Potential Involvement of Myostatin in Smooth Muscle Differentiation in Pleomorphic Leiomyosarcoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
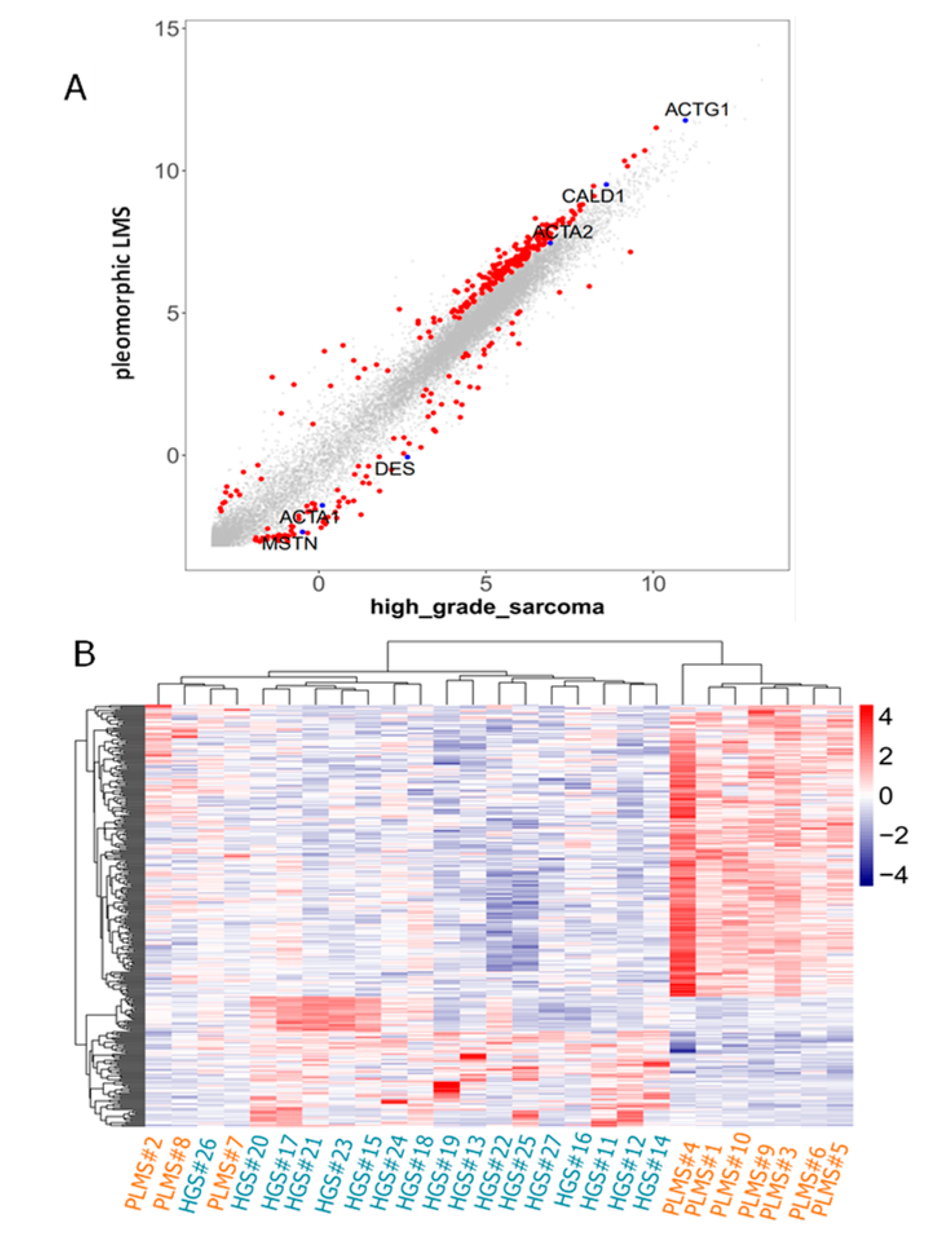
2.1. CAGE Data Identified the MSTN Promoter as Being More Activated in High-Grade Sarcomas than in PLMS
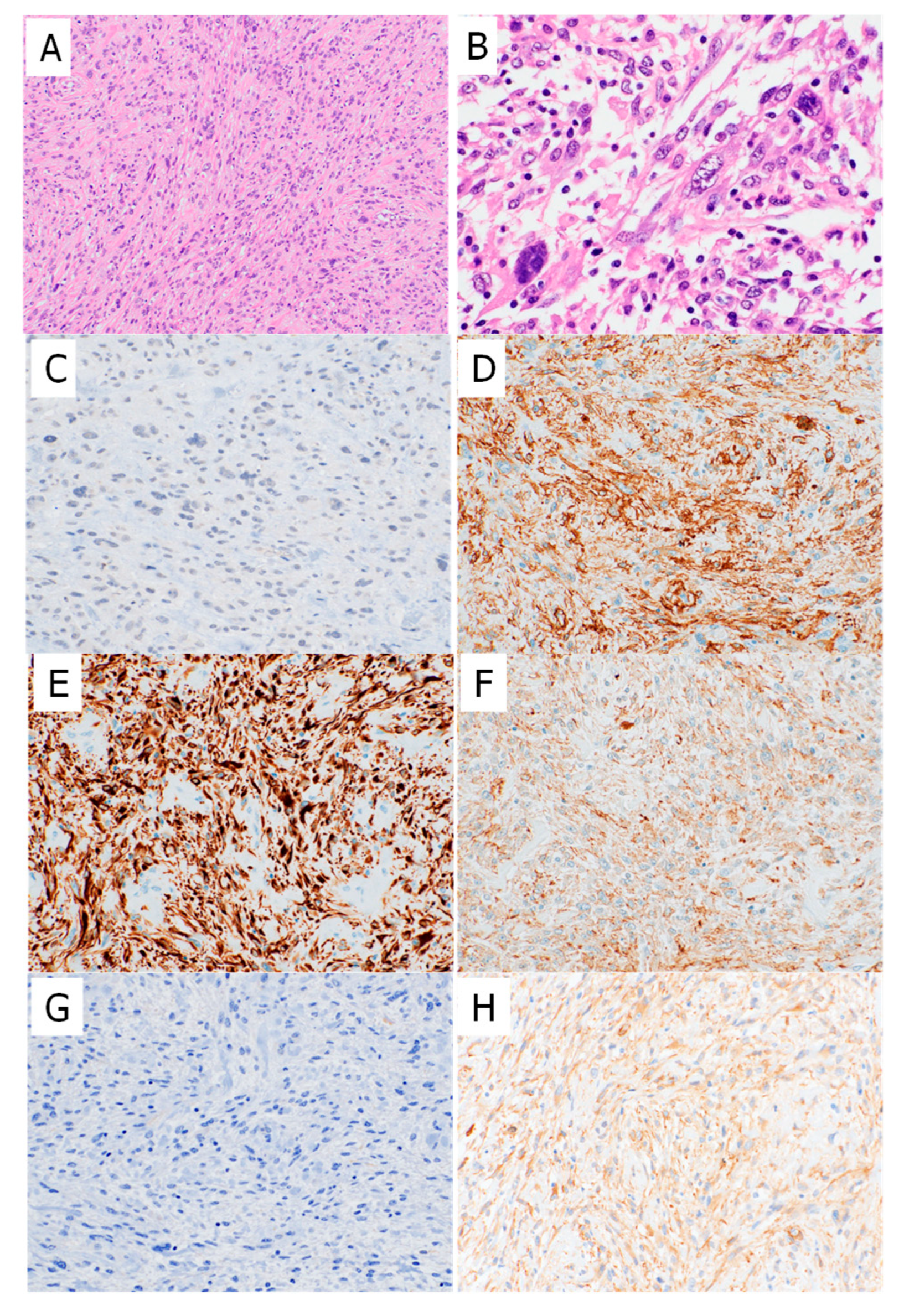
2.2. Myostatin and Myogenic Marker Expression in High-Grade Sarcomas and PLMSs
2.3. Double Staining Showed Near-Inverse Expression Patterns of Myostatin and Myogenic Markers in High-Grade Sarcomas
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
4.2. CAGE
4.3. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.4. Double Staining
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toro, J.R.; Travis, L.B.; Wu, H.J.; Zhu, K.; Fletcher, C.D.M.; Devesa, S.S. Incidence patterns of soft tissue sarcomas, regardless of primary site, in the surveillance, epidemiology and end results program, 1978–2001: An analysis of 26,758 cases. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 2922–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, H.; Nabeshima, K.; Nishio, J.; Jimi, S.; Aoki, M.; Koga, K.; Hamasaki, M.; Hayashi, H.; Mogi, A. Pathology of soft-tissue tumors: Daily diagnosis, molecular cytogenetics and experimental approach. Pathol. Int. 2009, 59, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblum, J.R. An approach to pleomorphic sarcomas: Can we subclassify, and does it matter? Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27 (Suppl. 1), S39–S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dei Tos, A.P.; Mertens, F.; Pillay, N. Undifferentiated sarcoma. In World Health Organization Classification of Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, 5th ed.; World Health Organ Classif Tumours Editorial Board, Ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2020; pp. 318–320. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, S.D.; Pissaloux, D.; Crombé, A.; Coindre, J.M.; Le Loarer, F. Pleomorphic sarcomas: The state of the art. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2019, 12, 63–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dry, S.M.; Frohling, S. Leiomyosarcoma. In World Health Organization Classification of Soft Tissue and Bone Tumours, 5th ed.; World Health Organ Classif Tumours Editorial Board, Ed.; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2020; pp. 195–197. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas, M.M.; Tamboli, P.; Gomez, J.A.; Czerniak, B.A. Pleomorphic and dedifferentiated leiomyosarcoma: Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 41 cases. Hum. Pathol. 2010, 41, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, C.D. Pleomorphic malignant fibrous histiocytoma: Fact. or fiction? A critical reappraisal based on 159 tumors diagnosed as pleomorphic sarcoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 1992, 16, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.; O’Connell, F.; Fletcher, C.D.M. Dedifferentiated leiomyosarcoma: Clinicopathological analysis of 18 cases. Histopathology 2011, 59, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, Y.; Miyajima, K.; Kawaguchi, K.; Tamiya, S.; Oshiro, Y.; Hachitanda, Y.; Oya, M.; Iwamoto, Y.; Tsuneyoshi, M. Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma: Clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study with special emphasis on its distinction from ordinary leiomyosarcoma and malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2001, 25, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherron, A.C.; Lawler, A.M.; Lee, S.J. Regulation of skeletal muscle mass in mice by a new TGF-beta superfamily member. Nature 1997, 387, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durieux, A.-C.; Amirouche, A.; Banzet, S.; Koulmann, N.; Bonnefoy, R.; Pasdeloup, M.; Mouret, C.; Bigard, X.; Peinnequin, A.; Freyssenet, D. Ectopic expression of myostatin induces atrophy of adult skeletal muscle by decreasing muscle gene expression. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3140–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazar, A.J.; McLellan, M.D.; Bailey, M.H.; Miller, C.A.; Appelbaum, E.L.; Cordes, M.G.; Fronick, C.C.; Fulton, L.A.; Fulton, R.S.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Comprehensive and integrated genomic characterization of adult soft tissue sarcomas. Cell 2017, 171, 950–965.e28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, M.; Abdullaev, Z.; Turakulov, R.; Quezado, M.; Luiña Contreras, A.L.; Curcio, C.A.; Rys, J.; Chlopek, M.; Lasota, J.; Aldape, K.D. Assessment of the utility of the sarcoma DNA methylation classifier in surgical pathology. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2024, 48, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherron, A.C.; Lee, S.J. Double muscling in cattle due to mutations in the myostatin gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12457–12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B.K.; Febbraio, M.A. Muscles, exercise and obesity: Skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Zhang, F.; Wen, J.; Ye, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Gong, P.; Jiang, S. The function of myostatin in the regulation of fat mass in mammals. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokouchi, K.; Numaguchi, Y.; Kubota, R.; Ishii, M.; Imai, H.; Murakami, R.; Ogawa, Y.; Kondo, T.; Okumura, K.; Ingber, D.E.; et al. l-Caldesmon regulates proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells and inhibits neointimal formation after angioplasty. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 2231–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Andersson, R.; Gebhard, C.; Miguel-Escalada, I.; Hoof, I.; Bornholdt, J.; Boyd, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Schmidl, C.; Suzuki, T.; et al. An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature 2014, 507, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grapotte, M.; Saraswat, M.; Bessière, C.; Menichelli, C.; Ramilowski, J.A.; Severin, J.; Hayashizaki, Y.; Itoh, M.; Tagami, M.; Murata, M.; et al. Discovery of widespread transcription initiation at microsatellites predictable by sequence-based deep neural network. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakawa, Y.; Yoshihara, M.; Kawaji, H.; Nishikawa, M.; Zayed, H.; Suzuki, H.; Fantom Consortium; Hayashizaki, Y. Enhanced identification of transcriptional enhancers provides mechanistic insights into diseases. Trends Genet. 2016, 32, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demicco, E.G.; Boland, G.M.; Brewer Savannah, K.J.; Lusby, K.; Young, E.D.; Ingram, D.; Watson, K.L.; Bailey, M.; Guo, X.; Hornick, J.L.; et al. Progressive loss of myogenic differentiation in leiomyosarcoma has prognostic value. Histopathology 2015, 66, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.H.; Lee, C.H.; Witten, D.M.; Gleason, B.C.; Edris, B.; Espinosa, I.; Zhu, S.; Li, R.; Montgomery, K.D.; Marinelli, R.J.; et al. Discovery of molecular subtypes in leiomyosarcoma through integrative molecular profiling. Oncogene 2010, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Jo, V.Y.; Mills, A.M.; Zhu, S.X.; Lee, C.