Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Colorectal Polyps
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Groups
2.2. Colonoscopy Results
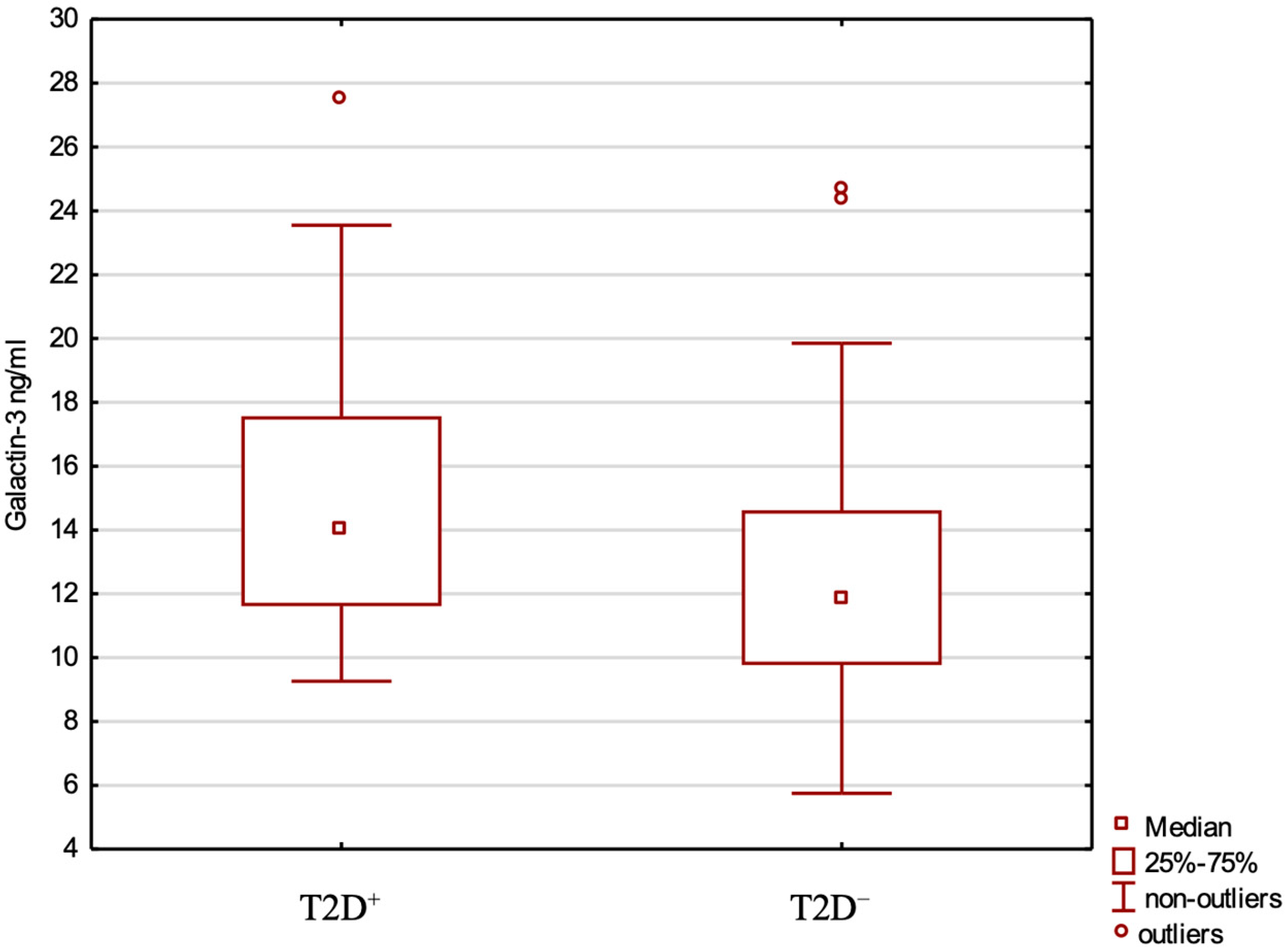
2.3. Gal-3, Clinical Variables
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations of This Study
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design and Population
4.2. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| T2D | type 2 diabetes |
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| Gal-3 | galectin-3 |
| HbA1c | glycated haemoglobin |
| CRPs | colorectal polyps |
| BMI | body mass index |
| SD | standard deviation |
| OR | odds ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| WHTR | waist-to-height ratio |
| FPG | fasting plasma glucose |
| IGF-1 | insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| HOMA-IR | homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance |
| AIP | atherogenic index of plasma |
| CH | total cholesterol |
| TGs | triglycerides |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
References
- World Health Organization. Diabetes. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes (accessed on 10 May 2025).
