Novel Anion-Exchange Resins for the Effective Recovery of Re(VII) from Simulated By-Products of Cu-Mo Ore Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
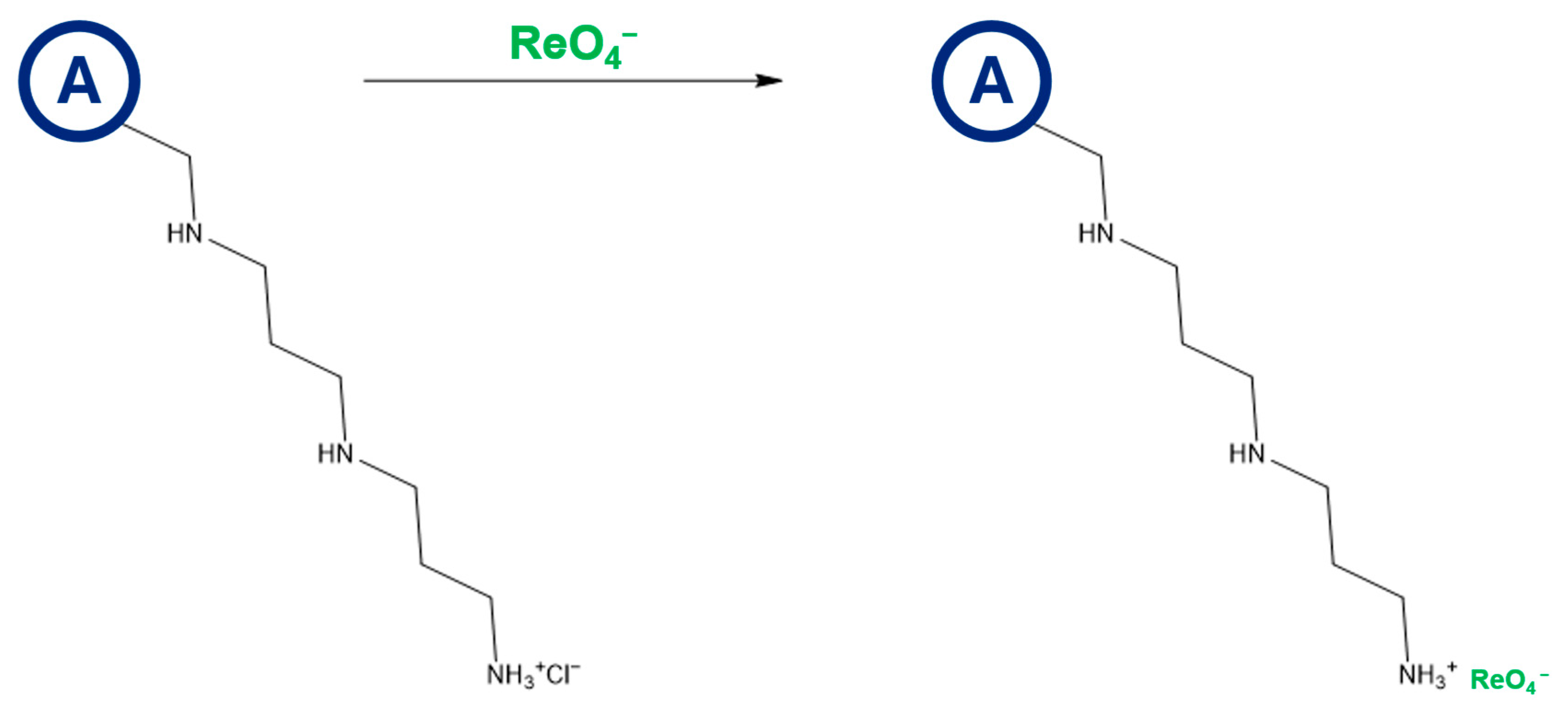
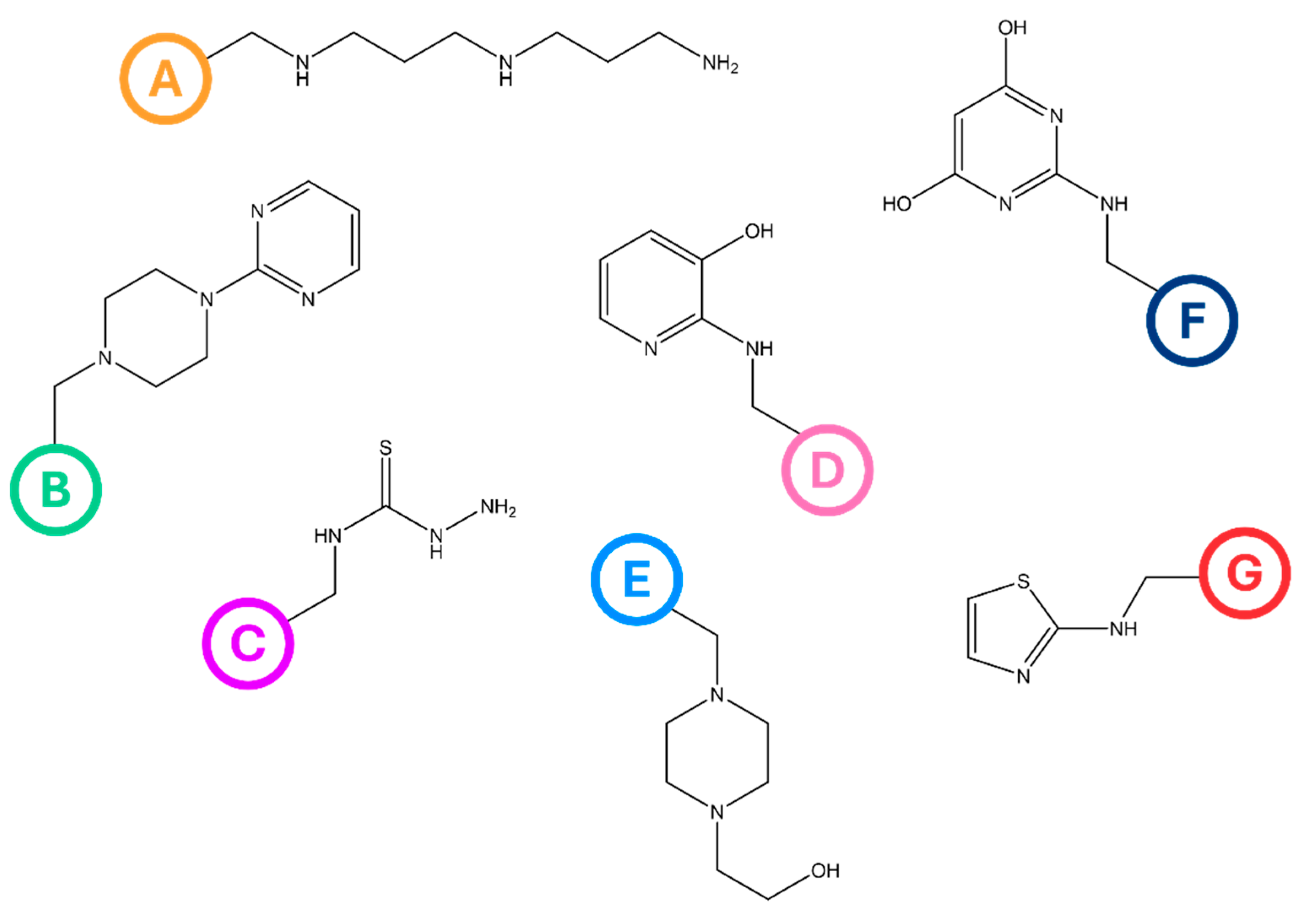
2.1. Synthesis of Anion-Exchange Resins
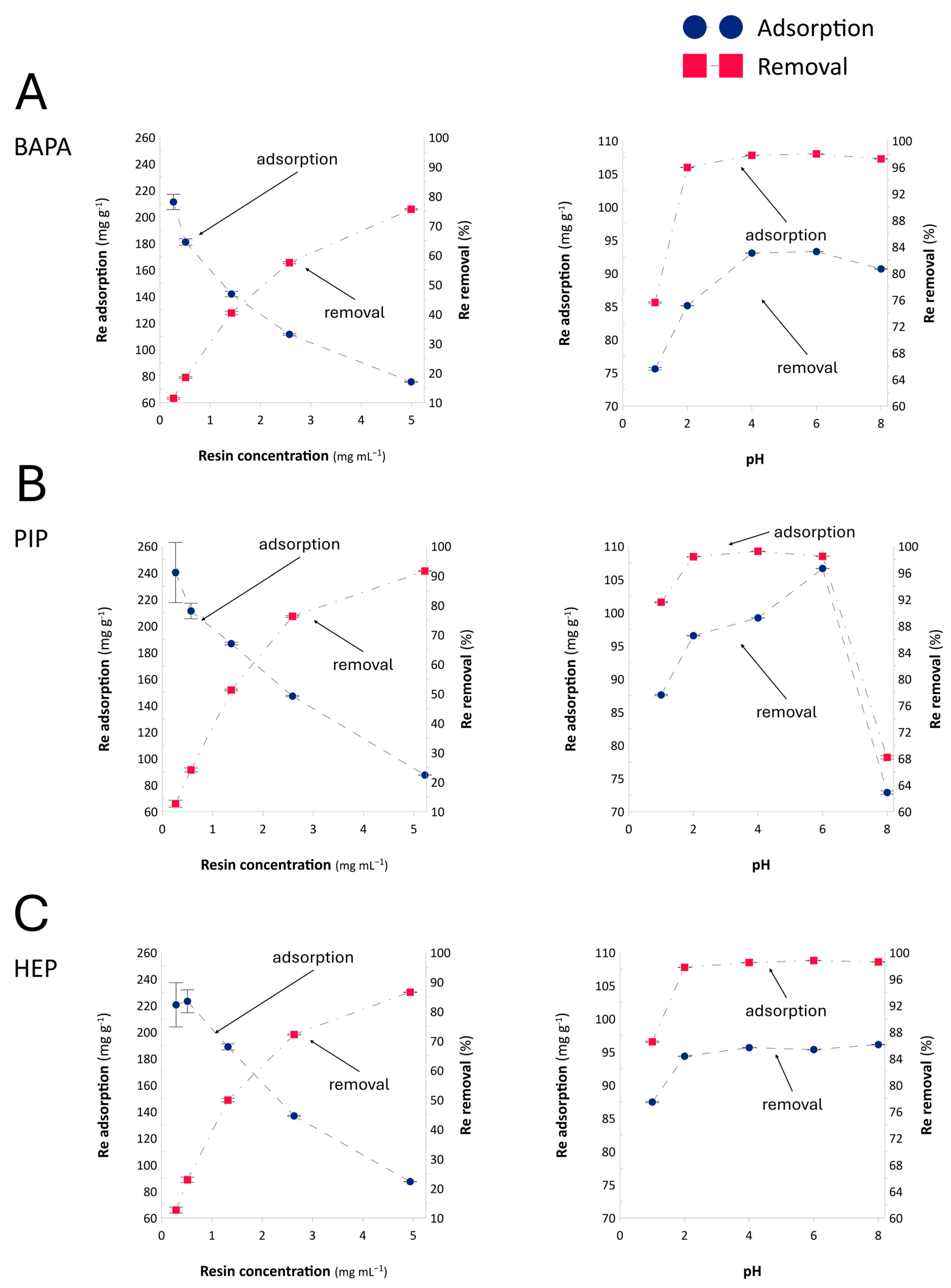
2.2. Resin Dose and Optimal Adsorption pH
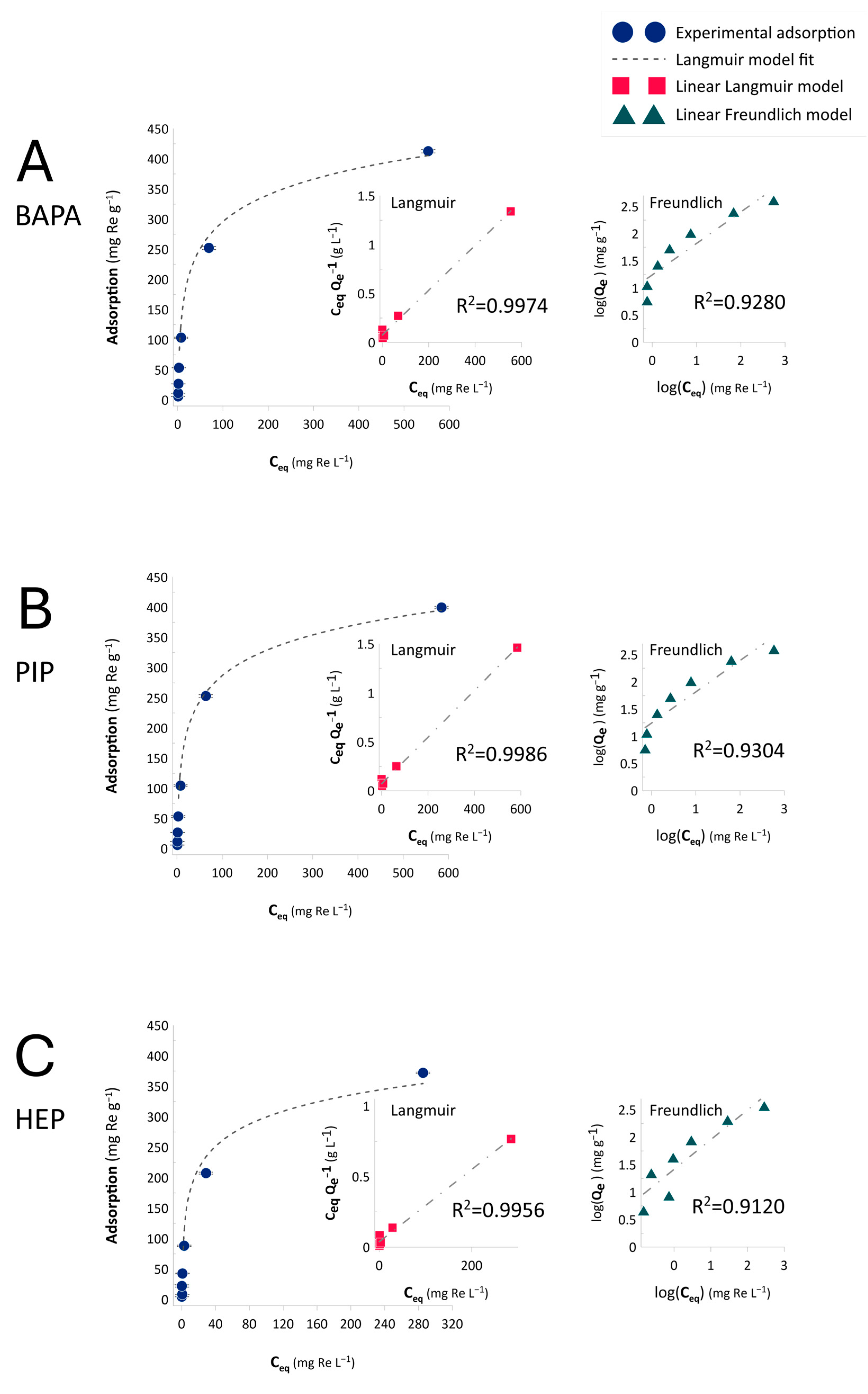
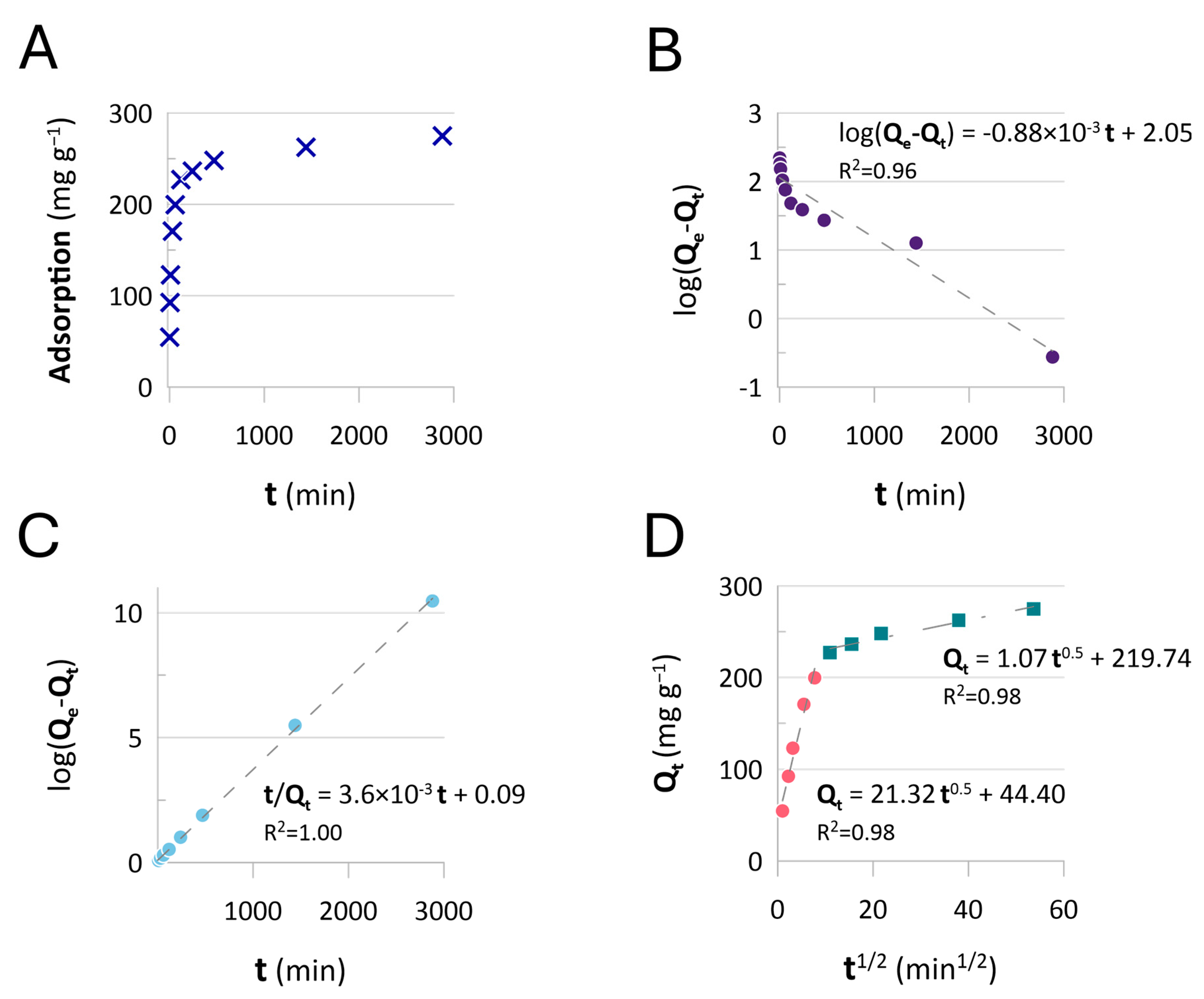
2.3. Adsorption Equilibrium
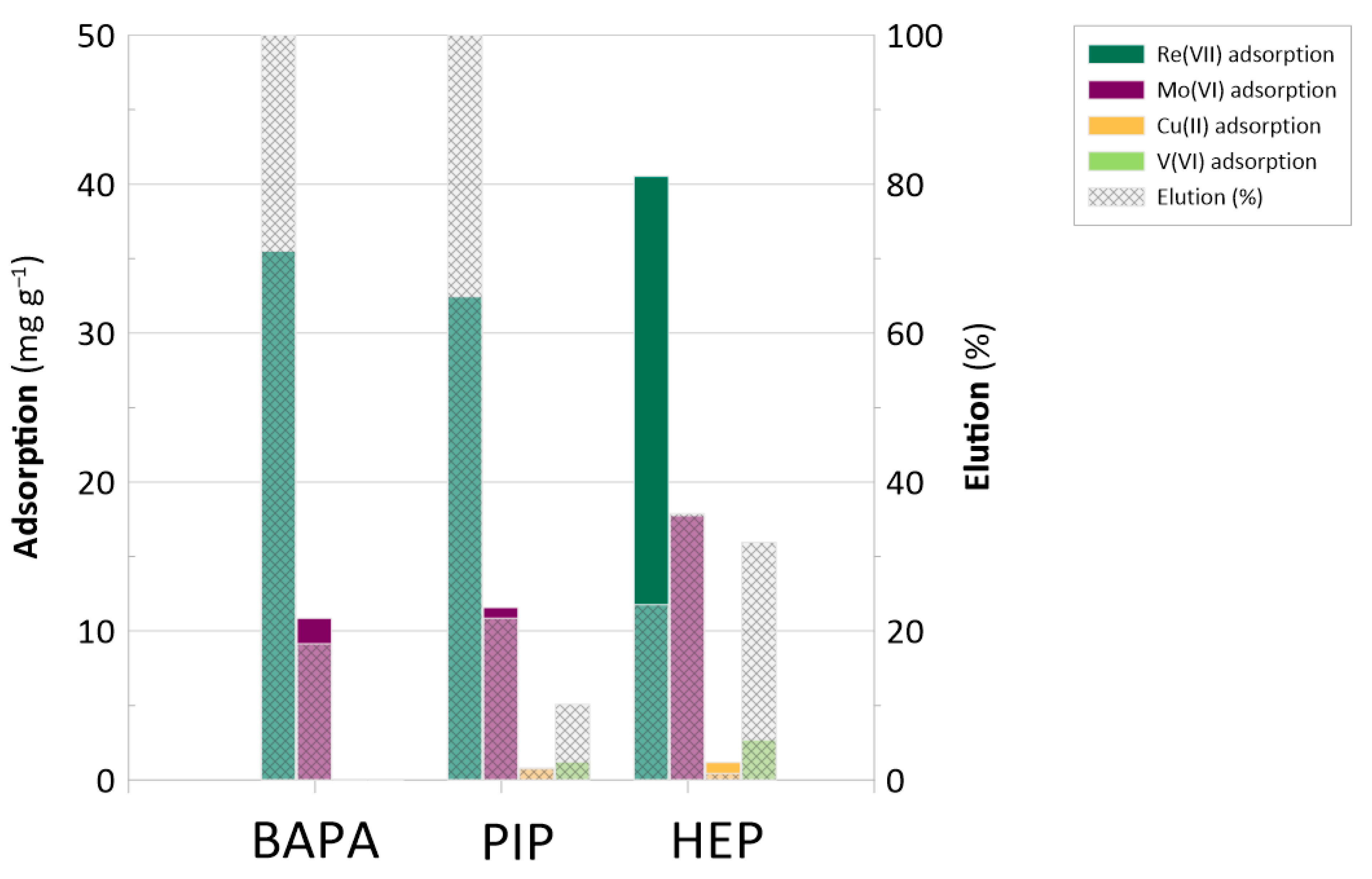
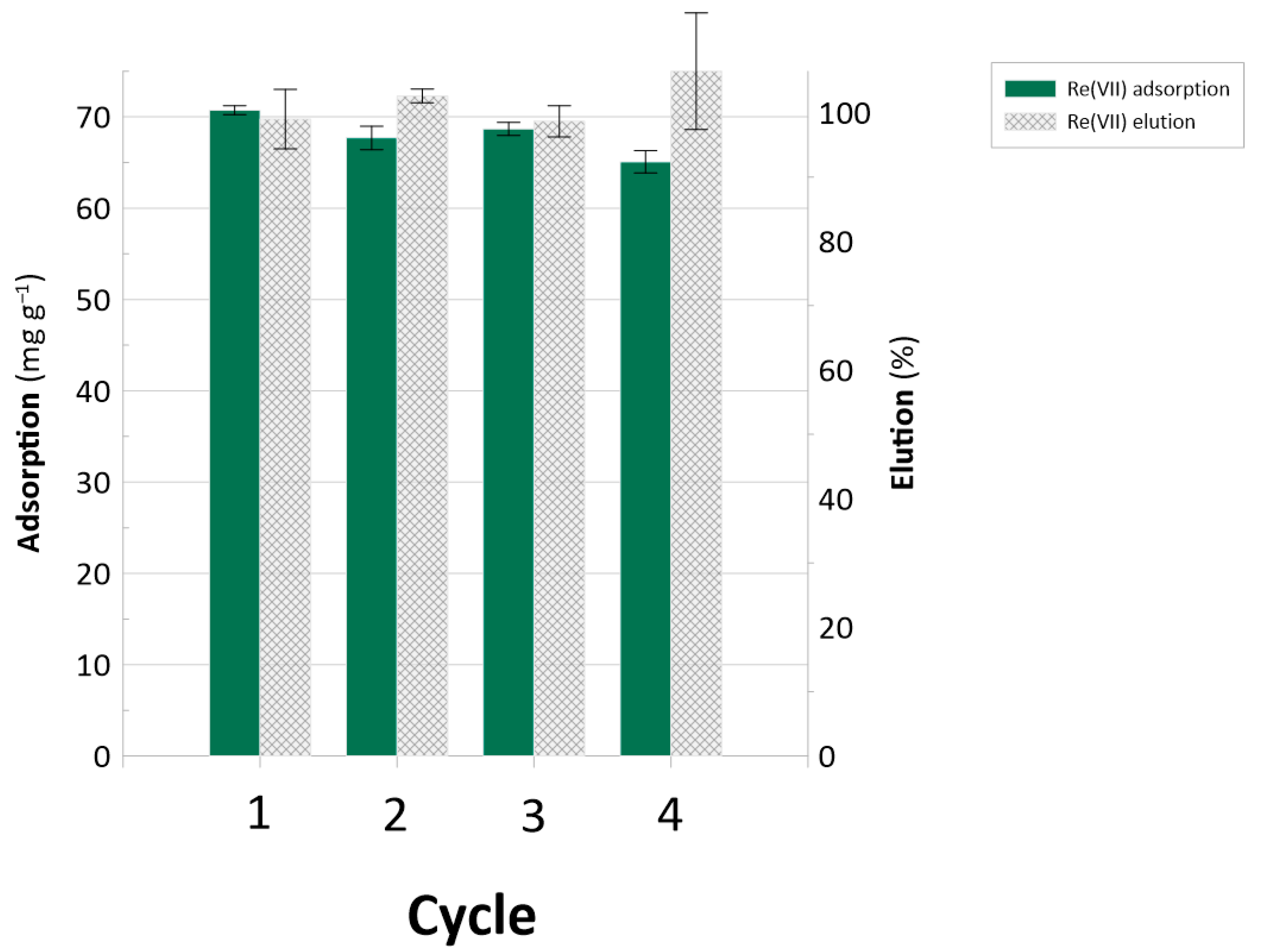
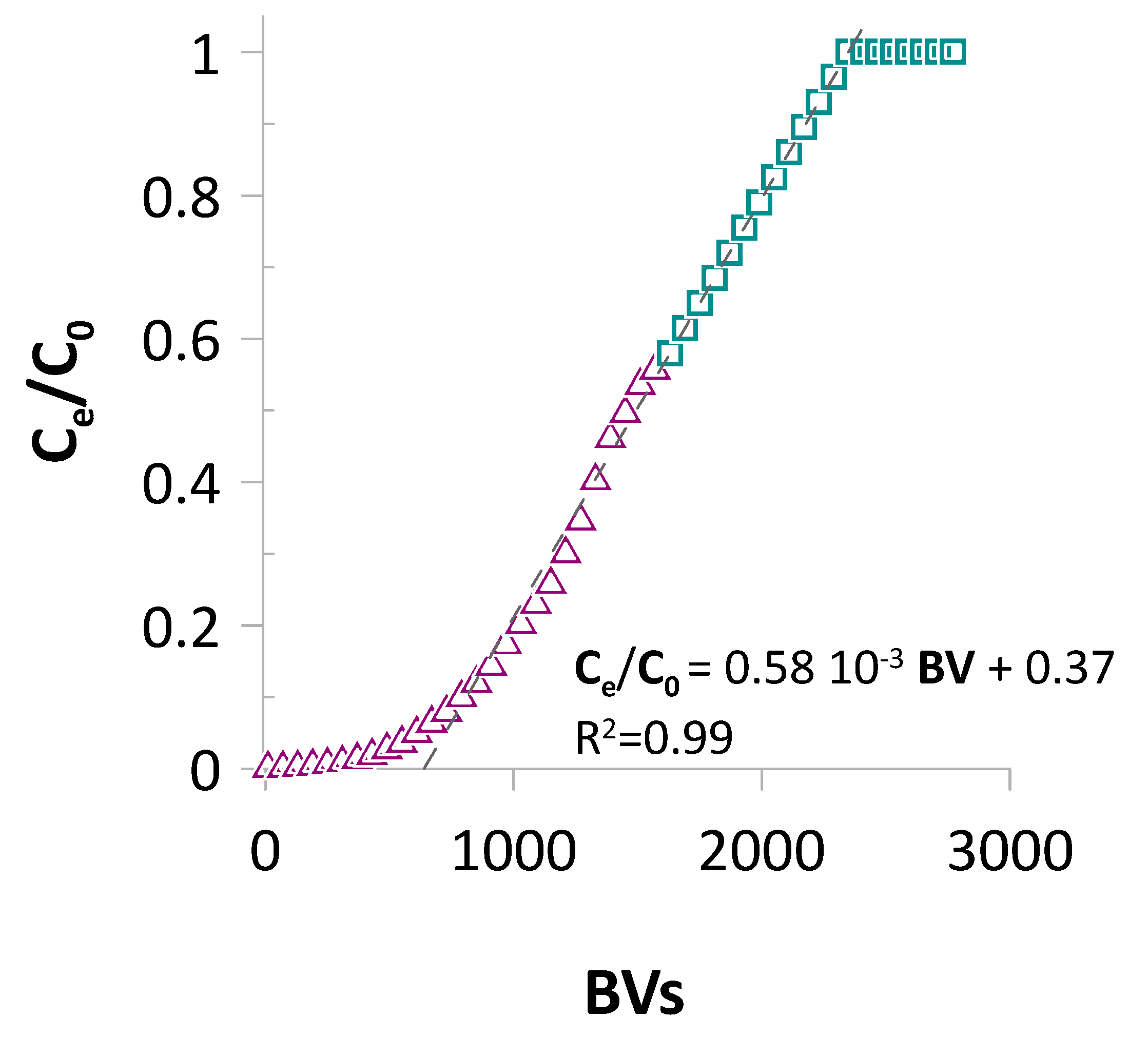
2.4. Adsorption Selectivity and Re(VII) Elution
2.5. Industrial Implications
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Anion-Exchange Resins
3.3. Characterization Methods and Instrumentation
3.4. Adsorption Equilibrium and Kinetics
3.5. Adsorption Selectivity and Re Elution
3.6. Flow Mode Adsorption of Re
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Naor, A.; Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E.; Taylor, S.R. Properties and applications of rhenium and its alloys. AMMTIAC Q. 2010, 5, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Rouschias, G. Recent advances in the chemistry of rhenium. Chem. Rev. 1974, 74, 531–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Recent advances of rhenium separation and enrichment in China: Industrial processes and laboratory trials. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.B.; Rezai, B.; Alamdari, E.K. Competitive adsorption characteristics of rhenium in single and binary (Re-Mo) systems using Purolite A170. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2017, 169 (Suppl. C), 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abisheva, Z.S.; Zagorodnyaya, A.N.; Bekturganov, N.S. Review of technologies for rhenium recovery from mineral raw materials in Kazakhstan. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 109, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.A. Rhenium: A Rare Metal Critical in Modern Transportation; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2015; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, T.T.; Mudd, G.M.; Jowitt, S.M.; Huston, D. Rhenium mineral resources: A global assessment. Resour. Pol. 2023, 82, 103441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, A.S.M.; Heidari, S.; Vergara, A.; Aguilera, M.V.A.; Preuss, P.; Camarada, M.B.; Fischer, A. Rhenium-Based Electrocatalysts for Water Splitting. ACS Mater. Au 2023, 3, 177–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothe, M.L.; Silva, K.L.; Figueredo, A.L.; Fiorio, J.L.; Rozendo, J.; Manduca, B.; Simizu, V.; Freire, R.S.; Garcia, M.A.; Vidinha, P. Rhenium–A Tuneable Player in Tailored Hydrogenation Catalysis. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021, 2021, 4043–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesieme, U.; Chrysanthou, A.; Catulli, M. Assessment of supply interruption of rhenium, recycling, processing sources and technologies. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 82, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, J.D.; Gribbin, D.G.; Shekhter, L.N. Recovery of rhenium from molybdenum and copper concentrates during the Looping Sulfide Oxidation process. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2014, 44, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakov, V.; Safonov, V.; Dogadkin, D. Characteristic features of molybdenum, copper, tungsten and rhenium accumulation in the environment. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2021, 6, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brainard, J.L. The availability of primary rhenium as a by-product of copper and molybdenum mining. Miner. Econ. 2024, 37, 445–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanturiya, V.A.; Matveeva, T.N.; Getman, V.V.; Karkeshkina, A.Y.; Gromova, N.K. Substantiation of New Reagent Compositions for the Effective Extraction of Rhenium in the Processing of Complex Molybdenum Ores. Minerals 2023, 13, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheema, H.A.; Ilyas, S.; Masud, S.; Muhsan, M.A.; Mahmood, I.; Lee, J.-C. Selective recovery of rhenium from molybdenite flue-dust leach liquor using solvent extraction with TBP. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 191 (Suppl. C), 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, H.-Z.; Wang, W.; Gao, Z.-G.; Cao, Y.-H. Recovery of rhenium from copper leach solutions using ion exchange with weak base resins. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 173 (Suppl. C), 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosough, M.; Shahtahmasebi, N.; Behdani, M. Recovery Rhenium from roasted dust through super Para-magnetic Nano-particles. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2016, 60 (Suppl. C), 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Park, J.S.; Seo, S.Y.; Tran, T.; Kim, M.J. Recovery of rhenium from a molybdenite roaster fume as high purity ammonium perrhenate. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 156, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, H.