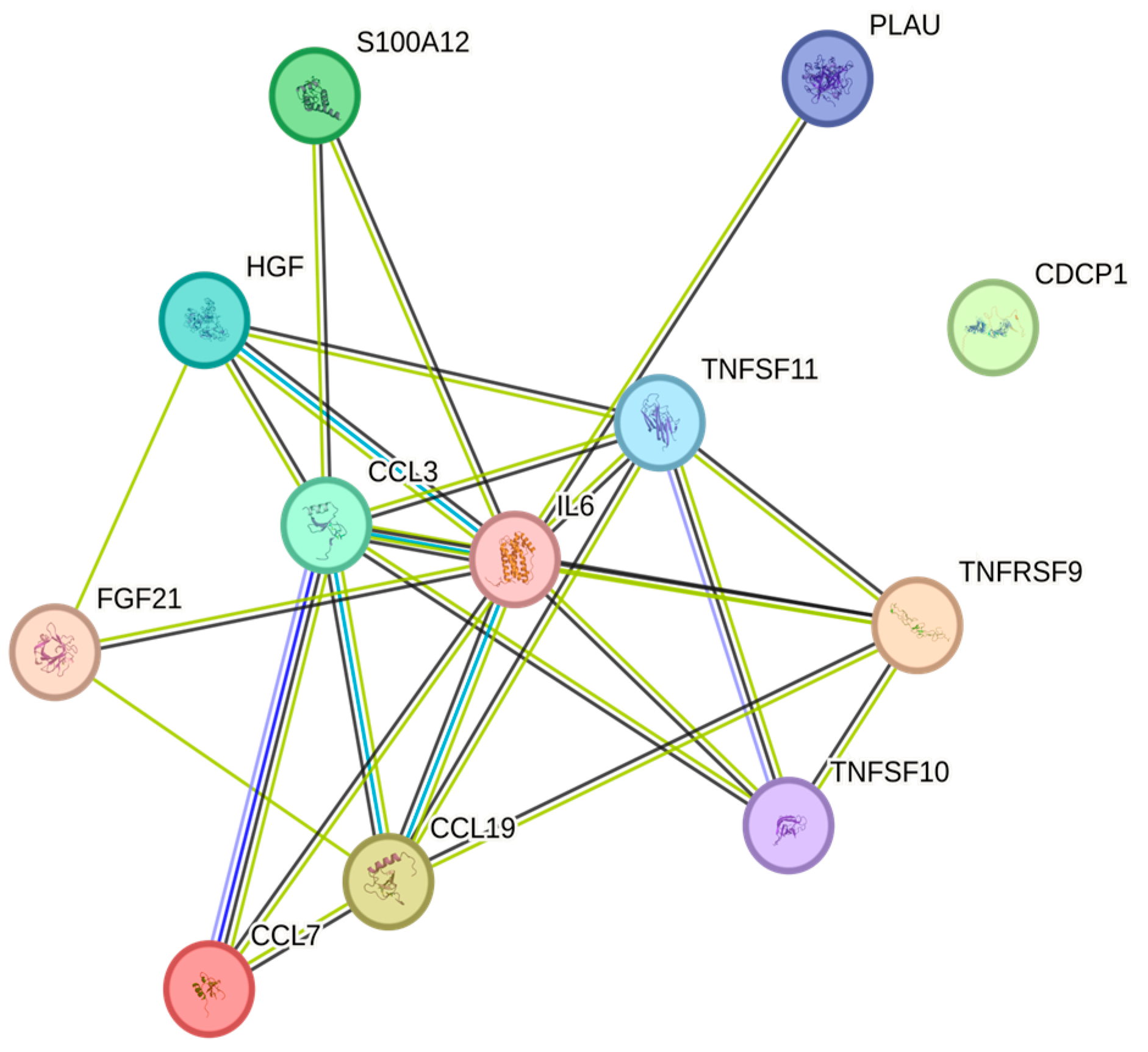

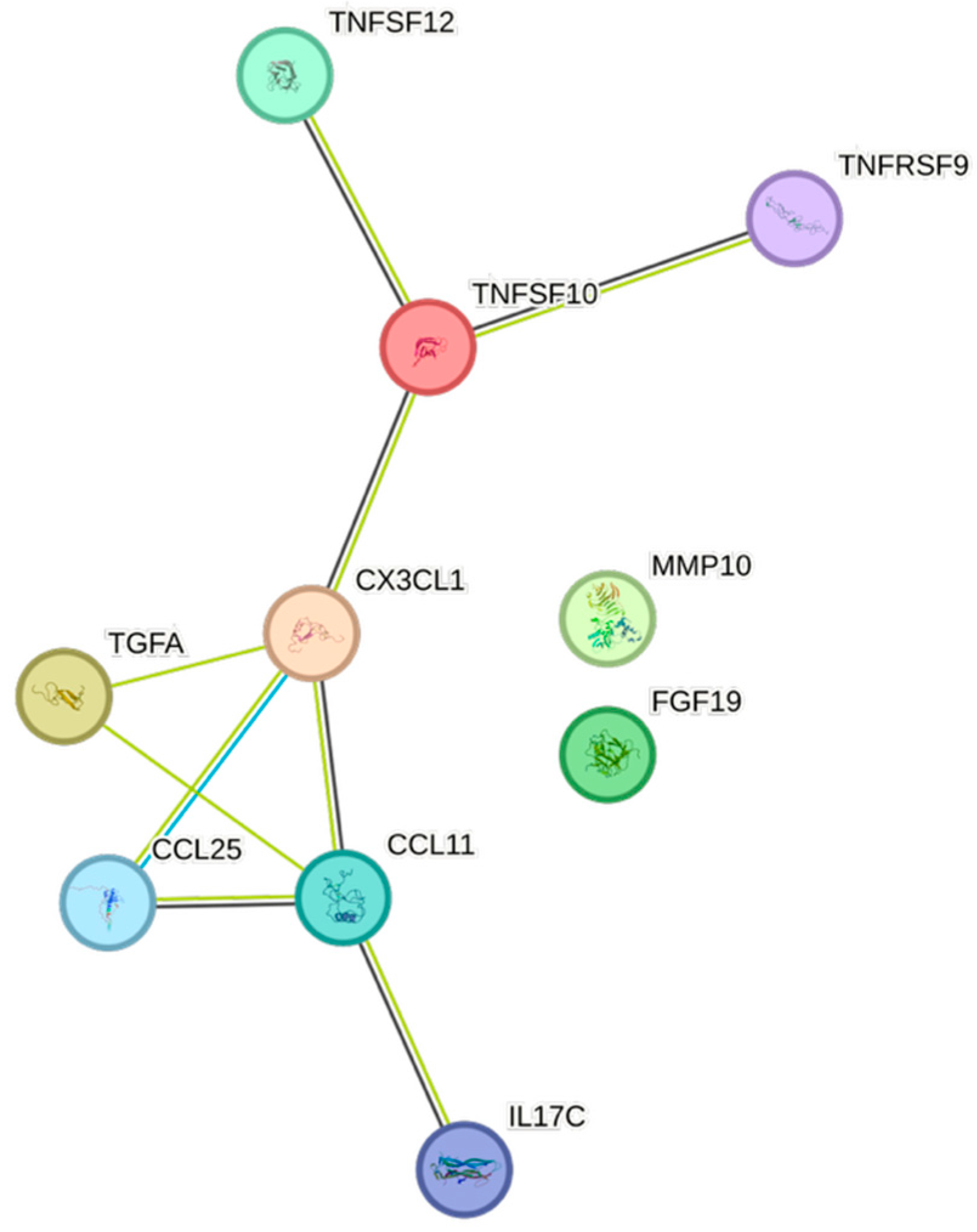
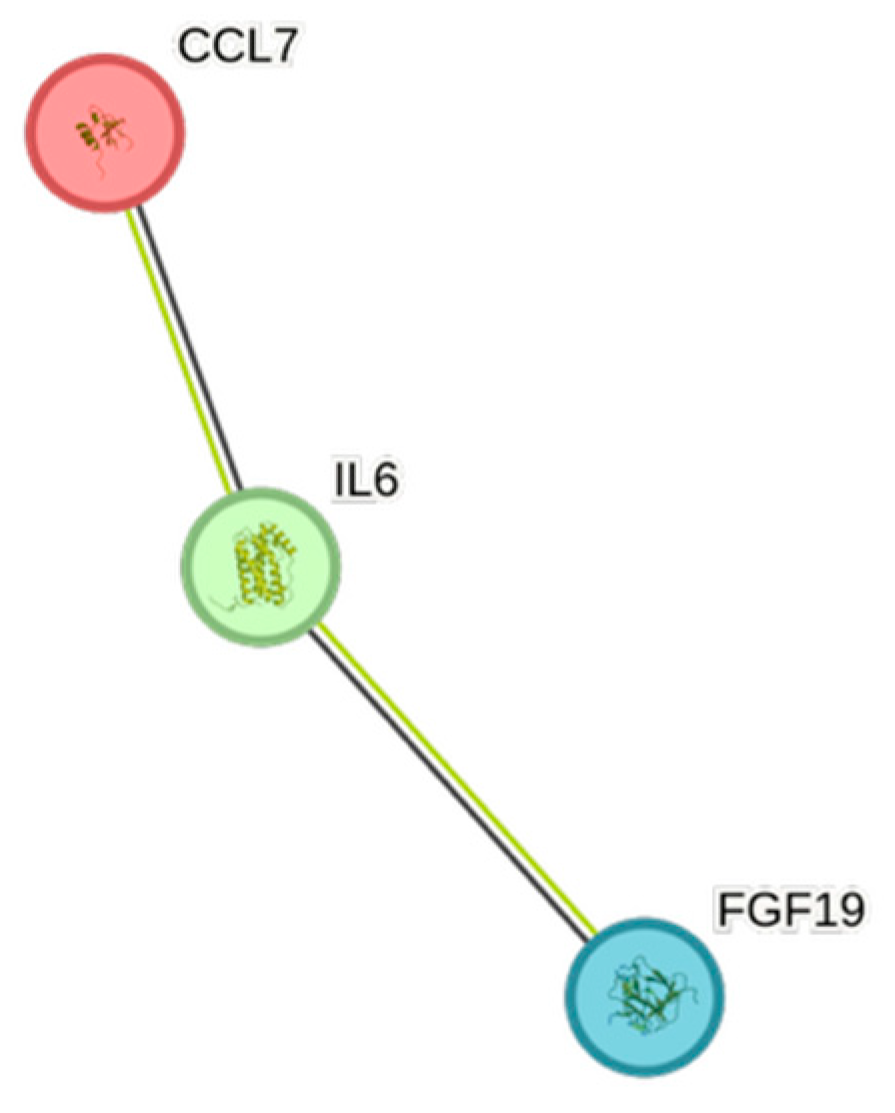
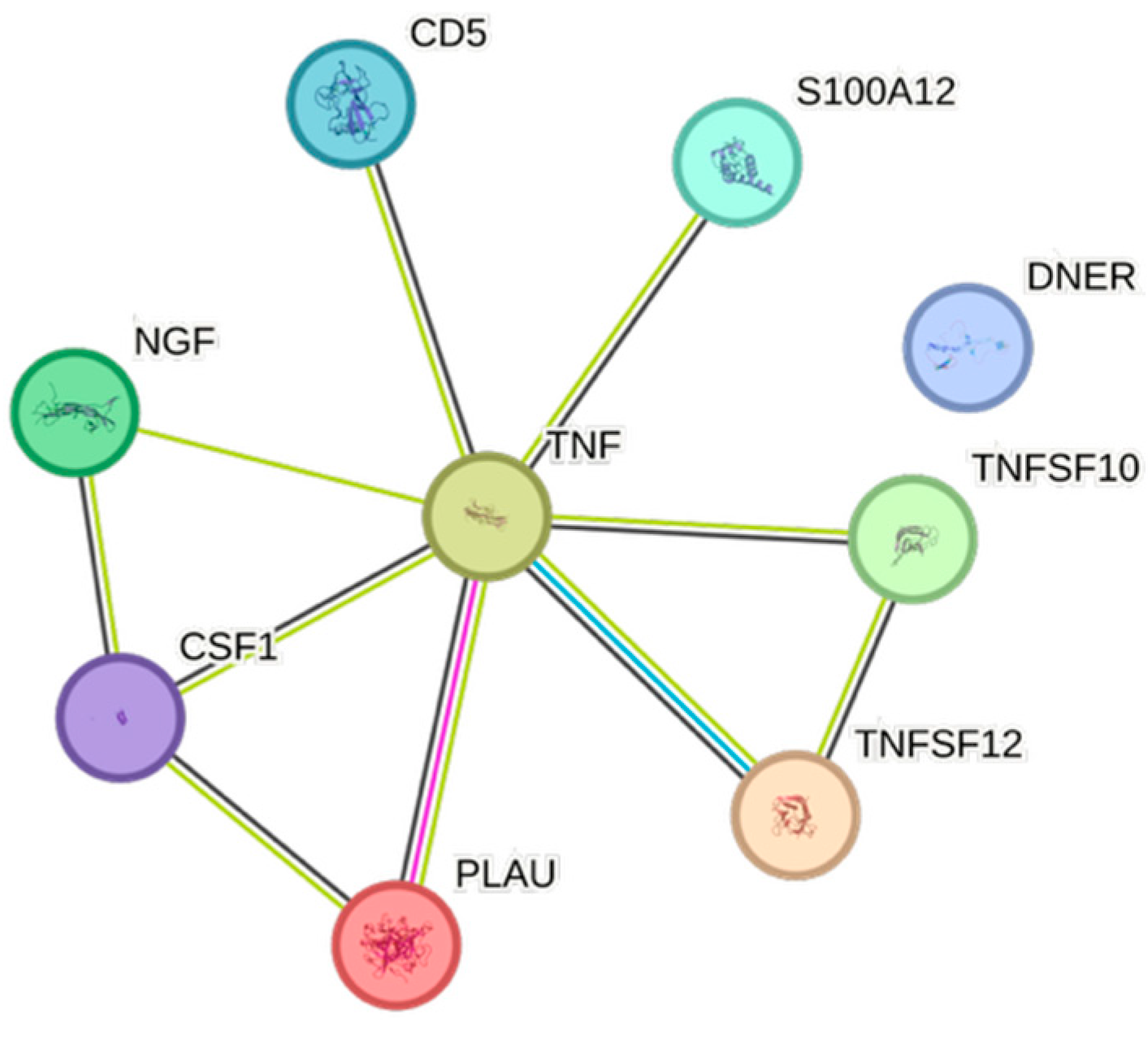
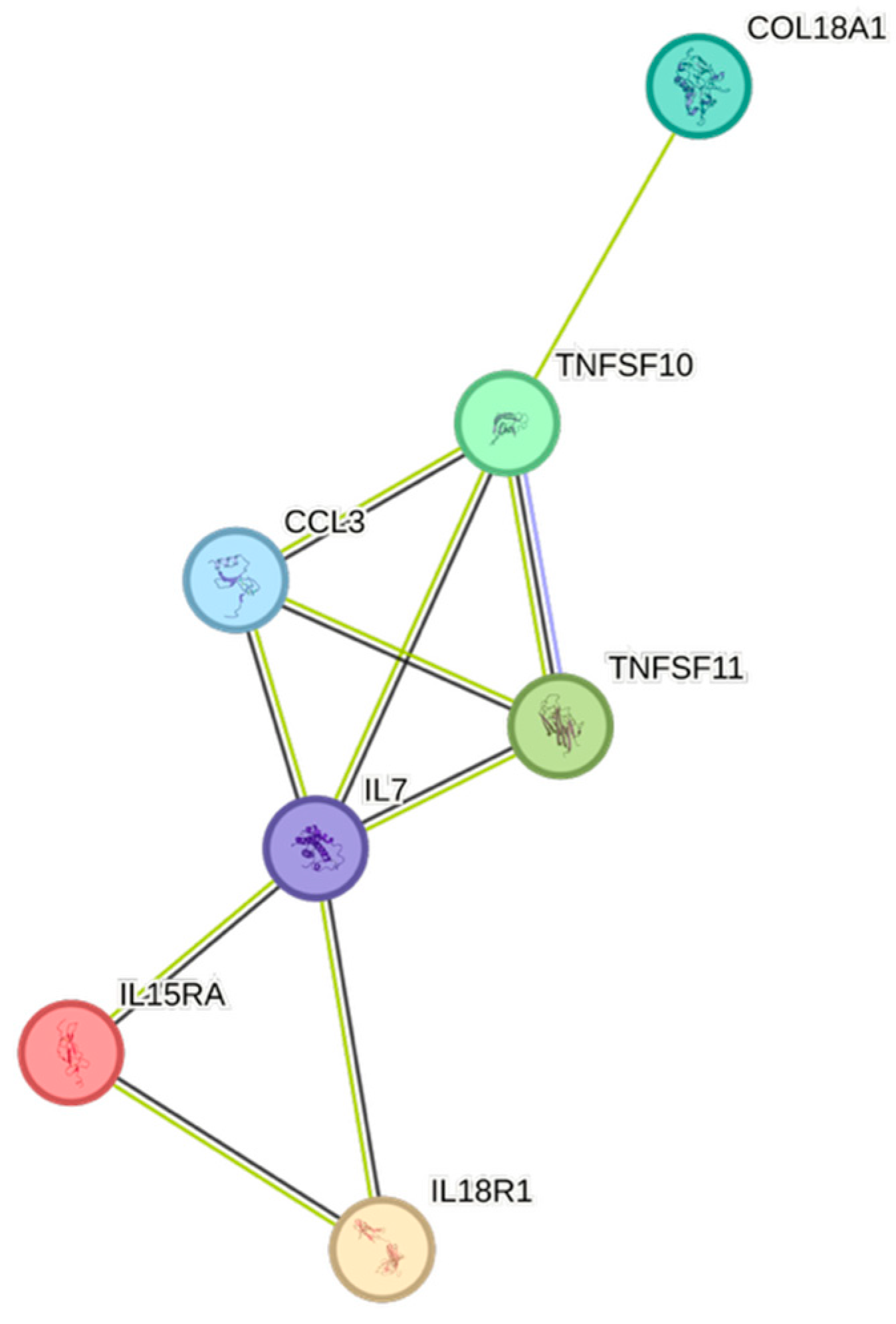
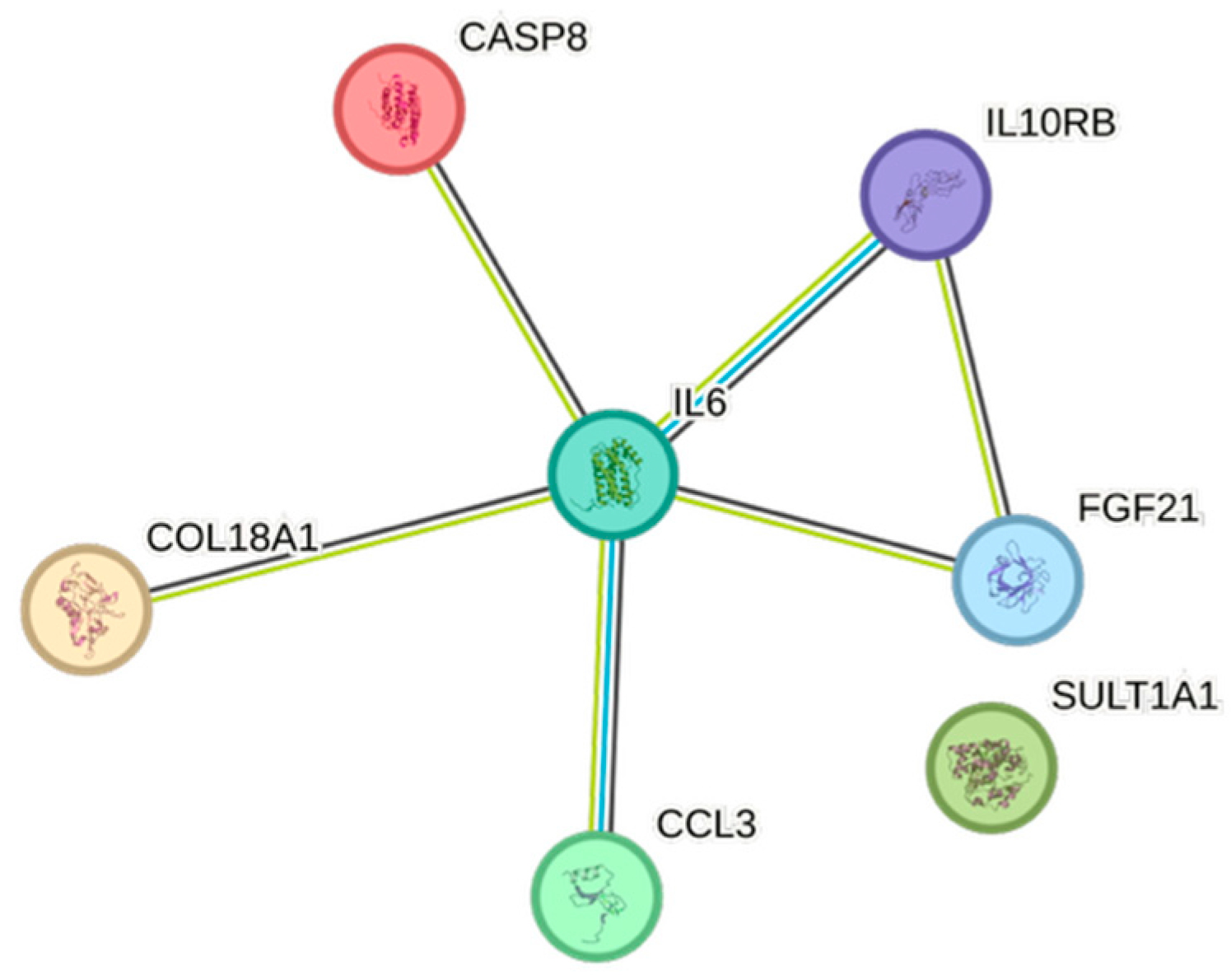
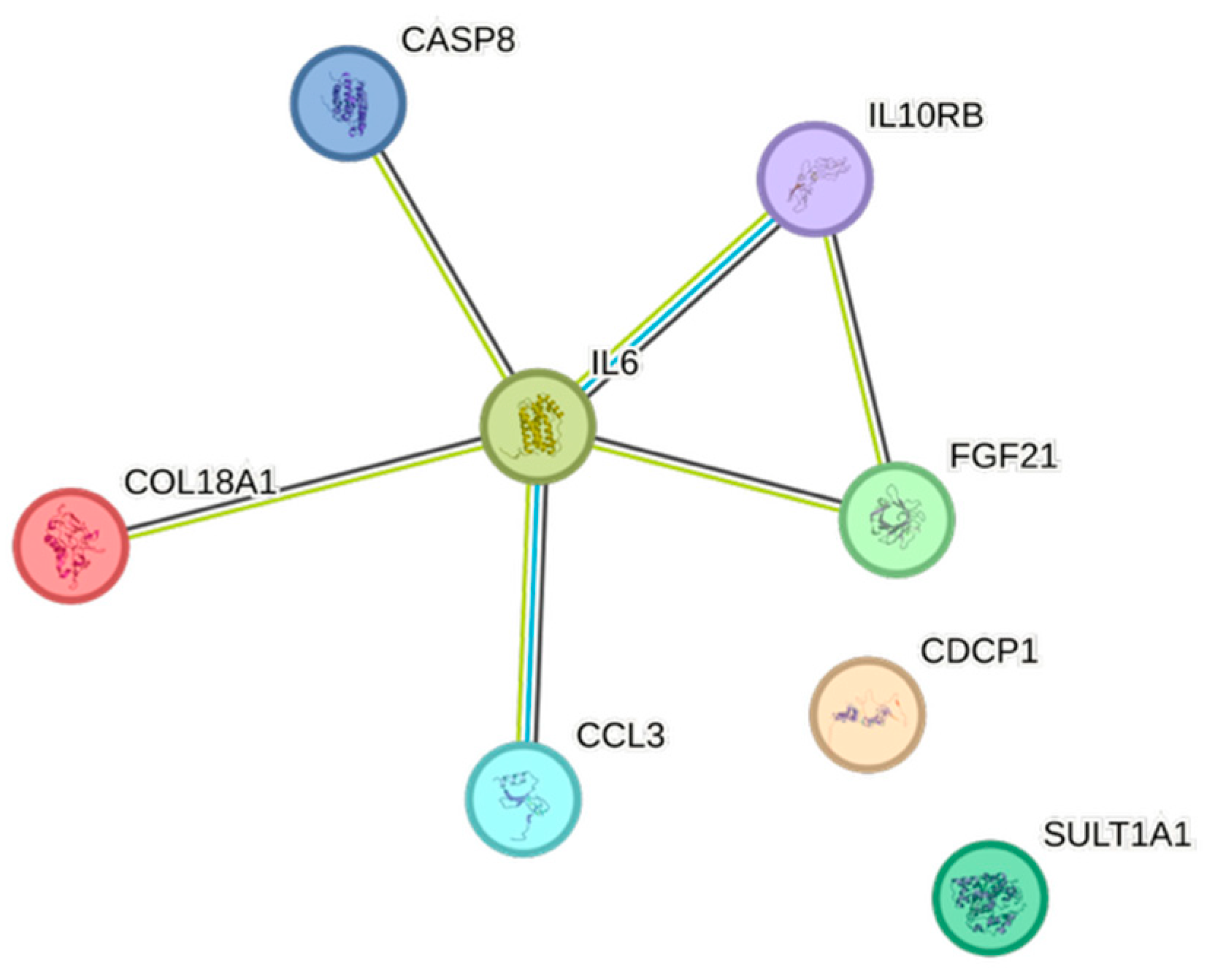

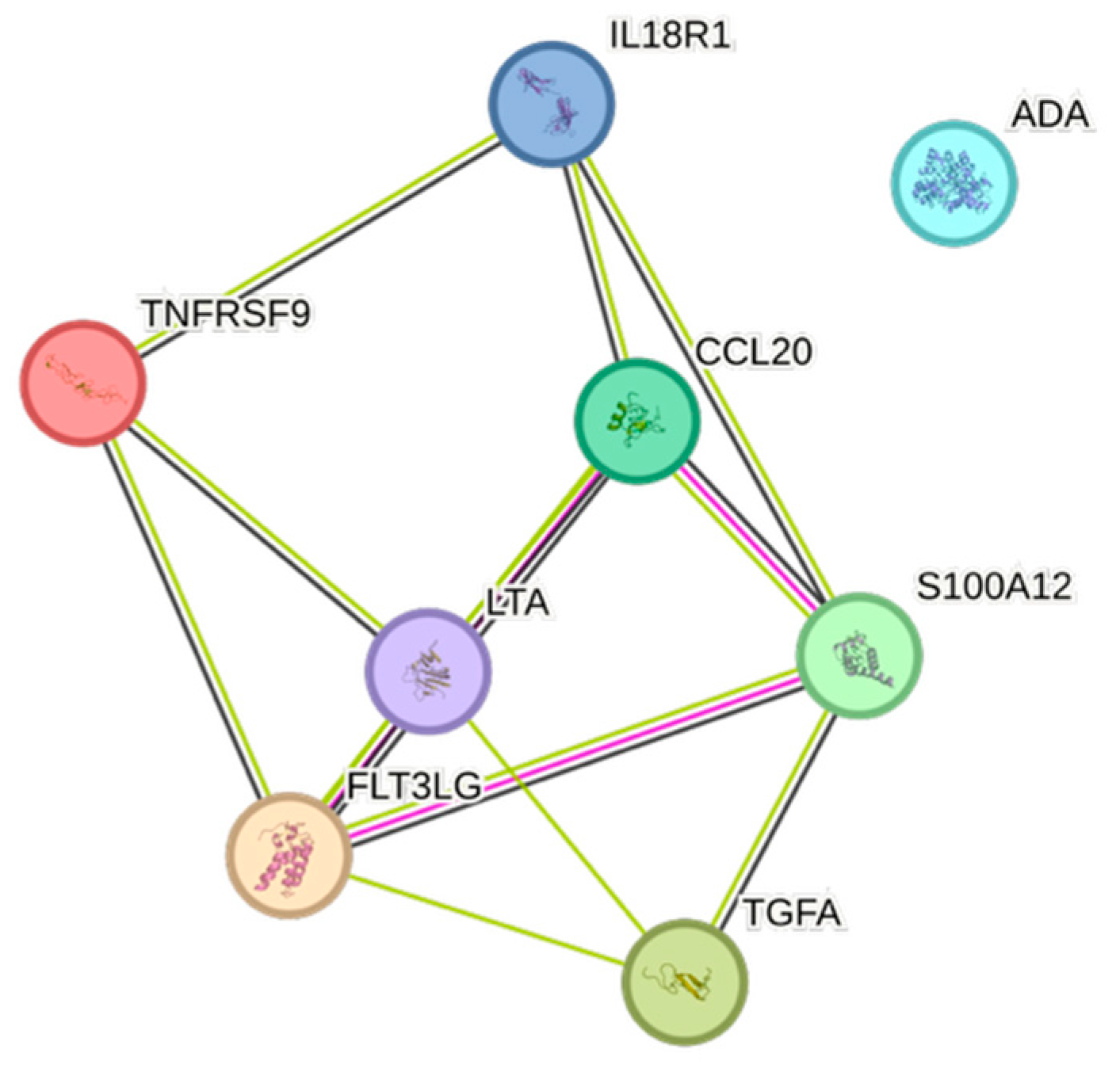
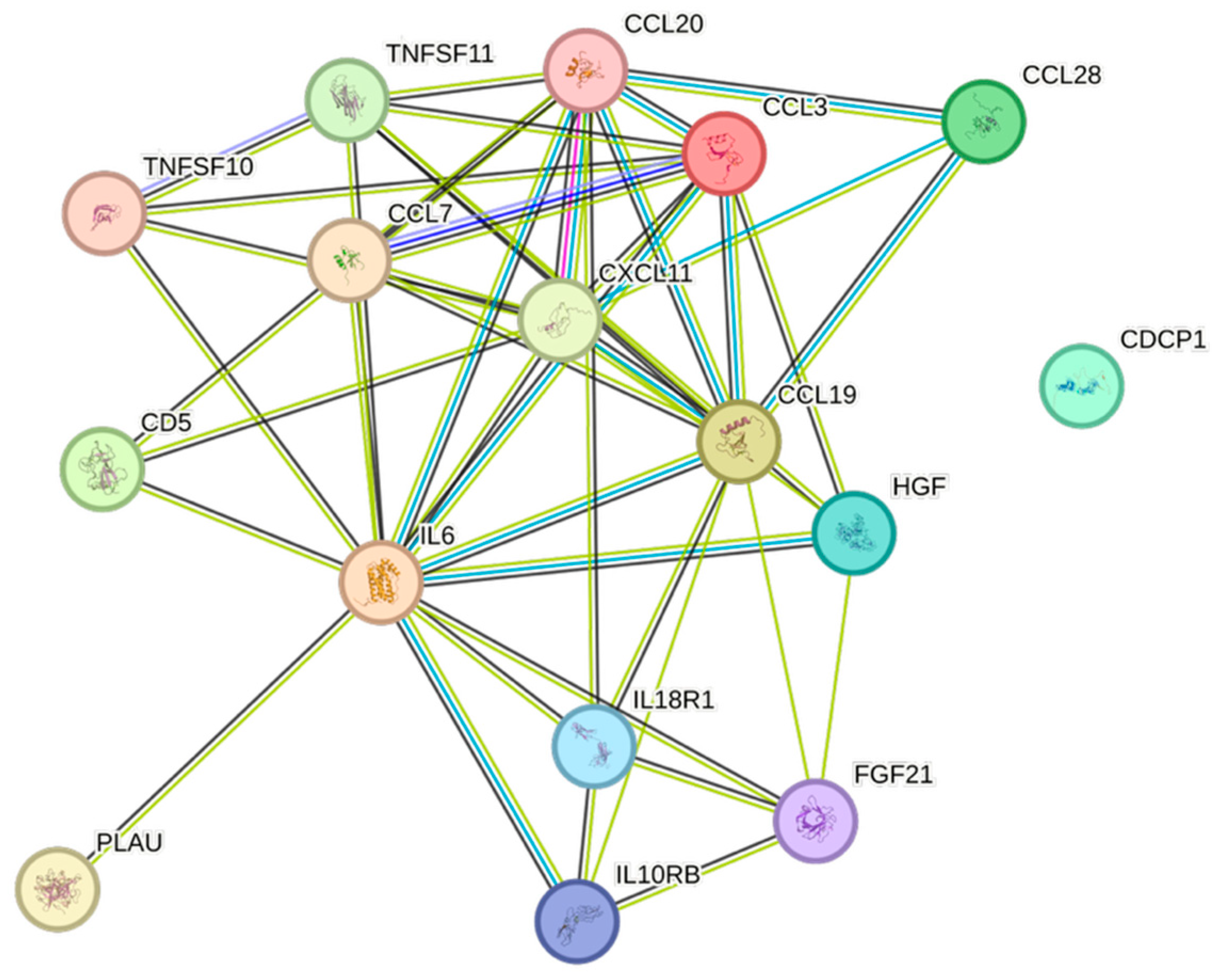
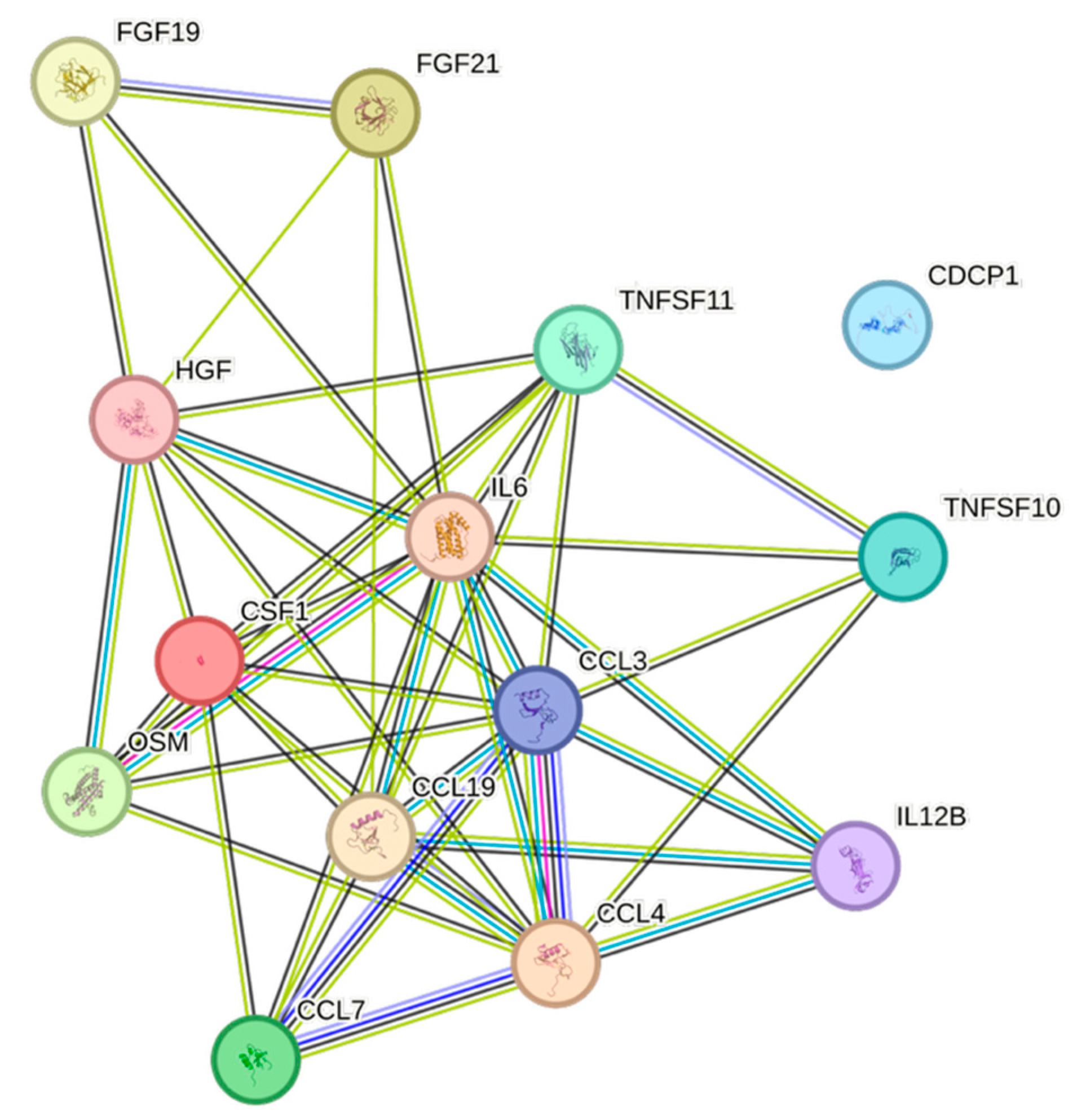
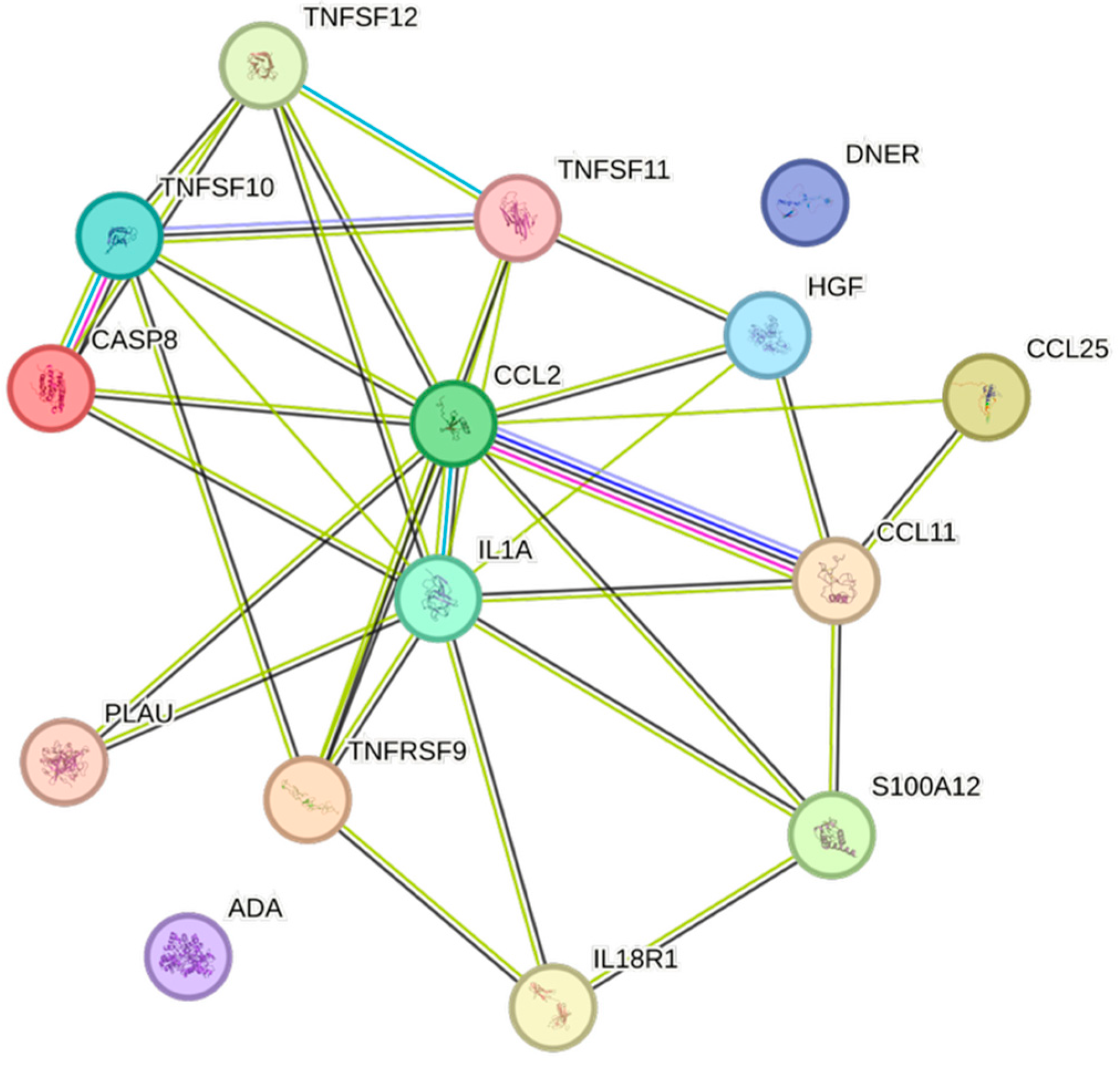
| Cytokine | Prevalence | Cytokine | Prevalence | Cytokine | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TNFSF10 | 10 | CASP-8 | 3 | CGCP1 | 1 |
| CCL3 | 8 | COL18A1 | 3 | CXCL11 | 1 |
| TNFSF11 | 7 | TNFSF12 | 3 | CX3CL1 | 1 |
| CDCP1 | 6 | CSF-1 | 2 | Flt3L | 1 |
| IL6 | 6 | SULT1A1 | 2 | IL-17C | 1 |
| FGF-21 | 5 | CD5 | 2 | OSM | 1 |
| S100A12 | 5 | TGF-alpha | 2 | CCL4 | 1 |
| TNFRSF9 | 5 | DNER | 2 | IL-12B | 1 |
| PLAU | 5 | ADA | 2 | IL-15RA | 1 |
| HGF | 5 | CCL11 | 2 | IL7 | 1 |
| CCL7 | 5 | CCL20 | 2 | CD6 | 1 |
| IL-18R1 | 4 | CCL25 | 2 | TNF | 1 |
| CCL19 | 4 | MMP-10 | 1 | Beta-NGF | 1 |
| IL-10RB | 3 | IL-1 alpha | 1 | LTA | 1 |
| FGF-19 | 3 | CCL2 | 1 | CCL28 | 1 |
