Differential Associations of PIVKA-II with Epithelial and Mesenchymal Features in HCC and PDAC
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
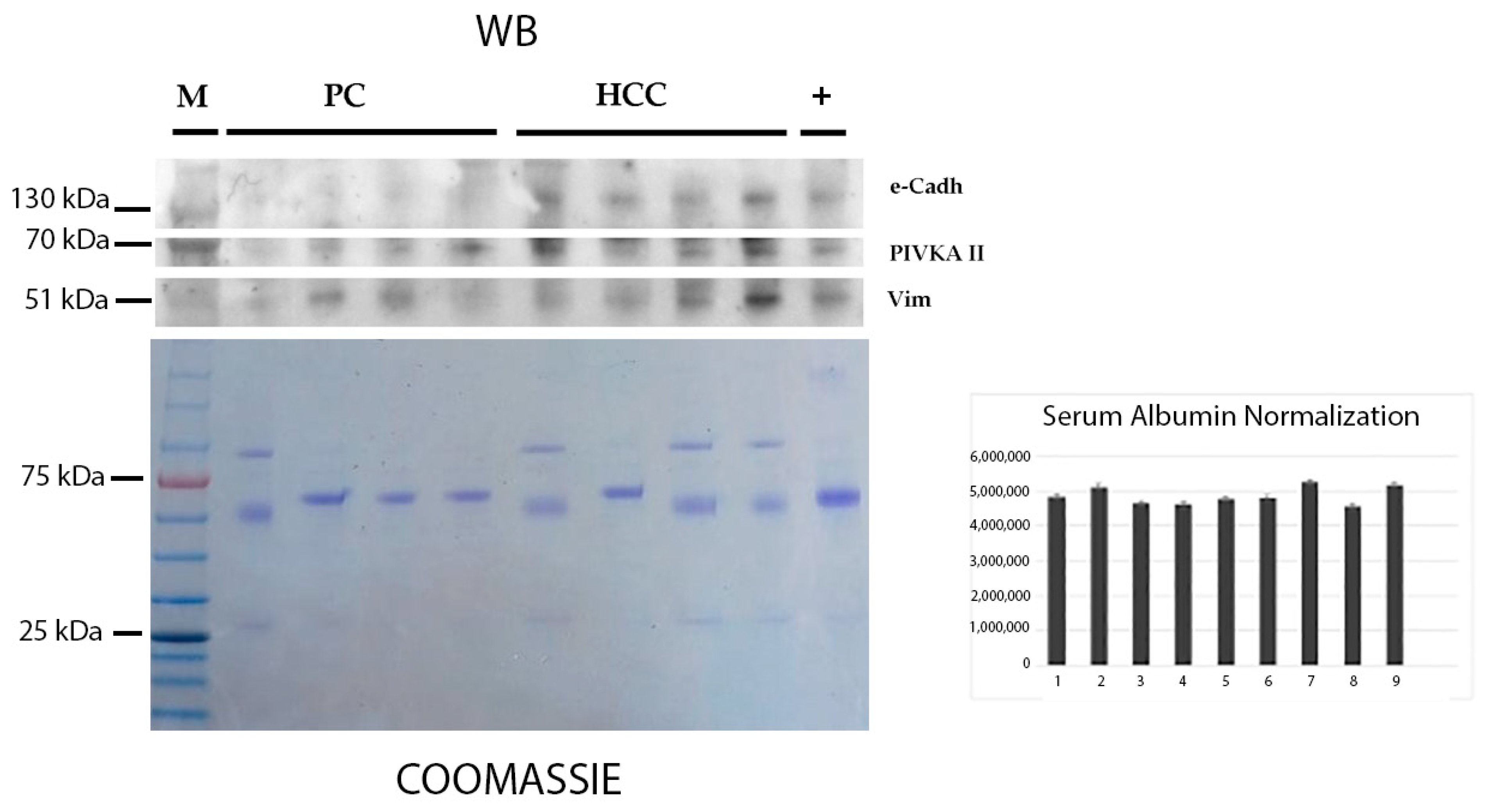
2.1. Detection of PIVKA-II and EMT Markers in the Sera of Patients with HCC and PDAC by Western Blot Analysis