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Lee, M.S. Separation of molybdenum (VI), rhenium (VII), tungsten (VI), and vanadium (V) by solvent extraction. Hydrometallurgy 2017, 171, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowa, R.; Arabasz, S.; Parlinska-Wojtan, M. Classification and microstructural stability of high generation single crystal Nickel-based superalloys. Zaštita Mater. 2016, 57, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Tesfaye, F.; Li, X.; Lindberg, D.; Taskinen, P. Review of rhenium extraction and recycling technologies from primary and secondary resources. Miner. Eng. 2021, 161, 106719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, R.R.; Kim, M.-S.; Lee, J.-C. Novel Aqueous Processing of the Reverted Turbine-Blade Superalloy for Rhenium Recovery. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 8191–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhang, B.; Han, G.; Wang, M.; Huang, Y.; Su, S.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y. Clean separation and purification for strategic metals of molybdenum and rhenium from minerals and waste alloy scraps–A review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 181, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaimerden, Z.B.; Zhumakynbai, N.; Berdikulova, F.; Ondiris, B.; Khamidulla, A. Review of methods for obtaining rhenium from man-made waste and secondary raw materials. Metallurgist 2022, 66, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylenko, M.; Blokhin, A. Ion exchange resins tailored for effective recovery and separation of rhenium, molybdenum and tungsten. In Proceedings of the 2012 SME Annual Meeting and Exhibit 2012, SME 2012, Seattle, WA, USA, 19–22 February 2012; Meeting Preprints. pp. 750–756. [Google Scholar]
- Guiqing, Z. Separation of Molybdenum and Vanadium. In The ECPH Encyclopedia of Mining and Metallurgy; Kuangdi, X., Ed.; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2024; pp. 1901–1902. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, H.T.; Lee, M.S. Separation of rhenium (VII), molybdenum (VI), and vanadium (V) from hydrochloric acid solution by solvent extraction with TBP. Geosystem Eng. 2017, 20, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yu, S.; Wang, T.; Lian, H.; Lv, C. Recovery of rhenium, a strategic metal, from copper smelting effluent. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 337, 126403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Liang, C. Rhenium in Heterogeneous Catalysis: A Rising Star for Hydrogenation Reactions. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 7032–7049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Park, C.W.; Park, Y.-K.; Ha, J.-M.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, K.-Y.; Jae, J. Investigation of the activity and selectivity of supported rhenium catalysts for the hydrodeoxygenation of 2-methoxyphenol. Catal. Today 2021, 375, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, I.F.; Rathkopf, C.A.; Barton, M.D. Rhenium in molybdenite: A database approach to identifying geochemical controls on the distribution of a critical element. Min. Metall. Explor. 2020, 37, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezari-Zarandi, A.; Azizi, D.; Nikolaychuk, P.A.; Larachi, F.; Pasquier, L.-C. Selective recovery of molybdenum over rhenium from molybdenite flue dust leaching solution using PC88A extractant. Metals 2020, 10, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, R.; Okabe, T.H. Rhenium and its smelting and recycling technologies. Int. Mater. Rev. 2024, 69, 142–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.-Z.; Zhang, B.; Jing, X.-J.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.-J. Adsorption and desorption properties for rhenium using a kind of weak-base anion resin. Rare Met. 2018, 37, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Fu, Z.; Luo, J.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Li, G. Selective separation of rhenium from oxygen-pressure leach solution of molybdenite concentrate using modified D201 resin: Experiments and theoretical calculations. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 408, 125371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirillov, E.; Bochkareva, Z.; Semenishchev, V.; Kirillov, S.; Bunkov, G.; Rychkov, V. Anion exchange recovery of rhenium from industrial liquors followed by direct synthesis of a rhenium halide salt. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 230, 106387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinas, S.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D.; Pohl, P.; Dzimitrowicz, A.; Cyganowski, P. On the path of recovering platinum-group metals and rhenium: A review on the recent advances in secondary-source and waste materials processing. Hydrometallurgy 2024, 223, 106222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, B. Industrial Application of Rhenium Comprehensive Recovery from Spraying Water by Ion Exchange Resin Method in Jinduicheng Molybdenum Company. Conserv. Util. Miner. Resour. 2021, 41, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Korovin, V.; Pohorielov, Y.; Shestak, Y.; Valiaiev, O.; Cortina, J.