-H.; Espinosa, I.; Nucci, M.R.; Varma, S.; Forgó, E.; Hastie, T.; et al. Clinically relevant molecular subtypes in leiomyosarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3501–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdelHafez, F.F.; Klausen, C.; Zhu, H.; Yi, Y.; Leung, P.C.K. Growth differentiation factor myostatin regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition genes and enhances invasion by increasing serine protease inhibitors E1 and E2 in human trophoblast cells. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, A.; Suehara, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Takagi, T.; Kubota, D.; Sasa, K.; Hasegawa, N.; Ishijima, M.; Yao, T.; Saito, T. Molecular and clinicopathological analysis revealed an immuno-checkpoint inhibitor as a potential therapeutic target in a subset of high-grade myxofibrosarcoma. Virchows Arch. 2022, 481, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tawbi, H.A.; Burgess, M.; Bolejack, V.; Van Tine, B.A.; Schuetze, S.M.; Hu, J.; D’Angelo, S.; Attia, S.; Riedel, R.F.; Priebat, D.A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in advanced soft-tissue sarcoma and bone sarcoma (SARC028): A multicentre, two-cohort, single-arm, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ami, E.; Barysauskas, C.M.; Solomon, S.; Tahlil, K.; Malley, R.; Hohos, M.; Polson, K.; Loucks, M.; Severgnini, M.; Patel, T.; et al. Immunotherapy with single agent nivolumab for advanced leiomyosarcoma of the uterus: Results of a phase 2 study. Cancer 2017, 123, 3285–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movva, S.; Seier, K.; Avutu, V.; Banks, L.B.; Chan, J.; Chi, P.; Dickson, M.A.; Gounder, M.M.; Kelly, C.M.; Keohan, M.L.; et al. Histology-specific clinical trial of lenvatinib and pembrolizumab in patients with sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 5612–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, N.; Hayashi, T.; Niizuma, H.; Kikuta, K.; Imanishi, J.; Endo, M.; Ikeuchi, H.; Sasa, K.; Sano, K.; Hirabayashi, K.; et al. Detection of novel tyrosine kinase fusion genes as potential therapeutic targets in bone and soft tissue sarcomas using DNA/RNA-based clinical sequencing. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2024, 482, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suehara, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Hayashi, T.; Akaike, K.; Kurisaki-Arakawa, A.; Sato, S.; Kobayashi, E.; Mizuno, S.; Ueno, T.; Morii, T.; et al. Identification of a novel MAN1A1-ROS1 fusion gene through mRNA-based screening for tyrosine kinase gene aberrations in a patient with leiomyosarcoma. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2021, 479, 838–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FANTOM Consortium and the RIKEN PMI and CLST (DGT); Forrest, A.R.R.; Kawaji, H.; Rehli, M.; Baillie, J.K.; de Hoon, M.J.L.; Haberle, V.; Lassmann, T.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Lizio, M.; et al. A promoter-level mammalian expression atlas. Nature 2014, 507, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasa, K.; Son, R.; Oguchi, A.; Ashizawa, K.; Hasegawa, N.; Kubota, D.; Suehara, Y.; Takagi, T.; Okubo, T.; Akaike, K.; et al. NTRK2 expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors with a special emphasis on the clinicopathological and prognostic impacts. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Case No. | Histological Type | Material | Myostatin | SMA | Desmin | M−Actin | h−Caldesmon | l−Caldesmon | Chemotherapy | Recurrence/Metastasis | Recurrence/Metastatic Site | Prognosis | Overall Survival (Months) | Chemotherapeutic Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (−) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (+) | (+) | Lung (46 months) | DOD | DOD 58 | |
| 2 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (−) | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | Alive | NED 68 | ||
| 3 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (−) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (+) | (+) | Lung (7 months) | Alive | AWD 60 | |
| 4 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (−) | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | Alive | NED 53 | ||
| 5 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (−) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (+) | Lung (3 months) | DOD | DOD 5 | |
| 6 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (+) | Lung/bone (41 months) | Alive | AWD 47 | |
| 7 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (+) | Lung/chest wall/lymph node (19 months) | Alive | AWD 28 | |
| 8 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (+) | (−) | Alive | NED 31 | ||
| 9 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | biopsy | (focally+) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | Neoadjuvant (+) | (+) | Lung (8 months) | Alive | AWD 81 | 20 |
| 9-#2 * | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (very focally+) | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | (very focally+) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 10 | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | biopsy | (−) | (very focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (focally +) | Neoadjuvant (+) | (+) | Lung (9 months) | DOD | DOD 17 | 0 |
| 10-#2 * | Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 11 | High−grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 12 | Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 13 | Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (focally +) | ||||||
| 14 | Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | (focally +) | ||||||
| 15 | High−grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (focally +) | ||||||
| 16 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 17 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 18 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) | ||||||
| 19 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 20 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 21 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 22 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 23 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (very focally +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 24 | High-grade myxofibrosarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 25 | High-grade sarcoma, NOS | resection | (diffuse +) | (focally +) | (very focally +) | (very focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 26 | Undifferentiated sarcoma | resection | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 27 | Undifferentiated sarcoma | biopsy | (very focally +) | (focally +) | (−) | (−) | (−) | (diffuse +) | ||||||
