Anti-CD26 Antibody Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
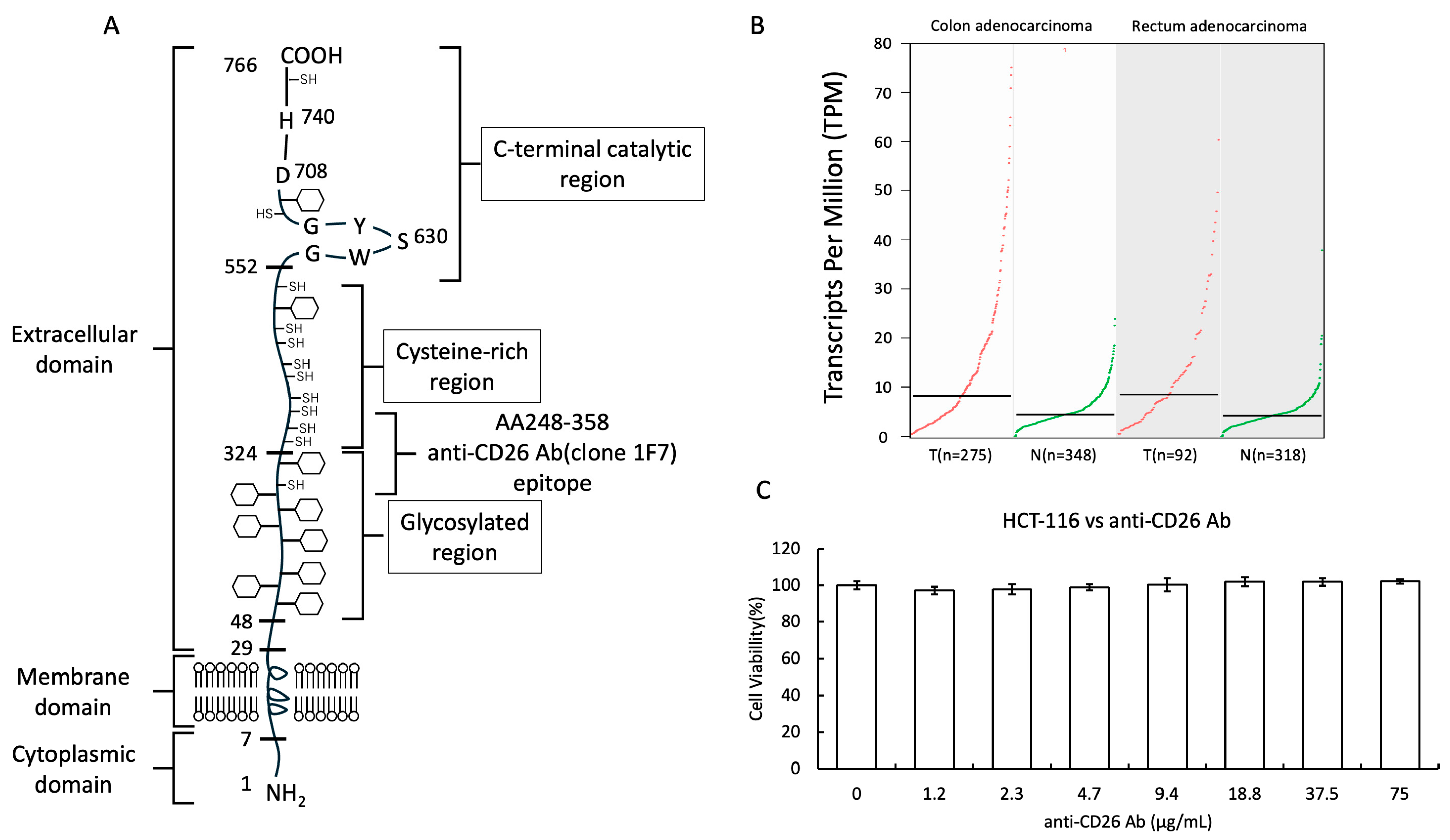
2.1. Structure of the CD26 Molecule and Cytotoxicity of Anti-CD26 Antibodies
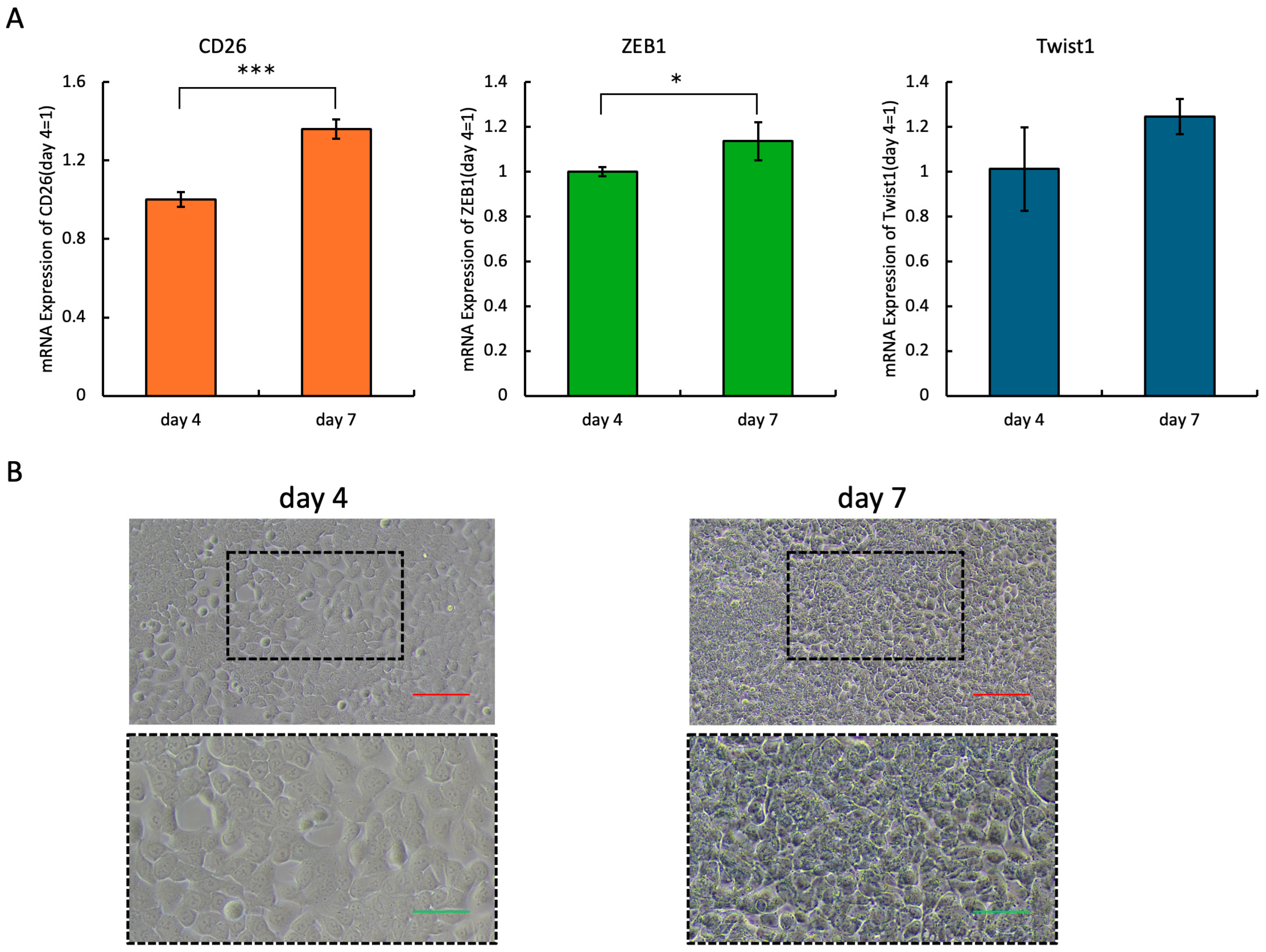
2.2. Expression Levels of CD26 and EMT-Related Molecules
2.3. Anti-CD26 Antibody Treatment Inhibits Migration and Invasion of HCT-116 Cells
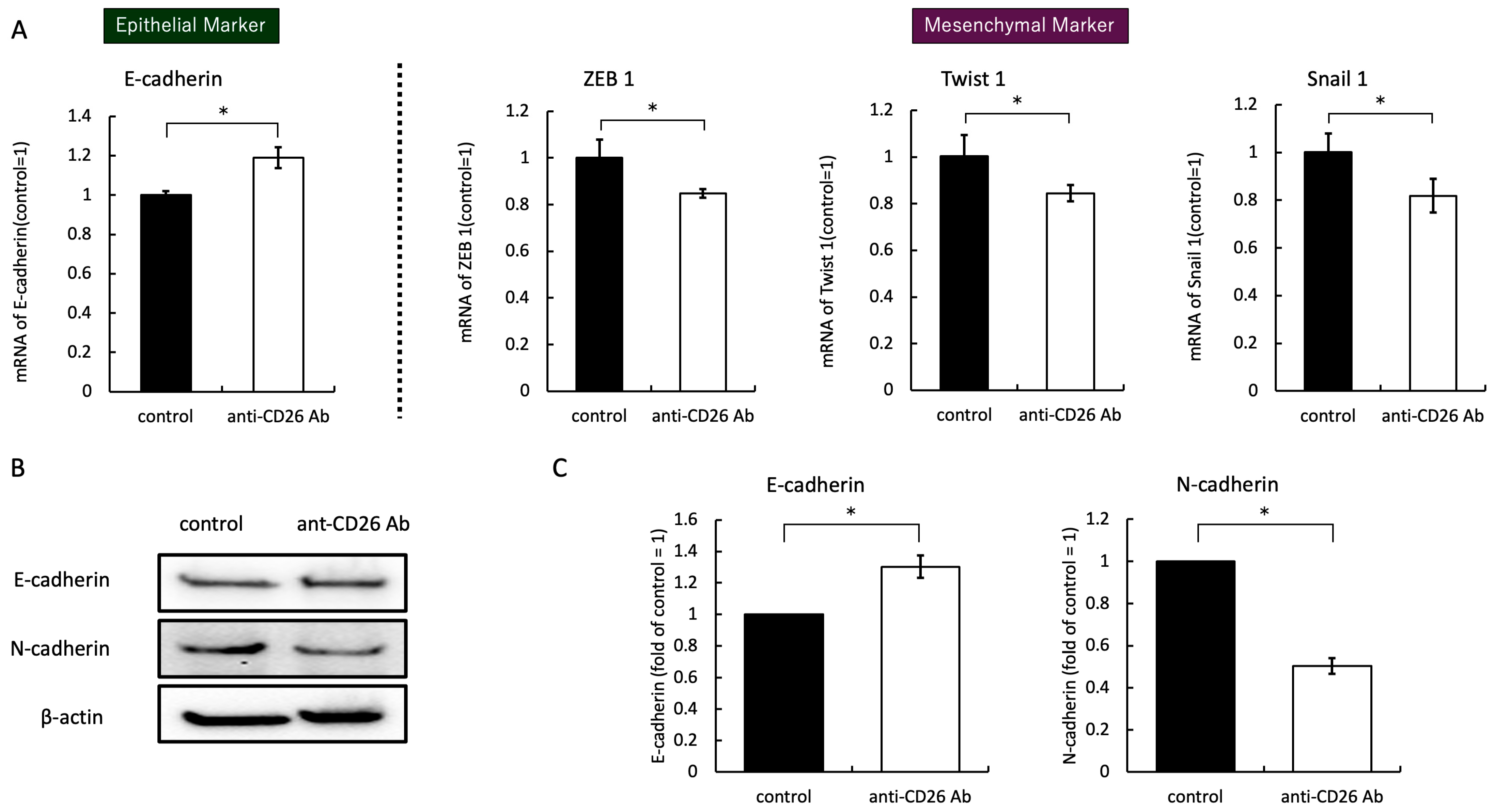
2.4. Anti-CD26 Antibody Treatment Suppresses EMT Signals
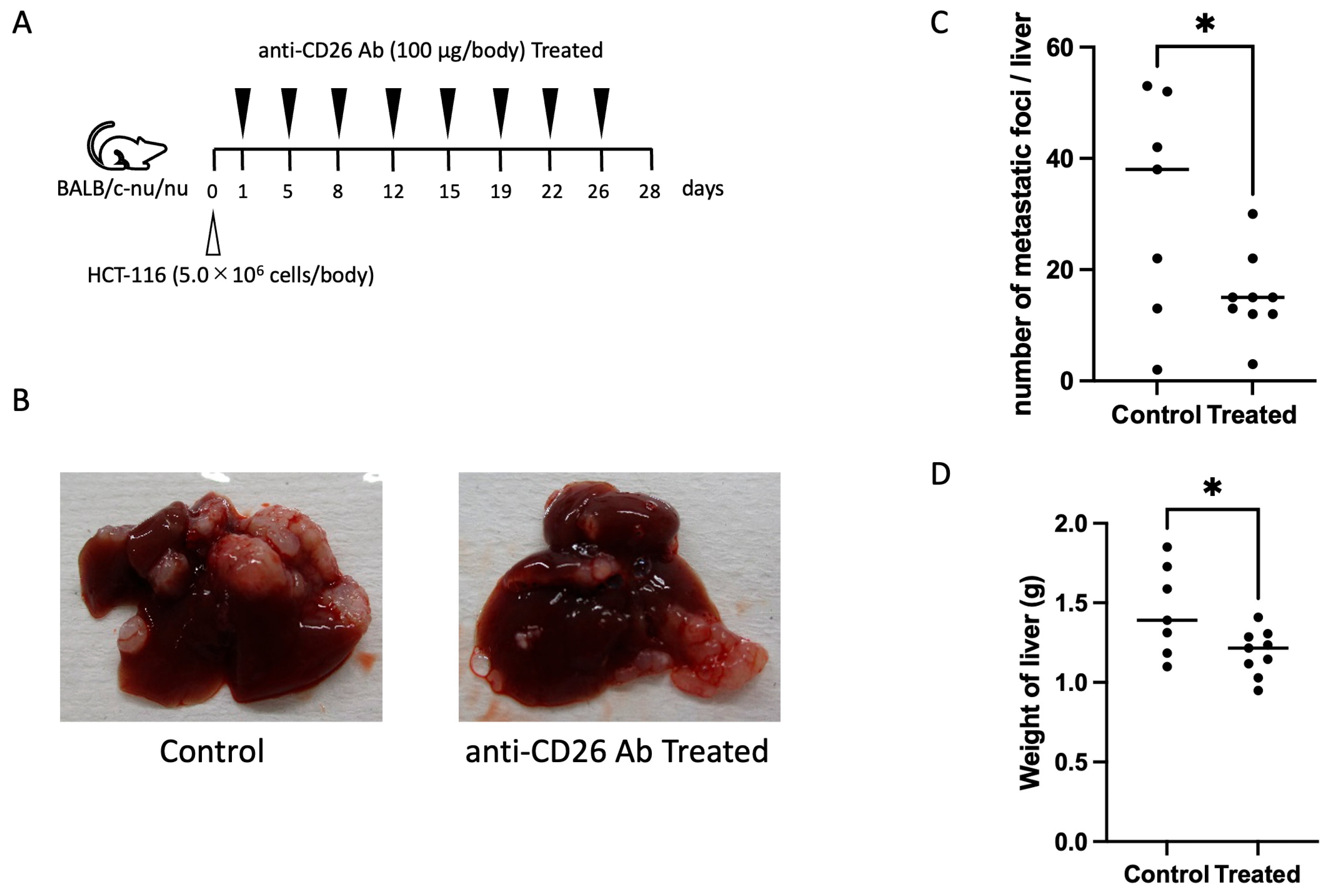
2.5. Anti-CD26 Antibody Suppresses Liver Metastasis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Line and Cell Culture
4.2. Antibodies
4.3. Cytotoxic Assay
4.4. Scratch Wound-Healing Assay
4.5. Western Blotting Analysis
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Migration and Invasion Assays
4.8. In Vivo Tumor Metastasis in a Cancer Mouse Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, C.A.; Pollett, A.; Gallinger, S.; Dick, J.E. A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumor growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature 2007, 445, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Law, W.L.; Chu, A.C.Y.; Poon, J.T.; Lam, C.S.; Chow, A.K.; Ng, L.; Cheung, L.W.; Lan, X.R.; Lan, H.Y.; et al. A subpopulation of CD26⁺ cancer stem cells with metastatic capacity in human colorectal cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 603–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, C.; Schlossman, S.F. The structure and function of CD26 in the T-cell immune response. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 161, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, K.; Hatano, R.; Komiya, E.; Otsuka, H.; Itoh, T.; Iwao, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Yamada, T.; Dang, N.H.; Morimoto, C. A novel role for CD26/dipeptidyl peptidase IV as a therapeutic target. Front. Biosci. 2018, 23, 1754–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesley, U.V.; Tiwari, S.; Houghton, A.N. Role for dipeptidyl peptidase IV in tumor suppression of human non–small cell lung carcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 109, 855–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, M.A.; Huang, R.Y.J.; Jackson, R.A.; Thiery, J.P. EMT: 2016. Cell 2016, 166, 21–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The epithelial–mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.P.; Lièvre, M.; Thomas, C.; Hinkal, G.; Ansieau, S.; Puisieux, A. Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, M.; Haver, P.A.; Urasaki, Y.; Ohnuma, K.; Morimoto, C.; Dang, L.H.; Dang, N.H. Mechanisms of confluence-dependent expression of CD26 in colon cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohnuma, K.; Dang, N.H.; Morimoto, C. Revisiting an old acquaintance: CD26 and its molecular mechanisms in T cell function. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffit, L.R.; Bilandzic, M.; Wilson, A.L.; Chen, Y.; Gorrell, M.D.; Oehler, M.K.; Plebanski, M.; Stephens, A.N. Hypoxia regulates DPP4 expression, proteolytic inactivation, and shedding from ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Ballestar, E.; Esteller, M.; Cano, A. Snail mediates E-cadherin repression by the recruitment of the Sin3A/HDAC1/2 complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 24, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tilló, E.; Lázaro, A.; Cuatrecasas, M.; Vaquero, E.C.; Castells, A.; Engel, P.; Postigo, A. ZEB1 represses E-cadherin and induces an EMT by recruiting the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling protein BRG1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 3490–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizu, K.; Sunose, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Tsuruo, T.; Sadahiro, S.; Makuuchi, H.; Yamori, T. Development and characterization of a model of liver metastasis using human colon cancer HCT-116 cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 30, 1779–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, O.J.; Salgado, F.J.; Nogueira, M. On the origin of serum CD26 and its altered concentration in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2009, 58, 1723–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, D.M.; Medici, C. Signaling mechanisms of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, re8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Min, P.