-L. Rhenium recovery from highly concentrated sulfuric media using AMR anionite in column mode. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1156, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virolainen, S.; Laatikainen, M.; Sainio, T. Ion exchange recovery of rhenium from industrially relevant sulfate solutions: Single column separations and modeling. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 158, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Cierlik, A.; Leśniewicz, A.; Pohl, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Separation of Re (VII) from Mo (VI) by anion exchange resins synthesized using microwave heat. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.A. Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2004; Volume 35. [Google Scholar]
- Helfferich, F.G. Ion Exchange; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Polowczyk, I.; Cyganowski, P.; Ulatowska, J.; Sawiński, W.; Bastrzyk, A. Synthetic Iron Oxides for Adsorptive Removal of Arsenic. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öztürk, N.; Kavak, D. Adsorption of boron from aqueous solutions using fly ash: Batch and column studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2005, 127, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.D.; Reilly, K.T.; Landmesser, J.E. Recovery of Rhenium. US Patent No. US4557906, 9 December 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Takeno, N. Geological Survey of Japan, Atlas of Eh-pH Diagrams, Geological Survey of Japan Open File Report No. 419; National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology Research Center for Deep Geological Environments: Tokyo, Japan, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Śmiechowski, M.; Persson, I. Hydration of Oxometallate Ions in Aqueous Solution. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 8231–8239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Isawi, W.A.; Philip, A.S.; Singh, P.; Zeller, M.; Mezei, G. Supramolecular Entrapping and Extraction of Selenate, Molybdate and Tungstate Ions from Water by Nanojars. Inorg. Chem. 2025, 64, 1048–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Dzimitrowicz, A.; Marzec, M.M.; Arabasz, S.; Sokołowski, K.; Lesniewicz, A.; Nowak, S.; Pohl, P.; Bernasik, A.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Catalytic reductions of nitroaromatic compounds over heterogeneous catalysts with rhenium sub-nanostructures. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 12789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Tylus, W.; Dzimitrowicz, A.