- Vekic, J.; Zeljkovic, A.; Stefanovic, A.; Giglio, R.V.; Ciaccio, M.; Rizzo, M. Diabetes and colorectal cancer risk: A new look at molecular mechanisms and potential role of novel antidiabetic agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, Y. Emerging roles of Galectin-3 in diabetes and diabetes complications: A snapshot. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, I.; Rodrigues, K.; Pietrani, N.; Bosco, A.; Gomes, K.; Alves, M. Evaluation of galectin-3 levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. J. Bras. Patol. Med. Lab. 2021, 57, e2172021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalar, M.N.; Abuşoğlu, S.; Ünlü, A.; Tok, O.; İpekçi, S.H.; Baldane, S.; Kebapcılar, L. Assessment of serum galectin-3, methylated arginine and Hs-CRP levels in type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, L.; Hu, S. Circulating Galectin-3 levels and diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Nephrol. 2023, 24, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Huang, E.; Yeh, W.; Hsiao, C.; Kuo, C. Synergistic interaction between galectin-3 and carcinoembryonic antigen promotes colorectal cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61935–61943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Ma, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jin, S.; Liang, W.; Shen, X.; Li, C.; et al. Galectin-3 may serve as a marker for poor prognosis in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 152612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Meng, X.; Song, N. Prognostic role of galectin-3 expression in patients with solid tumors: A meta-analysis of 36 eligible studies. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-W.; Chang, H.-T.; Chen, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H.; Lin, S.-W.; Hsu, T.-L.; Wong, C.-H. Galectin-3 binding protein and galectin-1 interaction in breast cancer cell aggregation and metastasis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 9685–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Dong, X.-W.; Guo, X.-L. Role of the interaction between galectin-3 and cell adhesion molecules in cancer metastasis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 69, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selemetjev, S.A.; Savin, S.B.; Paunovic, I.R.; Tatic, S.B.; Cvejic, D. Changes in the expression pattern of apoptotic molecules (galectin-3, Bcl-2, Bax, survivin) during progression of thyroid malignancy and their clinical significance. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2015, 127, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delso, J.G.; Larramona, S.F.; Olmo, J.F.; Amezaga, R.U. Factors associated with missed colorectal cancer after colonoscopy. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2019, 89, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, A.B.; Rutter, C.M.; Peterse, E.F.P.; Lietz, A.P.; Seguin, C.L.; Meester, R.G.S.; Perdue, L.A.; Lin, J.S.; Siegel, R.L.; Doria-Rose, V.P.; et al. Screening for colorectal cancer: Updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA 2021, 325, 1978–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, R.A.; Van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Muller Kobold, A.C.; Van Gilst, W.H.; Hillege HLBakker, S.J.L.; Van der Harst, P. The fibrosis marker galectin-3 and outcome in the general population. