Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and/or Angiotensin Receptor Blockade Modulate Cytokine Profiles and Improve Clinical Outcomes in Experimental COVID-19 Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
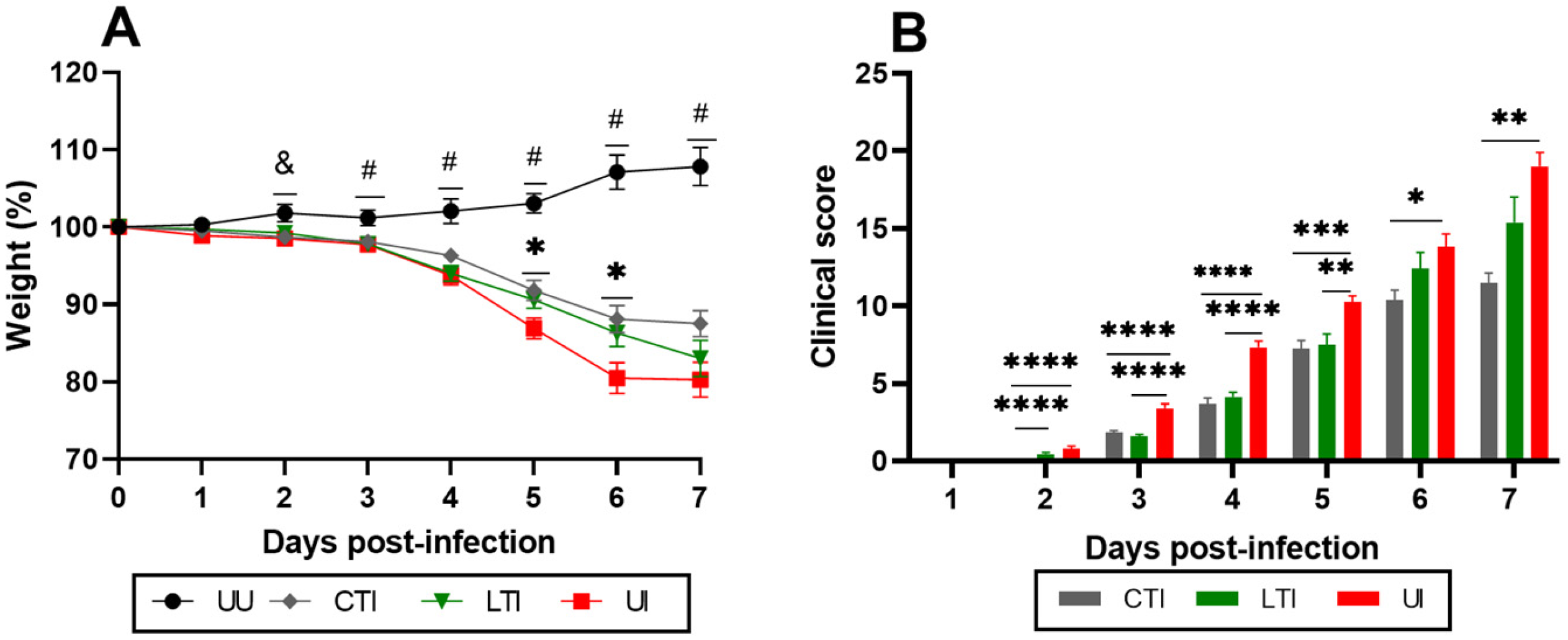
2.1. Losartan and Losartan + Lisinopril Combination Ameliorate Weight Loss and Clinical Manifestations in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Mice
2.2. The Combination of ACEi + ARB Improves Respiratory Capacity
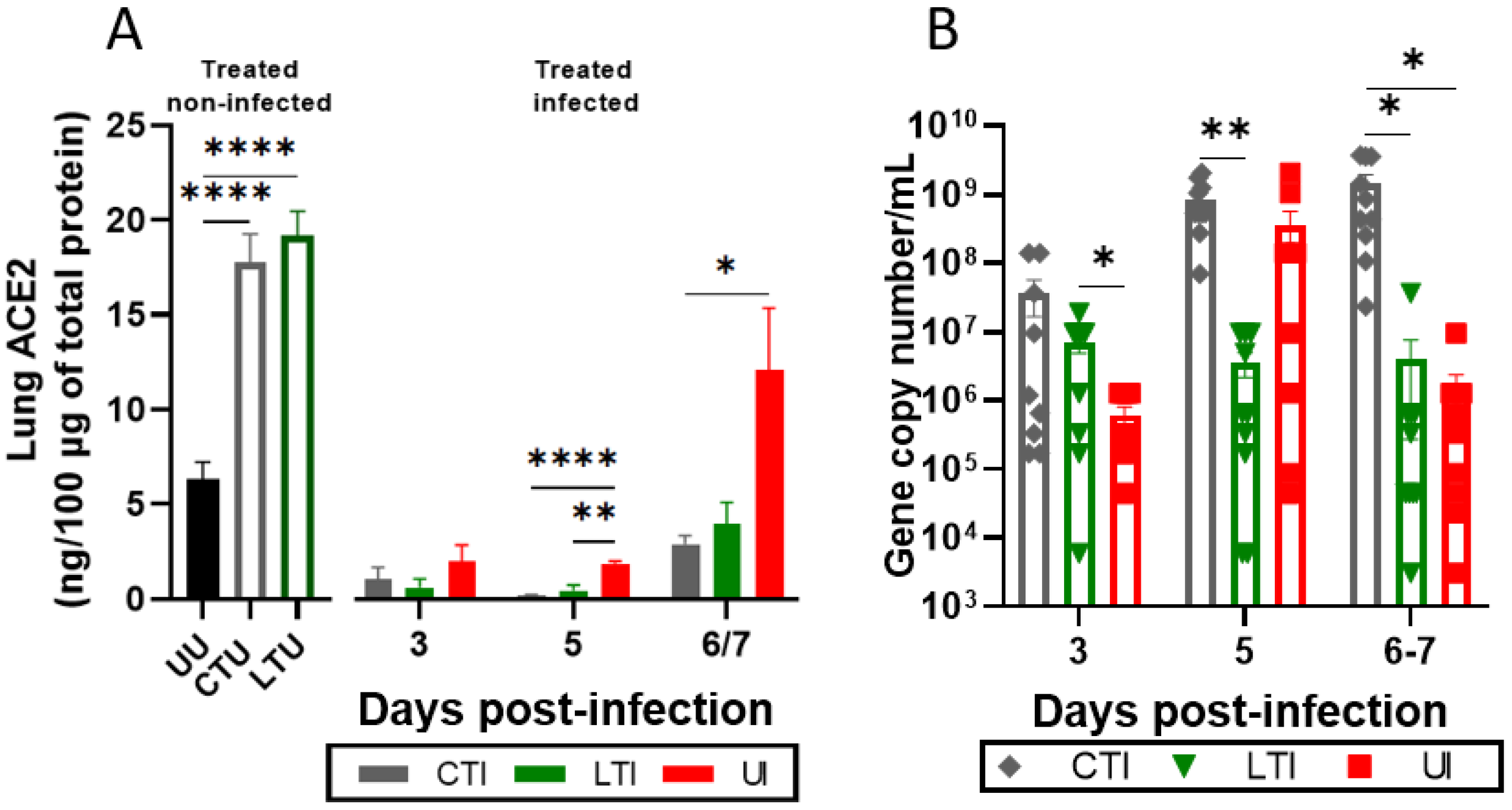
2.3. Treatments Modulate Lung ACE2 Levels, the RAS System, and SARS-CoV-2 Pulmonary Load
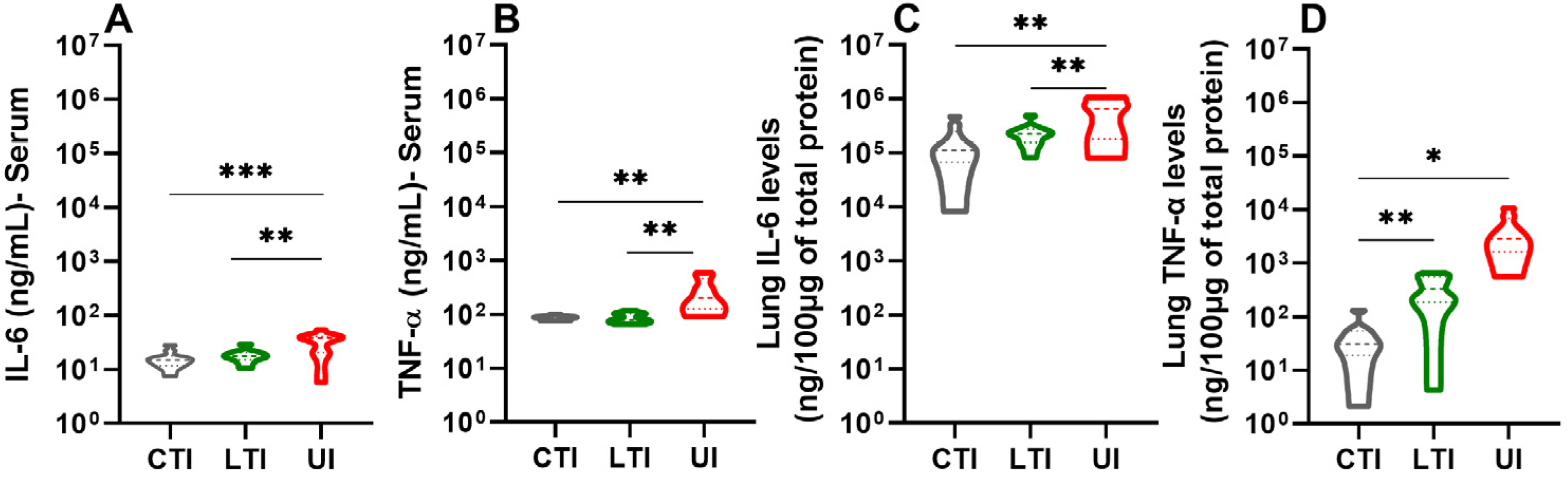
2.4. Losartan and Lisinopril + Losartan Combination Therapies Downregulate the Inflammatory Response During SARS-CoV-2 Infection
2.5. Losartan Treatment Decreases the Severity of Histopathological Findings
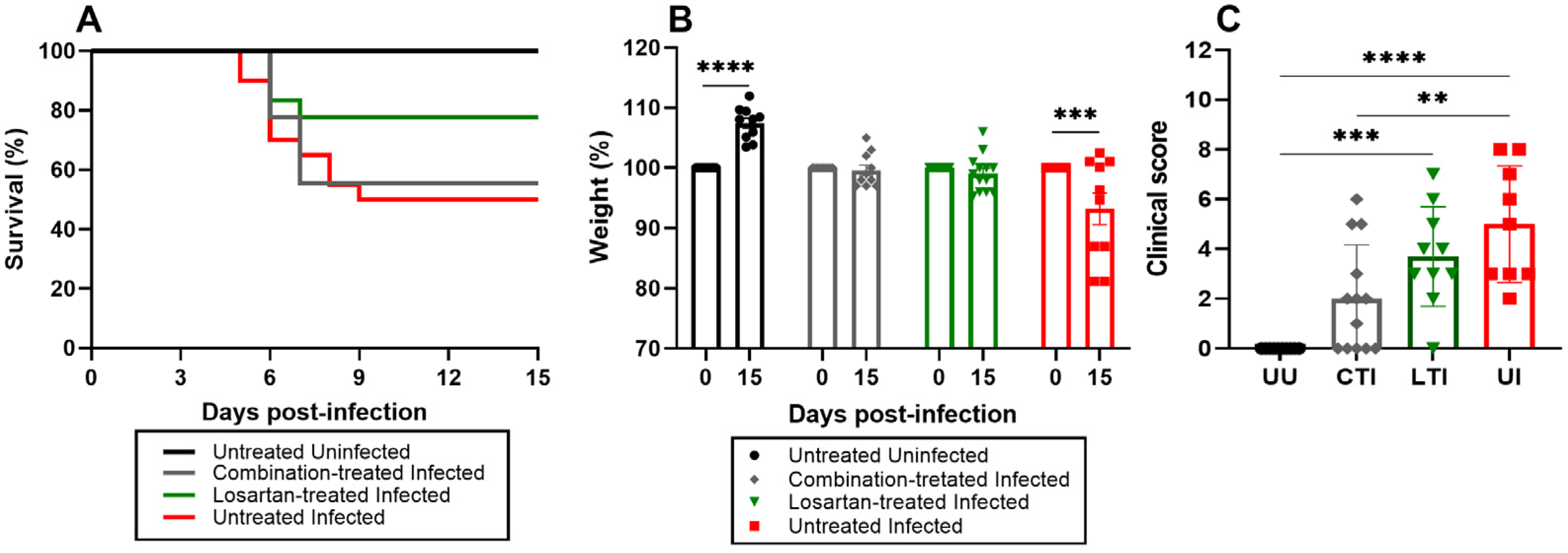
2.6. Treatment Does Not Impact the Mortality Rate but Improves Clinical Outcomes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Model and Ethics
4.2. Treatment
4.3. Virus, Infection, and Experimental Design
4.4. Assessment of Lung Capacity
4.5. Clinical Evaluation
4.6. Euthanasia and Sample Collection
4.7. Protein Extraction
4.8. Quantification of ACE2 in Tissue Samples by ELISA
4.9. RNA Extraction and Virus Detection
4.10. Cytokine Quantification
4.11. Survival
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- KFF Global COVID-19 Tracker. Available online: https://www.kff.org/coronavirus-covid-19/issue-brief/global-covid-19-tracker/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- World Health Organization. (2024). COVID-19 Epidemiological Update, Edition 169, 15 July 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-edition-169/ (accessed on 20 December 2024).
- Al-Aly, Z.; Davis, H.; McCorkell, L.; Soares, L.; Wulf-Hanson, S.; Iwasaki, A.; Topol, E.J. Long COVID Science, Research and Policy. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 2148–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, F.; Lavandero, S.; Xie, X.; Sabharwal, B.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Correa, A.; Narula, J.; Levy, P. Manipulation of ACE2 Expression in COVID-19. Open Hear. 2020, 7, e001424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, M.; Steckelings, U.M.; Alenina, N.; Santos, R.A.S.; Ferrario, C.M. Alternative Renin-Angiotensin System. Hypertension 2024, 81, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.; Bhat, S.A.; Shibata, T.; Giani, J.F.; Rader, F.; Bernstein, K.E.; Khan, Z. Diverse Biological Functions of the Renin-angiotensin System. Med. Res. Rev. 2024, 44, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrenak, J.; Simko, F. Renin–Angiotensin System: An Important Player in the Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fyhrquist, F.; Saijonmaa, O. Renin-angiotensin System Revisited. J. Intern. Med. 2008, 264, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Peng, J.; Wang, T.; Wen, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Counter-Regulatory Renin-Angiotensin System in Hypertension: Review and Update in the Era of COVID-19 Pandemic. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 208, 115370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, S.D.; Smith, R.L.; Moreira, A.S.; Ackerman, H.C. Oral Lisinopril Raises Tissue Levels of ACE2, the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor, in Healthy Male and Female Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 798349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerstein, R.; Kochen, M.M.; Messerli, F.H.; Gräni, C. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Do Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors/ Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Have a Biphasic Effect? J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.B.; Verma, A. COVID-19 and Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers What Is the Evidence ? JAMA 2020, 323, 1769–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashedi, J.; Mahdavi Poor, B.; Asgharzadeh, V.; Pourostadi, M.; Samadi Kafil, H.; Vegari, A.; Tayebi-Khosroshahi, H.; Asgharzadeh, M. Risk Factors for COVID-19. Le. Infez. Med. 2020, 28, 469–474. [Google Scholar]
- Snyder, E.M.; Johnson, B.D. ACE2 and COVID-19: Using Antihypertensive Medications and Pharmacogenetic Considerations. Pharmacogenomics 2020, 21, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Kuba, K.; Penninger, J.M. The Renin–Angiotensin System in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2006, 3, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguiano, L.; Riera, M.; Pascual, J.; Soler, M.J. Circulating ACE2 in Cardiovascular and Kidney Diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 3231–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.N.; Chappell, M.C.; Averill, D.B.; Diz, D.I.; Ferrario, C.M. Vasodepressor Actions of Angiotensin-(1–7) Unmasked During Combined Treatment with Lisinopril and Losartan. Hypertension 1998, 31, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taal, M.W.; Brenner, B.M. Combination ACEI and ARB Therapy: Additional Benefit in Renoprotection? Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2002, 11, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avanza Jr, A.C.; El Aouar, L.M.; Mill, J.G. Reduction in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Hypertensive Patients Treated with Enalapril, Losartan or the Combination of Enalapril and Losartan. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2000, 74, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, A.V.S.; de Barros e Silva, P.G.M.; de Paula, T.C.; Moll-Bernardes, R.J.; Mendonça dos Santos, T.; Mazza, L.; Feldman, A.; Arruda, G.D.S.; de Albuquerque, D.C.; de Sousa, A.S.; et al. Discontinuing vs Continuing ACEIs and ARBs in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 According to Disease Severity: Insights from the BRACE CORONA