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Design and kinetic optimization of a 3D-printed packed bed reactor for high-volume continuous hydrogenation of nitroaromatic compounds and simultaneous production of aromatic amines. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P. Fully recyclable gold-based nanocomposite catalysts with enhanced reusability for catalytic hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol. Colloids Surf. A 2021, 612, 125995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyganowski, P.; Leśniewicz, A.; Polowczyk, I.; Chęcmanowski, J.; Koźlecki, T.; Pohl, P.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Surface-activated anion exchange resins for synthesis and immobilization of gold and palladium nano- and microstructures. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 90–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, R.; Lefevre, L. Dowex Ion exchange resins: Fundamentals of ion exchange. Dow Liq. Seperations 2000. Available online: https://www.lenntech.com/Data-sheets/Dowex-Ion-Exchange-Resins-Fundamentals-L.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Ho, Y.S. Citation review of Lagergren kinetic rate equation on adsorption reactions. Scientrometrics 2004, 59, 171–177. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 44, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, V.; Torne-Fernandez, V.; Montane, D.; Celzard, A. Adsorption of phenol onto activated carbons having different textural and surface properties. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2008, 111, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Testing Process Parameters (Purolite). Available online: https://www.purolite.com/pl/index/Company/Resources/General-Information/lab-guide-for-ion-exchange-resins/Test-Parameters-and-Resin-sample-preparation (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Jing, H.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, H.; Gao, B.; Zhang, T.; Yin, Y. Advances in Enrichment and Purification Technology of Ammonium Perrhenate. Separations 2025, 12, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mal’tseva, E.; Blokhin, A.; Murashkin, Y.V. Specific features of rhenium desorption from weakly basic anion exchangers Purolite A170 and Purolite A172 with ammonia solutions. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2012, 85, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, J.; Ye, M.; Wang, P.; Tang, F.; He, L. Design of a strong-base anion exchanger and its adsorption and elution behavior for rhenium (VII). RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 18868–18873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecker, H. Beitrag zur basizitätsprüfung von stark basischen anionenaustauschern. J. Chromatogr. 