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.E.; Liu, C.; Lyass, A.; Courchesne, P.; Pencina, M.J.; Vasan, R.S.; Larson, M.G.; Levy, D. Galectin-3, a marker of cardiac fibrosis, predicts incident heart failure in the community. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Nguyen, V.T.; Rhodes, D.H.; Sullivan, M.E.; Braunschweig, C.; Fantuzzi, G. Relationship of galectin-3 with obesity, IL-6, and CRP in women. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 12, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, Ö.; Dikker, O.; Akarsu, M.; Arman, Y.; Yoldemir, Ş.A.; Kutlu, O.; Gümüşkaya, P.Ö.; Tükek, T. The relationship of serum galectin-3 levels with obesity and insulin resistance. J. Surg. Med. 2019, 3, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Liu, S.; Lu, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Oh, D.; Imamura, T.; Johnson, A.M.F.; Sears, D.; Shen, Z.; Cui, B.; et al. Hematopoietic-derived galectin-3 causes cellular and systemic insulin resistance. Cell 2016, 167, 973–984.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, H.; Cakmak, M.; Inan, O.; Darcin, T.; Akcay, A. Increased levels of galectin-3 were associated with prediabetes and diabetes: New risk factor? J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, T.; Fujioka, Y.; Nakanishi, R.; Shiochi, H.; Sumi, K.; Yamamoto, N.; Matsuzawa, K.; Izawa, S.; Ohkura, H.; Ueta, E.; et al. Low serum galectin-3 concentrations are associated with insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Kang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.; Shao, S.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, G.; Yu, X. Association of circulating galectin-3 with gestational diabetes mellitus, progesterone, and insulin resistance. J. Diabetes 2021, 13, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, J.; Neumeier, M.; Wanninger, J.; Bauer, S.; Farkas, S.; Scherer, M.N.; Schnitzbauer, A.; Aslanidis, C.; SchölMerich, J.; Buechler, C. Serum galectin-3 is elevated in obesity and negatively correlates with glycosylated hemoglobin in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobronnikova, L. Galectin-3 as a potential biomarker of metabolic disorders and cardiovascular remodeling in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Vessel. Plus 2017, 1, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seferovic, J.P.; Lalic, N.M.; Floridi, F.; Tesic, M.; Seferovic, P.M.; Giga, V.; Lalic, K.; Jotic, A.; Jovicic, S.; Colak, E.; et al. Structural myocardial alterations in diabetes and hypertension: The role of galectin-3. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Jin, L.; Dechun, L.; Hongqiang, Y.; Changhua, K.; Guijun, L. Galectin-3 expression in colorectal cancer and its correlation with clinical pathological characteristics and prognosis. Open Med. 2017, 12, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, G.; Yu, N.; Huang, Z.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Qiu, J.; Zeng, X.; Chen, S.; et al. Posttranscriptional regulation of galectin-3 by miR-128 contributes to colorectal cancer progression. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15242–15251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Pen, C.-T.; Yeh, W.-L.; Huang, E.-Y.