| 27-#2 * | Undifferentiated sarcoma | resection | (diffuse +) | (diffuse +) | (−) | (focally +) | (−) | (diffuse +) |
| Histological Type | IHC Expression | Myostatin | SMA | Desmin | M-Actin | h-Caldesmon | l-Caldesmon |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma | (−) | 7 (70%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (40%) | 3 (30%) | 9 (90%) | 0 (0%) |
| N = 10 | (very focally +) | 0 (0%) | 1 (10%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| (focally +) | 3 (30%) | 5 (50%) | 5 (50%) | 3 (30%) | 1 (10%) | 2 (20%) | |
| (diffuse +) | 0 (0%) | 4 (40%) | 1 (10%) | 4 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 8 (80%) | |
| p value | 0.02 | 0.37 | 0.18 | 0.58 | 0.003 | ||
| High-grade sarcoma | (−) | 2 (11%) | 6 (35%) | 8 (47%) | 11 (64%) | 17 (100%) | 1 (5%) |
| N = 17 | (very focally +) | 1 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (11%) | 1 (5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| (focally +) | 2 (11%) | 7 (41%) | 3 (17%) | 2 (11%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (17%) | |
| (diffuse +) | 12 (70%) | 4 (23%) | 4 (23%) | 3 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 13 (76%) | |
| p value | 0.28 | 0.032 | 0.003 | 0 | 0.6 |
| Diagnosis | Myostatin | SMA | Desmin | M-Actin | h-Caldesmon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V#1 | US | diffuse + | focal + | (−) | very focal + | (−) |
| V#2 | US | diffuse +, weak | − | − | − | − |
| V#3 | US | diffuse + | very focal + | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| V#4 | US | diffuse + | very focal + | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| V#5 | Low-grade FMS | diffuse + | − | − | − | − |
| V#6 | Low-grade sarcoma, NOS | diffuse + | very focal + | (−) | (−) | (−) |
| V#7 | Low-grade MFS | diffuse + | − | − | − | − |
| V#8 | Intermediate-grade MFS | diffuse + | − | − | − | − |
| V#9 | High-grade MFS | diffuse + | − | − | − | − |
| V#10 | High-grade MFS | diffuse + | − | − | − | − |
| V#11 | High-grade MFS | focal + | focal + | − | − | − |
| V#12 | High-grade MFS | very focal +, weak | focal + | − | − | − |
| V#13 | High-grade MFS | focal +, weak | focal + | − | − | − |
| V#14 | High-grade MFS | diffuse + | − | − | − | − |
| V#15 | PRMS | (−) | very focal + | diffuse + | diffuse + | − |
| V#16 | PRMS | (−) | very focal + | diffuse + | − | − |
| V#17 | PLMS | focal +, strong | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#18 | PLMS | very focal + | diffuse + | focal + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#19 | PLMS | (−) | very focal + | − | − | − |
| V#20 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | − | very focal + | − |
| V#21 | PLMS | diffuse +, weak | diffuse + | − | focal+ | very focal + |
| V#22 | PLMS | diffuse +, weak | very focal + | diffuse + | very focal + | − |
| V#23 | PLMS | very focal +, weak | − | − | − | − |
| V#24 | PLMS | (−) | very focal + | very focal + | − | − |
| V#25 | PLMS | (−) | diffuse + | very focal + | focal + | − |
| V#26 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | − | − | − |
| V#27 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | focal + | very focal + | − |
| V#28 | PLMS | (−) | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#29 | PLMS | (−) | very focal + | − | − | − |
