Oxidative Ferritin Destruction: A Key Mechanism of Iron Overload in Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatocyte Ferroptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Hepatotoxicity Induced by APAP
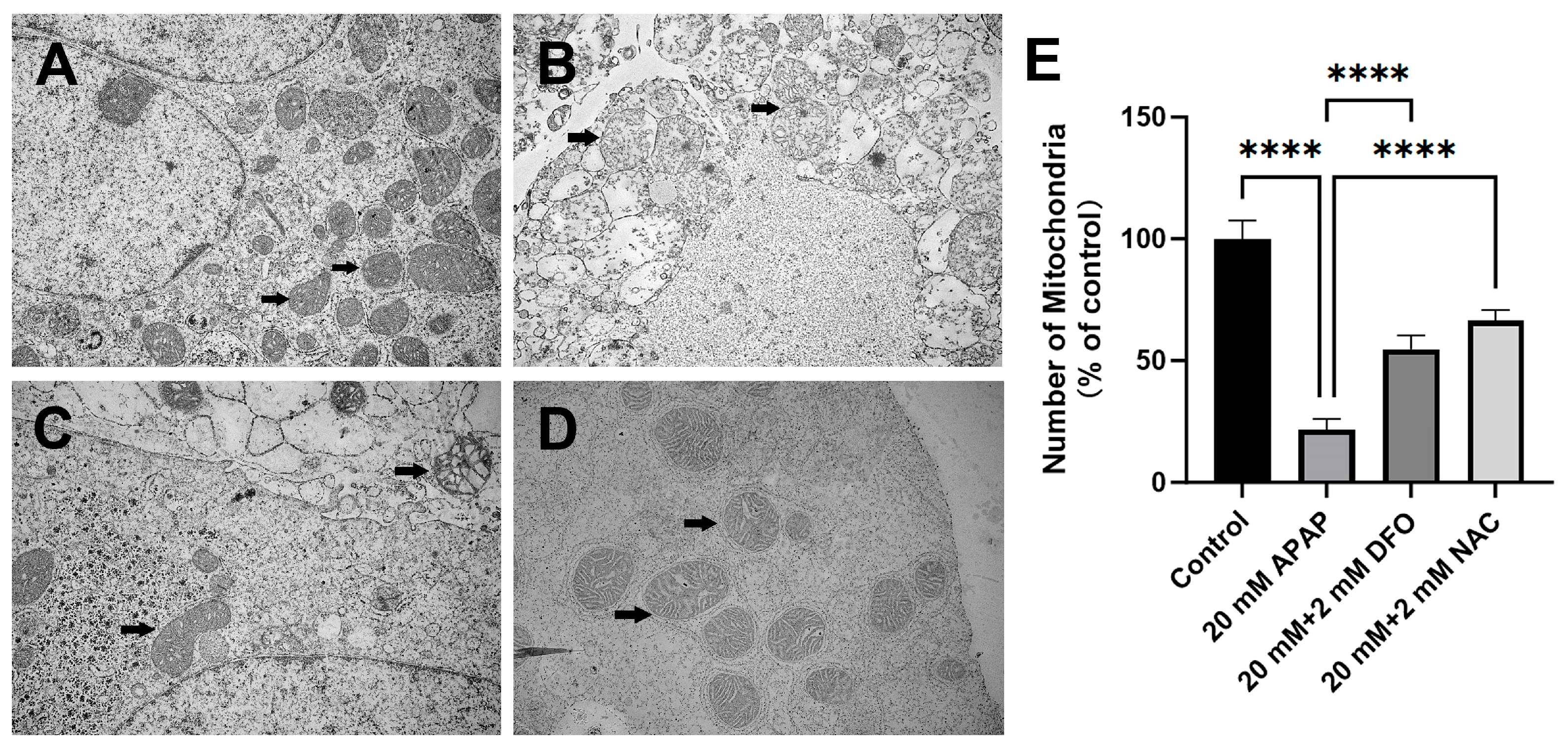
2.2. The Changes in PMHs’ Ultrastructure After APAP Treatment
2.3. Decrease in Intracellular GSH and Increase in LIP Caused by Treatment with APAP
2.4. Lipid Peroxidation and Mitochondrial Superoxide Production in PMHs After APAP Exposure
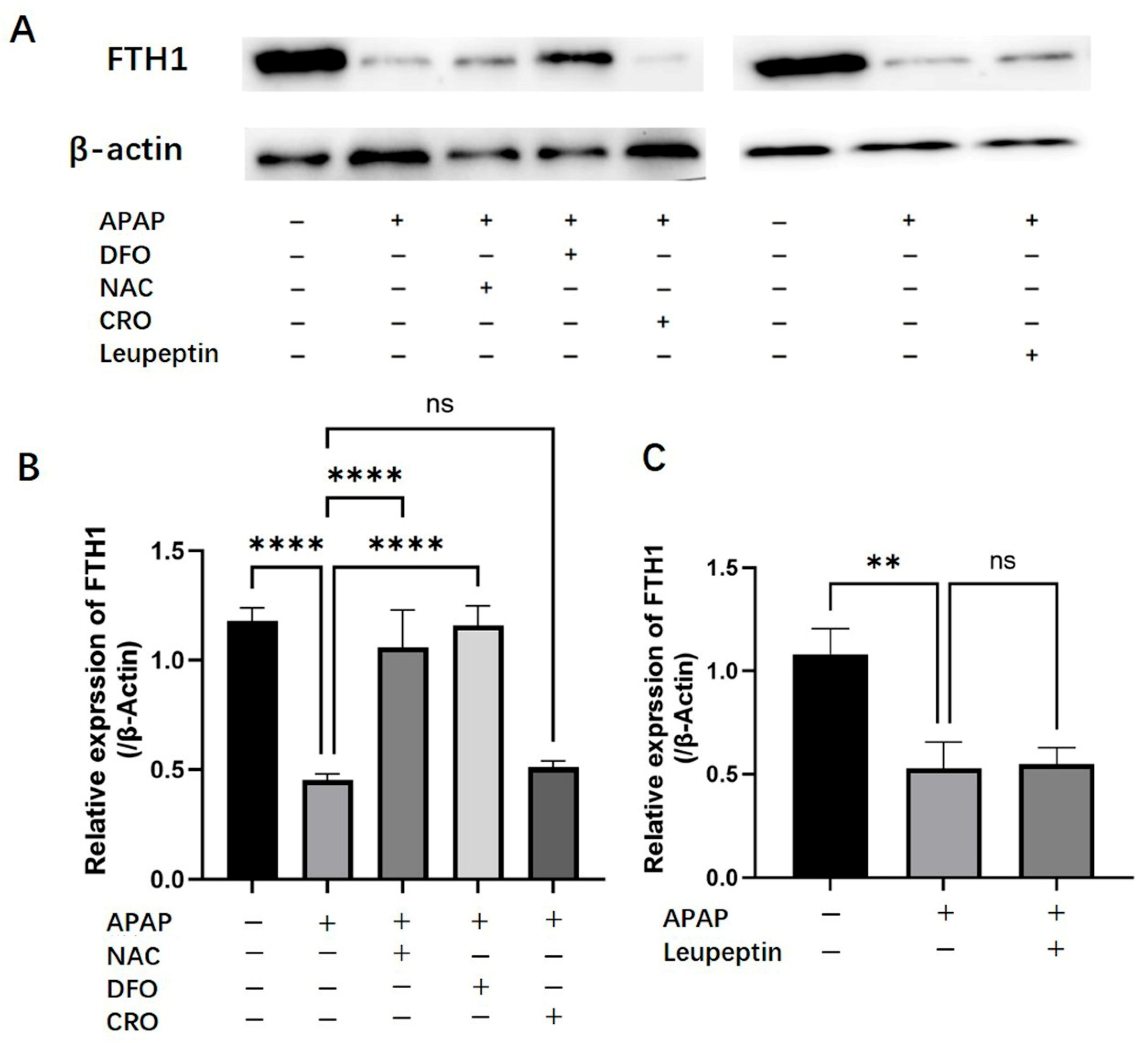
2.5. Effects of APAP on Hepatic Ferritin (FTH1) Expression
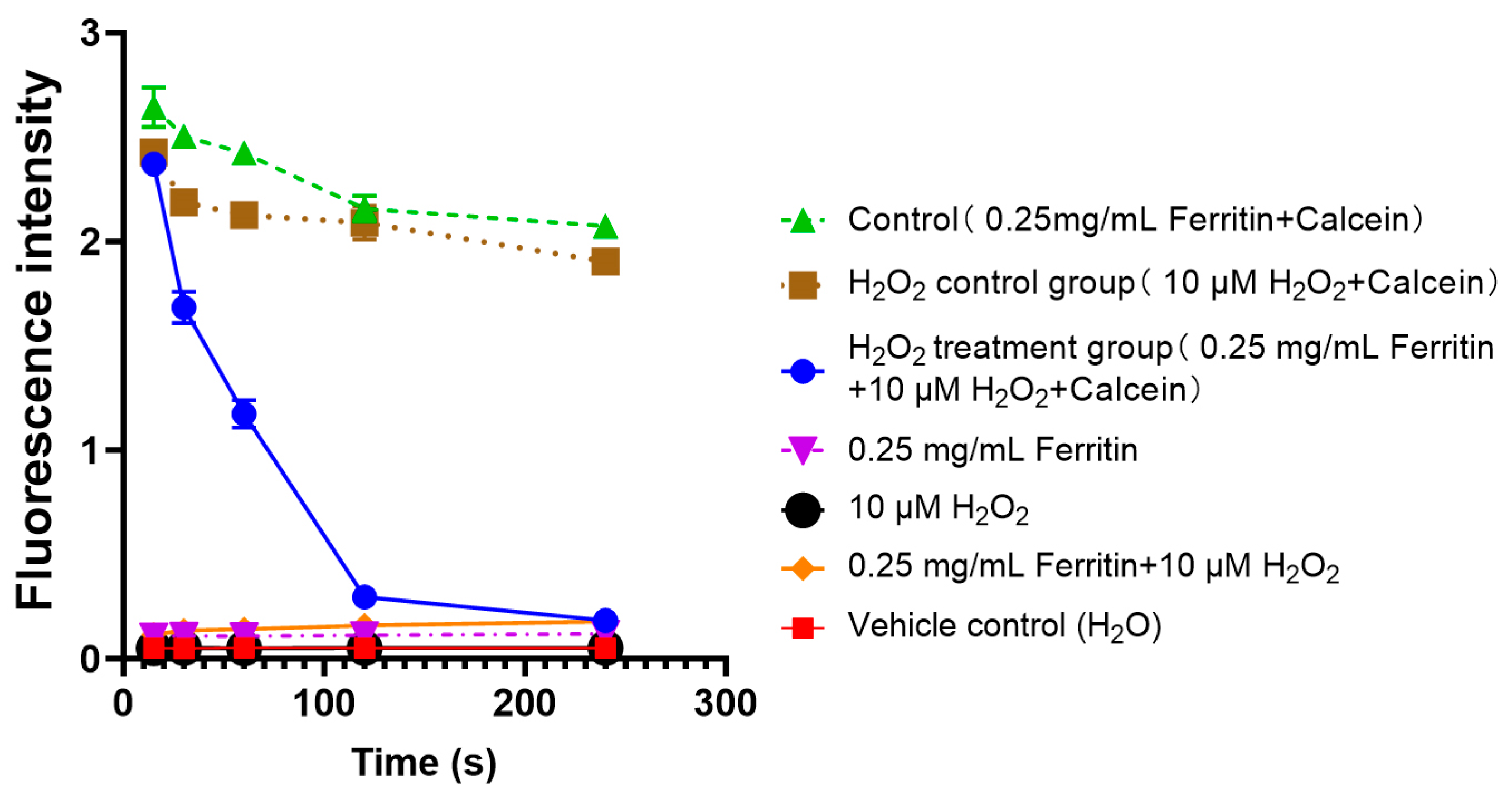
2.6. Iron Release from Ferritin Under Oxidative Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Isolation and Culture of Primary Mouse Hepatocytes
4.3. Evaluation of Cell Viability After Treatment with APAP
4.4. The Effect of DFO, NAC, Chloroquine or Leupeptin on APAP-Induced Hepatotoxicity
4.5. Electron Microscopy
4.6. Determination of GSH by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.7. Determination of Cellular Labile Iron Pool (LIP)
4.8. Lipid Peroxidation Measurements
4.9. Measurement of Mitochondrial Superoxide with MitoSOX-
4.10. Western Blotting Analysis of Ferritin
4.11. Determination of Iron Released from Ferritin Induced by Oxidative Injury Using Calcein Fluorescence
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
Abbreviations
| ALF | Acute liver failure |
| APAP | Acetaminophen |
| BSA | Albumin from bovine serum |
| Calcein-AM | Calcein acetoxymethyl ester |
| CMQT | 2-chloro-1-methylquinoline tetrafluoroborate |
| DFO | Deferoxamine |
| DILI | Drug-induced liver injury |
| DTT | DL-Dithiothreito |
| FBS | Fetal ovine serum |
| FITC | Flurorescein isothiocyanate |
| FTH1 | Ferritin heavy chain 1 |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyerhyl)piperazine-1-erhanesulfon |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LIP | Labile iron pool |
| MPT | Mitochondrial permeability transition |
| NAC | N-acetyleystein |