| CCGF | UniProt N° | Olink Assay ID | N° Below Limit of Quantification | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL8 | P10145 | OID00471 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | VEGFA | P15692 | OID00472 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CD8A | P01732 | OID05124 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | MCP-3 | P80098 | OID00474 | 74 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | GDNF | P39905 | OID00475 | 1 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CDCP1 | Q9H5V8 | OID00476 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CD244 | Q9BZW8 | OID00477 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL7 | P13232 | OID00478 | 1 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | OPG | O00300 | OID00479 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | LAP TGF-beta-1 | P01137 | OID00480 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | uPA | P00749 | OID00481 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL6 | P05231 | OID00482 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-17C | Q9P0M4 | OID00483 | 12 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | MCP-1 | P13500 | OID00484 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-17A | Q16552 | OID00485 | 55 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CXCL11 | O14625 | OID00486 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | AXIN1 | O15169 | OID00487 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TRAIL | P50591 | OID00488 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-20RA | Q9UHF4 | OID00489 | 125 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CXCL9 | Q07325 | OID00490 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CST5 | P28325 | OID00491 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-2RB | P14784 | OID00492 | 57 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-1 alpha | P01583 | OID00493 | 142 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | OSM | P13725 | OID00494 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL2 | P60568 | OID00495 | 155 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CXCL1 | P09341 | OID00496 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TSLP | Q969D9 | OID00497 | 128 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL4 | P13236 | OID00498 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CD6 | P30203 | OID00499 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | SCF | P21583 | OID00500 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL18 | Q14116 | OID00501 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | SLAMF1 | Q13291 | OID00502 