| V#30 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | very focal + | − | − |
| V#31 | PLMS | focal +, weak | very focal + | − | − | − |
| V#32 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | − | − | − |
| V#33 | PLMS | very focal +, weak | diffuse + | − | focal + | − |
| V#34 | PLMS | focal +, weak | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#35 | PLMS | (−) | very focal + | − | − | very focal + |
| V#36 | PLMS | (−) | diffuse + | focal + | very focal + | very focal + |
| V#37 | PLMS | (−) | very focal + | − | − | − |
| V#38 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | − | focal + | − |
| V#39 | PLMS | (−) | focal + | − | focal + | − |
| V#40 | PLMS | (−) | very focal + | focal + | − | − |
| V#41 | PLMS | (−) | − | focal + | − | − |
| V#42 | PLMS | diffuse +, weak | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#43 | PLMS | diffuse +, weak | very focal + | very focal + | very focal + | − |
| V#44 | LMS | diffuse +, weak | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#45 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#46 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | − | − | − |
| V#47 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#48 | LMS of bone | (−) | focal + | − | − | − |
| V#49 | LMS | very focal + | diffuse + | very focal + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#50 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | focal + | very focal+ | − |
| V#51 | LMS | (−) | focal + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#52 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | focal + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#53 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + | diffuse + |
| V#54 | LMS | diffuse +, weak | diffuse + | − | focal+ | − |
| V#55 | LMS | very focal +, weak | diffuse + | − | diffuse + | − |
| V#56 | LMS | very focal +, weak | diffuse + | − | focal + | − |
| V#57 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | very focal + | focal + | − |
| V#58 | LMS | (−) | diffuse + | − | focal + | − |
| V#59 | LMS | very focal +, weak | diffuse + | very focal + | focal + | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onagi, H.; Son, R.; Oguchi, A.; Sano, K.; Sasa, K.; Hasegawa, N.; Akaike, K.; Kubota, D.; Takagi, T.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Potential Involvement of Myostatin in Smooth Muscle Differentiation in Pleomorphic Leiomyosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167676
Onagi H, Son R, Oguchi A, Sano K, Sasa K, Hasegawa N, Akaike K, Kubota D, Takagi T, Hayashi T, et al. Potential Involvement of Myostatin in Smooth Muscle Differentiation in Pleomorphic Leiomyosarcoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167676
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnagi, Hiroko, Raku Son, Akiko Oguchi, Kei Sano, Keita Sasa, Nobuhiko Hasegawa, Keisuke Akaike, Daisuke Kubota, Tatsuya Takagi, Takuo Hayashi, and et al. 2025. "Potential Involvement of Myostatin in Smooth Muscle Differentiation in Pleomorphic Leiomyosarcoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167676
APA StyleOnagi, H., Son, R., Oguchi, A., Sano, K., Sasa, K., Hasegawa, N., Akaike, K., Kubota, D., Takagi, T., Hayashi, T., Ishijima, M., Yao, T., Suehara, Y., Murakawa, Y., & Saito, T. (2025). Potential Involvement of Myostatin in Smooth Muscle Differentiation in Pleomorphic Leiomyosarcoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167676