| NAPQI | N-Acetyl-benzo-quinoneimine |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| PMHs | Primary mice hepatocytes |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, P.N.; Cartlidge, P.; Manship, T.; Dillon, J.F. Guideline review: EASL clinical practice guidelines: Drug-induced liver injury (DILI). Frontline Gastroenterol. 2022, 13, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M. Drug-induced acute liver failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2013, 17, 575–586, viii. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattiuzzi, C.; Lippi, G. How Much has COVID-19 Contributed to Increase the Worldwide Consumption of Paracetamol and Ibuprofen? Evidence From an Infodemiological Analysis. Hosp. Pharm. 2023, 58, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidiac, A.S.; Buckley, N.A.; Noghrehchi, F.; Cairns, R. Paracetamol (acetaminophen) overdose and hepatotoxicity: Mechanism, treatment, prevention measures, and estimates of burden of disease. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2023, 19, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity: Sources, pathophysiological role and therapeutic potential. Redox Biol. 2016, 10, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karvellas, C.J.; Leventhal, T.M.; Rakela, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Durkalski, V.; Reddy, K.R.; Fontana, R.J.; Stravitz, R.T.; Lake, J.R.; Lee, W.M.; et al. Outcomes of patients with acute liver failure listed for liver transplantation: A multicenter prospective cohort analysis. Liver Transpl. 2023, 29, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, J.; Lin, B.; Zhou, M.; Wu, L.; Zheng, T. Role of ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaie, L.; Iorga, A.; Dara, L. Cell Death in Liver Diseases: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kučera, O.; Endlicher, R.; Rychtrmoc, D.; Lotková, H.; Sobotka, O.; Červinková, Z. Acetaminophen toxicity in rat and mouse hepatocytes in vitro. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 40, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganz, T. Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism and mediator of anemia of inflammation. Blood 2003, 102, 783–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusi, K. Role of obesity and lipotoxicity in the development of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 711–725.