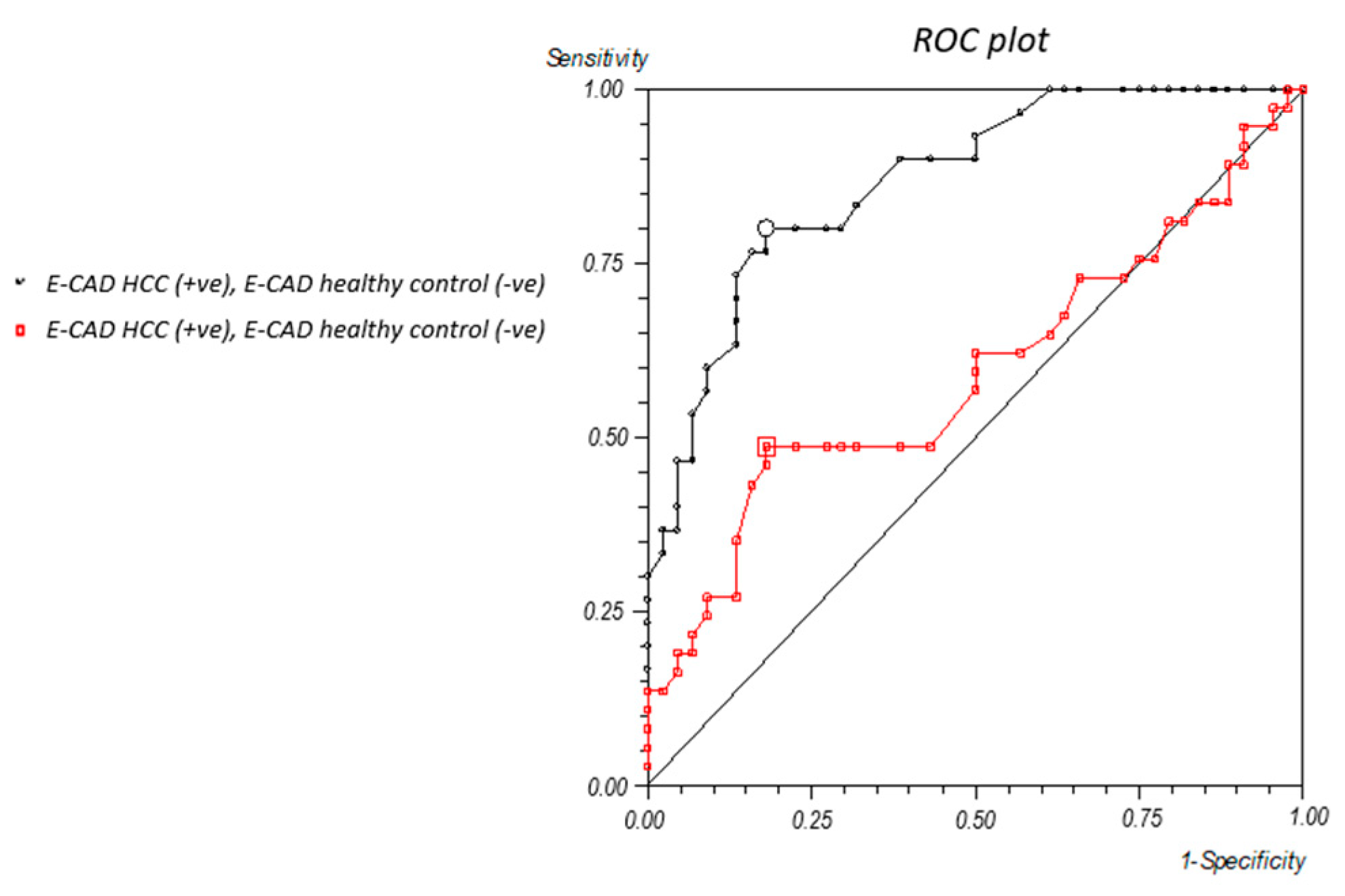
2.2. Vimentin and E-Cadherin Thresholds
2.3. Comparative Analysis of Circulating PIVKA-II, Vimentin, and E-Cadherin in Human Sera
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
- Thirty patients affected by HCC;
- Thirty-seven patients affected by PDAC.