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. CD26 upregulates proliferation and invasion in keloid fibroblasts through an IGF-1-induced PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Burns Trauma 2020, 8, tkaa025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohm, B.; Moneke, I.; Jungraithmayr, W. Targeting cluster of differentiation 26/dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 180, 2846–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.H.; Cheng, C.W.; Yang, Y.C.; Chen, W.S.; Hung, W.Y.; Chow, J.M.; Chen, P.S.; Hsiao, M.; Lee, W.J.; Chien, M.H. Downregulating CD26/DPPIV by apigenin modulates the interplay between Akt and Snail/Slug signaling to restrain metastasis of lung cancer with multiple EGFR statuses. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnuma, K.; Uchiyama, M.; Yamochi, T.; Nishibashi, K.; Hosono, O.; Takahashi, N.; Kina, S.; Tanaka, H.; Lin, X.; Dang, N.H.; et al. Caveolin-1 triggers T-cell activation via CD26 in association with CARMA1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10117–10131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagaki, Y.; Shi, S.; Katoh, M.; Kitada, M.; Kanasaki, K.; Koya, D. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 plays a pathogenic role in BSA-induced kidney injury in diabetic mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamoto, T.; Yamada, T.; Ohnuma, K.; Kina, S.; Takahashi, N.; Yamochi, T.; Inamoto, S.; Katsuoka, Y.; Hosono, O.; Tanaka, H.; et al. Humanized anti-CD26 monoclonal antibody as a treatment for malignant mesothelioma tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 4191–4200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angevin, E.; Isambert, N.; Trillet-Lenoir, V.; You, B.; Alexandre, J.; Zalcman, G.; Vielh, P.; Farace, F.; Valleix, F.; Podoll, T.; et al. First-in-human phase 1 of YS110, a monoclonal antibody directed against CD26 in advanced CD26-expressing cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1126–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Ohe, Y.; Horinouchi, H.; Hida, T.; Shimizu, J.; Seto, T.; Nosaki, K.; Kishimoto, T.; Miyashita, I.; Yamada, M.; et al. Phase I study of YS110, a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to CD26, in Japanese patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma. Lung Cancer 2019, 137, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, K.; Kijima, T.; Okada, M.; Morise, M.; Kato, M.; Hirano, K.; Fujimoto, N.; Takenoyama, M.; Yokouchi, H.; Ohe, Y.; et al. Phase 2 study of YS110, a recombinant humanized anti-CD26 monoclonal antibody, in Japanese patients with advanced malignant pleural mesothelioma. JTO Clin. Res. Rep. 2021, 2, 100178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.; Wong, S.K.-M.; Huang, Z.; Lam, C.S.-C.; Chow, A.K.-M.; Foo, D.C.-C.; Lo, O.S.-H.; Pang, R.W.