1974, 102, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D.; Cyganowski, P. Effect of Microwave Radiation on the Synthesis of Ion Exchange Resins: A Comparative Study. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2015, 33, 510–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D.; Cyganowski, P.; Kawałko, J. Microwave-assisted synthesis of anion-exchange resins for sorption of noble metals: How to boost sorption capacity using a proper reaction environment. Polym. Bull. 2017, 74, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, K.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, W. Se(IV) sorption on TiO2: Sorption kinetics and surface complexation modeling. Colloids Surf. A 2009, 349, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Ng, J.C.Y.; McKay, G. Kinetics of pollutant sorption by biosorbents: Review. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2000, 29, 189–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
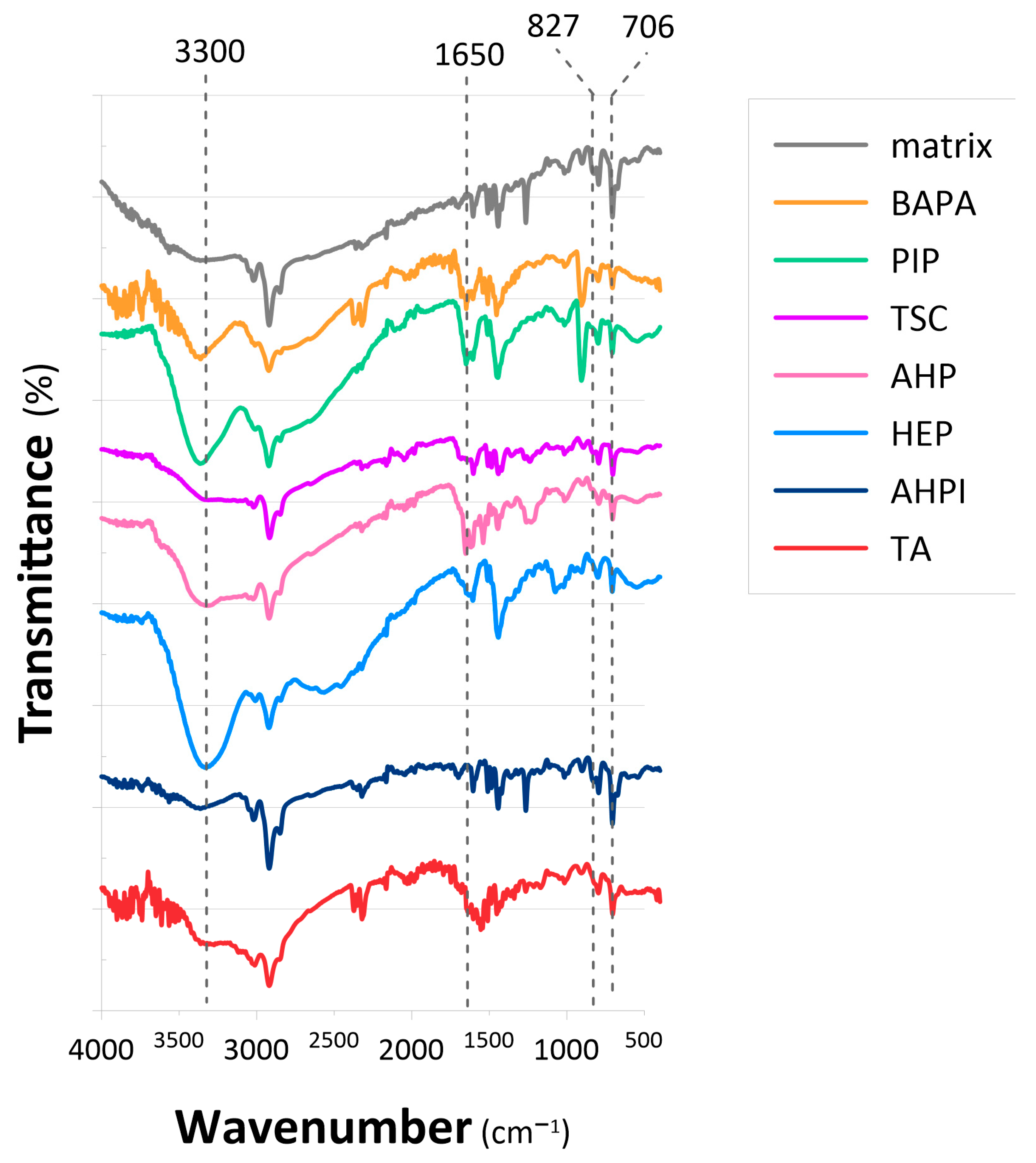
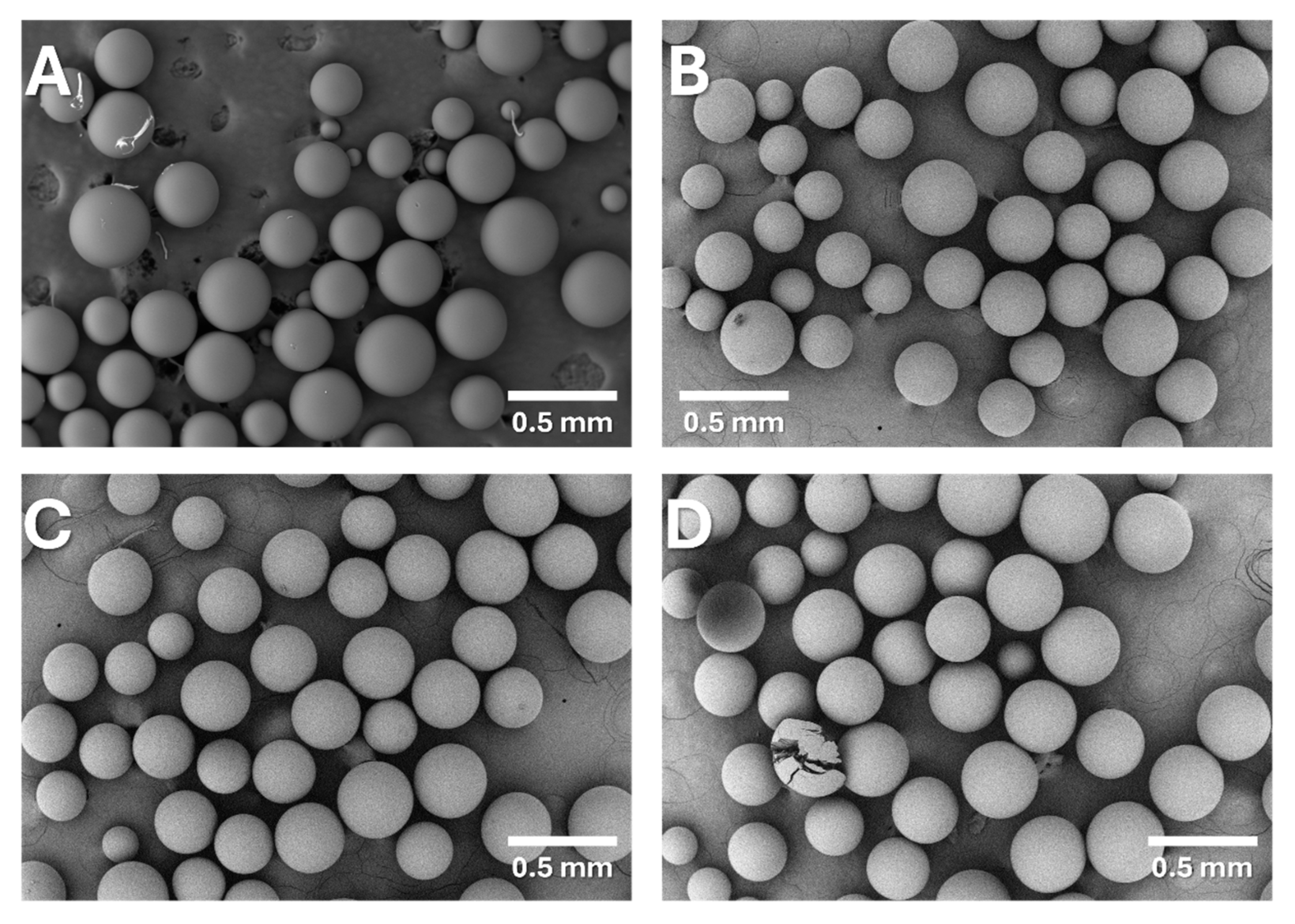


| Sample | Elemental Composition (wt%) | W a (RSD, %) | ZH b | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | N | S | O | |||
| BAPA | 65.36 ± 0.05 | 7.26 ± 0.03 | 5.08 ± 0.04 | - | 0.18 (0.16) | 2.14 | |
| PIP | 68.25 ± 0.06 | 6.58 ± 0.06 | 10.25 ± 0.08 | - | - | 0.10 (0.00) | 2.18 |
| TSC | 69.90 ± 0.03 | 5.70 ± 0.04 | 7.28 ± 0.02 | 10.88 ± 0.04 | - | 0.13 (3.77) | 0.44 |
| AHP | 72.99 ± 0.03 | 6.25 ± 0.04 | 3.45 ± 0.03 | - | 8.66 ± 0.07 | 0.22 (0.70) | 0.88 |
| HEP | 63.42 ± 0.16 | 7.30 ± 0.01 | 5.72 ± 0.04 | - | 11.68 ± 0.13 | 0.08 (1.06) | 1.74 |
| AHPI | 76.28 ± 0.09 | 6.26 ± 0.04 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | - | 4.37 ± 0.12 | 0.14 (1.37) | 0.00 |
| TA | 70.32 ± 0.04 | 6.08 ± 0.03 | 3.59 ± 0.17 | 4.18 ± 0.03 | - | 0.18 (0.38) | 0.00 |
| Resin | Q0 a | Q0m b | KL c | RL d | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAPA | 435.4 | 2.3 | 0.0023 | 0.4987 | 0.9974 |
| PIP | 419.2 | 2.3 | 0.0024 | 0.4993 | 0.9986 |
| HEP | 390.5 | 2.1 | 0.0026 | 0.4978 | 0.9956 |
| Re(VII) Selectivity Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Resin | vs. Mo(VI) | vs. V(V) | vs. Cu(II) |
| BAPA | 2.9 | ||
| PIP | 1.9 | 44 | 103 |
| HEP | 2.4 | 116 | 438 |