4.2. Blood Collection and Storage
4.3. Western Blot Analysis
4.4. Immunometry
4.5. Statistical Analysis
4.6. Densitometric Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Deng, B. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Molecular mechanism, targeted therapy, and biomarkers. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023, 42, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, V.M.; Kearney, J.F.; Yeh, J.J. The PDAC Extracellular Matrix: A Review of the ECM Protein Composition, Tumor Cell Interaction, and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 751311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Tamma, R.; Annese, T. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl. Oncol. 2020, 13, 100773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.; Mestre-Farrera, A.; Yang, J. Update on Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Cancer Progression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2024, 19, 133–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, S.; Schuhwerk, H.; Brabletz, T.; Stemmler, M.P. Dynamic EMT: A multi-tool for tumor progression. EMBO J. 2021, 40, e108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliekelman, M.J.; Taguchi, A.; Zhu, J.; Dai, X.; Rodriguez, J.; Celiktas, M.; Zhang, Q.; Chin, A.; Wong, C.-H.; Wang, H.; et al. Molecular portraits of epithelial, mesenchymal, and hybrid States in lung adenocarcinoma and their relevance to survival. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1789–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.-Y.; Chai, J.Y.; Tang, T.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Chong, P.P.; Looi, C.Y. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.-K.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Zhou, X.-X.; Wang, D.-M.; Song, X.-L.; Jiang, H.-B. Upregulation of vimentin and aberrant expression of E-cadherin/beta-catenin complex in oral squamous cell carcinomas: Correlation with the clinicopathological features and patient outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, C.; Sundaram, S.; Karunagaran, D. Vitamin K3 (menadione) suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal-transition and Wnt signaling pathway in human colorectal cancer cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 309, 108725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, M.J.; Okano, T. Key Pathways and Regulators of Vitamin K Function and Intermediary Metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2018, 38, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, H.; Ali, M.J.; Susheela, A.T.; Khan, I.W.; Luna-Cuadros, M.A.; Khan, M.M.; Lau, D.T.-Y. Update on the applications and limitations of alpha-fetoprotein for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, L.E.; Mellotte, G.S.; Mylod, E.; O’BRien, R.M.; O’COnnell, F.; Buckley, C.E.; Arlow, J.; Nguyen, K.; Mockler, D.; Meade, A.D.; et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Blood-based Biomarkers for Pancreatic Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, M.; Farina, A.; Angeloni, A.; Anastasi, E. Emerging horizons on molecular and circulating biomarkers in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1483306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.; Qiu, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, K.; Xu, X. Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist II: Experience to date and future directions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer. 2023, 1878, 189016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Toan, B.N.; Tan, C.-K.; Hasan, I.; Setiawan, L.; Yu, M.-L.; Izumi, N.; Huyen, N.N.; Chow, P.K.-H.; Mohamed, R.; et al. Utility of combining PIVKA-II and AFP in the surveillance and monitoring of hepatocellular carcinoma in the Asia-Pacific region. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, H.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Wei, Q.; Ren, L. PIVKA-II serves as a potential biomarker that complements AFP for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiani, V.; Palombi, S.; Gennarini, G.; D’ettorre, G.; De Vito, C.; Angeloni, A.; Frati, L.; Anastasi, E. Protein induced by vitamin K absence or antagonist-II (PIVKA-II) specifically increased in Italian hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1257–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglione, S.; Granato, T.; Anastasi, E.; Angeloni, A.; Marchese, C.; Manganaro, L.; Viggiani, V.; Zarrillo, S.R.; Pecorella, I. Protein Induced by Vitamin K Absence II (PIVKA-II) as a potential serological biomarker in pancreatic cancer: A pilot study. Biochem. Med. 2019, 29, 020707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Farina, A.; Viggiani, V.; Cortese, F.; Moretti, M.; Tartaglione, S.; Angeloni, A.; Anastasi, E. Combined PIVKA II and Vimentin-Guided EMT Tracking in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Combined Biomarker-Guided EMT Tracking in PDAC. Cancers 2024, 16, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, S.; Kurosaki, M.