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunchorntavakul, C.; Reddy, K.R. Acetaminophen (APAP or N-Acetyl-p-Aminophenol) and Acute Liver Failure. Clin. Liver Dis. 2018, 22, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillebeen, C.; Charlebois, E.; Wagner, J.; Katsarou, A.; Mui, J.; Vali, H.; Garcia-Santos, D.; Ponka, P.; Presley, J.; Pantopoulos, K. Transferrin receptor 1 controls systemic iron homeostasis by fine-tuning hepcidin expression to hepatocellular iron load. Blood 2019, 133, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Fang, X.; Duan, L.; et al. Hepatic transferrin plays a role in systemic iron homeostasis and liver ferroptosis. Blood 2020, 136, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nai, A. BMP5: A novel tile of the hepcidin regulatory pathway. Blood 2023, 142, 1260–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Stockwell, B.R. Unsolved mysteries: How does lipid peroxidation cause ferroptosis? PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Liu, X.; Feng, L.; Gong, Z.; Koppula, P.; Sirohi, K.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Lee, H.; et al. BAP1 links metabolic regulation of ferroptosis to tumour suppression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protchenko, O.; Baratz, E.; Jadhav, S.; Li, F.; Shakoury-Elizeh, M.; Gavrilova, O.; Ghosh, M.C.; Cox, J.E.; Maschek, J.A.; Tyurin, V.A.; et al. Iron Chaperone Poly rC Binding Protein 1 Protects Mouse Liver From Lipid Peroxidation and Steatosis. Hepatology 2021, 73, 1176–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaeschke, H.; Ramachandran, A.; Chao, X.; Ding, W.X. Emerging and established modes of cell death during acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Arch. Toxicol. 2019, 93, 3491–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; Ramachandran, A. Acetaminophen-induced apoptosis: Facts versus fiction. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2020, 6, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, E.; Meng, L.; Kang, R.; Wang, X.; Tang, D. ESCRT-III-dependent membrane repair blocks ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.M.; McGill, M.R.; Chao, X.; Du, K.; Williams, J.A.; Xie, Y.; Jaeschke, H.; Ding, W.X. Removal of acetaminophen protein adducts by autophagy protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.; Xie, Y.