Trial. Am. Heart J. 2022, 249, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, R.D.; Macedo, A.V.S.; de Barros E Silva, P.G.M.; Moll-Bernardes, R.J.; dos Santos, T.M.; Mazza, L.; Feldman, A.; D’Andréa Saba Arruda, G.; de Albuquerque, D.C.; Camiletti, A.S.; et al. Effect of Discontinuing vs Continuing Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on Days Alive and Out of the Hospital in Patients Admitted with COVID-19. JAMA 2021, 325, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, J.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, J.; He, X.; Ou, M.; Bi, J.; Yang, R.; Di, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors Improve the Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Hypertension. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 757–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Deng, A. Association of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors with Severity or Risk of Death in Patients with Hypertension Hospitalized for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection in Wuhan, China. JAMA Cardiol. 2020, 5, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najafi, N.; Davoudi, A.; Izadyar, H.; Alishahi, A.; Mokhtariani, A.; Soleimanpourian, B.; Tabarrayi, M.; Moosazadeh, M.; Daftarian, Z.; Ahangarkani, F. The Effect of ACE Inhibitors and ARBs on Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 1517–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choksi, T.T.; Zhang, H.; Chen, T.; Malhotra, N. Outcomes of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients Receiving Renin Angiotensin System Blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Cai, J.; Lei, F.; Qin, J.-J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.-M.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Huang, X.; Lin, L.; et al. Association of Inpatient Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers with Mortality Among Patients with Hypertension Hospitalized with COVID-19. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumbers, E.R.; Head, R.; Smith, G.R.; Delforce, S.J.; Jarrott, B.; Martin, J.H.; Pringle, K.G. The Interacting Physiology of COVID-19 and the Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System: Key Agents for Treatment. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2022, 10, e00917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparisi, Á.; Catalá, P.; Amat-Santos, I.J.; Marcos-Mangas, M.; López-Otero, D.; Veras, C.; López-Pais, J.; Cabezón-Villalba, G.; Cacho Antonio, C.E.; Candela, J.; et al. Chronic Use of Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone Inhibitors in Hypertensive COVID-19 Patients: Results from a Spanish Registry and Meta-Analysis. Med. Clin. 2022, 158, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-santos, Y.; Pagni, R.L.; Helena, T.; Gamon, M.; Santiago, M.; de Azevedo, P.; Bielavsky, M.; de Souza, E.E.; Wrenger, C.; Durigon, E.L.; et al. Lisinopril Increases Lung ACE2 Levels and SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load and Decreases in Fl Ammation but Not Disease Severity in Experimental COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1414406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, J.H. Hypothesis: Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers May Increase the Risk of Severe COVID-19. J. Travel. Med. 2020, 27, taaa041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Karakiulakis, G.; Roth, M. Are Patients with Hypertension and Diabetes Mellitus at Increased Risk for COVID-19 Infection? Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Pan, L.; Jiang, H. ACEI/ARB Use and Risk of Infection or Severity or Mortality of COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 158, 104927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, R.; Zhang, X. Antihypertensive Treatment with ACEI/ARB of Patients with COVID-19 Complicated by Hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2020, 43, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Y.; Goudis, C.A.; Tse, G.; Liu, T.; Li, G. Inhibition of Renin-Angiotensin Axis Reduces the Risk of Thrombus Formation in the Left Atrial Appendage in Patients with Hypertension Complicated by Atrial Fibrillation. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2018, 19, 147032031878262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Sun, S.; Cai, J.; Zeng, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Sun, L.; Huo, J. Effects of ACEI and ARB on COVID-19 Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst. 2020, 21, 147032032098132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Nikravesh, M.; Chukwuemeka, U.; Randazzo, M.; Flores, P.; Choday, P.; Raja, A.; Aseri, M.; Shivang, S.; Chaudhuri, S.; et al. Safety of ACEi and ARB in COVID-19 Management: A Retrospective Analysis. Clin. Cardiol. 2022, 45, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, G.N.; Kumar, A. ACEi/ARB and Deaths of COVID-19 Patients. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2022, 18, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá, K.S.G.; Amaral, L.A.; Rodrigues, T.S.; Caetano, C.C.S.; Becerra, A.; Batah, S.S.; Lopes, F.T.; de Oliveira, I.M.; Lopes, L.S.; Almeida, L.; et al. Pulmonary Inflammation and Viral Replication Define Distinct Clinical Outcomes in Fatal Cases of COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Jessup, J.; Gallagher, P.E.; Averill, D.B.; Brosnihan, K.B.; Ann Tallant, E.; Smith, R.D.; Chappell, M.C. Effects of Renin-Angiotensin System Blockade on Renal Angiotensin-(1-7) Forming Enzymes and Receptors. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rico-Mesa, J.S.; White, A.; Anderson, A.S. Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19 Infection Taking ACEI/ARB. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2020, 22, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcocer, L.A.; Bryce, A.; De Padua Brasil, D.; Lara, J.; Cortes, J.M.; Quesada, D.; Rodriguez, P. The Pivotal Role of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in Hypertension Management and Cardiovascular and Renal Protection: A Critical Appraisal and Comparison of International Guidelines. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Drugs 2023, 23, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Sendón, J.; Swedberg, K.; McMurray, J.; Tamargo, J.; Maggioni, A.P.; Dargie, H.; Tendera, M.; Waagstein, F.; Kjekshus, J.; Lechat, P.; et al. Expert Consensus Document on Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors in Cardiovascular Disease The Task Force on ACE-Inhibitors of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 1454–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Hödlmoser, S.; Eskandary, F.; Poglitsch, M.; Bonderman, D.; Strassl, R.; Aberle, J.H.; Oberbauer, R.; Zoufaly, A.; Hecking, M. ACE2 Elevation in Severe COVID-19. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 1191–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenn, K.; Kraft, F.; Mandroiu, L.; Tretter, V.; Reindl-Schwaighofer, R.; Clement, T.; Domenig, O.; Vossen, M.G.; Riemann, G.; Poglitsch, M.; et al. Renin–Angiotensin–Aldosterone System Activation in Plasma as Marker for Prognosis in Critically Ill Patients with COVID-19: A Prospective Exploratory Study. Ann. Intensive Care 2025, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Gheblawi, M.; Nikhanj, A.; Munan, M.; MacIntyre, E.; O’Neil, C.; Poglitsch, M.; Colombo, D.; Del Nonno, F.; Kassiri, Z.; et al. Dysregulation of ACE (Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme)-2 and Renin-Angiotensin Peptides in SARS-CoV-2 Mediated Mortality and End-Organ Injuries. Hypertension 2022, 79, 365–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S. SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19), Viral Load and Clinical Outcomes; Lessons Learned One Year into the Pandemic: A Systematic Review. World J. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 10, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Troyano, N.; Gabriel-Medina, P.; Weber, S.; Klammer, M.; Barquín-DelPino, R.; Castillo-Ribelles, L.; Esteban, A.; Hernández-González, M.; Ferrer-Costa, R.; Pumarola, T.; et al. Soluble Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 as a Prognostic Biomarker for Disease Progression in Patients Infected with SARS-CoV-2. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Nellgård, B.; Hultén, L.M.; Nilsson, S.; Dalla, K.; Börjesson, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Svanvik, J.; Gisslén, M. Sex Difference in Circulating Soluble Form of ACE2 Protein in Moderate and Severe COVID-19 and Healthy Controls. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1058120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, C.L.; Chappell, M.C.; Shotwell, M.S.; Joly, M.M.; Gibbs, K.W.; Barksdale, A.; Douglas, I.S.; Chen, P.; Levitt, J.E.; Puskarich, M.A.; et al. The Circulating Renin-Angiotensin System and Mortality among Patients Hospitalized for COVID-19: A Mechanistic Substudy of the ACTIV-4 Host Tissue Trials. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2025, 328, L405–L412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.B.; Bhargav, R.; Salacup, G.; Pelayo, J.; Albano, J.; McCullough, P.A.; Rangaswami, J. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers and Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2020, 18, 919–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golpe, R.; Pérez-de-Llano, L.A.; Dacal, D.; Guerrero-Sande, H.; Pombo-Vide, B.; Ventura-Valcárcel, P. Risk of Severe COVID-19 in Hypertensive Patients Treated with Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors. Med. Clin. 2020, 155, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puskarich, M.A.; Cummins, N.W.; Ingraham, N.E.; Wacker, D.A.; Reilkoff, R.A.; Driver, B.E.; Biros, M.H.; Bellolio, F.; Chipman, J.G.; Nelson, A.C.; et al. A Multi-Center Phase II Randomized Clinical Trial of Losartan on Symptomatic Outpatients with COVID-19. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgonje, A.R.; Abdulle, A.E.; Timens, W.; Hillebrands, J.; Navis, G.J.; Gordijn, S.J.; Bolling, M.C.; Dijkstra, G.; Voors, A.A.; Osterhaus, A.D.; et al. Angiotensin-converting Enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the Pathophysiology of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). J. Pathol. 2020, 251, 228–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva Santos, Y.; Gamon, T.H.M.; de Azevedo, M.S.P.; Telezynski, B.L.; de Souza, E.E.; de Oliveira, D.B.L.; Dombrowski, J.G.; Rosa-Fernandes, L.; Palmisano, G.; de Moura Carvalho, L.J.; et al. Virulence Profiles of Wild-Type, P.1 and Delta SARS-CoV-2 Variants in K18-HACE2 Transgenic Mice. Viruses 2023, 15, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menachery, V.D.; Gralinski, L.E.; Baric, R.S.; Ferris, M.T. New Metrics for Evaluating Viral Respiratory Pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechous, R.D.; Malaviarachchi, P.A.; Xing, Z.; Douglas, A.; Crane, S.D.; Theriot, H.M.; Zhang, Z.; Ghaffarieh, A.; Huang, L.; Yu, Y.E.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Infection Causes Heightened Disease Severity and Mortality in a Mouse Model of Down Syndrome. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Wu, P.; Gu, W.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Deng, X.; Xu, J.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, C. Potential of Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Telmisartan in Reducing Mortality among Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19 Compared with Recommended Drugs. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothlin, R.P.; Pelorosso, F.G.; Duarte, M.; Nicolosi, L.; Ignacio, F.C.; Salgado, M.V.; Vetulli, H. Telmisartan and Losartan: The Marked Differences between Their Chemical and Pharmacological Properties May Explain the Difference in Therapeutic Efficacy in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2023, 11, e01083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.; Pelorosso, F.; Nicolosi, L.N.; Victoria Salgado, M.; Vetulli, H.; Aquieri, A.; Azzato, F.; Castro, M.; Coyle, J.; Davolos, I.; et al. Telmisartan for Treatment of COVID-19 Patients: An Open Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 37, 100962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yun, X.; Lee, D.; DiCostanzo, J.R.; Donini, O.; Shikuma, C.M.; Thompson, K.; Lehrer, A.T.; Shimoda, L.; Suk, J.S. Telmisartan Nanosuspension for Inhaled Therapy of COVID-19 Lung Disease and Other Respiratory Infections. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, W.T.; Carabelli, A.M.; Jackson, B.; Gupta, R.K.; Thomson, E.C.; Harrison, E.M.; Ludden, C.; Reeve, R.; Rambaut, A.; Peacock, S.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Variants, Spike Mutations and Immune Escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 409–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalbandian, A.; Sehgal, K.; Gupta, A.; Madhavan, M.V.; McGroder, C.; Stevens, J.S.; Cook, J.R.; Nordvig, A.S.; Shalev, D.; Sehrawat, T.S.; et al. Post-Acute COVID-19 Syndrome. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Rio, C.; Collins, L.F.; Malani, P. Long-Term Health Consequences of COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carfì, A.; Bernabei, R.; Landi, F. Persistent Symptoms in Patients After Acute COVID-19. JAMA 2020, 324, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCray, P.B.; Pewe, L.; Wohlford-Lenane, C.; Hickey, M.; Manzel, L.; Shi, L.; Netland, J.; Jia, H.P.; Halabi, C.; Sigmund, C.D.; et al. Lethal Infection of K18-HACE2 Mice Infected with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, G.B.; Burgess, S.L.; Sturek, J.M.; Donlan, A.N.; Petri, W.A.; Mann, B.J. Evaluation of K18-HACE2 Mice as a Model of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 103, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinda, C.K.; Port, J.R.; Bushmaker, T.; Owusu, I.O.; Purushotham, J.N.; Avanzato, V.A.; Fischer, R.J.; Schulz, J.E.; Holbrook, M.G.; Hebner, M.J.; et al. K18-HACE2 Mice Develop Respiratory Disease Resembling Severe COVID-19. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, D.B.; Machado, R.R.G.; Amgarten, D.E.; Malta, F.d.M.; de Araujo, G.G.; Monteiro, C.O.; Candido, E.D.; Soares, C.P.; de Menezes, F.G.; Pires, A.C.C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Isolation from the First Reported Patients in Brazil and Establishment of a Coordinated Task Network. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2020, 115, e200342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomask, M. Further Exploration of the Penh Parameter. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2006, 57, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A. Low-Tidal-Volume Ventilation in the Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, S.; Toro, F.; Ashurst, J.V. Physiology, Tidal Volume; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- UNIFESP Guide to Implementation of Humanitarian End Point. Available online: https://ceua.unifesp.br/images/documentos/CEUA/Guia_EndPoint_CEUA_UNIFESP_2020.pdf (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Langford, D.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Chanda, M.L.; Clarke, S.E.; Drummond, T.E.; Echols, S.; Glick, S.; Ingrao, J.; Klassen-Ross, T.; LaCroix-Fralish, M.L.; et al. Coding of Facial Expressions of Pain in the Laboratory Mouse. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 447–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, G.J.; Kipke, D.R.; Shain, W. Whole Animal Perfusion Fixation for Rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, 65, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corman, V.M.; Landt, O.; Kaiser, M.; Molenkamp, R.; Meijer, A.; Chu, D.K.; Bleicker, T.; Brünink, S.; Schneider, J.; Schmidt, M.L.; et al. Detection of 2019 Novel Coronavirus (2019-NCoV) by Real-Time RT-PCR. Eurosurveillance 2020, 25, 2000045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
da Silva-Santos, Y.; Pagni, R.L.; Gamon, T.H.M.; de Azevedo, M.S.P.; Darido, M.L.G.; de Oliveira, D.B.L.; Durigon, E.L.; Luvizotto, M.C.R.; Ackerman, H.C.; Marinho, C.R.F.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and/or Angiotensin Receptor Blockade Modulate Cytokine Profiles and Improve Clinical Outcomes in Experimental COVID-19 Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167663
da Silva-Santos Y, Pagni RL, Gamon THM, de Azevedo MSP, Darido MLG, de Oliveira DBL, Durigon EL, Luvizotto MCR, Ackerman HC, Marinho CRF, et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and/or Angiotensin Receptor Blockade Modulate Cytokine Profiles and Improve Clinical Outcomes in Experimental COVID-19 Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167663
Chicago/Turabian Styleda Silva-Santos, Yasmin, Roberta Liberato Pagni, Thais Helena Martins Gamon, Marcela Santiago Pacheco de Azevedo, Maria Laura Goussain Darido, Danielle Bruna Leal de Oliveira, Edson Luiz Durigon, Maria Cecília Rui Luvizotto, Hans Christian Ackerman, Claudio Romero Farias Marinho, and et al. 2025. "Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and/or Angiotensin Receptor Blockade Modulate Cytokine Profiles and Improve Clinical Outcomes in Experimental COVID-19 Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167663
APA Styleda Silva-Santos, Y., Pagni, R. L., Gamon, T. H. M., de Azevedo, M. S. P., Darido, M. L. G., de Oliveira, D. B. L., Durigon, E. L., Luvizotto, M. C. R., Ackerman, H. C., Marinho, C. R. F., Carvalho, L. J. d. M., & Epiphanio, S. (2025). Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibition and/or Angiotensin Receptor Blockade Modulate Cytokine Profiles and Improve Clinical Outcomes in Experimental COVID-19 Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7663. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167663