| Resin | Re adsorption (mg Re g−1) | Selectivity (Re over Mo) | Regeneration Efficiency | Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Purolite A170 | ~100 | Reduced in Re-Mo systems | High; efficient with ammonia (based on prior research [60]) | Commercially available; performance affected by competing Mo ions. | [4] |
| Modified D201 | 92.16 | High; Re: 97.46%, Mo: 0.38% | ~95% | Excellent selectivity in acidic solutions; stable over multiple cycles. | [35] |
| ZS15 Weak-Base Resin | Not specified | High; effective in Re-Mo systems | Efficient desorption with low-concentration ammonia | Suitable for industrial applications; good selectivity and regeneration. | [34] |
| D990 Resin | 162 | Not specified | 97.3% with 6% ammonia | Strong adsorption from copper smelting solutions; effective regeneration. | [59] |
| PS-G-4VP-IE Resin | 252 | High over pH 1.5–6 | Not specified | High capacity across a wide pH range; suitable for various conditions. | [61] |
| VBC-co-DVB/1-(3-aminopropyl)imidazole | 303 | Selectivity index: 220 | Not specified | Resin synthesized entirely in a microwave radiation. | [41] |
| VBC-co-DVB/ bis(3-aminopropyl)amine VBC-co-DVB 1-(2-pyrimidinyl)piperazine | 435 419 | Selectivity index: 2.9 Selectivity index: 1.9 | ~100% Re elution | Maintained activity over 4 sorption/desorption cycles High processing ability in flow mode. | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cyganowski, P.; Pohl, P.; Pawlik, S.; Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. Novel Anion-Exchange Resins for the Effective Recovery of Re(VII) from Simulated By-Products of Cu-Mo Ore Processing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157563
Cyganowski P, Pohl P, Pawlik S, Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak D. Novel Anion-Exchange Resins for the Effective Recovery of Re(VII) from Simulated By-Products of Cu-Mo Ore Processing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(15):7563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157563
Chicago/Turabian StyleCyganowski, Piotr, Pawel Pohl, Szymon Pawlik, and Dorota Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak. 2025. "Novel Anion-Exchange Resins for the Effective Recovery of Re(VII) from Simulated By-Products of Cu-Mo Ore Processing" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 15: 7563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157563
APA StyleCyganowski, P., Pohl, P., Pawlik, S., & Jermakowicz-Bartkowiak, D. (2025). Novel Anion-Exchange Resins for the Effective Recovery of Re(VII) from Simulated By-Products of Cu-Mo Ore Processing. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(15), 7563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26157563