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TGF-alpha | P01135 | OID00503 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | MCP-4 | Q99616 | OID00504 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL11 | P51671 | OID00505 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TNFSF14 | O43557 | OID00506 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | FGF-23 | Q9GZV9 | OID00507 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-10RA | Q13651 | OID00508 | 52 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | FGF-5 | P12034 | OID00509 | 70 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | MMP-1 | P03956 | OID00510 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | LIF-R | P42702 | OID00511 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | FGF-21 | Q9NSA1 | OID00512 | 6 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL19 | Q99731 | OID00513 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-15RA | Q13261 | OID00514 | 102 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-10RB | Q08334 | OID00515 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-22 RA1 | Q8N6P7 | OID00516 | 142 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-18R1 | Q13478 | OID00517 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | PD-L1 | Q9NZQ7 | OID00518 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | Beta-NGF | P01138 | OID00519 | 155 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CXCL5 | P42830 | OID00520 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TRANCE | O14788 | OID00521 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | HGF | P14210 | OID00522 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-12B | P29460 | OID00523 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-24 | Q13007 | OID00524 | 151 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL13 | P35225 | OID00525 | 134 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | ARTN | Q5T4W7 | OID00526 | 130 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | MMP-10 | P09238 | OID00527 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL10 | P22301 | OID00528 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TNF | P01375 | OID05548 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL23 | P55773 | OID00530 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CD5 | P06127 | OID00531 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL3 | P10147 | OID00532 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | Flt3L | P49771 | OID00533 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CXCL6 | P80162 | OID00534 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CXCL10 | P02778 | OID00535 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | 4E-BP1 | Q13541 | OID00536 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL-20 | Q9NYY1 | OID00537 | 157 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | SIRT2 | Q8IXJ6 | OID00538 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL28 | Q9NRJ3 | OID00539 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | DNER | Q8NFT8 | OID01213 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | EN-RAGE | P80511 | OID00541 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CD40 | P25942 | OID00542 | 162 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL33 | O95760 | OID00543 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IFN-gamma | P01579 | OID05547 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | FGF-19 | O95750 | OID00545 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL4 | P05112 | OID00546 | 116 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | LIF | P15018 | OID00547 | 156 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | NRTN | Q99748 | OID00548 | 149 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | MCP-2 | P80075 | OID00549 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CASP-8 | Q14790 | OID00550 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL25 | O15444 | OID00551 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CX3CL1 | P78423 | OID00552 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TNFRSF9 | Q07011 | OID00553 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | NT-3 | P20783 | OID00554 | 3 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TWEAK | O43508 | OID00555 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CCL20 | P78556 | OID00556 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | ST1A1 | P50225 | OID00557 | 2 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | STAMBP | O95630 | OID00558 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | IL5 | P05113 | OID00559 | 127 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | ADA | P00813 | OID00560 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | TNFB | P01374 | OID00561 | 0 |
| Olink Target 96 Inflammation | CSF-1 | P09603 | OID00562 | 0 |
| Valid N | Median | IQR | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 68% females | |||
| Age | year | 164 | 29 | 12 |
| Weight | kg | 164 | 72.9 | 17 |
| BMI | kg/m2 | 164 | 24.3 | 5 |
| Hb | g/L | 164 | 134 | 16 |
| EVF | % | 164 | 41 | 4 |
| WBC | ×109/L | 164 | 5.5 | 2 |
| Plt | ×109/L | 164 | 239 | 66 |
| Alb | g/L | 164 | 42 | 4 |
| Crea | micromol/L | 164 | 67 | 17 |
| Cortisol | nanomol/L | 164 | 360 | 199 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eriksson, M.B.; Eriksson, L.B.; Larsson, A.O. Significant Interplay Between Lipids, Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Blood Cells in an Outpatient Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167746
Eriksson MB, Eriksson LB, Larsson AO. Significant Interplay Between Lipids, Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Blood Cells in an Outpatient Cohort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167746
Chicago/Turabian StyleEriksson, Mats B., Lars B. Eriksson, and Anders O. Larsson. 2025. "Significant Interplay Between Lipids, Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Blood Cells in an Outpatient Cohort" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167746
APA StyleEriksson, M. B., Eriksson, L. B., & Larsson, A. O. (2025). Significant Interplay Between Lipids, Cytokines, Chemokines, Growth Factors, and Blood Cells in an Outpatient Cohort. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7746. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167746