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yasui, Y.; Hayakawa, Y.; Inada, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Ishido, S.; Kirino, S.; Yamashita, K.; et al. Clinical evaluation of Elecsys PIVKA-II for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Takemura, N.; Yamashita, T.; Watadani, T.; Kaibori, M.; Kubo, S.; Shimada, M.; Nagano, H.; Hatano, E.; Aikata, H.; et al. Clinical Practice Guidelines for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Japan Society of Hepatology 2021 version (5th JSH-HCC Guidelines). Hepatol. Res. 2023, 53, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.-Q.; Wang, X.-Q.; Fan, G.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-W.; Song, X.; Pan, C.-C.; Chu, F.-L.; Liu, Z.-F.; Lu, B.-R.; et al. Value of AFP and PIVKA-II in diagnosis of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma and prediction of vascular invasion and tumor differentiation. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, L.; He, W.; Song, D.; Ji, X.; Shao, J.; Mei, J. The Diagnostic Value of Serum PIVKA-II Alone or in Combination with AFP in Chinese Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Dis. Markers 2021, 2021, 8868370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, J.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; Han, J.-Y.; Jeong, J.-S.; Choi, J.-C.; Kim, H.-Y.; Han, S.-Y. Diagnostic role and correlation with staging systems of PIVKA-II compared with AFP. Hepatogastroenterology 2009, 56, 763–767. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serrano-Gomez, S.J.; Maziveyi, M.; Alahari, S.K. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Card, D.J.; Gorska, R.; Harrington, D.J. Laboratory assessment of vitamin K status. J. Clin. Pathol. 2020, 73, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harauchi, T.; Takano, K.; Matsuura, M.; Yoshizaki, T. Liver and plasma levels of descarboxyprothrombin (PIVKA II) in vitamin K deficiency in rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1986, 40, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis-Yadley, A.H.; Malafa, M.P. Vitamins in pancreatic cancer: A review of underlying mechanisms and future applications. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 6, 774–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzini, E.; Furini, T.; Polito, A.; Scalfi, L.; Pinto, A.; Gasperi, V.; Savini, I.; on behalf of the SINU “Nutrition in Oncology” Working Group. Vitamin Nutritional Status in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, A.; Tartaglione, S.; Preziosi, A.; Mancini, P.; Angeloni, A.; Anastasi, E. PANC-1 Cell Line as an Experimental Model for Characterizing PIVKA-II Production, Distribution, and Molecular Mechanisms Leading to Protein Release in PDAC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xv, F.; Chen, J.; Duan, L.; Li, S. Research progress on the anticancer effects of vitamin K2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 8926–8934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Qiao, F.; Su, X.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, H. Epigenetic activation of E-cadherin is a candidate therapeutic target in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Gan, W.-J.; Wang, J.-R.; Zhu, X.-L.; He, X.-S.; Guo, P.-D.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.-M.; Li, J.-M.; Wu, H. RARγ-induced E-cadherin downregulation promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Anastasi, E.; Ialongo, C.; Labriola, R.; Ferraguti, G.; Lucarelli, M.; Angeloni, A. Vitamin K deficiency and COVID-19. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2020, 80, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameters | Patients with HCC | Patients with PDAC |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 73 1 | 68 1 |
| (54–85) | (41–89) | |
| Sex | ||
| Male | 19/30 male | 20/37 male |
| Female | 11/30 female | 17/30 female |
| Grade | ||
| I–II | 18/30 (60%) | 16/37 (43%) |
| III–IV | 12/30 (40%) | 21/37 (57%) |
| Stage | ||
| I–II | 16/30 (53%) | 10/37 (27%) |
| III–IV | 14/30 (47%) | 27/37 (73%) |
| Sera | PIVKA-II | AFP | CA19.9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | |||
| Number of patients | 83% (25/30) | 37% (11/30) | - |
| PDAC | |||
| Number of patients | 86% (32/37) | - | 92% (34/37) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Farina, A.; Cicolani, G.; Viggiani, V.; Maini, M.; Angeloni, A.; Anastasi, E. Differential Associations of PIVKA-II with Epithelial and Mesenchymal Features in HCC and PDAC. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157581
Farina A, Cicolani G, Viggiani V, Maini M, Angeloni A, Anastasi E. Differential Associations of PIVKA-II with Epithelial and Mesenchymal Features in HCC and PDAC. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157581
Chicago/Turabian StyleFarina, Antonella, Gaia Cicolani, Valentina Viggiani, Matteo Maini, Antonio Angeloni, and Emanuela Anastasi. 2025. "Differential Associations of PIVKA-II with Epithelial and Mesenchymal Features in HCC and PDAC" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157581
APA StyleFarina, A., Cicolani, G., Viggiani, V., Maini, M., Angeloni, A., & Anastasi, E. (2025). Differential Associations of PIVKA-II with Epithelial and Mesenchymal Features in HCC and PDAC. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157581