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1425–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.M. Acetaminophen (APAP) hepatotoxicity-Isn’t it time for APAP to go away? J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1324–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingold, I.; Berndt, C.; Schmitt, S.; Doll, S.; Poschmann, G.; Buday, K.; Roveri, A.; Peng, X.; Porto Freitas, F.; Seibt, T.; et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis. Cell 2018, 172, 409–422.E21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokare, A.D.; Choi, W. Review of iron-free Fenton-like systems for activating H2O2 in advanced oxidation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 275, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.N.; Zhang, W.X.; Gao, Y.R.; Wei, Y.N.; Shu, Y.; Wang, J.H. State-of-the-art advances of copper-based nanostructures in the enhancement of chemodynamic therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 250–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamchuea, K.; Batchelor-McAuley, C.; Compton, R.G. The Copper(II)-Catalyzed Oxidation of Glutathione. Chemistry 2016, 22, 15937–15944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoyue, W.; Kexiang, S.; Shan, T.W.; Jiamin, G.; Luyun, Y.; Junkai, W.; Wanli, D. Icariin promoted ferroptosis by activating mitochondrial dysfunction to inhibit colorectal cancer and synergistically enhanced the efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors. Phytomedicine 2025, 136, 156224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Q.; Luo, Z.; Ren, Y.; Chen, X.; Chen, G. Iron and copper: Critical executioners of ferroptosis, cuproptosis and other forms of cell death. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 21, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M.V.J.O.; Khalessi, A.A.; Kluck, B.W.; Lavine, S.; Meyers, P.M.; Ramee, S.; Rüfenacht, D.A.; Schirmer, C.M.; Vorwerk, D. Multisociety Consensus Quality Improvement Revised Consensus Statement for Endovascular Therapy of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Stroke 2018, 6, 612–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, P.; Bhattacharyya, S.; McCullough, S.; Letzig, L.; Mishra, P.J.; Luo, C.; Dweep, H.; James, L. MicroRNA regulation of CYP 1A2, CYP3A4 and CYP2E1 expression in acetaminophen toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreng, B.; Kimcheng, H.; Sovann, L.Y.; Huot, E. Epidemiology of Viral Hepatitis and Liver Diseases in Cambodia. Euroasian J. Hepatogastroenterol. 