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Yang, K.D. Circulating galectin-1 and 90K/mac-2BP correlated with the tumor stages of patients with colorectal cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 306964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, K.; Shimura, T.; Masuda, N.; Ide, M.; Tsutsumi, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Asao, T.; Kuwano, H. Galectin-3 expression in colorectal cancer: Relation to invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 2289–2296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, M.; Gajovic, N.; Zdravkovic, N.; Jovanovic, M.; Jurisevic, M.; Vojvodic, D.; Maric, V.; Arsenijevic, A.; Jovanovic, I. Galectin-3: A new promising biomarker for severity and progression of colorectal carcinoma. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8031328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Correlation of Gal-3 with | All Patients (N = 80) | CRP+ (N = 41) | CRP− (N = 39) | T2D+ (N = 36) | T2D− (N = 44) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spearman Correlation | p Value | Spearman Correlation | p Value | Spearman Correlation | p Value | Spearman Correlation | p Value | Spearman Correlation | p Value | |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 0.201 | 0.740 | 0.191 | 0.232 | 0.252 | 0.122 | 0.286 * | 0.112 * | −0.406 * | 0.009 * |
| CH (mg/dL) | −0.142 | 0.208 | −0.319 | 0.042 | 0.006 | 0.970 | 0.121 * | 0.509 * | −0.210 * | 0.194 * |
| TG (mg/dL) | 0.060 | 0.594 | 0.030 | 0.852 | 0.107 | 0.518 | −0.011 * | 0.954 * | 0.075 * | 0.646 * |
| HDL (mg/dL) | −0.184 | 0.102 | −0.177 | 0.267 | −0.192 | 0.242 | −0.093 * | 0.613 * | −0.296 * | 0.064 * |
| HOMA-IR | −0.117 | 0.303 | −0.016 | 0.919 | −0.192 | 0.241 | −0.315 * | 0.079 * | −0.119 * | 0.463 * |
| API | 0.141 | 0.211 | 0.116 | 0.470 | 0.168 | 0.305 | 0.015 * | 0.936 * | 0.211 * | 0.192 * |
| Fasting insulin (uIu/mL) | −0.171 | 0.128 | −0.068 | 0.671 | −0.232 | 0.155 | −0.301 * | 0.094 * | −0.137 * | 0.399 * |
| PEPTIDE C (ng/mL) | 0.957 | 0.006 | 0.048 | 0.764 | −0.043 | 0.796 | −0.313 * | 0.081 * | 0.100 * | 0.537 * |
| IGF-1 (ng/mL) | −0.417 | <0.001 | −0.450 | 0.003 | −0.433 | 0.006 | −0.342 * | 0.055 * | 0.319 * | 0.045 * |
| SEX | 0.220 | 0.049 | 0.326 | 0.037 | 0.102 | 0.537 | 0.531 * | 0.020 * | 0.110 * | 0.944 * |
| AGE (years) | 0.281 | 0.012 | 0.311 | 0.048 | 0.249 | 0.127 | - * | - * | - * | - * |
| Body weight | −0.010 | 0.931 | −0.018 | 0.910 | −0.038 | 0.818 | - * | - * | - * | - * |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.128 | 0.259 | 0.210 | 0.188 | 0.020 | 0.991 | - * | - * | - * | - * |
| WHTR | 0.158 | 0.161 | 0.193 | 0.226 | 0.086 | 0.602 | - * | - * | - * | - * |
| Lipid-lowering therapy | −0.058 | 0.610 | −0.111 | 0.491 | 0.066 | 0.688 | −0.230 | 0.205 | −0.189 | 0.267 |
| Duration of T2D (years) | 0.750 * | 0.794 * | 0.183 * | 0.532 * | 0.160 * | 0.383 * | ||||
| Duration of metformin (years) | 0.272 * | 0.347 * | 0.393 * | 0.164 * | 0.234 * | 0.197 * | ||||
| Duration of insulin (years) | 0.124 * | 0.673 * | 0.317 * | 0.270 * | 0.157 * | 0.384 * | ||||
| Dose of insulin (IU/d) | −0.096 * | 0.744 * | 0.411 * | 0.144 * | 0.159 * | 0.384 * | ||||
| All Patients, N = 80 (R2 = 0.3; R = 0.678) | CRP+, N = 41 (R2 = 0.011; R = 0.584) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standardised Coefficients | Partial Correlation | t | p Value | Standardised Coefficients | Partial Correlation | t | p Value | |
| AGE | −0.05 | −0.04 | −0.31 | 0.75 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.94 |
| BMI | 1.00 | 0.29 | 2.37 | 0.21 | 0.34 | 0.20 | 0.67 | 0.51 |
| WHTR | 0.16 | 0.09 | 0.69 | 0.50 | 0.20 | 8.25 | 0.29 | 0.78 |
| Body weight | −1.21 | −0.36 | −2.97 | 0.00 | −0.07 | −0.02 | −0.11 | 0.91 |
| Duration of T2D | 0.20 | 0.12 | 0.93 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.17 | 1.68 | 0.10 |