-C.; Law, W.-L. CD26 Induces Colorectal Cancer Angiogenesis and Metastasis through CAV1/MMP1 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, C.; Torimoto, Y.; Levinson, G.; Rudd, C.E.; Schrieber, M.; Dang, N.H.; Letvin, N.L.; Schlossman, S.F. 1F7, A novel cell surface molecule, involved in helper function of CD4 cells. J. Immunol. 1989, 143, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.P.; Tachibana, K.; Hegen, M.; Scharpe, S.; Cho, D.; Schlossman, S.F.; Morimoto, C. Correlation of the epitopes defined by anti-CD26 mAbs and CD26 function. Mol. Immunol. 1998, 35, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iwasawa, T.; Hatano, R.; Takeda, S.; Kurusu, A.; Okamoto, C.; Kato, K.; Morimoto, C.; Iwao, N. Anti-CD26 Antibody Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157620
Iwasawa T, Hatano R, Takeda S, Kurusu A, Okamoto C, Kato K, Morimoto C, Iwao N. Anti-CD26 Antibody Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157620
Chicago/Turabian StyleIwasawa, Takumi, Ryo Hatano, Satoshi Takeda, Ayumi Kurusu, Chikako Okamoto, Kazunori Kato, Chikao Morimoto, and Noriaki Iwao. 2025. "Anti-CD26 Antibody Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157620
APA StyleIwasawa, T., Hatano, R., Takeda, S., Kurusu, A., Okamoto, C., Kato, K., Morimoto, C., & Iwao, N. (2025). Anti-CD26 Antibody Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Stem Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157620