2015, 5, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, T.; Goto, T.; Hirotsu, Y.; Moriyama, M.; Omata, M. Molecular Mechanisms Driving Progression of Liver Cirrhosis towards Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Chronic Hepatitis B and C Infections: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, E.S.; Curry, S.C. Evaluation and treatment of acetaminophen toxicity. Adv. Pharmacol. 2019, 85, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Nunes, A.; Jakszyn, P.; Agudo, A. Iron and cancer risk--a systematic review and meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 12–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Lei, X.; Xu, Q.; Ju, Y.; Xu, D.; Mao, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, N.; Zhang, X.; et al. Protecting mitochondria via inhibiting VDAC1 oligomerization alleviates ferroptosis in acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 505–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, A.; Kim, J.S.; Kon, K.; Jaeschke, H.; Ikejima, K.; Watanabe, S.; Lemasters, J.J. Translocation of iron from lysosomes into mitochondria is a key event during oxidative stress-induced hepatocellular injury. Hepatology 2008, 48, 1644–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Xia, X.; Tan, X.; Zang, J.; Wang, Z.; Ei-Seedi, H.R.; Du, M. Advancements of nature nanocage protein: Preparation, identification and multiple applications of ferritins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 7117–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, H.; McGill, M.R.; Ramachandran, A. Oxidant stress, mitochondria, and cell death mechanisms in drug-induced liver injury: Lessons learned from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. Drug Metab. Rev. 2012, 44, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Lin, Z. Comparison of isolation and extraction of primary mouse hepatocytes by trypsin and collagenase perfusion. J. Shantou Univ. Med. Coll. 2022, 35, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Echtermeyer, F.; Eberhardt, M.; Risser, L.; Herzog, C.; Gueler, F.; Khalil, M.; Engel, M.; Vondran, F.; Leffler, A. Acetaminophen-induced liver injury is mediated by the ion channel TRPV4. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 10257–10268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathi, T.R.; Sunil Kumar, G.B.; Srinivas, L.; Revathi, C.J.; Bapat, V.A. Analysis of the limitations of hepatitis B surface antigen expression in soybean cell suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep. 2007, 26, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Li, H.; Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, W.; Lin, Z. Potential Antioxidative Activity of Homocysteine in Erythrocytes under Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, A.M.; Sacco, A.; Vecchio, E.; Scicchitano, S.; Petriaggi, L.; Giorgio, E. Iron affects the sphere-forming ability of ovarian cancer cells in non-adherent culture conditions. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1272667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, K.; Liang, K.; Li, H.; Luo, H.; Chen, Y.; Yin, K.; Liu, Z.; Luo, W.; Lin, Z. Oxidative Ferritin Destruction: A Key Mechanism of Iron Overload in Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatocyte Ferroptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157585
Gong K, Liang K, Li H, Luo H, Chen Y, Yin K, Liu Z, Luo W, Lin Z. Oxidative Ferritin Destruction: A Key Mechanism of Iron Overload in Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatocyte Ferroptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157585
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Kaishuo, Kaiying Liang, Hui Li, Hongjun Luo, Yingtong Chen, Ke Yin, Zhixin Liu, Wenhong Luo, and Zhexuan Lin. 2025. "Oxidative Ferritin Destruction: A Key Mechanism of Iron Overload in Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatocyte Ferroptosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157585
APA StyleGong, K., Liang, K., Li, H., Luo, H., Chen, Y., Yin, K., Liu, Z., Luo, W., & Lin, Z. (2025). Oxidative Ferritin Destruction: A Key Mechanism of Iron Overload in Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatocyte Ferroptosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157585