| FPG | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.96 | −0.15 | −0.01 | −0.82 | 0.42 |
| CH | −0.20 | −0.19 | −1.50 | 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.9 |
| TG | 0.37 | 0.10 | 0.82 | 0.42 | −0.15 | −0.01 | −0.29 | 0.77 |
| HDL | −0.36 | −0.13 | −1.04 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.91 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.56 | 0.08 | 0.61 | 0.54 | −1.31 | −4.69 | −1.40 | 0.17 |
| AIP | −0.54 | −0.10 | −0.82 | 0.42 | 0.11 | 1.69 | 0.17 | 0.87 |
| Fasting insulin | −0.75 | −0.11 | −0.87 | 0.39 | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.48 |
| PEPTIDE C | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 0.32 | 0.41 | 1.89 | 1.57 | 0.13 |
| IGF-1 | −0.16 | −0.16 | −1.30 | 0.20 | −0.03 | −0.00 | −0.14 | 0.89 |
| Variable | p Value | OR | CI −95% | CI +95% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model 1. | Gender | 0.62 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 2.64 |
| Age | 0.00 | 1.13 | 1.05 | 1.21 | |
| BMI | 0.02 | 1.14 | 1.02 | 1.27 | |
| HOMA-IR | 0.77 | 0.95 | 0.69 | 1.32 | |
| TG | 0.03 | 1.02 | 1.00 | 1.03 | |
| HDL | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 1.01 | |
| Gal-3 | 0.31 | 1.08 | 0.93 | 1.26 | |
| For the model: p < 0.001; Nagelkerke R-square 0.557, −2 log-likelihood 67.025, Hosmer–Lemeshow test: p 0.928 | |||||
| Model 2. | Age | 0.02 | 1.12 | 1.02 | 1.24 |
| BMI | 0.02 | 1.20 | 1.03 | 1.40 | |
| HOMA-IR | 0.13 | 0.65 | 0.37 | 1.14 | |
| HDL | 0.02 | 1.19 | 1.03 | 1.38 | |
| CH | 0.01 | 0.95 | 0.91 | 0.99 | |
| API | 0.01 | 98,504 | 21.8 | 444,516,456 | |
| FPG | 0.01 | 1.07 | 1.02 | 1.12 | |
| Gal-3 | 0.58 | 1.06 | 0.88 | 1.27 | |
| For the model: p < 0.001; Nagelkerke R-square 0.557, −2 log-likelihood 67.025, Hosmer–Lemeshow test: p 0.928 | |||||
| p Value | OR | CI −95% | CI +95% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.291 | 2.301 | 0.490 | 10.819 |
| Age | 0.003 | 1.116 | 1.038 | 1.201 |
| Body weight | 0.016 | 1.105 | 1.019 | 1.199 |
| Waist circumference | 0.153 | 0.941 | 0.865 | 1.023 |
| T2D | 0.156 | 0.350 | 0.082 | 1.491 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.059 | 0.049 | 0.002 | 1.122 |
| Fasting insulin | 0.107 | 2.002 | 0.061 | 4.658 |
| API | 0.007 | 2.743 | 1.314 | 5.728 |
| IGF-1 | 0.059 | 1.018 | 0.999 | 1.037 |
| CH | 0.792 | 0.998 | 0.982 | 1.014 |
| Gal-3 | 0.031 | 1.178 | 1.015 | 1.366 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Storman, M.; Przybyłkowski, A.; Czupryniak, L. Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Colorectal Polyps. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167662
Storman M, Przybyłkowski A, Czupryniak L. Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Colorectal Polyps. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(16):7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167662
Chicago/Turabian StyleStorman, Monika, Adam Przybyłkowski, and Leszek Czupryniak. 2025. "Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Colorectal Polyps" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 16: 7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167662
APA StyleStorman, M., Przybyłkowski, A., & Czupryniak, L. (2025). Cross-Sectional Study of Serum Galectin-3 Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Colorectal Polyps. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(16), 7662. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26167662






